Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine, involved in the pathogenesis and progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN). A bi-allelic polymorphism in the promoter region, at position -308 (G/A) of the TNF-α gene (rs1800629) is associated with an increased TNF-a production. However, several previous association studies of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and IgAN rendered contradictory findings. The objective of the present study is to shed light on these inconclusive results and clarify the role of TNF-α and any possible contribution of this factor in the development and progression of sporadic IgAN. Therefore, a meta-analysis of all available genetic association studies relating the TNF-α G-308A polymorphism to the risk for development and/or progression of IgAN was conducted. Seven studies were included in the meta-analysis. Three of them included populations of European descent (Caucasians) and four involved Asians. The generalized odds ratio (ORG) was used to estimate the risk for the development and/or progression of the disease. Overall, the meta-analysis did not detect any significant association between the G-308A variant and both the risk of developing IgAN and the risk for progression of IgAN. In conclusion, these results suggest that TNF-α does not constitute a key component in the genetic architecture of sporadic IgAN. However, further evidence deciphering the influence of TNF-α on IgAN is still needed.
1. Introduction
Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common primary glomerulonephritis for which only supportive care is available up to date [1]. It is characterized by prominent glomerular, primarily mesangial, deposits of polymeric subclass 1 IgA (IgA1), accompanied by mesangial cell proliferation, extracellular matrix accumulation and glomerular infiltration, predominantly consisting of monocytes and macrophages [2]. Many clinical and histological markers strive to predict the course of the disease. More specifically, clinical biomarkers include the presence of hypertension, proteinuria, high body mass index (BMI) and smoking, whereas histological markers refer to the Oxford MEST-C score which uses five indicators (mesangial and endocapillary hypercellularity, segmental sclerosis, interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy, and the presence of crescents) [3,4,5].
However, new biomarkers specific to the disease are needed for a more reliable estimation of risk. Genetic studies, such as genome-wide association studies (GWAS), have shed light on several variants, many of which are harbored in immunologic and inflammatory pathways [6,7,8,9,10,11,12], among which many are related to mucosal immune response, innate and adaptive immunity, as well as the complement activation [13]. More specifically, the study of Li et al. identified three novel loci, FCRL3, DUSP22.IRF4, and PADI4, three HLA polymorphisms and two variants harbored in the MHC region as susceptibility genes of IgAN [6]. Another study in Han Chinese identified associations at 17p13 (rs3803800), 8p23 (TNFSF13 and DEFA), 22q12 and multiple associations in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region [7]. ST6GAL1, ACCS, ODF1-KLF10, ITGAX-ITGAM and DEFA were highlighted as risk loci of IgAN [8]. One more GWAS investigated the common susceptibility loci of IgAN and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and identified 14 loci common between IgAN and SLE [9]. ITGAM-ITGAX, VAV3, CARD9, HLA-DQB1 and DEFA were also revealed as significant risk loci of IgAN proposing a potential influence of interactions between intestinal pathogens and the host on the genetic makeup of IgAN [10]. Rs2296136 in ANKRD16 was also significantly associated with IgAN in Koreans [12].
A crucial role in this process has been shown for various inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), which is a potent mediator with a central role in the inflammatory cascade [14]. There is recent experimental evidence that in IgAN mesangial cells derived TNF-α might be involved in the pathogenesis of tubular damage and interstitial fibrosis [15,16], both closely related to disease progression [17]. It is therefore conceivable to hypothesize a role of TNF-α in the pathogenesis and progression of IgA nephropathy. More specifically, recent findings suggest that the release of TNF-α from the mesangium following IgA deposition triggers the activation of renal tubular cells. This communication between the glomerulus and tubules may have a significant impact on the development of tubulointerstitial damage in IgAN. Based on in vitro results, it is indicated that podocytes may contribute to the progression of interstitial damage in IgAN by enhancing the activation of tubular epithelial cells through increased synthesis of TNF-a following inflammatory changes in human mesangial cells (HMC) [15,16].
The tumor necrosis factor-α gene (TNF-α; OMIM 191160) is located on the short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.33) [18,19]. A bi-allelic polymorphism has been long characterized in the promoter region of TNF-α, namely a G→A transition at position -308 [20]. Carriage of the infrequent allele A, in comparison to the allele G, is associated with increased gene transcription [20,21] and elevated TNF-α production by lymphocytes in vitro [22]. The association of the TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and IgAN has been investigated in several genetic studies [23,24,25,26,27,28,29], that rendered contradictory findings. Concretely, some of the studies indicated an association of the polymorphism with IgAN [23,24,25,28] and others urged that there is no association [26,27,29]. Among studies with significant results, one study did not detect an association with IgAN per se but only with gross hematuria [24], one study reported an association which was not remained significant after the application of Bonferroni correction [28], one study revealed a protective role of -308A allele in IgAN [25], whereas another study indicated -308A allele as a potent risk factor for the progression of the disease [23].
