Influence of Ambient Atmospheric Environments on the Mixing State and Source of Oxalate-Containing Particles at Coastal and Suburban Sites in North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Online Instruments and Data Analysis
2.3. Screening of Five HM-Containing Particles
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Characteristics of SPAMS Particles
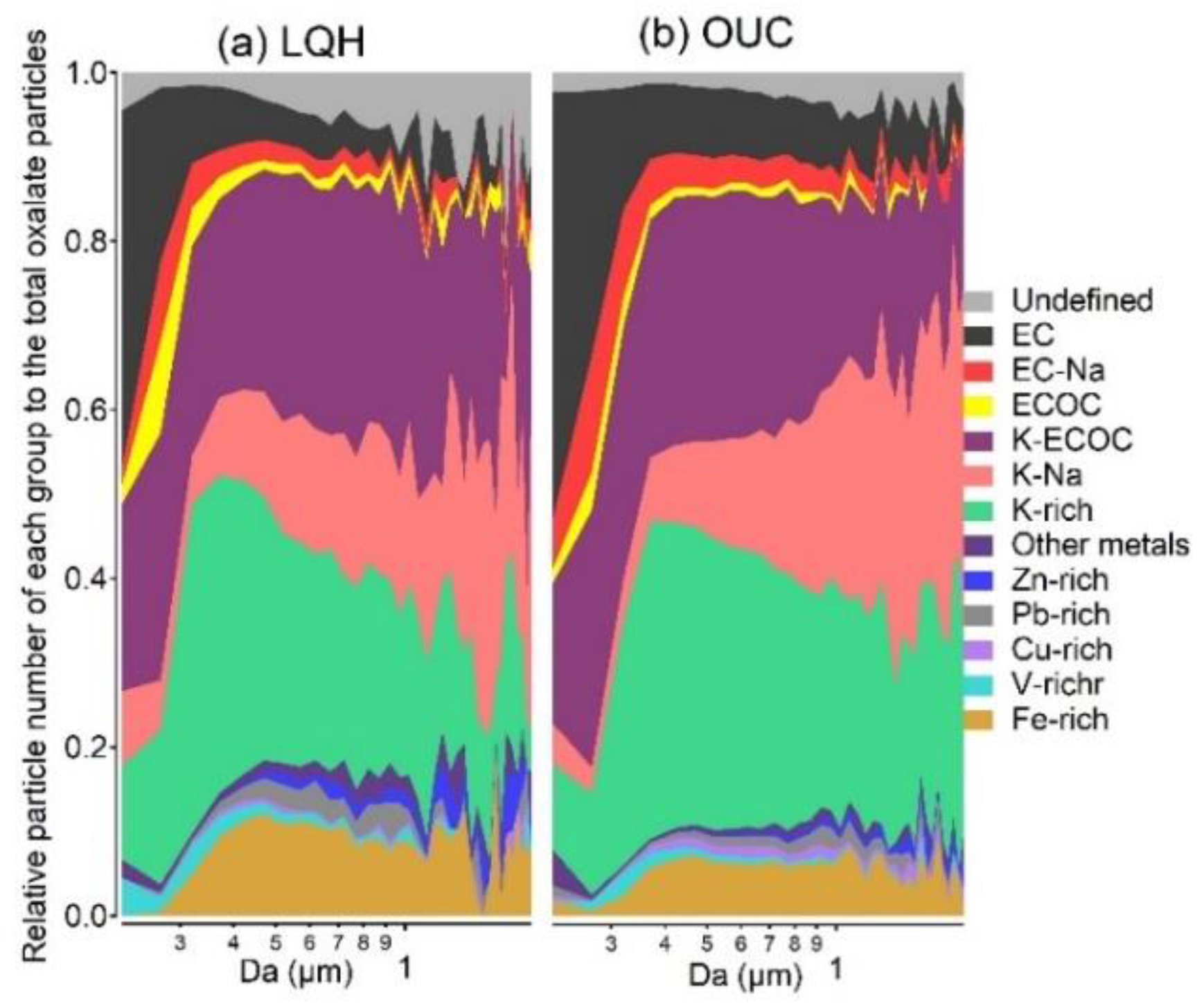
3.2. Individual Characteristics of Oxalate-Containing Particles
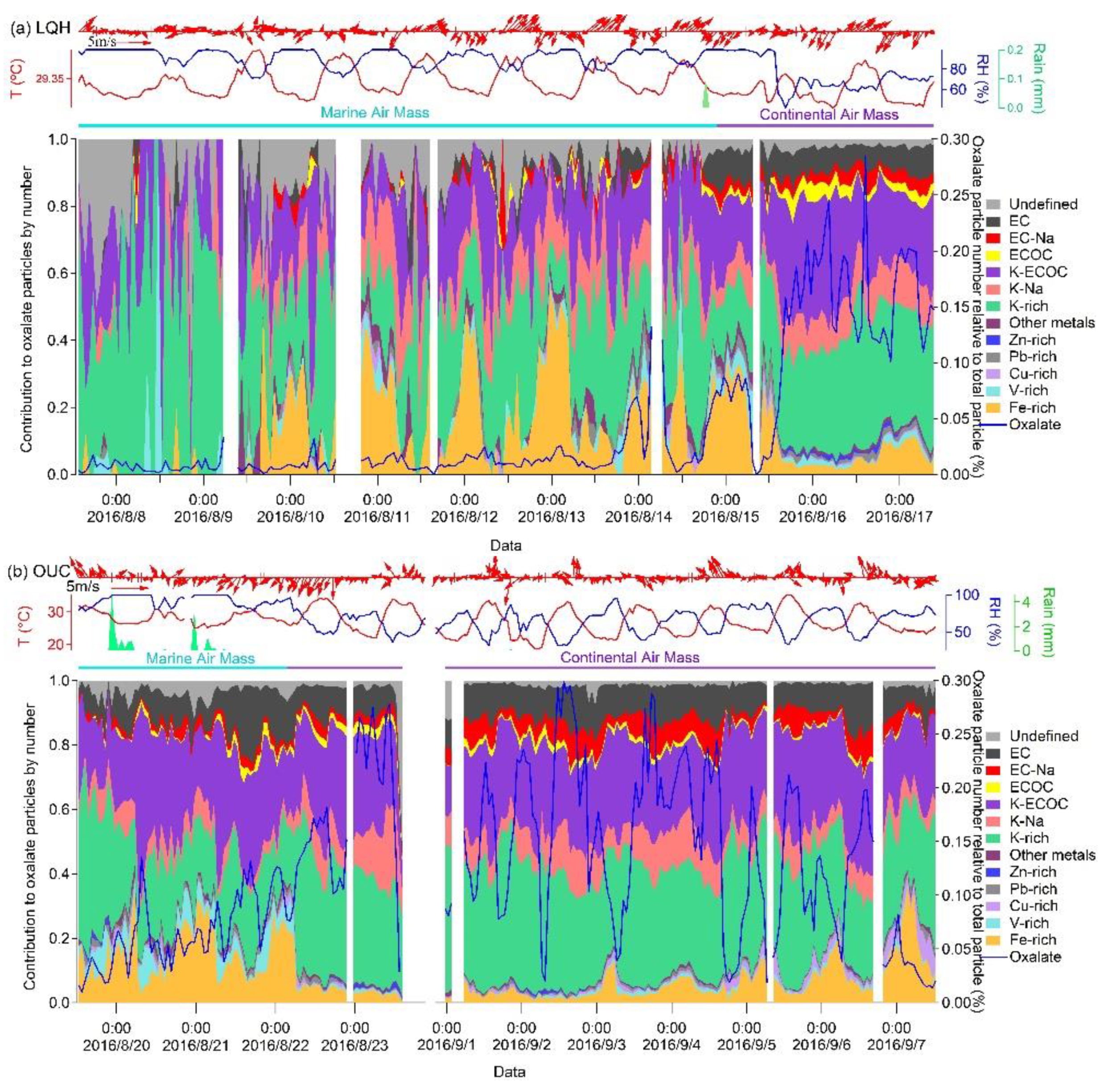
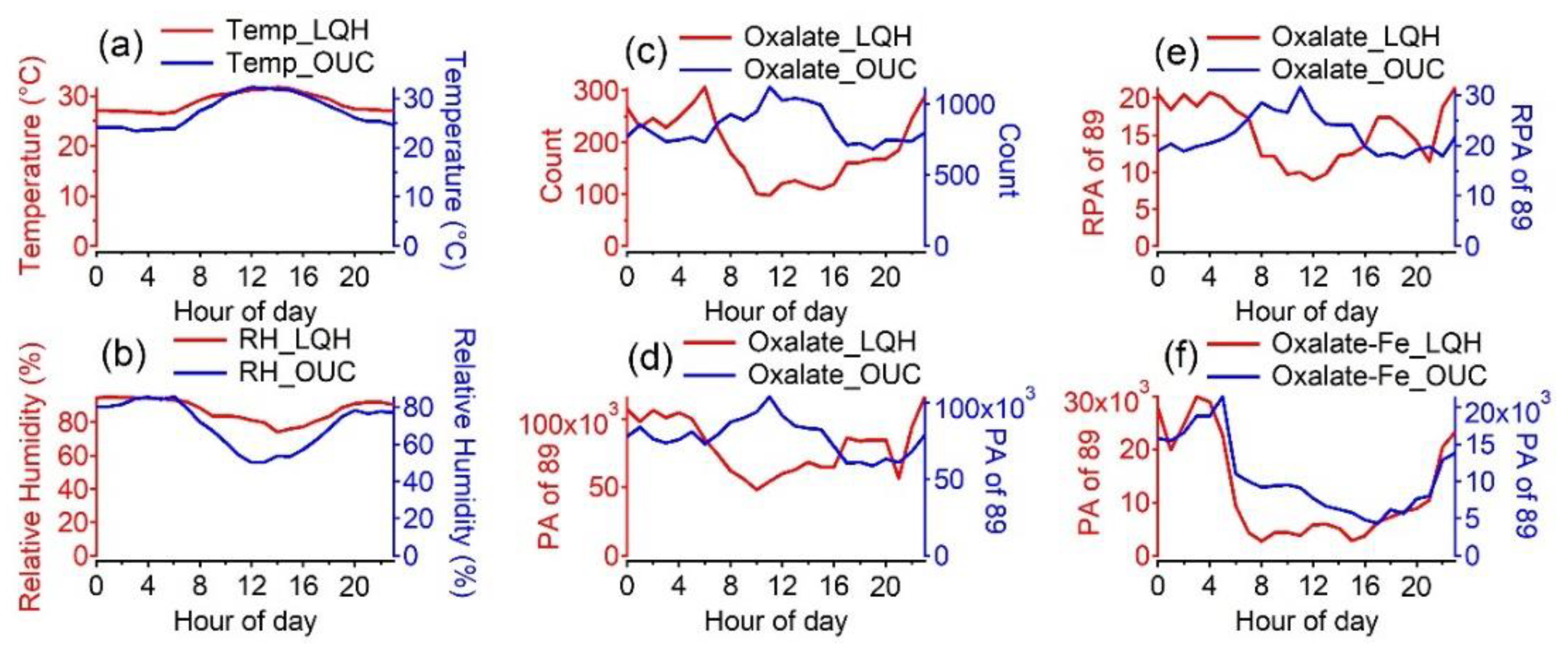
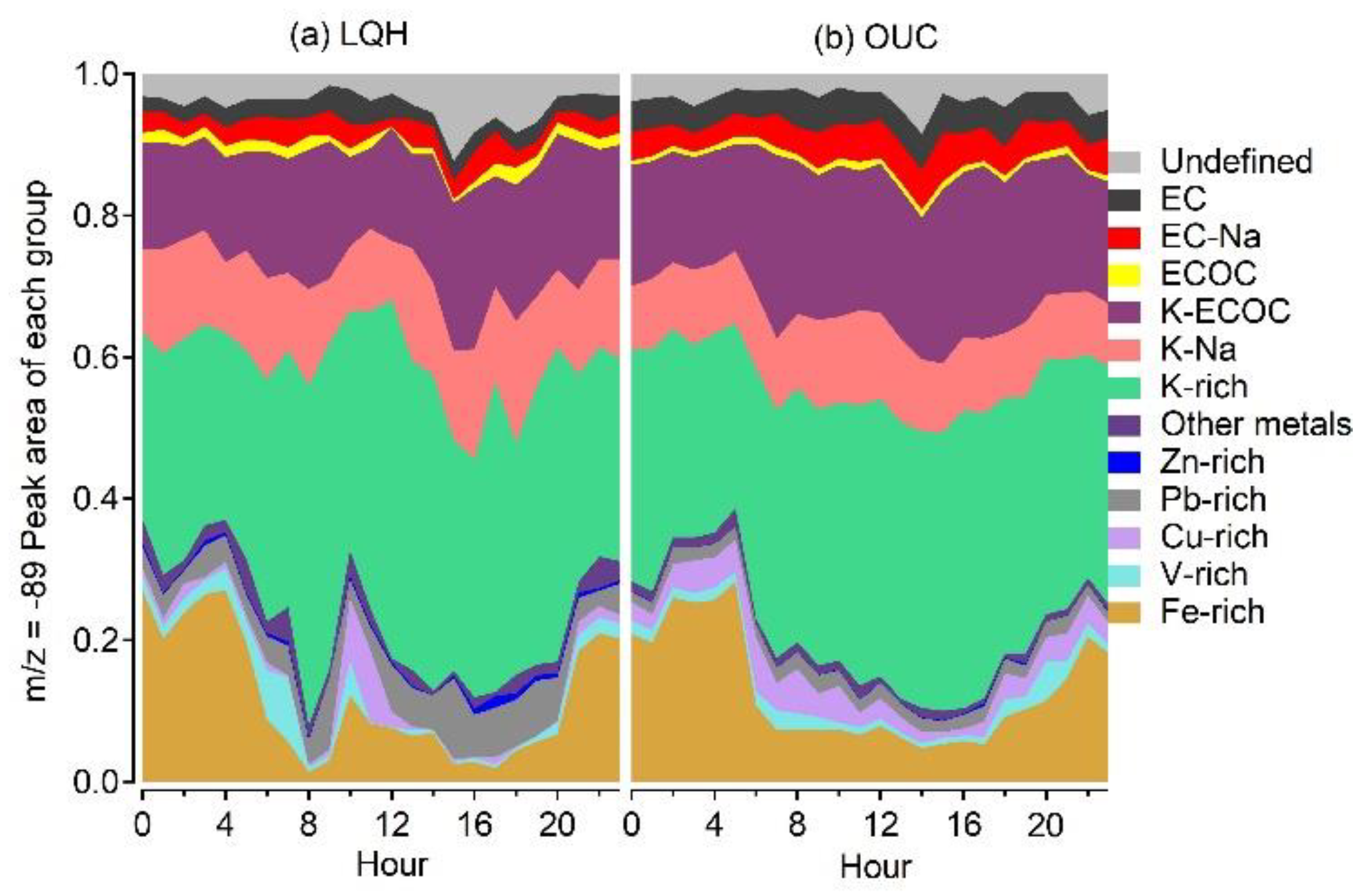
3.3. Diurnal Variation in Oxalate-Containing Particles
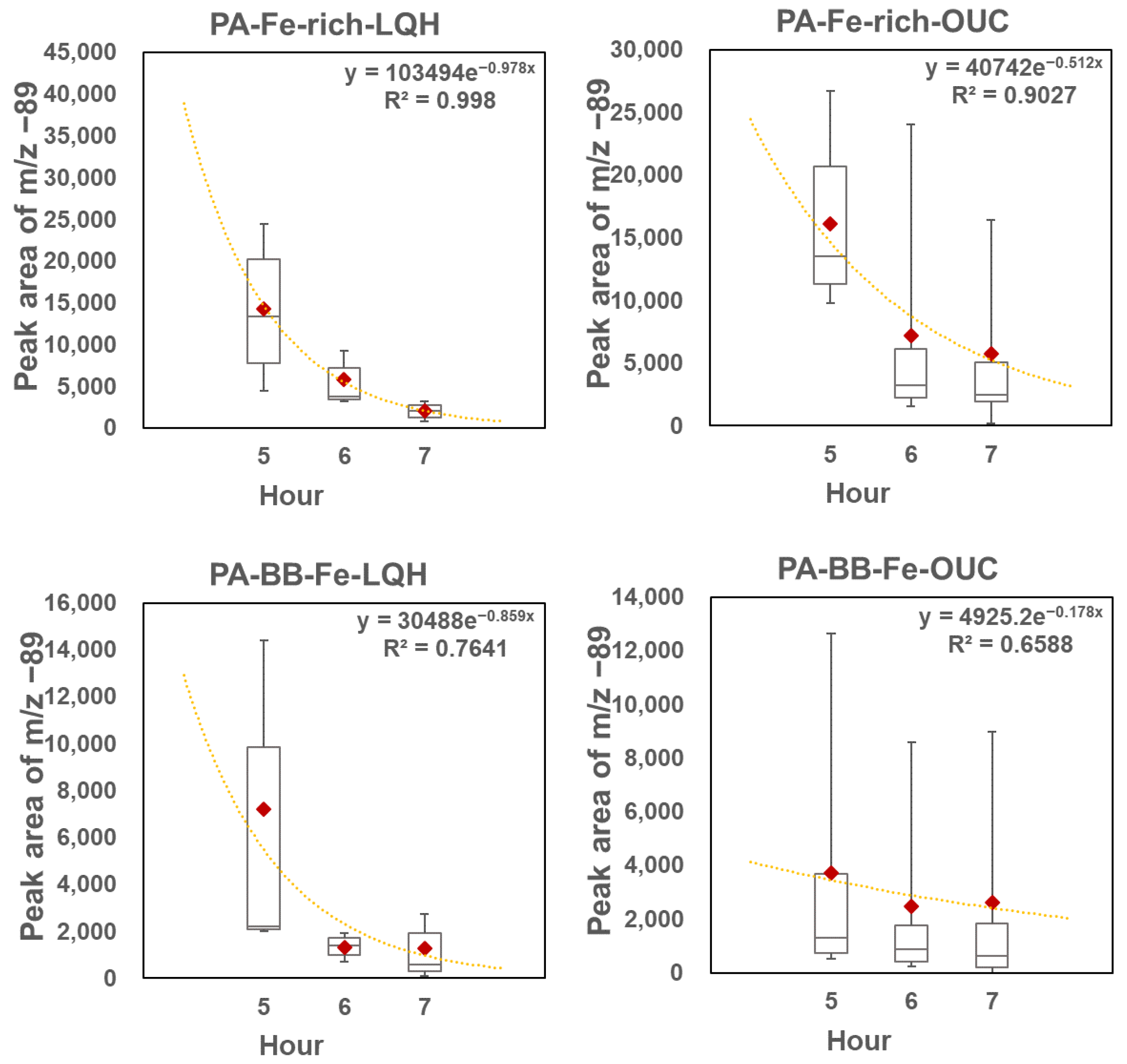
3.4. Decay of Oxalate in Different Oxalate–Fe Particle Types
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chebbi, A.; Carlier, P. Carboxylic acids in the troposphere, occurrence, sources, and sinks: A review. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 4233–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Du, J.; Chen, J. Single particle mass spectrometry of oxalic acid in ambient aerosols in Shanghai: Mixing state and formation mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3876–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, V.-M. Relative roles of secondary sulfate and organics in atmospheric cloud condensation nuclei production. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 17321–17333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; He, H.; Liu, C. Hygroscopic properties of oxalic acid and atmospherically relevant oxalates. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.H.H.; Griffith, S.M.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.; Meng, J.; Chan, C.K.; Louie, P.K.K.; et al. A field measurement based scaling approach for quantification of major ions, organic carbon, and elemental carbon using a single particle aerosol mass spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Griffith, S.M.; Wu, G.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, J.Z. Field Evidence of Fe-Mediated Photochemical Degradation of Oxalate and Subsequent Sulfate Formation Observed by Single Particle Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6562–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-F.; Yu, J.Z.; He, L.-Y.; Yuan, Z. Water-soluble organic carbon and oxalate in aerosols at a coastal urban site in China: Size distribution characteristics, sources, and formation mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D22212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narukawa, M.; Kawamura, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Nakajima, T. Distribution of dicarboxylic acids and carbon isotopic compositions in aerosols from 1997 Indonesian forest fires. