Abstract
Natural Killer (NK) cells are innate immune cells that mediate antiviral and antitumor responses. NK cell activation and induction of effector functions are tightly regulated by the integration of activating and inhibitory receptors such as killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR). KIR genes are characterized by a high degree of diversity due to presence or absence, gene copy number and allelic polymorphism. The aim of this study was to establish the distribution of KIR genes and genotypes, to infer the most common haplotypes in an admixed Colombian population and to compare these KIR gene frequencies with some Central and South American populations and worldwide. A total of 161 individuals from Medellin, Colombia were included in the study. Genomic DNA was used for KIR and HLA genotyping. We analyzed only KIR gene-content (presence or absence) based on PCR-SSO. The KIR genotype, most common haplotypes and combinations of KIR and HLA ligands frequencies were estimated according to the presence or absence of KIR and HLA genes. Dendrograms, principal component (PC) analysis and Heatmap analysis based on genetic distance were constructed to compare KIR gene frequencies among Central and South American, worldwide and Amerindian populations. The 16 KIR genes analyzed were distributed in 37 different genotypes and the 7 most frequent KIR inferred haplotypes. Importantly, we found three new genotypes not previously reported in any other ethnic group. Our genetic distance, PC and Heatmap analysis revealed marked differences in the distribution of KIR gene frequencies in the Medellin population compared to worldwide populations. These differences occurred mainly in the activating KIR isoforms, which are more frequent in our population, particularly KIR3DS1. Finally, we observed unique structural patterns of genotypes, which evidences the potential diversity and variability of this gene family in our population, and the need for exhaustive genetic studies to expand our understanding of the KIR gene complex in Colombian populations.
1. Introduction
The killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR, also known as CD158) are a highly polymorphic family of transmembrane glycoproteins expressed on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells [1,2] and a few subsets of CD4 and CD8 T cells as well as γδ T cells [3,4,5]. KIR molecules interact with classical human leukocyte antigens class I (HLA-I) molecules, mainly HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C; and nonclassical class I molecules, particularly HLA-G and HLA-F [6]. KIR-HLA-I interactions regulate NK cell development and activation and are particularly important to control NK cell education, responsiveness and to ensure self-tolerance. Thus, NK cells lacking the specific inhibitory KIR molecule or missing KIR-HLA-I self-interactions are considered uneducated and hyporesponsive [7]. To compensate for this, a large proportion of KIR negative cells express CD94/NKG2A that binds to HLA-E, and NK cell education and response can be mediated by this interaction [8]. Upon maturation, interaction between inhibitory KIR and HLA-I molecules in mature NK cells prevents NK cell activation. In contrast, downregulation of HLA-I upon viral infections, tumor transformation and transplantation favor NK cell activation and allows them to mediate “missing self” recognition of potential target cells [9,10,11].
The KIR nomenclature is determined according to the structure of the molecules: the number of extracellular Ig-like domains (D) and the length of the intracellular tail whether this is long (L) or short (S). Moreover, based on their ability to activate immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activating motif (ITAM)-containing adapter DAP12 or immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIM)-based signaling pathways, KIR are classified as activating or inhibitory respectively [12].
The genes encoding KIR are located on the chromosome 19q13.4, within a 100–200 Kb region of the Leukocyte Receptor Complex (LRC), one of the most variable regions of the human genome in terms of gene content and sequence polymorphisms [13]. Currently, 13 distinct KIR gene loci and two pseudogenes have been described, including KIR2DL1, KIR2DL23, KIR2DL4, KIR2DL5A, KIR2DL5B, KIR2DS1, KIR2DS2, KIR2DS3, KIR2DS4, KIR2DS5, KIR3DL1S1, KIR3DL2, KIR3DL3, KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1 [14]. KIR genes are classified in two functional haplotypes called A and B, each one showing variation in the number and type of KIR genes [15]. Group A or B haplotypes are characterized by the presence of four framework KIR genes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR2DL4 and KIR3DL2) which are present in almost all individuals [16]. Group A haplotypes are generally non-variable in their gene organization, containing the framework genes, inhibitory KIR genes KIR2DL1, KIR2DL3 and KIR3DL1, and the activating gene KIR2DS4. In contrast, Group B haplotypes are characterized by variations in gene content and they can include one or more of the following genes encoding the activating KIR2DS1, KIR2DS2, KIR2DS3, KIR2DS5 and KIR3DS1 and genes encoding the inhibitory KIR2DL5 and KIR2DL2 [17]. Based on this, individuals can be assigned to the A/A (homozygous for A), A/B or B/B genotype. Additionally, each haplotype has a region that exhibits a high relative asymmetric recombination rate, which divides the haplotype into a centromeric (Cen) and telomeric (Tel) region. The centromeric segment corresponds to the region including all genes located between KIR3DL3 and KIR3DP1 and the telomeric segment consists of all genes present between KIR2DL4 and KIR3DL2 [14].
The inhibitory receptors KIR2DL1, KIR2DL2/3, KIR3DL1 and KIR3DL2 are specific for the HLA class I ligands C2, C1, Bw4 and A3/11, respectively. In contrast, KIR2DL4 binds to HLA-G, a non-classical HLA class I molecule. HLA class I ligands for KIR3DL3 and KIR2DL5 are still unknown, nevertheless KIR2DL5 binds to the poliovirus receptor (PVR, CD155) [18,19], and KIR3DL3 binds to HERV–H LTR-associating 2 (HHLA2; also known as B7H5 and B7H7) [20]. Ligands for activating KIR were elusive for many years due to the difficulty to demonstrate KIR/ligand interactions. It is now known that KIR2DS1, KIR2DS2, KIR2DS4 and KIR2DS5 bind specific group 1 and 2 HLA-C molecules, although with lower affinity than the inhibitory KIR. KIR2DS2 and KIR2DS4 also bind HLA-A*11 while KIR3DS1 recognizes HLA-F or HLA-B*51 molecule [6,21].
Combinations of KIR and HLA polymorphisms have been associated with infections, autoimmune diseases, cancers, and pregnancy disorders. For instance, interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-Bw4-I-80 isoform is associated with delayed progression to AIDS and HIV-infection [22]; homozygosity of HLA-C1 and KIR2DL3 is associated with resolution of HCV infection [23]; combination of KIR2DS1 and/or KIR2DS2 with homozygosity of HLA-C1 or -C2 favors susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis [24]; KIR2DS2 combined with HLA-C1 in the absence of HLA-C2 and HLA-Bw4 is associated with increased susceptibility to type I diabetes [25]; HLA–KIR gene combinations that seem to favor NK cell activation are associated with predisposition to human papilloma virus (HPV)-induced cervical cancer [26]; whereas HLA–KIR gene combinations that seem to favor NK cell inhibition have been associated with preeclampsia [27]. Furthermore, expression of specific KIR alleles has been associated with better clinical outcomes in patients receiving hematopoietic cells transplant [28,29]. These findings highlight the contribution of HLA-KIR interaction to the outcome of various diseases and support the importance of including KIR analysis in future cell-based immunotherapies [30,31].
A comprehensive analysis of population-specific genes, genotype and haplotype frequencies of KIR might help to better understand their evolution and role in immunity. Although KIR gene and haplotype profiles have been studied worldwide, KIR diversity has not been extensively characterized in Colombia, a country with a high genetic admixture and combinations of genetic ancestry. At the time of sampling in 2019, KIR genes haplotypes have been only explored in two Colombian populations with very few individuals [32,33]. These studies analyzed different ancestral groups, with different genetic background. Hollenbach et al. investigated patterns of variation in the KIR cluster in 52 populations in the Human Genome Diversity Project—Centre d’Etude du Polymorphisme Human (HGDP-CEPH). They included 110 individuals of 5 Amerindian populations (12 of Colombian Indigenous Piapoco-Curripako). The Amerindian populations did not exhibit high levels of genotypic diversity, but they displayed distinctive patterns unique to the region [32]. Bonilla et al. analyzed KIR genotypes in 119 unrelated individuals of Caucasoid and Afro-descendant populations from the Andean and Pacific region of Colombia, and found 59 different profiles [33].
Interest in the characterization of worldwide KIR diversity is ongoing due to the genetic variation of KIR being the single most important factor that shapes NK cell function. The available data related to KIR in human populations have increased and the discoveries about KIR polymorphism, KIR gene content, and copy number/KIR allelic variation have guided the research into the impact of KIR genetic variation on human health. In Colombian populations, this research has been almost null. The present study aimed to use current knowledge of KIR gene profiles to characterize the distribution of KIR genes, genotypes, and inferred haplotypes in an admixed Colombian population. Furthermore, we performed an extensive comparison of the KIR gene frequencies and genotypes of our population with other populations in our region and worldwide.
