Effects of Phase Structure Regulation on Properties of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polyphenylpropylsiloxane-Modified Epoxy Resin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Synthesis of AG/P Resin
2.3. Preparation of AG/P30-S Resin
2.4. Curing of Resin
2.5. Characterization Methods
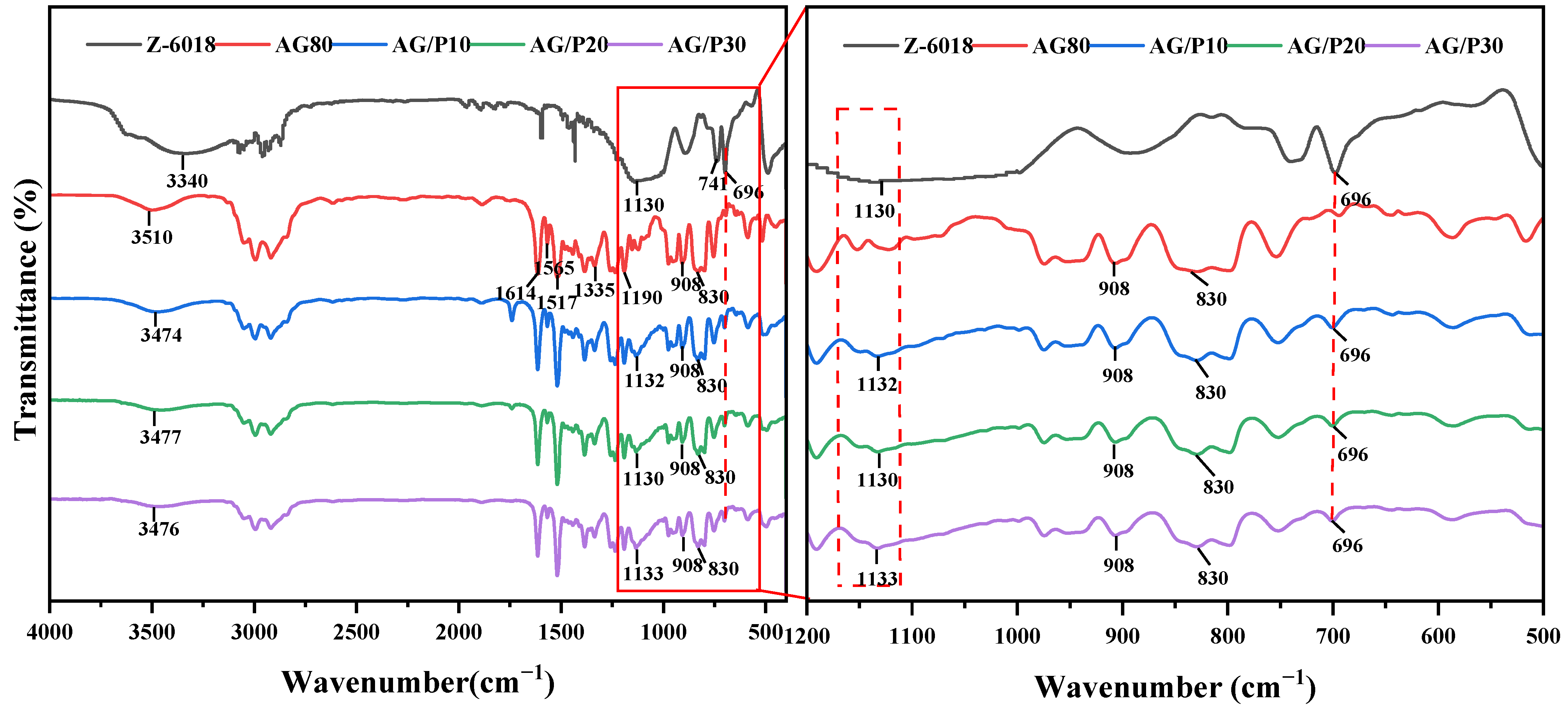
2.5.1. Fourier Transform Infrared
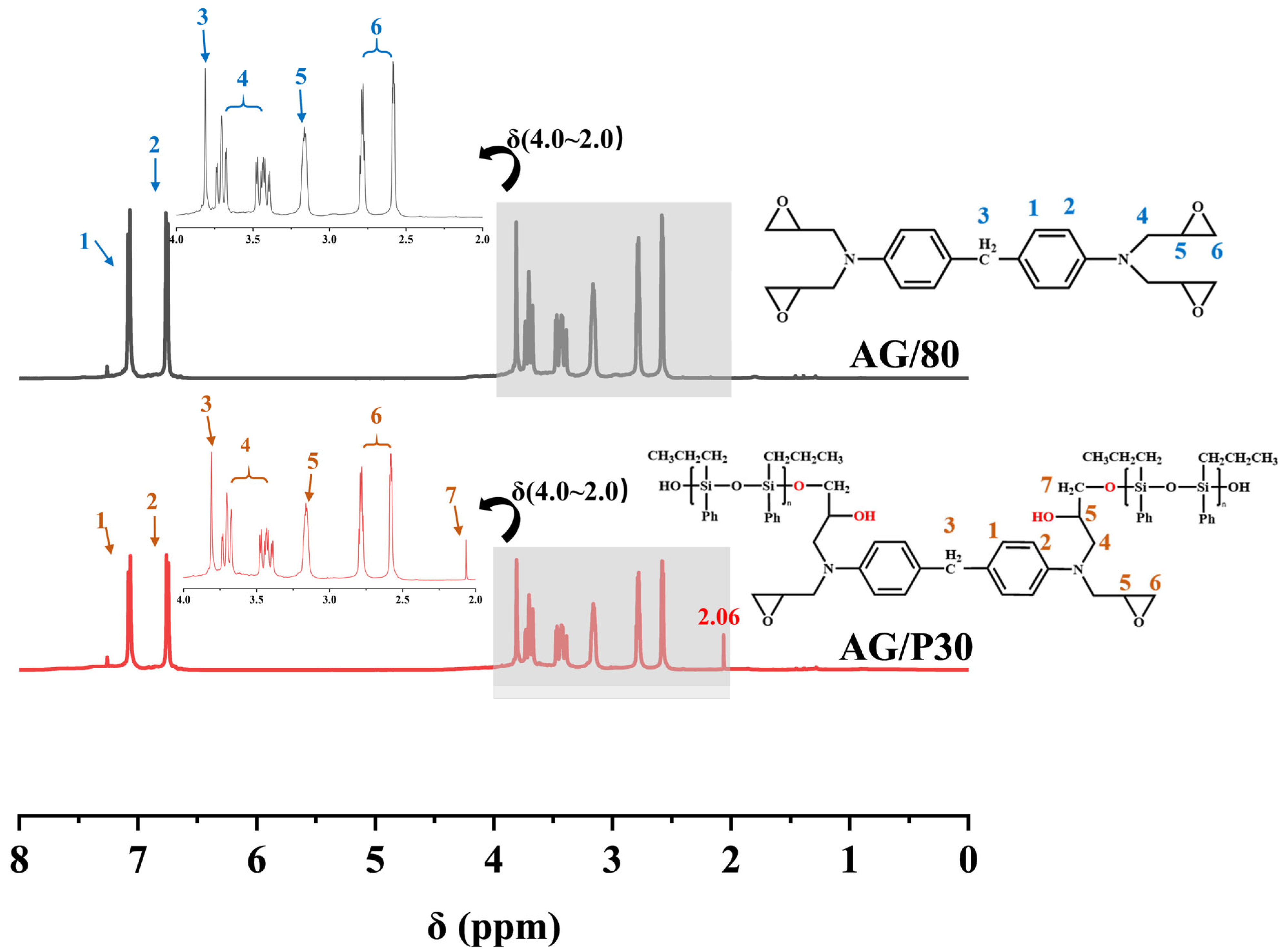
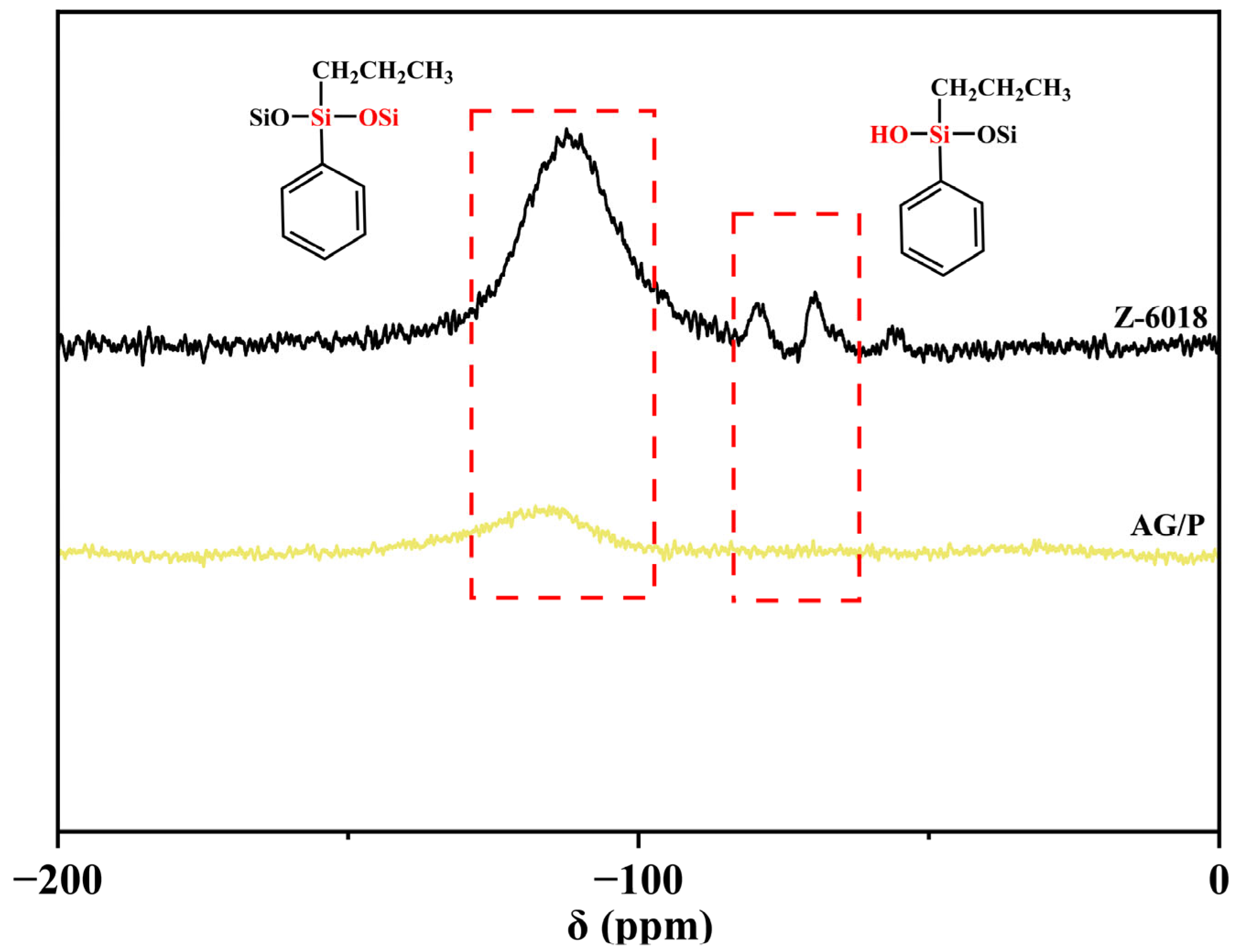
2.5.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonances
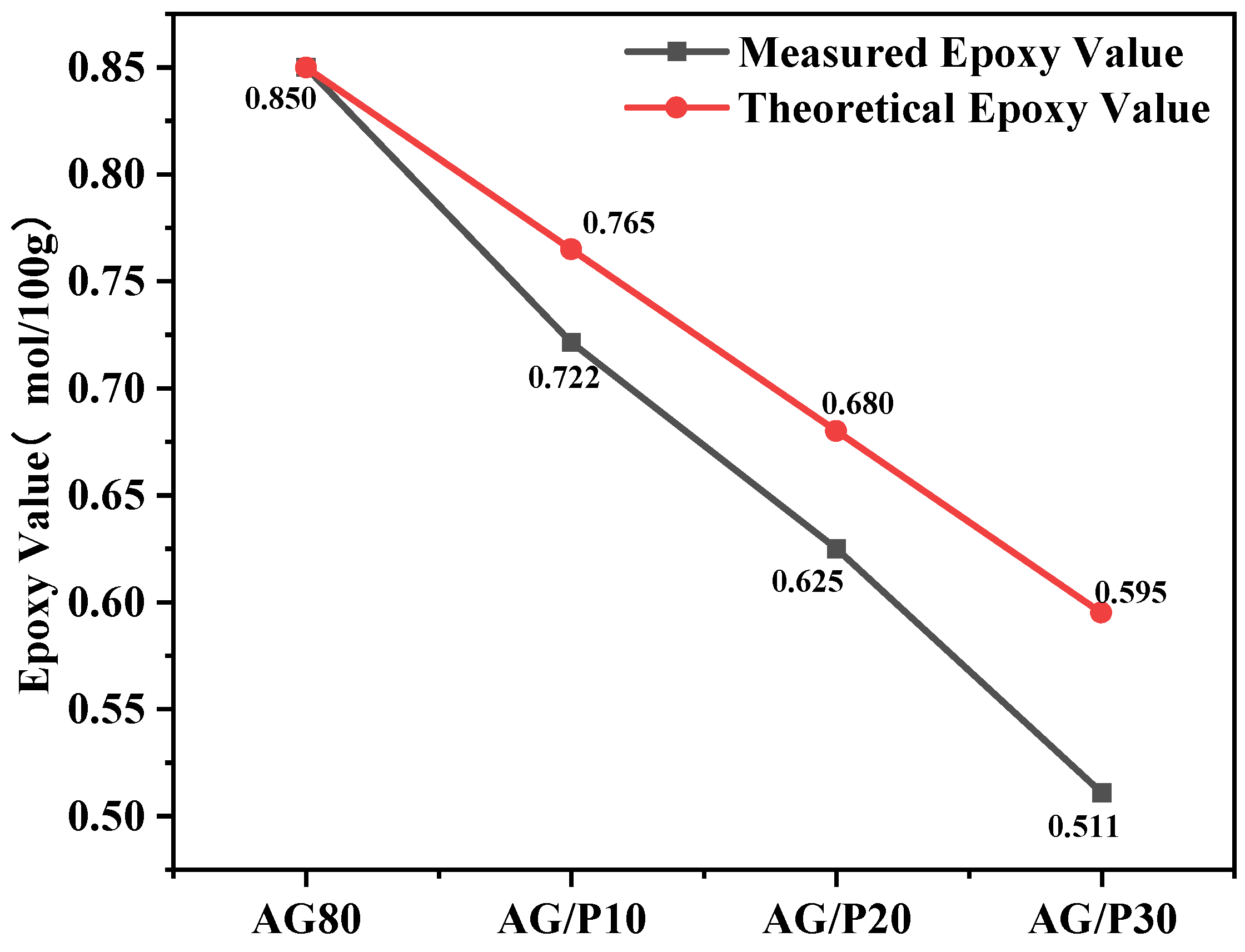
2.5.3. Epoxy Value Titration
2.5.4. Mechanical Properties Test
2.5.5. Morphological Analysis
2.5.6. Dynamic Thermomechanical Analysis Method
2.5.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Analysis
3.2. NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.3. Epoxy Value Analysis
