Abstract
In this study, cerium-based metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), cerium terephthalate (CeTPA), were synthesized and incorporated into nanofibers via electrospinning using poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). The synthesized materials were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), and Tauc plot analysis. The electrospun CeTPA nanofibers exhibited superhydrophobic properties, with water contact angles exceeding 150°. The adsorption and catalytic performance of the nanofibers were assessed for dye removal using Congo red (CR) and methylene blue (MB) as model organic pollutants. Adsorption studies demonstrated negligible dye uptake due to the hydrophobicity of the fibers, while catalytic degradation experiments in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) showed significant degradation of CR but limited effectiveness against MB, offering high selectivity toward anionic dyes. Structural and optical characterizations confirmed the stability and catalytic activity of CeTPA nanofibers, highlighting their potential for selective dye degradation in wastewater treatment applications.
1. Introduction
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising porous materials with unique chemical, physical, electrical, and spectroscopic properties [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Cerium-based MOFs (Ce-MOFs) have garnered considerable attention [9,10,11]. In general, Ce-based materials, including metal oxides (CeO2), offer varying valence states (Ce(III) and Ce(IV)) with unique structural properties and excellent chemical and physical properties [12,13,14,15,16]. They were applied to several fields, including biomedicine, energy storage and conversion, gas adsorption, separation, and conversion, catalysis and photocatalysis, chemical sensing, and water and wastewater treatment [9]. Cerium-based MOFs are redox-active materials [17] offering applications such as water oxidation [18]. They can be used as catalysts for the degradation of the nerve agent simulant [19]. Ce-MOF, i.e., Ce-MOF-808, was in situ synthesized on the carboxylic acid-functionalized carbon nanotube surface and applied as an electroactive material for supercapacitor applications [20]. However, most of the reported Ce-MOFs are in powder form, making their applications difficult.
Electrospinning is an efficient and straightforward method for continuously producing nanofibers in different forms, including mats or membranes, with unique properties such as porosity and tenability [21,22,23]. Electrospun MOF-based fibers were applied in several applications, including energy storage [24,25], oil–water separation [26], photocatalysis [27], antibacterial agents [28], air purifications via air filters [29], removal particulate matter (PM) [30], microextraction [31], self-powered and sterilizing masks [32], and removal of hexavalent chromium ions [33] or other heavy metal ions [34].
Materials with superhydrophobic surfaces are promising for several applications, including oil/water separation, antifouling, gas adsorption (e.g., carbon dioxide) in humid environments, self-cleaning, and catalysis. Over 20,000 MOFs have been synthesized, although only approximately 60 exhibit superhydrophobic properties [35]. MOFs with hydrophobic properties can be achieved using fluorinated organic linkers [36,37]. The surface of MOFs can also be treated with sodium oleate solutions [38], fluorosilane [39], fluoroethylene vinyl ether [40], fluoroalkyl (−CF3) [41], perfluorodecanethiol [42], and hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HDTMS) [43] to induce hydrophobicity. These methods enabled MOFs with a hydrophobic surface. However, most of the methods are for MOF powder, which requires a substrate for processing. Furthermore, most of these reagents, especially fluorinated compounds, are environmentally unfriendlly.
Herein, we synthesized and processed MOFs, i.e., cerium-based MOFs, into nanofibers via electrospinning. Cerium terephthalate (CeTPA) MOF was electrospun into poly(methylmethacrylate), PMMA. The materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), and Tauc plot. The electrospun CeTPA nanofibers exhibit superhydrophobic properties. The adsorption and catalytic performance of the materials were investigated for dye removal via catalytic degradation.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Ce-MOFs and Electrospinning
Cerium ions (Ce3+) can be coordinated with TPA via carboxylic groups, forming a solvothermal framework. Figure 1 illustrates that the secondary building unit (SBU) of Ce- MOFs is the cerium oxo-cluster (Ce6O4(OH)412+), comprising six cerium atoms arranged in an octahedral configuration. The eight faces of each cerium cluster are capped by alternating μ3-OH and μ3-O groups, leading to the creation of a hexanuclear Ce6(μ3-OH)4(μ3-O)412+ cluster (Figure 1). The hexanuclear Ce6(μ3-OH)4(μ3-O)412+ cluster of the material is interconnected by 12 chemical ligands of TPA2−. The material was dispersed into a solution of PMMA polymer and applied for electrospinning to form white CeTPA fibers. The material was characterized using XRD (Figure 2a), FT-IR (Figure 2b), DRS (Figure 3a), Tauc plot (Figure 3b), and SEM images (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6).