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3101–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamasoe, M.A.; Artaxo, P.; Miguel, A.H.; Allen, A.G. Chemical composition of aerosol particles from direct emissions of vegetation fires in the Amazon Basin: Water-soluble species and trace elements. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Cheng, C.; Li, M.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhong, Q.E.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, Z. The enhanced mixing states of oxalate with metals in single particles in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.B.; Tan, Y.; Perri, M.J.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Turpin, B.J. Aqueous chemistry and its role in secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10521–10539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilgner, A.; Herrmann, H. Radical-driven carbonyl-to-acid conversion and acid degradation in tropospheric aqueous systems studied by CAPRAM. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5415–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, G.; Meng, J.; Wang, Q.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Size-resolved airborne particulate oxalic and related secondary organic aerosol species in the urban atmosphere of Chengdu, China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 161–162, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, G.; Peng, L.; Lian, X.; Bi, X.; Li, L.; Chen, D.; et al. The reductions of oxalate and its precursors in cloud droplets relative to wet particles. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 235, 117632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, M.; Chan, C.K.; Tong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Wu, D.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Cheng, P.; et al. Mixing state of oxalic acid containing particles in the rural area of Pearl River Delta, China: Implications for the formation mechanism of oxalic acid. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9519–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, T.; Takahashi, Y. Oxalate metal complexes in aerosol particles: Implications for the hygroscopicity of oxalate-containing particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4289–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Lin, Q.; Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Liu, F.; Song, W.; Chen, D.; Cai, Z.; Bi, X.; et al. Oxalate Formation Enhanced by Fe-Containing Particles and Environmental Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Murphy, J.G. The Mechanisms Responsible for the Interactions among Oxalate, pH, and Fe Dissolution in PM2.5. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Arangio, A.M.; Lakey, P.S.J.; Berkemeier, T.; Liu, F.; Kampf, C.J.; Brune, W.H.; Pöschl, U.; Shiraiwa, M. Hydroxyl radicals from secondary organic aerosol decomposition in water. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Bi, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Peng, L.; Lian, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, D.; Miller, M.; et al. In-cloud formation of secondary species in iron-containing particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorooshian, A.; Wang, Z.; Coggon, M.M.; Jonsson, H.H.; Ervens, B. Observations of Sharp Oxalate Reductions in Stratocumulus Clouds at Variable Altitudes: Organic Acid and Metal Measurements During the 2011 E-PEACE Campaign. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7747–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weller, C.; Tilgner, A.; Bräuer, P.; Herrmann, H. Modeling the Impact of Iron–Carboxylate Photochemistry on Radical Budget and Carboxylate Degradation in Cloud Droplets and Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5652–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Gao, W.; Nian, H.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Cheng, P.; et al. Real time bipolar time-of-flight mass spectrometer for analyzing single aerosol particles. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.H.; Bian, Q.; Griffith, S.M.; Louie, P.K.K.; Yu, J.Z. Sources and atmospheric processes impacting oxalate at a suburban coastal site in Hong Kong: Insights inferred from 1 year hourly measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9772–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Prather, K.A. Investigations of the Diurnal Cycle and Mixing State of Oxalic Acid in Individual Particles in Asian Aerosol Outflow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8062–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-H.; Hopke, P.K.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Classification of Single Particles Analyzed by ATOFMS Using an Artificial Neural Network, ART-2A. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, H.; Jung, J.; Miura, K.; Takami, A.; Kato, S.; Kajii, Y.; Uematsu, M. Single-particle chemical characterization and source apportionment of iron-containing atmospheric aerosols in Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D18204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ault, A.P.; Gaston, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Dominguez, G.; Thiemens, M.H.; Prather, K.A. Characterization of the Single Particle Mixing State of Individual Ship Plume Events Measured at the Port of Los Angeles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.M.; O’Connor, I.P.; Hellebust, S.; Allanic, A.; Sodeau, J.R.; Wenger, J.C. Characterisation of single particles from in-port ship emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6408–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.C.; de Foy, B.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J.; Prather, K.A. Measurement of ambient aerosols in northern Mexico City by single particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4499–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Ma, L.; Cheng, C.; Pei, C.; Chan, C.K.; Bi, X.; Qin, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; et al. Real time analysis of lead-containing atmospheric particles in Guangzhou during wintertime using single particle aerosol mass spectrometry. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Allen, J.O. Source apportionment of lead-containing aerosol particles in Shanghai using single particle mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, W. Source appointment of PM2.5 in Qingdao Port, East of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, M.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Nian, H.; Tang, R.; Chan, C.K. Real-time chemical characterization of single ambient particles at a port city in Chinese domestic emission control area — Impacts of ship emissions on urban air quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Z. Mixing state of biomass burning particles by single particle aerosol mass spectrometer in the urban area of PRD, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3447–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Dai, S.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, N.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Peng, P.a.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; et al. Real-time and single-particle volatility of elemental carbon-containing particles in the urban area of Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 118, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-L.; Dai, X.