Abstract
Castanea mollissima Bl. is rich in nutrition and strong in stress resistance, and has nutritional, economic, and ecological values. A protoplast is impactful in somatic fusion and germplasm creation. Here, we propose an effective scheme for the construction of an embryonic suspension cell, protoplast isolation, and fusion. Studies have shown that when 1.0 g yellow loose embryonic callus was inoculated into MS + 1.5 mg∙L−1 6-BA + 0.2 mg∙L−1 NAA + 0.5 mg∙L−1 2, 4-D liquid medium, a stable suspension cell line can be obtained. After further culturing for 2–4 days, protoplast isolation was performed. First, single-factor screening was conducted on the four enzymes, and then a two-factor random block was further set up to screen the enzyme combinations based on the results. We found that 1.0%cellulase R-10 + 0.5%pectolase Y-23 led to the highest protoplast yield (9.27 × 106/g FW) and the highest activity (92.49%). Furthermore, the protoplast yield could be increased to 9.47 × 106/g FW by adding 0.4 M mannitol and shaking for 8 h. The protoplasts were purified by centrifuging at 40× g for 4 min and then mixed with 30% PEG 6000 at a volume ratio of 1.5:1 for 25 min. The fusion rate could reach 70.00%. This study laid a foundation for the creation of new germplasm by Castanea mollissima Bl.
1. Introduction
Castanea mollissima Bl. belongs to the Castanea genus of Fagaceae. It is one of the three major woody grain species in China [1].The seed contains a lot of starch, as well as nutrients such as protein, fat, and vitamins [2]. Chestnut exhibits remarkable stress resistance, and the PAT gene family plays a crucial role in this process. It was involved in the regulation of responses to salt stress, drought stress, and disease resistance [3]. Chestnuts are of excellent quality and possess nutritional, economic, and ecological values [4,5]. Traditional crossbreeding is mostly used in the breeding of chestnut varieties, and the breeding efficiency is low [6,7]. The application of modern biotechnology helps to overcome the limitations of crossbreeding. In recent years, tissue culture and other biotechnologies have been successfully applied in chestnut plants at home and abroad, and certain progress has been made in callus induction, somatic embryogenesis, and plant regeneration [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
The suspension cells obtained by EC (embryonic callus) through suspension culture have the advantages of unified origin and consistent genetic background. Meanwhile, the growth conditions of suspension cells are easy to control and the cell totipotency is good [18,19]. Plant suspension cells are considered to be one of the ideal materials to obtain protoplasts, which can improve the efficiency of protoplasmic preparation. Therefore, a stable plant cell suspension system plays a great role in promoting the acquisition of highly active and high-yield protoplasts. Suspension cell culture refers to the technique of transferring callus to liquid medium under aseptic in vitro, and finally obtaining dispersed cells or small cell clusters by shaking, so that it can maintain a good growth state and can continuously proliferate [20]. In 1975, Wilson et al. [21] established a suspension system for woody plant rubber. In 1991, the suspension cell system of the woody plant poplar was also established in China [22]. After a long period of development, China has also made a series of progress in the study of suspended cells in woody plants, such as establishing embryonic suspended cell lines and preparing protoplasts for culture and regeneration research [23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
Cell fusion technology can fuse somatic cells from different sources into hybrid cells. These hybrid cells can be cultivated to form new hybrid plants. This technology breaks through the obstacles of traditional hybrid sexual reproduction and makes long-distance hybridization possible [30,31]. This technology has been widely used in plant breeding such as citrus [32], oil tea [23], cotton [33,34], etc. The precondition of cell fusion technology is to isolate a large number of intact and active protoplasts from plant tissues. A protoplast is a kind of plant cell with totipotency that has undergone cell wall removal [35]. It is a suitable material for transgene and cell fusion. After cell wall removal, cell fusion can be promoted more effectively [36].
Protoplasts are mostly obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis, so the variety and concentration of enzymes, the time, temperature, osmotic pressure, and other factors affect the yield and activity of protoplasts [37]. There are many ways to obtain protoplasts, including leaves [38], callus [39], hypocotyl [40], suspension cells [41], young suckers [42], roots [43], etc. However, there are differences in protoplast separation conditions among different material sources or organs of the same plant [44]. Dahlia petal and leaf protoplasts were isolated through the same enzymatic digestion with 0.5% macerozyme, 1.0% cellulase, and 0.4% pectinase. Petal protoplasts were applied in 1.0 mol/L mannitol for 10 h, while leaf protoplasts were applied in 0.8 mol/L mannitol for 4 h [45].Therefore, in order to obtain a large number of protoplasts with high activity for cell fusion experiments, it is very important to establish a protoplast separation system.
As far as we know, Zhao et al. [46] conducted a preliminary exploration of enzyme concentration, combination, and time during the protoplast separation process of chestnut hypocotyl, but studies on suspension culture and protoplast fusion of chestnut have not been reported. Therefore, it is of great significance to establish the suspension culture, protoplast separation, and protoplast fusion system of chestnut. In this study, an effective method was established for the formation of embryonic suspension cell lines induced by embryonic callus, and an effective scheme for the separation, purification, and fusion of protoplasts of chestnut was established.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Embryogenic Callus Acquisition
According to the previous study, the young leaves of 3–4 seedlings that were fully stretched were selected, disinfected with 75% alcohol and 0.5% NaClO disinfectant, and then cut into small pieces of 0.5 cm2 after cleaning. Then, they were inoculated in Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 1.5 mg∙L−1 6-benzyleaminopurine (6-BA) and 0.1 mg∙L−1 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA). The entire process was completed in the dark. After 3–4 weeks of culture, the callus with good growth were subcultured. The subculture medium was MS + 1.0 mg∙L−1 6-BA + 0.2 mg∙L−1 NAA, and the medium was changed every 15 days, and yellow loose EC was cultured 2 times [17].
The reagents used in this study were purchased from the following sources: Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (Qingdao Hope Bio-Technology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China); 6-benzyleaminopurine, 1-naphthaleneacetic acid and 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China); cellulase R-10, macerozyme R-10, pectolase Y-23, and MES (Beijing Biodee Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China); CaCl2∙2H2O, NaH2PO4∙2H2O, NaCl, CaCl2, KCl and MgCl2 (Modern Oriental Technology Development Co., Ltd., Beijing, China); FDA (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China); all types of PEG (Biorigin Inc., Beijing, China).
