Abstract
The reduced N fertilization rate and N supplied by pea (Pisum sativum L.) residue may sustain subsequent spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth, yield, and quality. We examined the response of spring wheat growth, yield, and quality to cropping systems and N fertilization rates from 2012 to 2019 in the US northern Great Plains. Cropping systems were conventional till spring wheat–fallow (CTWF), no-till spring wheat–fallow (NTWF), no-till spring wheat–pea (NTWP), and no-till continuous wheat (NTCW), and N fertilization rates to spring wheat were 0, 50, 100, and 150 kg N ha−1. Wheat plant density and straw yield were 13–100% greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW in most years. Wheat grain yield and protein concentration were also 15–115% greater for CTWF and NTWF than other cropping systems at most N fertilization rates and years. In contrast, wheat grain test weight was 1–2% lower for CTWF and NTWF at most N fertilization rates and years. Increasing N fertilization rate mostly increased grain yield and protein concentration but reduced grain test weight for most cropping systems and years. Although CTWF and NTWF with or without N fertilization increased wheat yield and quality, these practices are not sustainable due to reduced annualized yield, soil health, and environmental quality. Because of similar or greater grain yields and test weights among NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 and NTWP and NTCW with other N rates, NTWP with reduced N rates may sustain spring wheat yield and grain size but not grain protein in the northern Great Plains.
1. Introduction
Wheat is one of the most important cereal crops grown, second only to rice (Oryza sativa L.), and provides food for one-third of the world population and one-fifth of the human calorific value [1]. In Montana, USA, spring wheat was grown on 2.2 million ha producing 6 Tg of grain yield in 2014 [2]. In dryland conventional cropping systems in the US northern Great Plains, spring wheat is grown once every two years, alternating with fallow, due to limited precipitation and a short growing season [2,3]. Fallowing can conserve soil water, control weeds, and reduce N fertilization rates to succeeding crops due to increased soil N availability from enhanced soil organic matter mineralization [3,4]. This has reduced not only annualized crop yields, soil health, and environmental quality due to reduced soil organic matter content and increased soil erosion and greenhouse gas emissions [3,5,6], but also decreased precipitation-use efficiency [7], thereby rendering the practice as inefficient and uneconomical [4].
No-till continuous cropping with spring wheat and spring wheat–pea rotation have been successfully used to replace the conventional till spring wheat–fallow system to enhance crop yields, soil organic matter [5], and water-use efficiency in the US northern Great Plains [8]. Lenssen et al. [8] showed that while tillage has no effect on wheat yield, spring wheat–pea rotation increased wheat plant density, aboveground biomass and grain yields, and harvest index by 23–40% compared to continuous spring wheat. This was due to the additional N supplied by pea residue due to higher tissue N concentration from increased N fixation compared to wheat residue, thereby reducing N fertilization rates [9,10] and increased soil water available for spring wheat because of low water use by pea compared to spring wheat due to its earlier maturity [8]. Additional benefits of using spring wheat–pea rotation compared to continuous spring wheat include reduced weed, disease, and pest pressure, thereby decreasing herbicide and pesticide applications [11,12]. Carr et al. [13] reported that spring wheat yield was similar following fallow compared to following annual crops, but grain protein concentration was higher following fallow, yet was ≤132 g kg−1, indicating N deficiency and further N fertilizer requirement to boost protein level in the spring wheat–fallow system. While Mohammed and Chen [14] found that spring wheat yield was lower following pea than following fallow, Koeshall et al. [15] demonstrated that spring wheat yield did not differ between spring wheat–fallow and spring wheat–pea rotations. Several researchers [16,17] reported that spring wheat–pea rotation increased spring grain yield, test weight, and protein concentration by 3–14% compared to continuous spring wheat.
Nitrogen fertilization is needed to enhance spring wheat yield and protein concentration [18,19]. Increasing N fertilization rate can increase spring wheat yield and protein concentration, but excessive N fertilization rate beyond the recommended rate can degrade soil and environmental quality through increased soil acidification, N leaching, NH3 volatilization, and greenhouse gas (N2O) emissions due to increased soil residual N accumulation, as crops can remove only 50–60% of applied fertilizer N [20,21]. Nitrogen fertilization can increase spring wheat yield only when growing season precipitation is >300 mm, with maximum yield occurring at 84 kg N ha−1 in dryland cropping systems [22,23]. Increasing N fertilization rate, however, can reduce grain test weight [19,24]. Otteson et al. [24] and Walsh et al. [21] observed that increasing N fertilization rate increased spring wheat protein concentration (10–22%) but had no effect on plant density and grain yield. Increasing N fertilization rate did not increase spring wheat yield in spring wheat–fallow [22] or spring wheat–pea rotations [2] but did so in continuous spring wheat [2].
Because of the rotational benefit of pea, it is necessary to know how much pea can reduce N fertilization rates and sustain spring wheat yield and quality in the spring wheat–pea rotation compared to continuous spring wheat. The reduction in N fertilization rates to spring wheat can vary by year due to variations in pea growth and N fixation as well as N mineralization from pea residue stemming from differences in growing season air temperature and precipitation among years. As limited information exists in the literature, we compared spring wheat growth, yield,, and quality among four cropping systems (conventional till spring wheat–fallow [CTWF], no-till spring wheat–fallow [NTWF], no-till spring wheat–pea [NTWP], and no-till continuous wheat [NTCW]) receiving four N fertilization rates (0, 50, 100, and 150 kg N ha−1) to hypothesize that NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 would sustain wheat yield and quality compared to NTCW with 100–150 kg N ha−1. Our objectives were (1) to determine whether spring wheat plant density, straw and grain yields, harvest index, and grain test weight and protein concentration vary among cropping sequences and N fertilization rates, and (2) to examine if NTWP with reduced N fertilization rate can sustain spring wheat growth, yield, and quality compared to NTCW with increased N fertilization rates.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Details
The experiment was performed from 2012 to 2019 in Sidney, Montana, USA (48° 33′ N, 104° 50′ W) (Figure 1). The soil is Williams loam (fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, frigid, Typic Argiustolls) with sand, silt, and clay concentrations of 350, 325, and 325 g kg−1, respectively, pH 7.2, and soil organic matter 22.8 g kg−1 at the 0–20 cm depth. The site has mean annual (30-year average) air temperature of 7 °C and an average annual precipitation of 396 mm. The mean growing season (April–August) precipitation is 264 mm. Cropping history before the initiation of the experiment was spring wheat–fallow rotation under conventional tillage for >10 years.
