Abstract
Background/Aims: Ledrinae comprises about 460 described species across five tribes and represents an early-branching, morphologically distinctive lineage of leafhoppers, yet its intra-subfamilial relationships remain ambiguous owing to limited mitogenomic sampling. Here, we sequence and annotate the complete mitochondrial genome of Petalocephala arcuata—only the 18th Ledrinae mitogenome—to broaden taxon coverage within the genus and furnish critical molecular data for rigorously testing Ledrinae monophyly and refining tribal and genus level phylogenetic hypotheses. Methods: In this study, we sequenced and annotated the complete mitochondrial genome of P. arcuata via Illumina sequencing and de novo assembly, and reconstructed the phylogeny of 62 Cicadellidae species using maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference methods. Results: The 14,491 bp circular mitogenome of P. arcuata contains 37 genes with 77.4% A+T. All PCGs use ATN start codons except ND5 (TTG), and codon usage is A or U biased. Of 22 tRNAs, only trnS1 lacks a DHU arm, while the others adopt the canonical cloverleaf structure. Bayesian inference and maximum likelihood analyses produced broadly congruent topologies with mostly high nodal support, recovering Ledrinae as monophyletic and clustering all Petalocephala species into a well-supported clade. Conclusions: In this study, we enriched the molecular resources for the genus Petalocephala by sequencing, annotating, and analyzing the complete mitochondrial genome of P. arcuata. Phylogenetic reconstructions based on these genomic data align closely with previous morphological diagnoses, further confirming the monophyly of the genus Petalocephala.
1. Introduction
The subfamily Ledrinae (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Cicadellidae) comprises five tribes—Ledrini, Rubrini, Xerophloeini, Afrorubrini, and Hespenedrini—and currently encompasses approximately 460 described species. Members of this lineage occur worldwide, with particularly high diversity in the Oriental region and Australia [1,2,3,4,5]. Li et al. [6] have identified China as a principal center of Ledrinae diversity, recording 28 genera and over 180 species within its borders. Owing to its early-branching position within Cicadellidae and its suite of distinctive morphological characters, Ledrinae has long been a focal group for taxonomic and phylogenetic investigations [7,8]. To date, most studies have been confined to α-taxonomy, relying on morphological diagnoses to describe new taxa; however, pronounced intraspecific variation in certain species has frequently led to taxonomic ambiguities and misidentifications [9,10].
Compared with traditional morphology-based taxonomy, molecular phylogenetic analyses effectively surmount the subjectivity inherent in morphological character scoring and the challenges of homology assessment. Single locus markers (e.g., 28S rDNA [11], COI [12]) often yield biased topologies due to limited phylogenetic signal and heterogeneous substitution rates. With the advent of high-throughput sequencing [13], a combined strategy—integrating complete mitochondrial genomes with multiple nuclear and mitochondrial loci—has become increasingly favored for its ability to substantially improve tree resolution and nodal support [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Mitochondrial genomes offer distinct advantages over nuclear markers: strict maternal inheritance, negligible recombination, and a compact gene arrangement (absence of introns and only one extensive intergenic spacer in the control region) [21]. Furthermore, genome-level characters—such as gene-order rearrangements, intergenic spacer length variation, and unconventional tRNA anticodon usage—provide a wealth of fine-scale phylogenetic signals for disentangling complex lineage relationships [22]. In earlier work, Wang et al. [10] employed mitochondrial, nuclear, and combined datasets to perform a multilocus phylogenetic reconstruction of Ledrinae, with particular emphasis on the internal relationships of its largest tribe, Ledrini. They observed that Destinoides and Petalocephala are morphologically congruent, prompting Jones and Deitz [2] to synonymize them; however, Sun et al. [23] challenged this synonymy, noting that these types specimens had not been examined. More analyses by Wang et al. [10] revealed that both Destinoides and Petalocephala are polyphyletic, with Petalocephala resolved into two distinct clades. One clade is sister to the Tituria + Laticorona lineage and can be diagnosed by the elongate apical process of the male genitalia; this lineage was therefore erected as the new genus Lataramus (comprising Lataramus gongshanensis and Lataramus dicondylicus), whose members are readily distinguished by their pronounced genital apical projections. Moreover, phylogenetic analyses of Petalocephala dicondylica, L. gongshanensis, and Petalocephala eurglobata—despite a limited taxon sampling of six Ledrinae genera—yielded a topology consistent with subsequent 2024 studies [10,24], uniformly supporting a non-sister relationship between L. gongshanensis and P. eurglobata. These congruent results further validate the stability and accuracy of the current subfamilial classification framework.