2.2. Establishment of Suspension Culture System
The EC was crushed with tweezers and transferred to a 100 mL triangular bottle with 40 mL liquid medium at different inoculations (0.5 g, 1.0 g, 1.5 g, 2.0 g) for suspension culture. Liquid callus induction medium MS + 30 g·L−1 sucrose was used as the basic medium [47], and different concentrations of plant growth regulators 6-BA, NAA, 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) were added (Table 1). The medium pH was 5.8–6.0.The culture was shaken at 110 rpm on a shaker in the dark [48], at a temperature of 25 °C. The culture was replaced once a week with fresh liquid medium, while pouring in 2/3 of the total volume to replace the same volume of the old, discarded medium. After changing the culture medium three times, a suspension cell line with good stability and uniform particle dispersion was obtained, which was then passed through a 150 μm mesh size sterile steel sieve [41].

Table 1.
The hormone combination of cell suspension culture.
From the day when the stable suspension line was subcultured, the suspension cells were taken every 2 days for the determination of cell growth. An amount of 2 mL of the suspended substance was centrifuged at 4500 r·min−1 for 5 min and was weighed, which is the fresh weight. After being dried at 60 °C for 12 h, the weight was measured, which is the dry weight (DW) [49].
The cell conditions in the suspension were observed after the cell line was stabilized. Nearly round cells refer to cells that were round, oval or kidneyshaped. These cells were relatively small in size, had more contents, thicker cytoplasm, and vigorous cell division and growth. The abundant presence of nearly round cells indicates that the suspension cell line tends to be stable, which is the best period for protoplast isolation [50].
2.3. Exploration of Protoplast Separation Conditions
Material enzymatic hydrolysis: Suspension cells were subcultured for 2–4 days for protoplast isolation (the optimal hormone conditions screened out by suspension culture continued to be used, and the medium was still MS medium). The ratio of suspension cells (fresh weight) to enzymatic hydrolysis solution was 1:10. The types of enzymes include cellulase R-10, macerozyme R-10, and pectolase Y-23. The enzyme was dissolved using the enzymatic hydrolysate. The composition of the enzymatic hydrolysate was 5.63 mM·L−1 MES, 24.49 mM·L−1 CaCl2·2H2O, 7.05 mM·L−1 NaH2PO4·2H2O, and the corresponding mass fraction of mannitol. For the enzymolysis solution formula, refer to Yu [23]. All treatments were placed on a shaker at 50 rpm and subjected to darkness for enzymatic hydrolysis.
Enzyme type and concentration test design: Under the same conditions, we determined different enzyme types and corresponding concentrations. The single factor level of various factors in the process of the experiment for cellulase R-10 (1.0%, 1.5%, 2.0%, 2.5%), pectolase Y-23 (0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, 2.0%), and macerozyme R-10 (0.25%,0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%). Based on the appropriate enzyme types and concentration ranges obtained from the pre-experiment, the enzyme combinations in the enzymatic hydrolysate were further screened (Table 2). The reference concentration of mannitol was 0.5 M, the time was 10 h, and the temperature was 25 °C.

Table 2.
Suspension cell line protoplast separation enzymolysis combination.
Mannitol concentration test design: At a fixed time (10 h), temperature (25 °C), and enzyme type and concentration (1.0% cellulase R-10 and 1.0% macerozyme R-10 [41]), the mannitol concentration was adjusted. The concentration levels of mannitol were 0.3 M, 0.4 M, 0.5 M, and 0.6 M.
Separation time test design: The time was adjusted at a fixed temperature (25 °C), mannitol concentration (0.5 M), and enzyme type and concentration (1.0% cellulase R-10 and 1.0% macerozyme R-10). The time range was 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 10 h, and 12 h.
Separation temperature test design: We adjusted the temperature at a fixed time (10 h), mannitol concentration (0.5 M), and enzyme type and concentration (1.0% cellulase R-10 and 1.0% macerozyme R-10). Temperature conditions: 24 °C, 26 °C, 28 °C.
2.4. Purification of Protoplasts
The protoplasts were washed and purified by the centrifugationmethod [24]. After enzymolysis, a 40 μm cell strainer was placed on a 50 mL centrifuge tube to filter the incomplete enzymolysis residue and then transferred to a 10 mL centrifuge tube, centrifuged at the corresponding rotation speed (20× g, 40× g, 60× g, 80× g, 100× g) for 4 min, and the supernatant was carefully removed. Care must be taken not to suck up the protoplasts that settle on the bottom.An equal volume of W5 solution (154 mM NaCl, 125 mM CaCl2, 15 mM MES, 5 mM KCl) was carefully added, the overlying liquid above the sedimented cells was gently aspiratedusing a pipette tip minus the narrow tip to clean the cells (the pipette tip minus the narrow tip should be used in the subsequent aspiration and cleaning steps),then centrifuged at the corresponding rotational speed for 4 min, carefully discarding the supernatant, and washed with W5 solution repeatedly, and transfered to MMG (corresponding mass fraction of mannitol, 15 mM MES, 15 mM MgCl2) solution for washing once. Then, it was stored in MMG solution with mannitol to keep the osmolality of protoplasts stable.
2.5. Protoplast Yield and Viability Assessment
The purified protoplasts were counted with a blood cell counting plate under a biological microscope (DM2500, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). The counting and yield calculation methods refer to Wang [51] and Kang [52]. Each sample was counted 3 times, and the average value was taken, and the protoplast yield was calculated according to the following formula:
Protoplast yield = total number of protoplasts in 5 large cells ×5 × 104 × dilution ratio
Y = n × p/FW
In Equation (2), Y is the protoplast yield (protoplast/g), that is, the number of protoplasts per gram of fresh explant weight (FW); n is the number of protoplasts/mL; p is the volume of protoplast suspension (mL); and FW (g) is the mass of suspended cells after centrifugation enrichment.
To test protoplast viability, 100 µL of protoplasts were stained with 10 µL 0.1% FDA in the centrifuge tube. The incubation time was 5 min. Protoplasts were observed under a biological microscope (Leica DM2500, Germany).Protoplasts that emit green fluorescence at 488 nm were regarded as living protoplasts, while dead protoplasts were not stained [53,54]. We counted each sample 3 times, took the average value, and calculated the protoplast activity according to the following formula:
Protoplast viability = (number of green fluorescent protoplasts/total number of observed protoplasts) × 100
Protoplast net yield = protoplast yield × protoplast viability
2.6. Protoplast Fusion
After purification, the protoplasts of the suspended cells were adjusted to 1 × 106 protoplasts/mL. The protoplasts were aspirated with a short pipette tip and dropped onto a culture dish. After standing for 15 min, Polyethylene glycol (PEG) was gently added to the culture dish to induce the fusion between the protoplasts. Initially, different types of PEG (PEG 4000, PEG 6000, PEG 8000) at the same concentration were added to induce fusion; then, the influence of different volume ratios of protoplasts to PEG solution (1.0, 1.5, 2.0) on the fusion results was examined. After this step, we examined the influence of different processing times (15 min, 25 min, 35 min) on protoplast fusion; finally, the effects of different concentrations (25%, 30%, 35%, 40%) of PEG on protoplast fusion were explored.