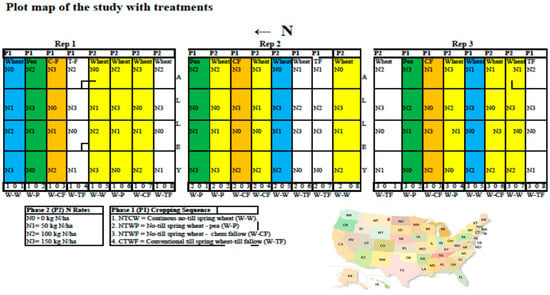
Figure 1.
Plot map of treatments and location of the study site.
A split-plot experiment with cropping system as the main-plot and N fertilization rate as the split-plot treatment was arranged in a randomized block design with three replications. The size of the main plot was 48.0 × 12.0 m and the split plot was 12.0 × 6.0 m. Cropping systems were CTWF, NTWF, NTWP, and NTCW, and N fertilization rates were 0, 50, 100, and 150 kg N ha−1 applied to spring wheat. The NTCW was a 1-year rotation, but other cropping systems were 2-year rotations where both phases of the crops in the rotation were present in each year. For this, the main plot was split into two subplots, where both phases of the crop rotations (e.g., wheat and pea phases in NTWP and fallow and wheat phases in CTWF and NTWF) occurred in each year. No N fertilizer was applied to pea and fallow. The CTWF was the conventional cropping system and 100 kg N ha−1 was the recommended N fertilization rate for spring wheat in the study area. Tillage in CTWF included plowing plots with a field cultivator equipped with C-shanks and 45 cm-wide sweeps and coiled-toothed spring harrows to a depth of 8 cm at planting and during fallow periods as needed to control weeds and seedbed preparation. Plots in other treatments were not tilled. The experiment was conducted in the same plots every year from 2012 to 2019 to evaluate the effect of treatments on soil health parameters, which take a long time to measure (Figure 1).
From 2012 to 2019, spring wheat (cv. Reeder) was planted at 80 kg ha−1 and dry pea (cv. Majoret) was planted at 90 kg ha−1 at a spacing of 20 cm using a no-till drill equipped with double-shoot Barton disk openers in late April of each year. Pea seeds were inoculated with Rhizobium leguminosarum before planting. At planting, P fertilizer as triple super phosphate at 11 kg P ha−1 and K fertilizer as muriate of potash at 27 kg K ha−1 were banded 5 cm to the side and 5 cm below seeds. Nitrogen fertilizer as urea (one dose) was broadcast to spring wheat a week after planting. Nitrogen fertilization rates were adjusted to soil NO3-N content to a depth of 60 cm determined after crop harvest in the autumn of the previous year to reduce soil residual N content and N loss to the environment. Therefore, N fertilization rates considered as plant-available N included both soil and fertilizer N (Table 1). Crops were grown in dryland conditions, and no irrigation was applied.

Table 1.
Effect of cropping system and N fertilization rate on autumn soil NO3-N content to a depth of 60 cm and amount of N fertilizer applied for spring wheat, averaged across years. Bold p values denote significance at ≤0.05.
In each year, spring wheat and pea were treated with a preplant application of glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) at 3.36 kg a.i. ha−1 in 38 L water to control early emerging weeds. In-season weeds under spring wheat were controlled with a fall application of 1.1 kg ha−1 trifluralin (α,α,α,trifluoro-2,6-N,N-dipropyl-p-toluidine) and 0.3 kg ha−1 of formulated triallate {S-(2,3,3-trichloroallyl) diisopropyl-thiocarbamate} in 38 L water. Postemergence weeds were controlled with 0.68 kg ha−1 of formulated bromoxynil (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) and MCPA (2-ethylhexyl ester of 2-methyl-4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) (0.92:1) and 0.09 kg a.i. ha−1 of fenoxaprop-P {ethyl (RS)-2-[4-(6-chloro-1,3-benzoxazol-2-yloxy)phenoxy]propionate} in 38 L water. Weeds in pea were managed with a fall-applied sonalan (ethalfluralin) at 0.12 kg a.i. ha−1 and post-emergence applications of formulated, tank-mixed bentazon (3-Isopropyl-1H-2,1,3-benzothiadiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide) and sethoxydim (2-[1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-5-[2-(ethylthio)propyl]-3-hydroxy-2-cyclohexen-1-one) at 1.68 kg a.i. ha−1 in 38 L water prior to flowering. Weeds during the fallow period in NTCW were managed by applying glyphosate and in CTWF with a combination of tillage and herbicides.
Plant density was determined by counting plants at one-to-two leaf stage from four 1 m rows in each plot. Two days before grain harvest in August of each year, plants were chopped at a height of 2 cm above the ground from four 1 m rows and separated into straw and grains, from which straw and grain yields were determined after oven drying straw and grains at 70 °C for 3 and 7 days, respectively. Harvest index was determined by dividing grain yield by the sum of grain and straw yields. Actual grain yield on an oven-dried basis from a large area was determined by harvesting grains with a self-propelled combine from an area of 11.0 × 1.5 m, from which a sample of the cleaned grain was oven-dried at 70 °C for 7 days. After grain harvest, crop residue was returned to the soil. Grain test weight was determined by weighing grains filled in a 0.95 L container. Nitrogen concentration in grain was determined by using a C and N analyzer (LECO, St. Joseph, MI, USA) after grinding a portion of the oven-dried grain to 1 mm. Grain protein concentration was determined by multiplying wheat grain N concentration by 5.73 [18].
2.2. Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using the MIXED model procedure of SAS/STAT 9.3 [25]. Cropping system was used as the main plot and N fertilization rate was used as the split-plot treatment for data analysis. Fixed effects included cropping system, N fertilization rate, and their interaction, random effects included replication and replication × cropping system, and the repeated measure variable was year, because the experiment was repeated in the same plots every year. When significant, means and interactions were separated by using the least square means test [25]. Because N fertilization rate was a quantitative variable, regression analysis was used to determine the relationship between N fertilization rate and crop parameters for various cropping systems [26]. For this, data were fitted in a linear or non-linear fashion, depending on the greatest R2 and lowest significant p values. A threshold value of p ≤ 0.05 was used to test the significant difference among treatments and interactions, unless stated otherwise.
