Abstract
Background: Normal tension glaucoma (NTG) is becoming a more and more serious problem, especially in Asia. But the pathological mechanisms are still not illustrated clearly. We carried out this research to uncover the gene polymorphisms with NTG. Methods: We searched in Web of Science, Embase, Pubmed and Cochrane databases for qualified case-control studies investigating the association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and NTG risk. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each SNP were estimated by fixed- or random-effect models. Sensitivity analysis was also performed to strengthen the reliability of the results. Results: Fifty-six studies involving 33 candidate SNPs in 14 genetic loci were verified to be eligible for our meta-analysis. Significant associations were found between 16 SNPs (rs166850 of OPA1; rs10451941 of OPA1; rs735860 of ELOVL5; rs678350 of HK2; c.603T>A/Met98Lys of OPTN; c.412G>A/Thr34Thr of OPTN; rs10759930 of TLR4; rs1927914 of TLR4; rs1927911 of TLR4; c.*70C>G of EDNRA; rs1042522/-Arg72Pro of P53; rs10483727 of SIX1-SIX6; rs33912345 of SIX1-SIX6; rs2033008 of NCK2; rs3213787 of SRBD1 and c.231G>A of EDNRA) with increased or decreased risk of NTG. Conclusions: In this study, we confirmed 16 genetic polymorphisms in 10 genes (OPA1, ELOVL5, HK2, OPTN, TLR4, EDNRA, P53, NCK2, SRBD1 and SIX1-SIX6) were associated with NTG.
1. Introduction
Glaucoma is a disease characterized by optic neuropathy with the symptoms of visual impairment and visual field loss. It is usually associated with an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) [1]. Normal-tension glaucoma (NTG) is always supposed to be a spectrum of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) [2,3] but with an IOP in the normal range [4], featured by normal anterior chamber depth, retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thinning and progressing optic neuropathy [5]. NTG is becoming a more and more serious problem, with especially high prevalence in Asia. The morbidity of POAG in East Asians is from 1–4% [6], of which NTG contributes up to 95% [7]. However, it is reported that European Caucasians suffer less from NTG, which takes up about one-third of POAG patients [6]. It is plausible for us to suggest the incidence of NTG differs among various ethnicities. What is more, it should be noted that with the increased longevity, the incidence of NTG is likely to rise.
The pathological mechanisms of NTG are still not illustrated clearly and may be ascribed to multiple factors. Some hypotheses related to the pathogenesis include cardiovascular and neurovascular diseases, vasospasm, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and abnormal biomechanics of the lamina cribrosa and so on [6,8]. Genetic polymorphism is supposed to play an important role in NTG. For one reason, people could suffer from glaucoma at different ages, and genetic predisposition may mean an earlier onset [9]. For another, gene detection has come into effect in the recognition of allele mutations, especially for young Mendelian glaucoma [10]. Some genes have been found to be associated with NTG, including Optineurin (OPTN), TANK-binding kinase (TBK1) and Myocilin (MYOC) [10].
In recent years, more interest has been attracted to the topic of the association between gene polymorphisms and NTG. Many studies have pointed out the relationship and statistical significance of gene mutations in the disease [11,12]. However, it confuses us that the former research studies differ from each other in involved SNPs and statistical significance influenced by different study areas, population ethnicity and research heterogeneity.
Our meta-analysis aims to collect and summarize all the satisfactory literature, and analyze the effect of allele mutations and gene functions specific to the onset of NTG, so as to provide an extensive exploration and evidence for us to uncover the gene polymorphisms with NTG.
2. Materials and Methods
The research protocol has been registered in PROSPERO with the ID CRD42022326782.
2.1. Search Strategy
We conducted the literature search and selection mainly from the following four databases: Web of Science, Embase, Pubmed and Cochrane. Three groups of MeSH terms were put into the search interface to frame the Boolean search strategy as follows, “(((Genes[MeSH Terms]) OR ((((((((Genes[Title/Abstract]) OR (Gene[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cistron[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cistrons[Title/Abstract])) OR (Genetic Materials[Title/Abstract])) OR (Genetic Material[Title/Abstract])) OR (Material, Genetic[Title/Abstract])) OR (Materials, Genetic[Title/Abstract]))) OR ((Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide[MeSH Terms]) OR (((((((Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide[Title/Abstract]) OR (Nucleotide Polymorphism, Single[Title/Abstract])) OR (Nucleotide Polymorphisms, Single[Title/Abstract])) OR (Polymorphisms, Single Nucleotide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms[Title/Abstract])) OR (SNPs[Title/Abstract])) OR (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism[Title/Abstract])))) AND ((“Low Tension Glaucoma”[Mesh]) OR ((((((Low Tension Glaucoma[Title/Abstract]) OR (Glaucoma, Low Tension[Title/Abstract])) OR (Low Tension Glaucomas[Title/Abstract])) OR (Normal Tension Glaucoma[Title/Abstract])) OR (Glaucoma, Normal Tension[Title/Abstract])) OR (Normal Tension Glaucomas[Title/Abstract])))”. In this way, a systematic retrospect of original articles of all types analyzing the association between gene polymorphisms and NTG risk was acquired.
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- The diagnostic standard of NTG should be indicated clearly;
- (2)
- Cohort studies involving NTG patients and healthy controls which evaluate the potential association of specific gene mutations, SNPs, allele variations related to pathogenesis of the disease;
- (3)
- Some important information should be included: demographic features such as age and sex, allele or genotype frequencies of SNPs in both case and control groups, index of association strength such as odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Studies published in the form of meta-analysis, review, case report, patent, guideline, conference abstract and book chapters;
- (2)
- Studied objects are animals;
- (3)
- Studies not written in English;
- (4)
- Studies which lack OR value, only refers to POAG but not NTG or did not indicate a clear definition of POAG.
The included studies were come to by agreement of all the contributors of this article.
2.2. Data Extraction
Two reviewers independently screened and searched for the needed data from all the eligible literature. Disparities were discussed and solved by all the reviewers until consensus were reached. The following data were extracted and recollected in the table: reference (first author, year of publication), involved ethnicity, sample size of both case and control groups, demographic features including age and sex of two groups and genotyping method. If the basic or allele data of NTG were reported together with high-tension glaucoma (HTG) in POAG, we selected data specifically for NTG to document.
2.3. Quality Assessment
The methodological quality of all the eligible articles were assessed according to the Newcastle–Ottawa scale (NOS) [13]. There are three evaluation criteria in consideration: case selection, comparability and exposure. The quality of studies was recorded in the form of stars and the maximum star was 9. Studies acquired 6 stars or greater were considered up to our analyzing standard and qualified for further assessment.
2.4. Meta-Analysis
SNPs and gene mutations were qualified for meta-analysis if they were investigated by at least two studies. The statistical significance was recorded as OR [95% CI]. Allele frequency in eligible studies was calculated and screened after data organization, and minor allele for specific SNP was determined if it was consistent in all ethnic groups. Meta-analysis was processed by pooling OR values from eligible studies for the allele model (B versus A), dominant model (BB+ AB versus AA), recessive model (BB versus AA+ AB), heterozygote model (AB versus AA) and homozygote model (BB versus AA), respectively. Stata version 15.1 software (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA) was used to perform statistical analyses. The difference was considered to be of statistical significance if the p value was less than 0.05.