Although the conflicting significant results about the contribution of G-308A polymorphism in the course of IgAN, in an effort to reconcile these findings and provide a resolution, a meta-analysis of case–control studies evaluating the TNF-α G-308A polymorphism to the risk for development and progression of sporadic IgAN was conducted.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Selection of Studies
In order to clarify the contribution of TNF-α in sporadic IgAN susceptibility and progression, we meta-analyzed all case–control studies regarding the G-308A polymorphism in the TNF-α gene in the context of sporadic IgAN published before June 2023. The studies were retrieved after an extensive search of the PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, Web of Science and Wiley Online Library databases using the search terms [“tumor necrosis factor” AND “IgA nephropathy” AND polymorphism] (accessed on 24 June 2023).
The retrieved publications were thoroughly reviewed to evaluate their eligibility. All references of the eligible studies were scrutinized to identify articles not indexed in the aforementioned databases. Abstracts, case reports, editorials, review articles, in vitro studies, as well as family-based studies were excluded. It is important to note that the search included only articles in English. Two investigators (M.T. and I.S.) evaluated the eligibility of the articles, and any disagreements were resolved through consensus.
In the association studies, that were eligible for meta-analysis concerning progression of IgA nephropathy, both cases and controls were patients with sporadic IgA nephropathy. Patients with a progressive IgAN were considered as cases (progressors) and those with stable nephropathy as controls (non-progressors). Eligibility was not dependent on a specific prefixed definition of IgAN progression. The definition of progression used in each study was accepted and is presented in Table 1. Subjects with other forms of IgAN, such as Henoch–Schönlein purpura, which is the systemic form of IgAN, and subjects with secondary IgAN were excluded.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the case–control studies considered in the meta-analysis.
2.2. Data Extraction
The following details were extracted from each study: the primary author, publication year, racial background of the study participants, selection criteria, demographic information, and complete genotype counts. Allele frequencies were calculated from genotype counts.
2.3. Data Synthesis and Analysis
To examine the connection between genotype distribution and the risk of developing sporadic IgAN or the risk of disease progression, the generalized linear odds ratio (ORG) was used [30,31]. Meta-analysis was conducted when at least two studies were available. The pooled odds ratio (OR) was estimated using random effects models (DerSimonian and Laird) [32]. All associations were reported as odds ratios (OR) with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (Cis). Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using the Q-statistic [33] and the degree of heterogeneity was quantified using the I2 metric [34]. Software implementing the generalized odds ratio methodology was used (ORGGASMA: https://biomath.med.uth.gr/default.aspx?lang=el&id=232164AC-9C6B-4A27-A595-2A22C35B6260&rid=576AB0F4-10AE-4BEA-8D97-C52B8B6BD4DA) (accessed on 1 May 2023) [30].
The distribution of the genotypes in the control group was tested for deviation from the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) using Fisher’s exact test. We also tested for small-study effects with the Egger test [35].
The meta-analysis comprised three components: the main analysis, encompassing all accessible data; subgroup analysis, considering each racial population separately; and sensitivity analyses, investigating the impact of excluding studies that were not confronted with the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE).
All analyses were performed using the Comprehensive Meta-analysis software package (CMA version 4; http://www.meta-analysis.com; 2005) (accessed on 1 May 2023) and StatsDirect software (StatsDirect Ltd., Wirral, UK, StatsDirect statistical software. http://www.statsdirect.com. England: StatsDirect Ltd. 2008) (accessed on 1 May 2023).
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
The literature review identified 846 titles in all databases. After the removal of the duplicates and a thorough review of the articles, seven studies were included in the meta-analysis. Figure 1 presents a flow chart of the retrieved articles, as well as the excluded articles with the reasons for exclusion. More specifically, seven studies investigated the association between TNF-a gene G-308A polymorphism (rs1800629) and sporadic IgAN susceptibility, whereas five studies investigated the association of the polymorphism to the risk of progressive IgAN. The study characteristics are described in Table 1.
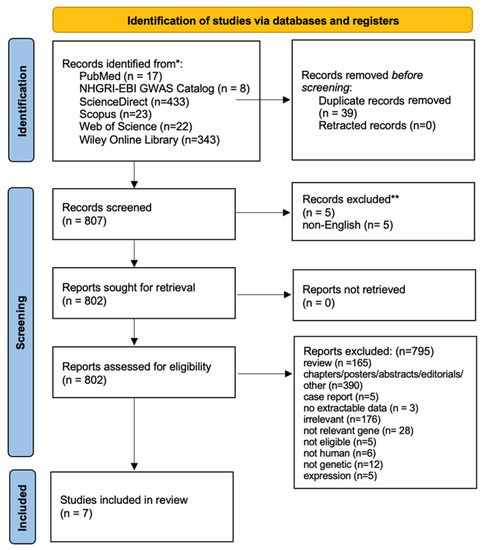
Figure 1.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram of retrieved articles with specifications of reasons for exclusion.