3. Results
3.1. Air Temperature and Precipitation
Monthly air temperatures from April to August were lower in most years than the 30-year average, except in April 2012, May 2018, June 2016, and July 2012 and 2017 (Table 2). As a result, the growing season air temperature was also lower than the 30-year average in all years, except in 2012. Notable intensive monthly precipitation greater than the 30-year average occurred in April 2016, May 2013 and 2014, June 2013, and August 2013 and 2014. In contrast, dry conditions (<20 mm precipitation) occurred in April 2013, 2015, and 2017, May 2017, July 2014 and 2017, and August 2012 and 2018. Growing season precipitation (April–August) greater than the 30-year average occurred only in 2013 and 2014. The average growing season precipitation was 67% of the total annual precipitation.

Table 2.
Monthly total precipitation and average air temperature from 2012 to 2019 at the study site.
3.2. Soil Nitrate Nitrogen Content and the Amount of Nitrogen Fertilizer Applied
Soil NO3-N content at 0–60 cm and the amount of N fertilizer applied were significant for N fertilization rate and year as well as cropping system × N fertilization rate and N fertilization rate × year interactions (Table 1). Soil NO3-N content, averaged across years, was lower for NTCW than other cropping sequences at 0 kg N ha−1 and lower for NTWP and NTCW than NTWF at 100 kg N ha−1. Soil NO3-N content increased with increasing N fertilization rate in all cropping systems.
Because the treatment 0 kg N ha−1 received no N fertilizer, the amount of N fertilizer applied for spring wheat for this treatment was zero for all cropping systems (Table 2). The amount of N fertilizer applied, averaged across years, was lower for NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at 100 kg N ha−1. As with soil NO3-N content, the amount of N fertilizer applied also increased with increasing N fertilization rate for all cropping systems. The amount of N fertilizer applied ranged from 5 kg N ha−1 for NTWF at 50 kg N ha−1 to 98 kg N ha−1 for CTWF at 150 kg N ha−1.
3.3. Plant Density
Spring wheat plant density varied with cropping systems, N fertilization rates, and years, with a significant interaction for cropping system × year (Table 3). Averaged across N fertilization rates, plant density was 13% greater for CTWF than NTWP in 2012 and 13–37% greater than NTWP and NTCW in 2017 (Table 4). Plant density was 21% greater for NTWF than NTCW in 2014 and 11–25% greater for NTWF than NTWP and NTCW in 2016. In 2019, plant density was 18–21% greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW. Plant density was also 13–22% greater for NTWP than NTCW in 2016 and 2017. Averaged across cropping systems and years, plant density was 6–9% lower for 50 than 0, 100, and 150 kg N ha−1 (Table 5).

Table 3.
Analysis of variance for spring wheat plant density, straw yield, grain yield, harvest index, grain test weight, and grain protein concentration with sources of variance for cropping system (CS), N fertilization rate (NR), and year (YR). Bold p values denote significance at ≤ 0.05.

Table 4.
Interaction between cropping system and year on spring wheat plant density, straw yield, and harvest index averaged across N fertilization rates.

Table 5.
Effect of N fertilization rate on spring wheat plant density and straw yield averaged across cropping systems and years.
3.4. Straw Yield
Straw yield also varied with cropping systems, N fertilization rates, and years, with a significant interaction for cropping system × year (Table 3). Averaged across N fertilization rates, straw yield was 64–116% greater for NTWF than NTWP and NTCW in 2012 (Table 4). Straw yield was 48% greater for CTWF than NTCW in 2013 and 24–78% greater than NTCW and NTWF in 2014. In 2016, straw yield was 28–31% greater for CTWF, NTWF, and NTWP than NRCW. In 2017 and 2019, straw yield was 53–123% greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW. Straw yield was also 25–56% greater for NTWP than NTCW in 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, and 2019. Averaged across cropping systems and years, straw yield was 8–27% greater for 100 and 150 than 0 and 50 kg N ha−1 and 11% greater for 50 than 0 kg N ha−1 (Table 5).
3.5. Grain Yield
Spring wheat grain yield was affected by cropping system, N fertilization rate, and year, with significant interactions for cropping system × N fertilization rate, cropping system × year, N fertilization rate × year, and cropping system × N fertilization rate × year (Table 3). Grain yield was normally greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at most N fertilization rates and year, except in 2014 and 2015 (Figure 2 and Figure 3). In 2014, compared to NTCW, grain yield was greater for other cropping systems at 0 and 50 kg N ha−1, greater for NTWF at 100 kg N ha−1, and greater for CTWF at 150 kg N ha−1. In 2015, grain yield was greater for NTCW than NTWF at 100 kg N ha−1. Grain yield was not different between CTWF and NTWF at all N fertilization rates and years. In contrast, grain yield was greater for NTWP than NTCW at most N fertilization rates and years, except in 2015 and 2018. Increasing N fertilization rate had a variable response for grain yield for various cropping systems and years. A significant linear relationship between N fertilization rate and grain yield was observed for CTWF in 2016, 2018, and 2019; for NTWP in 2017 and 2018; and for NTCW in 2017 and 2019. An increase in N fertilization rate by 1 kg N ha−1 increased grain yield from 0.010 Mg ha−1 for CTWF in 2019 to 0.025 Mg ha−1 for NTCW in 2019. Similarly, a significant nonlinear relationship was found for CTWF in 2013, 2014, and 2017 and for NTWP in 2016.