The heterogeneity tests for independent studies orienting the same SNPs were conducted by means of Q test and I2 test. p value was used as testing statistics for Q test, and heterogeneity existed if it was below 0.05. Similarly, if that I2 value was greater than 50% it suggested a possibility of heterogeneity [14]. Then we chose fixed-effect model for studies without obvious heterogeneity to analyze the OR value for each gene polymorphism. On the contrary, random-effect model was chosen. What is more, Begg’s Test was used to evaluate the publication bias among included articles [15].
Subjects with NTG were further classified into different ethnicities and stratified meta-analysis was conducted for them. Sensitivity analysis was alco carried out.
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Qualified Literature
The procedure of our selection strategy can be acquired from Figure 1.
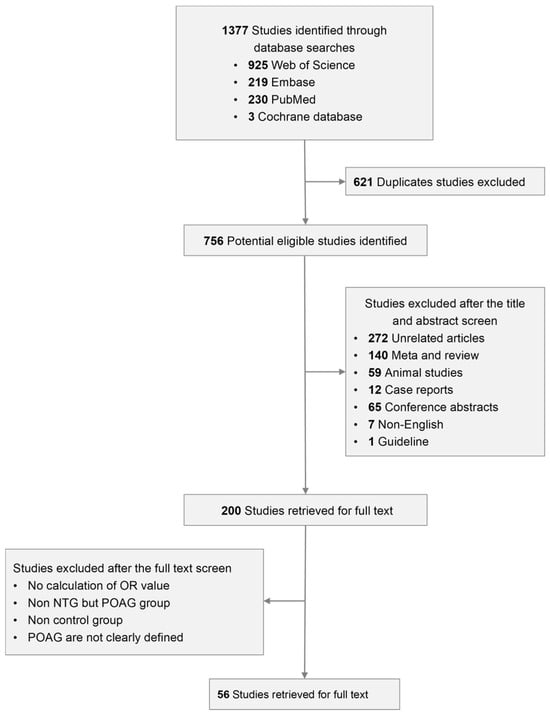
Figure 1.
The procedure of literature selection for meta-analysis.
A total of 1377 studies could be searched through the four databases, of which 925 were from Web of Science, 219 from Embase, 230 from Pubmed and the remaining 3 from Cochrane Database. Among them, 493 were duplicated articles which should be excluded. We then screened for the title as well as abstract of the other 621 studies and removed a large part of the literature, for there were 272 unrelated articles, 140 meta-analyses and reviews, 65 conference abstracts, 59 animal studies, 12 case reports, 7 non-English articles and 1 guideline. Two hundred studies were left for us to be read through and the articles were to be excluded if important information was absent such as if there was no calculation of the OR value, no NTG group but only POAG group, no control group or POAG was not defined clearly. Finally, 56 articles were verified to be eligible for our meta-analysis [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71].
3.2. Characteristics of Qualified Studies
The basic information of the included articles is summarized in Table 1. The qualified studies were published between November 2001 and January 2024. Among these studies, 55 were case control studies conducted in 11 countries and regions: 10 in China [22,26,37,40,53,54,57,66,69,70], 13 in Korea [20,25,30,39,47,58,59,60,62,63,64,67,71], 18 in Japan [18,19,23,24,27,31,32,33,34,38,41,42,46,48,49,51,52,56], 3 in Poland [55,61,65], 2 in the U.S [36,50], 3 in England [16,17,45], 2 in Australia [21,35] (one involving ethnicities of Caucasian and Asian with the other only Caucasian) and 1 each in four other countries or regions [28,29,43,68]. These studies involved 10,804 cases with NTG and 217,540 controls in all. Data from one GWAS were available whose cohort consisted of 305 Japanese NTG patients and 355 healthy controls [44]. The NOS scores of all the studies were above 6 stars (thus qualifying for the meta-analysis). Genotype frequency and minor allele frequency are shown in Table S1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of qualified studies involved in the meta-analysis.
3.3. Meta-Analysis Results
Among all the SNPs extracted from the candidate gene literature, only 33 in 14 genetic loci were reported by at least two studies and met the criteria of this study. The association analysis and heterogeneity test in different genetic models are shown in Table 2 (since minor allele was opposite for SNP c.*1222C>T of EDNRA in the two studies incorporated, further analysis was not carried out in view of the heterogeneity. The related information is exhibited in Table S1). Of the 33 SNPs, 16 SNPs exhibited significant association with NTG, in which 11 variations (rs166850 of OPA1; rs10451941 of OPA1; rs735860 of ELOVL5; rs678350 of HK2; c.603T>A/Met98Lys of OPTN; c.412G>A/Thr34Thr of OPTN; rs10759930 of TLR4; rs1927914 of TLR4; rs1927911 of TLR4; c.*70C>G of EDNRA and rs1042522/-Arg72Pro of P53) showed positive NTG risk, whereas 5 others (rs2033008 of NCK2; rs3213787 of SRBD1; c.231G>A of EDNRA; rs10483727 of SIX1-SIX6 and rs33912345 of SIX1-SIX6) showed negative correlation with the onset of NTG.

Table 2.
Significant association analysis of genetic polymorphisms with NTG.
3.3.1. Gene Polymorphisms Associated with NTG
The source articles and sample size for analysis of each SNP were summarized in Table 2.
EDNRA Polymorphisms
SNP c.-231G>A was associated with a decreased risk of NTG in the homozygote model (OR 0.61, 95%CI: 0.39–0.97, p = 0.035), but not in other models (Figure S1A).
SNP c.*70C>G was significantly associated with NTG in the dominant model (OR 1.67, 95%CI: 1.08–2.56, p = 0.020), but not in other models (Figure S1B).
ELOVL5 Polymorphism
A significant association between rs735860 of ELOVL5 gene and NTG was found in the heterozygote model (OR 1.51, 95%CI: 1.11–2.05, p = 0.009) (Figure S2A), but not in the other models (Figure S2B).
HK2 Polymorphism
A significant association between rs678350 and NTG could be seen in all genetic models (allele: OR 1.54, 95%CI: 1.23–1.91, p < 0.001; dominant: OR 1.75, 95%CI: 1.32–2.31, p < 0.001; recessive: OR 1.75, 95%CI: 1.09–2.80, p = 0.020; heterozygote: OR 1.65, 95%CI: 1.22–2.23, p = 0.001 and homozygote: OR 2.14, 95%CI: 1.31–3.48, p = 0.002) (Figure S3).
NCK2 Polymorphism
A significant association between rs2033008 and NTG could be seen in the allele (OR 0.70, 95%CI: 0.57–0.87, p = 0.001), recessive (OR 0.44, 95%CI: 0.27–0.70, p = 0.001) and homozygote models (OR 0.41, 95%CI: 0.25–0.67, p < 0.001) (Figure S4).