Despite being a descriptive study, our results represent one of the first approaches in the genetic variation of KIR research in Colombia, and we encourage future studies to obtain data using next generation technologies, with a greater number of individuals with different genetic background and from different country regions. Expanding our understanding of KIR genetic variation in Colombian populations and their comparison with other regions of the world might be useful for future research on ethnicity-based diseases. Furthermore, the understanding of KIR diversity can allow the identification of KIR and HLA genotypes that influence susceptibility to infectious, autoimmune diseases and the outcome of transplantation in our region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population and Samples
A total of 161 unrelated healthy individuals from Medellin, Colombia were included in the study. Medellin is located in the central region of the Andes Mountains in South America and its population shows a wide admixture contribution from ancestral source populations including European (75%), Native American (18%) and African (7%) descents [34].
We carried out a convenience sampling and we included 161 hematopoietic stem cell donors registered in the Instituto de Cancerologia of the Clinica Las Americas, and the Laboratorio de Trasplantes of the Universidad de Antioquia, between 2004 and 2018. The convenience sampling strategy can be used in situations where time is a constraint, because this method allows quick data collection. It also allows researchers to generate more samples with less or no investment and in a brief period. Another characteristic is that elements are easily accessible and samples are available to the researchers.
Between 2004 and 2018, the Instituto de Cancerologia performed 347 transplants, of which 195 attended the Laboratorio de Trasplantes of the Universidad de Antioquia, to carry out the immunological studies. Of these, 161 donor-recipient pairs had DNA samples in optimal conditions for KIR typing. As part of the pre-transplant studies, donor-recipient pairs were typed for HLA-A, -B, -DRβ, -DQβ and -DQα alleles by PCR-SSP (sequence-specific primers) or PCR-SSO (sequence-specific oligonucleotides). In the particular case of the HLA-C allele, we had performed genotyping only since 2013 by PCR-SSO (88 pairs had not previously been genotyped for the HLA-C allele).
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the local research Ethics Committee of Universidad de Antioquia and Clinica Las Americas, and all the samples used in this study were collected after an informed consent was obtained. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using a modified salting-out procedure as previously reported [35]. DNA was spectrometrically quantified (NanoDrop™ 2000) and the integrity was assessed in a 2% agarose gel with GelRed Nucleic Acid Gel Stain (Biotium, Fremont, CA, USA).
2.2. KIR and HLA Class I Genotyping
Genomic DNA was used for KIR and HLA genotyping. For KIR genotyping, the presence or absence of the genes KIR2DL1-5, KIR2DS1-5, KIR3DL1-3, KIR3DS1, KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1 was determined based on the oligonucleotide probe-hybridization method using the LIFECODES KIR-SSO typing Kit (Immucor, Peachtree Corners, GA, USA). Approximately 50 ng of genomic DNA were used for each PCR reaction and the amplification steps were performed according to the manufacturer instructions. To ensure accuracy in PCR reactions and hybridizations, two different internal controls (designated CON100 and CON200) were used to hybridize KIR3DP1 and KIR3DL3 respectively.
For the HLA genotyping, the HLA-A and -B genes were assessed using CTS-PCR-SSP Tray Kit (low resolution) or LIFECODES HLA-SSO Typing Kits (intermediate-resolution). For HLA-C typing we used SSO methodology. Approximately 100 ng of genomic DNA were used for each PCR reaction. Each kit contained two consensus SSO probes (designated CON200 and CON300) that hybridized to all alleles and acted as internal controls to verify amplification and to confirm that hybridizations occurred. PCR products from both kits were hybridized and measured separately using the Luminex 200™ System. For each KIR- and HLA-SSO typing at least 60 events for each of the Luminex Microspheres were collected.
2.3. KIR Gene, Genotype and Haplotype Frequencies Analysis
KIR gene frequencies were estimated from carrier frequencies obtained by direct counting. We used the Bernstein’s equation GF= 1-√(1-CF), where CF indicates carrier frequencies. For the same data, the confidence interval (IC) was calculated using the formula GF ± ε√(GF(1-GF)/n), where ε corresponds to standard error [36].
KIR genotype frequencies were determined with direct count according to the presence or absence of KIR genes. Genotype IDs for each sample were obtained from the Allele Frequency Net Database (AFND) (http://www.allelefrequencies.net, accessed on 28 July 2022). Genotypes that were not identified in the database were reported here as NPR (not previously reported). KIR haplotype diversity and frequencies were inferred using HAPLO-IHP (Haplotype inference using identified haplotype patterns) software [37]. For the inference of KIR haplotypes, we considered 23 reference haplotypes and patterns of linkage disequilibrium between pairs of KIR genes (Supplementary Table S1) [38]. Several assumptions were made for the analysis: (I) framework genes are always present in each haplotype, (II) if KIR2DL5 is present then KIR2DS3 and/or KIR2DS5 are also present, (III) if KIR2DL2 is present, KIR2DL3 is absent and vice versa, (IV) if KIR2DS4 is present, KIR3DL1 is also present [39]. We used a set of haplotype patterns labeled with the nomenclature described by Vierra-Green et al. [40]. For instance, ‘cA01~tB01 2DS5’ is a full-length haplotype comprised of the first centromeric A region in cis with the first telomeric B region, and this haplotype has the KIR2DS5 gene [41]. We were not able to confidently identify the less common haplotypes, therefore, for the analyzes we only took into account those haplotypes inferred in at least eight individuals.
2.4. HLA–KIR Combinations in Medellin Population
The frequencies of different combinations of KIR and HLA ligands (KIR2DL1 and HLA-C2, KIR2DL2/3 and HLA-C1 [42], KIR3DL1 and HLA-Bw4 [43], KIR3DL2 and HLA-A3/11 [44,45], KIR2DS1 and HLA-C2, KIR2DS2 and HLA-C1 [42] or HLA-A11, KIR3DS1 and HLA-Bw4-80I [6] and KIR2DS4F and HLA-A3/11 [46]) were determined by presence and absence of KIR and HLA genes.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
KIR carrier frequencies of 41 world populations were obtained from AFND and summarized in Supplementary Table S2. We selected the populations if the 16 KIR genes were evaluated in at least 100 individuals. Additionally, we included 14 Amerindian populations, and two Brazilian populations with different ancestry, even though they had not studied the frequency of KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1 genes (Supplementary Tables S2 and S3). Genetic distances were calculated by the Nei’s method using PHYLIP software version 3.698 [47]. Distances among Central and South American and worldwide populations were calculated based on 16 KIR genes (KIR2DL1, KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, KIR2DL4, KIR2DL5, KIR2DS1, KIR2DS2, KIR2DS3, KIR2DS4, KIR2DS5, KIR3DS1, KIR3DL1, KIR3DL2, KIR3DL3, KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1) carrier frequencies. For Amerindians, the distances were calculated based on 14 KIR genes (without KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1). Dendrograms based on genetic distance were constructed by the neighbor-joining (NJ) method, and visualized with MEGA-X software [48]. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed in R version 4.0.3 using KIR carrier frequencies data. In the case of PCA biplots, dots represent PC scores of each population and the arrows represent the loadings of the KIR genes frequencies. Package “pheatmap” (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pheatmap/index.html, accessed on 5 June 2022) based on statistical software R version 4.0.3, R Core Team, Vienna, Austria (https://www.r-project.org/, accessed on 5 June 2022) was used to draw a Heatmap containing Medellin and 14 other Central and South American populations or 41 worldwide populations with 16 KIR genes. Additionally, we drew a Heatmap containing Medellin and 57 other worldwide populations, including 14 Amerindian populations, with 14 KIR genes. The Heatmap is constructed using Hierarchical Clustering algorithm based on Euclidean distance.
3. Results
3.1. KIR Genes and Genotypes Frequencies in a Colombian Population
To characterize the diversity of KIR genotypes in an admixed South American population of Medellin, Colombia, we evaluated the presence or absence of 16 different KIR genes in 161 unrelated healthy individuals. Table 1 shows the frequencies of the tested KIR genes and their distribution in 37 different genotypes arranged according to the number of loci. As expected, the KIR genes KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR2DL4 and KIR3DL2 were present in all individuals. The most frequent genes detected in the Colombian population were: KIR2DP1 (77.7%), KIR2DL1 (77.7%), KIR3DL1 (75.1%), KIR2DS4 (73.9%) and KIR2DL3 (66.6%). The KIR2DS4 gene has two versions: one with the full-length and another with a deletion of 22bp in exon 5. In the Medellin population, KIR2DS4F/KIR2DS4F, KIR2DS4F/KIR2DS4D and KIR2DS4D/KIR2DS4D were present in 39.8%, 32.3% and 21.1% of all individuals (Gene Calculated Frequencies: 22.4%, 17.7% and 11.2% respectively).

Table 1.
KIR gene and genotype frequencies.
In Supplementary Figures S1–S3 the deeper color represented higher observed frequency. We found all KIR genes are present in the Medellin population. Strikingly, we observed that the Medellin population had high frequencies for KIR genes associated to Group B haplotypes, especially KIR3DS1. When Medellin KIR genes frequencies werecompared with Central and South American populations, we observed that the Uruguayan population had similar frequencies in genes of Group B (Supplementary Figure S1). Likewise, in worldwide populations, we observed that Medellin had similarities with Uruguayan, Indian [49] and Bogota populations [33]; where KIR activating genes were predominant (except for KIR2DS3) (Supplementary Figure S2). When Amerindian populations were included in the analysis, we observed that Warao [50], Yucpa [51] and Wichi [52] ethnic groups were clustered with the Colombian, Uruguayan and Indian populations [49,53] (Supplementary Figure S3).
