Abstract
This work presents the results of a ten-year investigation (2010–2019) on the characteristics and sources of precipitation pollution in typical cities locating in the economic belt on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang. The water-soluble ions’ characteristics (Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, F−, Cl−, SO42−, NO3−), neutralizing capacity, wet deposition and sources of precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining during 2010–2019 were compared and analyzed. The study showed that from 2010 to 2019, the pH value of precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining varied from 4.18 to 10.55 with a volume-weighted mean (VWM) pH of 6.33, and the pH value showed an upward trend overall. The VWM electrical conductivity (EC) of the precipitation was the highest in Urumqi and the lowest in Yining, indicating that Urumqi was the most polluted and Yining was relatively clean. The most important cation in the precipitation of the three cities was Ca2+, and the most important anion was SO42−. The ratio of SO42−/NO3− indicated that the air pollution in Urumqi and Yining belonged to the typical coal-smoke air pollution, while there was compound pollution in Karamay. As can be seen from the neutralization factor, Ca2+ had the strongest neutralization ability, followed by Na+ and NH4+. Nitrate and sulfate in the atmosphere of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining are likely to exist in the form of NH4NO3, CaSO4 and (NH4)2SO4•CaSO4•2H2O. Wet deposition flux analysis of S and N showed that S pollution of the precipitation in Urumqi showed a decreasing trend, while N pollution showed an increasing trend. S pollution of the precipitation in Karamay gradually decreased, while N pollution of the precipitation in Yining became more and more serious. By analyzing origins of major ions in precipitation, it is concluded that human activities (industry, agriculture, heating, and transportation) are the main sources of ions in precipitation, and natural sources (soil dust) also play an important role.
1. Introduction
The chemical composition of precipitation is the result of the interaction of atmospheric gases and particulate matter in raindrops. It is affected by climate conditions, natural processes and human activities [1,2], and can reflect the characteristics of the atmospheric environment and its pollution status [3]. By determining the chemical composition of precipitation to determine the contribution sources, we can understand the local and regional diffusion of pollutants and their potential impact on the environment through removal and deposition processes [4]. However, the chemical composition of precipitation varies with different study areas and pollution sources. Therefore, the study on the chemical characteristics of precipitation in different areas plays a very important role in evaluating the gaseous and particulate pollution in different regions [5,6].
Most studies on the characteristics of precipitation in China have focused on the distribution of pH and water-soluble ions in South China. Until now, there have been fewer studies focused on precipitation in North China. However, an increasing trend of chemical characteristics in precipitation was observed in many areas in northern and central China after 2010. The results showed that the main acidogenic factors of acid rain in the Pearl River Delta were SO42−, NO3− and Cl−, and the problem of acid rain was still serious [7,8]. The marine sources had a significant impact on the precipitation in Shenzhen [9]. The high proportion of SO42−, NO3− and NH4+ in summer precipitation in Shanghai indicated that the secondary pollution of the atmospheric environment in Shanghai was serious [10]. The pH value of non-urban precipitation in North China was 5.29, but more than 60% of the pH values in precipitation were greater than 6.0, indicating that alkaline aerosols in North China had considerable neutralization effects [11]. In recent years, the pH value in Xi’an had shown an upward trend and the total ion concentration had shown an obvious downward trend, indicating that the acidification of atmospheric precipitation in Xi’an had been improved in recent years [12]. The contribution rate of SO42− to the acidity of precipitation in Midong District of Urumqi decreased gradually, while NO3− increased gradually, indicating that the acidification type of the precipitation in Urumqi was sulfuric acid, but it had a trend of gradually changing to the nitric acid type [13].
Located in the middle of the northern slope of Tianshan Mountain, the southern margin of Junggar Basin, from Hami in the east to Yining in the west, the North Slope Economic Belt of Tianshan Mountain is a large channel and industrial economic belt connecting Central and Western Asia with the manufacturing industry as the main industry and the service industry as the auxiliary [14]. In recent years, the region has become the most economically developed area with the highest level of urban development in Xinjiang by virtue of its superior geographical conditions, relatively perfect infrastructure and abundant natural resources. At present, the research on precipitation chemistry in Xinjiang is relatively scarce, and the existing research mainly focuses on the precipitation chemical characteristics of a single city [13,15,16,17,18,19]. At the same time, the research on the long-term change of atmospheric precipitation chemical characteristics and wet deposition in several cities is rare, and there is little evaluation on the neutralization factor of acid precipitation in the past. In this paper, the long-term precipitation chemical characteristics and sources of three typical cities in Xinjiang are studied for the first time. The purpose is to have a preliminary understanding of the precipitation chemical characteristics in this region and determine the possible sources of chemical composition, hoping to provide reference for the treatment of the atmospheric environment in this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Urumqi, Karamay and Yining are important cities located in the economic belt on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountain, with a temperate continental climate. Urumqi, the capital of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, is surrounded by mountains on three sides and an open plain in the north. The annual mean temperature is 6.4 °C and the annual precipitation is 236 mm. Yining is located in the northwest of Xinjiang and the middle of the Ili River Valley, known as “a place with South-China-type scenery”. The annual mean temperature is 10.5 °C, and the annual precipitation is 297 mm. Karamay is located in the west of Junggar Basin. The terrain is inclined strip, long from north to south, narrow from east to west, dry and rainless. The annual mean temperature is 8.6 °C, and the annual precipitation is 109 mm. The observation points of the three cities are located at Urumqi national basic meteorological station (87.39° E, 43.47° N, altitude 935.9 m), Karamay national basic meteorological station (84.85° E, 45.62° N, altitude 452.8 m) and Yining national reference climate station (81.33° E, 43.95° N, altitude 663.4 m) (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Research area and location of meteorological stations.