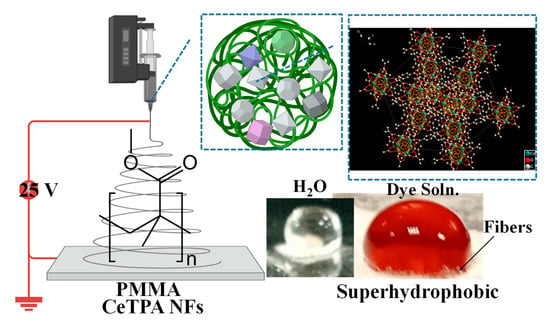
Figure 1.
Schematic representation for electrospinning CeTPA fibers. The inset shows the crystal structure of MOF (CCDC 1036904). The hydrophobicity was imaged using a drop of water and dye solution.
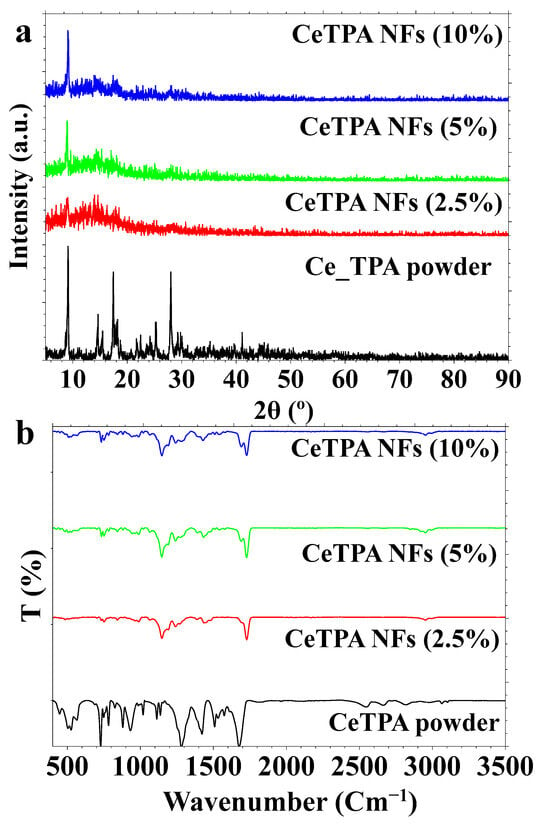
Figure 2.
(a) XRD and (b) FT-IR for CeTPA powder and CeTPA fibers.
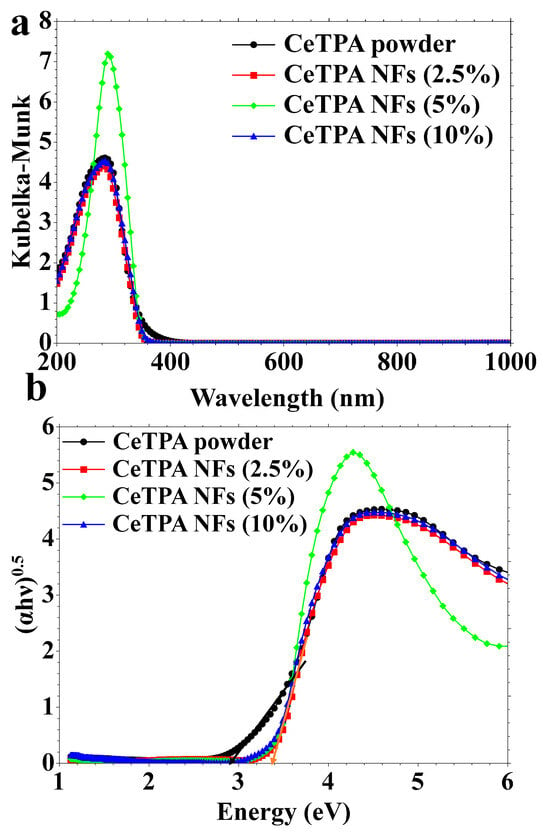
Figure 3.
(a) DRS and (b) Tauc plots.
