Abstract
Tuta absoluta is a major pest attacking tomato crops. This invasive species emerged in Europe (Spain) in 2006, and 3 years later it spread to Portugal. In 2009/2010, it was recorded for the first time in the Azores archipelago. Macrolophus pygmaeus is a predator widely used as biological control agent against the tomato leaf miner. This study contrasted the life-history traits and population growth parameters of two feral populations of M. pygmaeus, one from Portugal mainland and one from the Azores archipelago. The predators were tested on single prey diet, either of Ephestia kuehniella eggs, a factitious prey used for mass rearing of mirids, or T. absoluta eggs. We predicted that populations would express differences in its phenotypic characteristics, with the Azorean population displaying low performance due to likely low genetic diversity, as expected for insular populations. Our results revealed the inexistence of phenotypic differences in several life history traits, such as immature developmental time, female longevity, males’ body weight and sex ratio. Contrary to our predictions, traits with direct impact on fitness, such as lifetime fertility (95.78 ± 14.23 vs. 61.38 ± 13.52 nymphs), explain better performances for the population of the Azores. Azorean M. pygmaeus females were larger, matured earlier and reproduced at a higher rate for longer periods, than mainland females. Therefore, population growth parameters show a positive advantage for the population of the Azores, fed on T. absoluta (time required for doubling the population Azores, Ek: 8.42 ± 0.50, Ta: 5.76 ± 0.31 and mainland, Ek: 10.88 ± 1.94, Ta: 12.07 ± 3.15). Biological performance of M. pygmaeus was similar when fed with T. absoluta or E. kuehniella that could be beneficial both to optimize mass production of the predator and biological control of the pest. Our results are discussed as well in a fundamental perspective, seeking if differences in biological performance can be explained by lower genetic diversity driven by geographic isolation.
1. Introduction
Biological control of agricultural pests is a fundamental strategy for sustainable food production, as it provides a safe alternative to chemical control. However, classical approach of importing and introducing exotic natural enemies to control herbivorous pest populations poses some concerns in conservation biology [1,2]. One possible approach to control non-native pest populations is the use of native natural enemies, based on conservation biological control or augmentative releases [3].
The South American leafminer Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) is an alien species and a major pest of tomato crops in Europe, causing severe economic losses to growers [4]. The pest was firstly recorded outside of its native range in Eastern Spain in 2006, and it is now widely distributed in the Mediterranean Basin, including North Africa and Middle East [5,6]. In Portugal mainland, T. absoluta has been reported in protected tomato crops, since 2009 [7,8,9]. In the Azores archipelago (Portugal), the species was recorded in São Miguel Island in 2009/2010 [10]. Later on, in 2014/2015, populations were recorded in other islands, including Terceira, Faial, Pico and São Jorge Islands, infesting tomato crops in greenhouses and open fields [11]. More recently, it was observed in greenhouses of Graciosa Island (A.O. Soares, personal observations in 2020).
Macrolophus pygmaeus Rambur (Hemiptera: Miridae) is an omnivorous mirid, widely used in integrated pest management, especially against pest populations of vegetable crops, including T. absoluta in greenhouses and fields tomato crops. It has been successfully used in the regulation of other small arthropod pests, such as whiteflies, thrips, spider mites and aphids [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Due to its success, M. pygmaeus is among the most widely used biocontrol agents [3]. Macrolophus pygmaeus was reported to the Azores archipelago in 2012 [23]. However, the origin and date of colonization process are unknown. We can assume that Azorean populations were originated in Portugal mainland. Sanchez et al. [24] recognized three geographically based genetic populations, including one from the Iberian Peninsula and the Canary Islands. Sanchez et al. [24] found that Canary Islands populations present a lower allelic richness and expected heterozygosity, due to the bottleneck effect, and this might be a consequence of the loss of diversity in the process of colonization of the islands from the mainland.
Despite the extensive use of M. pygmaeus as biocontrol agent, many knowledge gaps persist, particularly concerning the genetic diversity of naturally occurring or mass-produced released insects [25], and how that diversity depict phenotypic variation in biological and ecological traits, such as host specificity, voracity, phytophagy, life-history, population growth parameters, and effectiveness as biological control agent. Previous studies about the genetic structure of naturally occurring or mass reared M. pygmaeus revealed differences among populations [24,25]. The context of the evolutionary history of M. pygmaeus may have contributed to the variation of the genetic structure in the Mediterranean area. Likely, isolation of M. pygmaeus during the last glaciations, when northern and center of Europe were covered either by ice fields or permafrost [26], might have had an important impact once geographically isolated populations evolved independently and may have become genetically differentiated [24]. Additionally, some results support the hypothesis that mass reared and “wild” populations of M. pygmaeus are genetically differentiated [25]. This is particularly important in understanding of how M. pygmaeus may perform in different agroecosystem contexts, and to support better designing biological control tactics by selecting the most effective biocontrol agents [25].