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
The observation points are located in the observation field of Urumqi national basic meteorological station, Karamay national basic meteorological station and Yining national reference climate station, respectively. The observation sites are open, and there are no tall buildings or obvious pollution sources around them. A standard rainfall bucket and a precipitation sampling bucket are arranged, respectively, in the observation field for measuring precipitation and collecting precipitation samples. The sampling interval of precipitation samples is 24 h, and the sampling node is from 08:00 of the current day to 08:00 of the next day. A continuous precipitation process in a sampling day is sampled only once. If there are multiple precipitation processes in a precipitation sampling day, multiple sampling can be carried out and combined into one precipitation sample.
Clean the sampling barrel with tap water before sampling, then clean it with pure water 2–3 times, dry and cover it for standby. Place the clean sampling bucket on the sampling rack of the observation field before precipitation, take the sampling bucket back indoors after precipitation, and measure the pH and electrical conductivity within four hours. Filter the remaining precipitation samples with a microporous filter membrane (0.45 μm), put them into a washed and dried polyethylene bottle, and refrigerate them in a 4 °C refrigerator for analysis of water-soluble ions. The collected solid precipitation samples shall be melted at room temperature before subsequent measurement and collection. In this study, a precipitation sample with a precipitation of 1 mm in a precipitation sampling day is regarded as an effective precipitation sample. The sampling time was from February 2010 to July 2019. A total of 1253 effective samples are collected, including 427 effective precipitation samples in Urumqi with a total precipitation of 2842.6 mm, 265 effective precipitation samples in Karamay with a total precipitation of 1178.9 mm and 561 effective precipitation samples in Yining with a total precipitation of 2880.6 mm. The pH values of the precipitation samples were measured by PHS-3B pH meter, and the electrical conductivity values were measured by DDS-307 conductivity meter. Concentrations of F−, Cl−, SO42−, NO3−, Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ in precipitation were measured by Dionex ICS-3000 ion chromatograph.
2.3. Data Analysis
The concentrations of H+ were obtained by the following equation:
pH = −log10 [H+]⇒[H+] = 10−pH
The volume-weighted mean (VWM) concentrations (μeq/L) of ions in precipitation were calculated by the following equation:
where Pi (mm) is the precipitation produced by a single precipitation event, and Ci (μeq/L) is the measured ion concentration of precipitation per time.
Relative acidity (FA) is an index to evaluate the neutralization degree of precipitation acidity. The formula proposed by Balasubramanian [20] is adopted:
where [H+], [SO42−], and [NO3−] are the concentrations of corresponding ions. If FA = 1, it indicates that the precipitation acidity produced by SO42− and NO3− is neutralized by alkaline substances.
FA = [H+]/([SO42−] + [NO3−])
Neutralization factors (NFs) is a parameter to evaluate the neutralization of precipitation by alkaline substances, which is calculated by the formula proposed by Possanzini [21]:
where [Xi] is the concentration of alkaline components (Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+). The ammonium availability index (AAI) represents the molar ratio of the ammonium concentration to fully neutralize sulfuric and nitric acids [22,23]. AAI is calculated by the following equation:
NF = [Xi]/([SO42−] + [NO3−])
If AAI < 100%, then there is an ammonium deficit, suggesting that sulfate and nitrate are acidic; if AAI = 100%, then ammonium just neutralizes sulfuric and nitric acids; if AAI > 100%, then there is sufficient ammonium to completely neutralize sulfuric and nitric acids.
The wet deposition fluxes were calculated according to the following formula [24]:
where WD is the wet deposition flux and VWM is the volume-weighted mean concentration, while RF is the annual precipitation.