We also characterized different KIR genotypes according to the set of KIR genes present per individual, which were numbered following known patterns of number and combination of genes (http://www.allelefrequencies.net/kir.asp, accessed on 28 July 2022). Genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 14 were the most predominant in our population (63.34% of all individuals). Interestingly, in this study we found three KIR genotypes that have not been previously reported (NPR) for any other ethnic group. The first genotype was characterized by the presence of KIR3DL3, KIR2DL5, KIR3DL1, KIR2DP1, KIR2DL1, KIR3DP1, KIR2DL4, KIR2DS4 and KIR3DL2; in the absence of KIR2DS2, KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, KIR2DS3, KIR3DS1, KIR2DS5 and KIR2DS1 genes. The second genotype had KIR3DL3, KIR2DS2, KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, KIR3DL1, KIR3DP1, KIR2DL4, KIR3DS1, KIR2DS4 and KIR3DL2; in the absence of KIR2DL5, KIR2DS3, KIR2DP1, KIR2DL1, KIR2DS5 and KIR2DS1 genes. The third genotype was characterized by the presence of KIR3DL3, KIR2DS2, KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, KIR2DL5, KIR3DL1, KIR3DP1, KIR2DL4, KIR3DS1, KIR2DS5, KIR2DS1 and KIR3DL2; and the absence of KIR2DS3, KIR2DP1, KIR2DL1 and KIR2DS4 (Table 1).
3.2. Haplotype Frequencies
Based on KIR gene content analysis and using previously well-characterized haplotypes [38,39,40,41], we identified the most common haplotypes in the Medellin population (Table 2). The KIR reference haplotypes explained 92.24% of the haplotype variation in the Colombian population [37,41]. The most frequent haplotypes were: cA01~tA01 (41.6%); cA01~tB01 2DS5 (16.5%); cB02~tB01 (10.9%); cB02~tA01 (9.9%); cA01~tB05 (5.9%); cB01~tA01 2DS3 (5%) and cB01~tB01 2DS3 (2.5%) (Table 2). In 135 individuals (83.85%) both haplotypes could be resolved with the 7 inferred haplotypes, while in 24 individuals (14.91%) only one haplotype could be assigned.

Table 2.
Most frequent KIR inferred haplotypes.
3.3. KIR-HLA Combinations
We also assessed the frequencies of known HLA I alleles identified as ligands of KIR molecules and further identified KIR-ligands sets more prevalent in our population. HLA-C1 and HLA-Bw4 alleles were predominant in our population and the frequency was in both cases above 85%. In contrast, the frequencies of HLA-C2 and HLA-A11/A3 were 58.39 and 22.36%, respectively (Figure 1).
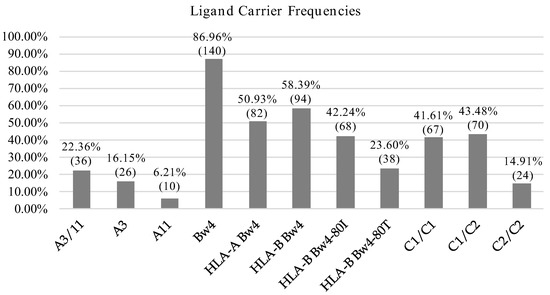
Figure 1.
HLA allotype frequencies. Percentage and number of individuals carrying KIR ligands.
KIR-ligand combinations were defined according to Closa et al. [54] considering the presence of KIR genes and their respective ligands described so far. For KIR2DS4-A3/A11 we only considered full-length variant. The most frequent KIR-ligand pairs were the inhibitory combinations KIR3DL1-Bw4 (81.4%), KIR2DL3-C1 (75.2%) and KIR2DL1-C2 (55.3%). In contrast, activating KIR-ligand pairs were expressed in a lower frequency: KIR2DS4F–A3 A11 (14.3%), KIR3DS1-Bw4-80I (26.7%), KIR2DS2-C1 (44.7%) and KIR2DS1-C2 (36%) (Table 3).

Table 3.
KIR –HLA combinations.
All tested individuals had a least one inhibitory KIR–ligand pair. When we analyzed the presence of more than one pair, the most common combination was KIR2DL2/3-C1 + KIR3DL1-Bw4 (36%), followed by KIR2DL1-C2 + KIR2DL2/3-C1 + KIR3DL1-Bw4 (22.4%) and KIR2DL1-C2 + KIR3DL1-Bw4 (9.3%). Finally, 19 individuals (11.8%) had all inhibitory KIR–ligand pairs evaluated (Table 4).

Table 4.
Inhibitory KIR and HLA ligand pairs.
3.4. Genetic Distance Comparative Analysis with Regional and Worldwide Populations
Next, we compared the diversity of our admixed population from Medellin, Colombia with other populations from Central and South America, including Bogota, Colombia [28]; populations around the word; and Amerindian populations. For this, we performed genetic distances analysis based on the KIR gene carrier frequencies. We analyzed publicly available datasets of 43 populations, including 19 American (n = 3569), 14 Asian (n = 3751), 8 European (n = 2196) and 2 African (n = 285) populations. We also included 14 Amerindian populations (n = 1099).
KIR genes frequencies summarized in Supplementary Tables S2 and S3 were used to construct dendrograms based on a neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm to estimate genetic distances between populations based on their gene frequencies and show these distances in a dendrogram that groups populations presenting similar frequencies. In Central and South American populations, we observed three clusters. The three Mexican populations evaluated clustered together with the Chilean and Venezuelan populations [55,56,57]. In addition, three out of the five Brazilian populations analyzed clustered with the Panamanian population [58,59,60] and the remaining two clustered with the Argentinian population [61]. Interestingly, Uruguayan and Colombian populations did not cluster with other Central and South American populations suggesting differences in the genetic composition of KIR genes (Figure 2). Between Bogota and Medellin populations the KIR gene frequencies variation was approximately 4.5%, while between Uruguayan and Medellin it was approximately 0.75%.
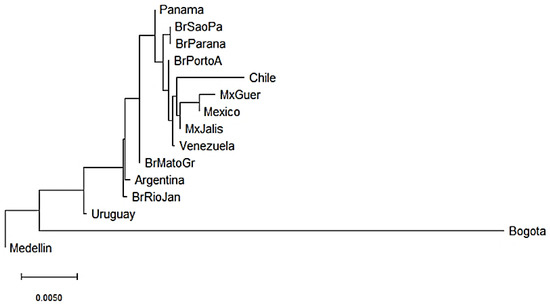
Figure 2.
Neighbor-joining (NJ) dendrogram of Nei’s genetic distances among Central and South American populations, based on the KIR genes frequencies. The NJ dendrogram was constructed with 15 American populations from Brazil (n = 1327), Mexico (n = 544), Argentina (n = 365), Venezuela (n = 205), Panama (n = 116), Chile (n = 90), Uruguay (n = 41), Bogota—Colombia (n = 119) and Medellin—Colombia (n = 161). The bar suggests a 0.005 (0.5%) KIR gene frequencies variation for the length of the scale.
We also constructed a neighbor-joining (NJ) dendrogram to assess potential genetic relationships of the admixed population from Medellin Colombia with 41 worldwide populations (Figure 3). In the dendrogram, we identified four different clusters. A first cluster encompassed the two African populations (South African and Senegal) [62,63], and three Asian populations (Turkey [64], Iran [65] and Saudi Arabia). The European and American populations were combined in two further different clusters. The second cluster grouped French, Italian, Irish, Mexican, Brazilian, North American and Thai populations [55,58,60,63,66,67,68,69]. The third cluster included Brazilian, Argentine, English, Panamanian, Venezuelan, Spanish, Chilean, North American and Mexican populations [55,56,57,61,67,70]. Finally, the fourth cluster included seven of the 14 Asian populations, mainly Chinese populations [71,72,73,74,75,76]. Interestingly, of the two Colombian populations, the Bogota group showed a KIR composition similar to the Indian populations [49,53]. Surprisingly, the Medellin population clustered alone suggesting a particular KIR composition in this population (Figure 3).
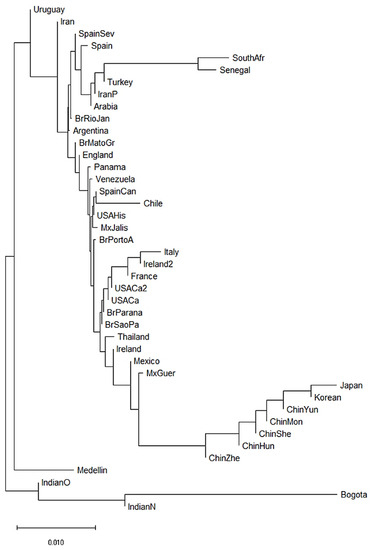
Figure 3.