2.7. Data Processing and Analysis
Excel 2007 was used for data processing, SPSS26.0 was used for variance analysis, and the Duncan method was used for difference significance comparison.
3. Results
3.1. Establishment of Embryonic Suspension Cell Lines
In general, the growth of suspended cells is directly related to the initial cell density. Different qualities (0.5 g, 1.0 g, 1.5 g, and 2.0 g) of the loose EC were used as test materials to determine the optimal initial inoculation amount. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the growth of suspended cells in treatment 2 (1.0 g) showed an “S” type growth curve (Figure 1), and the growth of suspended substances in 0–2 days was small and retarded. After 2 to 4 days, the cell growth increased significantly and entered the logarithmic stage, which was the most obvious stage of cell proliferation, growth, and development, and the DW reached 0.26 g. After 4–6 days, cell growth gradually stabilized, and the growth rate gradually decreased. Since the suspensions of the logarithmic growth phase are most suitable for protoplast separation, 1.0 g is the most appropriate initial inoculation amount. It was observed that in the early stage of suspension culture, the cells basically did not proliferate, and then, began to divide. With the extension of subculture time, the cells gradually divided and aggregated to form small embryonic cell clusters. After several successive cultures, the suspended cell lines were gradually stabilized, and the suspended cell clusters were uniform in size, and the suspensions were milky white.
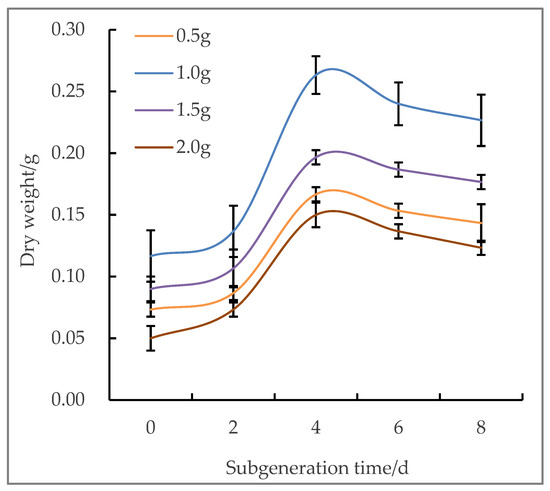
Figure 1.
Dry weight of callus with different inoculation amounts on different days.
The combination of 6-BA, NAA, and 2,4-D at different concentrations had significant effects on the state of chestnut suspension cells (Table 3). The 6-BA concentration had a great effect on the cell state; it can be seen that it has a significant influence on the test results from Table 4. At moderate concentration (1.5 mg∙L−1), the live cell rate and near-round cell rate were higher, and the suspension was milky white (Figure 2a), and the cells reached a good state (Figure 2b). 2,4-D had a greater effect on the state of suspended cells than NAA, and the addition of a higher concentration of 2,4-D (0.5 mg∙L−1) was relatively helpful in improving the rate of round cells and viable cells, and the suspension was in a milky and stable state (Figure 2c,d). When the concentration of the three hormones is low, the suspension is prone to browning (Figure 2e) and greater cell breakage (Figure 2f). In treatment 5, the active cell rate reached 86.66% and the near-round cell rate reached 87.54%, and the suspension state also reached its best. In summary, the most suitable culture conditions for chestnut suspension cell culture were MS + 6-BA 1.5 mg∙L−1 + NAA 0.2 mg∙L−1 + 2,4-D 0.5 mg∙L−1.

Table 3.
Effects of plant growth regulator ratio on suspended cells and suspension cultured for 4 days.

Table 4.
The test results of variance analysis of the hormone combination test in suspension culture.
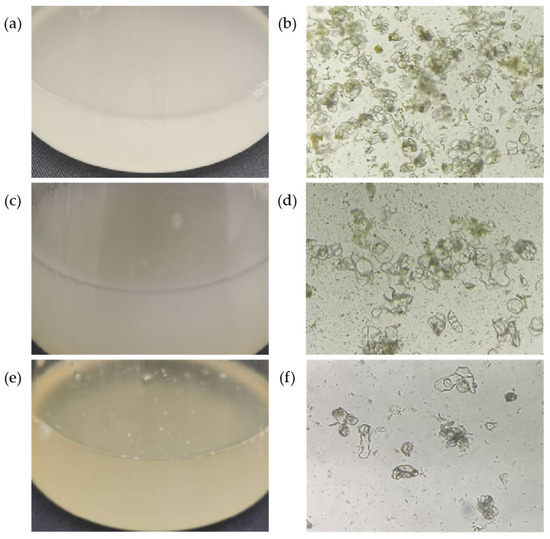
Figure 2.
Suspension and cell observation of different stabilities for 4 days of suspension culture. (a) Milky white suspension with good stability; (b) stable, active cells. There are many of them and they are close to being round. (c) Milky suspension with general stability; (d) cells with general stability and activity. The cells are in a long strip shape and have poor activity. (e) Brown suspension with poor stability; (f) cells with very poor stability. The cells were fragmented in large quantities and there was a large number of dead cells after staining.
3.2. Study on Protoplast Separation Enzyme Concentration in Suspended Cell Lines
The suspension cells cultured for 4 days were selected for the preparation of protoplasm, and protoplasts were prepared by adding a single enzyme type. The results showed that when only cellulase R-10 and only pectolase Y-23 were added, the enzymatic hydrolysis of the protoplasts was better, and the yield and viability of the protoplasts remained at a relatively high level (Figure 3a,b). The protoplasts were relatively complete and round, but there was still a certain cell wall. When only macerozyme R-10 was added, was there more fragmentation of the cell wall (Figure 3c). When only hemicellulase was added, the cell walls were largely broken, and the yield and viability were at a low level (Figure 3d).
