Abstract
Organic farming (OF) has been increasing in popularity over recent years, but unfortunately tends to have lower yield, due to lower nutrient availability and pest problems. To better understand how OF influences plant growth, we must elucidate the impact of such practices on the microbial community, an important factor in soil management. In this study, we examined the relationship between farming practice, changes in plant growth, and soil microbial community for green onion (Allium fistulosum L.) cultivated over 313 days in green houses with OF using composts with natural green tuff as soil conditioner (EF1) or inorganic fertilizer (EF2). Average yields of EF1 were generally higher than EF2, reaching up to 12% higher (p < 0.05; day 131). The observed soil microorganism phylotypes and phylogenetic diversity (Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (PD)) were both significantly higher (p < 0.05) in EF1 than EF2 on days 93, 191 (only for PD), and 261, based on microbial richness indices. Several phylotypes belonging to the Bacillus-related microbial order Bacillales were found at higher abundances in EF1 soils, positively correlated with specific soil properties (i.e., humus, ammonium, and pH), and may associate with plant growth promotion and/or fungal toxin degradation. These results point towards novel positive effects of OF and provide insights into the management of soil microorganisms using organic fertilizers.
1. Introduction
Soil management in agriculture is essential for the high productivity of plant cultivation [1]. Although the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides is a common practice for conventional farming (CF), the consequential decrease in soil biodiversity and environmental pollution are major concerns for agricultural sustainability [2,3]. According to literature from public institutions (e.g., Codex Alimentarius Guidelines (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations) [3], The International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM) basic standards [4], and low-input sustainable agriculture (LISA) [5]), the increasing popularity of organic foods has been reported to reduce the negative environmental effects successfully; however, yields in organic farming (OF) are generally lower than CF, due to a decrease in nutrient availability and pest problems [3,6]. Recent meta-analyses using large datasets suggested that the average yield of OF is 8–25% lower than CF [3], and Ponisio et al. have reported that multi-cropping and crop rotations can reduce the yield gap [7]. However, to further improve the yields and aim for sustainable agriculture, the relationships among soil/fertilizer characteristics, microbial diversity, and crop yields in OF must be investigated.
Soil microorganisms likely play an essential role, as these organisms are the fulcrum of soil nutrient cycling [8,9]. Many OF management studies have shown various benefits on microbial species richness, disease suppression, and higher microbial activities compared with CF [10,11,12,13,14,15]. In contrast, some studies have reported that OF has little effect on microorganisms [16,17]. For example, the availability of organic fertilizer comprising fermented rice bran and rapeseed oil cake affected bacterial community compositions in rice paddy field compared with CF, while no significant differences in rice production were observed [18]. The microbial communities in OF using cow slurry and green manure for long-term exposure (14 years) did not show great difference in those in CF system [17]. These observations strongly suggest the importance of developing a novel organic fertilization strategy that is able to improve the crop yield and proliferate the beneficial microorganisms. Chau et al. reported that soil texture, which corresponds to the availability of nutrients, may influence the increase of plant yields, pH, and species richness in agricultural soils [19]. Zeolites, natural aluminosilicates discovered in volcanogenic sedimentary rock, possess the ability for the adsorption/desorption of cation (e.g., ammonium ion, NH4+) and metals [20], and it has been widely used for agriculture and food production as a soil conditioner [21,22,23]. For example, OF with zeolite-fed sugarcane filter cake produced the highest yield of sugarcane compared with CF [22]. Thus, the addition of mineral material into organic fertilizer could be an effective way to improve soil characteristics, resulting in the success of OF management; however, little is known about the effects of supplying mineral materials to organic fertilizer on the diversity of soil microorganisms.