In this context, the present study aimed at contrasting life-history traits and population growth parameters, in two distinct feral populations of M. pygmaeus, one from Portugal mainland and one from Azores archipelago, fed on single prey diets of Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) eggs, a factitious prey used for mass rearing of predatory mirids, in comparison with T. absoluta eggs. From an applied point of view, we intend to test the ability of the predator from both populations to complete development and reproduction, assessing its potential to be mass-reared and to be used as biocontrol agent of this tomato pest. In a more fundamental perspective and considering the expected low genetic diversity of M. pygmaeus of insular population, such as that observed in Canary Islands, in comparison with Iberian Peninsula [24], we expected to find differences in the phenotypic characteristics of mainland and insular populations of M. pygmaeus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
Feral specimens of M. pygmaeus collected from two geographically distinct populations (Azorean and Portugal mainland) were brought to the laboratory. Mainland specimens were originated from a rearing established population, to which were added periodically collected specimens, mainly from the Western region of Portugal (Azueira, Mafra, 39°00′43.8″ N 9°16′49.1″ W; Silveira, Torres Vedras, 39°07′02.5″ N 9°21′54.1″ W; Tapada da Ajuda, Lisbon, 38°42′45.8″ N 9°11′02.8″ W), both in greenhouse and open field crops. The Azorean specimens were collected in S. Miguel Island, in five different locations, on tomato plants (37°47′48.1″ N 25°35′51.7″ W; 37°45′4.3″ N 25°34′27.2″ W; 37°48′49.59″ N 25°31′41.10″ W; 37°45′1.54″ N 25°41′28.70″ W; 37°45′1.54″ N 25°41′28.70″ W). Insular and mainland stock populations were kept in separate rooms inside rearing cages (40 × 40 × 40 cm3) covered by mousseline fabric. One potted tomato plant (var. Nacera, Gebroeders Bakker Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V., Netherlands) with approximately 3 months old was put in each rearing cage and E. kuehniella eggs were provided twice a week, as a source of animal protein. The diet was complemented with droplets of honey diluted in water (1:1), distributed over the leaflets. When necessary, the tomato plant was replaced by a new one. Rearing conditions were 25 ± 1 °C, 75 ± 5% relative humidity and light regime 16L:8D.
Ephestia kuehniella was mass-reared in a facility of the Biotechnology Centre of Azores, of the University of the Azores. The lepidopteran eggs for use in the experimentations were irradiated with UV light for 20 min to stop embryonic development. Then, the eggs were stored at 5 °C for use up to 1 month.
Tuta absoluta was reared at a small scale, according to the needs of the ongoing experimentations. Adults were collected in a greenhouse (37°45′19.28″ N 25°37′42.51″ W) and brought back to the laboratory to establish a trophic chain. Adults were kept in a rearing cage (40 × 40 × 40 cm3) covered with mousseline fabric, with a tomato plant leaf in a water pot to collect lepidopteran eggs. Droplets of honey diluted in water (1:1) were put over the tomato plant leaflets for adult feeding. For the experiments, the tomato leaf containing the eggs was retrieved 24 h later and put over a dated paper sheet and kept at 5 °C to a maximum of 10 days. A preliminary test showed that after 10 days at 5 °C the viability of T. absoluta eggs was not affected. Additionally, at this temperature, the embryonic development was negligible after 10 days. When transferred to 25 °C these eggs took 4–5 days to hatch, practically the same time if kept always at 25 °C. This method allowed us to obtain a continuous supply of T. absoluta eggs at the required amounts for the experimentations. For trophic chain maintenance, the tomato leaf was kept up to 5 days in the adult rearing cages and then transferred to plastic boxes with a paper towel on the bottom and fresh tomato plant leaves. Fresh food for the larvae was provided as necessary until pupation. Newly emerged adults were collected and transferred to the adult rearing cage.
2.2. Life-History Traits
2.2.1. Immature Development
To determine the effect of different diets (E. kuehniella vs. T. absoluta eggs) and different populations (Azorean vs. Portugal mainland) on the developmental time of M. pygmaeus, approximately 50 M. pygmaeus adults from the stock population were introduced in a new rearing cage for 24 h, as described in Section 2.1, biological material. One tomato leaf inserted in a water pot was put inside the rearing cage with E. kuehniella eggs and a few droplets of honey diluted in water (1:1) were placed on the leaflets. Considering the extremely low fecundities of M. pygmaeus when fed with T. absoluta [27,28], only E. kuehniella was provided to the mirid to obtain eggs.
To obtain enough nymphs (N = 30 for each diet, E. kuehniella or T. absoluta eggs) for the experiment, two rearing cages were set. These procedures were the same for the Azorean and mainland populations. From the 9th day on, tomato leaves were checked daily under stereomicroscope for the presence of newly hatched nymphs, to determine the embryonic development time. Each newly hatched nymph was transferred individually to a plastic box (3 cm Ø × 2 cm height) containing one tomato plant leaflet with E. kuehniella or T. absoluta eggs and one droplet of honey diluted in water (1:1). Nymphs were fed ad libitum (see additional details in Section 2.1). Every 2 days, the tomato plant leaflet was replaced. The presence of nymph exuviae was used as evidence of moulting and so the nymphal stage-specific and total immature development time were determined. At emergence, gender of each individual was determined based on the abdomen format, rounded for females and streamlined for males, and the individuals were weighed (10−4 mg Mettler AM50 analytical balance).
