Abstract
The hyperechogenicity of the substania nigra (SN) has been established as a valid finding in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), probably caused by an increased tissue iron concentration in the SN. The application of transcranial sonography (TCS) has been investigated for further echogenic basal ganglia alterations in patients with extrapyramidal movement disorders. Compared to PD, a hyperechogenic nucleus lentiformis (LN) has been reported to appear more frequently in atypical parkinsonian syndromes (aPS) such as the parkinsonian phenotype of multiple system atrophy (MSA-P) or the progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). As the evidence providing study sizes are small, we conduct the first meta-analysis of the prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in PD and aPS. We search for available studies providing prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in patients with PD and aPS (MSA-P and PSP) detected by TCS in MEDLINE and SCOPUS databases. We calculate the prevalence rates of LN hyperechogenicity detection in patients with clinical diagnosis of PD vs. aPS under the random-effects model. We include a total of 1330 patients, 1091 PD and 239 aPS (MSA-P and PSP). We find a significantly higher prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in aPS (76%, 95% CI: 0.62-0.88) compared to PD (16%, 95% CI: 0.10-0.23). After proving a higher prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in aPS compared to PD, its histopathological cause needs to be investigated. Furthermore, its full diagnostic accuracy and the qualification to serve as a risk factor for MSA-P and PSP should also be questioned in future studies.
1. Introduction
Transcranial sonography (TCS) in Parkinson’s disease (PD) has been increasingly applied over the last two decades and has proven to be a very helpful tool in the diagnostic process and risk stratification of extrapyramidal movement disorders [1]. Substantia nigra (SN) hyperechogenicity could be identified as a typical finding in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (PD), allowing a clear distinction between PD and healthy controls [2], while a distinction between idiopathic and atypical parkinsonian syndromes (aPS) is more difficult [3]. The meta-analysis by Shafieesabet et al. [4] found a prevalence of SN hyperechogenicity in 84% of PD patients and only in 28% of aPS patients. Reasons for hyperechogenic alterations in the SN are assumed to be caused by an increase in the amount of tissue iron content [5]. Apart from the SN, several other structures in the brain have been examined by TCS in extrapyramidal movement disorders [5,6]. A hyperechogenicity of the nucleus lentiformis (LN) was found to appear more frequently in patients with aPS, especially in patients with the parkinsonian phenotype of multiple system atrophy (MSA-P), or in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) [7]. Thus, LN hyperechogenicity has been considered as a promising marker of aPS, although the scientific evidence of this observation was based on several studies with only a small number of patients. Therefore, we perform the first meta-analysis to date on LN hyperechogenicity prevalence in PD and aPS.
2. Materials and Methods
The present systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [8]. We searched for available studies providing prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in patients with PD and aPS detected by TCS, which is defined as any echogenic signal at the anatomical site of the LN in comparison to the surrounding white matter that can be visually assessed [5]. Disease diagnosis was based on the respective clinical diagnostic criteria for PD (UK Brain Bank Criteria) [9] and PSP [10]. MSA-P patients met the international criteria for MSA [11] and in one study [12] for clinically probable MSA [13]. The literature search in the MEDLINE and SCOPUS databases was performed by two independent reviewers (D.R. and A.H.K.) using the following terms in combination: “nucleus lentiformis”, “basal ganglia”, “transcranial sonography”, “transcranial ultrasound”, “Parkinson”, “multiple system atrophy”, “progressive supranuclear palsy”, “movement disorder”. The complete algorithm used in the MEDLINE database search is available in the online supplement (File S1). No language or other search restriction was applied. The last literature search was performed on April 4th, 2019.
We calculated the rates of LN hyperechogenicity detection by TCS by dividing the number of cases (patients with LN hyperechogenicity) by the total number of patients receiving TCS. After the overall analysis, we performed subgroup analyses according to the clinical diagnosis of PD vs. aPS. For all proportion analyses we implemented the variance-stabilizing double arcsine transformation [14]. The random-effects model (DerSimonian and Laird) was used to calculate the pooled estimates in both the overall and subgroup analyses. We assessed heterogeneity between studies with the Cochrane Q and I2 statistics. For the subgroup analyses we used a standard test for heterogeneity across subgroup results to investigate potential differences between subgroups. All statistical analyses were performed with the use of the Stata Statistical Software Release 13 for Windows (College Station, TX, StataCorp LP).
3. Results
From research on MEDLINE and SCOPUS we found 150 potentially relevant articles. Figure 1 shows the selection process visualized as a flow chart. After assessing the abstracts, 135 articles were excluded.