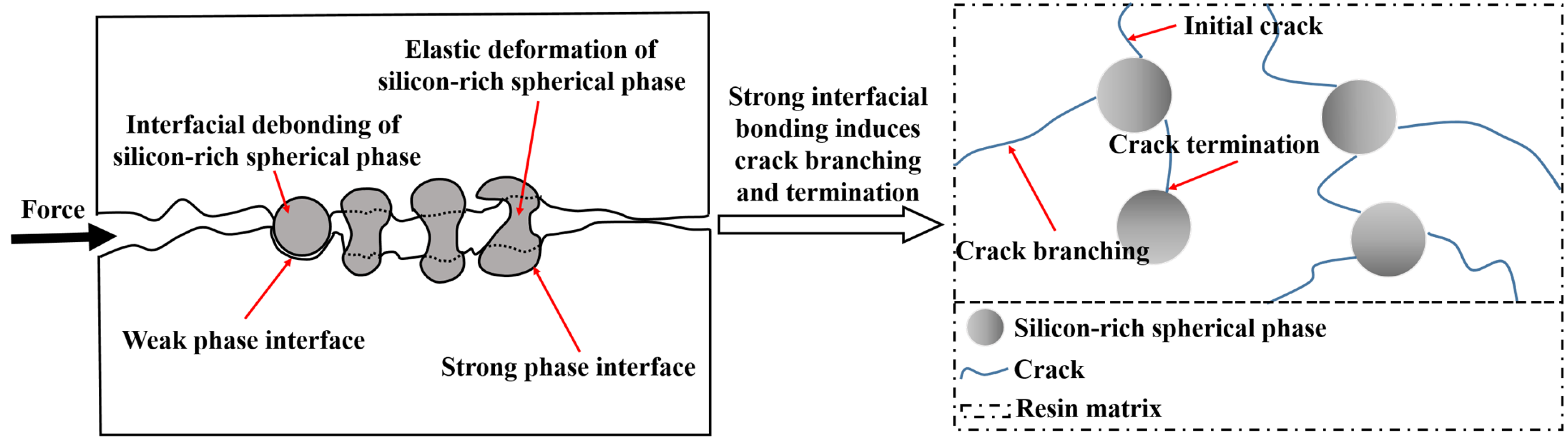
3.4. Mechanical Properties and Morphology Analysis
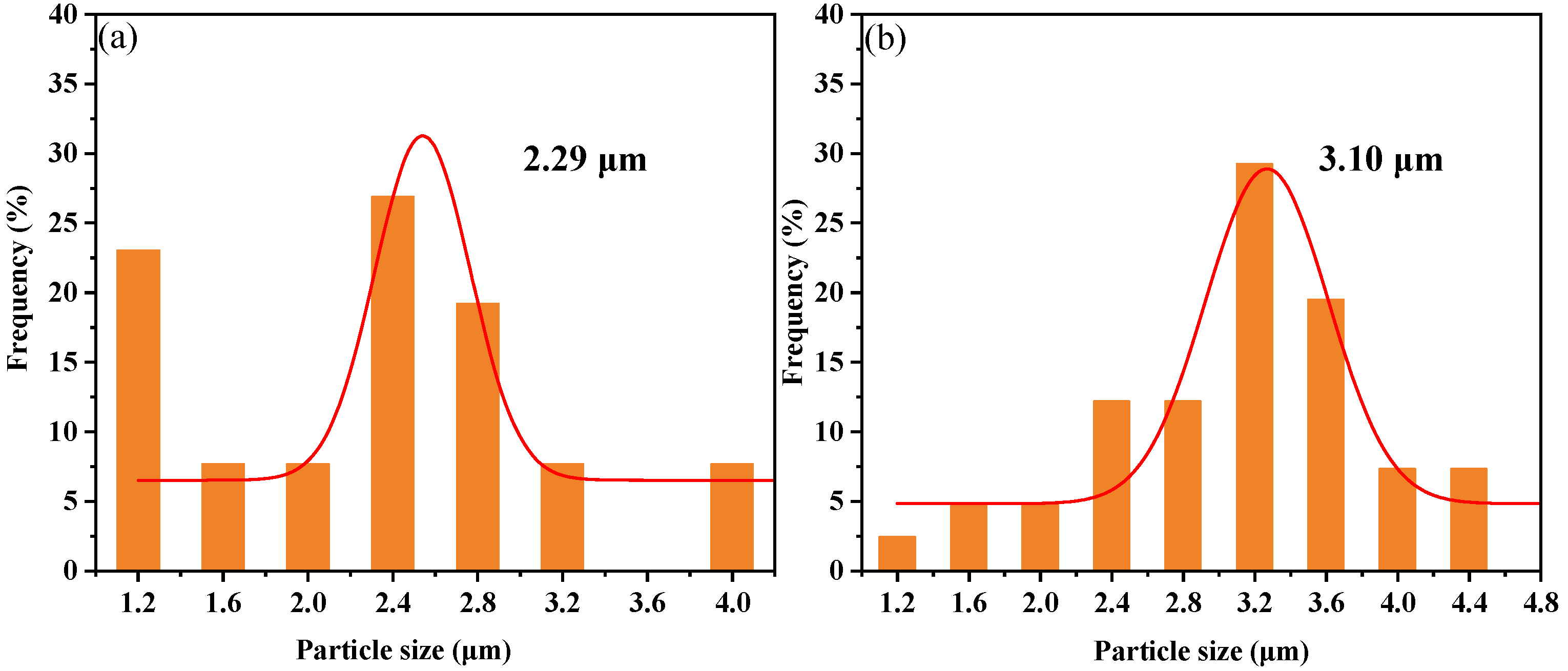
3.4.1. Mechanical Properties and Morphology Analysis of AG/P
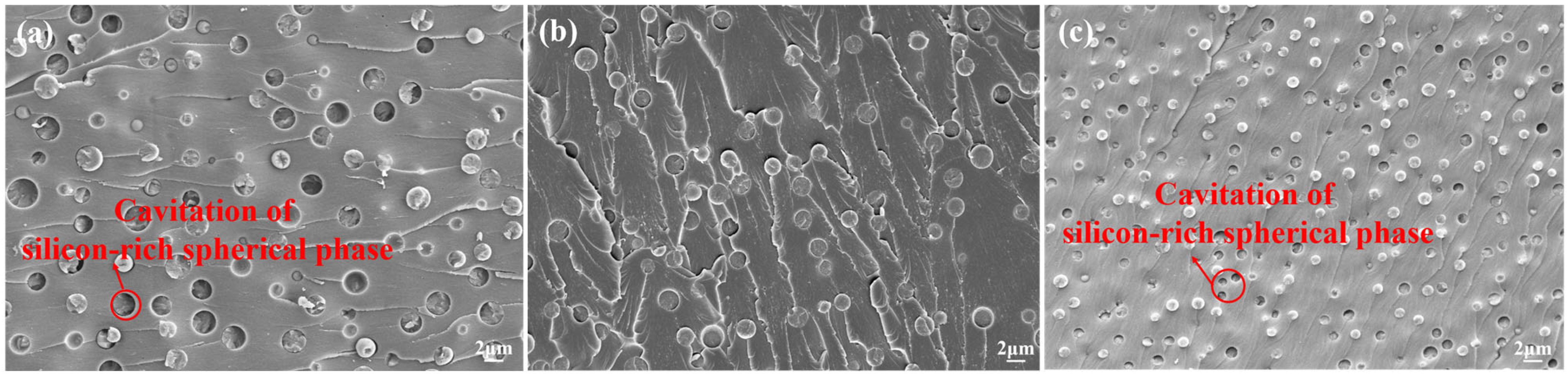
3.4.2. Mechanical Properties and Morphology Analysis of AG/P30-S
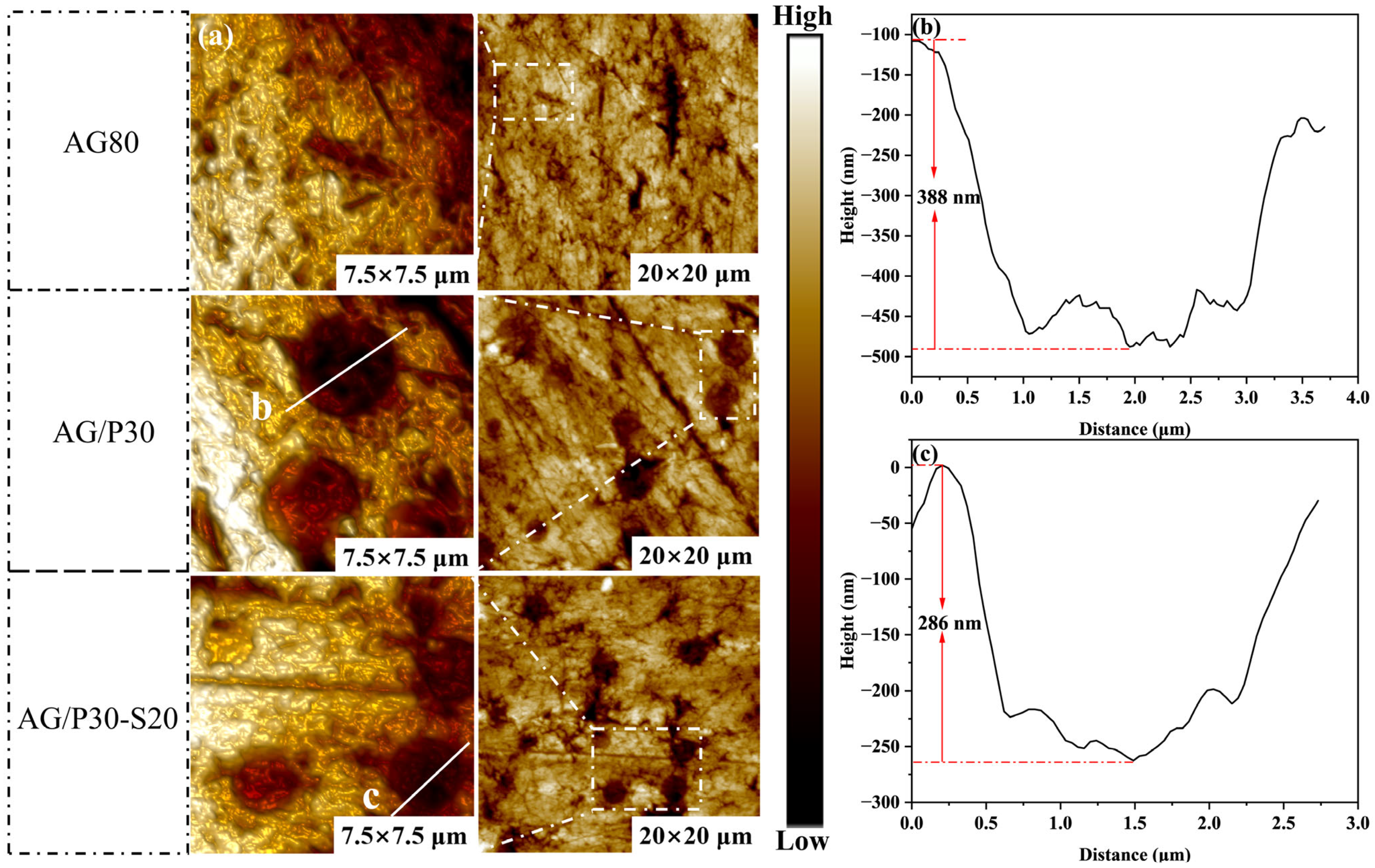
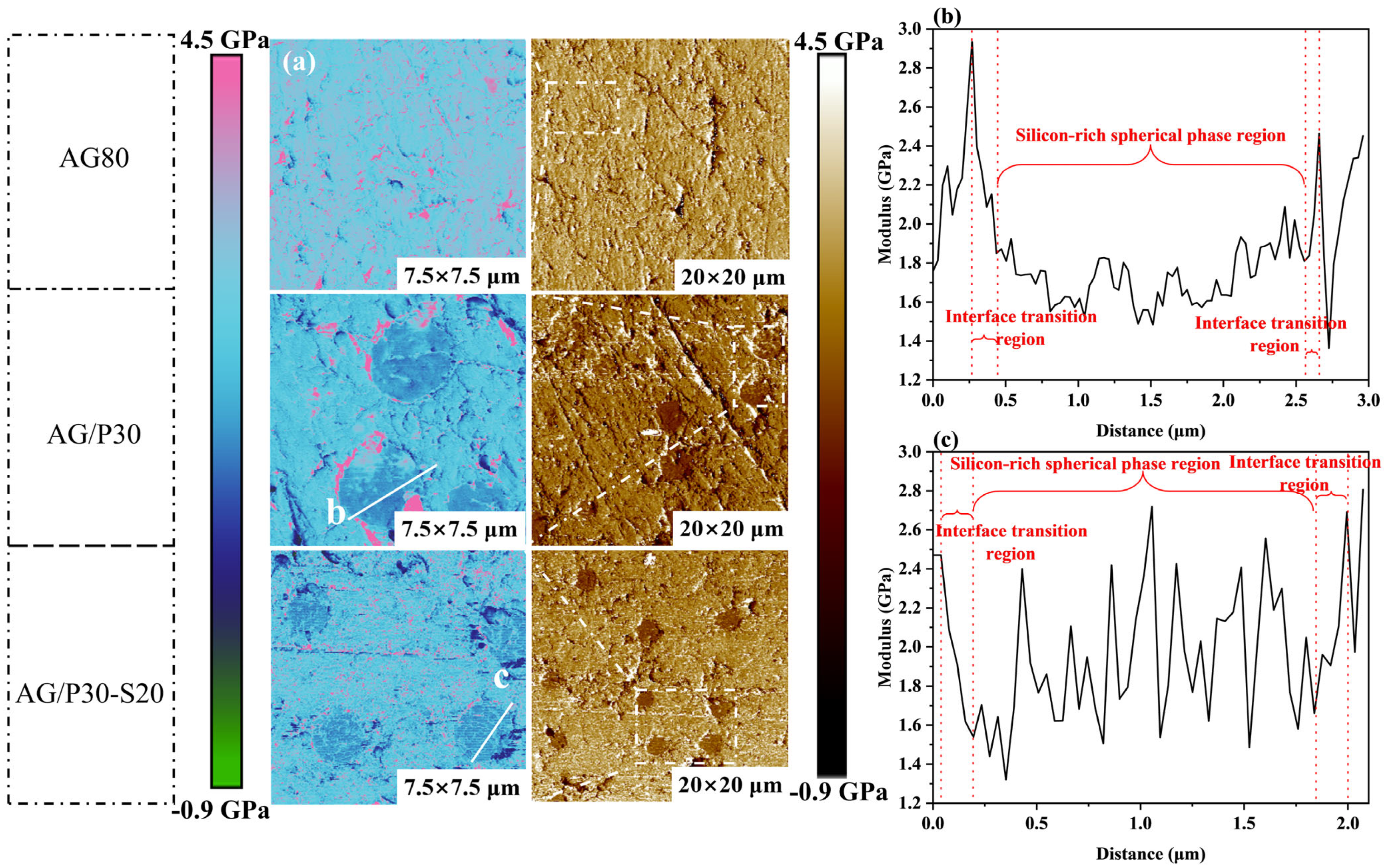
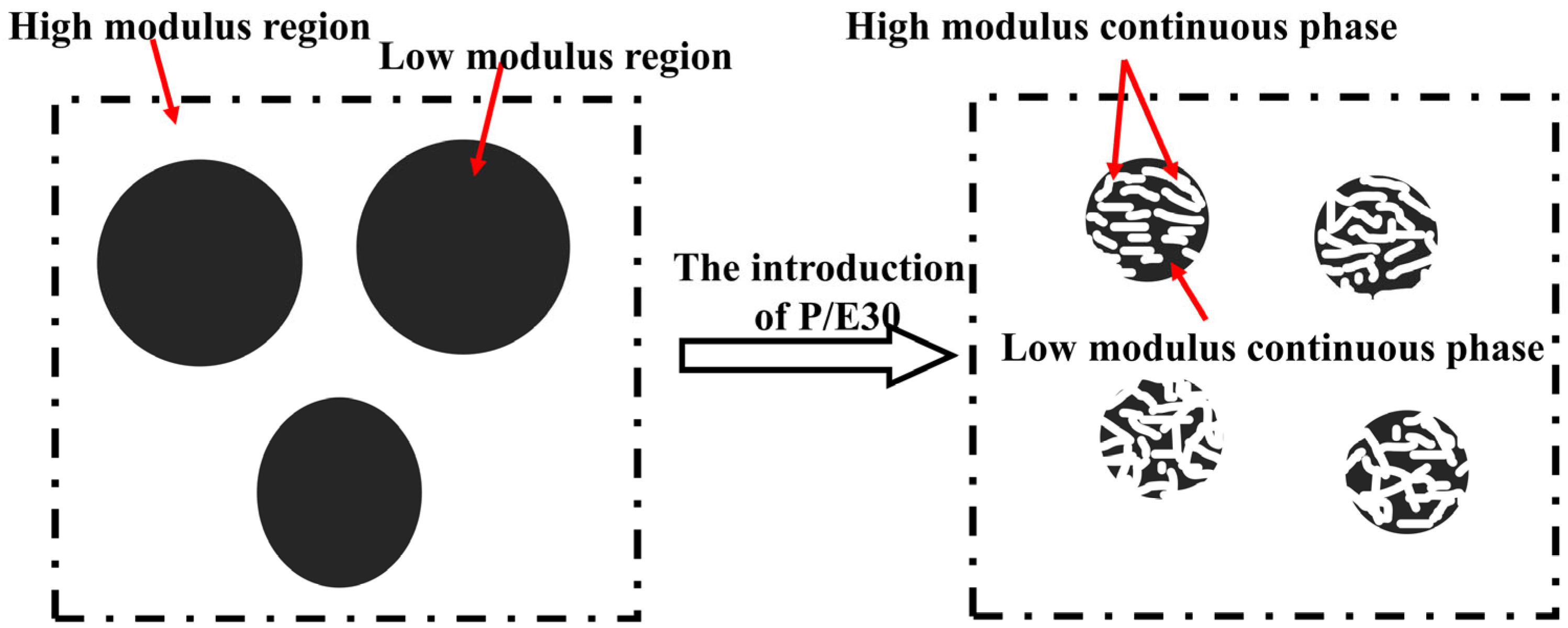
3.4.3. AFM Phase Structure Analysis
3.5. Thermal Performance Analysis
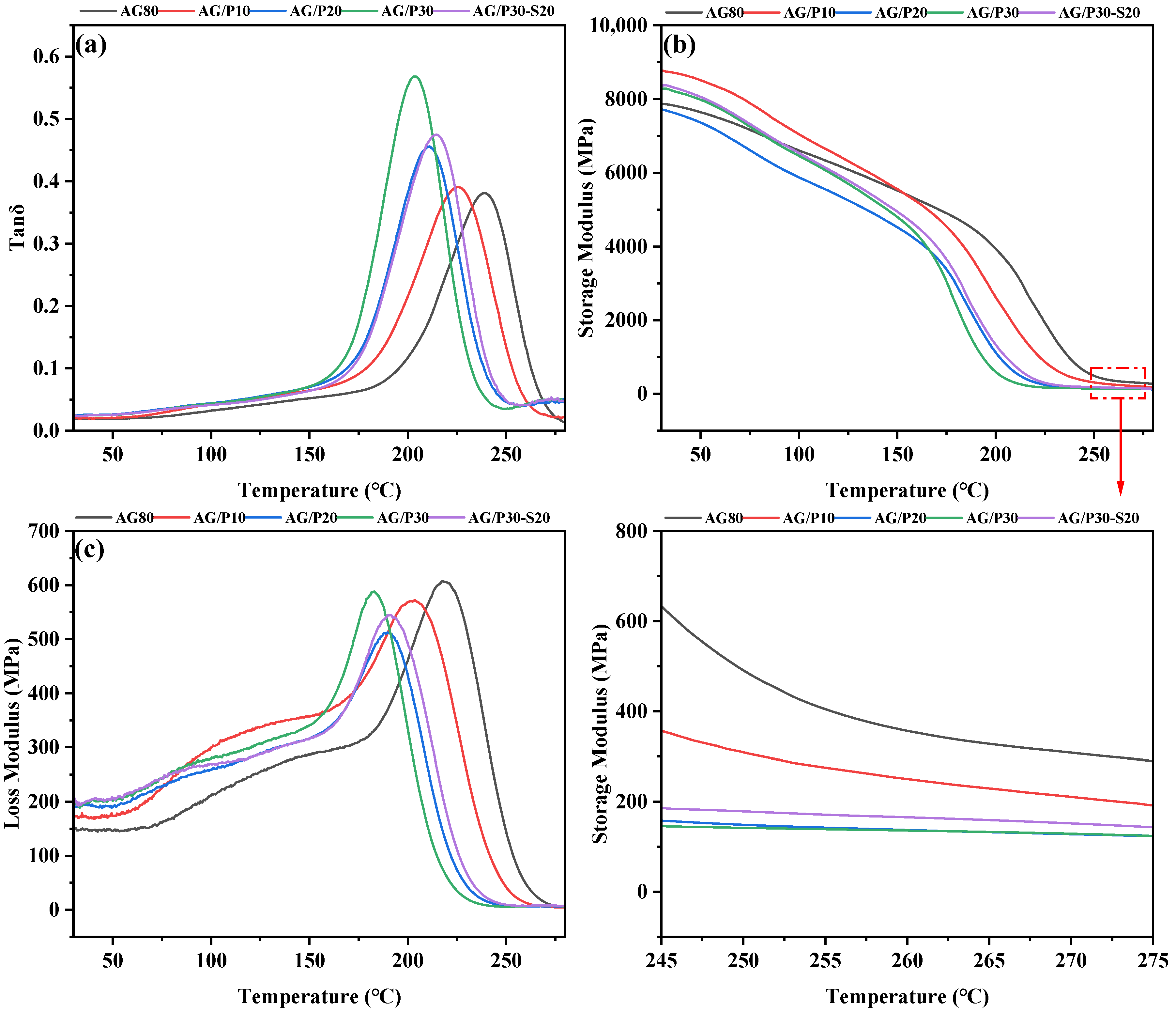
3.5.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
3.5.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, W.; Li, X. Facile synthesis of hyperbranched epoxy resin for combined flame retarding and toughening modification of epoxy thermosets. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Liang, N.; Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Nie, B.; Zhang, D. Toughness and its mechanisms in epoxy resins. Prog. Mater Sci. 2022, 130, 100977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Lu, Q.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Ge, F.; Wang, X. Siloxane-epoxy composite coatings for enhanced resistance to large temperature variations. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 139, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shang, C.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, W. Morphology and properties of TGDDM/DDS epoxy systems toughened by amino-bearing phenyl silicone resins. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4415–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaganapathi, A.; Alagar, M.; Gnanasundaram, P. Studies on synthesis and characterization of hydroxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane-modified epoxy bismaleimide matrices. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.X. Study on modified thermoplastic polymer toughened TGDDM epoxy resin. FRPC 2015, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.; Zou, H.; Liang, M. The preparation and properties study of methoxy functionalized silicone-modified epoxy resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Liang, M. Silicone modified epoxy resins with good toughness, damping properties and high thermal residual weight. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.J.; Tang, L.C.; Gong, L.X.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.B.; Wu, L.B.; Jiang, J.X.; Lai, G.Q. Grafting of epoxy chains onto graphene oxide for epoxy composites with improved mechanical and thermal properties. Carbon 2014, 69, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, S.; Cao, D.; Xu, C.; Ji, Y. Phenyl propyl polysiloxane modified epoxy resin II: The co-continuous phase, concurrently strengthening and toughening mechanism. Polymer 2024, 313, 127665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, S.; Yuan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Cao, D. Phenyl propyl polysiloxane modified epoxy resin I: The content, phase structures and macroproperties. Polymer 2024, 308, 127368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Cao, D.; Huang, D. Phenyl Propyl Polysiloxane-Modified Epoxy Resin III: The Reaction Condition, Phase Structures, and Macroproperties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, e56519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zheng, B.; Yang, J.P.; Xu, G.S.; Fu, S.Y. Preparation and cryogenic mechanical properties of epoxy resins modified by poly (ethersulfone). J. Polym. Sci., Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Guo, Q.; Hanley, T.; Mai, Y.W. Hydrogen bonding interactions, crystallization, and surface hydrophobicity in nanostructured epoxy/block copolymer blends. J. Polym. Sci., Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, W.; Gao, N.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis and properties of LED-packaging epoxy resin toughened by a novel polysiloxane from hydrolysis and condensation. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1677-2023; Determinating the Epoxy Value of Plasticizers. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2023.