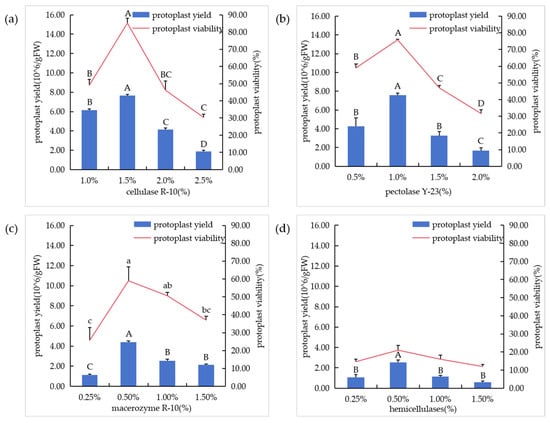
Figure 3.
Effects of different enzyme types on protoplasmic preparation. (a) Enzymolysis of different cellulase R-10 concentrations; (b) enzymolysis of different pectolase Y-23 concentrations; (c) enzymolysis of different macerozyme R-10 concentrations; (d) enzymolysis of different hemicellulase concentrations.In the figure, “A”, “B”, “C” and “D” means correlation is extremely significant at p < 0.01 level, “a”, “b”, “c” means correlation is significant at p < 0.05 level.
Further analysis of the single-factor test results of enzyme types showed that each single-factor level had a certain correlation with the net yield of protoplasts (Figure 4). However, under the action of hemicellulase at all levels, the net yield of protoplasts was relatively low, and more protoplasts were broken. Therefore, hemicellulase was not added in the subsequent experiments. Based on the results of the single-factor pre-experiment, we found that the protoplast net yield was higher at the level 2 of cellulase R-10, pectolase Y-23, andmacerozyme R-10. In conclusion, the enzymatic hydrolysis combination and concentration levels can be determined as shown in Table 2.
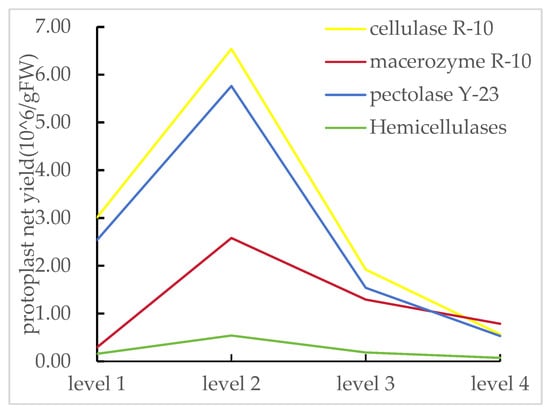
Figure 4.
Results of the net yield of protoplasts of enzyme types. Levels 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent different concentrations of various enzyme types.
In order to determine the optimal enzymolysis combination, different enzymolysis treatments were set as shown in Table 1. The results showed that different enzymolysis combinations and concentrations had significant effects on protoplast yield and activity (Figure 5a). For the addition of different concentrations of segregation enzymes, the combination of 1.0%cellulase R-10 + 0.5%pectolase Y-23 had the highest yield (Figure 5b), reaching 9.27 × 106/g FW, and the activity was 92.49% (Figure 5c). The difference between the addition of macerozyme R-10 and the addition of pectolase Y-23 treatment was that under the same cellulase R-10 concentration, the protoplast yield and activity decreased with the increase in macerozyme R-10 concentration. Under the same macerozyme R-10 concentration, the protoplast yield and activity increased with the increase in cellulase R-10 concentration. The opposite is true with the addition of pectolase Y-23. Overall, pectolase Y-23 performed better than macerozyme R-10. Therefore, 1.0% cellulase R-10 + 0.5% pectolase Y-23 is the best combination.
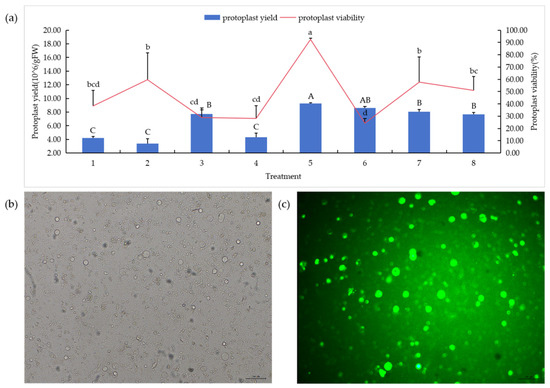
Figure 5.
Effects of different enzyme concentrations on protoplasmic preparation.Concentrations—1:1.0% cellulase R-10 + 0.5% macerozyme R-10; 2:1.0% cellulase R-10 + 1.0% macerozyme R-10; 3:1.5% cellulase R-10 + 0.5% macerozyme R-10; 4:1.5% cellulase R-10 + 1.0% macerozyme R-10; 5:1.0% cellulase R-10 + 0.5% pectolase Y-23; 6:1.0% cellulase R-10 + 1.0% pectolase Y-23; 7:1.5% cellulase R-10 + 0.5% pectolase Y-23; 8:1.5% cellulase R-10 + 1.0% pectolase Y-23. (a) Protoplast separation under different enzymolysis combinations; (b,c) 1.0% cellulase R-10 + 0.5% pectolase Y-23 combination of protoplasts in bright field and dark field. Bars = 50 μm. In the figure, “A”, “B”, “C” means correlation is extremely significant at p < 0.01 level, “a”, “b”, “c”, “d” means correlation is significant at p < 0.05 level.
3.3. Studies on Other Factors in Protoplast Separation of Suspended Cell Lines
In order to optimize the osmotic pressure in the enzyme solution, mannitol in the concentration range of 0.3–0.6 M was added. With the gradient change of mannitol concentration, the yield and activity of protoplasts first increased and then decreased (Figure 6a). When the dosage of mannitol was 0.4 M, the protoplast yield was 7.53 × 106/g FW and the activity was 85.0%. When the mannitol concentration exceeds this point, the yield and viability of the protoplasts decrease, and the degree of cell fragmentation increases, so the optimal concentration of mannitol in the enzyme solution is 0.4 M.
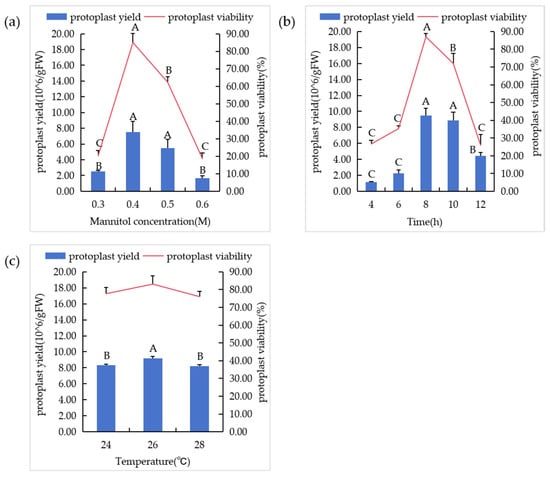
Figure 6.
