“Unraveling EMILIN-1: A Multifunctional ECM Protein with Tumor-Suppressive Roles” Mechanistic Insights into Cancer Protection Through Signaling Modulation and Lymphangiogenesis Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EMILIN-1: Structure, Expression and Physiological Functions
3. Mechanisms of Tumor Suppression by EMILIN-1
3.1. Inhibition of Proliferation and Survival
3.2. Lessons from In Vivo Models
3.3. Inactivation of EMILIN-1 by Proteolytic Activity
4. EMILIN-1 Expression in Tumors
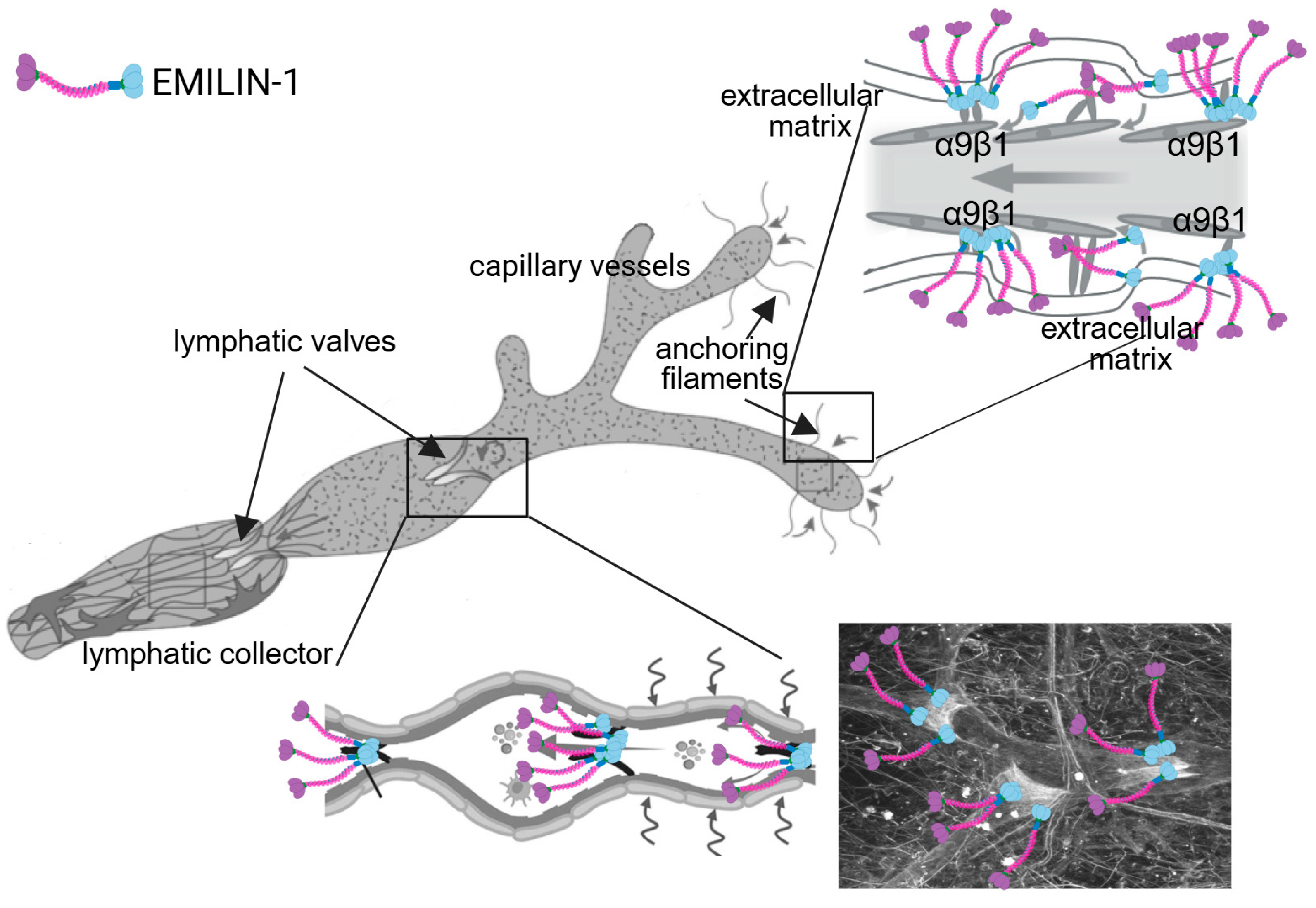
5. EMILIN-1 and Lymphangiogenesis: A Central Role in Malignancy Control
5.1. Regulation of Lymphangiogenesis
5.2. Impact on Tumor Metastasis and Inflammatory Landscape
6. Therapeutic and Diagnostic Implications
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| LV | Lymphatic Vessel |
| GgC1q | GC-terminal globular C1q-like |
| LN | Lymph node |
References
- Streuli, C.H. Integrins and Cell-Fate Determination. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic, V.; Chen, C.C.; Hay, N.; Lau, L.F. The Matrix Protein CCN1 (CYR61) Induces Apoptosis in Fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidler, D.G.; Goldoni, S.; Agnew, C.; Cardi, C.; Thakur, M.L.; Owens, R.T.; McQuillan, D.J.; Iozzo, R.V. Decorin Protein Core Inhibits In Vivo Cancer Growth and Metabolism by Hindering Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Function and Triggering Apoptosis via Caspase-3 Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26408–26418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombatti, A.; Bressan, G.M.; Castellani, I.; Volpin, D. Glycoprotein 115, a Glycoprotein Isolated from Chick Blood Vessels, Is Widely Distributed in Connective Tissue. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, S.; Andreuzzi, E.; Capuano, A.; Schiavinato, A.; Colombatti, A.; Doliana, R. Multiple-Interactions among EMILIN1 and EMILIN2 N- and C-Terminal Domains. Matrix Biol. 2015, 41, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P.; Doliana, R.; Mongiat, M.; Bressan, G.M.; Esposito, G. The EMILIN/Multimerin Family. Front. Immunol. 2011, 2, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spessotto, P.; Cervi, M.; Mucignat, M.T.; Mungiguerra, G.; Sartoretto, I.; Doliana, R.; Colombatti, A. Beta 1 Integrin-Dependent Cell Adhesion to EMILIN-1 Is Mediated by the gC1q Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6160–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danussi, C.; Petrucco, A.; Wassermann, B.; Pivetta, E.; Modica, T.M.; Del Bel Belluz, L.; Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P. EMILIN1-A4/A9 Integrin Interaction Inhibits Dermal Fibroblast and Keratinocyte Proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 195, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombatti, A.; Poletti, A.; Bressan, G.M.; Carbone, A.; Volpin, D. Widespread Codistribution of Glycoprotein Gp 115 and Elastin in Chick Eye and Other Tissues. Collagen Relat. Res. 1987, 7, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doliana, R.; Mongiat, M.; Bucciotti, F.; Giacomello, E.; Deutzmann, R.; Volpin, D.; Bressan, G.M.; Colombatti, A. EMILIN, a Component of the Elastic Fiber and a New Member of the C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily of Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 16773–16781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doliana, R.; Canton, A.; Bucciotti, F.; Mongiat, M.; Bonaldo, P.; Colombatti, A. Structure, Chromosomal Localization, and Promoter Analysis of the Human Elastin Microfibril Interfase Located proteIN (EMILIN) Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danussi, C.; Spessotto, P.; Petrucco, A.; Wassermann, B.; Sabatelli, P.; Montesi, M.; Doliana, R.; Bressan, G.M.; Colombatti, A. Emilin1 Deficiency Causes Structural and Functional Defects of Lymphatic Vasculature. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 4026–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danussi, C.; Del Bel Belluz, L.; Pivetta, E.; Modica, T.M.; Muro, A.; Wassermann, B.; Doliana, R.; Sabatelli, P.; Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P. EMILIN1/Alpha9beta1 Integrin Interaction Is Crucial in Lymphatic Valve Formation and Maintenance. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 4381–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spessotto, P.; Bulla, R.; Danussi, C.; Radillo, O.; Cervi, M.; Monami, G.; Bossi, F.; Tedesco, F.; Doliana, R.; Colombatti, A. EMILIN1 Represents a Major Stromal Element Determining Human Trophoblast Invasion of the Uterine Wall. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 4574–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; Fogolari, F.; Bucciotti, F.; Spessotto, P.; Nicolosi, P.A.; Mucignat, M.T.; Cervi, M.; Esposito, G.; Colombatti, A.; Doliana, R. The A4β1/EMILIN1 Interaction Discloses a Novel and Unique Integrin-Ligand Type of Engagement. Matrix Biol. 2018, 66, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, E.L.; Ruegg, C.; Ferrando, R.; Pytela, R.; Sheppard, D. Sequence and Tissue Distribution of the Integrin Alpha 9 Subunit, a Novel Partner of Beta 1 That Is Widely Distributed in Epithelia and Muscle. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombatti, A.; Doliana, R.; Bot, S.; Canton, A.; Mongiat, M.; Mungiguerra, G.; Paron-Cilli, S.; Spessotto, P. The EMILIN Protein Family. Matrix Biol. 2000, 19, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacchigna, L.; Vecchione, C.; Notte, A.; Cordenonsi, M.; Dupont, S.; Maretto, S.; Cifelli, G.; Ferrari, A.; Maffei, A.; Fabbro, C.; et al. Emilin1 Links TGF-Beta Maturation to Blood Pressure Homeostasis. Cell 2006, 124, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, T.M.E.; Maiorani, O.; Sartori, G.; Pivetta, E.; Doliana, R.; Capuano, A.; Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P. The Extracellular Matrix Protein EMILIN1 Silences the RAS-ERK Pathway via Alpha4beta1 Integrin and Decreases Tumor Cell Growth. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27034–27046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissino, E.; Pivetta, E.; Capuano, A.; Capasso, G.; Bomben, R.; Caldana, C.; Rossi, F.M.; Pozzo, F.; Benedetti, D.; Boldorini, R.; et al. Elastin MIcrofibriL INterfacer1 (EMILIN-1) Is an Alternative Prosurvival VLA-4 Ligand in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajan, P.; Garcia-Pardo, A.; D’Silva, N.J.; Kapila, Y.L. The CS1 Segment of Fibronectin Is Involved in Human OSCC Pathogenesis by Mediating OSCC Cell Spreading, Migration, and Invasion. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetto, A.; Vaisitti, T.; Benedetti, D.; Tissino, E.; Bertagnolo, V.; Rossi, D.; Bomben, R.; Dal, B.M.; Del Principe, M.I.; Gorgone, A.; et al. The CD49d/CD29 Complex Is Physically and Functionally Associated with CD38 in B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, S.A.; Wilson, C.L.; Raines, E.W.; Tang, J.; Giachelli, C.M.; Scatena, M. Osteopontin Mediates Macrophage Chemotaxis via Alpha4 and Alpha9 Integrins and Survival via the Alpha4 Integrin. J. Cell Biochem. 2013, 114, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niibori-Nambu, A.; Wang, C.Q.; Chin, D.W.L.; Chooi, J.Y.; Hosoi, H.; Sonoki, T.; Tham, C.