In all studies investigating the association of the polymorphism with sporadic IgAN the patients with IgAN were well defined following identical inclusion criteria. The existence of IgAN was documented histologically on the basis of a kidney biopsy logically accompanied by immune-fluorescence microscopy. Studies that included only transplanted patients were excluded. The controls were healthy individuals from the same region or healthy blood donors (Table 1). Subjects with other forms of IgAN, such as Henoch–Schönlein purpura and secondary IgAN were excluded.
Criteria applied to define progression were not identical in five studies investigating the association of the polymorphism with the progression of IgA nephropathy. However, per protocol, all were eligible for the meta-analysis (Table 1). For reasons of clarity, the definition of IgAN progression or not is presented in Table 1 for each study included in the meta-analysis.
3.2. Summary Statistics
In total, the studies examining the association of the TNF-α G-308A polymorphism with IgAN included 1486 cases (with IgA nephropathy), and 1715 healthy controls, whereas the studies that examined only the association of the TNF-α G-308A polymorphism with progression of IgAN included overall 196 cases (progressors), and 526 controls (non-progressors). In one study [25], the distribution of the genotypes in the control group was not confronted with HWE (p < 0.05), indicating population stratification or genotyping errors. Therefore, a sensitivity analysis was carried out for this study. Table 2 shows the distribution of the TNF-α genotypes for patients with sporadic IgAN and healthy controls, whereas Table 3 shows the distribution of the TNF-α genotypes for patients with progressive IgAN and patients with non-progressive IgAN.

Table 2.
The distribution of the TNF-α genotypes for patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and healthy subjects without IgA nephropathy (healthy controls) are shown.

Table 3.
The distribution of the TNF-α genotypes for patients with progressive IgA nephropathy (cases with progressive IgAN; PR) and patients with non-progressive IgAN (diseased controls; NPR) are shown.
3.3. Meta-Analyses Results
Risk of Sporadic IgAN
The main analysis, in which seven studies were included, did not reveal statistically significant results [ORG = 0.80 (95% CI 0.56–1.14)]. Similarly, no significant association was detected in sensitivity analysis in which only studies confronted with HWE were included [ORG = 0.94 (95% CI 0.70–1.26)] (Table 4).

Table 4.
The association of the TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk of sporadic IgA nephropathy: summary estimates for the odds ratio (OR) of various allele/genotype contrasts, the significance level (p-value) of the heterogeneity test (Q-test) and the I2 metric in overall analysis, as well as in the subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
In subgroup analyses regarding the Caucasian and Asian populations separately, there was large heterogeneity (I2 = 71.92% and 61.83%, respectively) between the studies with a polled ORG of 0.74 (95% CI 0.44–1.26) and 0.85 (95% CI 0.50–1.43), respectively (Table 4).
3.4. Risk for Progression of Sporadic IgAN
The main analysis included five studies and did not detect any significant association between G-308A polymorphism and the risk for progression of sporadic IgAN [ORG = 1.13 (95% CI 0.74–1.73)] (Table 4). Similarly, the sensitivity analysis did not also show significant results [ORG = 1.19 (95% CI 0.74–1.92)] (Table 4). Both main and sensitivity analyses were characterized by no heterogeneity (I2 = 7.13% and 14.09%, respectively).
In subgroup analyses regarding the Caucasian and Asian populations, no significant association was revealed with a pooled ORG of ORG = 1.16 (95% CI 0.61–2.23) and ORG = 0.85 (95% CI 0.37–1.93), respectively (Table 4). Figure 2 and Figure 3 are forest plot representations of TNF-a G-308A polymorphism and the risk of IgAN and the risk for progression of sporadic IgAN, respectively.
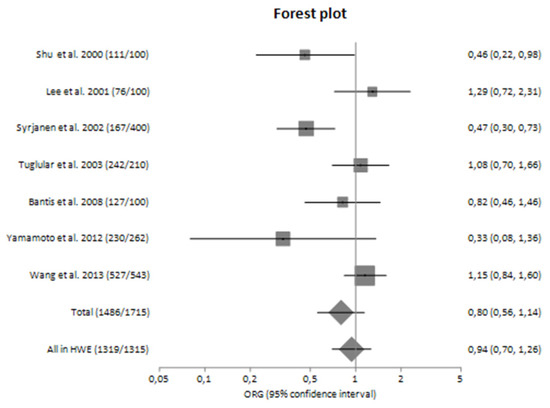
Figure 2.