OPA1 Polymorphisms
A significant association between rs166850 and NTG was found in three genetic models (allele: OR 1.49, 95%CI: 1.03–2.15, p = 0.034; dominant: OR 1.93, 95%CI: 1.09–3.45, p = 0.025 and heterozygote: OR 1.82, 95%CI: 1.04–3.19, p = 0.038) (Figure S5A), but no evidence of an association was found in other models (Figure S5C).
A significant association between rs10451941 and NTG was found in all genetic models (allele: OR 1.49, 95%CI: 1.30–1.71, p < 0.001; dominant: OR 1.55, 95%CI: 1.29–1.87, p < 0.001; recessive: OR 1.87, 95%CI: 1.43–2.45, p < 0.001; heterozygote: OR 1.41, 95%CI: 1.16–1.71, p = 0.001 and homozygote: OR 2.16, 95%CI: 1.59–2.95, p < 0.001) (Figure S5B).
OPTN Polymorphisms
For SNP c.603T>A/Met98Lys, random effects showed a significant association between it and NTG in the allele, dominant and heterozygote models (allele: OR 1.51, 95%CI: 1.14–2.02, p = 0.005; dominant: OR 1.55, 95%CI: 1.12–2.14, p = 0.007; heterozygote: OR 1.49, 95%CI: 1.07–2.07, p = 0.018), but no evidence of association was found in other models (Figure S6A).
Referring to SNP c.412G>A/Thr34Thr, a significant association was found in all genetic models (allele: OR 1.66, 95%CI: 1.29–2.13, p < 0.001; dominant: OR 1.69, 95%CI: 1.27–2.25, p < 0.001; recessive: OR 3.72, 95%CI: 1.41–9.79, p = 0.008; heterozygote: OR 1.58, 95%CI: 1.17–2.12, p = 0.002 and homozygote: OR 4.22, 95%CI: 1.59–11.18, p = 0.004) (Figure S6B).
The other three SNPs (IVS6-5T>C, IVS6-10G>A, IVS7+24G>A) exhibited no statistical significance with NTG (Figure S6C–G).
P53 Polymorphism
A significant correlation of rs1042522/-Arg72Pro with NTG risk was revealed in the dominant model (OR 2.32, 95%CI: 1.02–5.28, p = 0.045), but not in the other four models (Figure S7).
SRBD1 Polymorphism
A negative correlation of rs3213787 and NTG risk could be seen in allele (OR 0.40, 95%CI: 0.30–0.52, p = 0.001), dominant (OR 0.38, 95%CI: 0.26–0.51, p = 0.001) and heterozygote (OR 0.41, 95%CI: 0.30–0.56, p = 0.002) models but not in other models (Figure S8).
TLR4 Polymorphisms
For rs10759930, results showed a significant association between it and NTG in heterozygote (OR 1.27, 95%CI: 1.02–1.59, p = 0.031) and homozygote models (OR 1.43, 95%CI: 1.06–1.94, p = 0.001) (Figure S9A).
For rs1927914, there was a significant association between it and NTG risk in the homozygote model (OR 1.43, 95%CI: 1.06–1.94, p = 0.020) (Figure S9B).
For rs1927911, a significant association between it and NTG risk was found in the heterozygote model (OR 1.29, 95%CI: 1.04–1.61, p = 0.021) (Figure S9C).
Rs12377632, rs2149356, rs11536889, rs7037117, rs7045953 revealed no significant association with NTG (Figure S9).
SIX1–SIX6 Polymorphism
Significant associations between rs10483727 and rs33912345 with a decreased risk of NTG could be seen in all models except for the heterozygote model (Figure S10A,B).
3.3.2. Gene Polymorphisms Not Associated with NTG
Among all the genetic polymorphisms analyzed, 17 SNPs in 7 genes were found not to be statistically significant with NTG (see Table 2).
3.3.3. Stratified Analysis in Different Ethnicities
In the stratification analysis by ethnicity, four SNPs were further investigated, including MTHFR rs397507444, OPA1 rs166850 and rs10451941 as well as p53 rs1042522. These SNPs showed no significant association with NTG in Asians. However, OPA1 rs166850, OPA1 rs10451941 and p53 rs1042522 were significantly associated with NTG in Caucasians (Table S2).
3.4. Measurement of Publication Biases and Sensitivity Analysis
Begg’s Test did not reveal publication bias among the overall analysis for candidate SNPs and corresponding genes (z < 1.96, p > 0.05, Table 2), which strengthened the credibility of our results. In the sensitivity analysis, Suh’s study [47] was excluded for rs7037117 in the TLR4 gene; this followed with a different conclusion that this SNP was significantly associated with NTG risk in the allele model (OR 1.46, 95%CI: 1.19–1.81, p < 0.001; I2 = 0.0%; Figure S11). Other alterations were not detected.
4. Discussion
Results showed that 16 SNPs in 10 genes were significantly associated with NTG in at least one genetic model. Related functions and pathogenic mechanisms of these associated alleles are summarized in Table 3 and Figure 2.

Table 3.
Possible functions and pathogenic mechanisms of the associated SNPs in the development of NTG.
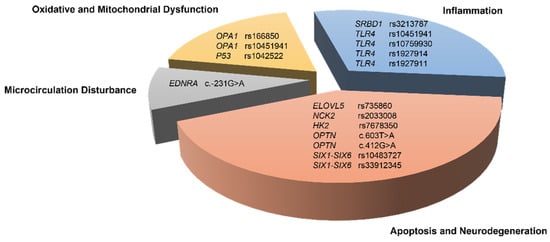
Figure 2.
SNPs significantly associated with the risk of NTG and their possible biological functions.
4.1. Oxidative Stress-Related Genes
The OPA1 gene encodes a kind of protein located in the inner membrane of mitochondria and plays an important role in cellular metabolism and activities, including stabilizing the mitochondrial construction, regulating mitochondrial fusion and fissure, taking part in oxidative phosphorylation and inhibiting chromosome c oxidase leaking, thus preventing cell apoptosis [72,73,74,75]. Aung [16] first conducted a study in Britain demonstrating that SNP rs166850 was significantly associated with NTG in 2002. We incorporated nine studies in our analysis with Caucasian, Asian and African-Caribbean populations, and finally elucidated that mutations in rs166850 and rs10451941 took effect in NTG in overall populations. This discovery reached the same conclusion as Guo’s meta-analysis in 2012 [76]. Compared with Guo, two more new studies were searched by us, thus confirming the reliability of the conclusion with a larger sample size. The interactions of the two polymorphisms with other genes may be a possible mechanism for NTG risk [65]. Interestingly, some scientists also found that TC/TC or CT/TT rs166850/rs10451941 combined genotype were more common in the Caucasian NTG population [16,45,65], which possibly indicated the overlapping pathogenetic effect of the two SNPs.
The P53 gene lies on the chromosome 17p13.1, encoding transcription factor p53 which regulates the cell circle, cell metabolism and senescence as well as DNA repair [77,78,79]. It is also related to cell apoptosis by stimulating the transcriptional activity of redox-related genes and producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) which damage the physiological function of mitochondria [80]. SNP rs1042522 has been reported to be located in the proline-rich region of p53 which would induce cell apoptosis by initiating the release of cytochrome c in the mitochondria into the cytosol [81]. Controversy exists about whether G allele or the mutant C allele would increase the susceptibility of POAG, with only different conclusions drawn in different ethnicities.