2.2.2. Longevity, Sex-Ratio and Reproductive Performance
To determine the reproductive performances of M. pygmaeus on the two diets tested, couples of each population were formed (N = 9) and kept isolated in Twin-Vented Mini Vivarium (10 × 8.8 × 21.5 cm3) + Water pot boxes (Bugzarre), along with a section of a tomato plant leaf with approximately 10 cm long stem containing a single leaflet. Eggs of E. kuehniella or T. absoluta were placed ad libitum on the leaflet every day, according to the diet regime. Tuta absoluta eggs provided were obtained as described in Section 2.1, ensuring that only eggs were available to predator. To complement diet, a droplet of honey diluted in water (1:1) was put over the leaflet every 2 days. In case of uneven sex ratio obtained in the development time experiment, males from the stock population were used to make as many couples as possible. Every day, the tomato plant leaf was replaced by a new one and the old one was labelled and kept in water for the next 9 days. At the 9th day, the leaves were removed from water and transferred individually to plastic boxes (10 cm Ø × 3 cm height), for observation under the stereomicroscope (for the next 5 days) to check for the presence of newly hatched nymphs and determine the pre-oviposition time and the daily reproductive rate. As M. pygmaeus females lay their eggs inside the tomato plant stem, they are very difficult to observe; therefore, reproductive performance of the predator was assessed based on the number of nymphs obtained. The females were followed until their death and males were substituted whenever they died.
2.3. Population Growth Parameters
To calculate the intrinsic rate of increase (rm), the Euler’s equation was solved iteratively [29,30,31] according to Carey’s method [32]:
where x is time (in days), lx is the age-specific survivorship and mx is the age-specific mean number of female offspring. The number of females produced by female, that is the net reproductive rate (R0), was calculated as [33,34]:
The time required for a population to increase in size by a factor of R0-fold (the mean generation time, ) was calculated according to Southwood & Henderson [35]:
The finite rate of increase (λ) and the doubling time (DT), were calculated as previous described [30,36,37,38]:
2.4. Statistical Analysis
We used generalized linear models (GZLM) to assess the effect of population origin and food resource (independent variables) on the developmental time, sex-ratio, females and males body weight, pre-oviposition time, lifetime fertility, length of the oviposition period and female longevity (dependent variables) of M. pygmaeus. Factors (Mainland vs. Azorean populations and E. kuehniella vs. T. absoluta eggs), and interactions were analyzed using the Wald Chi-Square test for a confidence level of 95%. Pairwise multi-comparisons were performed, and p values corrected using Bonferroni test. Due to the lack of normality of the data on the developmental time of eggs, a Mann–Whitney test was used to compare the populations (Mainland vs. Azorean populations) feed with E. kuehniella eggs. Normal distributions of data were assessed by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Accordingly, for dependent variables with normal distribution, analyses considered the normal error distribution and the identity link function. For dependent variables without normal distribution, we used Poisson error distribution and the log link function.
To compare population growth parameters, pseudo-values (Pj) of the parameters were calculated using jackknife analysis according to the formula [39]:
where n is the number of replicates, E−j is the estimate omitting female j and Eall is the estimate comprising all females. With n pseudo-values of the parameters, it is then possible to calculate a mean value (jackknife estimate of the statistic) and the respective standard errors (SE). Life table parameters for the two populations (island and mainland) on different diets (E. kuehniella or T. absoluta eggs) were compared with a GZLM, to assess the effect of population origin and food resource (independent variables) on population growth parameters (dependent variables) of M. pygmaeus. Factors (Mainland vs. Azorean populations and E. kuehniella vs. T. absoluta eggs), and interactions were analyzed using the Wald Chi-Square test for a confidence level of 95%. Pairwise multi-comparisons were performed, and p values corrected using Bonferroni test.
For survival analysis, the Online Application for Survival Analysis (OASIS 2) [40] was used. The survival curves intersected each other, therefore Cox Proportional Hazards and Log-Rank tests are inappropriate for data analysis because the hazards are not proportional [41,42,43,44]. Instead, a weighted Log-Rank test, the Fleming-Harrington test, was used to compare survival in early and late stages of life applying the Bonferroni correction.
All means in text and tables were calculated with untransformed data, followed by standard errors. All the statistical analyses were performed on the IBM SPSS 27.
3. Results
3.1. Life-History Traits
3.1.1. Immature Development
We found a significant difference in the embryonic development time of M. pygmaeus from Mainland and Azorean populations fed with E. kuehniella eggs (Mann–Whitney test, U = 705.0, N = 60, p < 0.001) (Table 1). For total developmental time of immature stages, we did not find a significant effect of the population origin and food resource (Wald Chi-Square ≈ 0, df = 1, p = 0.993). No differences were found between immature developmental time of Mainland (17.47 ± 0.11) and Azorean populations (18.35 ± 0.09) (Wald Chi-Square = 0.739, df = 1, p = 0.390), as well as between the offered preys, i.e., E. kuehniella eggs (17.74 ± 0.12) versus T. absoluta eggs (18.09 ± 0.12) (Wald Chi-Square = 0.118, df = 1, p = 0.731) (Table 1). Survival rates of the immature stages of M. pygmaeus were high for the Azorean population (Table 2).

Table 1.
Developmental time (days ± SE) of the embryo and immature stages of Macrolophus pygmaeus from the Azorean and Portugal mainland populations fed on single diets of Ephestia kuehniella or Tuta absoluta eggs (25 ± 1 °C; 75 ± 5% relative humidity and light regime 16L:8D).

Table 2.