Forest plot of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk of sporadic IgA nephropathy in main analysis [23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
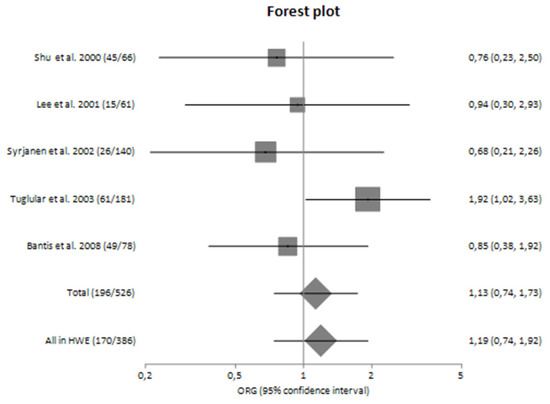
Figure 3.
Forest plot of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk for progression of IgA nephropathy in main analysis [23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 are also forest plot representations of TNF-a G-308A polymorphism and the risk of IgAN and the risk for progression of sporadic IgAN, respectively in subgroup analyses.
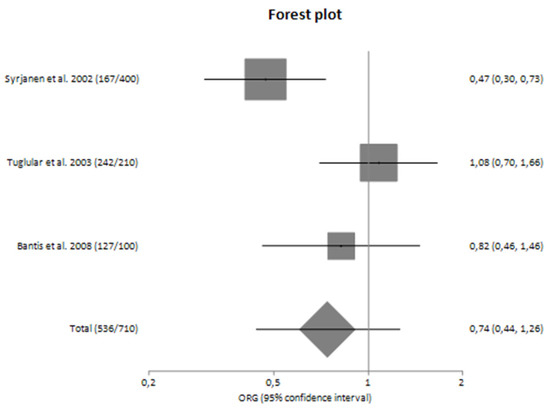
Figure 4.
Forest plot of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk of sporadic IgA nephropathy in Caucasians [25,26,27].
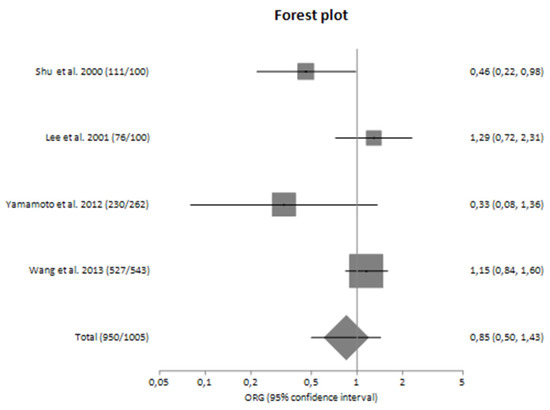
Figure 5.
Forest plot of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk of sporadic IgA nephropathy in Asians [23,24,28,29].
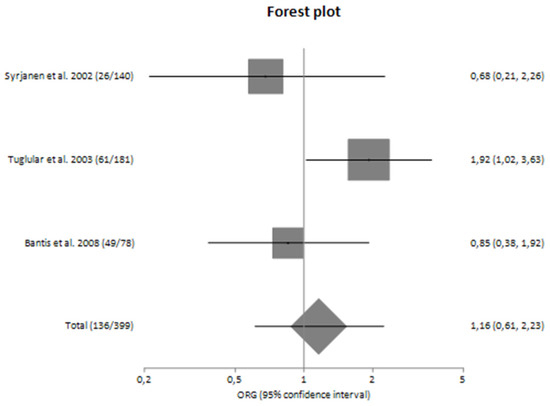
Figure 6.
Forest plot of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk for progression of sporadic IgA nephropathy in Caucasians [25,26,27].
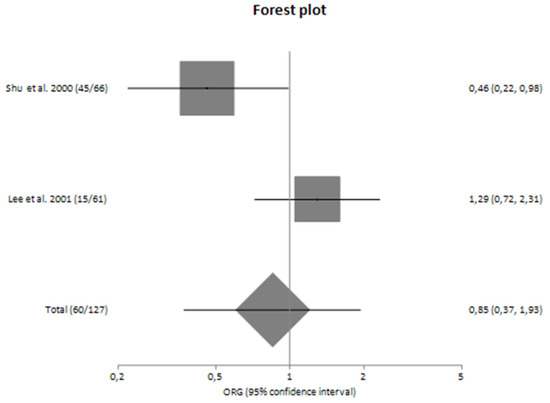
Figure 7.