In order to estimate the contribution of marine and continental atmospheric precipitation, Na+ and Ca2+ can be taken as the reference ions of marine and continental sources, and the enrichment coefficient (EF) in the atmospheric precipitation was calculated by the following formula [25,26]:
where X is the concentration of the element of interest in the precipitation; Na+(rainwater) is the concentration of Na+ in the precipitation; Na+(sea) is the concentration of Na+ in seawater; Ca2+(rainwater) is the concentration of Ca2+ in the precipitation; and Ca2+(soil) is the concentration of Ca2+ in soil.
In order to further study the contribution of various pollution sources to precipitation ion sources, the relative contribution of several sources is calculated by the following formula [27]:
% SSF = (X/Na+) sea/(X/Na+) rainwater × 100
% CF = (X/Ca2+) soil/(X/Ca2+) rainwater × 100
% ASF = 1 − % SSF − % CF
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variation Characteristics of pH and EC
The pH (volume-weighted mean) and EC (volume-weighted mean) of precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining from 2010 to 2019 are shown in Figure 2. The pH values of precipitation in the three cities ranged from 4.18 to 10.55, with an average value of 6.33. The pH values for mean annual precipitation in Urumqi and Karamay showed an upward trend, while the trend of change in Yining went up first, then went down and then went up again, with a non-obvious trend overall, indicating that the acidification of precipitation has been improved in varying degrees. The pH values of precipitation in Urumqi ranged from 4.48 to 8.87, with an average value of 6.69; the pH values of precipitation in Karamay ranged from 4.18 to 10.55, with an average value of 6.11; the pH values of precipitation in Yining ranged from 4.19 to 7.80, with an average value of 6.06. Natural precipitation can be regarded as an aqueous solution system in equilibrium with the atmosphere. It is generally considered that pH = 5.6 is the natural acidity of precipitation in equilibrium with uncontaminated CO2, NOx and SO2 in the atmosphere. Therefore, precipitation with a pH below 5.6 is usually regarded as acid precipitation, indicating that the impact of a large number of anthropogenic emissions of SO2 and NO2 mainly comes from industrial activities, coal combustion and the cold start of vehicles [19,28,29,30]. It can be seen from Figure 3 that the acidity of precipitation was not high; about 86.66% of pH values were higher than 5.6, and 82.75% were between 5.75–7.25. For pH values of precipitation, about 98.12% in Urumqi were higher than 5.6, 83.77% in Karamay and 79.32% in Yining. Combined with the results of water-soluble ions concentrations, it can be found that although the concentrations of SO42− of precipitation in the three cities were greater than 5.6, the high concentrations of Ca2+ and Na+ neutralized the acidogenic ions, resulting in the high pH value of precipitation, indicating that the impact of precipitation was not limited to human activities, but also generally natural factors. The EC values of precipitation can explain the pollution degree of precipitation. The higher the EC value is, the higher the total ion concentrations of precipitation and the more serious the precipitation pollution is. Among the three cities, the change trend of EC values in Urumqi and Karamay were similar, while the EC values in Yining were low. The average EC in Urumqi was the highest with 74.06 MS·M−1, followed by Karamay, and the lowest in Yining was 44.59 MS·M−1. It showed that Urumqi was the most polluted and Yining was cleaner.
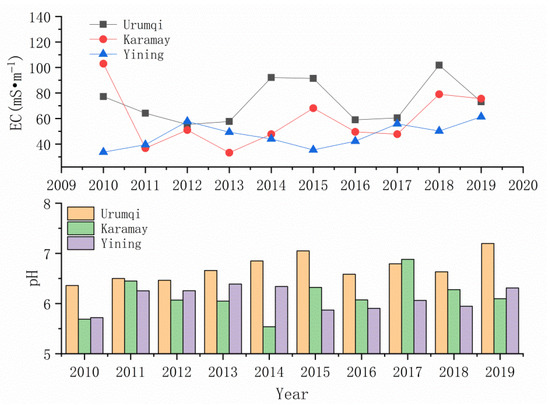
Figure 2.
The volume-weighted mean pH and EC of the precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining from 2010 to 2019.
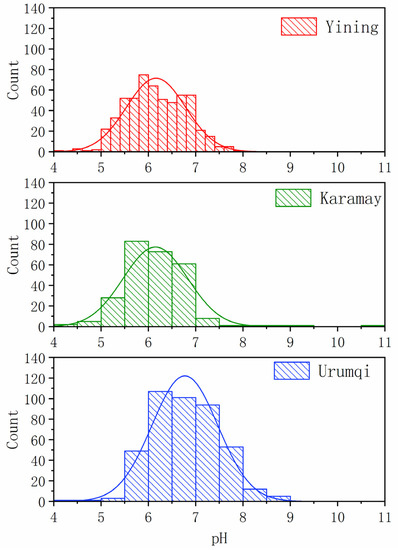
Figure 3.
Frequency distribution of pH for Urumqi, Karamay and Yining.