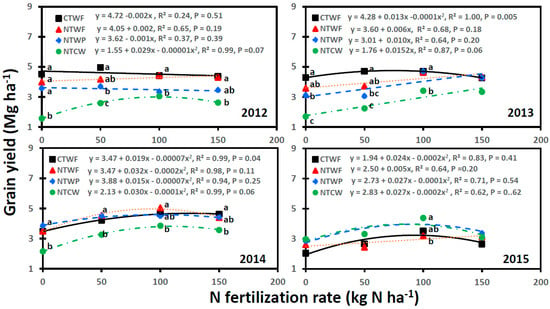
Figure 2.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain yield for various cropping systems from 2012 to 2015. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
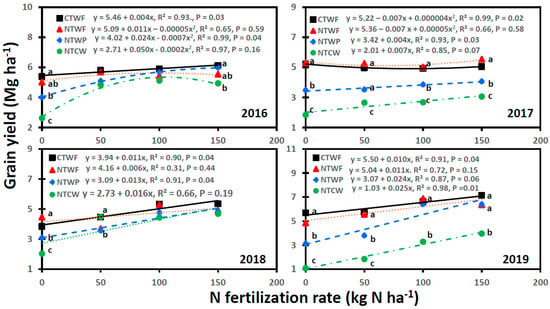
Figure 3.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain yield for various cropping systems from 2016 to 2019. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
Averaged across years, grain yield was 25–166% greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at 0 and 50 kg N ha−1 and 33–35% greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTCW at 100 and 150 kg N ha−1 (Figure 4A). However, annualized grain yield, calculated as the average yield of crops within a rotation in a year, considering that grain yield during the fallow period in CTWF and NTWF [4,5,10], was 44–87% (1.34–2.19 Mg ha−1) lower at 0–150 kg N ha−1 for CTWF and NTWF compared to NTCW and NTWP. Grain yield was also 21–70% greater for NTWP than NTCW at all N fertilization rates. A significant nonlinear relationship occurred between N fertilization rate and grain yield for NTCW. For NTCW grain yield of 3.72 Mg ha−1 was maximized at a N fertilization rate of 115 kg N ha−1. Grain yield was similar or greater for NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 than NTCW with 100–150 kg N ha−1.
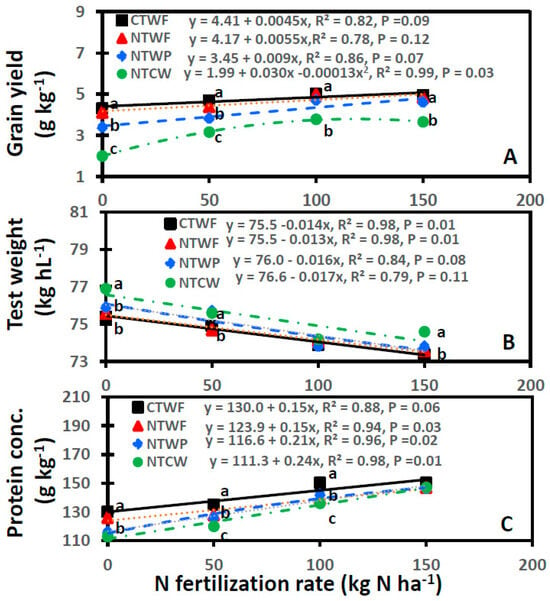
Figure 4.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain (A) yield, (B) test weight, and (C) protein concentration for various cropping systems averaged across years. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
3.6. Harvest Index
Harvest index varied among years, with a significant interaction for cropping system × year (Table 3). Harvest index was 10% greater for NTWF than NTCW in 2013, 15–16% greater for NTWF and NTCW than CTWF in 2014, and 13% greater for NTCW than CTWF and NTWF in 2015 (Table 4). Averaged across cropping systems and N fertilization rates, harvest index was greater in 2012, 2013, and 2018 than other years.
3.7. Grain Test Weight
Grain test weight was also affected by cropping system, N fertilization rate, and year, with significant interactions for cropping system × N fertilization rate, cropping system × year, N fertilization rate × year, and cropping system × N fertilization rate × year, a case similar to that observed for grain yield (Table 3). Grain test weight decreased with increasing N fertilization rate for all cropping systems and years, except for CTWF and NTCW in 2013, for CTWF in 2017, and for NTCW in 2019 where test weight increased with increasing N fertilization rate (Figure 5 and Figure 6). A significant linear relationship between N fertilization rate and test weight occurred for CTWF in 2012, 2014, 2016, and 2018; for NTWF in 2012 and 2016; for NTWP in 2012 and 2017; and for NTCW in 2014 and 2018. An increase in N fertilization rate by 1 kg N ha−1 decreased test weight by 0.012 kg L−1 for NTWP in 2017 to 0.052 kg L−1 for NTWF in 2012. Test weight was greater for NTWP or NTCW than CTWF and NTWF at most N fertilization rates in 2012, 2015, 2016, and 2017, but the trend reversed in 2019. In 2014 and 2018, test weight was greater for CTWF and NTCW than NTWP at 0 kg N ha−1 but was greater for NTWF than CTWF at 150 kg N ha−1. Test weight was also greater for NTCW and NTWF than NTWP at 100 kg N ha−1 in 2018.
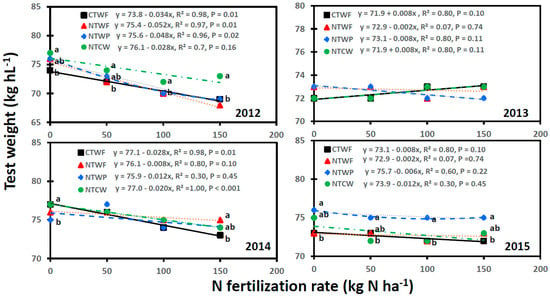
Figure 5.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain test weight for various cropping systems from 2012 to 2015. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
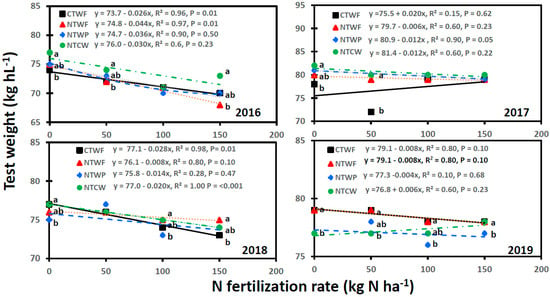
Figure 6.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain test weight for various cropping systems from 2016 to 2019. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
Averaged across years, test weight was 0.9–2.0% greater for NTCW than other cropping systems at 0, 50, and 150 kg N ha−1 (Figure 4B). Test weight linearly declined with increasing N fertilization rate for CTWF and NTWF. An increase in N fertilization rate by 1 kg N ha−1 decreased test weight from 0.013 kg hL−1 for NTWF to 0.014 kg hL−1 for CTWF. Test weight was also similar or greater for NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 than NTWP or NTCW with 100–150 kg N ha−1.