Forest plot of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism and the risk for progression of sporadic IgA nephropathy in Asians [23,24].
4. Discussion
IgAN is the prevailing form of glomerulonephritis, characterized by inflammation affecting both the glomeruli and blood vessels within the kidneys. Despite extensive efforts, its pathogenetic mechanism is not absolutely clear to date. On the basis of the GWAS results, which highlighted the contribution of several variants harbored in immunologic and inflammatory pathways, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to address the potential implication of TNF-α G-308A polymorphism in both the susceptibility and progression of sporadic IgAN. More specifically, the present meta-analysis included the genetic association studies that investigated the contribution of G-308A polymorphism in the risk of developing sporadic IgAN and in the risk for progression of sporadic IgAN.
Experimental data revealed that TNF-α is a pleiotropic cytokine with a variety of proinflammatory properties, which is produced by both infiltrating cells, mainly monocytes and macrophages, and mesangial cells [36]. TNF-α serum levels were elevated in patients with IgAN and were also correlated with histological activity [37]. Another study revealed an increased release of TNF-α from the white blood cells of patients with IgAN [38].
On the basis of the available data about TNF-α, G-308A polymorphism of this gene has also been studied in several genetic association studies with inconclusive results. Shu et al. (2000) found that G-308A polymorphism was not correlated with disease progression and long-term outcome and did not also correlate with disease activity, except for gross hematuria in Asians, suggesting that TNF-α may not play an important role in disease progression [24]. In contrast, Lee et al. (2001) found a statistically significant association between G-308A polymorphism and the progression of IgAN [23]. However, Syrjänen et al. concluded that the carriage of the -308A allele is protective against IgAN, but it did not affect the prognosis of the disease [25]. It is noteworthy to mention the synergistic effect of IL1b2, IL1RN and TNF-α because it was found that the carriage of both IL1b2 and IL1RN*2 together with the non-carriage of TNF-α -308A allele increased the risk of IgAN fivefold [25]. The study of Syrjänen et al. is important because it was conducted in a large sample of a Finnish population, a genetically homogenous population, with a long follow-up period and a low number of patients lost during the follow-up period [25]. Another strength of this study is its policy for renal biopsy even in cases of minor urinary abnormalities [25]. Another study revealed a significant association of G-308A polymorphism with susceptibility but not with the progression of the disease [26]. In addition, according to Bantis et al. (2008), G-308A polymorphism does not constitute a risk factor or marker of progression in Caucasians with IgAN [27]. Yamamoto et al. (2012) also did not reveal the G-308A polymorphism as a potential genetic contributor to IgAN [29]. Finally, in the study of Wang et al. (2013), the G-308A polymorphism exhibited a suggestive association with IgAN [28] which was not significant after the Bonferroni correction was applied. In our meta-analysis, TNF-α G-308A polymorphism was not associated with either the susceptibility or progression of sporadic IgAN, either in the main analysis or in sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
These conflicting results are difficult to interpret. The discrepancy in results could be related to racial differences. More specifically, it is known that the prevalence of IgAN is very high in East Asians, intermediate in European Caucasians and low in Africans [39]. It is also noteworthy to mention that the local policies regarding indications for renal biopsy vary among different countries and this fact could affect the proportion of reliable and early diagnosis of the disease. So, different policies could constitute another source of heterogeneity. It would also be very interesting to perform subgroup analyses regarding gender because according to a recent study conducted in Estonia, it has been observed that the advancement of renal disease is more rapid in males compared to females. Additionally, there is a correlation between higher Oxford MEST scores and the progression of the disease in male patients [40,41]. However, this is not feasible because the included studies do not present genotype counts for males and females separately. In addition, the interpretation of the results can be further complicated due to the dual function of TNF-α, as a pro-inflammatory factor in the initial infection and as an anti-inflammatory or immunoregulatory factor in the later phases of the response [25]. Therefore, the increased expression of TNF-α could also reflect the activation of protective mechanisms in the context of severe glomerular injury in an effort to suppress the inflammation. Further heterogeneity is also introduced by differences in patient material, such as the different proportions of patients in each study who have reached end-stage renal disease (ESRD), as well as the different characteristics of each study such as the period of follow-up and the number of patients lost during the follow-up period.
