Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], the image in Figure 1D is overlapping with Figure 1E [2]. The images have been inadvertently overleaped with previously published work. The corrected Figure 1D, R-Tf-D-LP4 has now been replaced with a different image, shown below.
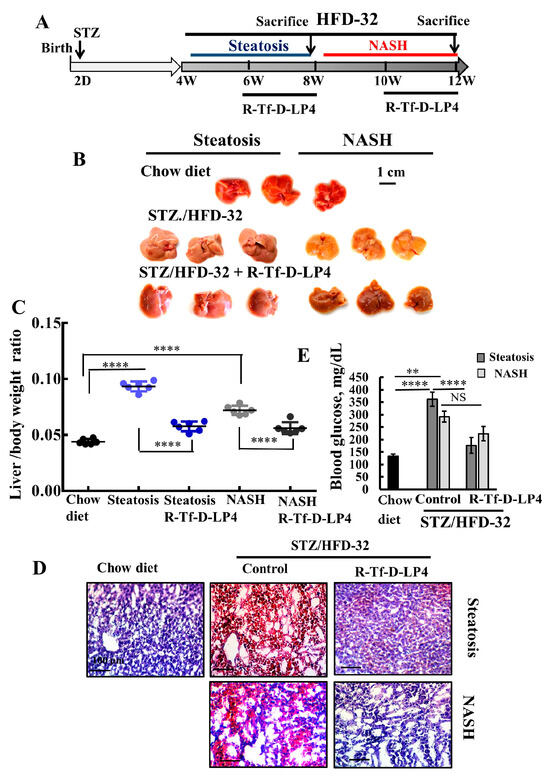
Figure 1.
R-Tf-D-LP4 peptide-mediated inhibition of steatotic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) liver pathology in a STZ/HFD-32 mouse model. (A). Schematic presentation of the course of steatosis and NASH induced by a STZ/HFD-32 diet and the effect of R-Tf-D-LP4 peptide treatment. (B–D). Liver from mice fed with chow (normal diet), HFD-32, or HFD-32 and treated with the R-Tf-D-LP4 peptide (14 mg/kg) by i.v. injection every two days from Week 6 to 8 for steatosis and from Week 8 to 10 for NASH, as described in the Methods section. Mice were then sacrificed, livers were removed, photographed (B), and weighed (C) Results are means ± SEM (n = 10), (p **** ≤ 0.0001). Representative liver sections were stained with Oil Red O (D). Blood glucose level of mice was measured. Results are means ± SEM (n = 5–10; ** p ≤ 0.01, p **** ≤ 0.0001) (E).
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
References
- Pittala, S.; Levy, I.; De, S.; Kumar Pandey, S.; Melnikov, N.; Hyman, T.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V. The VDAC1-based R-Tf-D-LP4 Peptide as a Potential Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2020, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittala, S.; Krelin, Y.; Kuperman, Y.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V. A Mitochondrial VDAC1-Based Peptide Greatly Suppresses Steatosis and NASH-Associated Pathologies in a Mouse Model. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1848–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).