In this study, to further elucidate the relationships between the soil microbial community, plant growth, and soil chemical parameters, we cultivated green onion (Allium fistulosum L.) for one year in green houses with OF, using “green tuff” as soil conditioner in addition to compost. Green tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash derived from vent eruption and following geochemical consolidation process and contains various minerals, including SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, K2O, CaO, Na2O, MgO, and P2O5, which are similar components with natural zeolite mainly containing SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, K2O, CaO, Na2O, MgO, and TiO2 [20]. In Japan, green tuff layer is observed in the north-west part of Honshu island (e.g., Niigata, Yamagata, and Akita prefectures), and it has been reported that, based on microscopic observations, diverse microorganisms attached to green tuff surface may be considered to play an important role in rice cultivation in this area [24]. Therefore, we expect that the addition of green tuff can increase the yield of green onion and stimulate the growth of soil microorganisms. Through 16S rRNA gene sequencing, we discover the improvement of plant growth caused by the possible proliferation of Bacillales organisms in OF using compost supplemented with green tuff.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation Conditions, Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Chemical Component Analysis
We prepared two types of experimental fields (EFs) (1: composts with natural green tuff as soil conditioner and 2: inorganic fertilizer). Quadruplicate EF1 and one EF2 were prepared (width: ca. 4 m, length: ca. 62.5 m, area ca. 250 m2) in green houses, located in Yame, Fukuoka, Japan (Figure 1). The application rate of the fertilizers was adjusted to have similar nutrients of total nitrogen, total phosphate, and total potassium between EF1 and EF2, as described below. For EF1, we used two types of organic composts mixed with green tuff (fertilization: 240 kg/1000 m2; diameter of 1–5 mm, Hinai Green®, Towada Green-tuff AgroScience Co., Ltd.): compost of mushroom cultivation wastes and wasted bamboo (Organic compost 1 (OC1); 1200 kg/1000 m2; total nitrogen: 1% (w/w), total phosphate: 0.5%, total potassium: 1.3%), and a commercial compost (OC2; 320 kg/1000 m2; total nitrogen: 8% (w/w), total phosphate: 2%, total potassium: 1%, Nangoku-Kosan Co., Ltd.). The chemical composition of Hinai Green® is SiO2 (71.4% (w/w)), Al2O3 (13.1%), Fe2O3 (3.6%), K2O (2.57%), CaO (1.2%), Na2O (3.5%), MgO (1.2%), and P2O5 (0.1%). The total application rates of total nitrogen, total phosphate, and total potassium in EF1 are 37.6 kg/1000 m2, 12.4 kg/1000 m2, and 18.8 kg/1000 m2, respectively. In EF2, we used a commercial inorganic fertilizer (150 kg/1000 m2; N: 25%, P: 8%, K: 8%, Fukuei fertilizer Co., Ltd.) The total application rates of total nitrogen, total phosphate, and total potassium in EF2 are 37.5 kg/1000 m2, 12 kg/1000 m2, and 12 kg/1000 m2, respectively. Seeds of green onion (Allium fistulosum L.) were sown in soils on 25 July 2017 (day 13). To normalize the influence of differences of microbial diversity in EF1 and EF2, soil fumigation was performed using dazomet (Basamid®, Agro Kanesho Co., Ltd.) prior to the start of green onion cultivation (12 June 2017-day 1). Initial fertilization of the above fertilizers into EF1 and EF2 was applied at day 13. Green leaves with one-quarter of white pseudostem of green onion were harvested three times (days 131, 189, and 261). After harvesting at days 131 and 189, we applied 30 kg/1000 m2 of inorganic fertilizer (Noruchisso, total nitrogen: 15.5% (w/w), nitrate: 14.7%, ammonium: 0.8%, carcium: 26.3%, Meikyo Trading Co., Ltd.) into EF1 and EF2, to further grow the green onion. In 2015–2016, green onion was cultivated with the same fertilization design of EF1 in the houses. In the 20 years before 2015, eggplant (Solanum melongena) was cultivated in the houses.
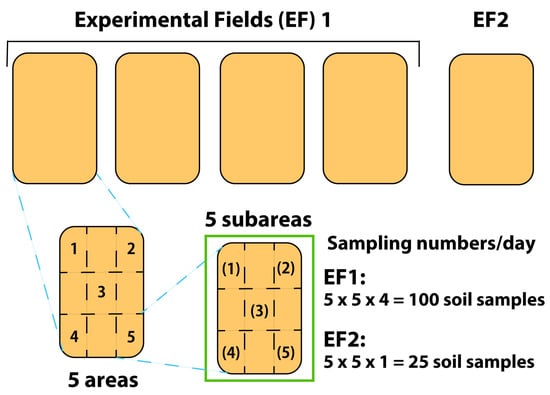
Figure 1.
