Polymeric 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays for Non-Transdermal Drug Delivery and Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of Polymeric 3D-Printed MNAs
2.1. Overview of 3D Printing Techniques
2.2. Polymeric Material Used for 3D Printing of MNAs
2.2.1. Photopolymer Resins
2.2.2. Biodegradable Polymers
2.2.3. Hydrogels
2.2.4. Composite Resins and Materials
2.2.5. Stimuli Responsive Materials
2.2.6. Materials for 4D-Printed MNAs
3. Non-Transdermal Applications of Polymeric 3D-Printed MNAs
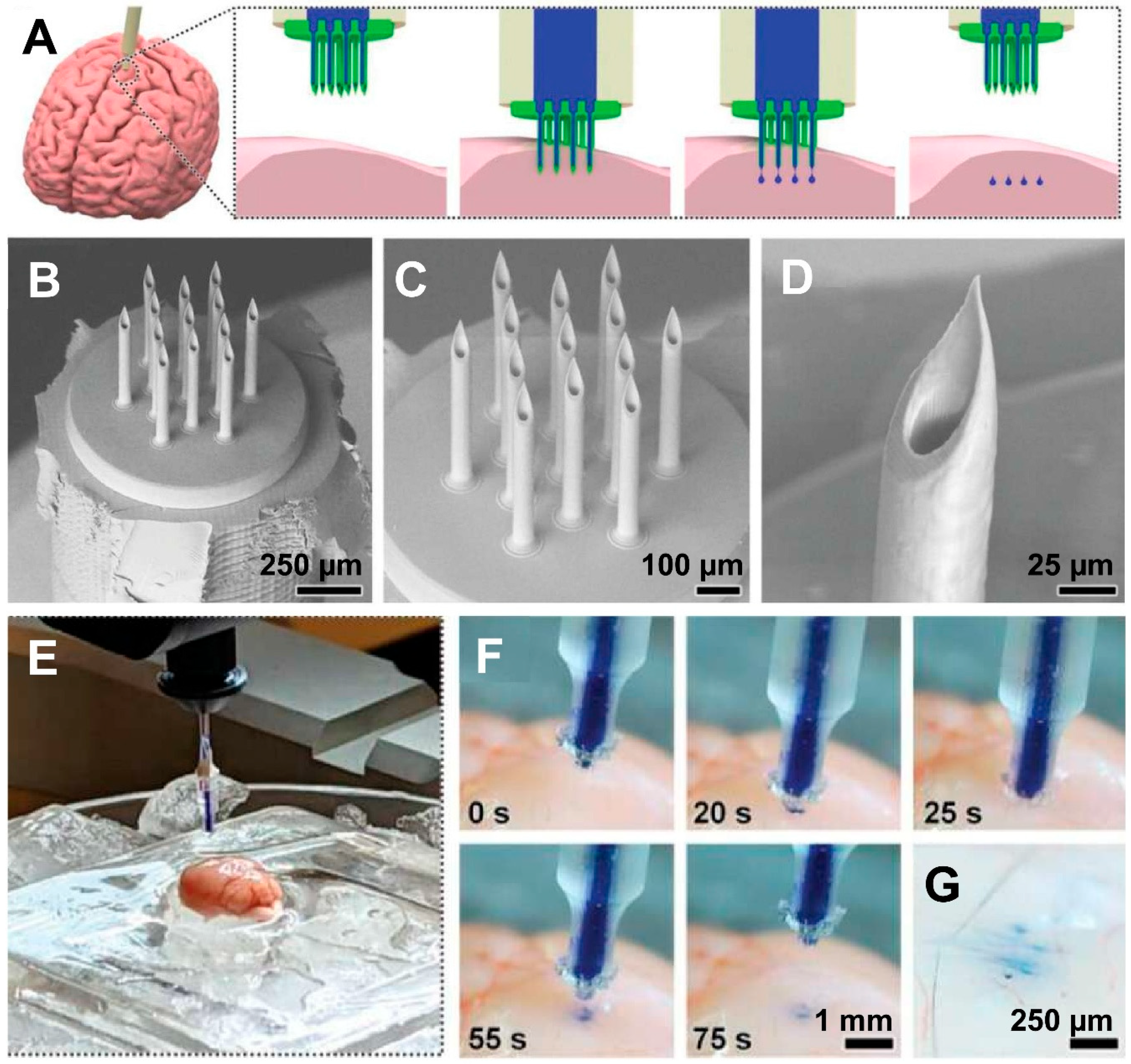
3.1. Brain/Central Nervous System (CNS)
3.2. Oral Cavity
3.3. Ocular (Eye)
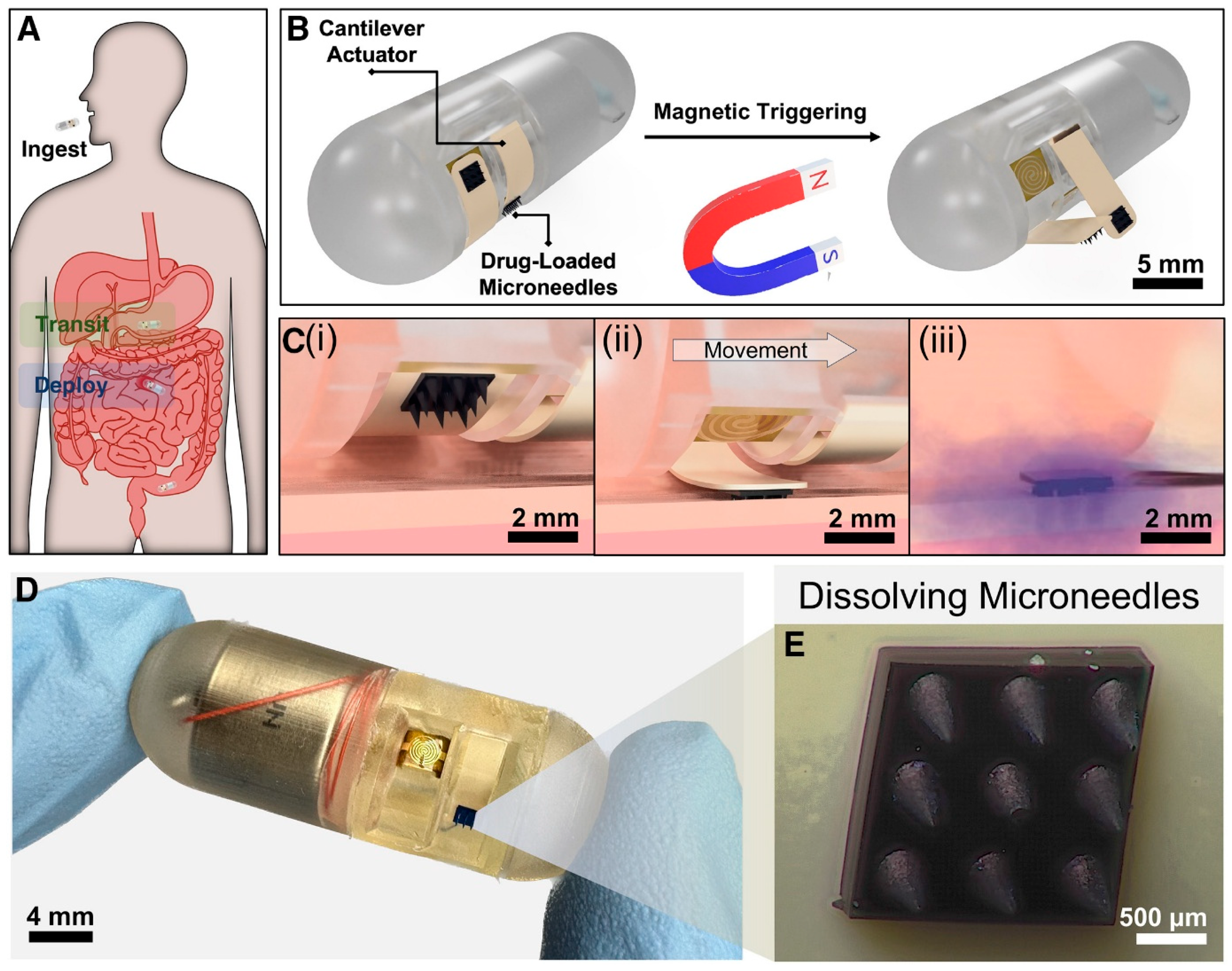
3.4. Gastrointestinal Tract
3.5. Cardiovascular System
3.6. Reproductive System
3.7. Other Emerging Areas
3.7.1. Inner Ear
3.7.2. Targeted Organ Delivery and Tumor Therapy
3.7.3. Point-of-Care 3D Printing of MNAs
4. Challenges and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szabó, A.; De Decker, I.; Semey, S.; Claes, K.E.Y.; Blondeel, P.; Monstrey, S.; Dorpe, J.V.; Van Vlierberghe, S. Photo-crosslinkable polyester microneedles as sustained drug release systems toward hypertrophic scar treatment. Drug Deliv. 2024, 31, 2305818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Han, Y.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Heo, Y.J.; Park, M. Development of an electrochemical biosensor for non-invasive cholesterol monitoring via microneedle-based interstitial fluid extraction. Talanta 2024, 280, 126771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hema; Jindal, A.; Bala, R.; Singh, A. A review on recent advances and challenges of microneedle technology for enhanced topical treatment of skin disorders. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2025, 317, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaghi, M.; Alexander Ninan, J.; Akbari, M. Advancements in Materials for 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays: Enhancing Performance and Biocompatibility. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.X. Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination. Medicines 2025, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzougui, C.; Yang, X.; Meng, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X. Microneedle Array-Based Dermal Interstitial Fluid Biopsy for Cancer Diagnosis: Advances and Challenges. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2404420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroche, A.F.; Nissan, H.E.; Daniele, M.A. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles and Applications in Interstitial Fluid Diagnostic Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2401782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Seong, K.-Y.; Kang, M.; Jang, S.; Yang, S.Y.; Hahn, Y.K. Turbulence-enhanced microneedle immunoassay platform (TMIP) for high-precision biomarker detection from skin interstitial fluid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 282, 117480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Ninan, J.A.; Azimzadeh, M.; Askari, E.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Khademhosseini, A.; Akbari, M. Remote-Controlled Sensing and Drug Delivery via 3D-Printed Hollow Microneedles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2400881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Seyfoori, A.; Pagan, E.; Askari, E.; Hassani Najafabadi, A.; Akbari, M. 3D Printed Hydrogel Microneedle Arrays for Interstitial Fluid Biomarker Extraction and Colorimetric Detection. Polymers 2023, 15, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Goudie, M.J.; Tebon, P.; Sun, W.; Luo, Z.; Lee, J.; Zhang, S.; Fetah, K.; Kim, H.-J.; Xue, Y.; et al. Non-transdermal microneedles for advanced drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 165–166, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Economidou, S.N.; Guiraud, L.; Kazi, M.; Alanazi, F.K.; Douroumis, D. Monoclonal Antibody Delivery Using 3D Printed Biobased Hollow μNe3dle Arrays for the Treatment of Osteoporosis. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 4465–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, C.; He, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Multichannel microneedle dry electrode patches for minimally invasive transdermal recording of electrophysiological signals. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Chen, G. Advances in microneedles for non-transdermal applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwersch, P.; Evens, T.; Van Bael, A.; Castagne, S. Design, fabrication, and penetration assessment of polymeric hollow microneedles with different geometries. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; Lay, E.; Jungwirth, U.; Varenko, V.; Gill, H.S.; Estrela, P.; Leese, H.S. 3D-Printed Hollow Microneedle-Lateral Flow Devices for Rapid Blood-Free Detection of C-Reactive Protein and Procalcitonin. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Colton, A.; Wen, Z.; Xu, X.; Erdi, M.; Jones, A.; Kofinas, P.; Tubaldi, E.; Walczak, P.; Janowski, M.; et al. 3D-Printed Microinjection Needle Arrays via a Hybrid DLP-Direct Laser Writing Strategy. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monou, P.K.; Andriotis, E.G.; Tsongas, K.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Tzetzis, D.; Anastasiadou, P.; Ritzoulis, C.; Vizirianakis, I.S.; Andreadis, D.; et al. Fabrication of 3D Printed Hollow Microneedles by Digital Light Processing for the Buccal Delivery of Actives. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 5072–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, X.; Gou, M. 3D-printed microneedle arrays for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbariamin, D.; Samandari, M.; Ghelich, P.; Shahbazmohamadi, S.; Schmidt, T.A.; Chen, Y.; Tamayol, A. Cleanroom-Free Fabrication of Microneedles for Multimodal Drug Delivery. Small 2023, 19, 2207131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Sharma, P.K.; Murty, U.S.; Mohan, N.H.; Thomas, R.; Dwivedy, S.K.; Banerjee, S. 3D printed hollow microneedles array using stereolithography for efficient transdermal delivery of rifampicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.E.A.-R.; Kohler, S.; Bartzsch, N.; Beuschlein, F.; Guentner, A.T. 3D printing by two-photon polymerization of hollow microneedles for interstitial fluid extraction. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawre, S.; Suryavanshi, P.; Lalchandani, D.S.; Deka, M.K.; Kumar Porwal, P.; Kaity, S.; Roy, S.; Banerjee, S. Bioinspired labrum-shaped stereolithography (SLA) assisted 3D printed hollow microneedles (HMNs) for effectual delivery of ceftriaxone sodium. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 204, 112702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Lim, Y.J.L.; Tay, J.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Tey, H.L.; Liang, K. Design and fabrication of customizable microneedles enabled by 3D printing for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 32, 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Liu, X.; Yuan, X.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Gou, M. Fast Customization of Hollow Microneedle Patches for Insulin Delivery. Int. J. Bioprint. 2022, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaznavi, A.; Xu, J.; Lee, C.U.; Hara, S.A. 3D-Printed Hollow Microneedles Array with Luer Lock Connection for Facile and Painless Intradermal Injection: A Proof of Concept. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, C.; Qiao, T.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Wan, Q.; Zhu, Z.; He, Y. Coral-Inspired Hollow Microneedle Patch with Smart Sensor Therapy for Wound Infection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Nail, A.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Bao, N.; Meng, D.; Zhu, L.; et al. Multi-material 3D printed eutectogel microneedle patches integrated with fast customization and tunable drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2024, 368, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Nail, A.; Meng, D.; Zhu, L.; Guo, X.; Li, C.; Li, H.-J. Recent progress in the 3D printing of microneedle patches for biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 668, 124995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, S.R.; Sarabi, M.R.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Sokullu, E.; Yetisen, A.K.; Tasoglu, S. 3D-printed microneedles in biomedical applications. iScience 2021, 24, 102012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahpour, N.; Pahlevanzadeh, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Berto, F. 3D printed microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: A brief review of two decades. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidleithner, C.; Kalaskar, D.M.; Schmidleithner, C.; Kalaskar, D.M. Stereolithography. In 3D Printing; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.; Chen, S.; King, B.; Lin, H.; King, K.; Akhtar, F.; Diaz, G.; Wang, B.; Zhu, J.; Sun, W.; et al. A 3D-printed microfluidic-enabled hollow microneedle architecture for transdermal drug delivery. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 064125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilla, M.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Steijlen, A.; Morais, S.; Maquieira, Á.; De Wael, K. A 3D-printed hollow microneedle-based electrochemical sensing device for in situ plant health monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 251, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundele, M.; Okafor, H.K. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Microneedles, Their Fabrication and Current Trends in Delivery Methods. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2017, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuskute, H.; Shende, P.; Prabhakar, B. 3D Printed Personalized Medicine for Cancer: Applications for Betterment of Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitaihi, R.; Abukhamees, S.; Chung, S.H.; Craig, D.Q.M. Optimization of stereolithography 3D printing of microneedle micro-molds for ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 658, 124195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, S.N.; Pere, C.P.P.; Reid, A.; Uddin, M.J.; Windmill, J.F.C.; Lamprou, D.A.; Douroumis, D. 3D printed microneedle patches using stereolithography (SLA) for intradermal insulin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, S.N.; Uddin, M.J.; Marques, M.J.; Douroumis, D.; Sow, W.T.; Li, H.; Reid, A.; Windmill, J.F.C.; Podoleanu, A. A novel 3D printed hollow microneedle microelectromechanical system for controlled, personalized transdermal drug delivery. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 38, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mantha, S.N.; Crowder, D.C.; Chinchilla, S.; Shah, K.N.; Yun, Y.H.; Wicker, R.B.; Choi, J.-W. Microstereolithography and characterization of poly(propylene fumarate)-based drug-loaded microneedle arrays. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenikakis, I.; Tzimtzimis, M.; Tsongas, K.; Andreadis, D.; Demiri, E.; Tzetzis, D.; Fatouros, D.G. Fabrication and finite element analysis of stereolithographic 3D printed microneedles for transdermal delivery of model dyes across human skin in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.R.; Procopio, A.T. Low cost additive manufacturing of microneedle masters. 3D Print. Med. 2019, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, S.; Sundar Sahoo, S.; Shukla, S.; Narayan, R.J. Development of 3D-printed conducting microneedle-based electrochemical point-of-care device for transdermal sensing of chlorpromazine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2025, 13, 2114–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnse, T.; Mendes, M.; Shu, W.; O’Cearbhaill, E. Development of Digital Light Processing 3D Printed Microneedles for Biomedical Applications. Appl. Mater. 2024, 41, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mapili, G.; Suhali, G.; Chen, S.; Roy, K. A digital micro-mirror device-based system for the microfabrication of complex, spatially patterned tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 77, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, E.; Pitzanti, G.; Larrañeta, E.; Lamprou, D.A. 3D Printing of Pharmaceuticals and Drug Delivery Devices. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, E.; Pitzanti, G.; Gomes dos Santos, A.L.; Lamprou, D.A. Optimization of Printing Parameters for Digital Light Processing 3D Printing of Hollow Microneedle Arrays. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Jin, G.; Liang, H.; Yang, R. 3D Printed Multi-Functional Hydrogel Microneedles Based on High-Precision Digital Light Processing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Continuous monitoring of diabetes with an integrated microneedle biosensing device through 3D printing. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Wei, T.; Peng, H.; Chen, Z. 3D-Printed Integrated Ultrasonic Microneedle Array for Rapid Transdermal Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 3314–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Akbari, M. The Effect of 3D Printing Tilt Angle on the Penetration of 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhooydonck, A.; Vleugels, J.; Parrilla, M.; Clerx, P.; Watts, R. Optimizing high accuracy 8K LCD 3D-printed Hollow Microneedles: Methodology and ISO-7864:2016 Guided Evaluation for Enhanced Skin Penetration. In Health Informatics and Biomedical Engineering Applications; AHFE Open Access: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenikakis, I.; Tsongas, K.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Tzetzis, D. Additive manufacturing of hollow microneedles for insulin delivery. Int. J. Mod. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 13, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenikakis, I.; Tsongas, K.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Demiri, E.; Zacharis, C.K.; Georgiou, D.; Kalogianni, E.P.; Tzetzis, D.; Fatouros, D.G. Transdermal delivery of insulin across human skin in vitro with 3D printed hollow microneedles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Photo-curing 3D printing technique and its challenges. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolakis, I.A.; Papaioannou, W.; Papadopoulou, E.; Dalampira, M.; Tsolakis, A.I. Comparison in Terms of Accuracy between DLP and LCD Printing Technology for Dental Model Printing. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, A.; Baliga, V.; Shenoy, R.; Dessai, A.D.; Nayak, U.Y. 3D printed microneedles: Revamping transdermal drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, A.S.; Tekko, I.A.; Jomaa, M.H.; Vora, L.; McAlister, E.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Nethery, M.; Baine, P.T.; Mitchell, N.; McNeill, D.W.; et al. Two-Photon Polymerisation 3D Printing of Microneedle Array Templates with Versatile Designs: Application in the Development of Polymeric Drug Delivery Systems. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji Rad, Z.; Prewett, P.; Davies, G. High-resolution two-photon polymerization: The most versatile technique for the fabrication of microneedle arrays. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsianikov, A.; Chichkov, B.; Mente, P.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Doraiswamy, A.; Narayan, R.J. Two Photon Polymerization of Polymer–Ceramic Hybrid Materials for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2007, 4, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, B.; Aksit, A.; Valentini, C.; Yu, M.; Werth, E.G.; Goeta, S.; Tang, C.; Brown, L.M.; Olson, E.S.; Kysar, J.W.; et al. Novel 3D-printed hollow microneedles facilitate safe, reliable, and informative sampling of perilymph from guinea pigs. Hear. Res. 2021, 400, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksit, A.; Rastogi, S.; Nadal, M.L.; Parker, A.M.; Lalwani, A.K.; West, A.C.; Kysar, J.W. Drug delivery device for the inner ear: Ultra-sharp fully metallic microneedles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Xiao, X.; Brener, I.; Burckel, D.B.; Narayan, R.; Polsky, R. Microneedle-Based Transdermal Sensor for On-Chip Potentiometric Determination of K+. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olowe, M.; Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. A Review of 3D-Printing of Microneedles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhong, W.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Yan, Q.; She, Y.; Yang, G. Recent progress of 3D-printed microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouassi, M.-C.; Kallel, A.; Abdallah, A.B.; Nouira, S.; Ballut, S.; Fitoussi, J.; Shirinbayan, M. Assessment of fused deposition modeling (FDM) parameters for fabrication of solid and hollow microneedles using polylactic acid (PLA). Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzuriaga, M.A.; Berry, D.R.; Reagan, J.C.; Smaldone, R.A.; Gassensmith, J.J. Biodegradable 3D printed polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosraviboroujeni, A.; Mirdamadian, S.Z.; Minaiyan, M.; Taheri, A. Preparation and characterization of 3D printed PLA microneedle arrays for prolonged transdermal drug delivery of estradiol valerate. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camović, M.; Biščević, A.; Brčić, I.; Borčak, K.; Bušatlić, S.; Ćenanović, N.; Dedović, A.; Mulalić, A.; Osmanlić, M.; Sirbubalo, M.; et al. Coated 3D Printed PLA Microneedles as Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. In Proceedings of the CMBEBIH 2019, Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 16–18 May 2019; Badnjevic, A., Škrbić, R., Gurbeta Pokvić, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, K.; Samykano, M.; Kadirgama, K.; Harun, W.S.W.; Rahman, M.M. Fused deposition modeling: Process, materials, parameters, properties, and applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1531–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Tsai, J. Enhancement of surface reflectivity of fused deposition modeling parts by post-processing. Opt. Commun. 2019, 430, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Xia, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, B. Morphology Design and Precision Control of Microneedles by PμSL 3D Printing. Polymers 2025, 17, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; He, D.; Ren, S.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. 3D-printed microneedles loaded with madecassoside for periodontal soft tissue regeneration. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 676, 125569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirbubalo, M.; Tucak, A.; Muhamedagić, K.; Rahić, O.; Čekić, A.; Vranić, E. Photopolymerization-Based Technologies for Microneedle Arrays Production. In Proceedings of the CMBEBIH 2021, Mostar, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 21–24 April 2021; IFMBE Proceedings. Badnjevic, A., Gurbeta Pokvić, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 84, pp. 