Neighbor-joining (NJ) dendrogram of Nei´s genetic distances among worldwide populations, based on the KIR genes frequencies. The NJ dendrogram was constructed with 42 populations from China (n = 1788), Brazil (n = 1327), Spain (n = 847), India (n = 673), England (n = 584), United States (n = 578), Mexico (n = 544), Iran (n = 448), Ireland (n = 440), Argentina (n = 365), Thailand (n = 235), Italy (n = 237), Venezuela (n = 205), South Africa (n = 167), Arabia (n = 162), South Korea (n = 159), Turkey (n = 154), Japan (n = 132), Senegal (n = 118), Panama (n = 116), France (n = 108), Chile (n = 90), Uruguay (n = 41), Bogota—Colombia (n = 119) and Medellin—Colombia (n = 161). The bar suggests a 0.01 (10%) KIR gene frequencies variation for the length of the scale.
Finally, we constructed three NJ dendrograms to assess potential genetic relationships of the admixed population from Medellin Colombia with Amerindian populations (Supplementary Figures S4–S6). In Supplementary Figure S4 we analyzed genetic distances among Colombian and Amerindian populations, and we identified two different clusters. The first cluster encompassed the Colombian populations with Venezuelan [50,51], Mexican [77] and Argentinean [52] ethnic groups. The second cluster grouped Brazilian and Paraguay Amerindian populations [78]. Interestingly, the Bogota group showed similar KIR frequencies to the Yucpa tribe from Venezuela [51], while the Medellin population clustered together Warao and Wichi tribes [50,52]. Supplementary Figure S5 shows genetic distances among admixed Central and South American and Amerindian populations, where we observed that the previous clustering patterns hold. Likewise, in Supplementary Figure S6 we note that Bogota–Yucpa and Medellin–Warao distances remained when genetic distances among worldwide and Amerindian populations were evaluated. As we observed in Figure 3, the Lucknow population from India [49], had similar KIR frequencies to the Bogota and Yucpa populations.
We used a different approach to evaluate differences between the populations using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) based on the frequencies of the 16 KIR genes. This method converts the KIR genes frequencies into a set of values of linearly uncorrelated variables (principal components). On the PCA for Central and South America (Figure 4), Colombian populations clustered separately from the other 13 populations. This distribution is mainly driven by differences in two specific KIR: KIR3DS1 and KIR2DL3. We found that Medellin exhibited the highest frequency of KIR3DS1 (0.741), and this population was positively associated with the variable KIR3DS1. KIR3DS1 frequency was the major contributor to the variability in the Medellin population in relation to Central and South American populations.
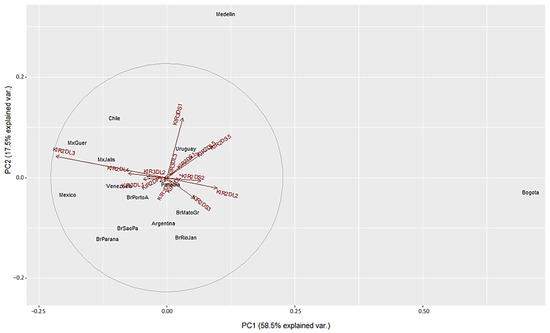
Figure 4.
Principal component analysis based on 16 KIR genes for Central and South American populations. The circle indicates the correlation between KIR gene frequencies. Red arrows show the relative contribution of each KIR gene frequency to the variability along the first two axes (PC1 and PC2). PC1 was strongly correlated with KIR2DL3 and KIR2DL2 genes and PC2 was strongly correlated with KIR3DS1 gene.
On the other hand, the Bogota population had the lowest KIR2DL3 frequency (0.31), and this population was associated negatively with the variable KIR2DL3 (Figure 4 and Supplementary Table S2). Unlike the NJ analysis, PCA analysis did not show other particular clustering between the Central and South American populations analyzed.
We next performed PCA analysis with the worldwide populations. Despite the marked differences in the NJ analysis, most of the worldwide populations did not show a clear grouping in the PCA with only twelve showing differential clustering. Seven out of the 14 Asian population clustered together in the right side of the biplot according to their highest KIR2DL3 frequencies. Two Africans populations grouped in upper center according to the lowest KIR3DS1 frequencies. Bogota clustered with Indian populations in the lower left side. In contrast, Medellin population showed genetic distance from the other populations evaluated, and this result can be explained by the highest KIR3DS1 frequency observed in this population (Figure 5). These results are in concordance with the dendrograms previously described.
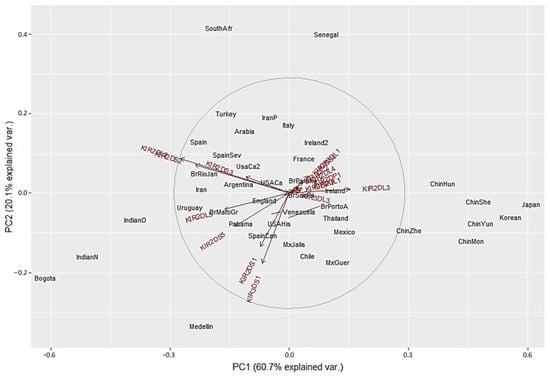
Figure 5.
Principal component analysis for worldwide populations. The circle indicates the correlation between KIR gene frequencies. Red arrows show the relative contribution of each KIR gene frequency to the variability along the first two axes (PC1 and PC2). PC1 was strongly correlated with KIR2DL3 and KIR2DL2 genes and PC2 was strongly correlated with KIR3DS1 gene.
Finally, we performed PCA analysis with the Amerindian populations (Supplementary Figures S7–S9) based on the frequencies of the 14 KIR genes. As observed in Supplementary Figure S4, Colombian populations clustered with Venezuelan and Argentinean ethnic groups. This distribution is mainly driven by differences in six KIR: KIR2DL2 and KIR2DS2; and KIR2DL5, KIR2DS5, KIR2DS1 and KIR3DS1. We found that Medellin exhibited higher frequencies of KIR3DS1 (0.741), KIR2DL5 (0.689), KIR2DS1 (0.596) and KIR2DS5 (0.571) and these frequencies were similar to Warao and Wichi populations. On the other hand, Bogota population had higher KIR2DL2 (0.68) and KIR2DS2 (0.58) frequencies, and these were similar to Yucpa tribe (Figure S7 and Supplementary Table S2). Supplementary Figure S9 shows PCA among worldwide and Amerindian populations and we observed that clustering remained according to the six KIR genes frequencies.
4. Discussion
Our study is the first to analyze the distribution of KIR genes, genotypes and haplotype combinations in an admixed population from Medellin, Colombia. We identified gene and genotypic variations with unique structural patterns that contributed to marked differences in KIR gene frequencies between our population and others from Central and South America, worldwide and Amerindians.
The most common KIR genes in the admixed population from Medellin, Colombia included KIR2DL1, KIR3DL1, KIR2DS4 and KIR2DL3, which correlates with the most common KIR genes reported in diverse populations across the world. Other KIR genes, namely KIR2DS2, KIR2DL2, KIR2DS5, KIR2DS1 and KIR2DL5 were frequent in our population compared to reports from Uruguay, Indian and Amerindian populations and comparable to those observed in Central and South American populations [50,55,56,77,79,80,81,82,83].
In the Medellin population, the KIR2DS3 gene was found in 10.5% of individuals, and the KIR2DS1 and KIR2DS5 genes in 36.5% and 34.5% respectively. Our data are in agreement with the results from Bonilla et al., who reported similar frequencies of the KIR2DS3, KIR2DS1 and KIR2DS5 genes in individuals from the Andean and Pacific region [33]. However, the frequencies of these KIR genes are different from those described in four American populations reported by Hollenbach et al. [32]. In particular, in the Piapoco-Curripako population (the Colombian indigenous group), the KIR2DS3 gene was completely absent. Gendzekhadze et al. also observed that the KIR2DS3 gene was not present in the Yucpa population from Venezuela [51]. KIR2DS5 and KIR2DS3 genes are located at the same locus, which is duplicated in the centromeric and telomeric motifs of the Bx haplotypes. Worldwide, in centromeric motifs, the KIR2DS3 gene occurs more frequently than the KIR2DS5 gene, while in Amerindian populations a fixation of the KIR2DS5 allele was evidenced [32,50]. These differences may be due to genetic isolation of these populations, in addition to the limited number of individuals studied (n = 12 and 61 respectively).