Survival rate of the immature stages of Macrolophus pygmaeus from the Azorean population and Portugal mainland fed on single diets of Ephestia kuehniella or Tuta absoluta eggs (25 ± 1 °C; 75 ± 5% relative humidity and light regime 16L:8D).
3.1.2. Longevity, Sex-Ratio and Reproductive Performance
The results about longevity, sex-ratio and reproductive performance of M. pygmaeus from the Azorean and Portugal mainland populations fed on single diets of T. absoluta eggs or E. kuehniella eggs are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Adults’ life-history traits of Macrolophus pygmaeus of the Azorean and Portugal mainland populations fed on single diets of Ephestia kuehniella or Tuta absoluta eggs (25 ± 1 °C; 75 ± 5% relative humidity and light regime 16L:8D). The information on the two additional columns (significance) stands for biological traits in which no significant effect between factors we found (origin of population and food resource).
No significant female-biased sex-ratio were obtained when comparing population origin (Chi-Square = 2.166, p = 0.141) as well as food resource (Chi-Square = 0.259, p = 0.611).
Comparing female body weight of M. pygmaeus, we did not find a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square = 1.143, df = 1, p = 0.285). Body weight of females from mainland (1.00 ± 0.02 mg) was significantly lower than of the Azorean females (1.01 ± 0.02 mg) (Wald Chi-Square = 6.797, df = 1, p = 0.009). In terms of food resources, females body weight did not significant differ when fed with E. kuehniella (1.07 ± 0.03 mg) or with T. absoluta eggs (1.05 ± 0.02 mg) (Wald Chi-Square = 0.730, df = 1, p = 0.393).
In relation to male’s body weight, we did not find a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi- Square = 1.962, df = 1, p = 0.161). Body weight of males from mainland (0.63 ± 0.02 mg) did not differ from that of the Azorean males (0.66 ± 0.02 mg) (Wald Chi-Square = 0.605, df = 1, p = 0.437). In terms of food resources, males body weight did not significant differ when fed with E. kuehniella (0.66 ± 0.02 mg) or with T. absoluta eggs (0.64 ± 0.02 mg) (Wald Chi-Square = 0.238, df = 1, p = 0.625).
Concerning pre-oviposition time, we found a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square = 13.257, df = 1, p < 0.001). Pre-oviposition duration in mainland females fed on T. absoluta was significantly higher than the remaining results.
In terms of lifetime fertility, we did not find a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square = 1.760, df = 1, p = 0.185). Lifetime fertility of mainland females (39.94 ± 11.46 nymphs) was significantly lower than Azorean females (95.78 ± 14.23 nymphs) (Wald Chi-Square = 10.524, df = 1, p = 0.001). In terms of food resources, fertility did not significantly differ when females were fed with E. kuehniella (61.39 ± 13.52 nymphs) or T. absoluta eggs (74.33 ± 15.42 nymphs) (Wald Chi-Square = 0.566, df = 1, p = 0.452).
Concerning the oviposition period of M. pygmaeus females, we did not find a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square ≈ 0, df = 1, p = 0.995). Oviposition period of mainland females (18.09 ± 2.73 days) did significantly differ from the Azorean females (23.94 ± 2.13 days) (Wald Chi-Square = 3.478, df = 1, p ≤ 0.062). Oviposition period also did not significantly differ when females fed on E. kuehniella (23.57 ± 5.74 days) or T. absoluta eggs (19.60 ± 2.20 days) (Wald Chi-Square = 1.672, df = 1, p = 0.196).
For female longevity of M. pygmaeus, we did not find a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square = 0.194, df = 1, p = 0.660). Longevity of mainland females (52.67 ± 1.71 days) did not significantly differ from the Azorean females (43.39 ± 4.02 days) (Wald Chi-Square = 1.925, df = 1, p = 0.165). Longevity also did significantly differ when females were fed on E. kuehniella (51.61 ± 5.01 days) or T. absoluta eggs (44.44 ± 5.01 days) (Wald Chi-Square = 1.148, df = 1, p = 0.289).
3.2. Population Growth Parameters
The results of population growth parameters of M. pygmaeus are presented in Table 4. The information on the two additional columns (significance) stands for population growth parameter in which no significant effect between factors was found (origin of population and food resource).

Table 4.
Population growth parameters of Macrolophus pygmaeus from the Azorean and Portugal mainland populations fed on single diets Tuta absoluta or Ephestia kuehniella eggs (25 ± 1 °C; 75 ± 5% relative humidity and light regime 16L:8D).
Concerning the intrinsic rate of increase (rm: Wald Chi-Square = 8.189, df = 1, p = 0.004) and the finite rate of increase (λ = Wald Chi-Square = 8.652, df = 1, p = 0.003), we found a significant interaction between factors (origin of population and food resource). We found that the intrinsic rate of increase and the finite rate of increase, were significantly higher for Azorean females fed on T. absoluta and lower for mainland females, especially fed on T. absoluta.
For net reproductive rate (R0), expressing the number of females produced by female, we found a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi- Square = 4.938, df = 1, p = 0.026). Again, net reproductive rate was significantly higher for Azorean females fed on T. absoluta and no difference were found between the remaining populations and food resources.