-Y.; Nah, G.S.S.; Cirovic, B.; Tan, D.Q.; et al. Integrin-A9 Overexpression Underlies the Niche-Independent Maintenance of Leukemia Stem Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Gene 2024, 928, 148761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanpanitkitchote, P.; Nuanpirom, J.; Pongsapich, W.; Asavapanumas, N.; Mendler, S.; Wiesmann, N.; Brieger, J.; Jinawath, N. EMILIN-1 Suppresses Cell Proliferation through Altered Cell Cycle Regulation in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2025, 195, 995–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Lv, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Qi, W.; Qiu, W. TSPAN9 and EMILIN1 Synergistically Inhibit the Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells by Increasing TSPAN9 Expression. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-Y.; Lv, J.; Qi, W.-W.; Zhao, S.-F.; Sun, L.-B.; Liu, N.; Sheng, J.; Qiu, W.-S. Tspan9 Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Human Gastric Cancer SGC7901 Cells via the ERK1/2 Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, S.C.; Wei, Y.; Luo, X.; Jia, Y.; Li, L.; Gopal, P.; Zhu, M.; Nassour, I.; Chuang, J.-C.; et al. Arid1a Has Context-Dependent Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressor Functions in Liver Cancer. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 574–589.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lv, C.; Xue, M.; Meng, P.; Qian, X. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Containing Gambogic Acid Inhibit Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer via the RORB/EMILIN1 Axis. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2024, 18, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danussi, C.; Petrucco, A.; Wassermann, B.; Modica, T.M.; Pivetta, E.; Del Bel Belluz, L.; Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P. An EMILIN1-Negative Microenvironment Promotes Tumor Cell Proliferation and Lymph Node Invasion. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, A.; Segatto, I.; Capuano, A.; Mattevi, M.C.; Rampioni Vinciguerra, G.L.; Musco, L.; D’Andrea, S.; Dall’Acqua, A.; Gava, C.; Perin, T.; et al. Loss of the Extracellular Matrix Glycoprotein EMILIN1 Accelerates Δ16HER2-Driven Breast Cancer Initiation in Mice. NPJ Breast Cancer 2024, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, A.; Pivetta, E.; Sartori, G.; Bosisio, G.; Favero, A.; Cover, E.; Andreuzzi, E.; Colombatti, A.; Cannizzaro, R.; Scanziani, E.; et al. Abrogation of EMILIN1-Β1 Integrin Interaction Promotes Experimental Colitis and Colon Carcinogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2019, 83, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, A.; Vescovo, M.; Canesi, S.; Pivetta, E.; Doliana, R.; Nadin, M.G.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Nomura, S.; Pilozzi, E.; et al. The Extracellular Matrix Protein EMILIN-1 Impacts on the Microenvironment by Hampering Gastric Cancer Development and Progression. Gastric Cancer 2024, 27, 1016–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; Bucciotti, F.; Farwell, K.D.; Tippin, D.B.; Mroske, C.; Hulick, P.J.; Weissman, S.M.; Gao, Q.; Spessotto, P.; Colombatti, A.; et al. Diagnostic Exome Sequencing Identifies a Novel Gene, EMILIN1, Associated with Autosomal-Dominant Hereditary Connective Tissue Disease. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, M.; Doliana, R.; Marchese, M.; Capuano, A.; Striano, P.; Spessotto, P.; Bosisio, G.; Iodice, R.; Manganelli, F.; Lanteri, P.; et al. Distal Motor Neuropathy Associated with Novel EMILIN1 Mutation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 137, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorani, O.; Pivetta, E.; Capuano, A.; Modica, T.M.; Wassermann, B.; Bucciotti, F.; Colombatti, A.; Doliana, R.; Spessotto, P. Neutrophil Elastase Cleavage of the gC1q Domain Impairs the EMILIN1-Alpha4beta1 Integrin Interaction, Cell Adhesion and Anti-Proliferative Activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, E.; Danussi, C.; Wassermann, B.; Modica, T.M.; Del Bel Belluz, L.; Canzonieri, V.; Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P. Neutrophil Elastase-Dependent Cleavage Compromises the Tumor Suppressor Role of EMILIN1. Matrix Biol. 2014, 34, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, A.M.; Rzymkiewicz, D.M.; Ji, H.; Gregory, A.D.; Egea, E.E.; Metz, H.E.; Stolz, D.B.; Land, S.R.; Marconcini, L.A.; Kliment, C.R.; et al. Neutrophil Elastase-Mediated Degradation of IRS-1 Accelerates Lung Tumor Growth. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, I.; de la Luz Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Rangel-Moreno, J.; Chiriboga, L.; Pan, C.; Nastiuk, K.L.; Krolewski, J.J.; Sen, A.; Hammes, S.R. Infiltrating Myeloid Cells Exert Protumorigenic Actions via Neutrophil Elastase. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.A.; Kang, Y. The Metastasis-Promoting Roles of Tumor-Associated Immune Cells. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, C.A.; Lang, S.; Brandau, S. Modulation of Neutrophil Granulocytes in the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanisms and Consequences for Tumor Progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocq, A.; Antoine, M.; Flahault, A.; Philippe, C.; Crestani, B.; Bernaudin, J.F.; Mayaud, C.; Milleron, B.; Baud, L.; Cadranel, J. Neutrophil Alveolitis in Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma: Induction by Tumor-Derived Interleukin-8 and Relation to Clinical Outcome. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eck, M.; Schmausser, B.; Scheller, K.; Brandlein, S.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K. Pleiotropic Effects of CXC Chemokines in Gastric Carcinoma: Differences in CXCL8 and CXCL1 Expression between Diffuse and Intestinal Types of Gastric Carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wislez, M.; Rabbe, N.; Marchal, J.; Milleron, B.; Crestani, B.; Mayaud, C.; Antoine, M.; Soler, P.; Cadranel, J. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Production by Neutrophils Infiltrating Bronchioloalveolar Subtype Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: Role in Tumor Progression and Death. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jensen, H.K.; Donskov, F.; Marcussen, N.; Nordsmark, M.; Lundbeck, F.; von der Maase, H. Presence of Intratumoral Neutrophils Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4709–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Metzler, K.D.; Hakkim, A.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Elastase and Myeloperoxidase Regulate the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor López, A.; Mazariegos, M.S.; Capuano, A.; Ximénez-Embún, P.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Recio, J.Á.; Muñoz, E.; Al-Shahrour, F.; Muñoz, J.; Megías, D.; et al. Inactivation of EMILIN-1 by Proteolysis and Secretion in Small Extracellular Vesicles Favors Melanoma Progression and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlikilicer, P.; Rashed, M.H.; Bayraktar, R.; Mitra, R.; Ivan, C.; Aslan, B.; Zhang, X.; Filant, J.; Silva, A.M.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Ubiquitous Release of Exosomal Tumor Suppressor MiR-6126 from Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7194–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhong, M.-E.; Chen, Y.; Pan, M.; Xu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, B. Proteomic Profiling and Functional Characterization of Serum-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Mucinous and Non-Mucinous Colon Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 9285–9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, J.; Bowden, P.; Thavarajah, T.; Florentinus-Mefailoski, A.; Chen, Z.Z.; Tucholska, M.; Norzin, T.; Ho, M.T.; Phan, M.; Mohamed, N.; et al. The Plasma Peptides of Breast versus Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Proteom. 