Abstract
The presence of the odorant 2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB) in drinking water sources is undesirable. Although 2-MIB production is known to be influenced by temperature, its regulation at the gene level and its relationship with Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) at different temperatures remain unclear. This study investigates the impact of temperature on 2-MIB production and related gene expression in Pseudanabaena strains PD34 and PD35 isolated from Lake Paldang, South Korea. The strains were cultured at three temperatures (15, 25, and 30 °C) to examine cell growth, 2-MIB production, and mic gene expression levels. 2-MIB production per cell increased with higher temperatures, whereas mic gene expression levels were higher at lower temperatures, indicating a complex regulatory mechanism involving post-transcriptional and enzyme kinetics factors. Additionally, the relationship between Chl-a and 2-MIB involved in metabolic competition was analyzed, suggesting that high temperatures appear to favor 2-MIB synthesis more than Chl-a synthesis. The distinct difference in the total amount of the two products and the proportion of 2-MIB between the two strains partially explains the variations in 2-MIB production. These findings highlight the significant effect of temperature on 2-MIB biosynthesis in Pseudanabaena and provide a valuable background for gene data-based approaches to manage issues regarding 2-MIB in aquatic environments.
1. Introduction
Odor compounds synthesized by microorganisms in surface water ecosystems are receiving continuous attention worldwide. Numerous studies have highlighted the issues caused by these odorants, including increased expenses for water treatment plants and consumer distrust of the safety of drinking water [1,2,3,4,5]. Among these odorants, 2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB) and geosmin are major contributors to earthy/musty odors in drinking water sources [6]. The structural properties of 2-MIB and its lower aqueous solubility result in the poor removal efficiency of 2-MIB in several oxidation processes compared with geosmin [7,8].
2-MIB is a secondary metabolite produced by various microorganisms, including actinomycetes, myxobacteria, fungi, and cyanobacteria [9,10,11,12]. 2-MIB production by cyanobacteria has been associated with temperature and eutrophication [1]. The temperature can influence cyanobacterial metabolic reactions, leading to a shift in algal communities to bloom-forming cyanobacteria [13,14] and altered cellular productivity and 2-MIB release [3,15,16].
Several Pseudanabaena species possess the biosynthetic genes for 2-MIB production. A close correlation has been reported between the 2-MIB concentration and Pseudanabaena cell density [17,18,19]. Although optimal growth temperatures vary by species, Pseudanabaena exhibits a broad temperature tolerance, surviving in both cultured and freshwater conditions. Wang and Li [20] and Shen et al. [21] reported 2-MIB production by Pseudanabaena sp. under lab-scale conditions, ranging from 10 °C to 35 °C. Remarkably, Khan et al. [22] observed an increase in the cell density of Pseudanabaena catenata at 4 °C. Additionally, field work by Gao et al. [23] confirmed that Pseudanabaena sp. was dominant during February and March at certain sampling sites. These findings suggest that the detection of 2-MIB may be directly related to the occurrence of Pseudanabaena sp. not only in the summer but also in the spring and autumn [24,25].
Some filamentous cyanobacteria, including Pseudanabaena, possess two genes mtf and mic, encoding geranyl diphosphate (GPP) methyltransferase (GPPMT) and 2-MIB synthase (MIBS), respectively, which catalyze the formation of 2-MIB via two serial reactions in the isoprenoid pathway [26,27]. GPPMT methylates GPP to form 2-methyl-GPP, which is subsequently cyclized by MIBS to 2-MIB in the presence of Mg2+. Some studies [11,21] have shown that mtf and mic have similar expression patterns under the same conditions. To further understand the biosynthetic activity of 2-MIB at the gene level, we targeted the mic gene.
Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) is commonly used as an indicator of cyanobacterial biomass in aquatic environments. Chl-a is significant in the study of 2-MIB and geosmin because it shares part of the biosynthetic pathway with these compounds. GPP is an intermediate precursor of Chl-a and the monoterpene precursor of 2-MIB, suggesting a competitive relationship between Chl-a and 2-MIB [28]. Indeed, opposing trends between 2-MIB and Chl-a have been observed under certain environmental conditions [3,29]. Thus, to understand the relationship between 2-MIB and Chl-a at different temperatures, in the current study, we considered Chl-a as a competitor to 2-MIB rather than merely as biomass.
To date, few studies have reported on gene regulation by temperature at the RNA level for 2-MIB production. By quantifying both DNA and RNA using digital PCR (dPCR), we confirmed the 2-MIB synthesis potential and expression level of the mic gene in Pseudanabaena sp.