Figure 1.
Flow chart of the selection process for the included studies.
The remaining 15 [7,12,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27] articles were included in our meta-analysis. These 15 articles provided the data of overall 1330 patients with a sufficient bone window subdivided into 1091 PD and 239 aPS (MSA-P and PSP) patients. The main characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main characteristics of the studies included.
For the PD group, the prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity was calculated to 16% (95% CI: 0.10-0.23) and ranged from 0% to 64%. In the aPS group, the corresponding prevalence was 76% (95% CI: 0.62–0.88) with a range from 0% to 100%. Heterogenicity was substantial for both groups (PD: I2 =8 7.08%, aPS: I2 = 69.35%). Figure 2 demonstrates the forest plots of the studies included.
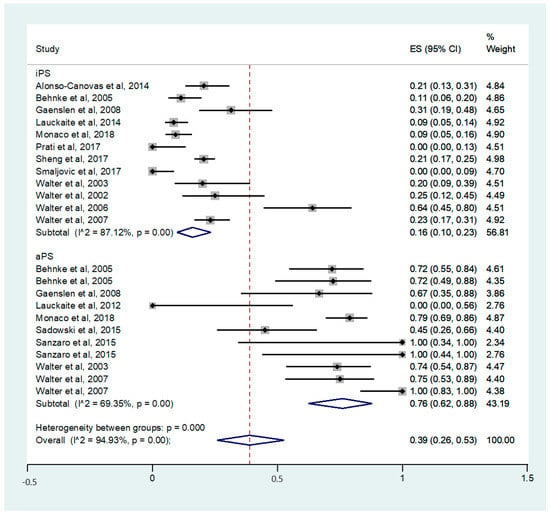
Figure 2.
Forest plots of the studies included for the calculation of prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in PD and aPS. PD = Parkinson’s disease; aPS = atypical parkinsonian syndromes.
4. Discussion
The results of this meta-analysis demonstrate the significant difference regarding the prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in patients with aPS compared to patients with PD. This strongly indicates that this finding is a valid and helpful marker in the discrimination of parkinsonian syndromes. A hyperechogenic lentiform nucleus frequently occurs in MSA-P and PSP, while it is an uncommon feature in PD. Additionally, the prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in the healthy population is assumed to be low (7.9% for marked LN hyperechogenicity), but studies specifically targeting this question are lacking [19,28]. Until today, the distinction of PD from MSA-P and PSP is not always easy, especially in early disease. The diagnostic criteria for these different disorders are still based on clinical findings [11,29,30] and, despite the presence of some useful imaging markers [31], biomarkers with high diagnostic accuracy, especially in the early stages, are generally lacking. Therefore, the sonographic evaluation of the LN could be a very helpful tool to identify patients with aPS in everyday practice. Moreover, the combination of the sonographic evaluation of the LN and SN could be a promising tool to distinguish between PD (SN hyperechogenicity without LN hyperechogenicity) and aPS (LN hyperechogenicity without SN hyperechogenicity).
TCS is a rapid, low-cost, non-invasive and safe examination with a very good and reliable interrater agreement. The SN hyperechogenicity has been identified as a risk factor to develop PD [1,32]. Despite all efforts, the correct diagnosis of MSA-P or PSP presenting as sole parkinsonism in the early stages may be difficult and may require an extensive diagnostic approach [33]. The detection of early stages is of major interest because new, potentially disease-modifying therapies are entering clinical trials. Whether LN hyperechogenicity could further serve as risk factor or prodromal marker for MSA-P or PSP remains to be evaluated in future studies.