For mean generation time (, there was a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square = 5.041, df = 1, p = 0.025). Mean generation time are relatively similar but tendentially lower for Azorean females fed on T. absoluta and higher for mainland females fed on T. absoluta.
For doubling time (DT), the time required for doubling the population, we did not find a significant effect between factors (origin of population and food resource: Wald Chi-Square = 1.192, df = 1, p = 0.275). Time required for doubling the population of mainland (11.4 ± 1.2 days) was significantly higher than for Azorean population (7.1 ± 1.2 days) (Wald Chi-Square = 6.165, df = 1, p = 0.013). In terms of food resources, doubling time did not significantly differ from females fed with E. kuehniella (9.6 ± 1.2 days) and with T. absoluta eggs (8.9 ± 1.2 days) (Wald Chi- Square = 0.173, df = 1, p = 0.677).
Fertility curves showed that reproductive investment of M. pygmaeus females were distributed within a similar time window (30–70 days) for island and mainland populations on both diets, but the island population produced much more eggs. The mainland population presented lower survival early in life but mortality during adult stage showed a steady decreasing pattern (Figure 1). Prey species and population origin did not affect significantly survival either on early (Azorean E. kuehniella vs. Azorean T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 0.040, p = 1; Azorean E. kuehniella vs. Mainland E. kuehniella: Chi-Square = 1.080, p = 0.895; Azorean E. kuehniella vs. Mainland T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 2.970, p = 0.254; Azorean T. absoluta vs. Mainland E. kuehniella: Chi-Square = 1.140, p = 0.856; Azorean T. absoluta vs. Mainland T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 3.170, p = 0.225; Mainland E. kuehniella vs. Mainland T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 2.780, p = 0.287) or late stages in life (Azorean E. kuehniella vs. Azorean T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 0.000, p = 1.000; Azorean E. kuehniella vs. Mainland E. kuehniella: Chi-Square = 4.100, p = 0.129; Azorean E. kuehniella vs. Mainland T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 0.740, p = 1.000; Azorean T. absoluta vs. Mainland E. kuehniella: Chi-Square = 4.040, p = 0.133; Azorean T. absoluta vs. Mainland T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 0.700, p = 1; Mainland E. kuehniella vs. Mainland T. absoluta: Chi-Square = 0, p = 1).
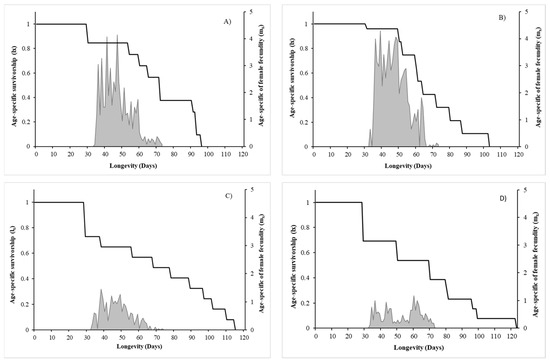
Figure 1.
Age-specific survivorship (lx) and age-specific of female fecundity (mx) curves of Macrolophus pygmaeus from the Azores fed on E. kuehniella (A) or T. absoluta (B), and from mainland fed on Ephestia kuehniella (C) or fed on Tuta absoluta (D). (25 ± 1 °C; 75 ± 5% relative humidity and light regime 16L:8D).
4. Discussion
We aimed at contrasting life-history traits and population growth parameters of M. pygmaeus from two different populations, one from Portugal mainland and the other from the Azores, either fed with E. kuehniella or T. absoluta eggs. To our knowledge, this is the first study on the life-history of feral populations of M. pygmaeus. We found that both preys were able to ensure the completion of the immature development of the predator, in about 18 days (between 17.29 ± 0.17 and 18.53 ± 0.15 days), with a high survival rate, varying from 69% to 96%. The registered developmental times were higher than the reported by Mollà et al. [27], both for E. kuehniella and T. absoluta diets and for both mainland and Azorean populations of M. pygmaeus. Females reached a similar body weight (approximately 1 mg), despite significantly higher for females of the Azores. Both preys allowed reproduction, but with a variable degree of fitness (differing from 35.00 ± 14.46 to 113.67 ± 20.66 nymphs produced), with an advantage for the Azorean population, independently of the prey consumed. Females’ longevity was slightly longer when feeding on E. kuehniella, results that differ from those of Mollà et al. [27]. Although the progeny (number of nymphs/female) was more or less similar to that of these authors in case of the mainland population, Azorean population presented a higher lifetime fertility (number of nymphs produced, i.e., 113.67 and 77.89, feeding on T. absoluta and E. kuehniella, respectively in our study, in comparison with 44.5 and 49.2 nymphs/female, respectively in Mollà et al. [27]), and reproductive investment is distributed within a similar time window (30–70 days). These results corroborate that both preys are suitable food sources for M. pygmaeus and suggest it is an adequate candidate to be mass reared and used as biological control agent against T. absoluta. Indeed, previous studies demonstrated that M. pygmaeus consume T. absoluta eggs either under laboratory [20] and greenhouse [45,46] conditions. In short, biological performances of the predator were similar when the predator was fed with T. absoluta and E. kuehniella, which may have positive implication for mass production and biological control programs of this tomato pest. Nevertheless, this result is in contradiction with the reported by other researchers, which observed that this lepidopteran is a poor food resource for ovipositing females of M. pygmaeus [27,28]. For that reason, further studies are needed with other feral populations to confirm those results.