4.2. Neurodegeneration and Apoptosis-Related Genes
ELOVL5 is a member of the ELOVL gene family encoding a kind of elongase in the production of long-chain fatty acids [82], especially the polyunsaturated omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. The polyunsaturated fatty acids’ (PUFAs) metabolites play an important part in neurogenesis, neuronal survival and synaptic transmission [83,84,85]. What is more, ω-3 PUFAs could inhibit the damage of ischemia, inflammation, light, oxygen and age to retina [86]. Others showed that lack of eicosapentaenoic, docosahexaenoic acid and total ω-3 PUFAs were correlated to POAG risk [87]. The evidence above implies that alteration of rs735860 in the ELOVL5 gene may increase NTG susceptibility by affecting the neurons’ metabolism and inducing apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). Overexpression of ELOVL5 was also seen in prostate and gastric cancer cells for its incapability to regulate redox and mitochondrial homeostasis, and maintain appropriate production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [88,89], which pointed out a new possible pathogenetic mechanism to be studied further.
NCK2 encodes proteins that regulate the cellular actin dynamics and polarity by interacting with tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors [90,91]. NCK2 is demonstrated to exist in the ganglion cell layer, inner nuclear layer and outer plexiform layer, which are highest in the ganglion cell layer [51]. D2S176, which is located in the locus GLC1B and is only 24 kb from the gene NCK2, was found to be associated with a genetic heterogeneity of adult-onset POAG, and recently was considered to increase NTG risk in the Japanese population [92,93], which indicated the possible correlation of NCK2 and NTG. In our study, the A allele in rs2033008 was negatively related to NTG onset in Korean and Japanese populations; we speculate that this variation changed the interaction of NCK2 with other genes resulting in a defensive effect of RGCs. Shi et al. [51] found that this SNP was associated with NTG but not POAG and supposed that the mechanisms of NTG were focused on optic nerve damage, but for POAG, changes in the anterior chamber weighed more heavily.
The HK2 gene is located in the outer membrane of mitochondria and catalyzes the first step of glycolysis [51]. It is expressed widely in photoreceptors (PRs) and plays a role in the aerobic glycolysis metabolizing glucose entering the cells [94]. HK2 inhibits the release of cytochrome c to prevent apoptosis through the Bax/Bak pathway [95]. Zhou et al. [96] found that the decreased expression of HK2 would lead to irreversible rod degeneration in animal models. Given the importance of HK2-encoding proteins in mitochondria, it is reasonable to believe that the variant phenotypes could induce metabolic dysfunction and, furthermore, optic neuropathy.
OPTN is a 67 kDa protein which is expressed in many cells and tissues, especially in retina, brain, heart and skeleton muscle [97]. It acts as an adaptor protein and participates in many physiological activities such as signal transduction, cell division, cell survival, exocytosis, autophagy, protein trafficking and so on [97]. Mutations of OPTN have been widely considered a pathogenesis of POAG [98] as well as NTG [99,100], of which E50K (c.148G>A) is the most common to be associated with POAG, and another mutation H486R (c.1457A>G) is correlated with juvenile open-angle glaucoma (JOAG). In our study, we drew a conclusion that c.603T>A and c.412G>A in OPTN were significantly associated with NTG, but another POAG meta-analysis [101] only found the association between the former with NTG in the stratified analysis. The reason may lie in the difference in studies included: the POAG meta-analysis included four studies, while we included three studies for one of the four failed to define NTG clearly and was thus excluded.
SIX1-SIX6 belong to the SIX gene family containing two protein domains, which could encode homeobox domain transcription factors and may play a role in regulating the development of the visual system [102]. Studies have shown that a missense variant in rs33912345 of SIX6 was associated with RNFL thinning [103,104], suggesting its function in RGC development or degeneration. The possible mechanism lies in its interaction with CDNK2A/CDNK2B and subsequently triggering RGC loss [105,106]. Our results, finding that the risk allele mutations of both rs10483727 and rs33912345 were associated with NTG, were consistent with the findings of previous studies [104,107], which confirmed the results of this research.
4.3. Inflammation-Related Genes
SRBD1 encodes proteins which modulate signal transduction via binding with RNA. Its overexpression is considered to promote proinflammatory cytokines accumulation, prevent cell proliferation and accelerate cell apoptosis [108,109,110], which would do harm to RGCs in NTG. Kanemaki et al. stated that SRBD1 polymorphisms were associated with NTG, despite IOP [111], suggesting the different pathogenetic factors of NTG from hyper-tension glaucoma (HTG). Rs3213787 was revealed to be negatively correlated with NTG, which indicates that the G allele may reduce SRBD1 activity and protect RGC from apoptosis.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a kind of pattern recognition receptor (PRR) which play an important role in innate immunity and initiate inflammatory response by recognizing and binding with pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) [112]. Among them, TLR4 is expressed in the conjunctiva, cornea, uvea and retina [49]. A study found the overexpression of TLR4 in glaucomatous retina and the optic nerve [113], which indicates that inflammation and chronic stress would have an effect on the microenvironment of RGCs, change the construction of lamina cribrosa and increase the susceptibility of remaining axons, leading to irreversible optic neuropathy. Recently, it was suggested that TLR4 was associated with POAG for its activation generates meshwork fibrosis via the TGF-β pathway, leading to elevation of IOP [114]; in addition, ligands of TLR4 (e.g., LPS and HSP) were considered as candidate antigens of NTG [115]. In our study, rs10759930, rs1927914 and rs1927911 were seen to show a significant association with NTG; we speculate that these polymorphisms change the expression of some important proteins by altering the translated regions or intron regions of mRNA in the translation process.
4.4. Microcirculation Disturbance-Related Gene
EDNRA is the specific receptor of endothelial-1 (ET-1), a 21-amino acid peptide performing as a vasoconstrictor [116], and can mediate ET-1 level in retinal blood flow. ET systems express greatly in most ocular tissues [117,118]. There have been studies which reported higher ET-1 concentration in the plasma of NTG patients compared with that of controls [119,120]. ET-1 system activation causes vasospasm, vascular endothelial injury and microvascular lesion, thus damaging the optic nerve. In addition, ET-1 affects the morphology and physiology of the optic nerve in rabbit models, resulting in optic disc excavation, loss of axons and demyelination of the optic nerve despite the level of IOP [121,122]. It also inhibits the anterograde axonal transport, lowers neural metabolic activity and promotes astrocytes’ proliferation, which is responsible for the optic neuropathy in glaucoma [123].
Concerns regarding the limitation of utilizing duplicated datasets from the same researchers or groups (ex. Study 2, 8, 10 and 11 shown in Table 1) were also taken into account. In some specific scenarios, these overlapping data should be selected for further utilization according to standard, otherwise bias may occur if the same subject is incorporated repeatedly. In view of this, we searched further similar literature for advice [101,124,125]. As a result, we found that those SNP-associated meta-analyses also incorporated studies from the “same dataset”. It seems reasonable because the overlapping data were not really included in the analysis for a specific SNP. Though duplicated in the cohort information in some studies, they were independent from each other because they targeted different genes and SNPs. Hence, a great deal of information would be missed once these data were deleted.