Based on animal and post-mortem studies, it has been suggested that SN hyperechogenicity in TCS is caused by an increase of the iron concentration in the SN [34,35,36,37]. An elevated cellular iron content was shown to be a potential damaging factor for nigral neurons [38,39]. Until now, it is unclear whether the increased tissue iron accumulation in the SN is the primary cause or a secondary consequence of the neuronal cell degeneration. On the one hand, there is evidence that iron homeostasis could have a causal link to neurodegeneration in different diseases [40]. In a postmortem study there are further hints underlining this finding. In three subjects, Zecca et al. [41] found an increase in the tissue iron concentration in a preclinical form of PD (incidental Lewy body disease) [42] compared to healthy controls without Lewy bodies and with low SN echogenicity. On the other hand, one of the main cellular functions of neuromelanin is to store iron in the SN. A reduction in neuromelanin levels has been linked to an increase of the SN echogenicity and low neuromelanin levels have been related to a low number of dopaminergic cells [43,44]. Additionally, neuromelanin has been discussed to have neuroprotective effects, especially because of its ability to chelate iron [45]. Thus, the increase of the tissue iron concentration could also be a secondary phenomenon of dopaminergic cell loss. Whether similar mechanisms are involved in LN hyperechogenicity is unknown, but MRI studies indicate different patterns of brain iron accumulation in aPS and PD [46]. Presumably, the increase of iron in specific regions of the brain is caused by the underlying disease pathologies. For PD, an iron overload with its inherent toxicity for dopaminergic neurons of the SN is assumed to play an important role in the disease pathogenesis [40]. Concerning MSA and PSP, pathological studies have demonstrated an increase of iron levels in the putamen and globus pallidus but also in the SN [47,48]. So far, there are no studies investigating the cellular and extracellular changes in PD patients with LN hyperechogenicity. However, an increase in the tissue iron level could possibly cause the hyperechogenic alterations of the LN visualized in TCS. Apart from that, Walter et al. conducted a tissue metal analysis in autopsy brains of 11 patients with Wilson’s disease (WD) in which the LN hyperechogenicity is a common ultrasound finding [49]. Diagnosis of WD was confirmed for all of these WD cases after autopsy and they all showed a LN hyperechogenicity in TCS. The authors found a clear correlation between the LN hyperechogenicity and the putaminal concentration of copper, but not of iron. Future studies should examine the histopathological alterations underlying hyperechogenic LN and its possible association to an increased tissue iron or copper concentration in patients with aPS.
5. Limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis assessing the prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in TCS for patients with PD and aPS (MSA-P or PSP). The literature search and data extraction were thoroughly conducted to avoid any bias, especially to exclude calculation with the same cohorts in case of identical authorships in different studies. Despite the greatest care, this is a general problem for meta-analysis and cannot be completely solved. Figure 3 demonstrates the funnel plot of this meta-analysis. Here, an asymmetric distribution is visible (Egger’s test, p = 0.024). A selection bias by failure to acquire unpublished or non-English data could have had an impact on the appearance of the plot. Additionally, publication bias as well as small study effects are common reasons for an asymmetric distribution of a funnel plot. We further observed a high grade of heterogeneity by meta-regression analyses which can be caused by random variation between the individual studies. We were not able to calculate the diagnostic accuracy because the corresponding values were not available. Furthermore, some studies did not provide the individual numbers of the MSA-P and PSP cases of their aPS cohort or other important information for a specific subgroup analysis were missing. Thus, we could only calculate the common prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity for MSA-P and PSP together. Due to the concept of the underlying studies, we were also not able to adjust potential confounders which are common limitations in observational studies. Additionally, it has to be mentioned that the methodological information of the TCS examination was inconsistently reported. In particular, the number of the TCS investigators and the data of investigator blinding to diagnosis were not always available. Regarding the sonographic equipment, there were slight differences in the applied TCS probe, which is summarized in Table 1.
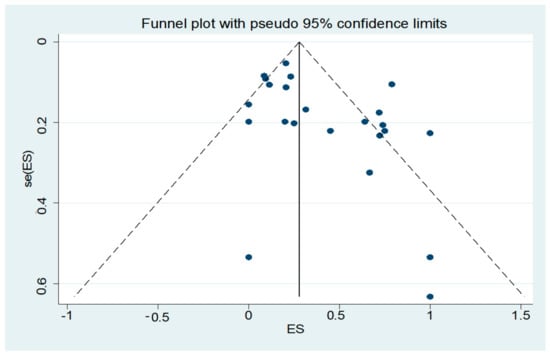
Figure 3.
Funnel plot of the studies included in the meta-analysis.