Information of experimental fields and soil sampling.
For soil sampling, EFs were divided into 5 sampling areas and each area was further divided into 5 subareas (Figure 1). We decided 5 sampling areas as 1 m2 (width: 1 m and length: 1 m), and No. 1, 2, 4, and 5 of the areas were 30 cm distant from both ends of the fields. No. 4 of the area was placed in the center of the fields. For soil microbial community analysis, 10 g of soil (wet weight) was sampled from each subarea (25 samples per EF) on each sampling date—days 1 (before soil fumigation), 13 (after fertilization), 93, 141, 191, 261, and 313. For soil chemical analysis, we sampled approx. 100 g soil from each sampling area (5 samples per EF). Samples for microbial community analysis were stored at −80 °C until the extraction of DNA. To reduce the influence of sample heterogeneity, the 5 subarea samples were mixed together to create a representative sample for each area (5 representative samples per EF). DNA was extracted from these soil samples and the two organic fertilizers (OC1 and OC2) using FastDNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Carlsbad, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Samples for soil chemical analysis were immediately analyzed; Fukuei Fertilizer Co., Ltd. performed soil chemical analyses immediately after sampling—humus [25], pH (glass electrode method), electric conductivity (glass electrode method), NH4+–N (indophenol and 1N KCl methods), NO3−–N (alkalinity reduction method), effective phosphate (Truog procedure and Murphy–Riley method), cation exchange capacity (CEC, Schollenberger method), phosphate absorption coefficient (vanadomolybdate and 2.5% ammonium phosphate methods), potassium (Frame photometry), calcium carbonate (Orthocresol phthalein complexone method), and magnesia (Xylidyl blue method). Yields of cultivated green onions were measured to each have a 1 m2 area (5 measurements per EF) as kg-wet/m2 (Figure 1).
2.2. PCR Amplification and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
We performed 16S rRNA gene amplification using the universal forward primer (Univ515F: 5’-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3’) and the universal reverse primer (Univ909R: 5’-CCCCGYCAATTCMTTTRAGT-3’) [26,27]. The PCR reaction (20 µL) containing 20 ng template DNA, 0.5 µM of forward and reverse primers, and 10 µL of Takara ExTaq HS (Takara Bio, Otsu, Japan) was carried out using Takara Thermal Cycler Dice (TP600, Takara Bio, Japan). The PCR conditions were set as initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, denaturation at 95 °C for 45 s, annealing at 55 °C for 60 s, elongation at 72 °C for 90 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The number of PCR cycles was carried out 25 times. PCR products were purified using a QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The 16S rRNA gene sequencing was conducted using the MiSeq Reagent kit v3 and MiSeq system (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.3. Data Analysis
Raw paired-end 16S rRNA gene sequences were analyzed using QIIME 2 ver. 2018.8 [28]. Quality trimming, primer sequence removal, paired-end assembly, and chimera-check were performed using DADA2 [29]. Assembled sequences were assigned a full-length taxonomy of Greengenes 16S rRNA gene database using classify-sklearn [30,31]. Alpha diversity indices (observed phylotypes and Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (PD) [32]) and the unweighted/weighted UniFrac distances were calculated by QIIME 2 (even sampling at 17,000 reads). The taxonomic placements of predominant phylotypes were confirmed using the web-based Blast search (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). Based on web-based Blast search and Greengenes database assignment, we exclude eukaryotic sequences. Significant differences of alpha diversity indices were calculated using Welch’s t-test. The statistical analysis of the metagenomic profiles software package was used to determine statistical differences of phylotypes abundance during green onion cultivation (days 1, 13, 93, 141, 191, 261, and 313) [33]. The correlations between microbial communities and environmental factors were analyzed and performed using canonical correlation analysis (CCA) in CANOCO software version 5.03 (Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, NY, USA).