In this study, we summarized the reported genotype polymorphisms and obtained an insight into SNPs’ association with the susceptibility to NTG. We adopted some measures such as Quality assessment, HWE test, Begg’s Test and sensitivity analysis to control possible statistical errors and assure the credibility of our meta-analysis. However, there are some limitations which should not be ignored in the meta-analysis. First, the sample size from different ethnicities should be enlarged. Second, only studies published in English met the inclusion criteria, which might cause a failure to incorporate other non-English articles, resulting in incomplete analysis. Finally, the functions and mechanisms of specific allele variants were not clearly explained, partly due to the different results of included articles and limited experimental evidence. Further studies should be conducted to explain the doubts.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the present study summarized the reported genotype polymorphisms and obtained an insight into SNPs’ association with susceptibility to NTG. The mechanisms of these mutations on NTG could possibly be attributed to changing the metabolisms and activities of RGCs via mitochondria functional alteration, inflammation and immunity. Experimental evidence and more large-scale studies are required for a greater understanding of these genes and polymorphisms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes15040491/s1, Figure S1. Associations between SNPs in EDNRA gene with NTG onset; Figure S2. Associations between SNPs in ELOVL5 gene with NTG onset; Figure S3. Associations between SNPs in HK2 gene with NTG onset; Figure S4. Associations between SNPs in NCK2 gene with NTG onset; Figure S5. Associations between SNPs in OPA1 gene with NTG onset; Figure S6. Associations between SNPs in OPTN gene with NTG onset; Figure S7. Associations between SNPs in P53 gene with NTG onset; Figure S8. Associations between SNPs in SRBD1 gene with NTG onset; Figure S9. Associations between SNPs in TLR4 gene with NTG onset; Figure S10. Associations between SNPs in SIX1-SIX6 gene with NTG onset; Figure S11. Sensitivity analysis for rs7037117 in TLR4 gene; Table S1. Genotype frequencies for candidate SNPs in the involved studies; Table S2. Genetic associations of NTG in different ethnicities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.P. and J.W.; Methodology, L.P. and J.W.; Software, L.P. and J.W.; Formal Analysis, L.P. and J.W.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, L.P.; Writing—Review and Editing, N.W.; Funding Acquisition, N.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (GZR-2012–009); Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Technology Development, Fund Project (JJ2018-50).
Institutional Review Board Statement
An ethics statement is not applicable because this study is based exclusively on published literature.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to all the colleagues who helped us.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Stein, J.D.; Khawaja, A.P.; Weizer, J.S. Glaucoma in Adults-Screening, Diagnosis, and Management: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, S.Y. [Modern view on normal-tension glaucoma]. Vestn. Oftalmol. 2020, 136, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esporcatte, B.L.; Tavares, I.M. Normal-tension glaucoma: An update. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2016, 79, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Killer, H.E.; Pircher, A. Normal tension glaucoma: Review of current understanding and mechanisms of the pathogenesis. Eye 2018, 32, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, M.B. Normal-tension glaucoma: Is it different from primary open-angle glaucoma? Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2008, 19, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, D.; Meyer, J.J. Normal Tension Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.J. Normal tension glaucoma in Asia: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Taiwan. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 10, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.L.; Tham, C.C. Normal-tension glaucoma: Current concepts and approaches-A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 50, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.F.; Gaier, E.D.; Wiggs, J.L. Genetics of Primary Inherited Disorders of the Optic Nerve: Clinical Applications. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a017277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggs, J.L.; Pasquale, L.R. Genetics of glaucoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R21–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alward, W.L.M.; van der Heide, C.; Khanna, C.L.; Roos, B.R.; Sivaprasad, S.; Kam, J.; Ritch, R.; Lotery, A.; Igo, R.P., Jr.; Cooke Bailey, J.N.; et al. Myocilin Mutations in Patients With Normal-Tension Glaucoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Rong, S.S.; Wu, Z.; Huang, C.; Matsushita, K.; Ng, T.K.; Leung, C.K.S.; Kawashima, R.; Usui, S.; Tam, P.O.S.; et al. Association of the CAV1-CAV2 locus with normal-tension glaucoma in Chinese and Japanese. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 48, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.; Ocaka, L.A.; Ebenezer, N.D.; Morris, A.G.; Brice, G.; Child, A.H.; Hitchings, R.A.; Lehmann, O.J.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Investigating the association between OPA1 polymorphisms and glaucoma: Comparison between normal tension and high tension primary open angle glaucoma. Hum. Genet. 2002, 110, 513–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, B.L.; Toomes, C.; Scott, S.; Yeung, A.; Marchbank, N.J.; Spry, P.G.; Lumb, R.; Inglehearn, C.F.; Churchill, A.J. Polymorphisms in OPA1 are associated with normal tension glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2003, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Funayama, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Ohtake, Y.; Tanino, T.; Kurosaka, D.; Kimura, I.; Suzuki, K.; Ideta, H.; Nakamoto, K.; Yasuda, N.; et al. Variants in optineurin gene and their association with tumor necrosis factor-α polymorphisms in Japanese patients with glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4359–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuse, N.; Takahashi, K.; Akiyama, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Seimiya, M.; Kuwahara, S.; Tamai, M. Molecular genetic analysis of optineurin gene for primary open-angle and normal tension glaucoma in the Japanese population. J. Glaucoma 2004, 13, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.J.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.S.; Ko, H.S.; Yoo, T. Investigation of the association between OPA1 polymorphisms and normal-tension glaucoma in Korea. J. Glaucoma 2004, 13, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimasi, D.P.; Hewitt, A.W.; Green, C.M.; Mackey, D.A.; Craig, J.E. Lack of association of p53 polymorphisms and haplotypes in high and normal tension open angle glaucoma. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, B.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Fan, D.S.; Tam, P.O.; Lam, D.S.; Tham, C.C.; Lam, C.Y.; Lau, T.C.; Pang, C.P. SNPs and interaction analyses of myocilin, optineurin, and apolipoprotein E in primary open angle glaucoma patients. Mol. Vis. 2005, 11, 625–631. [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume, K.; Mashima, Y.; Fumayama, T.; Ohtake, Y.; Kimura, I.; Yoshida, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Yasuda, N.; Fujimaki, T.; Asaoka, R.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms in the angiotensin II receptor gene and their association with open-angle glaucoma in a Japanese population. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, Y.; Mashima, Y.; Fuse, N.; Funayama, T.; Ohtake, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Murakami, A.; Hotta, Y.; Fukuchi, T.; Tsubota, K. Polymorphism of β-adrenergic receptors and susceptibility to open-angle glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 673–680. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.M.; Ko, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, T.; Hwang, S.; Park, S.S. Investigations on the association between normal tension glaucoma and single nucleotide polymorphisms of the endothelin-1 and endothelin receptor genes. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, C.Y.; Fan, B.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Tam, P.O.; Yung Tham, C.C.; Leung, D.Y.; Ping Fan, D.S.; Chiu Lam, D.S.; Pang, C.P. Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphisms with normal tension glaucoma in a Chinese population. J. Glaucoma 2006, 15, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, F.; Tang, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Iijima, H.; Tsukahara, S. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms c.677C/T and c.1298A/C are not associated with open angle glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Jiao, X.; Hejtmancik, J.F.; Leske, M.C.; Hennis, A.; Nemesure, B.; He, Q.; Wu, S.Y.; Mendell, N.; Jiang, L.; et al. Evaluation of the association between OPA1 polymorphisms and primary open-angle glaucoma in Barbados families. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- How, A.C.; Aung, T.; Chew, X.; Yong, V.H.; Lim, M.C.; Lee, K.Y.; Toh, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Vithana, E.N. Lack of association between interleukin-1 gene cluster polymorphisms and glaucoma in Chinese subjects. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2123–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeoung, J.W.; Kim, D.M.; Ko, H.S.; Park, S.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, T.W. Investigation of the association between normal-tension glaucoma and single nucleotide polymorphisms in natriuretic peptide gene. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 21, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mabuchi, F.; Tang, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Iijima, H.; Tsukahara, S. The OPA1 gene polymorphism is associated with normal tension and high tension glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, A.; Fuse, N.; Mengkegale, M.; Ryu, M.; Seimiya, M.; Wada, Y.; Nishida, K. Association between primary open-angle glaucoma and WDR36 DNA sequence variants in Japanese. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar]
- Tosaka, K.; Mashima, Y.; Funayama, T.; Ohtake, Y.; Kimura, I.; Glaucoma Gene Research, G. Association between open-angle glaucoma and gene polymorphism for heat-shock protein 70-1. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 51, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, E.; Meguro, A.; Ota, M.; Kashiwagi, K.; Mabuchi, F.; Iijima, H.; Kawase, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, M.; Negi, A.; et al. Association of Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms with normal tension glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4453–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, C.I.; Goldberg, I.; Healey, P.R.; Graham, S.L. Plasma homocysteine, MTHFR gene mutation, and open-angle glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2009, 18, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, C.L.; Curtis, H.; Realini, T.; Charlton, J.F.; Zareparsi, S. Primary open angle glaucoma in a Caucasian population is associated with the p53 codon 72 polymorphism. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Ko, W.C.; Lam, S.C.; Pang, C.P. Different WDR36 mutation pattern in Chinese patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 646–653. [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi, F.; Sakurada, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Iijima, H.; Tsukahara, S. Lack of association between p53 gene polymorphisms and primary open angle glaucoma in the Japanese population. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.M.; Park, S.S.; Ko, H.S.; Yoo, T. Investigation of the association between 677C>T and 1298A>C 5,10-methylenetetra- hydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms and normal-tension glaucoma. Eye 2009, 23, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.J.; Liu, K.; Wang, D.Y.; Tham, C.C.; Tam, P.O.; Lam, D.S.; Pang, C.P. Association of polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor and tumor protein p53 with primary open-angle glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, F.; Sakurada, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Iijima, H.; Tsukahara, S. Estrogen receptor β gene polymorphism and intraocular pressure elevation in female patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 826–830.e821–e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, F.; Sakurada, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Iijima, H.; Tsukahara, S. Lack of association of common variants on chromosome 2p with primary open-angle glaucoma in the Japanese population. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, E90–E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, C.; Gramer, E.; Muller-Myhsok, B.; Pasutto, F.; Gramer, G.; Wissinger, B.; Weisschuh, N. Lysyl oxidase-like 1 gene polymorphisms in German patients with normal tension glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma and exfoliation glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2010, 19, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Writing Committee for the Normal Tension Glaucoma Genetic Study Group of Japan Glaucoma Society; Meguro, A.; Inoko, H.; Ota, M.; Mizuki, N.; Bahram, S. Genome-wide association study of normal tension glaucoma: Common variants in SRBD1 and ELOVL5 contribute to disease susceptibility. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1331–1338.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Stewart, J.D.; Hudson, G.; Andrews, R.M.; Griffiths, P.G.; Birch, M.K.; Chinnery, P.F. OPA1 increases the risk of normal but not high tension glaucoma. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, F.; Sakurada, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Iijima, H.; Tsukahara, S. Association between SRBD1 and ELOVL5 gene polymorphisms and primary open-angle glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4626–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, W.; Kim, S.; Ki, C.S.; Kee, C. Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms do not associate with normal tension glaucoma in a Korean population. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumura, R.; Meguro, A.; Ota, M.; Nomura, E.; Uemoto, R.; Kashiwagi, K.; Mabuchi, F.; Iijima, H.; Kawase, K.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Investigation of the association between SLC1A3 gene polymorphisms and normal tension glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 792–796. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, Y.; Shi, D.; Shimizu, A.; Funayama, T.; Mashima, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Fukuchi, T.; Abe, H.; Ideta, H.; Zheng, X.; et al. Association of Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms in Japanese subjects with primary open-angle, normal-tension, and exfoliation glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggs, J.L.; Hewitt, A.W.; Fan, B.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Figueiredo Sena, D.R.; O’Brien, C.; Realini, A.; Craig, J.E.; Dimasi, D.P.; Mackey, D.A.; et al. The p53 codon 72 PRO/PRO genotype may be associated with initial central visual field defects in caucasians with primary open angle glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Funayama, T.; Mashima, Y.; Takano, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Mengkegale, M.G.; Miyazawa, A.; Yasuda, N.; Fukuchi, T.; et al. Association of HK2 and NCK2 with normal tension glaucoma in the Japanese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Takano, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Mengkegale, M.; Yokokura, S.; Nishida, K.; Fuse, N. Molecular genetic analysis of primary open-angle glaucoma, normal tension glaucoma, and developmental glaucoma for the VAV2 and VAV3 gene variants in Japanese subjects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Feng, S.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Wei, L.C.; Liang, C.Y.; Chang, C.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Wang, C.Y. Interleukin-6(-174) locus polymorphism and serum IL-6 levels in normal tension glaucoma. Ophthalmic Genet. 2014, 35, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Yin, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cai, H.; Tang, X. Association between Genetic Polymorphisms of the β Adrenergic Receptor and Diurnal Intraocular Pressure in Chinese Volunteers and Glaucoma Patients. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior-Jarecka, E.; Wróbel-Dudzińska, D.; Łukasik, U.; Aung, T.; Khor, C.C.; Kocki, J.; Żarnowski, T. Plasma endothelin-1 and single nucleotide polymorphisms of endothelin-1 and endothelin type A receptor genes as risk factors for normal tension glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2016, 22, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Nishisako, M.; Meguro, A.; Nomura, E.; Yamane, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Ota, M.; Kashiwagi, K.; Mabuchi, F.; Iijima, H.; Kawase, K.; et al. SLC1A1 Gene Variants and Normal Tension Glaucoma: An Association Study. Ophthalmic Genet. 