3.2. Chemical Composition of Precipitation
Ion balance refers to the balance between the sum of cation charge and anion charge in a solution. If the chemical components of precipitation are determined comprehensively, the sum of the final equivalent concentrations of cations must be equal to the sum of the equivalent concentrations of anions. Based on this, the equivalent concentrations of anions and cations in precipitation can be calculated respectively to check whether major ions are omitted. The ideal state is: Σ cation = Σ anion (Σ cat = Σ an). In this study, Σ cat = [Ca2+] + [Mg2+] + [Na+] + [K+] + [H+] + [NH4+], Σ an = [SO42−] + [NO3−] + [Cl−] + [F−]. It is generally believed that when pH > 5.6, the contribution of HCO3− to anions cannot be ignored. The higher the pH is, the greater the contribution HCO3− makes [28]. After rejecting the data that has not met the quality criteria, linear regression analysis was performed between the grand total concentration of anions and cations in precipitation for each region, respectively. Strong correlations were obtained between the sum of anions and the sum of cations in each case, and the R2 values were 0.77, 0.80 and 0.65 for Urumqi, Karamay and Yining, respectively (Figure 4). HCO3− and PO43− were not determined in this study, and there were still a variety of organic acids in precipitation, all of which may be an important reason for the imbalance of the total concentration of cations and anions. In addition, different air pollution properties and ion sources will also affect the balance of the total concentration of cations and anions.
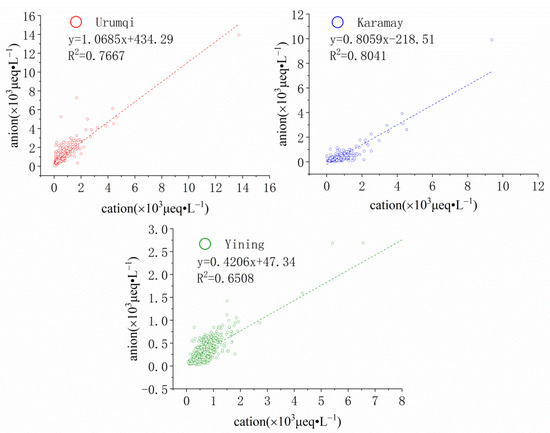
Figure 4.
Correlation between anions and cations of the precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining (ueq·L−1).
To evaluate the ionic composition of precipitation, the volume-weighted mean along with statistical analysis was analyzed in the study area of three cities. Figure 5 shows the volume-weighted mean concentration of ionic components in the precipitation of three cities. The orders of ion concentration in precipitation in the three cities are different, with the order Ca2+ > SO42− > Na+ > Cl− > NH4+ > Mg2+ > K+ > NO3− > F− in Urumqi, Ca2+ > SO42− > Na+ > NH4+ > Cl− > K+ > NO3− > Mg2+ > F− in Karamay and Ca2+ > SO42− > Na+ > NH4+ > Mg2+ > Cl− > NO3− > K+ > F− in Yining. Among the analyzed cations and anions, Ca2+ and SO42- presented the highest volume-weighted mean concentrations in the three stations. The average concentrations of Ca2+ were 32.15%, 36.10% and 34.21% in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining, respectively. Compared with the other two cities, Karamay had the highest proportion of Ca2+, indicating that Karamay has more dust. Compared with Urumqi and Karamay, the proportion of SO42− in the precipitation in Yining was the highest, accounting for 23.41%, 18.31% and 25.93% in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining, respectively. The proportions of NO3− in precipitation were low in the three cities.
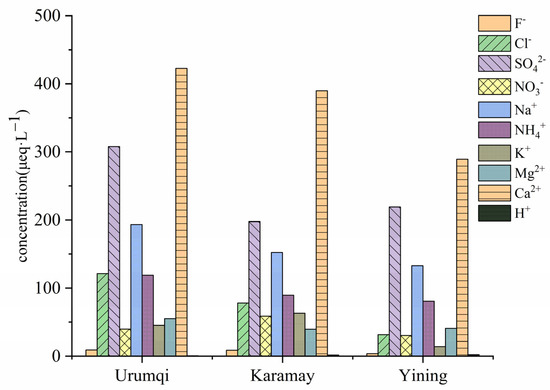
Figure 5.
Ion-weighted mean concentrations of the precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining during 2010–2019.