2.4. Deposition of DNA Sequence Data
The raw 16S rRNA gene sequences were deposited into the DDBJ Sequence Read Archive database (DRA008413). The 16S rRNA gene sequences of representative phylotypes were deposited into the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases (LC480657–LC480690).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Difference of Yields and Chemical Parameters between Different Farming Experimental Fields
In this study, we examined the effects of composts with natural green tuff as soil conditioner (EF1) and inorganic fertilizer (EF2) on yields of green onion and soil microbial community structures. On average, yields of EF1 were higher than EF2 (Table 1), especially on day 131 (p < 0.05), indicating that the OF designed in this study can increase the yield of green onion compared with CF. The probable reason for no significant differences on days 189 and 261 might be explained by the different harvesting periods of the green onion (day 13–131: growth from seeds; day 131–261: growth from white pseudostem). However, further investigation is required to clarify the mechanisms. EF1 tended to have lower ammonia and nitrate than EF2. The soil pH of EF1 was significantly higher than EF2 on days 93 and 261 (p < 0.05). Other chemical parameters such as effective phosphate, potassium, and magnesia are relatively similar between EF1 and EF2 (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials). The higher pH in OF management soils compared with CF soils often observed in previous studies [34,35]. Therefore, the supplementation of the green tuff in OF management is affected to the increase of plant yield and soil pH in EF1. On days 13, 191, and 313, the NH4+ concentration of EF1 is significantly lower (p < 0.05) than EF2 (Table 2). It is known that an inorganic ammonium fertilizer causes direct increase of NH4+ concentration in soil [36], while compost releases NH4+ and other nutrients slowly into the soil [37]. As for the growth of green onion, a high concentration of NH4+ is known as an inhibitor [38], and the yield of green onion in north Greece by compost-fed OF has been lower than CF [39], presumably caused by low nutrient availability [3]. Given the fact that zeolites have been reported to possess the ability of buffering and adsorption of NH4+ [40,41], green tuff seems to have similar positive effects on OF for green onion.

Table 1.
Yields of green onion at experimental fields during cultivation experiments.

Table 2.
Chemical parameters of pH, ammonia, and nitrate at experimental fields.
3.2. Influences of Organic and Conventional Farming on Soil Microbial Diversity
The soil microbial community was compared between EF1 and EF2, with different soil fertilization methods using 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. We observed 17,689–129,704 non-chimeric sequence reads and 366–1991 phylotypes from 157 samples using MiSeq-based sequences and QIIME 2 analyses. EF1 had significantly higher soil microbial diversity than EF2 on several sampling dates (Figure 2). The observed phylotypes were 51% and 16% higher on days 93 and 261 (p < 0.05), respectively, and phylogenetic diversity was 13–20% higher on days 93, 191, and 261 (p < 0.05). Previous studies report that carbon-rich organic fertilizers can significantly increase soil richness (e.g., observed operational taxonomic unit or species, Shannon index, and PD) compared with CF [12,42], and higher richness enhanced by organic fertilization is thought to positively influence soil productivity [43]. Soil pH in EF1 is continuously higher than EF2, and soil pH is known as an important factor of species richness [44,45]. The green tuff used in this study contains a relatively high concentration of CaO, which can be increased in soil pH, and the components are similar with natural zeolite [46]. Thus, green tuff application with organic fertilizers could be positively influenced to increase species richness and soil pH in EF1.
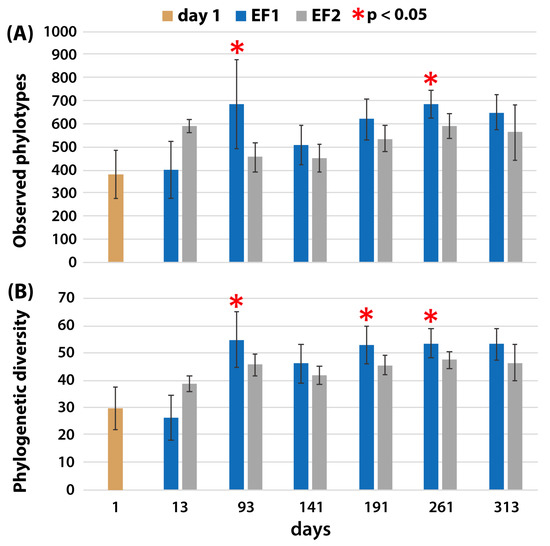
Figure 2.