-R.; Li, J.-R.; Tong, L.; Hui, Y.; Cao, M.-Y.; Li, M.; Xiao, H. The characteristics and mixing states of PM2.5 during a winter dust storm in Ningbo of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Shi, G.; Wang, H.; Tian, M.; Liu, S.; Huang, R.; et al. Single particle characterization of summertime particles in Xi’an (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Mi, T.; Cao, J.; Shi, G.; Huang, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Lou, S.; Wang, Q. Characterizing the composition and evolution of and urban particles in Chongqing (China) during summertime. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; An, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, B.; Xia, L.; Duan, Q.; Zou, J. Mixing state of ambient aerosols in Nanjing city by single particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; McGillicuddy, E.J.; Esser-Gietl, J.K.; Harrison, R.M.; Wenger, J.C. On the simultaneous deployment of two single-particle mass spectrometers at an urban background and a roadside site during SAPUSS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9693–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Li, M.; Shi, G.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, X.; Feng, Y. Mass spectra features of biomass burning boiler and coal burning boiler emitted particles by single particle aerosol mass spectrometer. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.Z.; Thepnuan, D.; Wiriya, W.; Janta, R.; Punsompong, P.; Hemwan, P.; Charoenpanyanet, A.; Chantara, S. Emission factors of metals bound with PM2.5 and ashes from biomass burning simulated in an open-system combustion chamber for estimation of open burning emissions. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamkaew, C.; Chantara, S.; Janta, R.; Pani, S.K.; Prapamontol, T.; Kawichai, S.; Wiriya, W.; Lin, N.-H. Investigation of Biomass Burning Chemical Components over Northern Southeast Asia during 7-SEAS/BASELInE 2014 Campaign. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2655–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyan, A.; Flament, P.; Locoge, N.; Deboudt, K.; Riffault, V.; Alleman, L.Y.; Schoemaecker, C.; Arndt, J.; Augustin, P.; Healy, R.M.; et al. Investigation on the near-field evolution of industrial plumes from metalworking activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J.; Healy, R.M.; Setyan, A.; Flament, P.; Deboudt, K.; Riffault, V.; Alleman, L.Y.; Mbengue, S.; Wenger, J.C. Characterization and source apportionment of single particles from metalworking activities. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, S. A full-scale analysis of chemical characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 during haze and non-haze episodes in Cixi city, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.; Hou, H.; Shangguan, Y.; Li, F. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468-469, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, H. Characterization of lead-containing aerosol particles in Xiamen during and after Spring Festival by single-particle aerosol mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, B.; Luo, J.; Zhang, W.; Rao, Z.; Yang, F. Characterization of lead-containing atmospheric particles in a typical basin city of China: Seasonal variations, potential source areas, and responses to fireworks. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.B.; Huang, C.K.; Wu, H.T.; Lin, J.J.; Chang, S.H. Characteristics of heavy metals on particles with different sizes from municipal solid waste incineration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 79, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.C.; Chillrud, S.N.; Simpson, H.J.; Bopp, R.F. Refuse Incinerator Particulate Emissions and Combustion Residues for New York City during the 20th Century. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ault, A.P.; Moore, M.J.; Furutani, H.; Prather, K.A. Impact of Emissions from the Los Angeles Port Region on San Diego Air Quality during Regional Transport Events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3500–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, S.; Huggins, F.E.; Huffman, G.P.; Linak, W.P.; Miller, C.A. XAFS Studies of Nickel and Sulfur Speciation in Residual Oil Fly-Ash Particulate Matters (ROFA PM). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shen, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and mixing state of aerosol at the summit of Mount Tai (1534 m) in Central East China: First measurements with SPAMS. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pei, C.; Li, L.; Wu, M.; Wu, M.; Huang, B.; Cheng, C.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Source-oriented characterization of single particles from in-port ship emissions in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Walters, W.W.; Hastings, M.G.; Song, L.; Huang, S.; Zhu, F.; Liu, D.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y. Atmospheric nitrate formation pathways in urban and rural atmosphere of Northeast China: Implications for complicated anthropogenic effects. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Yoon, J. pH effect on OH radical production in photo/ferrioxalate system. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, C.; Horn, S.; Herrmann, H. Photolysis of Fe(III) carboxylato complexes: Fe(II) quantum yields and reaction mechanisms. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 268, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, C.; Horn, S.; Herrmann, H. Effects of Fe(III)-concentration, speciation, excitation-wavelength and light intensity on the quantum yield of iron(III)-oxalato complex photolysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 255, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, D.; Liu, J. Diverse redox chemistry of photo/ferrioxalate system. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44654–44658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervens, B.; Feingold, G.; Frost, G.J.; Kreidenweis, S.M. A modeling study of aqueous production of dicarboxylic acids: 1. Chemical pathways and speciated organic mass production. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D15205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crahan, K.K.; Hegg, D.; Covert, D.S.; Jonsson, H. An exploration of aqueous oxalic acid production in the coastal marine atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3757–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Kanai, Y.; Uematsu, M.; Zheng, G.; Marcus, M.A. Seasonal changes in Fe species and soluble Fe concentration in the atmosphere in the Northwest Pacific region based on the analysis of aerosols collected in Tsukuba, Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7695–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Individual Particles | Total Particle | Oxalate | Fe | V | Cu | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LQH | Number | 670887 | 42226 | 22629 | 42934 | 22776 | 11672 | 3099 |
| % in total particle | 6.3% | 3.4% | 6.4% | 3.4% | 1.7% | 0.5% | ||
| OUC | Number | 1718778 | 211180 | 66465 | 95051 | 137227 | 36037 | 30847 |
| % in total particle | 12.3% | 3.9% | 5.5% | 8.0% | 2.1% | 1.8% | ||
| Oxalate | Oxalate-HMs | Oxalate-Fe | Oxalate-V | Oxalate-Cu | Oxalate-Pb | Oxalate-Zn | ||
| LQH | Number | 42226 | 12720 | 4636 | 3596 | 3612 | 3145 | 1105 |
| % in Oxalate | 100.0% | 30.1% | 11.0% | 8.5% | 8.6% | 7.4% | 2.6% | |
| % in Oxalate-metals | 100.0% | 36.4% | 28.3% | 28.4% | 24.7% | 8.7% | ||
| % in each HMs | 20.5% | 8.4% | 15.9% | 26.9% | 35.7% | |||
| OUC | Number | 211180 | 53324 | 16559 | 15385 | 21562 | 9448 | 7792 |