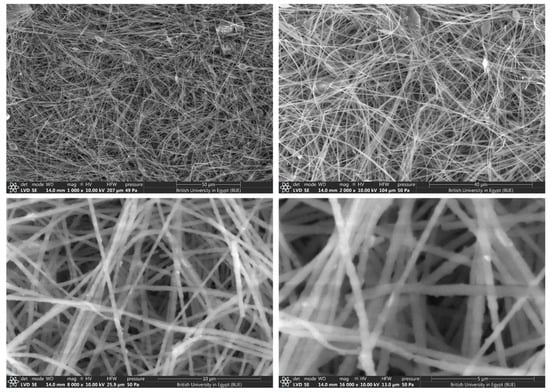
Figure 4.
SEM images at different magnifications for CeTPA fibers with 2.5 wt.%.
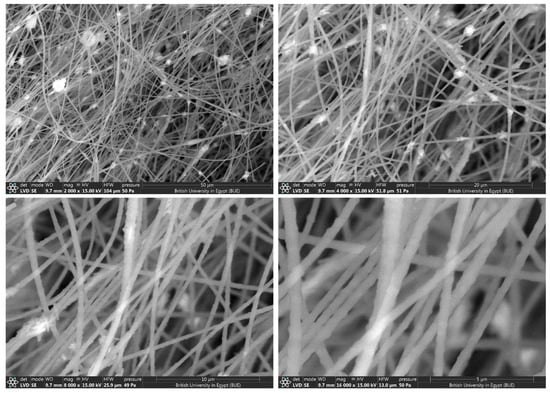
Figure 5.
SEM images at different magnifications for CeTPA fibers with 5 wt.%.
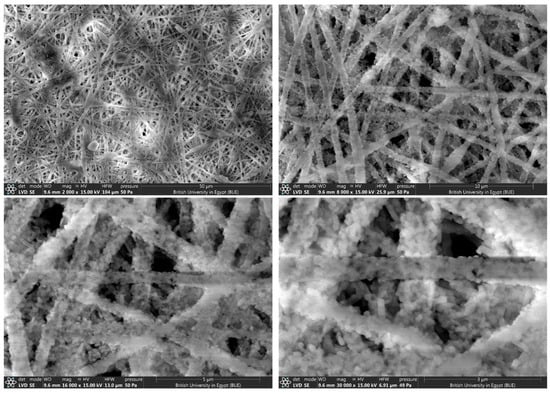
Figure 6.
SEM images at different magnifications for CeTPA fibers with 10 wt.%.
The XRD pattern for Ce-TPA (UiO-66, or [Zr6O4(OH)4(BDC)6]) encompasses powder and nanofiber (NFs) samples at varying concentrations (2.5%, 5%, and 10%, Figure 2a). The intensity and peak positions reveal variations in crystallinity among different samples. The XRD pattern for CeTPA powder exhibits sharp diffraction peaks, indicating a highly crystalline structure (Figure 2a). The peaks correspond to the simulated XRD pattern from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center (CCDC 1036904), confirming that the synthesized CeTPA exhibits the same crystal structure as the simulated data [44]. XRD patterns for CeTPA fibers at various concentrations (2.5–10 wt.%) were also compared in Figure 2a. The fiber samples display broader peaks with lower intensity relative to the powdered form, i.e., CeTPA. The reduction in peak sharpness indicates low crystallinity, likely resulting from the polymer’s high concentration (i.e., PMMA), as well as an electrospinning production process that introduces amorphous or low crystalline polymer, i.e., PMMA. However, the intensity for the crystalline phase can be increased with the increase in the concentration of CeTPA NFs (Figure 2a).