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabriz, A.G.; Viegas, B.; Okereke, M.; Uddin, M.J.; Lopez, E.A.; Zand, N.; Ranatunga, M.; Getti, G.; Douroumis, D. Evaluation of 3D Printability and Biocompatibility of Microfluidic Resin for Fabrication of Solid Microneedles. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Xia, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, B. Investigation of biosensing properties in magnetron sputtered metallized UV-curable polymer microneedle electrodes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2024, 35, 1008–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baykara, D.; Bedir, T.; Ilhan, E.; Mutlu, M.E.; Gunduz, O.; Narayan, R.; Ustundag, C.B. Fabrication and optimization of 3D printed gelatin methacryloyl microneedle arrays based on vat photopolymerization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1157541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Wang, X.; Ou, Z.; Lin, G.; Yin, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. UV-curable, 3D printable and biocompatible silicone elastomers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 137, 105372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Ito, Y. Visible light-curable polymers for biomedical applications. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Shrestha, P.; Iapichino, M.; Cai, Y.; Kim, B.; Stoeber, B. Characterization method for calculating diffusion coefficient of drug from polylactic acid (PLA) microneedles into the skin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, R.D.; Daniels, J.; Stafslien, S.; Nasir, A.; Lefebvre, J.; Narayan, R.J. Polyglycolic acid microneedles modified with inkjet-deposited antifungal coatings. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, R.D.; Jaipan, P.; Skoog, S.A.; Stafslien, S.; VanderWal, L.; Narayan, R.J. Inkjet deposition of itraconazole onto poly(glycolic acid) microneedle arrays. Biointerphases 2016, 11, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Sharma, P.K.; McCann, T.; Bloomekatz, J.; Repka, M.A.; Murthy, S.N. Fabrication and development of controlled release PLGA microneedles for macromolecular delivery using FITC-Dextran as model molecule. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 102712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz Gomes, K.; D’Souza, B.; Vijayanand, S.; Menon, I.; D’Souza, M.J. A dual-delivery platform for vaccination using antigen-loaded nanoparticles in dissolving microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 613, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek-Khatabi, A.; Sadat Razavi, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Rahimzadeghan, M.; Moammeri, F.; Sheikhi, M.; Tavakoli, M.; Rad-Malekshahi, M.; Faraji Rad, Z. Recent progress in PLGA-based microneedle-mediated transdermal drug and vaccine delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 5390–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, A.S.; Mooney, D.J. Regenerative medicine: Current therapies and future directions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14452–14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahnick, A.J.; Dziewior, C.S.; Li, Y.; Chou, A.; Segal, M.; Augustine, E.K.; Ji, R.-R.; Becker, M.L. Controlled Transdermal Delivery of Dexamethasone for Pain Management via Photochemically 3D-Printed Bioresorbable Microneedle Arrays. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2402113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, F.; Wei, L.; Yuan, W. Hydrogel Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiraton, T.; Suwantong, O.; Chuysinuan, P.; Ekabutr, P.; Niamlang, P.; Khampieng, T.; Supaphol, P. Biodegradable microneedle fabricated from sodium alginate-gelatin for transdermal delivery of clindamycin. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xu, B.; Zhou, J. Polymer microneedles fabricated from alginate and hyaluronate for transdermal delivery of insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Sun, W.; Fang, J.; Lee, K.; Li, S.; Gu, Z.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Biodegradable Gelatin Methacryloyl Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Jiang, G.; Liu, T.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jing, Y.; Feng, M.; Shi, Y. Fabrication of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel microneedles for transdermal delivery of metformin in diabetic rats. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2021, 4, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Morde, R.S.; Mariani, S.; La Mattina, A.A.; Vignali, E.; Yang, C.; Barillaro, G.; Lee, H. 4D Printing of a Bioinspired Microneedle Array with Backward-Facing Barbs for Enhanced Tissue Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, L.; Quint, J.; Derakhshandeh, H.; Samandari, M.; Aghabaglou, F.; Farzin, A.; Abbasi, L.; Bencherif, S.; Memic, A.; Mostafalu, P.; et al. 3D-Printed Hydrogel-Filled Microneedle Arrays. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serris, I.; Serris, P.; Frey, K.M.; Cho, H. Development of 3D-Printed Layered PLGA Films for Drug Delivery and Evaluation of Drug Release Behaviors. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shan, W.; Yang, Y.; Joralmon, D.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, H.; Rong, J.; Dai, R.; et al. Limpet Tooth-Inspired Painless Microneedles Fabricated by Magnetic Field-Assisted 3D Printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2003725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, Z.; Yu, H.; Meng, D.; Zhu, L.; Li, H. Direct 3D printing of triple-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel microneedles for controllable drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 670, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Jamaledin, R.; Chen, G.; Baghbantaraghdari, Z.; Zare, E.N.; Di Natale, C.; Onesto, V.; Vecchione, R.; Lee, J.; Tay, F.R.; et al. Stimuli-responsive transdermal microneedle patches. Mater. Today 2021, 47, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.S.; Mishra, S.K.; Kumar, D. Recent progress in conductive polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2932–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, N.; Vaut, L.; Schneider, M. Customized fast-separable microneedles prepared with the aid of 3D printing for nanoparticle delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease drug development and the problem of the blood-brain barrier. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2009, 5, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Soleymani Eil Bakhtiari, S.; Charest, G.; Fortin, D.; Akbari, M. Microneedle arrays for brain drug delivery: The potential of additive manufacturing. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2025, 49, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, B.G.; Alzaghari, L.F.; Alam, P.; Fareed, M.; Kapoor, D.U. Revolutionizing neurological therapies: The role of 3D printed microneedles in precision brain targeted drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 107, 106818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, K.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Jiao, K.; Liu, C.; Fan, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T.; et al. Microneedle/CD-MOF-mediated transdural controlled release of methylprednisolone sodium succinate after spinal cord injury. J. Control. Release 2023, 360, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Shi, Z.; Mao, Y.; Qin, N.; Tao, T.H. Silk Microneedle Patch Capable of On-Demand Multidrug Delivery to the Brain for Glioblastoma Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. From blood–brain barrier to blood–brain interface: New opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Xia, W.; Pan, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Zan, T.; Lai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, H. Engineered microneedle systems for topical cancer therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 31, 101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Son, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.K.; Choi, N.; Yoon, E.-S.; Cho, I.-J. A new thin silicon microneedle with an embedded microchannel for deep brain drug infusion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kang, T.; Cho, H.R.; Lee, G.J.; Park, O.K.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Kim, H.M.; Cha, G.D.; Shin, Y.; et al. Localized Delivery of Theranostic Nanoparticles and High-Energy Photons using Microneedles-on-Bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Han, R.; Shi, Z.; Mao, Y.; Tao, T.H.; Qin, N. Heterogeneous and Multifunctional Silk Microneedles for in Situ Treatment of Brain Glioma. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 January 2020; pp. 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Qin, N.; Tao, T.H. A Silk-Based Microneedle Patch for Controlled Multi-Drug Delivery in Glioma Treatment. In Proceedings of the 2021 21st International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (Transducers), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–24 June 2021; pp. 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, P.; McCrorie, P.; Smith, F.; Vasey, C.; Taresco, V.; Scurr, D.J.; Kern, S.; Smith, S.; Gershkovich, P.; Rahman, R.; et al. Development of nanoparticle loaded microneedles for drug delivery to a brain tumour resection site. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 182, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, J.R.; Kumar, S.; Girdhar, G.A.; Patel, S.; Parekh, N.H.; Patadiya, H.H.; Zinjala, A.N.; Haque, M.; Acharya, J.R.; Kumar, S.; et al. 3D Bioprinting: Shaping the Future of Periodontal Tissue Regeneration and Disease Management. Cureus 2025, 17, e82432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Zarubova, J.; Dashtimighadam, E.; Haghniaz, R.; Khademhosseini, A.; Butte, M.J.; Moshaverinia, A.; Aghaloo, T.; Li, S. Immunomodulatory microneedle patch for periodontal tissue regeneration. Matter 2022, 5, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tao, W.; Krebs, S.J.; Sutton, W.F.; Haigwood, N.L.; Gill, H.S. Vaccine Delivery to the Oral Cavity Using Coated Microneedles Induces Systemic and Mucosal Immunity. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, S.; Glover, K.; Mishra, D.; Sharma, S.; Guy, O.; Donnelly, R.F.; Vora, L.K.; Thakur, R.R.S. Hollow microneedles for ocular drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2024, 371, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.A.; Straker, M.A.; Stine, J.M.; Beardslee, L.A.; Ghodssi, R. Magnetically triggered ingestible capsule for localized microneedle drug delivery. Device 2024, 2, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, A.; Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Soares, V.; Minahan, D.; Tian, R.Y.; Lu, X.; Dellal, D.; Gao, Y.; Kim, S.; Wainer, J.; et al. A luminal unfolding microneedle injector for oral delivery of macromolecules. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engineers’ New Capsule Aims to Deliver Drugs—And Hope—To GI Patients. Maryland Today, 7 December 2022. Available online: https://today.umd.edu/engineers-new-capsule-aims-to-deliver-drugs-and-hope-to-gi-patients (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Hanaphy, P. Purdue University Researchers 3D Print Bacteria Grabbing Colonoscopy Capsules. 3D Printing Industry, 13 August 2020. Available online: https://3dprintingindustry.com/news/purdue-university-researchers-3d-print-bacteria-grabbing-colonoscopy-capsules-174540/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Chen, W.; Wainer, J.; Ryoo, S.W.; Qi, X.; Chang, R.; Li, J.; Lee, S.H.; Min, S.; Wentworth, A.; Collins, J.E.; et al. Dynamic omnidirectional adhesive microneedle system for oral macromolecular drug delivery. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liao, X.; Chen, D.; Jia, X.; Niu, X. Microneedles for non-transdermal drug delivery: Design strategies and current applications. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2025, 8, 243–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.D.; Choudhary, S.; Sen, S.; Pemmaraju, D.B.; Singh, S.K.; Kapoor, D.N. Microneedle patches: The next frontier in cardiovascular care. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhao, Y. Arrowhead Composite Microneedle Patches with Anisotropic Surface Adhesion for Preventing Intrauterine Adhesions. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhen, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Jiang, S.; Wang, T. Combining different types of multifunctional liposomes loaded with ammonium bicarbonate to fabricate microneedle arrays as a vaginal mucosal vaccine adjuvant-dual delivery system (VADDS). J. Control. Release 2017, 246, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3D-Printed Microneedles Open Ears to New Treatments. Columbia University Irving Medical Center. 3 December 2019. Available online: https://www.cuimc.columbia.edu/news/3d-printed-microneedles-open-ears-new-treatments (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Chiang, H.; Yu, M.; Aksit, A.; Wang, W.; Stern-Shavit, S.; Kysar, J.W.; Lalwani, A.K. 3D-Printed Microneedles Create Precise Perforations in Human Round Window Membrane in Situ. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAS3D. The First 3D-Printed Microneedle for Hearing Loss Treatment. RAS3D. 5 January 2025. Available online: https://www.ras.com.tw/en/post/the-first-3d-printed-microneedle-for-hearing-loss-treatment (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- vander Straeten, A.; Sarmadi, M.; Daristotle, J.L.; Kanelli, M.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Collins, J.; Pardeshi, A.; Han, J.; Varshney, D.; Eshaghi, B.; et al. A microneedle vaccine printer for thermostable COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listek, V. The Future of Vaccination? MIT’s 3D Printed Microneedles Show Promise. 3DPrint.com|The Voice of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing. 3 May 2023. Available online: https://3dprint.com/299867/the-future-of-vaccination-mits-3d-printed-microneedles-show-promise/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Che, Q.T.; Seo, J.W.; Charoensri, K.; Nguyen, M.H.; Park, H.J.; Bae, H. 4D-printed microneedles from dual-sensitive chitosan for non-transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.A.; Dhondale, M.R.; Agrawal, A.K.; Serrano, D.R.; Mishra, B.; Kumar, D. Advancements in microneedle fabrication techniques: Artificial intelligence assisted 3D-printing technology. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 1458–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defelippi, K.M.; Kwong, A.Y.S.; Appleget, J.R.; Altay, R.; Matheny, M.B.; Dubus, M.M.; Eribes, L.M.; Mobed-Miremadi, M. An Integrated Approach to Control the Penetration Depth of 3D-Printed Hollow Microneedles. Appl. Mech. 2024, 5, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C. Microneedles for Drug and Vaccine Delivery and Patient Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for transdermal drug delivery: Current trends and fabrication. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Cao, L.; et al. Customized flexible hollow microneedles for psoriasis treatment with reduced-dose drug. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedir, T.; Kadian, S.; Shukla, S.; Gunduz, O.; Narayan, R. Additive manufacturing of microneedles for sensing and drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, H.; Poly, T.S.; Tisha, Z.T.; Rahman, S.; Naveed, A.I.J.; Ahmed, A.; Ahmed, S.N.; Hassan, J.; Uddin, M.J.; Das, D.B. 3D Printed Hollow Microneedles for Treating Skin Wrinkles Using Different Anti-Wrinkle Agents: A Possible Futuristic Approach. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrole, R.S.J.; Azizoglu, E.; Dul, M.; Birchall, J.C.; Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Trends of microneedle technology in the scientific literature, patents, clinical trials and internet activity. Biomaterials 2021, 267, 120491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSimone, J.M.; Robbins, G.R.; Johnson, A.R. Polymeric Microneedles and Rapid Additive Manufacturing of the Same. 6 October 2020. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US10792857B2/en?q=(3D+printed+microneedle)&oq=3D+printed+microneedle+ (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Nguyen, T.D.; Tran, K. Method of Manufacturing a Microneedle Assembly. 1 May 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP3761864B1/en?q=(microneedle+additive+manufacturing+3D)&oq=microneedle++additive++manufacturing+3D&page=1 (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Hang, C. Microneedle Array Device, Methods of Manufacturing and Use Thereof. 7 March 2024. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20240075267A1/en?q=(US+patent+3D+printed+microneedle)&oq=US+patent+3D+printed+microneedle+ (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Creelman, B.; Frivold, C.; Jessup, S.; Saxon, G.; Jarrahian, C. Manufacturing readiness assessment for evaluation of the microneedle array patch industry: An exploration of barriers to full-scale manufacturing. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo-Martínez, Á.; Mallon, B.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Vora, L.K.; Anjani, Q.K.; Donnelly, R.F. Hollow microneedles: A perspective in biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, M. 3D Printing: Enabling a New Era of Opportunities and Challenges for Manufacturing. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. 2016, 4, 2320–9364. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Q.; Wang, L.; Dunn, C.K.; Kuang, X.; Duan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, H.J.; Wang, T. Digital light processing 3D printing of conductive complex structures. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 18, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Nale, T.; Ramavajhala, A.; Mahanta, D.; Sharma, O.; Wadhwa, H.H.; Dhingra, K.; Verma, S. The evolution of transdermal drug delivery: From patches to smart microneedle-biosensor systems. J. Knowl. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2024, 3, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-1:2018; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 1: Evaluation and Testing Within a Risk Management Process. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/68936.html (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- ISO/ASTM 52900:2021(en); Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Fundamentals and Vocabulary. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso-astm:52900:ed-2:v1:en (accessed on 12 July 2025).