To date, only 17 complete mitochondrial genomes of Ledrinae have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database, representing a marked underrepresentation relative to the number of described taxa. Consequently, expanded taxon sampling within the subfamily is essential to rigorously test its monophyly and to resolve the taxonomic status and interrelationships at the tribal, generic, and species levels. In this study, we sequenced, annotated, and analyzed the complete mitochondrial genome of P. arcuate [25], thereby enriching the genomic resources for the genus Petalocephala. By integrating these new data with annotations from 16 other validated Ledrinae mitochondrial genomes, we reconstructed a comprehensive phylogenetic framework for the subfamily. Our results provide critical molecular evidence and theoretical support for future phylogenetic and evolutionary studies of Ledrinae and broader Hemipteran lineages.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
In August 2022, adult specimens of P. arcuata were collected from Malipo County, Yunnan Province, China (22°57′ N, 104°47′ E) (Table 1). All specimens were obtained from natural habitats without the need for collection permits. Upon capture, individuals were immediately preserved in 100% ethanol and subsequently stored at −80 °C in the freezer of the School of Life Sciences, Qufu Normal University. Species identification was performed according to the morphological criteria delineated by Dietrich [26]. To reduce potential contamination from gut microbiota during sequencing library preparation, abdomens were removed and only the remaining abdominal muscle tissue was used for genomic DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was isolated using the SanPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). Voucher specimens of male genitalia and corresponding DNA samples are deposited in the collections of the School of Life Sciences, Qufu Normal University.

Table 1.
Sequences used in this study.
2.2. Mitogenome Sequencing, Assembly, Annotation, and Analyses
Genomic DNA extracted from each specimen was subjected to library preparation at Personalbio Inc. (Shanghai, China) and sequenced on an Illumina platform. Raw reads were trimmed of adapters and quality-filtered to yield approximately 2.5 Gb of high-quality sequence data, which were assessed in DNASTAR SeqMan v17.2 and subsequently de novo assembled in Geneious R9.0 [27,28]. The resulting mitochondrial genome assemblies were initially annotated via the MITOS v2.1.9 web server using the invertebrate mitochondrial code; annotations of protein-coding genes (PCGs) and ribosomal RNA genes were further validated by BLAST v2.12.0 comparisons against NCBI, and tRNA genes were confirmed through homology searches against published mitochondrial genomes. Intergenic regions and gene overlaps were manually inspected and delineated, while the secondary structures of 22 tRNA genes were predicted using tRNAscan-SE v1.21 and ARWEN v1.2 [29,30]. Annotated genomes were visualized with Proksee (https://proksee.ca/, accessed on 5 May 2025). For comparative genomic analyses, mitochondrial genome sequences from 59 Cicadellidae species and two Cercopoidea species (as outgroups)—a total of 62 taxa—were retrieved from GenBank and systematically evaluated for nucleotide composition and skew, PCG codon usage and relative synonymous codon usage, and overall genome architecture.