The production dynamics of odorants exhibit specificity within species and even among strains of odor-producing cyanobacteria [30,31]. However, strain-specific variations of odorants within the same species have been rarely studied. In this study, we cultured two strains of Pseudanabaena sp. that are major producers of 2-MIB; these strains were collected from different locations on different dates and cultured under laboratory conditions. We focused on the effect of temperature on the 2-MIB productivity of these two strains, examining the metabolic relationship between 2-MIB and Chl-a and the expression of the mic gene. Additionally, we explored the distinct characteristics of the two strains and the common influence of culture temperature on the biosynthesis of 2-MIB.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the Bacteria and Mic Gene
Two strains of Pseudanabaena sp., isolated from Lake Paldang, South Korea, were used as 2-MIB-producing cyanobacteria. Individual filaments of Pseudanabaena were collected using the pipetting method described by Belcher and Swale [32] and subsequently cultured. To identify the cultured Pseudanabaena, the 16S rRNA gene fragment was amplified using the 27F/1492R primers. The 16S rRNA sequences obtained from the two strains, coded as Pseudanabaena sp. PD34 and Pseudanabaena sp. PD35, were deposited in GenBank at NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information). A phylogenetic tree was constructed using 16S rRNA sequences of Pseudanabaena species closely related to these two strains retrieved from the NCBI GenBank database (Figure S1). The phylogenetic analysis indicated that PD34 and PD35 are variants of the species Pseudanabaena foetida. The presence of the 2-MIB synthase gene (mic) in both strains was determined using the MIB3324F/MIB4050R primers as described by Suurnäkki et al. [33]. Details of all primers/probes used in this study are presented in Table 1.
2.2. Culture Experiments
The strains were grown in 200 mL of BG11 medium [34] in a shaking incubator set at 100 rpm under 32 µmol photons/s/m2 (12-hour light/dark cycle). The incubation temperatures were set to 15, 25, and 30 °C, reflecting the temperature points at which Pseudanabaena sp. and 2-MIB were significantly observed in the Lake Paldang basin [35]. The experiments were carried out over 7 weeks (8 time points), with one culture per week used for analysis from a total of nine independent cultures, including a control culture. To verify repeatability, the cultivation was carried out in duplicate under the same conditions. Chl-a and cell density (cells/mL) were measured as indicators of cell growth. Chl-a was analyzed as described by Lee and Gil [36] using a Cary 3500 UV/Vis spectrophotometer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to measure absorbance at 630, 645, 663, and 750 nm.
2.3. DNA and RNA Extraction
Cultured cyanobacteria were collected and immediately filtered using a membrane filter (0.45 µm pore size; Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). DNA and RNA were extracted from the filtered cells using the DNeasy PowerWater Kit and RNeasy PowerWater Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), respectively, following the manufacturer’s protocols, with an additional cell lysis step at 65 °C for 10 min. All samples were extracted with 100 µL of the elution solution. RNA purity was confirmed by measuring the A260/A280 ratio using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) immediately after extraction.
2.4. dPCR Setup for Mic Gene Quantification
dPCR was used for quantifying target DNA/RNA genes due to its precision and higher detection sensitivity for low-copy-number nucleic acids [37]. Eluted nucleic acids stored at −70 °C were analyzed using the QIAcuity nanoplate-based dPCR system (Qiagen) with QIAcuity Software Suite V2.5.0.
The PCR targeted the mic gene in the 2-MIB operon. The mic gene was specifically amplified using the 3909F/4028R primers [38] and a TaqMan probe (3987P) with 6-carboxyfluorescein (FAM) and black hole quencher 1 (BHQ-1) (Table 1). To normalize mic gene expression, the CYAN 328R probe and the CYAN 108F/CYAN 377R primers were used as Pseudanabaena-specific primers/probe sets, modified from Rinta-Kanto et al. [39].

Table 1.
Primers and probes used in this study.
Table 1.
Primers and probes used in this study.
| Primers /Probes | Target | Sequence (5′→3′) | Target Size (bp) | Ta (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27F | Universal bacteria | AGAGTTTGATYMTGGCTCAG | >1200 | 56 | Sung et al. [40] |
| 1492R | TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACT | ||||
| CYAN 108F | Pseudanabaena- specific 16S rRNA | ACGGGTGAGTAACRCGTRA | 270 | 55 | Modified from Rinta-Kanto et al. [39] |
| CYAN 377R | CCATTGCGGAAAATTCCCC | ||||
| CYAN 328R | FAM-CTCAGTTCCAGTGTGACTGGTC-BHQ1 | ||||
| MIB3324F | Cyanobacterial MIB synthase | CATTACCGAGCGATTCAACGAGC | 726 | 52 | Suurnäkki et al. [33] |
| MIB4050R | CCGCAATCTGTAGCACCATGTTGA | ||||
| 3909F | Cyanobacterial MIB synthase (mic) | CACCAGATCTTTTCTTCGATC | 140 | 59 | Lee et al. [38] |
| 4028R | AATCTGTAGCACCATGTTGAC | ||||
| 3987P | FAM-TCCTTTCGGTTGCCA-BHQ1 | this study |
For DNA analysis, a 40 µL reaction mixture was prepared containing 10 µL of 4× Probe Master Mix, 1.6 µL of each primer (10 µM), 0.8 µL of probe, and 4 µL of template DNA. The thermal cycling conditions included an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 50 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 59 °C for 30 s (primer annealing/extension).
For RNA analysis, the QIAcuty OneStep Advanced Probe Kit (Qiagen) was used for one-step reverse transcription dPCR (RT-dPCR). The 40 µL reaction mixture included 10 µL of 4× OneStep Advanced Probe Master Mix, 0.4 µL of 100× OneStep RT Mix, 1.6 µL of each primer (10 µM), 0.8 µL of probe (10 µM), and 5 µL of RNA extract. After a 40 min reverse transcription step at 50 °C, dPCR was performed with an initial heat activation at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 50 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s and 59 °C (or 55 °C) for 30 s. The concentration of target genes (copies/mL) in the samples was calculated using the following equation:
where VR and VT represent the total reaction volume and template volume in dPCR, respectively. In this equation, the filtered volume of the cultivation sample (Filtration V) and the extracted volume of DNA or RNA (Elution V) were considered.