- GB/T 2567-2021; Test Methods for Properties of Resin Casting Body. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 41932-2022; Plastics—Determination of Fracture Toughness (GIC and KIC)—Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM) Approach. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chang, J.; Zou, H.; Liang, M. The effect of epoxy–silicone copolymer content on the thermal and mechanical properties of cured epoxy resin modified with siloxane. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 60685–60693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Deng, Z.; Lv, Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Z. Preparation and properties of phenolic epoxy modified silicone resin. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B. 2024, 63, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.J.; Zhang, W.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 52–226. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Song, J.; He, L.; Liang, X.; Ding, H.; Li, Q. Alkoxysilane functionalized polycaprolactone/polysiloxane modified epoxy resin through sol-gel process. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, L.; Ling, Y.; Ge, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, S.; Xia, S.; Liang, M.; Zou, H. Enhanced mechanical and adhesive properties of PDMS coatings via in-situ formation of uniformly dispersed epoxy reinforcing phase. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 174, 107319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kinloch, A.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A. The mechanical properties and toughening mechanisms of an epoxy polymer modified with polysiloxane-based core-shell particles. Polymer 2013, 54, 4276–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.B.; Sang, Y. Plastic Materials and Formulations, 4th ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2024; pp. 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Lin, L.; Cao, Z. The synthesis of an epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polysiloxane toughener and its application at low temperature. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 195, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Tan, J.; Zhu, X. High-branched organosilicon epoxy resin with low viscosity, excellent toughness, hydrophobicity, and dielectric property. Molecules 2023, 28, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Q.; Liu, W.Q.; Hu, C.H.; Wang, Z.F. Modification of epoxy resins with polyether-g-polysiloxanes. Iran. Polym. J. 2010, 19, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H. Phase morphology modulation of silicone-modified epoxy resins and effects on thermal, mechanical and ablative properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 196, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Gan, B.; Li, C.; Molina-Aldareguia, J.; Kalali, E.N.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.Y. A sustainable, eugenol-derived epoxy resin with high biobased content, modulus, hardness and low flammability: Synthesis, curing kinetics and structure–property relationship. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, N.; Macfarlane, I. The thermal degradation of polysiloxanes—I. Poly (dimethylsiloxane). Eur. Polym. J. 1978, 14, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Guo, X.; Lu, J. Thermal degradation behaviors of some branched and linear polysiloxanes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, N. Sustainable Epoxy Thermosets and Nanocomposites; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Shen, M.Y.; Kuan, C.F.; Kuan, H.C.; Ke, C.Y.; Chiang, C.L. Improving thermal stability of polyurethane through the addition of hyperbranched polysiloxane. Polymers 2019, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H. Construction of “Rigid-Flexible” Cocrosslinked Networks by Grafting Bismaleimide and Silicone to Prepare Tough, Heat-Resistant, and Ablation-Resistant Epoxy Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 13623–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

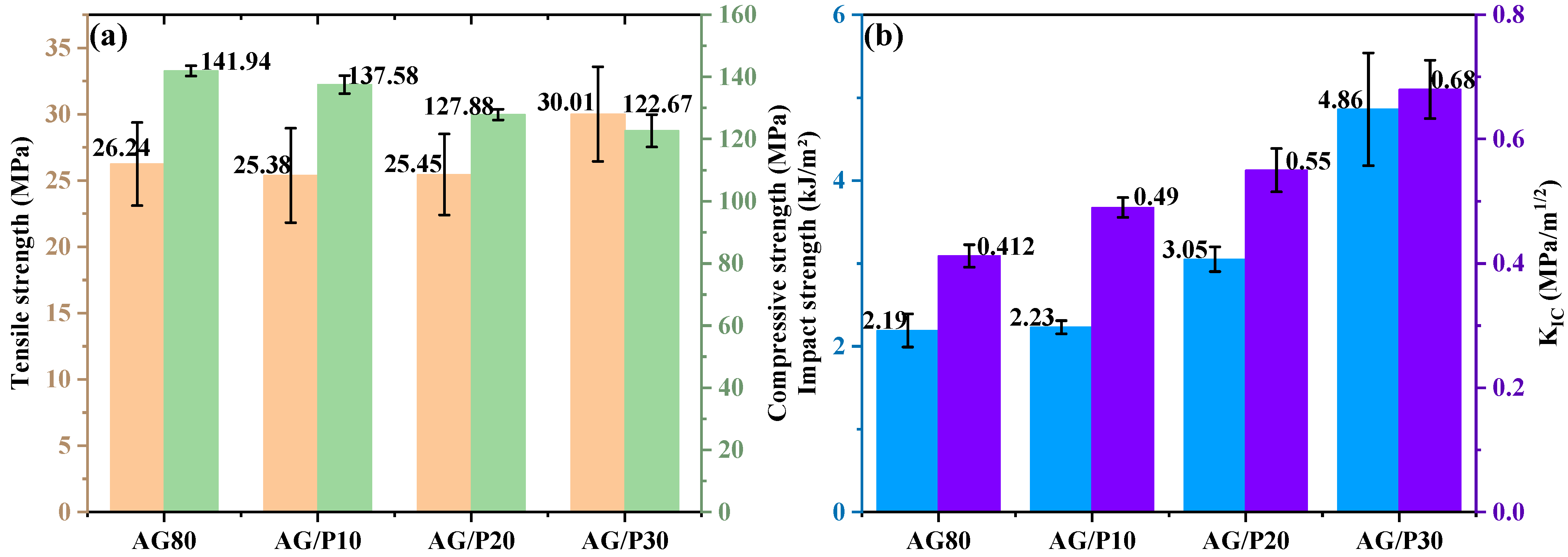

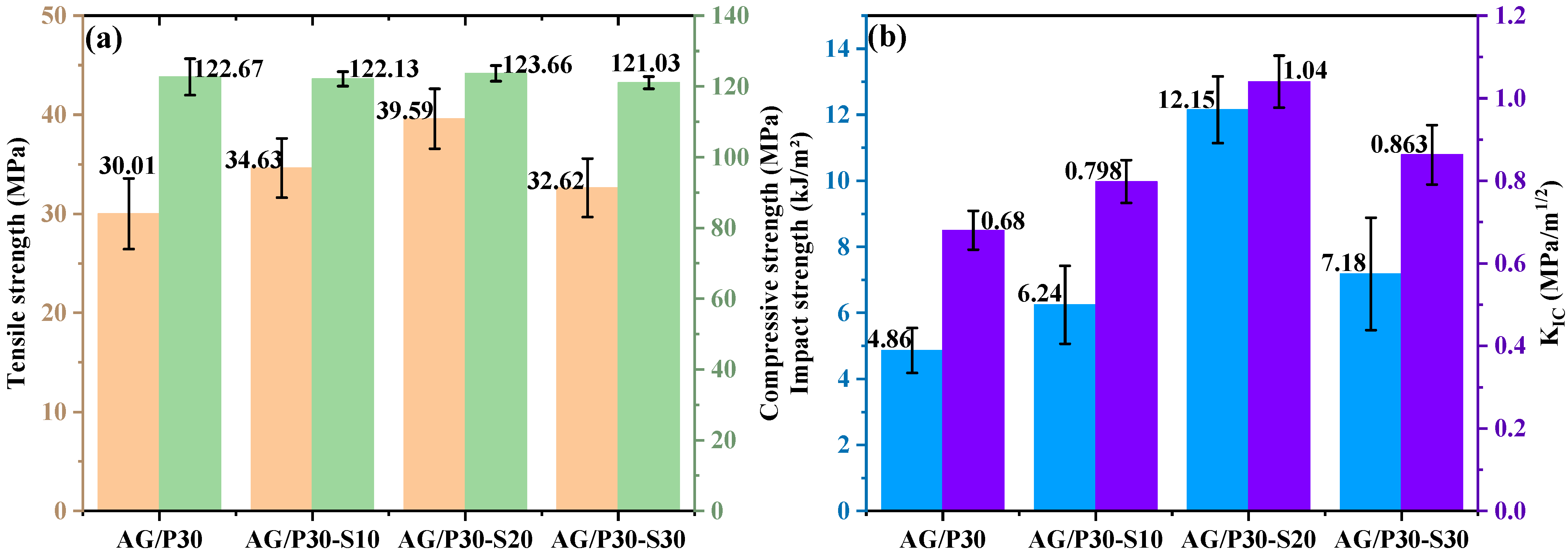


| Sample | AG80/g | Z-6018/g | DMP-30/g | 4-MHHPA/g | P/E30/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG80 | 100 | 0 | 0.5 | 142.97 | 0 |
| AG/P10 | 90 | 10 | 0.5 | 121.61 | 0 |
| AG/P20 | 80 | 20 | 0.5 | 108.49 | 0 |
| AG/P30 | 70 | 30 | 0.5 | 85.95 | 0 |
| AG/P30-S10 | 63 | 27 | 0.5 | 114.86 | 10 |
| AG/P30-S20 | 56 | 24 | 0.5 | 108.12 | 20 |
| AG/P30-S30 | 49 | 21 | 0.5 | 101.37 | 30 |
| Sample | Phase Size/μm | Tg/°C | tanδ | E’/MPa | ρ × 10−3/(mol/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG80 | -- | 239 | 0.36 | 258 | 18.4 |
| AG/P10 | -- | 225 | 0.36 | 189 | 13.8 |
| AG/P20 | 2.29 | 210 | 0.41 | 136 | 10.2 |
| AG/P30 | 3.10 | 204 | 0.53 | 130 | 9.8 |
| AG/P30-S20 | 1.89 | 214 | 0.43 | 159 | 11.9 |
| Sample | Air | N2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5%/°C | T1max%/°C | T2max%/°C | R1000 °C/% | T5%/°C | Tmax%/°C | R1000 °C/% | |
| AG80 | 268 | 303 | 522 | 2.81 | 317 | 363 | 8.50 |
| AG/P10 | 264 | 306 | 532 | 4.31 | 266 | 348 | 12.07 |
| AG/P20 | 261 | 308 | 540 | 6.07 | 280 | 349 | 17.54 |
| AG/P30 | 259 | 304 | 545 | 9.98 | 285 | 354 | 23.17 |
| AG/P30-S20 | 262 | 307 | 535 | 9.53 | 289 | 355 | 21.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Y.; Pan, J.; Xu, C.; Cao, D. Effects of Phase Structure Regulation on Properties of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polyphenylpropylsiloxane-Modified Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2025, 17, 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152099
Ji Y, Pan J, Xu C, Cao D. Effects of Phase Structure Regulation on Properties of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polyphenylpropylsiloxane-Modified Epoxy Resin. Polymers. 2025; 17(15):2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152099
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Yundong, Jun Pan, Chengxin Xu, and Dongfeng Cao. 2025. "Effects of Phase Structure Regulation on Properties of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polyphenylpropylsiloxane-Modified Epoxy Resin" Polymers 17, no. 15: 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152099
APA StyleJi, Y., Pan, J., Xu, C., & Cao, D. (2025). Effects of Phase Structure Regulation on Properties of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polyphenylpropylsiloxane-Modified Epoxy Resin. Polymers, 17(15), 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152099