2.3. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
In this study, 62 mitochondrial genomes from Cicadellidae and the outgroup superfamily Cercopoidea—specifically C. dorsimacula and C. bispecularis—were analyzed, including the newly sequenced P. arcuata (GenBank accession numbers are provided in Table 1). After excising stop codons, the nucleotide sequences of 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs) and two rRNA genes were concatenated for phylogenetic reconstruction. Alignments were generated in MAFFT v7.205: each PCG was aligned codon-by-codon with the L-INS-i algorithm, whereas the two rRNAs were aligned with Q-INS-i to account for secondary-structure constraints [31]. Nucleotide saturation was assessed with DAMBE 5 and found to be non-significant; poorly aligned regions were removed using Gblocks v0.91b with default settings [32]. The filtered alignments were concatenated in PhyloSuite v1.2.3. [33]. Partition schemes and the best-fitting substitution models were selected with ModelFinder [34]. Maximum-likelihood (ML) analysis was performed in IQ-TREE v1.6.12 [35], with branch support evaluated by 5000 ultrafast bootstrap replicates. Bayesian inference (BI) was carried out in MrBayes v3.2.6 [36], employing one cold and three heated chains in two independent MCMC runs of 2,000,000 generations each, sampling every 1000 generations and discarding the first 25% as burn-in. Convergence was accepted when the average standard deviation of split frequencies fell below 0.01 and all key parameters had effective sample sizes (ESSs) greater than 200. The final phylogenetic tree was visualized and taxonomically annotated in iTOL v6.7.4. [37].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mitogenome Organization and Nucleotide Composition
As illustrated in Figure 1 and Table 2, the mitochondrial genome of P. arcuata is a 14,491 bp double-stranded circular DNA molecule that harbors the canonical set of 37 mitochondrial genes: 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs), 22 tRNA genes, two rRNA genes and one single A+T-rich control region (CR). Twenty-three genes reside on the heavy (H) strand and fourteen on the light (L) strand. The CR is positioned between rrnS and trnI and spans 1149 bp (positions 13,342–14,490); variation in its length largely accounts for the differences in mitogenome size observed among Ledrinae species, whose gene order is otherwise conserved.
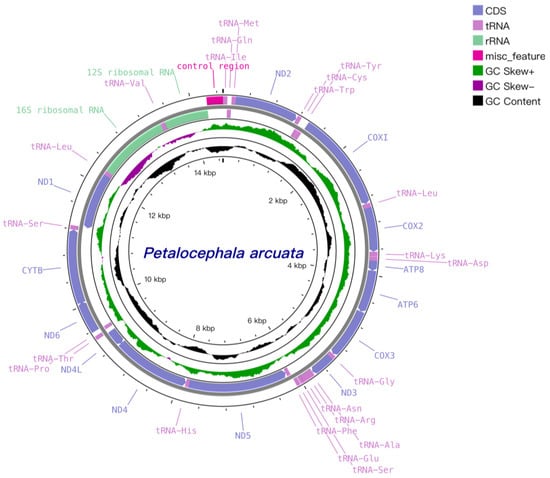
Figure 1.
Mitogenomes of P. arcuata.

Table 2.
Mitogenomic organization of P. arcuata.
Nine gene overlaps, totaling 43 bp, were detected, the longest (10 bp) occurring between trnS2 and ND1. Ten intergenic spacers, together comprising 37 bp, were also identified, the longest (8 bp) situated between trnP and ND6; the lengths of both overlaps and spacers fall within the typical range for congeneric mitogenomes. Notably, the customary 7–8 bp overlap between Atp8 and Atp6 reported in other subfamilies is absent in P. arcuata and its two congeners [24]. The nucleotide composition is strongly A+T biased, with an overall A+T content of 77.4% and 76.3% in the PCGs. Genome-wide AT-skew and GC-skew values are −0.264 and 0.136, respectively, indicating a relative deficit of adenine versus thymine and an excess of guanine over cytosine (Table 3).

Table 3.
Base composition of the mitochondrial genome of P. arcuata.