Figure 2b presents FT-IR spectra of CeTPA in both powdered and fiber forms at differing concentrations. CeTPA comprises a Ce6(μ3-OH)4(μ3-O)412+ cluster linked by 12 TPA2− ligands. The FT-IR spectra should have distinctive peaks corresponding to these functional groups, including carboxylate stretching vibrations from TPA ligands. Ce–O stretching modes indicate metal–oxygen bonding within the Ce6 cluster. FT-IR spectrum of CeTPA showed the carboxylate (-COO−) groups exhibit characteristic asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations at 1670 and 1420 cm−1, respectively (Figure 2b). The FT-IR spectra indicate the existence of several functional groups in the pure CeTPA powder and its nanofiber composites with PMMA. The C=O and C-O stretching at 1730 cm−1 and 1150 cm−1 indicate the presence of the ester functional group and C-O groups in PMMA, respectively (Figure 2b). The C-H stretching of the alkyl group was observed at 2800–3000 cm−1. The Ce–O vibrations were observed at 500–800 cm−1, indicating the interactions between metal and oxygen within the Ce6 cluster. As CeTPA concentration rises (2.5%, 5%, and 10%), the strength of CeTPA-associated peaks increases, whereas certain CeTPA-related peaks exhibit wavenumber shifts or broadening attributable to polymer interactions. The FT-IR spectra validate the integration of CeTPA into the PMMA fibers. Data analysis confirms the integration between CeTPA and PMMA without considerable structural disturbance.
The optical properties of CeTPA and its fibers are evaluated using DRS (Figure 3a) and Tauc plots (Figure 3b). The DRS spectrum of CeTPA powder exhibits a distinct absorbance pattern within the wavelength range of 200 to 400 nm. DRS spectra of all materials exhibit similar profiles with a maximum absorption at 285 nm, explaining the white color of the materials (Figure 3a). The same profile was observed for all CeTPA fibers (Figure 3a). The optical bandgap of the materials was assessed using the Tauc plot for CeTPA powder and CeTPA/PMMA nanofibers (2.5%, 5%, and 10 wt.%, Figure 3b). The Tauc plots for the fibers at varying concentrations elucidate the relationship between band gap energy and CeTPA concentration. The plots show insignificant variations in the band gap energy, suggesting that the electronic characteristics of the material are affected by the concentration of CeTPA in the nanofibers. CeTPA powder and its fibers show optical bandgaps of 2.9–3.2 eV (Figure 3b).
The morphology and fiber diameters were evaluated using SEM images for CeTPA loadings of 2.5% (Figure 4), 5% (Figure 5), and 10% (Figure 6). SEM images show unwoven fibers with random orientations. All images confirm the formation of fibers with variable diameters. At low concentrations (2.5%), the fibers exhibit small diameters in the 350–400 nm range (Figure 4). The diameter increases with the increase in CeTPA loading. High CeTPA loading of 10 wt.% shows diameters of 1000 nm (1 µm, Figure 6).
2.2. Application for Water Treatment
Water treatment via removal of organic pollutants was evaluated using CeTPA-based nanofibers. Two dyes, CR and MB, were used as models for the water pollutants (Figure 7a). The dyes cover anionic and cationic pollutants using CR and MB, respectively. The dye solutions exhibit visible light with maximum absorption at 490 nm and 660 nm for CR and MB solutions, respectively (Figure 7b).
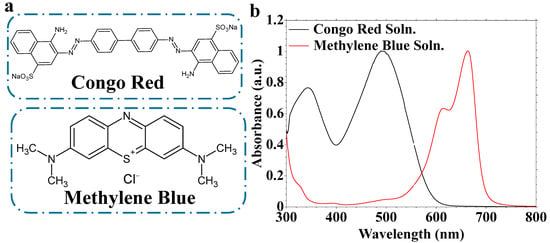
Figure 7.
(a) Dyes chemical structure and (b) UV-Vis spectra for dye solutions.
The surface properties of the materials are essential for water treatment. The angle between a water droplet containing CR and MB dyes and a solid phase coated with MOFs is measured to assess how resistant a MOF is to water (Figure 8). MOFs that exhibit exceptional water repellency can possess a contact angle above 150°, categorizing them as superhydrophobic. Their surface energy and roughness primarily determine the wettability of hydrophobic surfaces. The drops of CR and MB were investigated on the surface of the CeTPA electrospun fibers (Figure 8). Surfaces with low surface energy and heightened roughness exhibit enhanced hydrophobic properties, forming water droplets that readily roll off and maintain their water-repellent characteristics (Figure 8). The CR and MB solutions exhibit contact angles of 150° and 160° for MB and CR drops, respectively (Figure 8). The droplets were also investigated for an extended 0–60 min (Figure 8). No contact angle changes with time, except for minor changes for the MB drop (Figure 8). The contact angle for the MB drop decreases to 145°. However, the surface is still hydrophobic. These features enhance the material’s water-repellent properties by reducing the contact surface area between the water droplet and the substrate.

Figure 8.