3.8. Grain Protein Concentration
Grain protein concentration also varied with cropping systems, N fertilization rates, and years, with significant interactions for cropping system × N fertilization rate, cropping system × year, N fertilization rate × year, and cropping system × N fertilization rate × year (Table 3). In contrast to test weight, grain protein concentration increased with increasing N fertilization rates for all cropping systems, except for CTWF in 2013 and 2017, for NTWF in 2015, and for NTCW in 2019, which declined (Figure 7 and Figure 8). A significant linear relationship between N fertilization rate and protein concentration was found for CTWF in 2012, 2014, and 2018; for NTWF in 2012 and 2013; for NTWP in 2012, 2013, 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019; and for NTCW in 2012, 2013, 2014, 2016, 2017, and 2018. An increase in N fertilization rate by 1 kg N ha−1 increased grain protein concentration from 0.11 g kg−1 for NTWF in 2013 to 0.46 g kg−1 for NTWP in 2012. A significant nonlinear relationship occurred for CTWF in 2016 and 2019. Protein concentration was greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at N fertilization rates ≤ 50 kg N ha−1 in 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2019. In 2012, 2014, and 2018, protein concentration tended to be greater for NTWP and CTWF than other cropping systems at N fertilization rates ≤100 kg N ha−1. In 2016, protein concentration was lower for NTWF than CTWF at 100 kg N ha−1 but was greater for NTCW than NTWF at 150 kg N ha−1.
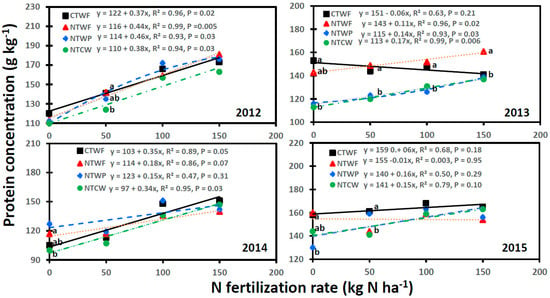
Figure 7.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain protein concentration for various cropping systems from 2012 to 2015. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
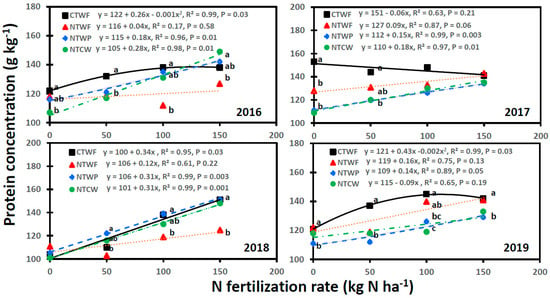
Figure 8.
Relationship between N fertilization rate and spring wheat grain protein concentration for various cropping systems from 2016 to 2019. Cropping systems are CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous spring wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea. Markers accompanied by different letters at a N fertilization rate are significantly different at p ≤ 0.05 by the least square means test.
Averaged across years, protein concentration linearly increased with increasing N fertilization rates for all cropping systems, except for CTWF (Figure 4C). An increase in N fertilization rate by 1 kg N ha−1 increased grain protein concentration by 0.15 g kg−1 for NTWF, 0.21 g kg−1 for NTWP, and 0.24 g kg−1 for NTCW. Protein concentration was greater for CTWF than NTCW from 0 to 100 kg N ha−1. There was no difference in protein concentration between NTWP and NTCW at any N fertilization rate.
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Nitrate Nitrogen
Increased N taken up by spring wheat every year likely reduced soil NO3-N content for NTCW compared to CTWF and NTWF where crops were absent during the fallow year to take up N. In contrast, increased N mineralization from soil organic matter during the fallow period [23], as well as that from pea residue with higher tissue N concentration than wheat residue, may have increased NO3-N content for CTWF, NTWF, and NTWP. Because spring wheat can take up only 35–50% of applied N fertilizer [20,21], the greater soil NO3-N content with increasing N fertilization rate was likely due to increased accumulation of soil residual N after crop harvest. Even without N fertilization, substantial NO3-N content (23–44 kg N ha−1 to a depth of 60 cm) remained in the soil (Table 2), suggesting that the mineralization of soil organic matter can contribute a significant portion of NO3-N content in the soil. Because N fertilization rate was adjusted to soil NO3-N content to a depth of 60 cm, the amount of N fertilizer applied to spring wheat increased as NO3-N content decreased, resulting in increased amount of N fertilizer with increasing N fertilization rate. This also resulted in greater amount of N fertilizer applied for NTWP and NTCW than NTWF with 100 kg N ha−1.
4.2. Plant Density
Increased soil water conservation during the fallow period may have increased seed germination and, therefore, enhanced spring wheat plant density for CTWF and NTWF compared to NTWP and NTCW in 5 out of 8 years. Absence of crops during the fallow period increases soil water content which becomes available for following crops [3,4,7]. Similarly, greater water availability due to reduced water uptake by pea compared to spring wheat [8] may have increased plant density for NTWP compared to NTCW in 2016 and 2017. Our results are similar to those reported by Lenssen et al. [8], who found that spring wheat plant density was greater for spring wheat–pea rotation than continuous spring wheat in eastern Montana, USA. A non-significant difference in plant density between CTWF and NTWF suggests that tillage has no effect in spring wheat plant density. Dry periods during late April and early May (Table 1) likely resulted in non-significant differences in plant density among cropping systems in 2013, 2015, and 2018. The reasons for lower plant density for 50 kg N ha−1 than other N fertilization rates (Table 5) were not known.
4.3. Straw Yield
Greater spring wheat straw yield for CTWF and NTWF than other cropping systems in 6 out of 8 years (Table 4) was likely due to increased plant density stemming from enhanced soil water conservation during the fallow period. Lin and Chen [2] found that winter wheat–fallow rotation had greater winter wheat straw yield than winter wheat–pea rotation and continuous winter wheat in central Montana, USA. Similarly, greater straw yield for NTWP than NTCW in 5 out of 8 years was likely a result of increased plant density as well as rotational and non-rotational benefit of pea on spring wheat. These benefits include increased N supplied by pea residue compared to spring wheat residue, reduced water uptake by pea, and reduced weed and pest pressure [8,12]. As with plant density, a non-significant difference in straw yield between CTWF and NTWF in all years suggests that tillage had no effect on straw yield.