2.5. GC-MS Analysis of 2-MIB
The concentration of 2-MIB was analyzed using a gas chromatography system (Varian 450-GC; Agilent, USA) equipped with mass spectrometry (Agilent 5977B; Agilent, USA). Detection of total 2-MIB followed a modified method by Hurlburt et al. [41]. Samples were treated via headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) with a CombiPAL autosampler before injection into the GC-MS system. A 10 mL sample was stirred with 3 g of NaCl and incubated at 70 °C for 30 min, allowing volatile organic compounds, including 2-MIB, to transfer to the headspace of the vial. These compounds were adsorbed onto a 50/30 µm DVB/CAR/PDMS SPME fiber (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA) and extracted by heating at 270 °C for 4 min. Separated compounds were measured qualitatively and quantitatively based on their physicochemical properties using the DB-5MS column in the GC and the MS detector. A calibration curve prepared with a spiked standard mixed solution (47525-U; Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA) was used to determine the concentration of 2-MIB in the samples.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out to evaluate the effect of temperature on 2-MIB production and differences among cyanobacterial strains. Significant differences between data groups were determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and independent t-tests. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Data statistics were analyzed using SPSS Statistics v.21 software (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cell Growth, 2-MIB Production, and Mic Gene Abundance
The two strains of Pseudanabaena sp., both 2-MIB producers, exhibited different patterns of cell growth and odorant production under the three temperatures (15 °C, 25 °C, and 30 °C). For both strains, the maximum cell density was highest at 25 °C and lowest at 30 °C (Figure 1a,b). At the optimal growth temperature of 25 °C, the specific growth rate of PD34 was 0.12 d−1, which was higher than PD35’s rate of 0.07 d−1. An unusual drop in cell density was observed after 6 weeks at 15 °C; this appears to be an error during the random selection and analysis of independent cultures (Figure 1b).
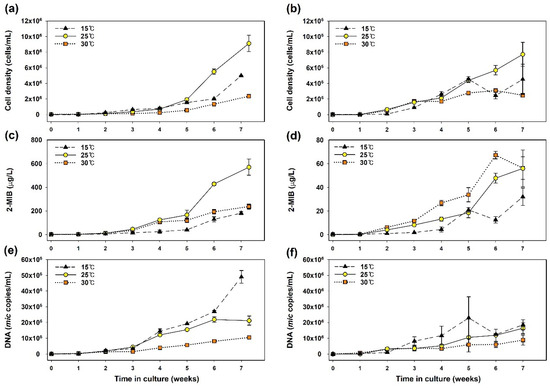
Figure 1.
Temporal variations in components in the Pseudanabaena cultures: (a,b) cell density; (c,d) the concentration of 2-MIB; and (e,f) mic gene abundance in DNA samples. The left and right plots represent Pseudanabaena sp. PD34 and PD35, respectively.
The levels of each variable related to 2-MIB increased over time with cell growth. Notably, significant differences in 2-MIB production were observed between the strains. The 2-MIB concentration with PD34 was 10-fold higher than that with PD35 (evident from the y-axis scale in Figure 1c,d). The maximum 2-MIB concentrations with PD34 were 181 μg/L, 570 μg/L, and 237 μg/L at 15 °C, 25 °C, and 30 °C, respectively. For PD35, the maximum concentrations were 32 μg/L, 56 μg/L, and 67 μg/L at 15 °C, 25 °C, and 30 °C, respectively.
Interestingly, the abundance of the mic gene in the DNA samples did not correlate with 2-MIB concentrations at the three temperatures during the incubation period (Figure 1e,f). The 2-MIB concentration was the lowest, while the mic gene copy number was the highest for both strains at 15 °C compared to those at other temperatures. The mic gene copies did not increase proportionally with cell growth across temperatures. At 30 °C, both cell density and mic gene copy number were low, but the gene abundance at 15 °C exceeded that at 25 °C, which is the temperature that showed optimal growth. The average DNA retention per cell in the exponential phase was 10–11 copies/cell for PD34 and 3–7 copies/cell for PD35, with the highest abundance at 15 °C. Although it may vary depending on the growth or metabolic state, the effect of temperature on DNA content has not been verified [42,43]. Our results show that the mic DNA content can vary slightly with temperature and with strain.
Watson et al. [9] reviewed odorant yields per unit quantity of cyanobacteria across various studies, showing a wide range of geosmin and 2-MIB production yields among genera or species in lab cultivation. Production yields can vary with physiological states such as growth phase and environmental stress [44,45]. During the decay period, cell death leads to the release of cell-bound 2-MIB into the extracellular space [3,46]. Furthermore, the odorant productivity of cyanobacteria may be overestimated in the early stages of cultivation due to insufficient population. In this study, 2-MIB production by Pseudanabaena was measured during the exponential phase (from week 2 onwards), which will be discussed in the following section. The exponential phase was determined by referencing the linear portion of the semi-log graph of cell growth.