Translating our data of biological traits into the population growth parameters, we found a slightly advantage for the Azorean population of M. pygmaeus when fed with T. absoluta and a marginal disadvantage for mainland population. The intrinsic rate of increase (rm) was higher, except for the mainland population fed with T. absoluta eggs. The time required for doubling the population (DT) was lower in the case of the Azorean population fed on T. absoluta and higher for mainland populations. Life table parameters of M. pygmaeus are strongly dependent on temperature and food resources [47]. For instance, under experiments performed at 25 °C, M. pygmaeus fed on Solanum nigrum L. (Solanaceae) leaves infested with the aphid prey Aphis fabae solanella Theobald (Homoptera Aphididae), showed a lower performance (rm = 0.0392, λ = 1.0399, R0 = 5.76, = 46.04 and DT = 17.68), than the populations tested in our study, independently of the prey. The predator performed even worst when fed on Dittrichia viscosa L. (W. Greuter) (Asteraceae) leaves infested with the aphid Capitophorus inulae (Passerini) [48]. As M. pygmaeus is a zoophytophagous predator, the availability of prey, simultaneously with a host plant, is fundamental to ensure the development and reproduction of the predator [47]. Even in the absence of prey, eggplant is more suitable than tomato plant [49].
We predicted that the studied populations would express differences in its phenotypic characteristics with the Azorean populations displaying low performance due to likely low genetic diversity, as expected for insular populations, e.g., [24]. Indeed, for arthropods, there are growing evidence about the effect of insular conditions to inbreeding depression, loss of genetic diversity and mutation accumulation, and this contributes to increase extinction risk [50]. For some of the life-history traits, our results revealed the inexistence of phenotypic differences. This holds true for embryonic and immature developmental time, female longevity, males’ body weight and sex ratios. Contrary to our predictions, traits with direct impact on fitness, such as females body weight, pre-oviposition time, oviposition period and lifetime fertility translated in better biological performances in the Azorean population. Azorean M. pygmaeus females were larger, matured earlier and reproduced at a higher rate for longer periods than mainland females. Pulling the individual data on phenotypic traits into the models of population growth parameters, we found a significant positive advantage for populations of the Azores. Indeed, the values of net reproductive rate, intrinsic rate of increase, finite rate of increase were significantly higher for Azorean females and consequently, mean generation time and doubling time were significantly lower. Thus, it is expected that Azorean populations of M. pygmaeus will achieve higher population densities more rapidly than that of mainland.
Both Mollá et al. [27] and Sylla et al. [28] studies have used mass-reared mirids acquired from mass rearing facilities. It is known that mass rearing insects for long periods may lead to decreased biological performance and adaptation to the food source used. In our study, we used feral populations reared in laboratory conditions and the number of generations was not enough to develop this adaptation, even because refreshments were made periodically. Furthermore, the mainland and Azorean populations were collected in areas without known previous release of M. pygmaeus. In mainland, collections occurred in Tapada da Ajuda, a green area inside the metropolitan area of Lisbon, and in Azueira, a farm surrounded by pear orchards, vineyards and forestry. Streito et al. [25], however, found that some of the supposedly feral populations might not be so and M. pygmaeus has been commercialized in Europe since 1994 [3]. Therefore, we should consider the possibility of the feral mainland population being affected by commercial populations released in the area or neighboring areas, as there is a large area of protected crops in the Western region (≈860 ha [51]). By the way, this can be an explanation for the higher similarity between the mainland population and the results of Mollà et al. [27]. The release of conspecific populations may have different potential impacts in natural populations, including the loss of genetic variation, breakdown of adaptations, changes to genetic composition within populations, and breakdown of population structure [52]. For example, Sethuraman et al. [53] found that multilocus genotypes of the commercially distributed populations of the predatory lady beetle Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) from California were admixed into Eastern populations.
To understand if the lower biological performance of the mainland population is related with an unlikely lower genetic diversity, a study on the population genetic structure is required, sampling a much larger area together with historic information about biological control practices in the collection sites and their surroundings. Anyway, it is not always possible to relate biological or behavioural differences from the analysis of some genes [54].