2016, 37, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Jia, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Wang, N. Association of three single nucleotide polymorphisms at the SIX1-SIX6 locus with primary open angle glaucoma in the Chinese population. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 59, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeoung, J.W.; Kim, D.M.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.S.; Kim, J.Y. The Relation Between Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Polymorphisms and Normal Tension Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2017, 26, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, W.; Won, H.H.; Kee, C. The Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the MMP-9 Gene with Normal Tension Glaucoma and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Shin, H.Y. Association of HK2 and NCK2 with normal-tension glaucoma in a population from the Republic of Korea. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 2717–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior-Jarecka, E.; Sagan, M.; Wrobel-Dudzinska, D.; Lukasik, U.; Aung, T.; Khor, C.C.; Kocki, J.; Zarnowski, T. Estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms and their influence on clinical status of Caucasian patients with primary open angle glaucoma. Ophthalmic Genet. 2019, 40, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Shin, H.Y. Lack of Correlation between ASB10 and Normal-tension Glaucoma in a Population from the Republic of Korea. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Shin, H.Y. Lack of correlation between S1 RNA binding domain 1 SNP rs3213787/rs11884064 and normal-tension glaucoma in a population from the Republic of Korea. Medicine 2020, 99, e20066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Jeoung, J.W.; Oh, S.; Kim, D.M.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Seong, M.W.; Park, S.S.; Kim, J.Y. No association between POU4F1, POU4F2, ISL1 polymorphisms and normal-tension glaucoma. Ophthalmic Genet. 2020, 41, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanowski, P.; Kosior-Jarecka, E.; Lukasik, U.; Wrobel-Dudzinska, D.; Milanowska, J.; Khor, C.C.; Aung, T.; Kocki, J.; Żarnowski, T. Associations between OPA1, MFN1, and MFN2 polymorphisms and primary open angle glaucoma in Polish participants of European ancestry. Ophthalmic Genet. 2022, 43, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.L.; Zheng, S.F. Analysis of association between MALAT1 haplotype and the severity of normal-tension glaucoma (NTG). J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9918–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Bak, E.; Wy, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, K.H.; Jeoung, J.W. Genetic Risk and Phenotype Correlation of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Based on Rho-Kinase Gene Polymorphisms. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuska, P.J.; Lemmela, S.; Havulinna, A.S.; Kaarniranta, K.; Uusitalo, H.; Laivuori, H.; Kiiskinen, T.; Daly, M.J.; Palotie, A.; Turunen, J.A.; et al. Association of the MYOC p.(Gln368Ter) Variant With Glaucoma in a Finnish Population. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021, 139, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.N.; Ng, T.K.; Lu, S.Y.; Tam, P.O.S.; Chan, P.P.; Tham, C.C.; Pang, C.P.; Chen, L.J.; Chu, W.K. Genetic association of ANGPT2 with primary open-angle glaucoma. Eye Vis. 2022, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, T.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Hsu, B.; Shih, R.J.; Lo, N.W.; Wang, C.Y. Association between HSPA5 Promoter Polymorphisms and a Reduced Risk of Normal Tension Glaucoma. Ophthalmic Res. 2022, 65, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, M.Y. Association of Polymorphisms at the SIX1/SIX6 Locus With Normal Tension Glaucoma in a Korean Population. J. Glaucoma 2022, 31, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olichon, A.; Emorine, L.J.; Descoins, E.; Pelloquin, L.; Brichese, L.; Gas, N.; Guillou, E.; Delettre, C.; Valette, A.; Hamel, C.P.; et al. The human dynamin-related protein OPA1 is anchored to the mitochondrial inner membrane facing the inter-membrane space. FEBS Lett. 2002, 523, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, C.; Cipolat, S.; Martins de Brito, O.; Micaroni, M.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Rudka, T.; Bartoli, D.; Polishuck, R.S.; Danial, N.N.; De Strooper, B.; et al. OPA1 controls apoptotic cristae remodeling independently from mitochondrial fusion. Cell 2006, 126, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanita, T.; Soriano, M.E.; Romanello, V.; Zaglia, T.; Quintana-Cabrera, R.; Semenzato, M.; Menabò, R.; Costa, V.; Civiletto, G.; Pesce, P.; et al. The OPA1-dependent mitochondrial cristae remodeling pathway controls atrophic, apoptotic, and ischemic tissue damage. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chan, D.C. OPA1 and cardiolipin team up for mitochondrial fusion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Yang, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, K. Association of OPA1 polymorphisms with NTG and HTG: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.; Wahl, G.M. Regulating the p53 pathway: In vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lane, D.P. p53 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artandi, S.E.; Attardi, L.D. Pathways connecting telomeres and p53 in senescence, apoptosis, and cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.S.; Hu, W.; Belyi, V.; Rabadan, R.; Levine, A.J. Differential levels of transcription of p53-regulated genes by the arginine/proline polymorphism: p53 with arginine at codon 72 favors apoptosis. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, A. Very long-chain fatty acids: Elongation, physiology and related disorders. J. Biochem. 2012, 152, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Laye, S. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Dalli, J.; Levy, B.D. Lipid mediators in the resolution of inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, H.; Zadravec, D.; Martin, P.G.; Jacobsson, A. The key roles of elongases and desaturases in mammalian fatty acid metabolism: Insights from transgenic mice. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SanGiovanni, J.P.; Chew, E.Y. The role of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in health and disease of the retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2005, 24, 87–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Magulike, N.; Ghebremeskel, K.; Crawford, M. Primary open-angle glaucoma patients have reduced levels of blood docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2006, 74, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centenera, M.M.; Scott, J.S.; Machiels, J.; Nassar, Z.D.; Miller, D.C.; Zinonos, I.; Dehairs, J.; Burvenich, I.J.G.; Zadra, G.; Chetta, P.M.; et al. ELOVL5 Is a Critical and Targetable Fatty Acid Elongase in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1704–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Nam, M.; Son, H.Y.; Hyun, K.; Jang, S.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, M.W.; Jung, Y.; Jang, E.; Yoon, S.J.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis pathway determines ferroptosis sensitivity in gastric cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32433–32442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xu, H.; Tang, Q.; Kong, X.; Hu, L. SKAP2, a novel target of HSF4b, associates with NCK2/F-actin at membrane ruffles and regulates actin reorganization in lens cell. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrac, A.; Genet, G.; Ola, R.; Zhang, F.; Pibouin-Fragner, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Thomas, J.L.; Chedotal, A.; Schwartz, M.A.; et al. Targeting NCK-Mediated Endothelial Cell Front-Rear Polarity Inhibits Neovascularization. Circulation 2016, 133, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, D.; Child, A.; Trifan, O.C.; Crick, R.P.; Coakes, R.L.; Sarfarazi, M. Localization of a locus (GLC1B) for adult-onset primary open angle glaucoma to the 2cen-q13 region. Genomics 1996, 36, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Yatsu, K.; Ota, M.