Unfortunately, there is no specific treatment for IgAN to date. Patients with IgAN receive treatment that applies to virtually any glomerular disease [3]. More specifically, the current treatment of IgAN includes supportive care, immunosuppression therapy, as well as alternative therapies to conventional immunosuppression [13]. Regarding supportive care, it comprises medications for lowering blood pressure and reducing proteinuria, along with comprehensive education on lifestyle modifications and the importance of avoiding combinations of medications that can harm the kidneys [13]. Therefore, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) constitute the first-line treatment for IgAN. Currently, there is no evidence suggesting that combining ACE inhibitors and ARBs should be avoided in IgA nephropathy (IgAN) [13]. The armamentarium of the single renin–angiotensin system (RAS) blockade is further expanded with the use of sparsentan, a dual endothelin angiotensin receptor antagonist (DEARA) whose reno-protective effects were evaluated in PROTECT trial versus irbesartan [42]. Furthermore, sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) constitute a novel therapeutic approach with promising results, although the precise mechanism of action has not been deciphered yet [43,44].
The second category of therapeutic interventions of IgAN involves immunosuppressive agents. According to the KDIGO guidelines, IgAN patients who continue to be at a high risk of disease progression even after receiving optimized supportive care for at least 90 days should contemplate undergoing a six-month regimen of systemic corticosteroid therapy [13]. Nevertheless, the effectiveness and safety of corticosteroids remain a subject of debate and uncertainty [45]. Except for corticosteroids, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) has been evaluated in several studies in populations of different racial descent, leading to conflicting results. More specifically, in Caucasians it showed no benefit, whereas in Chinese patients with IgAN, it reduced proteinuria and retarded the decline of eGFR [46,47,48], although several cases of severe pneumonia were reported in a cohort of Chinese patients [49]. Similarly, cyclophosphamide produced inconclusive data and, as a result, the KDIGO guideline does not endorse its utilization in the majority of patients with IgAN [3]. It is not also recommended the use of azathioprine in IgAN [3].
It is noteworthy to mention that many ongoing trials are performed in an effort to develop new therapeutic agents for the treatment of IgAN and new pathogenetic pathways are revealed [47,50,51,52]. These new approaches include agents that target the regulation of pathogenic IgA1 and CIC production, like inhibition of TLRs/BAFF/APRIL signaling (hydroxychloroquine, blisibimod, VIS649, BION-1301, atacicept and telitacicept) and the depletion of Gd-IgA1-producing plasma cells, the clearance of IgA deposits (fostamatinib) and the modulation of mucosal immunity, such as the modulation of NALT and the modulation of GALT and gut microbiota [13,50]. Last but not least, a case report reported the beneficial effects of aliskiren, the first direct inhibitor of renin activity [53].
In this study, we used the generalized odds ratio (ORG) to estimate the magnitude of the association. This metric overcomes the problem of multiple comparisons of the different genetic models (dominant, recessive, additive, co-dominant, and allele contrast) by utilizing the full genotypic counts and prevents confusion in cases when more than one genetic model is significant. Therefore, the interpretation of the results is straightforward and more robust. In addition, the choice of a specific genetic model a priori is not required. This metric has been used in various studies of other diseases, like diabetic nephropathy [54,55,56,57,58].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the current meta-analysis reviews the latest genetic epidemiology findings regarding the contribution of G-308A polymorphism in the risk of developing IgAN and the progression of IgAN. Since this meta-analysis did not detect any significant association of G-308A polymorphism with risk for the development or progression of IgAN, we conclude that this genetic component does not constitute a key genetic component in the pathogenesis of sporadic IgAN at least alone. However, the results should be interpreted with caution because the number of studies in the meta-analysis is relatively small.
Author Contributions
I.S. and T.E. designed the research; I.C., G.P., C.C., I.S. and M.T. reviewed the literature; I.C. and M.T. performed the statistical analysis and drafted the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This manuscript has received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lai, K.N.; Tang, S.C.W.; Schena, F.P.; Novak, J.; Tomino, Y.; Fogo, A.B.; Glassock, R.J. IgA nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattrapornpisut, P.; Avila-Casado, C.; Reich, H.N. IgA Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2021. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floege, J.; Feehally, J. Treatment of IgA nephropathy and Henoch–Schönlein nephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.N. Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaskjold, Y.L.; Bjørneklett, R.; Bostad, L.; Bostad, L.S.; Lura, N.G.; Knoop, T. Utilizing the MEST score for prognostic staging in IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Shi, D.-C.; Foo, J.-N.; Zhong, Z.; Khor, C.-C.; Lanzani, C.; Citterio, L.; Salvi, E.; Yin, P.-R.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Three Novel Susceptibility Loci and Reveals Ethnic Heterogeneity of Genetic Susceptibility for IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2949–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Low, H.-Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.