Considering the recent arrival of T. absoluta to the Azores archipelago, the observed fitness of a feral population of M. pygmaeus on a new prey abundantly available in its habitat may have direct impact on T. absoluta control and on its diet breadth. More studies on other preys would contribute to clarify this question. It would be also important to address what will be the impact of releasing commercially available strains on the Azorean population of M. pygmaeus.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B., L.O., E.F., J.C.F., E.L. and A.O.S.; methodology, I.B., L.O., E.F., J.C.F., E.L. and A.O.S.; formal analysis, I.B. and A.O.S.; investigation, I.B., A.C.D. and P.A.; writing—Original draft preparation, I.B. and A.O.S.; writing—Review and editing, I.B., L.O., A.C.D., P.A., E.F., J.C.F., E.L. and A.O.S.; supervision, I.B.; project administration, A.O.S.; funding acquisition, A.O.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financed by FEDER in 85% and by Azorean Public funds by 15% through Operational Program Azores 2020, under the project ECO2–TUTA (ACORES-01-0145-FEDER-000081). L.O. was funded by Portuguese national funds FCT under the project UIDP/05292/2020 and UIDB/05292/2020. E.F. was funded by Portuguese national funds FCT Umbert-ECO PTDC/ASP-PLA/29110/2017. J.C.F. and E.F. received backing from Forest Research Centre (CEF) and Linking Landscape, Environment, Agriculture and Food (LEAF) research center, respectively, research units funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal (UIDB/00239/2020 and UIDB/AGR/04129/2020, respectively), and both researchers from the Laboratory for Sustainable Land Use and Ecosystem Services–TERRA (LA/P/0092/2020).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Soares, A.O.; Honěk, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Brown, P.M.J.; Borges, I. Can native geographical range, dispersal ability and development rates predict the successful establishment of alien ladybird (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) species in Europe? Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoni, G.; Borges, I.; Collatz, J.; Conti, E.; Costamagna, A.; Dumont, F.; Evans, E.W.; Grez, A.A.; Howe, A.G.; Lucas, E.; et al. Exotic ladybirds for biological control of herbivorous insects—A review. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2021, 169, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenteren, J.C. The state of commercial augmentative biological control: Plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. BioControl 2012, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, A.; Narciso, R.; Guedes, C.; Wan, F.-H.; Desneux, N. Ecology, worldwide spread, and management of the invasive south American tomato pinworm, Tuta absoluta: Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desneux, N.; Wajnberg, E.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Burgio, G.; Arpaia, S.; Narváez-Vasquez, C.A.; González-Cabrera, J.; Catalán Ruescas, D.; Tabone, E.; Frandon, J.; et al. Biological invasion of European tomato crops by Tuta absoluta: Ecology, geographic expansion and prospects for biological control. J. Pest Sci. 2010, 83, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Luna, M.G.; Guillemaud, T.; Urbaneja, A. The invasive South American tomato pinworm, Tuta absoluta, continues to spread in Afro-Eurasia and beyond—The new threat to tomato world production. J. Pest Sci. 2011, 84, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, E.; Rodrigues, S.; Payer, R.; Mexia, A. Situación actual de Tuta absoluta en Portugal. Phytoma España 2010, 217, 118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, T.; Figueiredo, E.; Mexia, A. Armadilhas de feromona sexual com luz para captura em massa de Tuta absoluta (Meyrick), sim ou não? Rev. De Ciências Agrárias 2012, 35, 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Payer, R.; Figueiredo, E.; Mexia, A. Evaluation of parasitism and predation of Tuta absoluta (Meyrick, 1917) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) by Diglyphus isaea (Walker, 1838) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). SHIL. Rev. lepidopterol. 2015, 43, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- DSA (Direção de Serviços de Agricultura). Relatório de Atividades DSA 2013. 2014. Available online: http://servicos.srrn.azores.gov.pt/grastore/DRADR/RelatorioAtividades2013.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Vieira, V. A traça-do-tomateiro Tuta absoluta (Meyrick, 1917) nas ilhas dos Açores (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). SHIL. Rev. lepidopterol. 2016, 44, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, G.; Malausa, J.C.; Kaspar, B. Laboratory studies on the main biological characteristics of Macrolophus caliginosus (Heteroptera: Miridae). Entomophaga 1987, 32, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, P.; Balta, O.; Alomar, O. Efficiency of four Heteroptera as predators of Aphis gossypii and Macrosiphum euphorbiae (Hom.: Aphididae). Entomophaga 1997, 42, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnadas, I.; Gabarra, R.; Albajes, R. Predatory capacity of two mirid bugs preying on Bemisia tabaci. Entomol. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1998, 86, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riudavets, J.; Castañé, C. Identification and evaluation of native predators of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in the Mediterranean. Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Tsitsipis, J.A.; Perdikis, D.C. Biological characteristics of the mirids Macrolophus costalis and Macrolophus pygmaeus preying on the tobacco form of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididade). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2003, 93, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikis, D.; Kapaxidi, E.; Papadoulis, G. Biological control of insect and mite pests in greenhouse solanaceous crops. Eur. J. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 2, 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Arnó, J.; Sorribas, R.; Prat, M.; Matas, M.; Pozo, C.; Rodríguez, D.; Garreta, A.; Gómez, A.; Gabarra, R. Tuta absoluta, a new pest in IPM tomatoes in the northeast of Spain. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2009, 49, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, J.; Blockmans, K.; Stansly, P.A.; Urbaneja, A. Predation by Nesidiocoris tenuis on Bemisia tabaci and injury to tomato. BioControl 2009, 54, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaneja, A.; Montón, H.; Mollá, O. Suitability of the tomato borer Tuta absoluta as prey for Macrolophus pygmaeus and Nesidiocoris tenuis. J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 133, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaneja, A.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, J.; Arnó, J.; Gabarra, R. Prospects for the biological control of Tuta absoluta in tomatoes of the Mediterranean basin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañé, C.; Arnó, J.; Gabarra, R.; Alomar, O. Plant damage to vegetable crops by zoophytophagous mirid predators. Biol. Control 2011, 59, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerzhner, I.M.; Josifov, M. Cimicomorpha II: Miridae. In Catalogue of the Heteroptera of the Palaearctic Region; Aukema, B., Rieger, C., Eds.; Netherlands Entomological Society: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1999; p. 577. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Spina, M.L.; Perera, O.P. Analysis of the population structure of Macrolophus pygmaeus (Rambur) (Hemiptera: Miridae) in the Palaearctic region using microsatellite markers. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 3145–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streito, J.-C.; Clouet, C.; Hamdi, F.; Gauthier, N. Population genetic structure of the biological control agent Macrolophus pygmaeus in Mediterranean agroecosystems. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, G. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 2000, 405, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollá, O.; Biondi, A.; Alonso-Valiente, M.; Urbaneja, A. A comparative life history study of two mirid bugs preying on Tuta absoluta and Ephestia kuehniella eggs on tomato crops: Implications for biological control. BioControl 2014, 57, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylla, S.; Brévault, T.; Diarra, K.; Bearez, P.; Desneux, N. Life-history traits of Macrolophus pygmaeus with different prey foods. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.G.; Mauchline, N.A.; Hall, A.J.; Stannard, K.A. Life table parameters of two armoured scale insect (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) species on resistant and susceptible kiwifruit (Actinidia spp.) germplasm. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2009, 37, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, I.; Soares, A.O.; Hemptinne, J.-L. Contrasting population growth parameters of the aphidophagous Scymnus nubilus and the coccidophagous Nephus reunioni. BioControl 2013, 58, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Feng, J. Development of insect life tables: Comparison of two demographic methods of Delia antiqua (Diptera: Anthomyiidae) on different hosts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.R. Applied Demography for Biologists: With Special Emphasis on Insects; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Pianka, E.R. Evolutionary Ecology; Addison Wesley Educational Publishers, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000; p. 411. [Google Scholar]
- Begon, M.; Townsend, C.R.; Harper, J.L. Ecology: From Individuals to Ecosystems; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, MI, USA, 2006; p. 750. [Google Scholar]
- Southwood, T.R.E.; Henderson, P.A. Ecological Methods; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2000; p. 593. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, S.; Soares, A.O.; Moura, R.; Garcia, P. Suitability of Aphis fabae, Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae) and Aleyrodes proletella (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) as prey for Coccinella undecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol. Control 2006, 39, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontodimas, D.; Milonas, P.G.; Stathas, G.J.; Economou, L.P.; Kavallieratos, N.G. Life table parameters of the pseudococcid predators Nephus includens and Nephus bisignatus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2007, 104, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.A.; Soares, A.O.; Garcia, P. Temperature dependence for development of the whitefly predator Clitostethus arcuatus (Rossi). BioControl 2008, 53, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Maia, A.H.N.; Luiz, A.J.B.; Campanhola, C. Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique: Computational aspects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.K.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.; Son, H.G.; Yang, J.; Lee, S.V.; Kim, S. OASIS 2: Online application for survival analysis 2 with features for the analysis of maximal lifespan and healthspan in aging research. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56147–56152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.R.; Klein, J.P.; Zhang, M.-J. Comparing treatments in the presence of crossing survival curves: An application to bone marrow transplantation. Biometrics 2008, 64, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouliotis, G.; Billingham, L. Crossing survival curves: Alternatives to the log-rank test. Trials 2011, 12, A137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, D.; Hou, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z. Statistical Inference Methods for Two Crossing Survival Curves: A Comparison of Methods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormuth, I.; Liu, T.; Xu, J.; Yu, M.; Pauly, M.; Marc Ditzhaus, M. Which test for crossing survival curves? A user’s guideline. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2022, 22, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompard, A.; Jaworski, C.C.; Bearez, P.; Desneux, N. Sharing a predator: Can an invasive alien pest affect the predation on a local pest? Pop. Ecol. 2013, 55, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, F.J.; Lorente, M.J.; Stansly, P.A.; Belda, J.E. Preplant release of Nesidiocoris tenuis and supplementary tactics for control of Tuta absoluta and Bemisa tabaci in greenhouse tomato. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2012, 143, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikis, D.; Lykouressis, D. Effects of various items, host plants, and temperatures on the development and survival of Macrolophus pygmaeus Rambur (Hemiptera: Miridae). Biol. Control 2000, 17, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykouressis, D.; Giatropoulos, A.; Perdikis, D.; Favas, C. Assessing the suitability of noncultivated plants and associated insect prey as food sources for the omnivorous predator Macrolophus pygmaeus (Hemiptera: Miridae). Biol. Control 2008, 44, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikis, D.; Lykouressis, D. Macrolophus pygmaeus (Hemiptera: Miridae) population parameters and biological characteristics when feeding on eggplant and tomato without prey. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankham, R. Genetics and extinction. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 126, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INE–Instituto Nacional de Estatística. Inquérito à Estrutura das Explorações Agrícolas-2016–Destaque. 2017. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_destaques&DESTAQUESdest_boui=281413215&DESTAQUESmodo=2 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Laikre, L.; Schwartz, M.K.; Waples, R.S.; Ryman, N. Compromising genetic diversity in the wild: Unmonitored large-scale release of plants and animals. TREE 2010, 25, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, A.; Janzen, F.J.; Obrycki, J. Population genetics of the predatory lady beetle Hippodamia convergens. Biol. Control 2015, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.E.; Roehrdanz, R.L.; Allen, K.C.; Musser, F.R. Comparisons of Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae) populations from two distinct geographical regions of Mississippi. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).