Alpha diversity indices of (A) observed phylotypes and (B) phylogenetic diversity. Red asterisks indicate statistical difference between Experimental Fields (EF) 1 and EF2 based on Welch’s t-test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Changes of Soil Microbial Community Structures during Green Onion Cultivation
The predominant phyla were assigned to the Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Acidobacteria, which accounted for over 70% of the community in total (Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials). At order-level, the most predominant phylotypes belonged to Bacillales (Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials). Many of Bacillales bacteria can degrade a wide variety of organic compounds and inhabit in organics- and mineral-rich environments [10,47]. In particular, members of the genus Bacillus have the ability to prohibit the growth of fungi through the production of two lipopeptides: iturinA and surfactin [48]. Differences in microbial composition between EF1 and EF2 could not be observed based on principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) with unweighted and weighted UniFrac (Figure S3 in Supplementary Materials), suggesting that the major microbial constituents are not influenced by fertilizer type. A previous study also reported the minor differences of core microbial community compositions between OF and CF systems for cereal cultivation [17].
Through comparing abundances of individual phylotypes between EF1 and EF2, we were able to identify 34 phylotypes with abundances differentiable between fields with different fertilization application (Welch’s t-test—p < 0.05; > 0.2% difference between abundance; Figure 3). During green onion cultivation, 13 phylotypes associated with Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Gammaproteobacteria, and Actinobacteria were statistically more abundant in EF1 (Figure 3). Among these phylotypes, members of the Firmicutes were more abundant in EF1 (8 out of 12 phylotypes). The EF1-associated Firmicutes phylotypes are closely related to known plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB), such as B. niacini (phylotype no. 1, 100% similarity) [49] and Paenibacillus spp. (phylotype no. 6, 100% similarity) [50] (Table S2 in Supplementary Materials). In addition, we found a potential aflatoxin-degrading Bacillus-related phylotype (B. shackletonii, phylotype no. 3, 100% similarity [51]). Fungal toxin such as aflatoxin is produced by Aspergillus spp., which is frequently found in soil [52]. The fungal contamination from soil causes decaying vegetation in a food storage system; therefore, optimal soil management practices such as the microbial degradation of the toxin is considered the primary prevention from fungal infestation and toxin contamination [53]. Therefore, B. shackletonii (no. 3) may contribute to controlling hazardous fungal growth in the system.
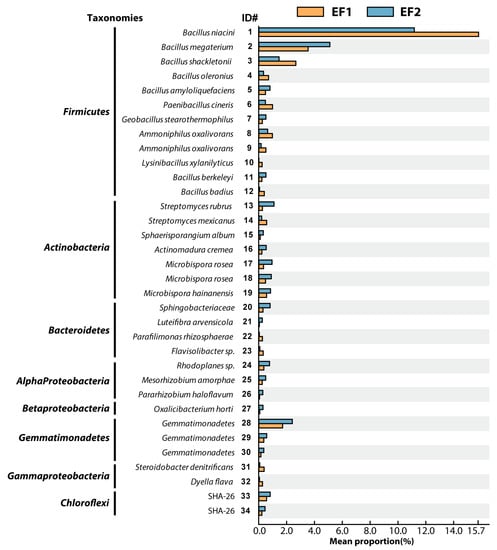
Figure 3.
Extended error bar plot with significantly different phylotype abundances (p < 0.05) between experimental fields (EF) 1 and EF2.