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes
The 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs) of P. arcuata span 10,923 bp, representing 76.3% of the mitochondrial genome, with an A+T content comparable to that of the full genome. All but one PCG initiate translation with the canonical ATN start codons (ATA, ATG, ATT); only ND5 employs the non-standard TTG initiation codon. This contrasts with the two congeners analyzed by Wang et al. [24], which uniformly use ATN start sites, suggesting an independent shift in ND5 initiation within the genus. Termination codons are either complete (TAA or TAG) or truncated (T–), the latter being presumably restored by post-transcriptional polyadenylation.
The A+T content at the first, second, and third codon positions is 72.3%, 68.7%, and 87.7%, respectively, reflecting a strong preference for A or U at synonymous sites. Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU; Figure 2) further highlights this bias: codons ending in A or U are markedly overrepresented, with UUU (Phe) exhibiting the highest RSCU value, followed by AUU (Ile) and AUA (Met). Correspondingly, amino acid frequency analysis (Figure 3) shows that Phe is the most abundant residue (12.86%), followed by Leu2 (9.47%) and Met (9.42%). In contrast, Gln, Arg, Cys, His, Ala, and Asp each account for less than 2% of residues, their cognate codons typically terminating in C or G, further corroborating the genome-wide A+T bias.
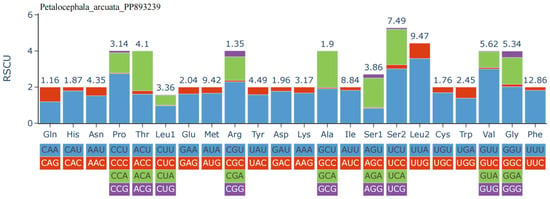
Figure 2.
Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of the mitogenome of P. arcuata.
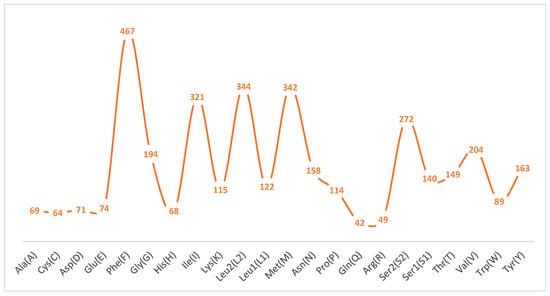
Figure 3.
Amino acid composition analysis of protein-coding genes.
3.3. Transfer and Ribosomal RNA Genes
P. arcuata harbors 22 canonical mitochondrial tRNA genes ranging from 56 bp (trnS1) to 73 bp (trnV) in length (Table 2); their combined A+T content is 79% (Table 3). With the exception of trnS1, all tRNAs fold into the standard clover-leaf secondary structure, in which the dihydrouridine (DHU) arm is reduced to a simple loop. Across the 22 tRNAs, seven non-canonical base pairs were identified, all of the UU type (Figure 4).
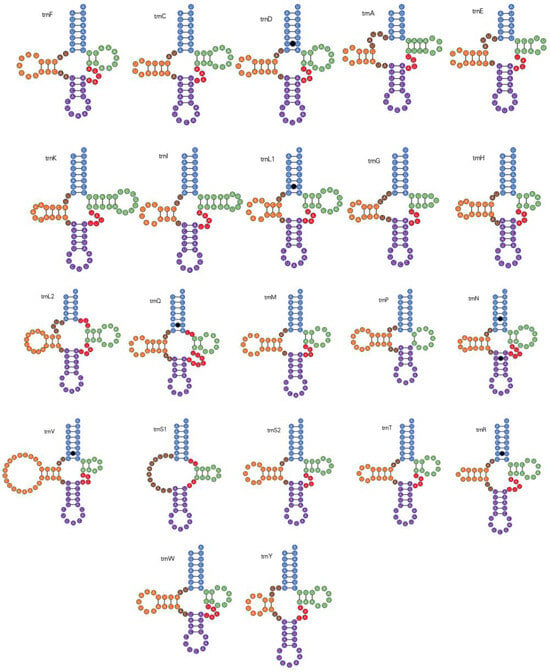
Figure 4.