-Q.; Sun, L.-D.; Sim, K.-S.; Li, Y.; Foo, J.-N.; et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Foo, J.-N.; Wang, J.-Q.; Low, H.-Q.; Tang, X.-Q.; Toh, K.-Y.; Yin, P.-R.; Khor, C.-C.; Goh, Y.-F.; Irwan, I.D.; et al. Identification of new susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy in Han Chinese. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhou, X.-J.; Wang, Y.-N.; Liu, X.-Z.; Wang, Y.-F.; Lau, Y.-L.; Yang, W.-L.; Zhang, H. Shared genetic study gives insights into the shared and distinct pathogenic immunity components of IgA nephropathy and SLE. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 296, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Li, Y.; Scolari, F.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Choi, M.; Verbitsky, M.; Fasel, D.; Lata, S.; Prakash, S.; Shapiro, S.; et al. Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Moon, J.-Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptible loci of IgA nephropathy in Koreans. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cheng, T.; Liu, C.; Zhu, T.; Guo, C.; Li, S.; Rao, X.; Li, J. IgA Nephropathy: Current Understanding and Perspectives on Pathogenesis and Targeted Treatment. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, D.R.; Bean, A.G.D.; Demangel, C.; France, M.P.; Briscoe, H.; Britton, W.J. TNF Regulates Chemokine Induction Essential for Cell Recruitment, Granuloma Formation, and Clearance of Mycobacterial Infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.Y.Y.; Leung, J.C.K.; Tsang, A.W.L.; Tang, S.C.W.; Lai, K.N. Activation of tubular epithelial cells by mesangial-derived TNF-alpha: Glomerulotubular communication in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.N.; Leung, J.C.K.; Chan, L.Y.Y.; Saleem, M.A.; Mathieson, P.W.; Lai, F.M.; Tang, S.C.W. Activation of podocytes by mesangial-derived TNF-α: Glomerulo-podocytic communication in IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F945–F955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, M.G., Jr.; Donadio, J.V., Jr.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Grande, J.P. Predicting Renal Outcome in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedwin, G.E.; Naylor, S.L.; Sakaguchi, A.Y.; Smith, D.; Jarrett-Nedwin, J.; Pennica, D.; Goeddel, D.V.; Gray, P.W. Human Lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor genes: Structure, homology and chromosomal localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 6361–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, T.; Morton, C.C.; A Nedospasov, S.; Fiers, W.; Pious, D.; Strominger, J.L. Genes for the tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta are linked to the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8699–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.G.; Symons, J.A.; Mcdowell, T.L.; Mcdevitt, H.O.; Duff, G.W. Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor promoter on transcriptional activation (geneticsmajor histocompatibility complexcytokinegene regulationau-toimmune diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroeger, K.M.; Carville, K.S.; Abraham, L.J. The −308 Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Promoter Polymorphism Effects Transcription. Mol. Immunol. 1997, 34, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, G.; Crusius, J.B.A.; Pool, M.O.; Kolkman, J.J.; VON Blomberg, B.M.E.; Kostense, P.J.; Giphart, M.J.; Schreuder, G.M.T.; Meuwissen, S.G.M.; Peña, A.S. Secretion of Tumour Necrosis Factor α and Lymphotoxin α in Relation to Polymorphisms in the TNF Genes and HLA-DR Alleles. Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 1996, 43, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.Y.; Yang, D.H.; Hwang, K.Y.; Hong, S.Y. Is Tumor Necrosis Factor Genotype (TNFA2/TNFA2)a Genetic Prognostic Factor of an Unfavorable Outcome in IgA Nephropathy? J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, K.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Cheng, C.-H.; Wu, M.-J.; Lian, J.-D. Impact of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor necrosis factor-α gene polymorphism on IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrjänen, J.; Hurme, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Mustonen, J.; Pasternack, A. Polymorphism of the cytokine genes and IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuglular, S.; Berthoux, P.; Berthoux, F. Polymorphisms of the tumour necrosis factor gene at position −308 and TNFd microsatellite in primary IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantis, C.; Heering, P.; Aker, S.; Kuhr, N.; Grabensee, B.; Ivens, K. Influence of Cytokine Gene Polymorphisms on IgA Nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 2008, 30, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, M. Interaction of C1GALT1–IL5RA on the susceptibility to IgA nephropathy in Southern Han Chinese. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Nagasawa, Y.; Shoji, T.; Katakami, N.; Ohtoshi, K.; Hayaishi-Okano, R.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamauchi, A.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Imai, E.; et al. A candidate gene approach to genetic contributors to the development of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 27, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzaras, E. The Generalized Odds Ratio as a Measure of Genetic Risk Effect in the Analysis and Meta-Analysis of Association Studies. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2010, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzaras, E. The power of generalized odds ratio in assessing association in genetic studies with known mode of inheritance. J. Appl. Stat. 2012, 39, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, W.G. The Combination of Estimates from Different Experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, L.; Oudinet, J.