Our results of KIR gene frequencies show a genetic organization in the Medellin population where the activating KIR are dominant compared to the inhibitory KIR isoforms (Table 1 and Supplementary Figures S1–S3). The low frequencies of the KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, KIR2DL1, KIR3DL1 and KIR2DS4 genes are in agreement with the low frequencies of haplotype A in our population (13% haplotype A and 87% of haplotype B). These percentages are similar to other populations in Central and South America, where there is a predominance of Bx haplotypes [50,55,56,77,79,80,81,82,83]. Comparative analyses of KIR haplotypes by the Rajalingam group found an association between patterns of human prehistoric migration and the distribution of KIR haplotypes in different human populations [84]. Based on the distribution of KIR A and B haplotypes, the Rajalingam group divided the populations into three groups: populations carrying dominant A haplotypes (Asian populations), populations carrying dominant B haplotypes (American and Australian populations), and populations carrying balanced A and B haplotypes (European populations). A significant finding to emerge from this investigation is the clear dominance of KIR B haplotypes in the Medellin population, which coincides with Rajalingam patterns.
KIR diversity among different populations and ethnicities has been attributed to variations in genotype and haplotype frequencies. Additionally, polymorphisms in KIR genes, variations in gene content and gene copy numbers of each KIR haplotype also contribute to diversity in KIR expression [85]. There is a set of genotypes and haplotypes that typically explains up to 90% of the variations observed worldwide, even in geographically distant populations [37,86]. However, extensive variation in genotypes and haplotypes as well as virtual absence of the most common genotypes in some populations denotes the plasticity and high degree of variation in the gene content of the human KIR cluster [32].
Interestingly, we found three KIR genotypes that have not been previously described in the literature (Table 1). Among the new genotypes, NPR1 had nine KIR genes, which is partially similar to the genotype described for Arnheim et al. [87] in a Swedish population. However, in their study, they did not confirm the presence of the KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1 genes. NPR2 genotype had ten KIR genes and was found to be similar to the genotype described in an individual from the Cook Islands [88], but unlike our data, the KIR2DP1 gene was present. Finally, the gene composition pattern of NPR3 genotype did not show similarities with any other genotypes described to date. These results support the idea that in Central and South American populations, the genotypic diversity is not high, but there are unique patterns found in the region.
In relation to haplotype frequencies in South American populations, previous works have shown a limited number of KIR gene content haplotypes in Amerindians populations (the estimated KIR gene-content haplotypes are shown in Supplementary Table S4). Taken together, these results validate our inferred haplotypes with the HAPLO-IHP software (the three most common haplotypes in our population were observed in Amerindian populations of Central and South America). However, family segregation studies or long-range sequencing are needed to identify unknown haplotype structures or to precisely infer those haplotypes observed in lower frequencies. For example, de Brito Vargas et al. [78] identified haplotypes carrying large structural deletions or duplications involving multiple loci. Moreover, the low-frequency haplotypes are usually variations of the most common ones, differing by only a few alleles in some specific genes (allelic variation on KIR3DL3 and KIR3DL1 genes on centromeric and telomeric haplotypes respectively).
In relation to studies on KIR haplotypes, two important points are worth noting. First, in Amerindians populations have demonstrated a reduced KIR allelic richness compared with worldwide populations [50,51,78]. It must be taken into account that, at the allelic level, there may be low KIR diversity in our population. Second, our study population could exhibit an overall great population differentiation. The admixture and genetic heterogeneity are possibly resulting from different migration processes from other continents (e.g., during the Spanish colonization) and within the country, suggested by the results of our genetic distance analysis. Indeed, Conley et al. [89] used a dataset of 239,989 SNP in a comparative analysis of two Colombian populations (Chocó and Medellin), and they demonstrated that the Medellin population (n = 94) showed admixture events, with European–Native American admixture followed by subsequent African admixture. Additionally, the analysis of subcontinental ancestries in the study of Conley et al. [89] revealed that the African ancestry of Medellin was intermediate between Nigerian and other West African populations; the European fraction of Medellin was similar to the Spanish population; and Native America ancestry showed that the Medellin population grouped together with the Colombian Native American populations: Embera, Waunana, Arhuaco, Kogi and Wayuu. These findings underline a similar ancestral source population (in particular Native American Ancestry), with different relative frequencies of African and European ancestors, and these differences could explain variations in KIR gene frequencies among Colombian populations [89].
The analysis of several KIR-HLA combinations revealed that inhibitory combinations were the most frequent in the Medellin population. All the individuals in the Medellin population had at least one KIR-HLA pair, and 83.23% have two or three inhibitory KIR-HLA combinations. KIR3DL1/Bw4 pair was present in 131 individuals in our cohort (81.4%). This frequency is above the worldwide frequencies, in contrast to e.g., American cohorts, in which about 29.4% (Veracruz—Mexico) to 68.6% (Havana, Cuba) of the individuals have the KIR3DL1/Bw4 pair (http://www.allelefrequencies.net/KIR-HLA/stats.asp, accessed on 28 July 2022). KIR3DL1/Bw4 (HLA-A) and KIR3DL1/Bw4 (HLA-B) were present in 48.5% and 53.4% individuals respectively. These frequencies are higher than those observed in Amerindian populations, among which Guarani Ñandeva and Kaingang from Ivaí have the highest frequencies (5% and 13% for KIR3DL1/Bw4 (HLA-A) and KIR3DL1/Bw4 (HLA-B) respectively) [78]. KIR2DL3/C1 pair was the second most common inhibitory combination (75.2%). This frequency is similar to that observed in worldwide populations, where the lowest values reported are 40% in Xhosa ethnic group from South Africa [90], and 41% in Kaiowá and Mbya Guaraní populations [78], while the highest values reported are 92% and 95.7% in Hong Kong and Singapore populations [91]. KIR2DL1/C2 was observed in 55.3%, similar to the frequencies observed in Central and South American populations (lowest: 39.4% in Curitiba, Brazil individuals [92]; highest: 76.7% in Belo Horizonte, Brazil individuals). In Amerindians, the KIR2DL1/C2 frequencies are lower, ranging from 6% in Guarani Mbya to 26% in Aché from Paraguay [78]. Finally, the KIR2DL2/C1 frequency in our population was 44.7%. In Central and South American populations these frequencies range from 23.5% in Curitiba [92] to 61% in Montevideo, Uruguay (http://www.allelefrequencies.net/KIR-HLA/stats.asp, accessed on 28 July 2022). Furthermore, KIR2DL2 and KIR2DL3 exhibit capability to bind HLA-C C2 allotype [93], although with low affinity. KIR2DL2/C2 and KIR3DL2/C2 frequencies were 29.8% and 50.9% respectively (data not shown).
Our genetic distance and PCA data presented in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 confirmed that KIR gene frequencies in our South American population are different compared with worldwide populations. Particularly in PCA, the first principal component (PC1) identified strongly correlated with KIR2DL3 and KIR2DL2 genes whereas the PC2 strongly correlated with KIR3DS1 gene. Medellin population showed genetic distance from the other populations in both PCA biplots and these differences may be explained by the highest frequency of KIR3DS1 gene (71.4%) when compared to the others populations (Supplementary Table S2). KIR3DS1 represents the only activating receptor with three extracellular domains and several studies have identified this gene to be associated with the outcome of various diseases, including viral infection like HIV-1 (slower progression to AIDS and lower viral load in individuals carrying KIR3DS1 and HLA-B Bw4 I80) [22], HBV (increased rate of spontaneous recovery) [94] and HCV (viral clearance and sustained virological response) [95]. Moreover, KIR3DS1 expression is associated with several malignancies including hepatocellular carcinoma, Hodgkin´s lymphoma and respiratory papillomatosis (reduced risk) [96] or cervical neoplasia (increased risk) [26].
Finally, with regard to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), Gabriel et al. [97] showed a decreased progression-free survival of patients carrying KIR3DS1 with multiple myeloma after autologous transplantation. In contrast, a beneficial effect of KIR3DS1 in the context of unrelated HSCT has also been observed, showing a decreased acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) from transplantation with KIR3DS1+ donors [98]. Due to the high frequency of KIR3DS1 in the Medellin population, it would be important to evaluate its association with the previously listed diseases. In fact, in the context of identical related HSCT, we found that transplant patients whose donors were KIR2DS1+ and KIR3DS1+ had a 92% and 97% lower risk of acute GVHD respectively (unpublished data).
Using KIR as the panel of genetic marker, the results showed that Medellin had a close relationship with the Warao and Wichi ethnic groups, and we found three to five activating KIR and one to two inhibitory KIR genes of group B haplotype (KIR2DL5, KIR2DS5, KIR2DS1 and KIR3DS1) were responsible for it. In previous studies, it has been argued that group B haplotypes may be under strong diversifying selection processes, related to several factors including reproduction, unfavorable genes that carry risk of autoimmunity or the creation or loss of novel functional genes to infection responses [86]. These processes ensure that the large majority of individuals within a population have different KIR genotypes, a situation analogous to that seen for HLA, and this diversity in human KIR genotype is probably the result of natural selection [54,99].