The equivalence ratio of SO42−/NO3− in precipitation can reveal the characteristics of acid rain, estimate the relative contribution of SO42− and NO3− to precipitation acidity, and reflect the contribution of fixed sources (coal combustion) and mobile sources (motor vehicles) to precipitation acidity [3]. For the variation range of SO42−/NO3− ratio, it was 0.48–117.86 in Urumqi with an average value of 8.01, 0.06–40.36 in Karamay with an average value of 3.66, and 0.12–148.89 in Yining with an average value of 7.63. The ratios between Urumqi and Yining were higher than the average level of China (6.24) [31], which indicated that SO42− was the main contributor to precipitation acidity and also the main factor in air pollution in Urumqi and Yining, showing that Urumqi and Yining belong to typical soot-type air pollution. The ratio of Karamay was about half of the national average, indicating that the contribution of SO42− to precipitation acidity in Karamay precipitation is relatively small, and its pollution tends to be complex pollution.
3.3. Neutralization Ability
The acidity of precipitation depends on the concentration of acidogenic precursors and neutralizing ions. The acidity of precipitation in most parts of the northern hemisphere is mainly caused by strong acids H2SO4 and HNO3 and organic acids. SO42− and NO3− are usually used as the main acidogenic ions [32]. Previous studies have shown that in the cloud, Ca (OH)2 and Mg (OH)2 neutralize with condensate H2SO4 and HNO3, while under the cloud, ammonia neutralizes with SO2 adsorbed on suspended particles containing Ca2+ and Mg2+ [20,33]. H+ concentration reflects the acidity of raindrops neutralized by Ca2+ and NH4+ [34], and the relative acidity (FA) is an index to evaluate the neutralization degree of precipitation acidity [20]. In this study, the FA values of precipitation were 0.002, 0.006 and 0.01 in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining, respectively, indicating that 99.8%, 99.4% and 99% of precipitation acidity was neutralized by alkaline components in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining. Multi-annual mean values of the neutralization factors (NFs) of three cities were shown in Figure 6. NFs below 1 indicate that acidic substances have a significant effect on neutralizing substances. It can be seen that Ca2+ had the highest neutralization capacity of precipitation in the three cities, with an average value of 1.69 in Karamay, 1.38 in Urumqi and 1.42 in Yining, respectively, being followed by Na+ and NH4+. The other ions, such as K+ and Mg2+, did not have obvious effect in neutralizing the rainwater acidity. The difference between Karamay and the other two stations was that the value of NF (Mg2+) is higher than NF (K+).
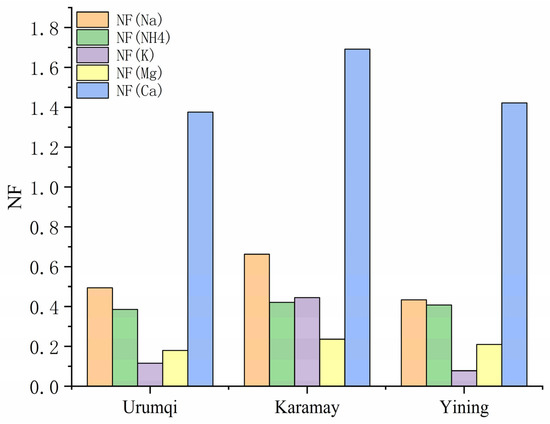
Figure 6.
Multi-annual mean values of NFs of the precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining.
To further examine the relationship between acidic substances and neutralizing ones, ionic ratios such as (NO3− + Cl−)/SO42−, NH4+/NO3−, and NH4+/SO42− were calculated [35]. The (NO3− + Cl−)/SO42− ratios of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining were 0.53, 1.13 and 0.40, respectively. The (NO3− + Cl−)/SO42− ratio of Karamay was higher than 1, indicating that nitric acid and hydrochloric acid contributed significantly to the acidity of precipitation in Karamay, while the ratios of Urumqi and Yining were lower than 1, indicating that the contribution of sulfuric acid in precipitation was more significant. The NH4+/NO3− ratios of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining are 2.98, 1.61 and 2.67, respectively. The NH4+/NO3− ratios of the three stations were greater than 1, indicating that ammonium neutralizes nitric acid and may form NH4NO3 in the atmosphere [36]. The NH4+/SO42− ratios of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining are 0.46, 0.63 and 0.50, respectively. If this ratio was lower than 1, it indicated that CaSO4 and (NH4)2SO4·CaSO4·2H2O may be formed possibly. If the ratio was close to 1, NH4HSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 were likely to exist in the atmosphere [37]. Therefore, sulfates in the atmosphere of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining are likely to exist in the form of CaSO4 and (NH4)2SO4·CaSO4·2H2O.
In order to evaluate the availability of ammonia in neutralizing acidic substances (H2SO4 and HNO3) in the atmosphere, the ammonium availability index (AAI) was determined [21,22]. In this study, the AAI values of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining were 20.90%, 25.05% and 22.47%, respectively, indicating that there was not enough ammonium to neutralize sulfuric and nitric acids. AAI is only an evaluation index to evaluate the neutralizing capacity of NH4+ over sulfuric and nitric acids. Other alkaline ions, such as Ca2+ or Na+, could contribute to the pH value of precipitation, so the AAI value didn’t correspond to the pH value.