The greater straw yields for 100 and 150 than 0 and 50 kg N ha−1 (Table 5) suggest that increasing N fertilization rate increased straw yield due to enhanced N availability. However, a non-significant difference in straw yield between 100 and 150 kg N ha−1 indicates that further increases in N fertilization rate beyond 100 kg N ha−1 did not affect straw yield. Increased spring and winter wheat straw yields with increasing N fertilization rates have been reported by several researchers in central Montana and southern Idaho, USA [2,19]. Enhancing straw yield using improved management practices is not only important for increasing grain yield, but also for increasing C and N inputs to the soil for promoting C and N sequestration, for conserving soil and water, and for reducing weed pressure [27].
4.4. Grain Yield
Enhanced soil water conservation due to the absence of plants during the fallow period may have increased spring wheat grain yield for CTWF and NTWF than other cropping systems at most N fertilization rates in 6 out of 8 years (Figure 2 and Figure 3), a case similar to that observed for straw yield. Our results are similar to those reported by several researchers [2,28] who found that spring and winter wheat grain yields were greater following fallow than following pea and spring wheat at all N fertilization rates in central Montana and North Dakota, USA. However, other researchers [13,15] showed that spring wheat grain yields were not different between spring wheat–fallow and spring wheat–pea rotations in North Dakota and Nebraska, USA. This happened in 2014 and 2015 in our study when grain yield was either similar to or greater for NTWP than CTWF and NTWF. Adequate precipitation during the growing season and normal air temperature during the grain filling stage in July (Table 1) may have enhanced N availability from increased mineralization of pea residue compared to wheat residue, thereby resulting in similar or greater grain yield for NTWP than CTWF and NTWF in these years. A lack of difference in grain yield between CTWF and NTWF at all N fertilization rates and years shows that tillage has no effect on grain yield. Similar results in spring wheat grain yield between till and no-till fallow have been reported by Johnston et al. [29]. Increased grain yield for NTWP compared to NTCW at most N fertilizations rates in 6 out of 8 years indicates that pea increased spring wheat grain yield by increasing soil water content and N supply from its residue and reducing the infestation of weeds and pests, similar to those obtained for straw yield. Lenssen et al. [8] demonstrated that pea uses less soil water than spring wheat, thereby increasing the amount of water available for succeeding spring wheat for enhanced yield. Increased spring wheat grain yield following pea compared to following spring wheat have been reported by a number of researchers [17,30,31].
The reduced impact of N fertilization rate on grain yield for CTWF and NTWF compared to NTWP and NTCW was likely due to high soil NO3-N content. Soil NO3-N content was greater for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at N fertilization rates ≤100 kg N ha−1 (Table 2). Spring wheat does not respond to increasing N fertilization rate when soil NO3-N content is high [17,22,32]. In contrast, lower soil NO3-N content may have resulted in a linear or nonlinear response of grain yield with increasing N fertilization rate for NTWP and NTCW in all years, except in 2015. Grain yield response to increasing N fertilization rate was either negative or slow in 2017 when the growing season precipitation was lowest (100 mm) (Table 1). Halvorson et al. [22] reported that spring wheat yield was better with increasing N fertilization rate when the growing season precipitation was >260 mm in dryland cropping systems. Increased spring wheat grain yield with increasing N fertilization rate has been reported by numerous researchers [20,21,33,34]. Various researchers [21,23,35,36] have demonstrated that maximum spring wheat grain yield occurred at 105–168 kg N ha−1, depending on soil and climatic conditions and management practices. Our maximum spring wheat grain yield of 3.72 Mg ha−1 at 115 kg N ha−1 for NTCW (Figure 4A) was between these ranges.
Grain yields were similar or greater for NTWP with 0 kg N ha−1 than NTCW with 50 kg N ha−1, for NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 than NTCW with 100 kg N ha−1, and for NTWP with 100 kg N ha−1 than NTCW with 150 kg N ha−1 (Figure 4A). This suggests that sustainable grain yields can be obtained by reducing N fertilization rate by 50 kg N ha−1 when NTWP instead of NTCW is used for growing spring wheat in dryland cropping systems. Reducing N fertilization rate can also sustain soil health and environmental quality by decreasing soil acidity, N leaching, and N2O emissions, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming [20,21]. Using CTWF and NTWF with increasing N fertilization rate to enhance grain yield is not recommended because the fallow system has numerous disadvantages, such as the reduced response of grain yield to increasing N fertilization rate, decreased annualized yield, and lower soil health, precipitation-use efficiency, and net return for crop–fallow compared to continuous cropping [3,4,5,7].
4.5. Harvest Index
Increased grain yield compared to aboveground biomass (grain plus straw yield) increased the harvest index for NTWF compared to NTCW in 2013, for NTWF and NTCW compared to CTWF in 2014, and for NTCW in 2015 (Table 4). In 2013 and 2014, when the growing season precipitation was above-the average (Table 1), increased soil water conservation by no-tillage and fallow practices may have increased grain yield relative to aboveground biomass, thereby increasing the harvest index for NTWF in those years. The reverse trend occurred during the below-average growing season precipitation in 2015 when increased grain yield relative to aboveground biomass increased the harvest index for NTCW. These results indicate that higher soil water content due to above-average precipitation favored more grain than aboveground biomass yield, thereby increasing the harvest index in the crop–fallow system. In contrast, greater grain relative to straw yield during below-average precipitation increased the harvest index in the continuous cropping system. Greater grain yield than aboveground biomass also increased the harvest index in 2013 due to higher growing season precipitation than other years.