Secondary structure models for the 22 mitochondrial tRNAs encoded by the P. arcuata. mitogenome.
The rrnL (1180 bp) is situated between trnL1 and trnV, whereas the rrnS (734 bp) resides between trnV and the control region; this arrangement is congruent with that reported for other Cicadellidae species. The two rRNA genes exhibit an average A+T content of 80.8%, mirroring the values reported by Wang et al. [24] for two congeners and making them, aside from the control region, the most A+T-rich coding segments of the mitogenome.
3.4. Control Region
The control region of P. arcuata was found to be 250 bp in length, positioned between rrnS and trnI, and exhibits a pronounced A+T content of 88% (Table 2).
3.5. Phylogenetic Relationships
A concatenated nucleotide matrix comprising the 13 mitochondrial protein-coding genes and both ribosomal RNA genes was assembled for 60 ingroup taxa representing nine subfamilies of Cicadellidae, together with two Cercopoidea species (C. dorsimacula and C. bispecularis) as outgroups. Phylogenetic reconstruction was conducted under maximum-likelihood (ML) (Figure 5) and Bayesian-inference (BI) (Figure 6) frameworks. The two optimal trees were topologically congruent and exhibited uniformly high nodal support (ML bootstrap, BS; Bayesian posterior probability, PP). At the family level, eight of the nine sampled subfamilies were recovered as monophyletic with strong support; the sole exception was Evacanthinae. The backbone topology can be summarized as (((((Ledrinae + Evacanthinae) Evacanthinae) + Cicadellinae) + Typhlocybinae) + ((Iassinae + Coelidiinae) + (Megophthalminae + Ulopinae))) + Deltocephalinae, where Evacanthinae is resolved as the well-supported sister group of Ledrinae (BS = 100; PP = 1.00). Evacanthinae itself forms two deeply divergent lineages (BS = 99.6; PP = 1.00): lineage I joins Ledrinae, Cicadellinae and Typhlocybinae, whereas lineage II is allied to Iassinae, Coelidiinae, Megophthalminae and Ulopinae. Deltocephalinae is placed as the basal clade of the family, consistent with earlier studies [10].
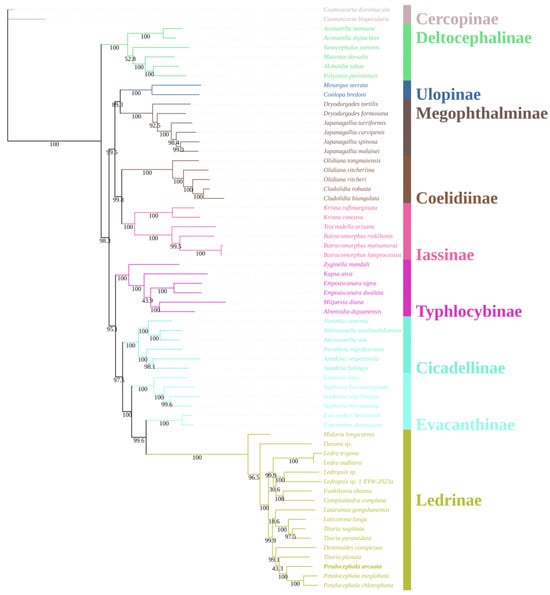
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree Cicadellidae species inferred via maximum likelihood analyses of the whole mitogenomes sequences.