3.4. Wet Deposition Rates of Main Ions
Wet deposition (WD) is an important way to remove pollutants from the atmosphere, giving further insights on the chemical composition of precipitation and providing information on long-range transported pollutants [35]. Inorganic sulfur and nitrogen in the atmosphere mainly arrive at the surface in the form of SO42−, NO3− and NH4+ through dry deposition and wet deposition. Excessive S and N deposition will lead to vegetation damage, soil acidification and other problems [12,38]. The multiannual wet deposition fluxes of inorganic S and N for the 2010–2019 period in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining were shown in Table 1. The multiannual WD fluxes of Urumqi, Karamay and Yining stations were dominated by S, of which the highest value was 42.46 kg·hm−2·a−1 in Urumqi, and the lowest was 11.19 kg·hm−2·a−1 in Karamay. The highest multiannual WD flux of NO3− was 6.91 kg·hm−2·a−1 in Urumqi and the lowest was 4.30 kg·hm−2·a−1 in Karamay. The highest multiannual WD flux of NH4+ was 6.15 kg·hm−2·a−1 in Urumqi and the lowest was 1.90 kg·hm−2·a−1 in Karamay. It can be seen that the multiannual WD fluxes of inorganic S and N in Urumqi were significantly higher than those in the other two stations. This was because of the high content of pollutants in the atmosphere firstly, and secondly it was closely related to precipitation. From the perspective of interannual variation, the multiannual WD fluxes of inorganic S in Urumqi generally showed a downward trend, which was directly related to the gradual completion of coal to gas heating in 2012. The multiannual WD fluxes of inorganic N in Urumqi showed a slow upward trend, which indicated that the pollution type of Urumqi was gradually changing from typical coal-burning pollution to compound pollution. The multiannual WD fluxes of inorganic S in Karamay also showed an obvious downward trend, while the changing trend of inorganic N was not obvious. Compared with the other two stations, the decreasing trend of the multiannual WD fluxes of inorganic S in Yining was not obvious, while the change of non-organic N showed an upward trend. In recent years, more and more factories have been built around Yining city, leading to the increasingly serious N pollution in the atmosphere.

Table 1.
The multiannual wet deposition fluxes of SO42−, NO3− and NH4+ for the 2010–2019 period in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining.
3.5. Origins of Major Ions in Precipitation
The chemical composition of precipitation is mainly affected by anthropogenic sources, sea fog, volcanic activity, biogenic material and terrestrial dust produced by weathering [27,39]. Therefore, the chemical composition of precipitation can reflect the source of air pollution. In atmospheric chemistry research, enrichment factors (EFs) are often applied to identify and examine the sources and contributions of major ions in precipitation [40,41]. Due to the single source and stable composition, Na+ and Ca2+ are generally used as reference ions of marine and continental sources, respectively [25,26]. The ion is enriched or diluted with respect to the reference ion depending on whether the EFs value is much higher or much lower than one. The EFs value is approximately equal to one, indicating that it has the same source as the reference element [11,27]. It can be seen from Table 2 that the EFsoil for Cl− in precipitation of the three stations ranged between 35.48 in Yining and 92.58 in Urumqi, whilst the EFseawater for Cl− ranged between 0.21 in Yining and 0.54 in Urumqi. The results indicated that Cl− had marine origins. The EFsoil and EFseawater for SO42− and NO3− were much higher than one, which were highly enriched relative to the ocean and soil, so it can be considered that most of them came from the contribution of human sources. The EFseawater for Ca2+ was much higher than one, indicating that it was mainly contributed by continental sources. The EFsoil for K+ was far less than one, while the EFseawater was far greater than one, indicating that the main source of K+ was land sources. The EFsoil for Mg2+ was far less than one and the EFseawater was close to one, indicating that the source of Mg2+ was both land sources and sea sources.

Table 2.
Enrichment factors for sea salt and soil components relative to the precipitation in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining.