2019, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlund, K.; Lindskog, C.; Saito, A.; Berglund, A.; Ponten, F.; Goransson-Kultima, H.; Isaksson, A.; Jirstrom, K.; Planck, M.; Johansson, L.; et al. CD99 Is a Novel Prognostic Stromal Marker in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgueira, M.A.; Carraro, D.M.; Brentani, H.; Patrao, D.F.; Barbosa, E.M.; Netto, M.M.; Caldeira, J.R.; Katayama, M.L.; Soares, F.A.; Oliveira, C.T.; et al. Gene Expression Profile Associated with Response to Doxorubicin-Based Therapy in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7434–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Huang, R.; Huang, J. Stemness-Related Gene Signatures as a Predictive Tool for Breast Cancer Radiosensitivity. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1536284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, C.K.; Kurozumi, S.; Fujii, T.; Pourquier, D.; Khellaf, L.; Boissiere, F.; Horiguchi, J.; Oyama, T.; Shirabe, K.; Colinge, J.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Spatial Heterogeneity and EMILIN1 Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment Modulate TGF-β Activity and CD8+ T-Cell Infiltration in Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2024, 14, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Chatterjee, B.; Wang, Y.; Stevenson, H.S.; Edelman, D.C.; Meltzer, P.S.; Barr, F.G. Distinct Methylation Profiles Characterize Fusion-Positive and Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xing, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Mutch, D.G.; Hagemann, I.S.; Wang, T. Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Epigenetic Signatures of Uterine Carcinosarcoma. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, U.N.; Hood, B.L.; Jones-Laughner, J.M.; Sun, M.; Conrads, T.P. Distinct Profiles of Oxidative Stress-Related and Matrix Proteins in Adult Bone and Soft Tissue Osteosarcoma and Desmoid Tumors: A Proteomics Study. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Xun, J.; Feng, H. Bioinformatics Analysis of Ewing’s Sarcoma: Seeking Key Candidate Genes and Pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6008–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Liu, L.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. Glycolysis-Metabolism-Related Prognostic Signature for Ewing Sarcoma Patients. Mol. Biotechnol. 2024, 66, 2882–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salani, R.; Neuberger, I.; Kurman, R.J.; Bristow, R.E.; Chang, H.W.; Wang, T.L.; Shih, I. Expression of Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Ovarian Serous Tumors. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2007, 26, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucaryilmaz Metin, C.; Ozcan, G. Comprehensive Bioinformatic Analysis Reveals a Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Gene Signature as a Poor Prognostic Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Gastric Cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; He, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, W. Candidate Genes in Gastric Cancer Identified by Constructing a Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, G.; Gao, M.; Tian, X. Increased Expression of MMP14 Correlates with the Poor Prognosis of Chinese Patients with Gastric Cancer. Gene 2015, 563, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formolo, C.A.; Williams, R.