Superhydrophobic properties using a solution of CR and MB solutions. A drop of the organic dye was added above the fibers to confirm the hydrophobility.
Adsorption of CR and MB using CeTPA fibers was evaluated (Figure 9a). There are no changes in the dye light absorption, indicating no adsorption because of the surface hydrophobicity (Figure 9a). Different CeTPA nanofiber loadings (2.5%, 5%, and 10%) exhibit similar adsorption behavior, implying that CeTPA has a small adsorption capacity for the dyes. Figure 9b illustrates the catalytic degradation characteristics of organic dye solutions employing CeTPA as a catalyst and hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizing agent. The degradation efficiency (%) was recorded over time. The catalytic activity for CR dye is markedly higher, progressively enhancing efficiency over time. Data analysis reveals an efficiency of 60% for all fibers. The catalytic degradation of MB dye is negligible (5–7%) at all CeTPA loadings, suggesting low efficacy in MB degradation under the examined conditions. High CeTPA concentrations (10%) exhibit high degradation efficiency, indicating that more significant catalyst loading enahnces the oxidative degradation process. The low catalytic performance of MB is mainly due to the dye’s structure. MB dye has no site for oxidation (Figure 7a). CeTPA NFs demonstrate small adsorption ability for both CR and MB. CeTPA efficiently degrades CR in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, whereas MB degradation is ineffective. High CeTPA concentrations improve catalytic degradation without substantially affecting adsorption.
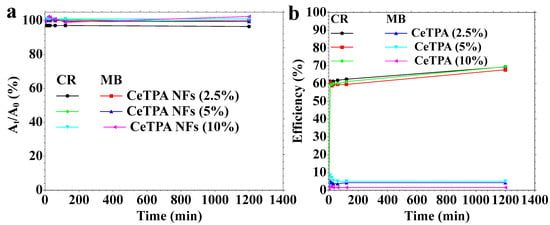
Figure 9.
(a) Adsorption and (b) catalytic degradation of organic dye solutions.
The changes in the dye’s chromophoric groups were evaluated using UV-Vis spectra (Figure 10a). CeTPA fibers after catalysis were also characterized using FT-IR spectra (Figure 10b). Figure 10a depicts the variations in the absorbance of the CR solution at various phases of the catalytic reaction. It illustrates the initial CR solution, exhibiting distinct absorption peaks near 500 nm. The UV-Vis spectrum for the dye in the presence of H2O2 alone demonstrates a decrease in absorbance values, implying that hydrogen peroxide alone exerts a low influence on the breakdown of CR. The spectrum for the CR solution in the presence of the catalyst, i.e., CeTPA NFs and oxidant H2O2, exhibits a notable reduction in absorbance, indicating that CeTPA nanofibers augment the catalytic breakdown of CR. The decrease in peak strength suggests that the chromophoric groups in CR are undergoing degradation during the reaction, resulting in dye deterioration. Furthermore, the visible light absorption peak for the CR solution becomes broader with a shoulder absorption in the wavelength range of 580–800 nm, confirming the changes in the dye chromophoric groups due to catalytic oxidation.
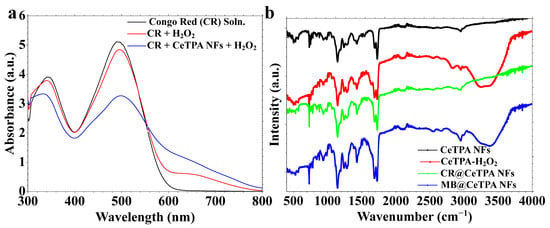
Figure 10.
(a) UV-Vis spectra of dye after catalysis and (b) FT-IR for electrospun fibers after reaction.
FT-IR spectra of electrospun fibers after catalytic reaction have been investigated (Figure 10b). They elucidate the functional groups in the CeTPA nanofibers before and following catalysis. The FT-IR spectrum of CeTPA NFs denotes the unaltered nanofibers, exhibiting distinctive peaks for functional groups. The spectrum for CeTPA-H2O2 exhibits small changes, suggesting interactions between the fibers and the oxidant. The spectra for CR@CeTPA NFs and MB@CeTPA NFs display significant shifts or supplementary peaks, indicating the interaction of CR and MB dyes with the nanofibers. Variations in peak locations and intensities signify modifications in the surface chemistry of CeTPA fibers post-catalytic reactions. The UV-Vis data validate that CeTPA nanofibers substantially improve the catalytic degradation of CR in the presence of H2O2.