Assuming that the natural sources of ion components in precipitation are ignored, the sources of these ions are mainly sea salt fractions (SSF), crustal fractions (CF) and anthropogenic source fractions (ASF). Overall, the results were consistent with the enrichment factors. The contribution rates of human activities of SO42− in Urumqi, Karamay and Yining were 89.81%, 86.97% and 90.19%, respectively, indicating that a large amount of energy consumption was the main source of SO42−, such as the combustion of minerals and the emission of thermal power plants. The marine contribution rate of Cl− was close to one, indicating that Cl− was the mainly sea salt ion, while non-marine origins were mainly due to various human activities, such as automobile exhaust and steel production. The contribution rate of NO3− to human activities is greater than 97%, which basically came from human activities, such as automobile exhaust and petrochemical production. The marine contribution rate of Ca2+ was only 2%, showing that Ca2+ basically came from land sources, such as soil dust, quarries and cement plants. The marine contribution rates of Mg2+ accounted for 79.65%, 86.96% and 73.48%, respectively. Xiao [42] found that magnesium had higher concentrations than calcium in some remote ocean areas, which explained that most of Mg2+ in the precipitation of the three cities could be attributed to sea salts. The marine contribution rates of K+ were 9.36%, 5.3% and 20.56% in the three cities respectively, indicating that K+ was basically terrestrial. Potassium can exist in soil in the form of coarse particles, and can also come from fine particles produced by biomass combustion and agricultural activities [43,44]. It is generally believed that Na+ comes from the ocean and F− and NH4+ come from human activities.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the chemical composition, pH variations, neutralization ability, wet deposition flux and source contributions of precipitation were discussed meticulously in three typical cities on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountain in Xinjiang over a period of 10 years. Results showed that the chemical composition characteristics of precipitation in the three cities were almost the same, which was related to the common policies and economic development characteristics of Xinjiang. The difference in concentration was mainly due to the differences in local pollution sources, precipitation and atmospheric circulation characteristics in different areas. Urumqi and Yining were dominated by typical soot-type air pollution, while Karamay tended to compound pollution. The volume-weighted mean pH value of precipitation was alkaline. Through the analysis of neutralizing process, it also showed that the three cities were facing serious acid pollution, but their alkaline substances such as Ca2+, NH4+ and Na+ had a strong neutralization ability, causing the precipitation to be alkaline in the study areas. The variations of the multiannual wet deposition fluxes of inorganic S and N for precipitation in the three cities were different. The pollution type of Urumqi was gradually changing from typical coal-burning pollution to compound pollution. Karamay was still compound pollution, and the inorganic N pollution in Yining was becoming more and more serious. SO42− mainly came from human activities in the three cities, such as the combustion of minerals and the emission of thermal power plants. The main sources of Cl− were marine sources, but non-marine sources were mainly attributed to various human activities. NO3− primarily came from human activities, including automobile exhaust and petrochemical production. Ca2+ came from land sources basically, such as soil dust, quarries and cement plants. Most of the Mg2+ came from marine sources, and K+ came primarily from land. Generally, Na+ came from the ocean, while F− and NH4+ were produced as a result of human activities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and X.L. (Xinchun Liu); methodology, Y.Z. and X.L. (Xia Li); formal analysis, Y.Z.; investigation, Z.F.; resources, X.L. (Xinchun Liu); writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. and Z.F.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z., X.L. (Xinchun Liu) and X.L. (Xia Li); visualization, M.A. and S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Grant No. IDM2016007), Xinjiang Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2022D01A161) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41405124).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are also extended to members of Urumqi Meteorological Bureau, Karamay Meteorological Bureau and Yining Meteorological Bureau for their support and many contributions to the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Mehr, M.R.; Keshsvarzi, B.; Sorooshian, A. Influence of natural and urban emissions on rainwater chemistry at a southwestern Iran coastal site. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Luo, X.; Liu, D.; Su, Y.; Wu, Z. The effect of construction dust and agricultural fertilization on the precipitation chemical composition during summer in the Yangtze River Delta area, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101121. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.M.; He, K.B.; Lei, Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Yu, X.C.; Tanaka, S.; Okuda, T.; Iwase, T. Chemical characters of atmospheric precipitation in Beijing in years of 2001~2003. China Environ. Sci. 2004, 24, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouli, P.C.; Mohan, S.V.; Reddy, S.J. Rainwater chemistry at a regional representative urban site: Influence of terrestrial sources on ionic composition. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Jin, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of acid rain patterns in northeastern China using a decision tree method. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wen, Z.; Shang, B.; Dore, A.J.; Tang, A.; Xia, X.; Zheng, A.; Han, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Precipitation chemistry and atmospheric nitrogen deposition at a rural site in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.W.; He, L.Y.; Hu, M. Chemical composition of atmospheric precipitation in Shenzhen. Environ. Sci. 2008, 29, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Z.; Liu, S.J.; Yu, X.N. Characteristics of Precipitation Chemistry and Wet Deposition in Zhuhai, China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Tian, D.; Yang, L.; Qiu, Z.J.; Wang, X.; Tan, B. Chemical composition of precipitation and its marine source at Liuxihe of Guangzhou. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 4924–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, D.S.; Zheng, X.M.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, G.Y.; Ren, S.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, H. Geochemical character of precipitation in summer of Shanghai 2008–2009. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Yu, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X. Chemical compositions of precipitation at three non-urban sites of Hebei Province, North China: Influence of terrestrial sources on ionic composition. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Qiu, C.; Ding, C.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. Analysis on chemical composition of precipitation and its source apportionment in Xi’an City. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudureheman, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Bai, X.; Jiang, H.; Yusufujiang, N. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric precipitation in Urumqi City. Environ. Chem. 2022, 41, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y. Build an economic belt on the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang, China. China Soft Sci. Mag. 2002, 3, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, Z.L. Chemical composition and provenance analysis of atmospheric precipitation in Xi’an area. Earth Environ. 2008, 36, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Liu, X.C.; Fan, Z.A.; Lu, H.; He, F.; Qu, T. Chemical Characteristics and Source Assessment of atmospheric precipitation at Urumqi. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2016, 10, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Liu, X.C.; He, Q.; Fan, Z.A.; Han, X.; Qu, T. Chemical characteristics and source assessment of atmospheric precipitation at Yining. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2016, 10, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.F. Temporal and spatial variation of chemical characteristics of precipitation in Urumqi. Arid Environ. Monit. 2013, 27, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Fan, Z.A.; Liu, X.C.; He, F. Chemical Characteristics and Source Assessment of atmospheric precipitation at Karamay. Arid Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Victor, T.; Chun, N. Chemical and statistical analysis of precipitation in Singapore. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possanzini, M.; Buttini, P.; Palo, V.D. Characterization of a rural area in terms of dry and wet deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 1988, 74, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M. Investigating the potential role of ammonia in ion chemistry of fine particulate matter formation for an urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3569–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S. PM2.5 episodes as observed in the speciation trends network. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5237–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Tiwari, S.; Matwale, J.; Pervez, S.; Tunved, P.; Safai, P.; Srivastava, A.; Bisht, D.; Singh, S.; Hopke, P. Sources of chemical species in rainwater during monsoon and non-monsoonal periods over two mega cities in India and dominant source region of secondary aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 146, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keene, W.C.; Pszenny, A.A.P.; Galloway, J.N.; Hawley, M.E. Sea salt correction and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 6647–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R. Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: A new table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, J.; Lu, S. Chemical characteristics of wet precipitation at an urban site of Guangzhou, South China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, M. Atmospheric Environmental Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 365–446. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.-J.; Liang, C.-S.; Ji, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X. Chemical composition of rainwater and the acid neutralizing effect at Beijing and Chizhou city, China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164–165, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhuang, G.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, A. The chemistry of the severe acidic precipitation in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Ding, G.A. Sources assessment of acid rain in eastern coastal areas of China. China Environ. Sci. 1997, 17, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Barrie, L.A.; Hales, J. The spatial distributions of precipitation acidity and major ion wet deposition in North America during 1980. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1984, 36, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, R.M.; Pio, C.A. Size-differentiated composition of inorganic atmospheric aerosols of both marine and polluted continental origin. Atmos. Environ. 1983, 17, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chate, D.M.; Devara, P.C.S. Acidity of raindrop by uptake of gases and aerosol pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keresztesi, Á.; Birsan, M.V.; Nita, I.A.; Bodor, Z.; Szép, R. Assessing the neutralization, wet deposition and source contributions of the precipitation chemistry over Europe during 2000–2017. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Air Pollution; Wiley: Hoboken, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, F.K.; Liu, X.D.; He, K.B.; Lu, Y.Q.; Wang, L. Atmospheric aerosol concentration level and chemical characteristics of water-soluble ionic species in wintertime in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Monit. JEM 2003, 5, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Du, J.; Kota, S.; Ying, Q.; Xiao, W.; Tang, Y. Wet deposition of sulfur and nitrogen in Jiuzhaigou national nature reserve, Sichuan, China during 2015–2016: Possible effects from regional emission reduction and local tourist activities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 233, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Chemical composition and source identification of rainwater constituents at an urban site in Xi’an. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2016, 75, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szép, R.; Bodor, Z.; Miklóssy, I.; Nita, I.-A.; Oprea, O.A.; Keresztesi, Á. Influence of peat fires on the rainwater chemistry in intra-mountain basins with specific atmospheric circulations (Eastern Carpathians, Romania). Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 647, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatkin, S.; Ad Ali, M.; Bayram, A. A study on the precipitation in Izmir, Turkey: Chemical composition and source apportionment by receptor models. J. Atmos. Chem. 2016, 73, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-W.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Luo, L.; Shen, C.-Y.; Long, A.-M.; Chen, L.; Long, Z.-H.; Li, D.-N. Atmospheric aerosol compositions over the South China Sea: Temporal variability and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y. Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a developing urban site in southeastern China. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szép, R.; Mateescu, E.; Niță, I.A.; Birsan, M.V.; Bodor, Z.; Keresztesi, Á. Effects of the Eastern Carpathians on atmospheric circulations and precipitation chemistry from 2006 to 2016 at four monitoring stations (Eastern Carpathians, Romania). Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).