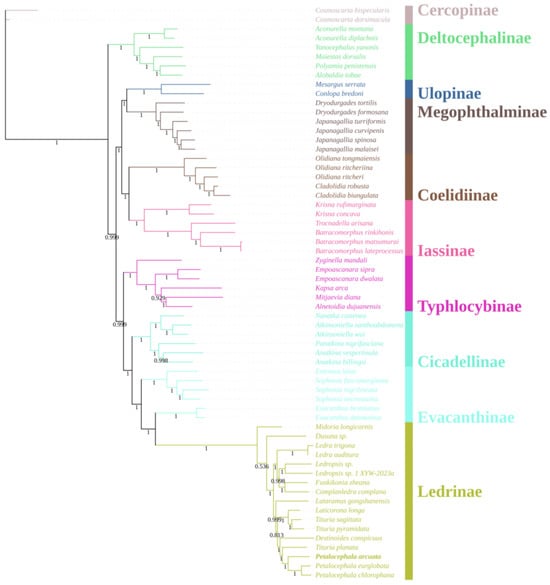
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic tree of Cicadellidae species inferred via Bayesian analyses of the whole mitogenomes sequences.
Within Ledrinae, the ML and BI topologies are virtually identical: Ledra and Ledropsis each constitute highly supported monophyletic clades. Two additional, strongly supported sister-group relationships were identified: (i) Laticorona is recovered as the sister lineage to Tituria (BS = 100; PP = 1.00), and (ii) Destinoides forms the sister lineage to the composite clade (Petalocephala + Tituria) (BS = 100; PP = 1.00). These results not only reinforce the monophyly of Petalocephala but also concur with the revision by Wang et al. [24], which removed L. gongshanensis from Petalocephala and erected a separate genus for the species.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we sequenced and characterized the complete mitochondrial genome of P. arcuata, a representative species of the Ledrinae. The circular mitogenome (14,491 bp) contains the typical 37 mitochondrial genes and an A+T-rich control region. Comparative analysis revealed that all protein-coding genes (PCGs) employ standard ATN initiation codons, with the notable exception of ND5 which utilizes TTG as its start codon. Secondary structure predictions showed that 21 of the 22 tRNAs adopt the canonical cloverleaf configuration, while tRNA-Ser1 (AGN) exhibits structural simplification through the loss of its DHU arm.
To clarify intrafamilial relationships within Cicadellidae, we compiled a concatenated dataset of the nucleotide sequences of 13 mitochondrial protein-coding genes (PCGs) and two rRNA genes from 62 representative species spanning nine subfamilies. Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed under both a Bayesian framework (MrBayes) and a maximum-likelihood framework. The resulting topologies were highly congruent, with most nodes exhibiting strong statistical support. Importantly, our analyses unequivocally corroborate the monophyly of the genus Petalocephala.
Author Contributions
Y.L. (Yujian Li) and Y.G. contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors. Y.L. (Yongcheng Liu), X.Y. and R.L. designed the study; R.L., S.J., C.X., L.J., Y.L. (Yongcheng Liu) and W.W. collected the data; Y.G., Y.L. (Yujian Li) and R.L. conducted the analyses; Y.L. (Yujian Li), Y.G. and Y.L. (Yongcheng Liu) wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation, grant number ZR2024MC092.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. Our research subject is not a protected species, and ethical committee approval is not required for experiments involving this insect group.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The mitogenome of Petalocephala arcuata has been deposited in the GenBank database under the accession number PP893239. The genomic Illumina sequencing data were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under accession numberPP893239.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Bin Zhang of Inner Mongolia Normal University and Xun Bian of Guangxi Normal University for their assistance in sampling.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Oman, P.W.; Knight, W.J.; Nielson, M.W. Leafhoppers (Cicadellidae): A bibliography, generic check-list and index to the world literature 1956–1985. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1990, 84, 569. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.R.; Deitz, L.L. Phylogeny and systematics of the leafhopper subfamily Ledrinae (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). Zootaxa 2009, 2186, 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Jones, J.R.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. A representative of the modern leafhopper subfamily Ledrinae in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae). Cretac. Res. 2019, 95, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Li, Z.Z. Descriptions of three new species of Petalocephala Stål, 1853 from China (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Ledrinae). Munis Entomol. Zool. 2011, 6, 499–503. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, C.R.; Deitz, L.L.; Dmitriev, D.A.; Sanborn, A.F.; Soulier-Perkins, A.; Wallace, M.S. The diversity of the true hoppers (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha). Insect Biodivers. Sci. Soc. 2018, 2, 501–590. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Jiang, L.N.; Li, Z.Z.; Xing, J.C. Parathlasia gen. nov.(Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Ledrinae, Ledrini), a new leafhopper genus from Guizhou, China. ZooKeys 2023, 1138, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.W. Character selection in systematics with special reference to the classification of leafhoppers (Insecta, Homoptera, Cicadelloidea). Syst. Zool. 1958, 7, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, H.H. Evolutionary developments in the leafhoppers, the insect family Cicadellidae. Syst. Zool. 1957, 6, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dietrich, C.H.; Skinner, R.K.; Zhang, Y. Phylogeny of Membracoidea (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha) based on transcriptome data. Syst. Entomol. 