3.2. The Effect of Temperature on 2-MIB Production Yield
Figure 2 shows the effect of temperature on the biosynthesis of 2-MIB by the two strains. The 2-MIB yields per cell and per mic DNA copy increased with culture temperature. The average 2-MIB cell quota (pg/cell) for PD34 increased from 0.034 to 0.211 pg/cell as the temperature rose, whereas PD35 showed a significantly lower increase, from 0.006 to 0.015 pg/cell. One-way ANOVA with the Games–Howell test for unequal variance revealed that the cellular 2-MIB yield of PD34 exhibited significant differences (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01) at each of the three temperatures (Figure 2a). For PD35 cultured at 30 °C, the cell quota was significantly affected (p < 0.01) compared to that at the other two temperatures (Figure 2b).
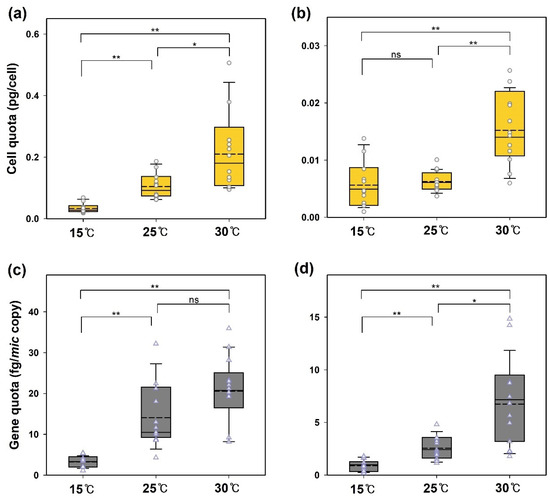
Figure 2.
The effect of temperature on the 2-MIB yield of Pseudanabaena. 2-MIB cell quotas (pg/cell) in Pseudanabaena sp. (a) PD34 and (b) PD35 and gene quotas (fg/mic copy) in (c) PD34 and (d) PD35 were determined in the exponential phase. In the box plot, the solid line and the dashed line indicate the median and mean value, respectively (ANOVA with the Games–Howell test, n = 12. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; ns = not significant).
The 2-MIB productivity of cyanobacteria in laboratory cultures at different temperatures has been investigated in various studies. Most studies report that 2-MIB production per microbial unit (MIB mass per Chl-a or cell) increases at higher temperatures after the lag phase or during the logarithmic growth period [15,20,21]. In the culture experiments of Pseudanabaena sp. FACHB 1277 conducted by Zhang et al. [3] across temperatures ranging from 10 °C to 35 °C, the 2-MIB cell quota followed the described pattern, except at 10 °C, where growth was inadequate. Meanwhile, Wang and Li [20] found a negative correlation between biomass abundance and 2-MIB productivity in temperature-controlled cultures. However, some studies conducted under controlled temperature and light intensity found lower 2-MIB productivity quotas in cultures with growth limitations [15,47]. Despite different results, these studies commonly indicated that high temperatures positively affect the unit yield of 2-MIB.
Although many studies have investigated the 2-MIB productivity of cyanobacterial cells, few have focused on the biosynthesis gene quotas. Wang et al. [48] reported values of 10–45 fg/mic copy from Pseudanabaena sp. dqh15 cultures, probably grown at similar temperatures. In our experiments, the average 2-MIB gene quota (fg/mic copy) ranged from 3.3 to 21.8 fg/copy for PD34 and from 0.9 to 6.8 fg/copy for PD35. These findings suggest a wider range of 2-MIB mass per gene among species and strains. However, both strains exhibited a similar increase (approximately seven-fold) in the gene quota at 30 °C than at 15 °C.
These results demonstrate that temperature consistently influences the production yield of 2-MIB in cyanobacteria, regardless of their growth benefits, individual differences, and even the abundance of the 2-MIB synthase gene. In other words, 2-MIB-producing cyanobacteria in the environment can dominate over a wide range of seasons, but their potential to produce 2-MIB may increase at higher water temperatures. To understand odorant patterns in the field, the synthase gene has been quantified along with cyanobacterial cells as a credible indicator for predicting the source and occurrence of odorants [27,38,49,50]. Previous studies have proposed guidelines for managing odor issues based on the copy number of relevant genes in reservoirs [20,51]. However, field data, including within-site and within-species differences in odorant production per cell and genes, make the determination of the threshold level for alternative values difficult [45]. There may be limitations related to differences in dominant odorant-producing species or the presence of mixed species in freshwater. However, this study still suggests the need for seasonal fractionated management and improving criteria at higher temperatures to predict the occurrence of 2-MIB in the field based on genetic or cellular abundance.
3.3. Temperature and Expression Level of the 2-MIB Synthase Gene
RNA gene analysis was conducted to evaluate the effect of temperature stress on 2-MIB biosynthesis in Pseudanabaena at the gene level. mic gene expression was normalized using 16S rRNA as a control gene to determine the expression level. The calculated RNA expression level provides information about the relative transcriptional regulation of the cell in response to external stress on the target gene.