Enzymolysis conditions of suspended cell lines. (a) The influence of mannitol concentration on protoplasts. (b) The influence of different enzymatic hydrolysis times on protoplasts. (c) The influence of different temperature conditions on protoplasts. In the figure, “A”, “B”, “C” means correlation is extremely significant at p < 0.01 level.
The effect of enzymolysis time on protoplast yield and viability was evaluated by setting a series of time gradients (Figure 6b). The yield of protoplasts increased from 1.13 × 106/g FW to 9.47 × 106/g FW when the enzymatic hydrolysis time was increased from 4 h to 8 h. At this stage, the protoplast activity was always high, and the activity reached 87.0% at 8 h. When the digestion time was longer than 8 h, the protoplast yield and activity decreased. Many protoplasts were destroyed and therefore could not survive. The results indicated that the protoplast yield and activity were the best when the enzymatic hydrolysis time was 8 h.
The results of protoplast separation were affected by different temperatures (Figure 6c). Three temperature gradients were set, and it was found that 9.20 × 106/g FW protoplasts could be obtained when the shaking table temperature was 26 °C, and the activity was up to 83.3%. However, the increase or decrease in temperature had a poor effect on the separation effect. Therefore, 26 °C was the best enzymatic hydrolysis temperature.
3.4. Protoplast Purification
The protoplasts were enriched and purified by centrifugal precipitation, and the centrifugal speed also had a great influence on the state of protoplasts (Figure 7a). When the rotation speed was 20× g, the protoplasts were intact and highly active, but there was still adhesion phenomenon. When the rotation speed was adjusted to 40× g, the protoplast dispersion was good, and the activity was high (Figure 7b). However, as the rotational speed gradually increased, the protoplast fragmentation increased, and when the rotational speed reached 100× g, the protoplasts were largely broken and basically inactive.
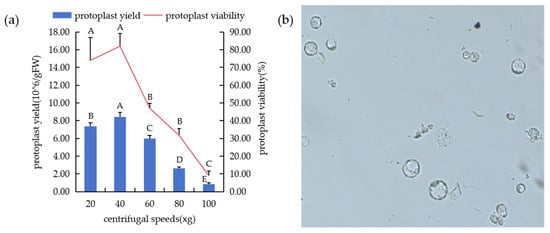
Figure 7.
Preparation of protoplasmic system at different centrifugation speeds. (a) Protoplast yield and activity at different rotational speeds. (b) The protoplasts were separated and purified at 40× g rotation speed, and the cells were dispersed and broken less. In the figure, “A”, “B”, “C”, “D”, “E” means correlation is extremely significant at p < 0.01 level.
3.5. PEG-Induced Fusion
Different types of PEG were used to induce protoplast fusion of suspended cells, and the results showed that there were significant differences in induction among different types of PEG. PEG 4000 induced a low fusion rate and PEG 8000 induced more cell fragmentation, which may be due to the increased toxic effect of PEG molecular weight on cells. PEG 6000 induced a good cell fusion effect; the fusion rate reached 56.83% (Figure 8a).
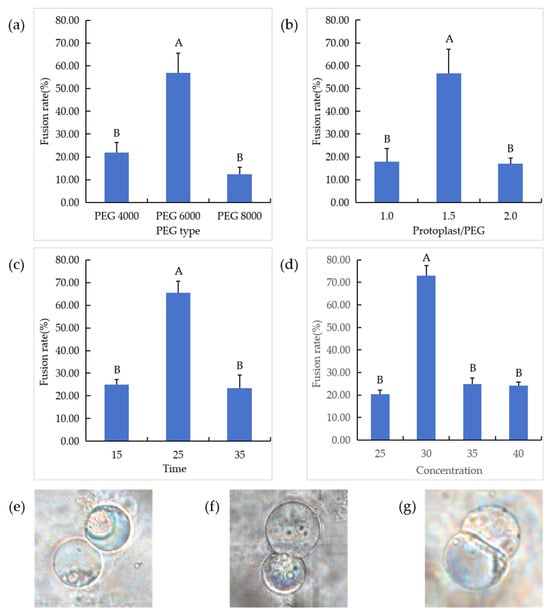
Figure 8.
Exploration of fusion conditions of suspension cell lines and cell fusion situations. (a) Protoplast fusion induced by different PEG types. (b) Different volume ratios of protoplasts to PEG; “1.0”: the protoplast was mixed with PEG in equal volume; “1.5”: protoplast volume was 1.5 times that of PEG; “2.0”: PEG was mixed with double protoplasts. (c) PEG 6000 induces fusion at different times; (d) PEG 6000 induces fusion at different concentrations; (e) two protoplasts are just in contact; (f) protoplast cell membrane fusion; (g) two protoplasts fuse to form a heterozygous cell.In the figure, “A”, “B” means correlation is extremely significant at p < 0.01 level.
The addition of different volumes of protoplasts in the PEG fusion solution had significant effects on the fusion results (Figure 8b). When the same volume of protoplasts was added to the PEG fusion solution, the contact of protoplasts was less and the fusion rate was lower. When the volume ratio of protoplasts to PEG was increased to 1.5:1, the protoplast fusion rate was greatly improved (56.71%). However, with the further increase in protoplast volume, the phenomenon of multiple fusion also increased, which was not conducive to the development of subsequent experiments.
PEG induction time also has an effect on protoplast fusion. In order to determine the appropriate induction time and calculate the protoplast fusion rate, a series of time gradients (15, 25, 35 min) were set in this study. The results showed that 25% PEG 6000 induction time had a significant effect on the protoplast fusion of suspended cells (Figure 8c). In the range of 15–25 min, the fusion rate between protoplasts continued to increase, and reached the highest (65.56%) at 25 min of continuous induction. Therefore, the optimal time of protoplast fusion of chestnut suspended cells was 25 min.