4.6. Grain Test Weight
The decreased spring wheat grain test weight with increasing N fertilization rate for most cropping systems and years (Figure 5 and Figure 6) reflects the fact that spring wheat grains become less dense at higher N fertilization rates, probably due to increased grain yields. Several researchers [19,24] have reported that spring wheat grain test weight decreased with increasing N fertilization rate. However, the reasons for increased test weight for CTWF and NTCW with increasing N fertilization rate in 2013, 2017, and 2019 were not known. Similar or lower test weights for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at most N fertilization rates and years were probably due to increased grain yield (Figure 1 and Figure 2). An exception, however, occurred in 2019, where the reasons for greater test weight for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at all N fertilization rates were not known. It is likely that lower air temperature favored increased grain size for CTWF and NTWF in 2019. Carr et al. [31] and Amato et al. [37] found that crop rotation had inconsistent effect on spring wheat grain test weight in North Dakota and Nebraska, USA.
The greater grain test weight for NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 than NTWP and NTCW with 100 and 150 kg N ha−1 (Figure 4B) was probably due to increased N supplied by pea residue and reduced N fertilization rate to spring wheat. This indicates that N fertilization rate can be reduced by one-half to one-third using NTWP and can still sustain spring wheat grain size compared to using NTCW with higher N fertilization rates. Nyiraneza et al. [38] reported that spring wheat grain test weight of ≥75 kg hL−1 is desirable for higher prices, which can be achieved by using NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1.
4.7. Grain Protein Concentration
Greater N availability from increasing N fertilization rate probably increased spring wheat grain protein concentration with increasing N fertilization rate for most cropping systems and years (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Increased spring wheat grain protein concentration with increasing N fertilization rate have been reported by various researchers [18,20,21,23,33]. However, the significant nonlinear relationship between N fertilization rate and protein concentration for CTWF in 2016 and 2019 and decreased or non-difference in protein concentration with increasing N fertilization rate for CTWF and NTWF in 2013, 2015, and 2017 suggest that increasing N fertilization rate had a slight or negative effect on protein concentration for crop–fallow rotations compared to continuous cropping. This may be due to high residual soil NO3-N content (Table 2), which resulted in the slow response to increasing N fertilization rate in protein concentration for CTWF and NTWF. Ortiz-Monastero et al. [39] found that increasing N fertilization rate decreased grain protein concentration in spring wheat.
Increased soil NO3-N content likely increased grain protein concentration for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at most N fertilization rates in 3 out of 8 years (2013, 2017, and 2019). Carr et al. [13] observed that spring wheat grain protein concentration was greater for spring wheat–fallow than continuous spring wheat in western Montana. However, similar protein concentration between NTWP and NTWC at all N fertilization rates in 6 out of 8 years suggests that grain protein concentration was not affected by the type of crop in the crop rotation, regardless of N fertilization rates. This is similar to results reported by Carr et al. [31], who observed that spring wheat grain protein concentration was not different between spring wheat–pea rotation and continuous spring wheat in western North Dakota, USA. In contrast, Lafond et al. [16] and Miller et al. [17] showed that spring wheat following pea had 3–9% greater protein concentration than following spring wheat in western Montana, USA, and western Canada. Because these areas receive 50–100 mm more annual precipitation than our site, increased N mineralization from pea residue due to greater soil water availability from increased precipitation may have increased spring wheat grain protein concentration following pea compared to following spring wheat in these sites. The similar protein concentration between CTWF and NTWF at all N fertilization rates (Figure 4C) suggests that tillage had no effect on protein concentration. Our results contrast with those found by Carr et al. [31], who demonstrated that spring wheat grain protein concentration was greater in conventional till than no-till in western North Dakota, USA. This may be due to differences in soil and climatic conditions between the study sites. Increased N availability due to greater mineralization of soil organic matter from tillage in sandy loam soil and higher precipitation (429 mm) may have increased spring wheat protein concentration in North Dakota compared to slower mineralization in loam soil and lower precipitation (396 mm) in our site.
Average grain protein concentration across years was lower for NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 (126 g kg−1) than NTWP and NTCW with 100 and 150 kg N ha−1 (136–145 g kg−1) (Figure 4C), indicating that N fertilization rate >50 kg N ha−1 is required to boost protein concentration using NTWP. The critical spring wheat protein concentration to maintain grain quality is 128–140 g kg−1 [18]. To reach this protein level, N fertilization rate between 54 to 111 kg N ha−1, as predicted by the regression equation, is required when NTWP is used. The CTWF and NTWF with or without N fertilization and NTCW with 100–150 kg N ha−1 can also be used to reach this protein level. However, because of the negative consequences of these cropping systems in annualized grain yield, soil health, and environmental quality, these cropping systems with or without N fertilization are not recommended to enhance spring wheat grain protein concentration in dryland cropping systems of the US northern Great Plains.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study revealed that spring wheat plant density, straw and grain yields, and grain protein concentration were greater, but grain test weight was lower for CTWF and NTWF than NTWP and NTCW at most N fertilization rates and years. Increasing N fertilization rate increased grain yield and protein concentration but reduced grain test weight more for NTWP and NTCW than CTWF and NTWF. Because of the non-significant difference in grain yield and grain test weight among NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 and NTCW with 100–150 kg N ha−1, NTWP with 50 kg N ha−1 can be used to sustain spring wheat grain yield and grain size compared to NTCW with 100–150 kg N ha−1. This helps to reduce the N fertilization rate by one-half to one-third, thereby reducing farm input cost and sustaining soil health and environmental quality. Although CTWF and NTWF can enhance spring wheat growth, yield, and quality compared to NTWP and NTCW, these cropping systems are not recommended to sustain dryland grain yield and quality due to their adverse effect on annualized grain yield, soil health, and environmental quality.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15081806/s1, Table S1: Spring wheat and pea yields from GRACEnet plots (2012–2019). Table S2: Test Weight.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Data analysis, Writing—original draft, and Writing—review and editing, U.M.S.; Methodology, Data curation, Plot maintenance, Investigation, and Writing—review and editing, G.P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We are sincerely grateful for the field assistance and data collection provided by Michael Johnson; Mark Gaffri, Joy Barsotti, Chloe Turner, and James Allen for plot management; and for Chloe Turner, Nancy Webb, and Margaret Duffy for collection and analysis of soil and plant samples. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by USDA. The USDA is an equal opportunity employer.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
CTWF, conventional till spring wheat–fallow; NTCW, no-till continuous wheat; NTWF, no-till spring wheat–fallow; and NTWP, no-till spring wheat–pea.