As shown in Figure 2, the 2-MIB yield per cell and the genomic mic gene copy number were proportional to the culture temperature. However, the expression levels of the mic gene exhibited an opposing pattern in both strains. In the PD34 culture, the expression level decreased during the first 3 weeks and then gradually increased (Figure 3a). The expression level was higher at low temperatures and was particularly low at 30 °C. The PD35 strain showed a similar trend, except in week 6, where it had low cell density and 2-MIB concentration (Figure 1b), with expression decreasing as the culture temperature increased from week 3 onwards (Figure 3b). In particular, the gene expression level was higher at 15 °C than at the optimal growth temperature (25 °C) for both strains.
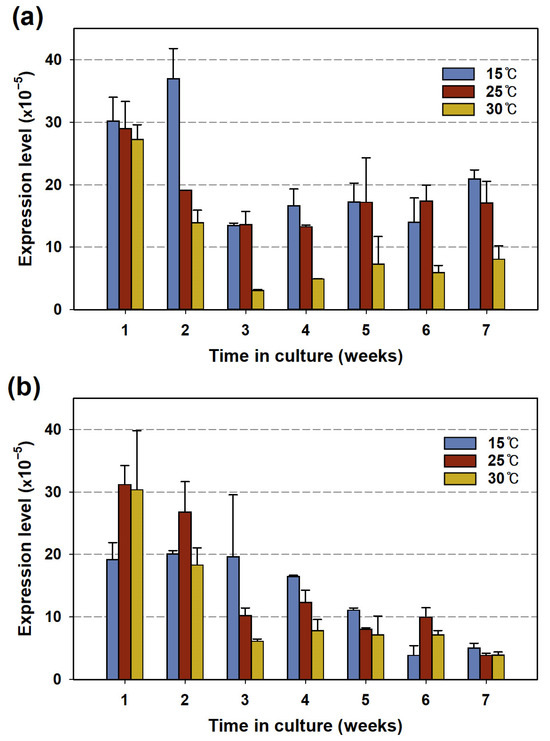
Figure 3.
Expression levels of mic genes normalized by that of 16S rRNA in Pseudanabaena sp. (a) PD34 and (b) PD35 under the three temperatures.
A similar observation was made by Shen et al. [21] in a study on 2-MIB-producing Pseudanabaena foetida var. intermedia NIES-512 based on Chl-a. The expression levels showed varying dominance between the 2-MIB Chl-a quota and cell growth at different temperatures, with the highest expression level at 15 °C, while population growth and MIB per Chl-a were higher at elevated temperatures. Conversely, in another similar study, the expression level of the 2-MIB synthase gene and the biomass of Pseudanabaena galeata NIES-512 were observed to increase at higher temperatures [26]. Additionally, few studies have focused on the expression levels of odorant synthase genes normalized to 16S rRNA levels under controlled environmental conditions such as nitrogen and light intensity [11,29,52]. However, no common patterns were found between gene expression, cell growth, and odorant productivity in these studies. Furthermore, relevant studies for a clear interpretation of the external factors, including temperature, on the cellular regulation of 2-MIB synthesis are currently lacking.
Combining our results, the transcription of the odorant synthase gene appears to have an indistinct correlation with metabolic regulation related to cell proliferation. In other words, it is difficult to consider that growth inhibition due to external stress promotes expression of odorant synthase genes. The actual protein productivity in cells, which is a complex result of internal and external factors, is distinct from the presence of rRNA and RNA transcripts that indicate potential synthesis activity [53].
These results suggest that post-transcriptional processes, such as translational regulation and enzyme kinetics, are more crucial factors in 2-MIB synthesis than the transcription step. In the post-transcriptional steps, the formation of 2-MIB was likely limited at low temperatures. For instance, in terpenoid biosynthesis in cyanobacteria under microbial stress, low temperatures reduce enzyme activity, efficiency of protein folding, and membrane fluidity [54,55]. Therefore, future research should focus on understanding the connection between complex metabolic activities for odorant biosynthesis and temperature stress beyond transcriptional regulation.
3.4. Relationship between Chl-a and 2-MIB Production
Chl-a is a pigment found in certain photosynthetic bacteria and is essential for the growth of cyanobacteria. Cellular Chl-a content can vary depending on environmental stress, and differences exist among strains of the same cyanobacteria species [56,57]. The relationship between temperature conditions and Chl-a concentration in cells remains unclear and shows different trends among taxa [58,59]. Terpenoids, which are secondary metabolites that require GPP, are closely associated with photosynthetic pigments [60,61]. Chl-a has a competitive relationship with 2-MIB or geosmin, sharing a common precursor (GPP or farnesyl diphosphate, FPP) [28]. In our experiment, Chl-a was measured to investigate the relationship between Chl-a and 2-MIB in Pseudanabaena under controlled temperature conditions.
Figure 4 shows the quantitative relationship between Chl-a and 2-MIB synthesized by each strain. The 2-MIB proportion (% MIB/(Chl-a + MIB)) of PD34 was significantly lower at 15 °C (p < 0.01) than at the other two temperatures. For PD35, the 2-MIB% significantly increased (p < 0.05) with higher temperatures. These results suggest that high temperatures promote the 2-MIB synthesis pathway in the metabolic competition between Chl-a and 2-MIB. Some researchers have shown that excessive light conditions reduce Chl-a content [56,62] and instead enhance odorant production [3,63]. Espinosa et al. [63] noted that geosmin, which requires relatively less energy, is synthesized when the need for Chl-a decreases depending on light intensity. However, the influence of temperature on the metabolic relationship between the two products has not been studied extensively. In the present experiments, culture temperature affected the 2-MIB synthesis but was not considered to inhibit Chl-a synthesis; the amount of cellular Chl-a did not decrease at the temperature at which the 2-MIB% increased (Figure 4c).