When the fusion time was 25 min, the fusion results were significantly different with different concentrations of PEG (Figure 8d). The results showed that pin–pair fusion was less in 25% PEG 6000 induction, and the fusion rate was 40.00%. Then, 30% PEG 6000-induced contact fusion between cells increased significantly; the fusion rate was as high as 70.00%. However, with the increase in PEG 6000 concentration, the fusion rate decreased and multiple fusion appeared in the cells, which was not conducive to the subsequent screening of dinuclear heterologous fusion cells. Therefore, 30% PEG 6000 is the optimal concentration for protoplast fusion of suspended cells. Under the action of PEG at this concentration, the two protoplasts gradually come together (Figure 8e), the cell membrane fuses (Figure 8f), and heterozygous cells are gradually formed (Figure 8g).
4. Discussion
Suspension cells have the characteristics of good dispersion, similar cell size, rapid growth, and good repeatability, and are good materials for protoplast separation. The physiological state and initial inoculation amount of callus played a decisive role in establishing a stable cell suspension system. In general, callus with fast growth rate and loose structure is more suitable for suspension culture. It was found that the stable cell suspension line could be obtained by adding 1.0 g loose and easily dispersed callus in 40 mL liquid medium, which was consistent with the results in Camellia [41] and Rose [55].The proportion of new and old liquid medium is also an important factor in the whole suspension culture process. In this study, 2/3 of the old liquid medium was substituted each time, and then fresh medium with the same volume as the discarded liquid was added. The growth curve of chestnut suspended cells showed an “S” shape, which was consistent with previous studies [55]. The “S” type cell growth curve includes a lag period (0–2 days) with slow growth and little biomass. This is followed by an exponential growth period (2–4 days), when the growth is rapid and the biomass reaches its maximum. Finally, there is a stable stage (4–8 days), during which the cell mass is stable and tends to decline.
Appropriate types and concentrations of exogenous hormones are the key factors for the rapid proliferation of suspension cells. The results of this study showed that the mass concentration of 2,4-D played a key role in the suspension of EC cells, and the cell density volume increased with the increase in 2,4-D concentration, which was consistent with previous studies [56].In this experiment, the cell suspension system of chestnut was established by using MS + 1.5 mg∙L−1 6-BA + 0.2 mg∙L−1 NAA + 0.5 mg∙L−1 2,4-D in combination with cytokinin and auxin.The suspension state of suspended cells, the rate of live cells and near-round cells, the growth amount of suspended cells, and the later growth of suspended cells are important indicators to determine whether the growth of suspended cells is normal and whether the suspension culture system is successfully established [47]. In this study, it was found that the cell stability in the milky suspended cell solution was good, and the rate of live cells reached 86.66% and the rate of near-round cells reached 87.54%, which was basically consistent with previous studies [28,29].
The stable suspension cell line was obtained, and then the separation conditions of its protoplasts were investigated. The main factors affecting the enzymatic separation of protoplasts include enzyme type and concentration, enzymolysis time, enzymolysis temperature, osmotic pressure, etc. [57]. The enzyme concentration in the enzymatic hydrolysis process should be appropriate. If the enzyme concentration is too large, the cell wall is excessively removed, and the harmful substances in the enzyme will damage the de-walled protoplast, resulting in a great reduction in the regeneration rate of the protoplast; if the enzyme concentration is too low, the enzymatic hydrolysis will be insufficient and the protoplast cannot be completely released [58]. The types and concentrations of enzymes required for protoplast separation of different plants are different. Wang [59] showed in her study that the enzymatic solution combination of 3.0% cellulase + 1.5% pectinase + 0.5% hemicellulase had a better effect on the protoplast of the embryonic cell suspension line of Chezi 312. In addition, the protoplasts with high yield and strong activity were separated by 3% cellulase and 1.0% segregation enzyme. The optimal concentration of the enzyme solution required for the enzymolysis of the suspended culture of Chinese jujube was cellulase 10 g/L + segregation enzyme 4 g/L, while winter jujube required cellulase 15 g/L + segregation enzyme 4 g/L [60]. In this study, it was found that when 1.0% cellulase R-10 and 0.5% pectolase Y-23 were used together, the protoplast preparation effect was the best, the yield was as high as 9.27 × 106/g FW, and the highest activity was 92.49%. Proper concentration of osmotic pressure can prevent protoplasts from breaking or contracting and maintain a normal physiological state. In this study, the use of 0.4 mol∙L−1 mannitol to separate protoplasts had the best effect, which was consistent with the results in oil tea [41] and tea [61]. The time is the key factor affecting the effect of enzymatic hydrolysis. Too short will lead to insufficient release of protoplasts and low yield. If the time is too long, the protoplast will break and the vitality will be reduced [60]. The optimum enzymolysis time in this study was 8 h.
There are many factors influencing PEG-induced protoplast fusion. The type of PEG is a key factor, and the use of high concentrations or high molecular weight PEGs results inmore cohesive protoplasts but less fused cytoplasm [62]. In this study, PEG 6000 has the best effect, and when the concentration of PEG 6000 is 30%, the fusion rate is the highest, up to 70.00%. PEG has a certain toxic effect on cells, causing irreversible damage to protoplasts [63]. The longer the fusion time, the worse the state. The results showed that the optimum fusion time of chestnut suspension cells was 25 min.
The protoplast is a good material for somatic cell hybridization [64], genetic transformation, and gene editing [64], because it easily accepts exogenous organelles and nucleic acids without the restriction of a cell wall. Protoplasts have regenerative ability and can differentiate into complete plants under suitable culture conditions [65]. Protoplast separation and cell fusion of an embryogenic suspension cell line provide a new method for chestnut breeding and a new idea for breeding new varieties of chestnut.
5. Conclusions
The most suitable inoculation amount for establishing a stable suspension system of chestnut cells was 1.0 g. The selected callus tissue should be yellow in appearance and loose in texture, representing embryogenic callus tissue. Adding 1.5 mg∙L−1 6-BA + 0.2 mg∙L−1 NAA + 0.5 mg∙L−1 2,4-D to the MS medium is beneficial for establishing a white, stable suspension system. The live cell rate reaches 86.66%, and the nearly spherical cell rate reaches 87.54%. The stable cell suspension system is taken and darkly enzymatically digested in the enzymatic solution containing 1.0% (w/v) cellulase R-10 + 0.5% (w/v) pectolase Y-23 for 8 h. The osmotic pressure regulator used is mannitol with a concentration of 0.4 M, and the shaking speed is 50 rpm; the shaking temperature is 26 °C. Under these conditions, high-yield (9.27 × 106/g FW) and highly active (92.49%) protoplasts can be obtained. The purification method of protoplasts is centrifugation precipitation, and the most suitable centrifugation speed is 40× g. After purification, the protoplasts (w/v):30%PEG 6000 (w/v) = 1.5:1, and is then placed in the petri dish for 25 min. Under this condition, the fusion rate between the protoplasts of the suspended cell line was the highest, up to 70.00%.This study proposed a more successful and productive way of devising an effective scheme for the construction of an embryonic suspension cell, protoplast isolation, and fusion of Castanea mollisisima Bl. to facilitate cell hybridization for improved cultivation properties of this economically important tree. Furthermore, it is also hoped that this research will provide assistance for the future fusion of chestnut cells of different genotypes to create new germplasm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, S.G.; resources, supervision, S.G. and R.Z.; methodology, writing—review and editing, S.Z. and S.G.; software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, visualization, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD2200400).