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; MacDonald, T.J.; Lee, N.H.; Hathout, Y. Secretome Signature of Invasive Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3149–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Jin, Z.; Liu, C. Expression Patterns and the Prognostic Value of the EMILIN/Multimerin Family Members in Low-Grade Glioma. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengzhen, Z.; Xinwei, H.; Zeheng, T.; Nan, L.; Yang, Y.; Huirong, Y.; Kaisi, F.; Xiaoting, D.; Liucheng, Y.; Kai, W. Integrated Machine Learning-Driven Disulfidptosis Profiling: CYFIP1 and EMILIN1 as Therapeutic Nodes in Neuroblastoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunbanjerdsuk, S.; Vorasan, N.; Saethang, T.; Pongrujikorn, T.; Pangpunyakulchai, D.; Mongkonsiri, N.; Arsa, L.; Thokanit, N.; Pongsapich, W.; Anekpuritanang, T.; et al. Oncoproteomic and Gene Expression Analyses Identify Prognostic Biomarkers for Second Primary Malignancy in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.B.; Khora, S.S.; Suresh, A. Molecular Prognosticators in Clinically and Pathologically Distinct Cohorts of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma-A Meta-Analysis Approach. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skobe, M.; Hawighorst, T.; Jackson, D.G.; Prevo, R.; Janes, L.; Velasco, P.; Riccardi, L.; Alitalo, K.; Claffey, K.; Detmar, M. Induction of Tumor Lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharinen, P.; Tammela, T.; Karkkainen, M.J.; Alitalo, K. Lymphatic Vasculature: Development, Molecular Regulation and Role in Tumor Metastasis and Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacker, S.A.; Williams, S.P.; Karnezis, T.; Shayan, R.; Fox, S.B.; Achen, M.G. Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Vessel Remodelling in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro-Navarro, N.; García-Báez, C.; García-Caballero, M. Molecular and Metabolic Orchestration of the Lymphatic Vasculature in Physiology and Pathology. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, L.C.; Tacconi, C.; Ducoli, L.; Detmar, M. Lymphatic Vessels in Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1837–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; Pivetta, E.; Baldissera, F.; Bosisio, G.; Wassermann, B.; Bucciotti, F.; Colombatti, A.; Sabatelli, P.; Doliana, R.; Spessotto, P. Integrin Binding Site within the GC1q Domain Orchestrates EMILIN-1-Induced Lymphangiogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2019, 81, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litteri, G.; Carnevale, D.; D’Urso, A.; Cifelli, G.; Braghetta, P.; Damato, A.; Bizzotto, D.; Landolfi, A.; Ros, F.D.; Sabatelli, P.; et al. Vascular Smooth Muscle Emilin-1 Is a Regulator of Arteriolar Myogenic Response and Blood Pressure. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Groopman, J.E. Stimulation of Beta 1 Integrin Induces Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-3 and Modulates Cell Migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41950–41957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Groopman, J.E.; Wang, J.F. Extracellular Matrix Regulates Endothelial Functions through Interaction of VEGFR-3 and Integrin Alpha5beta1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivetta, E.; Wassermann, B.; Del Bel Belluz, L.; Danussi, C.; Modica, T.M.; Maiorani, O.; Bosisio, G.; Boccardo, F.; Canzonieri, V.; Colombatti, A.; et al. Local Inhibition of Elastase Reduces EMILIN1 Cleavage Reactivating Lymphatic Vessel Function in a Mouse Lymphoedema Model. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; He, R.; Wang, T. Neutrophil Elastase: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kataru, R.P.; Koh, G.Y. Inflammation-Associated Lymphangiogenesis: A Double-Edged Sword? J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueni, L.N.; Detmar, M. The Lymphatic System in Health and Disease. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2008, 6, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, F.; Severini, F.L.; Calice, G.; Zoppoli, P.; Falco, G.; Notarangelo, T. The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammatory Pathways in Driving Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Ding, P.; Sun, C.; Chen, S.; Lowe, S.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Q. Lymphangiogenesis in Gastric Cancer: Function and Mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Hu, X.; Wei, P.; Shan, G. Molecular Background of the Regional Lymph Node Metastasis of Gastric Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3409–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivetta, E.; Capuano, A.; Vescovo, M.; Scanziani, E.; Cappelleri, A.; Rampioni Vinciguerra, G.L.; Vecchione, A.; Doliana, R.; Mongiat, M.; Spessotto, P. EMILIN-1 Deficiency Promotes Chronic Inflammatory Disease through TGFβ Signaling Alteration and Impairment of the GC1q/A4β1 Integrin Interaction. Matrix Biol. 2022, 111, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Application Area | Implication | Notes/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Biomarker | Reduced EMILIN-1 expression or proteolysis correlates with tumor aggressiveness | Potential use in tumor grading, prognosis, and monitoring |
| Prognostic Marker | Loss of EMILIN-1 associated with poor clinical outcomes | Especially relevant in cancers with lymphatic dissemination |
| Therapeutic Target | Restoration of expression/function | Gene therapy, recombinant protein delivery, or ECM-targeted therapies |
| Protease Inhibition | Preventing EMILIN-1 degradation | Use of MMP or neutrophil elastase inhibitors to preserve EMILIN-1 structure |
| Peptide Mimetics | Design of EMILIN-1-derived peptides | Mimicking integrin-binding domains to block pro-oncogenic signaling |
| Pathway Modulation | Targeting EMILIN-1-regulated pathways (e.g., TGF-β, VEGF-C, ERK/AKT) | Possible synergy with targeted therapies or immunotherapies |
| TME Modulation | Rebalancing TME via lymphangiogenesis control | May reduce metastasis and improve immune cell infiltration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muzzin, S.; Timis, E.; Doliana, R.; Mongiat, M.; Spessotto, P. “Unraveling EMILIN-1: A Multifunctional ECM Protein with Tumor-Suppressive Roles” Mechanistic Insights into Cancer Protection Through Signaling Modulation and Lymphangiogenesis Control. Cells 2025, 14, 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130946
Muzzin S, Timis E, Doliana R, Mongiat M, Spessotto P. “Unraveling EMILIN-1: A Multifunctional ECM Protein with Tumor-Suppressive Roles” Mechanistic Insights into Cancer Protection Through Signaling Modulation and Lymphangiogenesis Control. Cells. 2025; 14(13):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130946
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuzzin, Samanta, Enrica Timis, Roberto Doliana, Maurizio Mongiat, and Paola Spessotto. 2025. "“Unraveling EMILIN-1: A Multifunctional ECM Protein with Tumor-Suppressive Roles” Mechanistic Insights into Cancer Protection Through Signaling Modulation and Lymphangiogenesis Control" Cells 14, no. 13: 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130946
APA StyleMuzzin, S., Timis, E., Doliana, R., Mongiat, M., & Spessotto, P. (2025). “Unraveling EMILIN-1: A Multifunctional ECM Protein with Tumor-Suppressive Roles” Mechanistic Insights into Cancer Protection Through Signaling Modulation and Lymphangiogenesis Control. Cells, 14(13), 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130946