| % in Oxalate | 100.0% | 25.3% | 7.8% | 7.3% | 10.2% | 4.5% | 3.7% | |
| % in Oxalate-metals | 100.0% | 31.1% | 28.9% | 40.4% | 17.7% | 14.6% | ||
| % in each HMs | 24.9% | 16.2% | 15.7% | 26.2% | 25.3% |
| LQH | OUC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Number | Fraction | Number | Fraction |
| K-rich | 13,507 | 32.0% | 70,354 | 33.3% |
| K-ECOC | 11,078 | 26.2% | 60,610 | 28.7% |
| K-Na | 4531 | 10.7% | 21,209 | 10.0% |
| EC | 3080 | 7.3% | 20,963 | 9.9% |
| EC-Na | 1472 | 3.5% | 11,138 | 5.3% |
| ECOC | 1177 | 2.8% | 3386 | 1.6% |
| Fe-rich | 3725 | 8.8% | 11,983 | 5.7% |
| V-rich | 788 | 1.9% | 2762 | 1.3% |
| Pb-rich | 660 | 1.6% | 1518 | 0.7% |
| Zn-rich | 241 | 0.6% | 366 | 0.2% |
| Cu-rich | 205 | 0.5% | 1946 | 0.9% |
| Other metals | 508 | 1.2% | 1155 | 0.5% |
| Undefined | 1254 | 3.0% | 3790 | 1.8% |
| Oxalate | 42,226 | 6.3% | 211,180 | 12.3% |
| mass | 670,887 | 100.0% | 1,718,778 | 100.0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Feng, L.; Xie, H.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Sheng, L.; et al. Influence of Ambient Atmospheric Environments on the Mixing State and Source of Oxalate-Containing Particles at Coastal and Suburban Sites in North China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050647
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Li L, Feng L, Xie H, Li W, Liu X, Zhu Y, Sheng L, et al. Influence of Ambient Atmospheric Environments on the Mixing State and Source of Oxalate-Containing Particles at Coastal and Suburban Sites in North China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(5):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050647
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yunhui, Yanjing Zhang, Xiaodong Li, Lei Li, Limin Feng, Huan Xie, Wenshuai Li, Xiaohuan Liu, Yujiao Zhu, Lifang Sheng, and et al. 2022. "Influence of Ambient Atmospheric Environments on the Mixing State and Source of Oxalate-Containing Particles at Coastal and Suburban Sites in North China" Atmosphere 13, no. 5: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050647
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Li, L., Feng, L., Xie, H., Li, W., Liu, X., Zhu, Y., Sheng, L., Qi, J., Gao, H., Zhou, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2022). Influence of Ambient Atmospheric Environments on the Mixing State and Source of Oxalate-Containing Particles at Coastal and Suburban Sites in North China. Atmosphere, 13(5), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050647