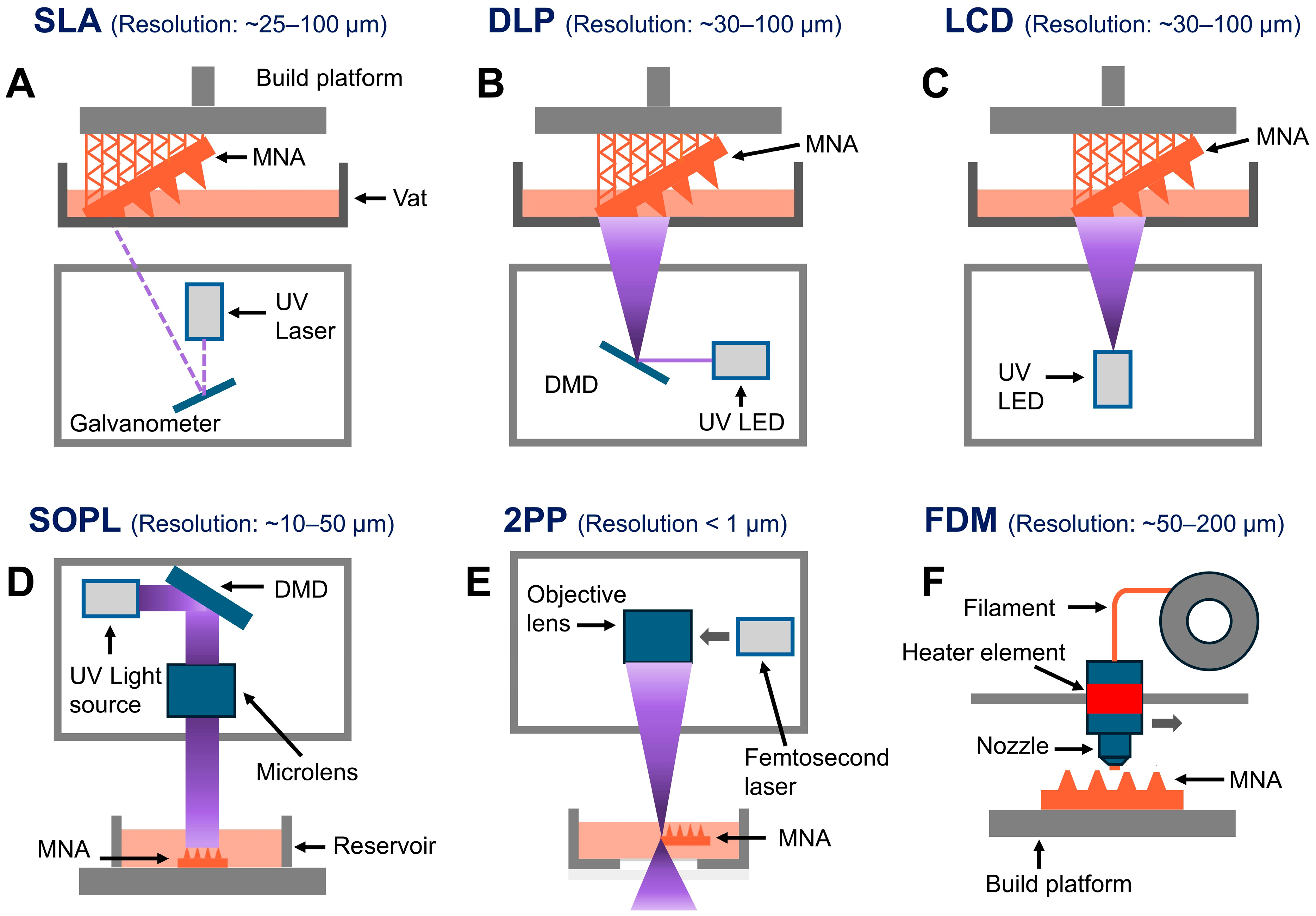

| Fabrication Technique | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA | High-resolution, smooth surface finishes, ideal for intricate designs. | Slower speed com pared to DLP, limited build volume. | [16,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,74] |
| DLP | Faster printing speed, high resolution, suitable for intricate designs. | Potential pixelation effects. | [9,18,42,47,48,49,50,75] |
| LCD | Affordable, large build volume, avoids pixel distortion. | Slightly lower resolution and accuracy compared to DLP. | [41,53,54,55] |
| SOPL | High precision, efficient for specific patterns, suitable for intricate designs. | Limited flexibility in pattern changes during printing. | [25] |
| 2PP | Extremely high resolution, suitable for nanoscale features. | Expensive, slow printing speed, limited material options. | [22,59,60,61,62,63,64] |
| FDM | Cost-effective, wide range of materials, user-friendly. | Low resolution. Often requires post-fabrication processes | [68,69,70,71] |
| Organ/Tissue Applied | Results | Study Type | Model System | Development Stage | Reference Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Reduced tumor size and increased survival via spatiotemporal multidrug release using silk microneedle patch. | In vivo | Mice | Preclinical | [107] |
| Enabled precise sequential release of multiple drugs, significantly inhibiting tumor growth and prolonging survival. | In vivo | Rodent | Preclinical | [112] | |
| Spatiotemporal multidrug release led to reduced tumor volume and significantly prolonged survival in GBM-bearing mice. | In vivo | Rodent | Preclinical | [113] | |
| Achieved controlled release and deep tissue penetration of nanoparticles using dissolving microneedles. | Ex vivo/In vitro | Rat brain tissue | Proof-of-concept | [114] | |
| Enabled precise and minimally invasive delivery of biomolecules into brain tissue. | Ex vivo, Simulation | Mouse brain tissue | Proof-of-concept | [17] | |
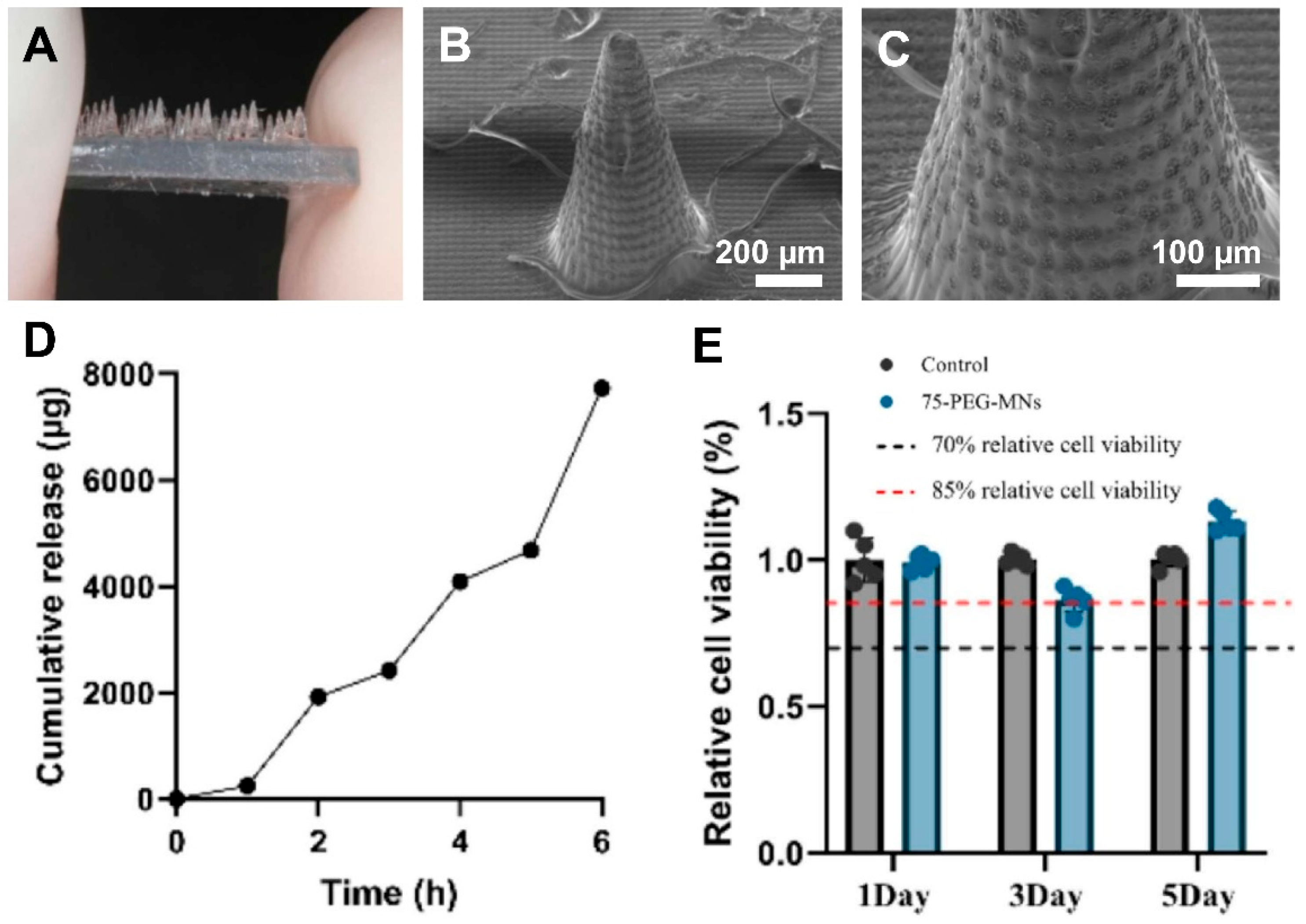
| Oral cavity | Promoted gingival regeneration by enhancing fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition using madecassoside-loaded MNAs. | In vitro, In vivo | Rabbits | Preclinical | [75] |