Our study has several limitations. First, we carried out a convenience sampling, so the results could not be generalized to a larger population. The Medellin population is highly mixed and potential bias of the sampling technique exists due to under-representation of subgroups in the sample. Second, genotyping methods used based on SSP and SSOP are prone to errors. HLA-SSP genotyping depends on the quality and quantity of the DNA used, therefore, PCR amplification failure could lead to a failure in typification result. Meanwhile, SSO genotyping depends on the hybridization process, and therefore, low bead count or low median fluorescent intensity value can lead to typing misunderstanding. Additionally, these methods cannot identify new alleles and allelic diversity, so there may be a deviation in the results on the genotypic and haplotypic diversity. Third, for NJ and PCA analyses, we included studies with heterogeneous methodologies and these may contain inaccurate data. Moreover, internal nodes of a dendrogram based on genetic distances do not necessarily represent common ancestry, and the similarities and differences between populations can be consequences of demographic factors. Despite these limitations this represents the first study to examine KIR diversity in an admixed Medellin—Colombian population. However, these findings will require validation in larger, multicenter datasets, with stratified random sampling and high-resolution genotyping technologies.
5. Conclusions
We report, for the first time, an analysis of KIR genotypes; observed carrier frequency; estimated genetic frequency and inferred haplotype patterns in an admixed Medellin—Colombian population. In particular, estimation of haplotype frequencies and KIR-HLA combinations as well as genetic distance and principal component analysis (PCA) with several population groups from Central and South America, worldwide and Amerindian populations revealed distinct patterns of KIR genes and haplotypes in this population. Currently, efforts have been made to understand NK cell function and diversity through genetic studies and their association with disease susceptibility. Our findings on KIR genetic diversity and frequencies of KIR-HLA pairs in the Medellin population are likely to shed light on the formation of KIR repertoires and the potential implications in processes of NK cell education and function, and their impact in immune response against viral infections, anti-tumor response or transplant outcomes, however these associations remain unexplored in Colombia.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cells11182776/s1, Table S1. Reference haplotypes. Supplementary Table S2. Worldwide KIR gene frequencies. Table S3. Amerindians KIR gene frequencies. Table S4. The most common estimated KIR haplotypes in Amerindians. Figure S1. Heatmap for KIR gene frequencies from South and Central American populations. Figure S2. Heatmap for KIR gene frequencies from worldwide populations. Figure S3. Heatmap for KIR gene frequencies from worldwide populations, including Amerindians. Figure S4. Neighbor-joining (NJ) dendrogram of Nei´s genetic distances among Amerindian populations, based on the KIR genes frequencies. Figure S5. Neighbor-joining (NJ) dendrogram of Nei´s genetic distances among Amerindian, Central and South American populations, based on the KIR genes frequencies. Figure S6. Neighbor-joining (NJ) dendrogram of Nei´s genetic distances among worldwide populations, based on the KIR genes frequencies. Figure S7. Principal component analysis based on 14 KIR genes for Amerindian populations. Figure S8. Principal component analysis based on 14 KIR genes for Amerindian, Central and South American populations. Figure S9. Principal component analysis based on 14 KIR genes for worldwide populations, including Amerindians. Reference [100] is referred to in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.D.M., S.Y.V. and C.M.A.; Methodology, M.C. and A.J.K.-U.; Software, M.C.; Validation, M.C.; Formal analysis, M.C. and C.M.A.; Writing—original draft preparation, M.C.; Writing—review and editing, N.D.M., S.Y.V. and C.M.A.; Visualization, M.C.; Supervision, C.M.A.; Project administration, C.M.A.; Funding acquisition, N.D.M. and S.Y.V.; Co-Senior Authorship, S.Y.V. and C.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Convocatoria Programática Ciencias de la Salud—2015. Comité para el Desarrollo de la Investigación, CODI—Universidad de Antioquia (U-de-A), Medellín 050010, Colombia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Instituto de Investigaciones Médicas—Universidad de Antioquia (U-de-A), Medellín 050010, Colombia (certificate of approval No. 015—11 October 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
We thank Angelica M. Cardona from Instituto de Cancerología Las Américas for help in database organization. We are also grateful to Mabel C. Giraldo, Cesar A. Buitrago and Juan J. Serrano from Universidad de Antioquia, for excellent technical assistance with Luminex assays; and greatly acknowledge to Instituto de Cancerología Las Américas for institutional support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Valiante, N.M.; Lienert, K.; Shilling, H.G.; Smits, B.J.; Parham, P. Killer cell receptors: Keeping pace with MHC class I evolution. Immunol. Rev. 1997, 155, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilches, C.; Parham, P. KIR: Diverse, rapidly evolving receptors of innate and adaptive immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 217–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bergen, J.; Thompson, A.; van der Slik, A.; Ottenhoff, T.H.; Gussekloo, J.; Koning, F. Phenotypic and functional characterization of CD4 T cells expressing killer Ig-like receptors. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6719–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingari, M.C.; Ponte, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Schiavetti, F.; Bertone, S.; Bellomo, R.; Cappai, A.T.; Biassoni, R. HLA-class I-specific inhibitory receptors in human cytolytic T lymphocytes: Molecular characterization, distribution in lymphoid tissues and co-expression by individual T cells. Int. Immunol. 1997, 9, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Libero, G. Control of gammadelta T cells by NK receptors. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Munari, E.; Bertaina, A.; Moretta, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Pietra, G.; et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 28, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, P.; Brodin, P. Current perspectives of natural killer cell education by MHC class I molecules. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.; Djaoud, Z.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Blokhuis, J.; Hilton, H.G.; Béziat, V.; Malmberg, K.J.; Norman, P.J.; Guethlein, L.A.; Parham, P. Class I HLA haplotypes form two schools that educate NK cells in different ways. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 3, eaag1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, L.; Locatelli, F.; Pende, D.; Sivori, S.; Falco, M.; Bottino, C.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, A. Human NK receptors: From the molecules to the therapy of high risk leukemias. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Baratin, M.; Walzer, T.; Ugolini, S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L. Up on the tightrope: Natural killer cell activation and inhibition. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.S.; Purdy, A.K. Structure/function of human killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors: Lessons from polymorphisms, evolution, crystal structures and mutations. Immunology 2011, 132, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, H.; Colonna, M.; Ziegler, A.; Volz, A. Organization of the leukocyte receptor cluster (LRC) on human chromosome 19q13.4. Mamm. Genome. 1999, 10, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, D.; Gonzelez, F. The extensive polymorphism of KIR genes. Immunology 2010, 129, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhrberg, M.; Valiante, N.M.; Shum, B.P.; Shilling, H.G.; Lienert-Weidenbach, K.; Corliss, B.; Tyan, D.; Lanier, L.L.; Parham, P. Human diversity in killer cell inhibitory receptor genes. Immunity 1997, 7, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Chida, S.; Geraghty, D.E.; Dupont, B. The killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genomic region: Gene-order, haplotypes and allelic polymorphism. Immunol. Rev. 2002, 190, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béziat, V.; Hilton, H.G.; Norman, P.J.; Traherne, J.A. Deciphering the killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor system at super-resolution for natural killer and T-cell biology. Immunology 2017, 150, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, B.; Ramani, S.R.; Chiang, E.; Lehoux, I.; Paduchuri, S.; Arena, T.A.; Patel, A.; Wilson, B.; Chan, P.; Franke, Y.; et al. A Platform for Extracellular Interactome Discovery Identifies Novel Functional Binding Partners for the Immune Receptors B7-H3/CD276 and PVR/CD155. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 11, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittje, P.; Hœlzemer, A.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Vollmers, S.; Niehrs, A.; Hagemann, K.; Martrus, G.; Körner, C.; Kirchhoff, F.; Sauter, D.; et al. HIV-1 Nef-mediated downregulation of CD155 results in viral restriction by KIR2DL5+ NK cells. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.S.; Berjis, A.; Konge, J.C.; Mahoney, K.M.; Klee, A.N.; Freeman, S.S.; Chen, C.H.; Jegede, O.A.; Catalano, P.J.; Pignon, J.C.; et al. KIR3DL3 Is an Inhibitory Receptor for HHLA2 that Mediates an Alternative Immunoinhibitory Pathway to PD1. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Hölzemer, A.; Martrus, G.; Chung, A.W.; Pacheco, Y.; Simoneau, C.R.; Rucevic, M.; Lamothe-Molina, P.A.; Pertel, T.; Kim, T.E.; et al. Open conformers of HLA-F are high-affinity ligands of the activating NK-cell receptor KIR3DS1. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.P.; Gao, X.; Lee, J.H.; Nelson, G.W.; Detels, R.; Goedert, J.J.; Buchbinder, S.; Hoots, K.; Vlahov, D.; Trowsdale, J.; et al. Epistatic interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-B delays the progression to AIDS. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakoo, S.I.; Thio, C.L.; Martin, M.P.; Brooks, C.R.; Gao, X.; Astemborski, J.; Cheng, J.; Goedert, J.J.; Vlahov, D.; Hilgartner, M.; et al. HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science 2004, 305, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, G.W.; Martin, M.P.; Gladman, D.; Wade, J.; Trowsdale, J.; Carrington, M. Cutting edge: Heterozygote advantage in autoimmune disease: Hierarchy of protection/susceptibility conferred by HLA and killer Ig-like receptor combinations in psoriatic arthritis. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4273–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Slik, A.R.; Koeleman, B.P.; Verduijn, W.; Bruining, G.J.; Roep, B.O.; Giphart, M.J. KIR in type 1 diabetes: Disparate distribution of activating and inhibitory natural killer cell receptors in patients versus HLA-matched control subjects. Diabetes. 2003, 52, 2639–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, M.; Wang, S.; Martin, M.P.; Gao, X.; Schiffman, M.; Cheng, J.; Herrero, R.; Rodriguez, A.C.; Kurman, R.; Mortel, R.; et al. Hierarchy of resistance to cervical neoplasia mediated by combinations of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor and human leukocyte antigen loci. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiby, S.E.; Walker, J.J.; O’shaughnessy, K.M.; Redman, C.W.; Carrington, M.; Trowsdale, J.; Moffett, A. Combinations of maternal KIR and fetal HLA-C genes influence the risk of preeclampsia and reproductive success. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, T.; Marin, D.; Cao, K.; Li, L.; Mehta, P.; Shaim, H.; Sobieski, C.; Jones, R.; Oran, B.; Hosing, C.; et al. Specific combinations of donor and recipient KIR-HLA genotypes predict for large differences in outcome after cord blood transplantation. Blood 2016, 128, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Losada, C.; Martín, C.; Gonzalez, R.; Manzanares, B.; García-Torres, E.; Herrera, C. Patients Lacking a KIR-Ligand of HLA Group C1 or C2 Have a Better Outcome after Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 13, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solloch, U.V.; Schefzyk, D.; Schäfer, G.; Massalski, C.; Kohler, M.; Pruschke, J.; Heidl, A.; Schetelig, J.; Schmidt, A.H.; Lange, V.; et al. Estimation of German KIR Allele Group Haplotype Frequencies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.H.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.A.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.M. NK Cell-Based Immunotherapies in Cancer. Immune. Netw. 2020, 9, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenbach, J.A.; Nocedal, I.; Ladner, M.B.; Single, R.M.; Trachtenberg, E.A. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene content variation in the HGDP-CEPH populations. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, C.; Yunis, E.J.; Yunis, J.J. Diversity of KIR profiles in Colombian populations. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ASHI Meeting Abstracts 2010, Hollywood, FL, USA, 26–30 September 2009; p. S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishishwar, L.; Conley, A.B.; Wigington, C.H.; Wang, L.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A.; Jordan, I.K. Ancestry, admixture and fitness in Colombian genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, H.; Forouzandeh, M.; Rasaee, M.J.; Rahbarizadeh, F. Modified salting-out method: High-yield, high-quality genomic DNA extraction from whole blood using laundry detergent. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2005, 19, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, S.J.; Gourraud, P.A.; Single, R.M.; Thomson, G.; Hollenbach, J.A. Analytical methods for immunogenetic population data. In Immunogenetics: Methods and Applications in Clinical Practice; Christiansen, F.T., Tait, B.D., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.J.; Tang, J.; Kaslow, R.A.; Zhang, K. Haplotype inference for present-absent genotype data using previously identified haplotypes and haplotype patterns. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pyo, C.W.; Guethlein, L.A.; Vu, Q.; Wang, R.; Abi-Rached, L.; Norman, P.J.; Marsh, S.G.; Miller, J.S.; Parham, P.; Geraghty, D.E. Different patterns of evolution in the centromeric and telomeric regions of group A and B haplotypes of the human killer cell Ig-like receptor locus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourraud, P.A.; Meenagh, A.; Cambon-Thomsen, A.; Middleton, D. Linkage disequilibrium organization of the human KIR superlocus: Implications for KIR data analyses. Immunogenetics 2010, 62, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierra-Green, C.; Roe, D.; Hou, L.; Hurley, C.K.; Rajalingam, R.; Reed, E.; Lebedeva, T.; Yu, N.; Stewart, M.; Noreen, H.; et al. Allele-level haplotype frequencies and pairwise linkage disequilibrium for 14 KIR loci in 506 European-American individuals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierra-Green, C.; Roe, D.; Jayaraman, J.; Trowsdale, J.; Traherne, J.; Kuang, R.; Spellman, S.; Maiers, M. Estimating KIR Haplotype Frequencies on a Cohort of 10,000 Individuals: A Comprehensive Study on Population Variations, Typing Resolutions, and Reference Haplotypes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, H.G.; Guethlein, L.A.; Goyos, A.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Bushnell, D.A.; Norman, P.J.; Parham, P. Polymorphic HLA-C Receptors Balance the Functional Characteristics of KIR Haplotypes. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3160–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, B.A.; De Santis, D.; Van Beelen, E.; Lathbury, L.J.; Christiansen, F.T.; Witt, C.S. The reactivity of Bw4+ HLA-B and HLA-A alleles with KIR3DL1: Implications for patient and donor suitability for haploidentical stem cell transplantations. Blood 2008, 112, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhring, C.; Scheidegger, D.; Samaridis, J.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. A human killer inhibitory receptor specific for HLA-A1,2. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 3098–3101. [Google Scholar]
- Hansasuta, P.; Dong, T.; Thananchai, H.; Weekes, M.; Willberg, C.; Aldemir, H.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Braud, V.M. Recognition of HLA-A3 and HLA-A11 by KIR3DL2 is peptide-specific. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moesta, A.K.; Graef, T.; Abi-Rached, L.; Older Aguilar, A.M.; Guethlein, L.A.; Parham, P. Humans differ from other hominids in lacking an activating NK cell receptor that recognizes the C1 epitope of MHC class I. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4233–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) Version 3.698; Distributed by the author; Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington: Seattle, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Alam, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Sonawane, A.; Imran, M.; Agrawal, S. Distribution of Killer cell immunoglobulin like receptor genes in end stage renal disease among North Indian population. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendzekhadze, K.; Norman, P.J.; Abi-Rached, L.; Layrisse, Z.; Parham, P. High KIR diversity in Amerindians is maintained using few gene-content haplotypes. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendzekhadze, K.; Norman, P.J.; Abi-Rached, L.; Graef, T.; Moesta, A.K.; Layrisse, Z.; Parham, P. Co-evolution of KIR2DL3 with HLA-C in a human population retaining minimal essential diversity of KIR and HLA class I ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18692–18697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.C.; Marcos, C.Y.; Paladino, N.; Capucchio, M.; Theiler, G.; Arruvito, L.; Pardo, R.; Habegger, A.; Williams, F.; Middleton, D.; et al. KIR genes polymorphism in Argentinean Caucasoid and Amerindian populations. Tissue Antigens 2007, 69, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Silva, S.Z.; Dhanda, S.K.; Singh, M. Killer immunoglobulin like receptor gene profiling in Western Indian population. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closa, L.; Vidal, F.; Herrero, M.J.; Caro, J.L. Distribution of human killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors and ligands among blood donors of Catalonia. HLA 2020, 95, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Sulbaran, A.C.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Ramírez-Dueñas, M.G.; Baños-Hernández, C.J.; Graciano-Machuca, O.; Velarde-De la Cruz, E.E.; Parra-Rojas, I.; Sánchez-Hernández, P.E. Distribution of KIR genes and KIR2DS4 gene variants in two Mexican Mestizo populations. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, P.; Verdugo, R.A.; Díaz-Peña, R. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genotypes in a Chilean population from Talca. Hum. Immunol. 2018, 79, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Fernández-Mestre, M.; Padrón, D.; Toro, F.; Silva, N.; Tassinari, P.; Blanca, I.; Martin, M.P.; Carrington, M.; Layrisse, Z. Distribution of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genes in the mestizo population from Venezuela. Tissue Antigens 2010, 75, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, D.S.; Mazini, P.S.; Rudnick, C.C.; Sell, A.M.; Tsuneto, L.T.; de Melo, F.C.; Braga, M.A.; Peixoto, P.R.; Visentainer, J.E. Association between killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genotypes and leprosy in Brazil. Tissue Antigens 2008, 72, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perce-da-Silva, D.S.; Silva, L.A.; Lima-Junior, J.C.; Cardoso-Oliveira, J.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Santos, F.; Porto, L.C.; Oliveira-Ferreira, J.; Banic, D.M. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene diversity in a population naturally exposed to malaria in Porto Velho, Northern Brazil. Tissue Antigens 2015, 85, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, A.V.; Silva, G.F.; de Moraes, C.F.; Grotto, R.M.; Pardini, M.I.; de Pauli, D.S.; Sell, A.M.; Visentainer, J.E.; Moliterno, R.A. KIR genes and their human leukocyte antigen ligands in the progression to cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, D.G.; Lobo-Alves, S.C.; Melo, M.F.; Pereira, N.F.; Petzl-Erler, M.L. Activating KIR and HLA Bw4 ligands are associated to decreased susceptibility to pemphigus foliaceus, an autoimmune blistering skin disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentle, N.L.; Loubser, S.; Paximadis, M.; Puren, A.; Tiemessen, C.T. Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I genetic diversity in four South African populations. Hum. Immunol. 2017, c8, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, L.; Sivula, J.; Gourraud, P.A.; Kerdudou, N.; Chout, R.; Ricard, C.; Moisan, J.P.; Gagne, K.; Partanen, J.; Bignon, J.D. Genetic diversity of KIR natural killer cell markers in populations from France, Guadeloupe, Finland, Senegal and Réunion. Tissue Antigens 2005, 66, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, D.; Meenagh, A.; Sleator, C.; Gourraud, P.A.; Ayna, T.; Tozkir, H.; Köse, A.A.; Azizleri, G.; Diler, A.S. No association of KIR genes with Behcet’s disease. Tissue Antigens 2007, 70, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, E.; Farjadian, S.; Reed, E.F.; Ghaderi, A.; Rajalingam, R. KIR gene content diversity in four Iranian populations. Immunogenetics 2009, 61, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, S.E.; Ní Chorcora, C.; Dring, M.M.; Stallings, R.L.; O’Meara, A.; Gardiner, C.M. Increased frequencies of the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor genes KIR2DL2 and KIR2DS2 are associated with neuroblastoma. Tissue Antigens 2015, 86, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Gjertson, D.W.; Reed, E.F.; Rajalingam, R. Receptor-ligand analyses define minimal killer cell Ig-like receptor (KIR) in humans. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenbach, J.A.; Meenagh, A.; Sleator, C.; Alaez, C.; Bengoche, M.; Canossi, A.; Contreras, G.; Creary, L.; Evseeva, I.; Gorodezky, C.; et al. Report from the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) anthropology component of the 15th International Histocompatibility Workshop: Worldwide variation in the KIR loci and further evidence for the co-evolution of KIR and HLA. Tissue Antigens 2010, 76, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisri, S.; Kitcharoen, K.; Romphruk, A.V.; Romphruk, A.; Witt, C.S.; Leelayuwat, C. Polymorphisms of killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) and HLA ligands in northeastern Thais. Immunogenetics 2013, 65, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiby, S.E.; Ashrafian-Bonab, M.; Farrell, L.; Single, R.M.; Balloux, F.; Carrington, M.; Moffett, A.; Ebrahimi, Z. Distribution of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) and their HLA-C ligands in two Iranian populations. Immunogenetics 2010, 62, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, W. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genes in 4 distinct populations and 51 families in mainland China. Hum. Immunol. 2012, 73, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Zou, H.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Yang, B.; Deng, Z. Genetic profile of KIR and HLA in southern Chinese Han population. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Guo, C.; Shi, L.; Yao, Y.; Yu, J. Distribution of KIR genes in Han population in Yunnan Province: Comparison with other Han populations in China. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2013, 40, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; He, Y.; Dong, L.; He, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, W.; Han, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Zhu, F. Associations of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors with acute myeloid leukemia in Chinese populations. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawata, M.; Yawata, N.; Draghi, M.; Little, A.M.; Partheniou, F.; Parham, P. Roles for HLA and KIR polymorphisms in natural killer cell repertoire selection and modulation of effector function. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.B.; Jang, J.P.; Baek, I.C.; Choi, E.J.; Park, M.; Kim, T.G.; Oh, S.T. HLA-Cw polypmorphism and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene analysis in Korean colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, M.E.; Sandoval-Ramírez, L.; Díaz-Flores, M.; Marsh, S.G.; Valladares-Salgado, A.; Madrigal, J.A.; Mejía-Arangure, J.M.; García, C.A.; Huerta-Zepeda, A.; Ibarra-Cortés, B.; et al. KIR gene in ethnic and Mestizo populations from Mexico. Hum. Immunol. 2006, 67, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, L.B.; Beltrame, M.H.; Ho, B.; Marin, W.M.; Dandekar, R.; Montero-Martín, G.; Fernández-Viña, M.A.; Hurtado, A.M.; Hill, K.R.; Tsuneto, L.T.; et al. Remarkably Low KIR and HLA Diversity in Amerindians Reveals Signatures of Strong Purifying Selection Shaping the Centromeric KIR Region. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msab298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, D.G.; Piovezan, B.Z.; Tsuneto, L.T.; Callegari-Jacques, S.M.; Petzl-Erler, M.L. KIR gene content in Amerindians indicates influence of demographic factors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Single, R.M.; Martin, M.P.; Gao, X.; Meyer, D.; Yeager, M.; Kidd, J.R.; Kidd, K.K.; Carrington, M. Global diversity and evidence for coevolution of KIR and HLA. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewerton, P.D.; Leite Mde, M.; Magalhães, M.; Sena, L.; Melo dos Santos, E.J. Amazonian Amerindians exhibit high variability of KIR profiles. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, D.G.; Amorim, L.M.; Farias, T.D.; Petzl-Erler, M.L. KIR and HLA genotyping of Japanese descendants from Curitiba, a city of predominantly European ancestry from Southern Brazil. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alencar, J.B.; Zacarias, J.M.V.; Moura, B.L.D.S.G.; Braga, M.A.; Visentainer, J.E.L.; Sell, A.M. KIR and HLA ligands demonstrate genetic inheritance diversity in Japanese descendants from Paraná, Brazil. Hum. Immunol. 2018, 79, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalingam, R.; Du, Z.; Meenagh, A.; Luo, L.; Kavitha, V.J.; Pavithra-Arulvani, R.; Vidhyalakshmi, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Balazs, I.; Reed, E.F.; et al. Distinct diversity of KIR genes in three southern Indian populations: Comparison with world populations revealed a link between KIR gene content and pre-historic human migrations. Immunogenetics 2008, 60, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilling, H.G.; Guethlein, L.A.; Cheng, N.W.; Gardiner, C.M.; Rodriguez, R.; Tyan, D.; Parham, P. Allelic polymorphism synergizes with variable gene content to individualize human KIR genotype. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Johnson, C.; Jayaraman, J.; Simecek, N.; Noble, J.; Moffatt, M.F.; Cookson, W.O.; Trowsdale, J.; Traherne, J.A. Copy number variation leads to considerable diversity for B but not A haplotypes of the human KIR genes encoding NK cell receptors. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnheim, L.; Dillner, J.; Sanjeevi, C.B. A population-based cohort study of KIR genes and genotypes in relation to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Tissue Antigens 2005, 65, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velickovic, M.; Velickovic, Z.; Dunckley, H. Diversity of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genes in Pacific Islands populations. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, A.B.; Rishishwar, L.; Norris, E.T.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A.; Mariño-Ramírez, L.; Medina-Rivas, M.A.; Jordan, I.K. A Comparative Analysis of Genetic Ancestry and Admixture in the Colombian Populations of Chocó and Medellín. G3 (Bethesda) 2017, 7, 3435–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.; duToit, E.D.; Middleton, D. KIR allele frequencies in a Xhosa population from South Africa. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 1084–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.; Hawkins, B.; Middleton, D. HLA-A and -B and KIR Gene Allele Frequencies in a Chinese Population from Hong Kong. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, D.G.; Zehnder-Alves, L.; Pincerati, M.R.; Martin, M.P.; Carrington, M.; Petzl-Erler, M.L. Diversity of the KIR gene cluster in an urban Brazilian population. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Stankovic, S.; O’Connor, G.M.; Pymm, P.; MacLachlan, B.J.; Faoro, C.; Retière, C.; Sullivan, L.C.; Saunders, P.M.; Widjaja, J.; et al. Structural plasticity of KIR2DL2 and KIR2DL3 enables altered docking geometries atop HLA-C. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi-ming, L.; Yu-lian, J.; Zhao-lei, F.; Chun-xiao, W.; Zhen-fang, D.; Bing-chang, Z.; Yue-ran, Z. Polymorphisms of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor gene: Possible association with susceptibility to or clearance of hepatitis B virus infection in Chinese Han population. Croat. Med. J. 2007, 48, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Juarez, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Camacho, A.; Manzanares-Martin, B.; Caruz, A.; Martinez-Peinado, A.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Pineda, J.A.; Peña, J.; Rivero, A. Natural killer KIR3DS1 is closely associated with HCV viral clearance and sustained virological response in HIV/HCV patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, C.; Altfeld, M. Role of KIR3DS1 in human diseases. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, I.H.; Sergeant, R.; Szydlo, R.; Apperley, J.F.; DeLavallade, H.; Alsuliman, A.; Khoder, A.; Marin, D.; Kanfer, E.; Cooper, N.; et al. Interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-Bw4 predicts for progression-free survival after autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 2010, 116, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venstrom, J.M.; Gooley, T.A.; Spellman, S.; Pring, J.; Malkki, M.; Dupont, B.; Petersdorf, E.; Hsu, K.C. Donor activating KIR3DS1 is associated with decreased acute GVHD in unrelated allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2010, 115, 3162–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lienert, K.; Parham, P. Evolution of MHC class I genes in higher primates. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Peña, R.; Vidal-Castiñeira, J.R.; Moro-García, M.A.; Alonso-Arias, R.; Castro-Santos, P. Significant association of the KIR2DL3/HLA-C1 genotype with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).