-P.; Bens, M.; Noe, L.; Peraldi, M.-N.; Rondeau, E.; Etienne, J.; Ardaillou, R. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rat mesangial cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Kidney Int. 1989, 35, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-H.; Wu, S.-C.; Huang, T.-P.; Yu, C.-L.; Tsai, C.-Y. Increased Excretion of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Interleukin 1 β in Urine from Patients with IgA Nephropathy and Schönlein-Henoch Purpura. Nephron 1996, 74, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K. Increased release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by monocytes from patients with glomerulonephritis. Clin. Nephrol. 1993, 40, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Gharavi, A.G. Pathogenesis of Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy: Recent Insight from Genetic Studies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2013, 64, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riispere, Ž.; Laurinavičius, A.; Kuudeberg, A.; Seppet, E.; Sepp, K.; Ilmoja, M.; Luman, M.; Kõlvald, K.; Auerbach, A.; Ots-Rosenberg, M. IgA nephropathy clinicopathologic study following the Oxford classification: Progression peculiarities and gender-related differences. Medicina 2016, 52, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Monteiro, R.C.; Coppo, R.; Suzuki, H. The Phenotypic Difference of IgA Nephropathy and its Race/Gender-dependent Molecular Mechanisms. Kidney360 2021, 2, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.; Rovin, B.; Wong, M.G.; Alpers, C.E.; Bieler, S.; He, P.; Inrig, J.; Komers, R.; Heerspink, H.J.; Mercer, A.; et al. IgA Nephropathy Patient Baseline Characteristics in the Sparsentan PROTECT Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beernink, J.M.; Persson, F.; Jongs, N.; Laverman, G.D.; Chertow, G.M.; McMurray, J.J.; Langkilde, A.M.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; et al. Efficacy of Dapagliflozin by Baseline Diabetes Medications: A Prespecified Analysis From the DAPA-CKD Study. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Eitner, F.; Fitzner, C.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Peters, H.; Benck, U.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Intensive Supportive Care plus Immunosuppression in IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, G.; Lin, J.; Rosenstock, J.; Markowitz, G.; D’Agati, V.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Preddie, D.; Crew, J.; Valeri, A.; Appel, G. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) vs placebo in patients with moderately advanced IgA nephropathy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, B.D.; Oyen, R.; Claes, K.; Evenepoel, P.; Kuypers, D.; Vanwalleghem, J.; Van Damme, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y.F.C. Mycophenolate mofetil in IgA nephropathy: Results of a 3-year prospective placebo-controlled randomized study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.; Tang, A.W.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, J.C.; Ho, Y.W.; Lai, K.N. Long-term study of mycophenolate mofetil treatment in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Z.; Su, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Delayed severe pneumonia in mycophenolate mofetil-treated patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S.; Kronbichler, A.; Sharma, P.; Geetha, D. Advances in Understanding of Pathogenesis and Treatment of Immune-Mediated Kidney Disease: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, M.G.; Jardine, M.J.; Hladunewich, M.; Jha, V.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Reich, H.; et al. Effect of Oral Methylprednisolone on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. JAMA 2017, 318, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellström, B.C.; Barratt, J.; Cook, H.; Coppo, R.; Feehally, J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Floege, J.; Hetzel, G.; Jardine, A.G.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Targeted-release budesonide versus placebo in patients with IgA nephropathy (NEFIGAN): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoni, M.; Nicotera, R.; Pelagi, E.; Libri, E.; Comi, N.; Fuiano, G. Successful Use of Aliskiren in a Case of IgA- Mesangial Glomerulonephritis Unresponsive to Conventional Therapies. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2019, 14, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziastoudi, M.; Stefanidis, I.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Stravodimos, K.; Zintzaras, E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of genetic association studies for the role of inflammation and the immune system in diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Kidney J. 2017, 10, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziastoudi, M.; Stefanidis, I.; Zintzaras, E. The genetic map of diabetic nephropathy: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziastoudi, M.; Dardiotis, E.; Pissas, G.; Filippidis, G.; Golfinopoulos, S.; Siokas, V.; Tachmitzi, S.V.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Tsironi, E.; et al. Serpin Family E Member 1 Tag Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: An Association Study and Meta-Analysis Using a Genetic Model-Free Approach. Genes 2021, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziastoudi, M.; Theoharides, T.C.; Nikolaou, E.; Efthymiadi, M.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Stefanidis, I. Key Genetic Components of Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, I.; Tziastoudi, M.; Tsironi, E.E.; Dardiotis, E.; Tachmitzi, S.V.; Fotiadou, A.; Pissas, G.; Kytoudis, K.; Sounidaki, M.; Ampatzis, G.; et al. The contribution of genetic variants of SLC2A1 gene in T2DM and T2DM-nephropathy: Association study and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).