Data Availability Statement
The data associated with this study were not deposited into a publicly available repository before. All data are included in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Beijing Forestry University forsupport and assistance in experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| EC | embryonic callus |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog |
| 6-BA | 6-benzyleaminopurine |
| NAA | 1-naphthaleneacetic acid |
| 2,4-D | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid |
References
- Fan, X.Y.; Guo, S.J.; Li, Y.H.; Jiang, X.B. Study on correlation between browning degree of chestnut fruit and total phenols and flavonoids. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2023, 47, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.Y.; Guo, S.J. Comparative Analysis of Photosynthetic Traits, Yield, and Fruit Quality Among Different Chestnut Cultivars. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Nie, X.H.; Ge, J.Y.; Chu, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Xing, Y. Identification of PAT gene family members and analysis of their response to different stresses in Chinese chestnut. J. Fruit. Sci. 2024, 41, 847–860. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, L.; Liang, W.J. The Chinese Fruit Tree: Chestnut Hazelnut Roll; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Guo, S.J. Suitability Analysis and Distribution Prediction of Castanea mollissima under Climate Change. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2024, 60, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.L.; Lv, P.H.; Peng, S.B.; Yang, Y.; He, J.L. Research on callus induction and explant browning of chestnut (Castanea mollissima Bl.). J. Cent. South. Univ. For. Technol. 2016, 36, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.B.; Guo, S.J. Establishment and infl uencing factors of micropropagation system in mature Castanea mollissima. J. Cent. South. Univ. For. Technol. 2015, 35, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, K.; Cao, Q.; Qin, L. The MADS-box transcription factor CmAGL11 modulates somatic embryogenesis in Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume). J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrcedeh, T.; Seyed, M.H.N.; Hamid, J.; Dariush, B. Plant regeneration through indirect organogenesis of chestnut Castanea sativa Mill. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 7063–7069. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.J.; Sun, X.B.; Qin, T.T.; Liu, Z.M. Establishment and Optimization of in vitro Regeneration System of Mature Embryo of Castanea mollissima. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2015, 30, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Cheng, S.S.; Wang, J.J.; Qin, L.; Cao, Q.Q. Establishment and optimization of efficient micropropagation system in Castanea mollissima. J. Beijing Univ. Agric. 2013, 28, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Su, D.M.; Luo, L.H.; Yang, D.H. Research on Callus Induction of Chinese Chestnut. Nonwood For. Res. 2004, 22, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.C.; Lu, Z.G.; Theophilus, M.A.; Paul, E.R. In Vitro Callus Induction and Shoot Initiation of American Chestnut (Castanea dentata). J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2008, 30, 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet, S.; Hatice, D. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature cotyledons of European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2014, 50, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.J. Construction of the Primary Tissuecultivation System and Physiologicalanalysis of Explant Development in Chinese Chestnut. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology, Qinhuangdao, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.L.; Liu, B.; Li, X.W.; Tian, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, Q.Q. Functional research of transcription factor CmHAT1 regulating the development ofsomatic embryo in Castanea mollissima. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2024, 46, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.W.; Sun, Z.L.; Gao, Y.R.; Ge, J.Y.; Tian, Y.Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, S.K.; Fang, K.F.; Qin, L.; Cao, Q.Q. A strategy for establishing an efcient somatic embryo regeneration system in Castanea mollissima Blume. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2022, 150, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpoor, F.; Zare, N.; Asghari, R.; Mosadeg, S.P. The effect of plant growth regulators on the antioxidant enzyme activity and secondary metabolite production in the cell suspension cultures of Melia azedarach L. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dom, D.A.; Su, S.P.; Faisal, S.E.; Richard, T.J.; Zhang, X. Effect of Plant Growth Regulators on Osmotic Regulatory Substances and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of Nitraria tangutorum. Plants 2022, 11, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Peng, S.N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, R.; Miao, Y.H.; Liu, D.H. Establishment of cell suspension culture and genetic transformation systems for production of bioactive metabolites of medicinal plant Artemisia argyi Levl. et Vant. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2025, 161, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.M.; Street, H.E. The growth, anatomy and morphogenetic potential of callus and cell suspension cultures of Hevea brasiliensis. Ann. Bot. 1975, 39, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, M.R.; Chen, D.M.; Xu, M. A study on cell suspension culture and somatic embryogenesis of Populus simonii. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 1991, 9, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Y.; Xu, L.J.; Xu, X.S.; Yi, D.D.; Hou, S.L.; Yuan, D.Y.; Xiao, S.X. Embryogenic callus induction, proliferation, protoplast isolation, and PEG induced fusion in Camellia oleifera. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2024, 157, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhao, Z. Isolation and Purification of Mesophyll Protoplasts from Ginkgo biloba L. Jpn. Mendel. Soc. 2020, 85, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Mohamed, A.A.; Miao, M.; Pratsinakis Emmanouil, D.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, M.L.; Lftikhar, J.; Yousef Ahmed, F.; Madesis, P.; et al. Protoplast Isolation, Fusion, Culture and Transformation in the Woody Plant Jasminum spp. Agriculture 2021, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.X.; Huang, Q.; Lin, X.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Lai, C.C.; Cai, Y.Q. Rapid establishment of embryogenic cell suspensions and plan regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in litchi. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2007, 10, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q. Establishment of Grapevine Embryogenic Suspension System and Protoplast Isolation; Gansu Agricultural University: Lanzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.J. Studies on Cell Suspension Culture and Protoplast Isolation of Zanthoxylum bungeanum; Northwest A & F University: Xianyang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z. Studies on Suspension Cell Line Establishment and Protoplast Culture of Populus spp.; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, M. Somatic hybridization. Historical studies. Nat. Sci. 2018, 48, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.W.; Xia, G.M. The place of asymmetric somatic hybridization in wheat breeding. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.A.; Dutt, M.; Frederick, G.; Grosser, J.W. Somatic Embryogenesis: Still a Relevant Technique in Citrus Improvement In Vitro Embryogenesis in Higher Plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1359, 289–327. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.L.; Pu, Y.C.; Muhammad, A.A.; Kang, L.L.; Ye, Y.L.; Zhang, M.; Liang, C.Z.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhang, R.; Meng, Z.G. A Rapid and efficient method for isolation and Transformation of Cotton Callus Protoplast. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, S.H.; Fu, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Yang, X.B.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, D.M.; Li, J. Establishment of an efficient cotton root protoplast isolation protocol suitable for single-cell RNA sequencing and transient gene expression analysis. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Qiao, W.J.; Hu, F.; Jiang, H.S.; Zhu, S.F. A simple and effective method to encapsulate tobacco mesophyll protoplasts to maintain cell viability. MethodsX 2015, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyini, M.; Balaji, R.P.K. Isolation, Regeneration and PEG-Induced Fusion of Protoplasts of Pleurotus pulmonarius and Pleurotus florida. Mycobiology 2006, 34, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.D.; Shen, Y.B. Nitraria sibirica cell suspension culture:establishment, characterization and application. J. For. Res. 2017, 28, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, Z.X.; Xia, Y.; Jing, D.L.; Guo, Q.G.; Liang, G.L.; He, Q. An Efficient System for Mesophyll Protoplast Isolation, Purification, and Transformation in Loquat: Studies on Fluorescent Marker Analysis and Subcellular Localization. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.L.; Xie, X.Y.; Zhang, W.T.; Ma, Y.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Fu, F.F.; Wang, G.B.; Cao, F.L.; Yang, X.M. Development and application of a Ginkgo biloba L. callus-derived protoplast transient expression system for exploring the roles of GbMYB11 and GbbHLH3 in flavonoid metabolism. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 226, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shin, J.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, W.C. Establishment of efficient hypocotyl-derived protoplast isolation and its application in soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.). Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Ye, T.W.; Xu, X.; Yuan, D.Y.; Xiao, S.X. Callus induction, suspension culture and protoplast isolation in Camellia oleifera. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 286, 100193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.H.; Li, S.Y.; Du, C.J.; Gao, H.; Yang, D.; Fu, G.; Cui, H.T. Establishment of a Protoplasts-Based Transient Expression System in Banana (Musa spp.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- María, V.; Javier, G.Z.; Catalina, A.G.; Víctor, M.J. Protoplast isolation from different explant sources in pitahaya (Selenicereus costaricensis, Cactaceae): Insights from roots, callus, and shoot tissues. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2025, 161, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Naing, A.H.; Adedeji OS Kim, C.K. Protoplast technology in ornamental plants: Current progress and potential applications on genetic improvement. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 283, 110043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, D.; Tian, Y.B.; Tian, Z.; Duan, Q.; Ahmed, M.A.A.; Wang, L.H.; Wu, X.W. Efficient protoplast isolation and transient gene expression in dahlia (Dahlia sp.). Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2025, 19, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Chen, S.S.; Fang, K.F.; Xing, Y.; Cao, Q.Q.; Jiang, Y.C.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L. Isolation and purification of protoplasts from chestnut hypocotyl. J. Fruit. Sci. 2013, 30, 994–997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, M.D.; Li, T.; Xin, Q.Y.; Zhou, M.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Ma, H.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Qi, B.X.; Xu, J.F. Establishment and application of callus induction and suspension culture system of pear anther. J. Fruit. Sci. 2023, 40, 577–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz, R.; Casimiro, B.; Cordeiro, D.; Canhoto, J.; Correia, S. Mediated Transformation of Tamarillo (Solanum betaceum) Callus Cell Suspension Cultures: A Novel Platform for Biotechnological Applications. Plants 2025, 14, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtiar, Z.; Khalili, F.A.; Ghasemi, M.; Mirjalili, M.H. Micropropagation, callus induction and cell culture establishment of Zataria multiflora (Lamiaceae): An efficient biotechnological platform for the production of rosmarinic acid. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 226, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.M.; Hou, Y.Q.; Bao, M.N.; Hu, D.; Chen, Y.L.; Yue, C.L. The Suspended Single Cell Culture and Embryogeny and Plant Regeneration of Pinellia ternata. China Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.F.; Xi, Y.; Feng, Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, Y. Protoplast Isolation and Fusion Induced by PEG with Callus of Robinia pseudoacacia L. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2014, 42, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, H.K.; Aung, H.N.; Chang, K.K. Protoplast Isolation and Shoot Regeneration from Protoplast-Derived Callus of Petunia hybrida Cv. Mirage Rose. Biology 2020, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widholm, J.M. The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain. Technol. 1972, 47, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P.J. Purification and viability determinations of plant protoplasts. Planta 1976, 128, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.T.; Cai, Y.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Ma, Y.W.; Chen, Z.R. Suspension culture of rose cells. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023, 1–8. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230301.1044.007.html (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Liu, L.; Gu, Y.H.; Meng, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Establishment of suspension cell cultures and cell growth characteristics of Xanthoceras sorbifolia. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2010, 46, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.Y.; Wei, T.; Gao, D.D.; Zang, R.X.; Xu, H.W.; Guo, P.H. Application of plant protoplast culture technology in medicinal plants. Life Sci. Res. 2021, 25, 176–182. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Song, H.Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Mao, W.M.; Wu, J.S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P. Research progress of plant protoplast isolation and transient expression system. Plant Physiol. J. 2023, 59, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jinger, W. Study on Cotton Protoplast Culture and Somatic Cell Hybridization. Doctoral Dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.F. Study on Protoplast Separation and Electrofusion of Jujube Tree. Master’s Thesis, South China Tropical Agricultural University, Haikou, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Tong, H.R.; Liang, G.R.; Shi, Y.Q.; Yuan, L.Y. Protoplast Isolation and Fusion Induced by PEG with Leaves and Roots of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis L. O. Kuntze). Acta Agron. Sin. 2018, 44, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.L. Study on Protoplast Fusion of Panax Quinquefolium and Panax Notoginseng. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural Univercity, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M. Research About the Isolation, Purification and Regeneration of Carnation ‘Master’. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; He, M.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhu, X.Y. Establishment of efficient transient transformation method of Tieguanyin protoplasts. Acta Phytol. Sin. 2022, 57, 340–349. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.X.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, Q.; Lei, X.J. Research progress of plant protoplast regeneration mechanism. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 1–8. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.s.20211223.1007.008.html (accessed on 25 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).