2023, 48, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Dietrich, C.H.; Dai, R. Molecular phylogeny of the leafhopper tribe Ledrini (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) with a reclassification and key to genera. Insect Syst. Divers. 2024, 8, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.H.; Rakitov, R.A.; Holmes, J.L.; Black, W.C., IV. Phylogeny of the major lineages of Membracoidea (Insecta: Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha) based on 28S rDNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2001, 18, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y. DNA barcoding of Deltocephalus Burmeister leafhoppers (Cicadellidae, Deltocephalinae, Deltocephalini) in China. Zookeys 2019, 867, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Dai, R.H. The complete mitochondrial genome of Tituria pyramidata (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Ledrinae) from China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 1757–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Dai, R.; Yang, M. Comparative mitogenomes of six species in the subfamily Iassinae (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and phylogenetic analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Li, C.; Song, Y. Complete mitochondrial genome of Eupteryx (stacla) minusula (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Typhlocybinae) from China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 2375–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnankutty, S.M.; Dietrich, C.H.; Dai, W.U.; Siddappaji, M.H. Phylogeny and historical biogeography of leafhopper subfamily Iassinae (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) with a revised tribal classification based on morphological and molecular data. Syst. Entomol. 2016, 41, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, R.; Gao, H.; Zhang, A.; Yan, Y.; Zou, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Yi, X.; et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of Coccotorusbeijingensis Lin et Li, 1990 (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Curculioninae, Anthonomini) and its phylogenetic implications. Biodivers. Data J. 2022, 10, e95935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, R.; Jiang, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xing, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. The complete mitochondrial genomes of three Evacanthini species, Evacanthus bivittatus, Carinata ganga, and Carinata recurvata, and phylogenomic analysis of the Evacanthini. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1410546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, R.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xing, J.; Li, Y. The Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Five Nivanini Species (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Evacanthinae) with Phylogenetic Analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Dietrich, C.H.; Zhang, Y. Phylogeny and classification of the leafhopper subfamily Eurymelinae (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) inferred from molecules and morphology. Syst. Entomol. 2020, 45, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.W.O.; Whitlock, M.C. The incomplete natural history of mitochondria. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F.; et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Webb, M.D.; Zhang, Y.L. Revision of the Oriental leafhopper genus Destinoides Cai & He (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Ledrinae), with a new synonym and two new combinations. Zootaxa 2014, 3786, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Li, D.F.; Li, H.; Wang, J.J.; Li, Y.J.; Dai, R.H. Comparison of mitogenomes of three Petalocephala species (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Ledrinae) and their phylogenetic analysis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 111, e21902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Ge, Z.L. Three new species of the genus Petalocephala from China (Homptera: Cicadelloidea: Ledrinae). Zool. Res. 1992, 13, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.H. Keys to the families of Cicadomorpha and subfamilies and tribes of Cicadellidae (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha). Fla. Entomol. 2005, 88, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. In Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, D.; Canbäck, B. ARWEN: A program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE5: A comprehensive software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).