6. Conclusions
This meta-analysis revealed a high prevalence of LN hyperechogenicity in aPS compared to PD, underlining the importance of TCS examination for the diagnostic process of parkinsonian syndromes. From the neuropathological point of view, MSA-P and PSP are distinct diseases [11,29] which makes this finding even more interesting. Therefore, the cellular and extracellular changes that are related to LN hyperechogenicity, its single or combined diagnostic accuracy, and, respective to the evidence of the SN hyperechogenicty, the ability to serve as a risk factor or early biomarker of aPS should be further investigated in future studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/9/1/2/s1. File S1: Complete search algorithm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.R., C.K.; methodology: D.R., A.H.K, C.K.; formal analysis: D.R., A.H.K., C.K.; writing—original draft preparation: D.R.; writing—review and editing: D.R., A.H.K., C.S., G.T., G.P.P., T.M., A.V.A., R.G., L.T., C.K.; project administration: C.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
A.H.K. has been supported by a European Academy of Neurology Research Fellowship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berg, D.; Postuma, R.B.; Adler, C.H.; Bloem, B.R.; Chan, P.; Dubois, B.; Gasser, T.; Goetz, C.G.; Halliday, G.; Joseph, L.; et al. MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; He, Y.C.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.D. Diagnostic Accuracy of Transcranial Sonography of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson’s disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, A.; Chen, G.; Deng, Y.; Xu, R. Accuracy of Transcranial Sonography of the Substantia Nigra for Detection of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 3, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafieesabet, A.; Fereshtehnejad, S.M.; Shafieesabet, A.; Delbari, A.; Baradaran, H.R.; Postuma, R.B.; Lökk, J. Hyperechogenicity of substantia nigra for differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.; Godau, J.; Walter, U. Transcranial sonography in movement disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogias, C.; Eyding, J.; Postert, T. Transcranial sonography in Huntington’s disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2010, 90, 237–257. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, S.; Berg, D.; Naumann, M.; Becker, G. Differentiation of Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes by transcranial ultrasound. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico- pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvan, I.; Agid, Y.; Calne, D.; Campbell, G.; Dubois, B.; Duvoisin, R.C.; Goetz, C.G.; Golbe, L.I.; Grafman, J.; Growdon, J.H.; et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson- Olszewski syndrome): Report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 1996, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.K.; Low, P.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.Y.; Colosimo, C.; Dürr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Niehaus, L.; Probst, T.; Benecke, R.; Meyer, B.U.; Dressler, D. Brain parenchyma sonography discriminates Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology 2003, 60, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenning, G.K.; Ben Shlomo, Y.; Magahaes, M.; Daniel, S.E.; Quinn, N.P. Clinical features and natural history of multiple system atrophy. An analysis of 100 cases. Brain 1994, 117, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.F.; Tukey, J.W. Transformations related to the angular and the square root. Ann. Math. Stat. 1950, 21, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Cánovas, A.; López-Sendón, J.L.; Buisán, J.; deFelipe-Mimbrera, A.; Guillán, M.; García-Barragán, N.; Corral, I.; Matute-Lozano, M.C.; Masjuan, J.; Martínez-Castrillo, J.C.; et al. Sonography for diagnosis of Parkinson disease-from theory to practice: A study on 300 participants. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaenslen, A.; Unmuth, B.; Godau, J.; Liepelt, I.; Di Santo, A.; Schweitzer, K.J.; Gasser, T.; Machulla, H.J.; Reimold, M.; Marek, K.; et al. The specificity and sensitivity of transcranial ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: A prospective blinded study. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laučkaitė, K.; Rastenytė, D.; Šurkienė, D.; Vaidelytė, B.; Dambrauskaitė, G.; Sakalauskas, A.; Vaitkus, A.; Gleiznienė, R. Ultrasonographic (TCS) and clinical findings in overlapping phenotype of essential tremor and Parkinson’s disease (ET-PD). BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laučkaitė, K.; Rastenytė, D.; Šurkienė, D.; Vaitkus, A.; Sakalauskas, A.; Lukoševičius, A.; Gleiznienė, R. Specificity of transcranial sonography in parkinson spectrum disorders in comparison to degenerative cognitive syndromes. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, D.; Berg, D.; Thomas, A.; Di Stefano, V.; Barbone, F.; Vitale, M.; Ferrante, C.; Bonanni, L.; Di Nicola, M.; Garzarella, T.; et al. The predictive power of transcranial sonography in movement disorders: A longitudinal cohort study. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, P.; Bignamini, A.; Coppo, L.; Naldi, A.; Comi, C.; Cantello, R.; Gusmaroli, G.; Walter, U. The measuring of substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in an Italian cohort of Parkinson disease patients: A case/control study (NOBIS Study). J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2017, 124, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, A.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Sheng, Y.J.; Wang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Luo, W.F.; Liu, C.F. Transcranial sonography image characteristics in different Parkinson’s disease subtypes. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajlovic, D.; Ibrahimagic, O.C. Transcranial Brain Sonography in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Parkinsonian Disorders: A Hospital Study from Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Med. Arch. 2017, 71, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, U.; Wittstock, M.; Benecke, R.; Dressler, D. Substantia nigra echogenicity is normal in non-extrapyramidal cerebral disorders but increased in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2002, 109, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, U.; Dressler, D.; Wolters, A.; Wittstock, M.; Greim, B.; Benecke, R. Sonographic discrimination of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease with dementia. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, U.; Dressler, D.; Probst, T.; Wolters, A.; Abu-Mugheisib, M.; Wittstock, M.; Benecke, R. Transcranial brain sonography findings in discriminating between parkinsonism and idiopathic Parkinson disease. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sadowski, K.; Serafin-Król, M.; Szlachta, K.; Friedman, A. Basal ganglia echogenicity in tauopathies. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2015, 122, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sanzaro, E.; Lemolo, F. Transcranial sonography in movement disorders: An interesting tool for diagnostic perspectives. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenah, J.; König, I.R.; Kötter, C.; Seidel, G.; Klein, C.; Brüggemann, N. Basal ganglia hyperechogenicity does not distinguish between patients with primary dystonia and healthy individuals. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Müller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Movement Disorder Society-endorsed PSP Study Group; et al. Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS Clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Velonakis, G.; Toulas, P.; Stamboulis, E.; Kapaki, E. MRI Planimetry and Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in the Differential Diagnosis of Patients with Parkinsonism. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.; Merz, B.; Reiners, K.; Naumann, M.; Becker, G. Five-year follow-up study of hyperechogenicity of the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxer, A.L.; Yu, J.T.; Golbe, L.I.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; Höglinger, G.U. Advances in progressive supranuclear palsy: New diagnostic criteria, biomarkers, and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Grote, C.; Rausch, W.D.; Mäurer, M.; Wesemann, W.; Riederer, P.; Becker, G. Iron accumulation in the substantia nigra in rats visualized by ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1999, 25, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Roggendorf, W.; Schroder, U.; Klein, R.; Tatschner, T.; Benz, P.; Tucha, O.; Preier, M.; Lange, K.W.; Reiners, K.; et al. Echogenicity of the substantia nigra: Association with increased iron content and marker for susceptibility to nigrostriatal injury. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D. In vivo detection of iron and neuromelanin by transcranial sonography—A new approach for early detection of substantia nigra damage. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2006, 113, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Tao, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Duan, Y. Iron accumulation and microglia activation contribute to substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in the 6-OHDA-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 36, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, M.; Ben-Shachar, D.; Riederer, P.; Youdim, M.B. Altered brain metabolism of iron as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases? J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Gerlach, M.; Youdim, M.B.; Double, K.L.; Zecca, L.; Riederer, P.; Becker, G. Brain iron pathways and their relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The role of iron in brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Berg, D.; Arzberger, T.; Ruprecht, P.; Rausch, W.D.; Musicco, M.; Tampellini, D.; Riederer, P.; Gerlach, M.; Becker, G. In vivo detection of iron and neuromelanin by transcranial sonography: A new approach for early detection of substantia nigra damage. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, C.H.; Connor, D.J.; Hentz, J.G.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Caviness, J.N.; Shill, H.A.; Noble, B.; Beach, T.G. Incidental Lewy body disease: Clinical comparison to a control cohort. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Gallorini, M.; Schunemann, V.; Trautwein, A.X.; Gerlach, M.; Riederer, P.; Vezzoni, P.; Tampellini, D. Iron, neuromelanin and ferritin content in the substantia nigra of normal subjects at different ages: Consequences for iron storage and neurodegenerative processes. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zecca, L.; Fariello, R.; Riederer, P.; Sulzer, D.; Gatti, A.; Tampellini, D. The absolute concentration of nigral neuromelanin, assayed by a new sensitive method, increases throughout the life and is dramatically decreased in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett. 2002, 510, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Double, K.L.; Gerlach, M.; Schunemann, V.; Trautwein, A.X.; Zecca, L.; Gallorini, M.; Youdim, M.B.; Riederer, P.; Ben-Shachar, D. Iron binding characteristics of neuromelanin of the human substantia nigra. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Brain Iron Accumulation in Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes: In vivo MRI Evidences for Distinctive Patterns. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, D.T.; Carayon, A.; Javoy-Agid, F.; Agid, Y.; Wells, F.R.; Daniel, S.E.; Lees, A.J.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Alterations in the levels of iron, ferritin and other trace metals in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia. Brain 1991, 114, 1953–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaindlstorfer, C.; Jellinger, K.A.; Eschlböck, S.; Stefanova, N.; Weiss, G.; Wenning, G.K. The relevance of iron in the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: A viewpoint. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 61, 1253–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Skowrońska, M.; Litwin, T.; Szpak, G.M.; Jabłonka-Salach, K.; Skoloudík, D.; Bulska, E.; Członkowska, A. Lenticular nucleus hyperechogenicity in Wilson’s disease reflects local copper, but not iron accumulation. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2014, 121, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).