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Mabuchi, F.; Iijima, H.; Kawase, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Microsatellite analysis of the GLC1B locus on chromosome 2 points to NCK2 as a new candidate gene for normal tension glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.J.; Tan-Sah, V.P.; Ding, E.Y.; Smith, J.M.; Miyamoto, S. Hexokinase-II positively regulates glucose starvation-induced autophagy through TORC1 inhibition. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, N.; Nogueira, V.; Bhaskar, P.; Coy, P.E.; Skeen, J.E.; Gottlob, K.; Chandel, N.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Robey, R.B.; Hay, N. Hexokinase-mitochondria interaction mediated by Akt is required to inhibit apoptosis in the presence or absence of Bax and Bak. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Doggett, T.A.; Sene, A.; Apte, R.S.; Ferguson, T.A. Autophagy supports survival and phototransduction protein levels in rod photoreceptors. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medchalmi, S.; Tare, P.; Sayyad, Z.; Swarup, G. A glaucoma- and ALS-associated mutant of OPTN induces neuronal cell death dependent on Tbk1 activity, autophagy and ER stress. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 4576–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Allingham, R.R. Molecular genetics in glaucoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Lugo, R.M.; Pawar, H.; Reed, D.M.; Lichter, P.R.; Moroi, S.E.; Page, M.; Eadie, J.A.; Azócar, V.; Maul, E.J.; Ntim-Amponsah, C.T.; et al. Variation in optineurin (OPTN) allele frequencies between and within populations. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Alward, W.L.; Kwon, Y.H.; Kawase, K.; Craig, J.E.; Hayreh, S.S.; Johnson, A.T.; Khanna, C.L.; Yamamoto, T.; Mackey, D.A.; Roos, B.R.; et al. Evaluation of optineurin sequence variations in 1048 patients with open-angle glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 136, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Gu, Y.; Wang, K. Association of Gene Polymorphisms With Primary Open Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Sato, S.; Ozaki, H.; Ikeda, K. Six family genes--structure and function as transcription factors and their roles in development. Bioessays 2000, 22, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnes, M.U.; Liu, Y.P.; Allingham, R.R.; Whigham, B.T.; Havens, S.; Garrett, M.E.; Qiao, C.; Neighborhood Consortium Investigators; Katsanis, N.; Wiggs, J.L.; et al. Discovery and functional annotation of SIX6 variants in primary open-angle glaucoma. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.Z.; Zangwill, L.M.; Medeiros, F.A.; Liebmann, J.M.; Girkin, C.A.; Hammel, N.; Rotter, J.I.; Weinreb, R.N. Quantitative Trait Locus Analysis of SIX1-SIX6 With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Individuals of European Descent. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 123–130.e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowronska-Krawczyk, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, J.; Weinreb, R.N.; Cao, G.; Luo, J.; Flagg, K.; Patel, S.; Wen, C.; Krupa, M.; et al. P16INK4a Upregulation Mediated by SIX6 Defines Retinal Ganglion Cell Pathogenesis in Glaucoma. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.N.; Loomis, S.J.; Kang, J.H.; Allingham, R.R.; Gharahkhani, P.; Khor, C.C.; Burdon, K.P.; Aschard, H.; Chasman, D.I.; Igo, R.P., Jr.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies TXNRD2, ATXN2 and FOXC1 as susceptibility loci for primary open-angle glaucoma. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Allingham, R.R.; Aung, T.; Tham, Y.C.; Hauser, M.A.; Vithana, E.N.; Khor, C.C.; Wong, T.Y. Association of common SIX6 polymorphisms with peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness: The Singapore Chinese Eye Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 56, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Emdad, L.; Kang, D.C.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr.; Fisher, P.B. Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPaseold-35): A potential link between aging and inflammation. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7473–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leszczyniecka, M.; Kang, D.C.; Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.Z.; Holmes, M.; Valerie, K.; Fisher, P.B. Identification and cloning of human polynucleotide phosphorylase, hPNPase old-35, in the context of terminal differentiation and cellular senescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16636–16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Leszczyniecka, M.; Kang, D.C.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Valerie, K.; Dhar, S.; Pandita, T.K.; Fisher, P.B. Down-regulation of Myc as a potential target for growth arrest induced by human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPaseold-35) in human melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24542–24551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemaki, N.; Tchedre, K.T.; Imayasu, M.; Kawarai, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Yoshino, A.; Itoh, N.; Meguro, A.; Mizuki, N. Dogs and humans share a common susceptibility gene SRBD1 for glaucoma risk. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Coyne, C.B.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. PAMPs and DAMPs: Signal 0s that spur autophagy and immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 249, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezel, G.; Hernandez, R.; Wax, M.B. Immunostaining of heat shock proteins in the retina and optic nerve head of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, H.; Medina-Ortiz, W.E.; Luan, T.; Clark, A.F.; McDowell, C.M. Crosstalk Between Transforming Growth Factor β-2 and Toll-Like Receptor 4 in the Trabecular Meshwork. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, J.; Meguro, A.; Ota, M.; Nomura, E.; Nishide, T.; Kashiwagi, K.; Mabuchi, F.; Iijima, H.; Kawase, K.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Association of toll-like receptor 2 gene polymorphisms with normal tension glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, A.; Yanagisawa, M.; Kimura, S.; Kasuya, Y.; Miyauchi, T.; Goto, K.; Masaki, T. The human endothelin family: Three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2863–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripodas, A.; de Juan, J.A.; Roldan-Pallares, M.; Bernal, R.; Moya, J.; Chao, M.; Lopez, A.; Fernandez-Cruz, A.; Fernandez-Durango, R. Localisation of endothelin-1 mRNA expression and immunoreactivity in the retina and optic nerve from human and porcine eye. Evidence for endothelin-1 expression in astrocytes. Brain Res. 2001, 912, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Durango, R.; Rollin, R.; Mediero, A.; Roldan-Pallares, M.; Garcia Feijo, J.; Garcia Sanchez, J.; Fernandez-Cruz, A.; Ripodas, A. Localization of endothelin-1 mRNA expression and immunoreactivity in the anterior segment of human eye: Expression of ETA and ETB receptors. Mol. Vis. 2003, 9, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, T.; Moriya, S.; Oku, H.; Azuma, I. Association of endothelin-1 with normal tension glaucoma: Clinical and fundamental studies. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1995, 39 (Suppl. S1), S49–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellini, M.; Possati, G.L.; Profazio, V.; Sbrocca, M.; Caramazza, N.; Caramazza, R. Color Doppler imaging and plasma levels of endothelin-1 in low-tension glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. Suppl. 1997, 75, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, G.A.; Sullivan, P. The effect of chronic ischemia on the primate optic nerve. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 9 (Suppl. S1), S34–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Kojima, S.; Watanabe, T.; Azuma, I. Experimental optic cup enlargement caused by endothelin-1-induced chronic optic nerve head ischemia. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1999, 44 (Suppl. S1), S74–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokely, M.E.; Brady, S.T.; Yorio, T. Effects of endothelin-1 on components of anterograde axonal transport in optic nerve. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Rong, S.S.; Chen, Z.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Tham, J.A.; Chan, P.P.; Yam, J.C.; Wiggs, J.L.; Pang, C.P.; et al. Genetic Associations of Primary Angle-Closure Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024, 123, e240363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.S.; Tang, F.Y.; Chu, W.K.; Ma, L.; Yam, J.C.; Tang, S.M.; Li, J.; Gu, H.; Young, A.L.; Tham, C.C.; et al. Genetic Associations of Primary Angle-Closure Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).