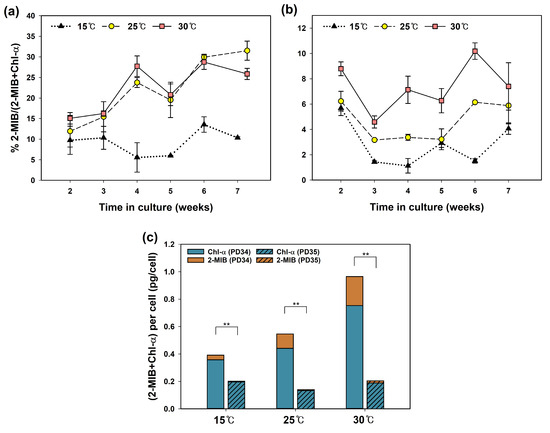
Figure 4.
The effect of temperature on the quantitative relationship between 2-MIB and Chl-a: proportion of 2-MIB (%) synthesized by Pseudanabaena sp. (a) PD34 and (b) PD35, and (c) significant differences between the two strains with regard to the total mass of 2-MIB and Chl-a (independent t-test; ** p < 0.01).
There was a distinct difference in the proportion of Chl-a and 2-MIB between the two strains, with PD35 having less 2-MIB content than PD34. In addition, the total amount of Chl-a and 2-MIB produced per cell differed significantly (p < 0.01) between the two strains (Figure 4c). Previous studies have reported that the carbon flux in competing pathways with pigments and the limitation of the GPP pool are crucial for determining the production of terpenoids [61,64,65]. Therefore, the difference in 2-MIB proportion % between the two strains can be attributed to the greater allocation of carbon flux to the 2-MIB pathway in PD34 than in PD35. From these results, we identified two characteristics of the cultured Pseudanabaena sp. First, the biosynthesis process from the common precursor to 2-MIB was promoted at high temperatures. This supports the fact that high temperatures contribute to the upregulation of 2-MIB through processes other than transcriptional regulation. Second, the difference in 2-MIB production levels between the two strains has been speculated to be due to variations in the GPP pool and resource distribution. These findings suggest that temperature stress significantly impacts the production of 2-MIB in Pseudanabaena from genetic and biochemical perspectives. However, further studies are needed to clearly demonstrate the mechanisms by which high temperatures promote 2-MIB synthesis in other cyanobacterial taxa.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we show the effect of the culture temperature (15, 25, and 30 °C) on 2-MIB productivity and mic gene expression of two strains, Pseudanabaena sp. PD34 and PD35. The 2-MIB production yield per cell and mic gene (in the DNA sample) in both strains increased across temperatures ranging from 15 °C to 30 °C, regardless of their optimal growth. However, the expression level of the mic gene was lowest at 30 °C, suggesting that high temperatures may promote post-transcriptional processes related to the biosynthetic metabolism of 2-MIB. Consistent with this, 2-MIB synthesis was upregulated compared to Chl-a at high temperatures through the quantitative relationship of 2-MIB and Chl-a in metabolic competition. Additionally, there was a distinct difference in the productivity of 2-MIB between the Pseudanabaena strains, although the production patterns and genetic regulation of 2-MIB in the two strains in response to temperature stress were similar. Our findings, which reveal that the characteristics of 2-MIB vary depending on temperature and cyanobacterial strain, provide new insights for managing the complex 2-MIB issues in aquatic resources by utilizing data on the relevant gene and cyanobacteria.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cells13161386/s1, Figure S1: Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences of Pseudanabaena sp. PD34 and PD35 with Pseudanabaena strain information obtained from NCBI. The 16S rRNA sequence of Synechococcus sp. was used as an outgroup taxon. The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method with the maximum composite likelihood model, employing MEGA10 with 1000 bootstrap replications, and bootstrap values (%) are indicated at nodes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-E.L. and J.-H.P.; methodology, R.P., M.-N.Y. and J.-E.L.; software, R.P.; validation, R.P. and M.-N.Y.; formal analysis, R.P. and J.-E.L.; investigation, R.P. and M.-N.Y.; resources, T.K.; data curation, J.-E.L. and J.-H.P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.P.; writing—review and editing, J.-E.L.; visualization, R.P. and J.-H.P.; supervision, J.-E.L.; project administration, J.-E.L. and T.K.; funding acquisition, T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER), funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea (NIER-2023-01-01-114).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Srinivasan, R.; Sorial, G.A. Treatment of taste and odor causing compounds 2-methyl isoborneol and geosmin in drinking water: A critical review. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Wang, M.; Ge, X.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, S.; Jia, R. Highly efficient removal of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol by carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Monatshefte Chem. Chem. Mon. 2014, 145, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Li, L.; Song, L. 2-Methylisoborneol production characteristics of Pseudanabaena sp. FACHB 1277 isolated from Xionghe Reservoir, China. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3353–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, C.J.; Lawton, L.A.; Kaloudis, T. Removal and/or Destruction of Cyanobacterial Taste and Odour Compounds by Conventional and Advanced Oxidation Processes. In Water Treatment for Purification from Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 207–230. [Google Scholar]
- Manganelli, M.; Testai, E.; Tazart, Z.; Scardala, S.; Codd, G.A. Co-occurrence of taste and odor compounds and cyanotoxins in cyanobacterial blooms: Emerging risks to human health? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.B. Aquatic taste and odor: A primary signal of drinking-water integrity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2004, 67, 1779–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.; Yu, M.; Go, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, H. Comparison between ozone and ferrate in oxidising geosmin and 2-MIB in water. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Berlt, M.M.G.; Schneider, R.D.C.D.S.; Machado, Ê.L.; Kist, L.T. Comparative assessment of the degradation of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin in freshwater using advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 3832–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Monis, P.; Baker, P.; Giglio, S. Biochemistry and genetics of taste-and odor-producing cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.S.; Kassim, A.A.; Utsumi, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Goto, M.; Shimizu, K.; Nor, A.O.; Zakaria, Z.; Sugiura, N.; Hara, H. Characterization of musty odor-producing actinomycetes from tropics and effects of temperature on the production of musty odor compounds. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, R. Genes associated with 2-methylisoborneol biosynthesis in cyanobacteria: Isolation, characterization, and expression in response to light. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Kuzuyama, T.; Komatsu, M.; Shin-Ya, K.; Omura, S.; Cane, D.E.; Ikeda, H. Terpene synthases are widely distributed in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Paerl, H.W. Climate Change at a Crossroad for Control of Harmful Algal Blooms; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Żelazna-Wieczorek, J.; Skrobek, I.; Ziułkiewicz, M.; Adamski, M.; Kaminski, A.; Żmudzki, P. Persistent cyanobacteria blooms in artificial water bodies—An effect of environmental conditions or the result of anthropogenic change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Su, M.; Su, Y.; Wu, B.; Cao, T.; Fang, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M. Driving forces for the growth of MIB-producing Planktothricoides raciborskii in a low-latitude reservoir. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.; Majedi, S.M.; Pavagadhi, S.; Te, S.H.; Boo, C.Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Swarup, S. Effects of light and temperature on the metabolic profiling of two habitat-dependent bloom-forming cyanobacteria. Metabolites 2022, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, G.; Taylor, W.D. A Pseudanabaena species from Castaic Lake, California, that produces 2-methylisoborneol. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Yu, M.N.; Yu, S.; Byeon, M. Occurrence and phylogenetic analysis of Pseudanabaena sp. producing 2-methylisoborneol in drinking water source of South Korea. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2022, 14, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Nan, J.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, C. Distribution, driving forces, and risk assessment of 2-MIB and its producer in a drinking water source-oriented shallow lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 71194–71208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, R. Effects of light and temperature on the odor production of 2-methylisoborneol-producing Pseudanabaena sp. and geosmin-producing Anabaena ucrainica (cyanobacteria). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 58, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, H.; Shimada, M.; Utsumi, M.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Nishimura, O.; Asada, Y.; Fujimoto, N. Temperature affects growth, geosmin/2-methylisoborneol production, and gene expression in two cyanobacterial species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12017–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Wan Omar, W.M.; Merican, F.M.M.S.; Azizan, A.A.; Foong, C.P.; Convey, P.; Najimuddin, N.; Smykla, J.; Alias, S.A. Identification and phenotypic plasticity of Pseudanabaena catenata from the Svalbard archipelago. Pol. Polar Res. 2017, 38, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Dong, W. Dominance and growth factors of Pseudanabaena sp. in drinking water source reservoirs, Southern China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizuka, K.; Ikenaga, M.; Murase, J.; Nakayama, N.; Matsuya, N.; Kakino, W.; Taruya, H.; Maie, N. Diversity of 2-MIB-Producing cyanobacteria in Lake Ogawara: Microscopic and molecular ecological approaches. Aquac. Sci. 2020, 68, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Zhu, Y.; Andersen, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Lu, J.; Song, Y.; Cao, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y. Light-dominated selection shaping filamentous cyanobacterial assemblages drives odor problem in a drinking water reservoir. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Miyagi, A.; Saito, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Asaeda, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Uchimiya, H.; Kawai-Yamada, M. Culture temperature affects gene expression and metabolic pathways in the 2-methylisoborneol-producing cyanobacterium Pseudanabaena galeata. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Fang, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Su, M.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Early warning of MIB episode based on gene abundance and expression in drinking water reservoirs. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimba, P.V.; Dionigi, C.P.; Millie, D.F. Evaluating the relationship between photopigment synthesis and 2-methylisoborneol accumulation in cyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Shimizu, K.; Miao, H.; Tsukino, S.; Utsumi, M.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Nishimura, O.; Asada, Y.; Fujimoto, N. Effects of elevated nitrogen on the growth and geosmin productivity of Dolichospermum smithii. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B. Cyanobacterial and eukaryotic algal odour compounds: Signals or by-products? A review of their biological activity. Phycologia 2003, 42, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.; Jüttner, F. Biological production of taste and odour compounds. In Taste and Odour in Source and Drinking Water: Causes, Controls, and Consequences; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; pp. 63–112. [Google Scholar]
- Belcher, H.; Swale, E. Culturing Algae. A Guide for Schools and Colleges; Institute of Terrestrial Ecology: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Suurnäkki, S.; Gomez-Saez, G.V.; Rantala-Ylinen, A.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Sivonen, K. Identification of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in cyanobacteria and molecular detection methods for the producers of these compounds. Water Res. 2015, 68, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong Hwan, B.; Kim, H.N.; Kang, T.G.; Kim, B.-H.; Byeon, M.-S. Study of the cause of the generation of odor compounds (geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol) in the Han River system, the drinking water source, Republic of Korea. Water Supply 2023, 23, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gil, K. Spatial optimization of operating microalgae bioreactor for nitrogen removal and electricity saving. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.L.; Loganathan, N.; Agarwalla, S.; Yang, C.; Yuan, W.; Zeng, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, W.; Duraiswamy, S. Current commercial dPCR platforms: Technology and market review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Park, R.; Yu, M.; Byeon, M.; Kang, T. qPCR-based monitoring of 2-Methylisoborneol/Geosmin-producing cyanobacteria in drinking water reservoirs in South Korea. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.; Ouellette, A.; Boyer, G.; Twiss, M.; Bridgeman, T.; Wilhelm, S. Quantification of toxic Microcystis spp. during the 2003 and 2004 blooms in western Lake Erie using quantitative real-time PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.Y.; Hwang, Y.; Shin, M.H.; Park, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yong, D.; Lee, K. Utility of conventional culture and MALDI-TOF MS for identification of microbial communities in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in comparison with the GS junior next generation sequencing system. Ann. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlburt, B.; Lloyd, S.W.; Grimm, C.C. Comparison of analytical techniques for detection of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.; Helmstetter, C.E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli Br. J. Mol. Biol. 1968, 31, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukenik, A.; Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Welch, J.M.; Post, A.F. Massive multiplication of genome and ribosomes in dormant cells (akinetes) of Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Cyanobacteria). ISME J. 2012, 6, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüttner, F.; Watson, S.B. Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-T.; Yen, H.-K.; Lin, T.-F. An alternative method to quantify 2-MIB producing cyanobacteria in drinking water reservoirs: Method development and field applications. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, L.; Cheng, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Production and release of 2-MIB in Pseudanabaena: Effects of growth phases on cell characteristics and 2-MIB yield. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Su, M.; Liu, T.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Burch, M.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Light as a possible regulator of MIB-producing Planktothrix in source water reservoir, mechanism and in-situ verification. Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Song, G.; Shao, J.; Tan, W.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Establishment and field applications of real-time PCR methods for the quantification of potential MIB-producing cyanobacteria in aquatic systems. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Song, L. The Emergent Integrated Constructed Wetland-Reservoir (CW-R) Is Being Challenged by 2-Methylisoborneol Episode—A Case Study in Yanlonghu CW-R. Water 2022, 14, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Burch, M.; Yang, M. Identification of MIB producers and odor risk assessment using routine data: A case study of an estuary drinking water reservoir. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Burch, M.; Senoro, D.; Lin, T.-F. A molecular-based method to estimate the risk associated with cyanotoxins and odor compounds in drinking water sources. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, S.; Saint, C.P.; Monis, P.T. Expression of the geosmin synthase gene in the cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis AWQC318 1. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazewicz, S.J.; Barnard, R.L.; Daly, R.A.; Firestone, M.K. Evaluating rRNA as an indicator of microbial activity in environmental communities: Limitations and uses. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, D.A.; Murata, N. Membrane fluidity and its roles in the perception of environmental signals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos, M.; Garbeva, P.; Vader, L.; van Wezel, G.P.; Dickschat, J.S.; Ulanova, D. Biosynthesis, evolution and ecology of microbial terpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, R.L.; da Silva, A.P.R.; de Magalhães, V.F. Use of the cell quota and chlorophyll content for normalization of cylindropermopsin produced by two Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains grown under different light intensities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2013, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Li, G.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Tan, Y. The increasing aluminum content affects the growth, cellular chlorophyll a and oxidation stress of cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. WH7803. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2015, 44, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigaud, T.C.S.; Aidar, E. Salinity and temperature effects on the growth and chlorophyll-α content of some planktonic aigae. Bol. Inst. Oceanogr. 1993, 41, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, J.; Dai, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, F. Effect of phosphorus and temperature on chlorophyll a contents and cell sizes of Scenedesmus obliquus and Microcystis aeruginosa. Limnology 2011, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Morgan, R.M.L.; Fraser, P.D.; Hellgardt, K.; Nixon, P.J. Crystal structure of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase (CrtE) involved in cyanobacterial terpenoid biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-C.; Pakrasi, H.B. Engineering cyanobacteria for production of terpenoids. Planta 2019, 249, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.F.; de Wit, R.; Mur, L.R. Interactions between temperature and light intensity on growth and photosynthesis of the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii. J. Plankton Res. 1985, 7, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, C.; Abril, M.; Guasch, H.; Pou, N.; Proia, L.; Ricart, M.; Ordeix, M.; Llenas, L. Water flow and light availability influence on intracellular geosmin production in river biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formighieri, C.; Melis, A. Sustainable heterologous production of terpene hydrocarbons in cyanobacteria. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 130, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-C.; Saha, R.; Zhang, F.; Pakrasi, H.B. Metabolic engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway for enhanced limonene production in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).