| Ocular (Eye) | Enabled precise intrascleral delivery using hollow MNAs and 3D-printed adapters with minimal tissue disruption. | Ex vivo | Porcine eye tissue | Proof-of-concept | [118] |
| Achieved precise penetration with optimized MN geometry and SLA parameters for ocular patch fabrication. | Ex vivo | Porcine corneal and scleral tissues | Proof-of-concept | [37] | |
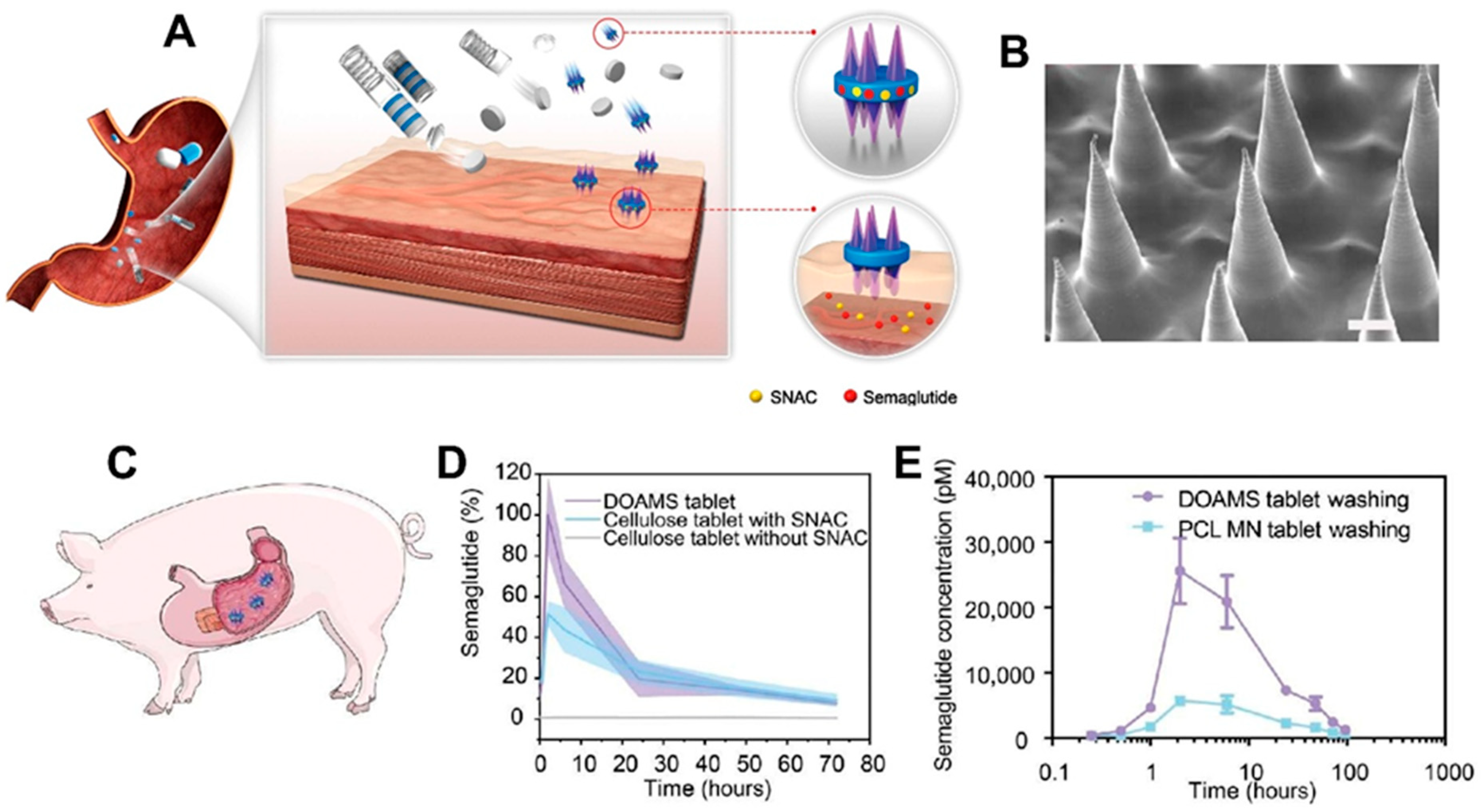
| GI Tract | Enabled oral insulin delivery with significant systemic absorption using ingestible unfolding MNA system. | In vivo, Ex vivo | Human intestinal tissue (ex vivo); pigs (in vivo) | Preclinical | [120] |
| Enabled rapid, targeted drug delivery with magnetically triggered MNA deployment and improved diffusion. | Ex vivo | Porcine intestinal tissue | Proof-of-concept | [119] | |
| Achieved anchored, sustained protein delivery with significant improvement in macromolecule absorption and glycemic control. | In vivo | Pigs | Preclinical | [123] | |
| Inner ear | Enabled safe and precise HRWM perforation, with minimal force and structural integrity maintained. | Ex vivo | Human temporal bone tissue | Proof-of-concept | [129] |
| Point-of-care 3D printing | Induced strong immune response with thermostable mRNA-loaded MNAs and demonstrated vaccine dose scalability. | In vivo | Mice | Preclinical | [131] |
| Demonstrated temperature-responsive shape change and sustained drug release from 4D-printed HBCMA MNAs. | Ex vivo | Chicken breast tissue | Proof-of-concept | [133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razzaghi, M. Polymeric 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays for Non-Transdermal Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. Polymers 2025, 17, 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141982
Razzaghi M. Polymeric 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays for Non-Transdermal Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141982
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazzaghi, Mahmood. 2025. "Polymeric 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays for Non-Transdermal Drug Delivery and Diagnostics" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141982
APA StyleRazzaghi, M. (2025). Polymeric 3D-Printed Microneedle Arrays for Non-Transdermal Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. Polymers, 17(14), 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141982