References
- Alan, R.E. Wheat. In Hybridization of Crop Plants; Fehr, W.R., Hadley, H.H., Eds.; ASA, CSSA, and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1980; pp. 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Chen, C. Tillage, crop rotation, and nitrogen management strategies for wheat in central Montana. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, A.L.; Tanaka, D.L. A conservation tillage system study in the northern Great Plains of the United States. In Soil Organic Matter in Temperate Agroecosystems: Long Term Experiments in North America; Paul, E.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; pp. 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aase, J.K.; Schaefer, G.M. Economics of tillage practices and spring wheat and barley crop sequence in the northern Great Plains. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Lenssen, A.W.; Caesar, T.; Waddell, J.T. Carbon sequestration in dryland soil and plant residue as influenced by tillage and crop rotation. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Wang, J.; Barsotti, J.L. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity affected by cropping sequence and nitrogen fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 78, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, J.J.; Peterson, G.A.; Westfall, D.G. Dryland cropping intensification: A fundamental solution to efficient use of precipitation. Adv. Agron. 1998, 64, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenssen, A.W.; Sainju, U.M.; Jabro, J.D.; Iversen, W.M.; Allen, B.G.; Evans, R.G. Crop diversification, tillage, and management system influence spring wheat yield and water use. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Gan, Y.; McConkey, B.G.; McDonald, C.L. Pulse crops for the northern Great Plains: I. Grain productivity and residual effects on soil water and nitrogen. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M. The impact of no-till crop rotation on dryland soil properties and crop yields. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 2796–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.M.; Horsey, R.D.; Martin, G.B. Impact of tillage and crop rotation on grain yield of spring wheat. I. Rotation effect. Crop Manag. 2006, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.C.; van Kissel, C. The nitrogen and non-nitrogen rotational benefits of pea to succeeding crops. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1996, 76, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.; Fordyce, S.I.; Lachowiec, J.; Bishop, S.; Fryer, H.K.; Dahlhausen, S. Replacing fallow with warm-season annual crops in dryland cropping systems. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4142–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.A.; Chen, C. Cropping system affect wheat yields, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrous oxide emissions. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeshall, S.T.; Easterly, A.C.; Werle, R.; Stepanovic, S.; Creech, C.F. Replacing fallow with pea in wheat production systems across western Nebraska. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 3329–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafond, G.P.; May, W.E.; Holzapfel, C.B.; Lemke, R.L.; Lupwayi, N.Z. Intensification of field pea production. Impact on agronomic performance. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Engel, R.E.; Holmes, J.A. Cropping sequence effect of pea and pea management on spring wheat in the northern Great Plains. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.S.; McCallum, J.D.; Reardon, C.L.; Engel, R.E. Nitrogen requirement to change protein concentration of spring wheat in semiarid Pacific Northwest. Agron. J. 2017, 107, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, O.S. Nitrogen fertility and residue management effects on dryland no-till hard red spring wheat. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2019, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Moulin, A.P.; Tremblay, N. Nitrogen management effects on spring wheat yield and protein concentration vary with seeding date and slope position. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, O.S.; Marshall, J.; Nambi, E.; Shafron, S.; Jayawardane, D.; Jackson, C.; Lamichhane, R.; Ansah, E.O.; McClintok, J. Spring wheat yield and grain quality response to nitrogen rate. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 2562–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Black, L.A.; Krupinsky, J.M.; Merrill, S.D.; Wienhold, B.J.; Tanaka, D.L. Spring wheat response to tillage and nitrogen fertilization in rotation with sunflower and winter wheat. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Nielsen, D.C.; Reule, C.A. Nitrogen fertilization and rotation effects on no-till dryland wheat production. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otteson, B.N.; Mergram, M.; Ransom, J.K. Seeding rate and nitrogen management effects on spring wheat yield and yield components. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, R.C.; Milliken, G.A.; Stroup, W.W.; Wolfinger, R.D. SAS System for Mixed Models; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Heggenstaller, A.H.; Moore, K.J.; Liebman, M.; Anex, R.P. Nitrogen influences biomass and nutrient partitioning by perennial, warm-season grasses. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Amado, C.; Trujillo-Negrellos, E.; Molero, G.; Reynolds, M.P.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Foulkes, M.J. Optimizing dry matter partitioning for increased spike growth, grain number, and harvest index in spring wheat. Field Crops Res. 2019, 240, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.M.; Martin, G.B.; Poland, W.W. Yield and quality of hard red spring wheat cultivars following fallow and wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2001, 81, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.M.; Larney, F.J.; Lindwell, C.W. Spring wheat and barley response to long-term fallow management. J. Prod. Agric. 1995, 8, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.A.; Soon, Y.K.; Azooz, R.H. Modified no-till and crop sequence effects on spring wheat production in northern Alberta, Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 65, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.M.; Martin, G.B.; Horsey, R.D. Wheat grain quality response to tillage and rotation with field pea. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.A.; Zentner, R.P.; Selles, F.; McConkey, B.G.; Dyck, F.B. Nitrogen management for spring wheat grown annually on zero tillage. Yield and nitrogen-use efficiency. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, K.D.; Ma, B.L.; Xue, A.G. Planting date and nitrogen effects on grain yield and protein content of spring wheat. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmaha, B.S.; Sims, A.L.; Wisersna, J.J. Impact of nitrogen fertility on the production and performance of four hard red spring wheat cultivars. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Steiner, J.J.; Wright, S.D.; Bhangoo, M.S.; Millhouse, D.E. Intensive crop management practices on wheat yield and quality. Agron. J. 1990, 82, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Li, L.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Z.; Cai, L.; Wang, L. Long-term nitrogen addition impact on agronomic traits, nitrogen uptake, and nitrogen resorption efficiency of wheat in a rainfed region. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Ruisi, P.; Frenda, A.S.; Di Miceli, G.; Sala, S.; Plaia, A.; Giambalvo, D. Long-term tillage and crop sequence effects on wheat grain yield and quality. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiranez, J.; Cambouris, A.N.; Zaidi, N.; Tremblay, N.; Nolin, M.C. Spring wheat yield and quality related to soil texture and nitrogen fertilization. Agron. J. 2012, 104, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Monastero, J.I.R.; Penna, R.T.; Sayre, K.D.; Rajaram, S. CIMMYT’s genetic programs in wheat grain quality under four nitrogen rates. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).