Based on a canonical correlation analysis of the abundances of each phylotype and physico-chemical factors (Figure 4), we found that soil humus content, pH, and NH4+ are positively correlated with several Bacillales populations predominant in EF1; i.e., B. niacini (no. 1), B. shackletonii (no. 3), P. cineris (no. 6), and Ammoniphilus oxalivorans (no. 8 and no. 9). The simultaneous increase of Bacillales abundance, soil organic carbon, and pH was also previously observed in soils with organic manure application [36,54,55]. As discussed above, green tuff likely affects the plant growth yield by controlling soil pH and NH4+. Thus, we suspect that the organic matter from fertilizer and green tuff supplementation may stimulate the growth of PGPB and the degradation of fungal toxin [49,50,51]. Microbial community compositions of seed compost (OC1 and OC2) at genus level indicated that both organic fertilizers contain several Bacillales organisms (Table S3 in Supplementary Materials). Most of the Bacillales organisms predominated in EF1 were not detected in OC1 and OC2, while some of those were found in EF2 (e.g., B. niacin (no. 1), B. megaterium (no. 2), and B. shackletonii (no. 3)), indicating that Bacillales spp. have different niches for nutrition condition and microbial interaction in OF and CF system (Figure 4). Therefore, the growth of the predominant Bacillales organisms including possible PGPB and fungal toxin degrading bacteria in EF1 might be stimulated by physico-chemical characteristics in green tuff with organic fertilizers. Overall, green tuff-enhanced organic fertilization increased not only the yield of green onion, but also the abundance of potentially beneficial Bacillales organisms.
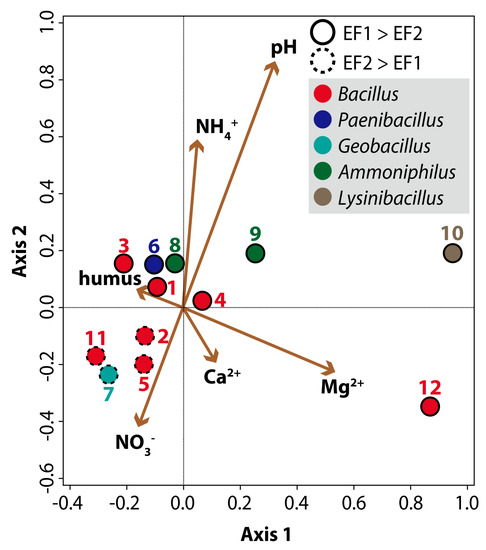
Figure 4.
Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) plots based on representative phylotypes 1–12 belonging to order Bacillales and soil chemical parameters during green onion cultivation for 313 days. Solid circles and dashed circles indicate higher abundance rates in EF1 and EF2, respectively. Total variation is 0.22375 and explanatory variables account for 12.7%. Permutation test of all axes showed F = 1.4 and p = 0.022. Explained fitted variation (cumulative %) of Axis 1 and Axis 2 are 35.44% and 60.65%, respectively.
4. Conclusions
High throughput 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses revealed that green tuff material, in addition to fertilizer compost, may enhance the growth of Bacillales-type microorganisms, which may play important roles in plant growth promotion and fungal toxin degradation. The increase of green onion growth with lower nitrogen availability may be due to the activity of these Bacillales populations. Uncovering the metabolic and ecological impact of microbial populations stimulated by green tuff-enhanced organic fertilizer through future RNA-based studies will be helpful for elucidating the benefit of OF and optimizing its management.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4395/10/7/929/s1, Figure S1: Microbial community composition of experimental fields (EF) 1 and EF2 at phylum level., Figure S2: Microbial community composition of experimental fields (EF) 1 and EF2 at order level., Figure S3: Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plots with (A) unweighted UniFrac and (B) weighted UniFrac in experimental fields., Table S1: Chemical parameters of soil samples at experimental fields., Table S2: Taxonomic assignment of representative phylotypes of this study, Table S3: Microbial community compositions at genus level in fertilized composts of this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and T.O.; Data curation, K.K., H.K., T.A., A.M. and T.N.; Formal analysis, K.K., H.K., T.A., A.M., M.K.N., M.H.; Funding acquisition, K.K.; Investigation, K.K., H.K., T.A., A.M., M.K. and T.O.; Methodology, K.K.; Project administration, K.K., T.O., S.M. and T.Y.; Resources, T.O.; Supervision, K.K., T.N., M.H., S.M. and T.Y.; Validation, K.K., M.K.N., T.N. and M.H.; Visualization, K.K., H.K., T.A., A.M. and M.K.; Writing—original draft, K.K., H.K. and M.K.N.; Writing—review & editing, K.K., H.K., T.A., A.M., M.K., M.K.N., T.N., T.O., M.H., S.M. and T.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partly supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), KAKENHI Grant number 18K13862.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Kuroda Laboratory members M. Kotsusa and Y. Ikedo in National Institute of Technology, Miyakonojo College, for their assistance with the experiments and data analyses, and Haruguchi farm in Fukuoka, Japan, for providing experimental fields of green houses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T.; Pimentel, D.; Paoletti, M.G. Environmental impact of different agricultural management practice: Conventional vs. organic agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plan. Sci. 2011, 30, 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reganold, J.P.; Wachter, J.M. Organic agriculture in the twenty-first century. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFOAM. Principles of Organic Agriculture. Preamble In Movement 2020. Available online: https://www.ifoam.bio/principles-organic-agriculture-brochure (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Schaller, N. Low-input sustainable agriculture. In 1989 Yearbook of Agriculture; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Tuomisto, H.L.; Hodge, I.D.; Riordan, P.; Macdonald, D.W. Does organic farming reduce environmental impacts? —A meta-analysis of European research. J. Env. Manag. 2012, 112, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponisio, L.C.; M’Gonigle, L.K.; Mace, K.C.; Palomino, J.; de Valpine, P.; Kremen, C. Diversification practices reduce organic to conventional yield gap. Proc. R. Soc. 2015, 282, 20141396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloter, M.; Dilly, O.; Munch, J.K. Indicators for evaluating soil quality. Agric. Ecosyst Env. 2003, 98, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; Deyn, G.D.; Goede, R.D.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Frey, B.; Mayer, J.; Mäder, P.; Widmer, F. Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, D.; Schulz, E.; Lentendu, G.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T. Mineral vs. Organic Amendments: Microbial Community Structure, Activity and Abundance of Agriculturally Relevant Microbes Are Driven by Long-Term Fertilization Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupatini, M.; Korthals, G.W.; de Hollander, M.; Janssens, T.K.; Kuramae, E.E. Soil microbiome is more heterogeneous in organic than in conventional farming system. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Williams, M.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Sanderlin, J.S.; Reeves, J.H.; Jenkins, M.B.; Endale, D.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil micr Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plots with (A) weighted UniFrac and (B) unweighted UniFrac in experimental fields obial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Yuan, J.; Raza, W.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Long-term application of bioorganic fertilizers improved soil biochemical properties and microbial communities of an apple orchard soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Liang, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Nie, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Manipulation of the rhizosphere microbial community through application of a new bio-organic fertilizer improves watermelon quality and health. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, D.G.; Perkins, A.J.; Wilson, J.D.; Alexander, I.H.; Grice, P.V.; Evans, A.D. Does organic farming benefit biodiversity? Biol. Cons. 2005, 122, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershina, E.; Valkonen, J.; Kurki, P.; Ivanova, E.; Chirak, E.; Korvigo, I.; Provorov, N.; Andronov, E. Comparative Analysis of Prokaryotic Communities Associated with Organic and Conventional Farming Systems. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Takemura, M.; Miki, T.; Nonaka, M.; Harada, N. Differences in Soil Bacterial Community Compositions in Paddy Fields under Organic and Conventional Farming Conditions. Microbes Env. 2019, 34, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.F.; Bagtzoglou, A.C.; Willig, M.R. The effect of soil texture on richness and diversity of bacterial communities. Environ. Forensics 2011, 12, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eprikashvili, L.; Zautashvili, M.; Kordzakhia, T.; Pirtskhalava, N.; Dzagania, M.; Rubashvili, I.; Tsitsishvili, V. Intensification of bioproductivity of agricultural cultures by adding natural zeolites and brown coals into soils. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2016, 14, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, P.C.; de Armas, J.M.; Artiles, P.T.; Martin, B.D.; Carrazana, R.J.; Lopez, O.R. Effects of zeolite and organic fertilizers on soil quality and yield of sugarcane. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2017, 11, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGilloway, R.L.; Weaver, R.W.; Ming, D.W.; Gruener, J.E. Nitrification in a zeoponic substrate. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazaki, K. Green-tuff landslide areas are beneficial for rice nutrition in Japan. Acad Bras. Cienc. 2006, 78, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kumada, K.; Sato, O.; Ohsumi, Y.; Ohta, S. Humus composition of mountain soils in Central Japan with special reference to the distribution of P type humic acid. J. Soil Sci. 1967, 13, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Nobu, M.K.; Mei, R.; Narihiro, T.; Bocher, B.T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Liu, W.T. A Single-Granule-Level Approach Reveals Ecological Heterogeneity in an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing Strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. QIIME 2, Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. Peerj Prepr. 2018, 6, e27295v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2, High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Beiko, R.G. Identifying biologically relevant differences between metagenomic communities. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdag, O.; Kovács, R.; Parádi, I.; Füzy, A.; Ködöböcz, L.; Mucsi, M.; Szili-Kovács, T.; Inubushi, K.; Takács, T. Density and Diversity of Microbial Symbionts under Organic and Conventional Agricultural Management. Microbes Environ. 2019, 34, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fließbach, A.; Oberholzer, H.R.; Gunst, L.; Mader, P. Soil organic matter and biological soil quality indicators after 21 years of organic and conventional farming. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatiadisa, S.; Wernerb, M.; Buchananb, M. Field assessment of soil quality as affected by compost and fertilizer application in a broccoli field (San Benito County, California). Appl. Soil Ecol. 1999, 12, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivell, P.; Susilawati, K.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M. Compost and crude humic substances produced from selected wastes and their effects on Zea mays L. nutrient uptake and growth. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perner, H.; Schwarz, D.; Krumbein, A.; Li, X.; George, E. Influence of nitrogen forms and mycorrhizal colonization on growth and composition of Chinese bunching onion. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2007, 170, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoulas, N.; Koukounaras, A.; Ilić, Z.S. Nutritional quality of lettuce and onion as companion plants from organic and conventional production in north Greece. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 17, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Lopez-Real, J.M. Natural zeolites and sepiolite as ammonium and ammonia adsorbent materials. Bioresour. Technol. 1993, 43, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithome, M.; Paul, J.W.; Lavkulich, L.M.; Bomke, A.A. Kinetics of ammonium adsorption and desorption by the natural zeolite clinoptilolite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, S.L.; Winqvist, C.; Mota, F.; Ahnström, J.; Turnbull, L.A.; Bengtsson, J. Land-use intensity and the effects of organic farming on biodiversity: A hierarchical meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, J.A.; Deng, S.P.; Da, H.N.; Sun, H.Y.; Raun, W.R. Long-term cattle manure application in soil. II. Effect on soil microbial populations and community structure. Biol. Fertil. Soil 2003, 38, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, L.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M.A. Amending chemical fertilizers with rice straw compost and clinoptilolite zeolite and their effects on nitrogen use efficiency and fresh cob yield of Zea mays L. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2018, 49, 1795–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamoto, M.; Kaneko, T.; Takimoto, Y.; Ito, T.; Miyazato, N.; Maki, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Aoi, T. Microbial community structure and enumeration of Bacillus species in activated sludge. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2017, 15, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Kuipers, O.P. Identification and classification of known and putative antimicrobial compounds produced by a wide variety of Bacillales species. Bmc Genom. 2016, 17, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Kaushik, R.; Saxena, A.K.; Arora, D.K. Diversity and phylogeny of plant growth-promoting bacilli from moderately acidic soil. J. Basic Microbiol. 2011, 51, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Liu, L.; Richman, A.; Yuan, Z.C. Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: A review. Microbiol. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Eisa Ahmed, M.F.; Sangare, L.; Zhao, Y.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Xing, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Novel Aflatoxin-Degrading Enzyme from Bacillus shackletonii L7. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, C.; Abbas, H.K.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Wilkinson, J.R. Aspergillus flavus aflatoxin occurrence and expression of aflatoxin biosynthesis genes in soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouché, T.; Claassens, S.; Maboeta, M. Aflatoxins in the soil ecosystem: An overview of its occurrence, fate, effects and future perspectives. Mycotoxin Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, R.; Hu, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Chu, H.; Zhang, J.; Dolfing, J.; Lin, X. Bacillus asahii comes to the fore in organic manure fertilized alkaline soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Lin, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Bolan, N.; Fan, J.; Ding, W. Long-term application of manure over plant residues mitigates acidification, builds soil organic carbon and shifts prokaryotic diversity in acidic Ultisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 133, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).