The FT-IR spectra elucidate the chemical interactions between CeTPA nanofibers and hydrogen peroxide, together with the organic dyes, i.e., CR or MB (Figure 10b). A new and strong peak detected in the 3200–3600 cm−1 range is attributed to O-H stretching vibrations, which intensify with the presence of hydrogen peroxide (CeTPA-H2O2), suggesting hydrogen bonding interactions and potential adsorption of H2O2 on the nanofiber surface (Figure 10b). Moreover, peaks within the 1500–1700 cm−1 range indicate C=O stretching and O-H bending, with significant changes observed in CeTPA-H2O2, CR@CeTPA NFs, and MB@CeTPA NFs, implying interactions among the fibers, H2O2, and dye molecules (Figure 10b). The spectral range of 1000 to 1300 cm−1, associated with C-O stretching and O-H vibrations, demonstrates changes with hydrogen peroxide exposure, reinforcing its adsorption (Figure 10b). Additionally, peaks within the 500–900 cm−1 range may correspond to peroxide bond vibrations (O-O) or interactions between H2O2 and CeTPA. The O-H stretching band’s heightened intensity and expansion validate CeTPA nanofibers’ involvement in the activation of hydrogen peroxide, producing reactive oxygen species (e.g., hydroxyl radicals), which promote the catalytic destruction of organic dyes. These findings underscore the capacity of CeTPA nanofibers to enhance H2O2activation in the oxidative degradation process for the organic dyes.
Water treatment via removing organic pollutants such as dyes is essential. Organic dyes are widely used for applications such as textiles and can be quickly released into aquatic systems. A summary of the removal technologies and materials used for dye removal is tabulated in Table 1. Electrospun MOFs fibers were reviewed for their application in dye removal [45]. They can be considered a step further for real applications in water treatment. They are optimal surfaces for engineering technologies used in water treatment compared to powdery materials. Hydrophilic polymers such as poly(vinyl alcohol)(PVA)/chitosan were used for electrospinning Ce-MOF, denoted as FCCP, referring to functionalized cerium coordination polymers. The electrospun fibers can be used for the malachite green dye (MG) dye with an adsorption capacity of 359.2 mg/g, representing an efficiency of 35.9% efficiency [46]. An electrospun cross-linked PVA/chitosan (CTS) nanofiber with Ce-UiO-66 MOF, denoted as EPCNF, was utilized to eliminate organic dyes from water [47]. The adsorption results indicated that the adsorption capabilities of both anionic dyes (CR, methyl orange (MO), and methyl red (MR)) and cationic dye (MB) on the produced electrospun nanofibers were higher with higher loadings of Ce-UiO-66 MOFs (10 wt.%). The adsorption capacities of EPCNF-10 for different organic dyes were 102.04 mg/g, 87.71 mg/g, 65.35 mg/g, and 34.24 mg/g for CR, MO, MR, and MB, respectively [47]. These fibers offer good adsorption capacities (Table 1). However, the efficiency of the dye removal is still low. Furthermore, the adsorption process requires tons of the adsorbent materials for dye removal. On the other hand, catalytic degradation of the organic pollutants require small amount of the materials as catalysts. Furthermore, the organic dye degrades into small molecules that could be digested in the human body or the environment.
Cerium-based MOF, i.e., Ce-UiO-66, was synthesized under ambient conditions utilizing water as an eco-friendly solvent [48]. It was used as an adsorbent to remove anionic CR dye from wastewater-containing dyes with a maximum CR adsorption capacity of approximately 285.71 mg/g [48]. Because of the superhydrophobic nature of our electrospun fibers, we cannot record any adsorption of the organic dyes. However, the catalytic performance of Ce-based MOF enables dye degradation. The intrinsic enzymatic activity of cerium-based MOFs enabled the activation of oxidants such as H2O2 to degrade organic molecules of species [49,50,51]. Our electrospun fibers enable selective degradation of anionic dyes such as CR compared to cationic dyes, i.e., MB (Table 1).
Our electrospun fibers can be further investigated to improve their performance. For example, the catalytic performance can be enhanced by integrating light into the process, i.e., photocatalytic degradation. It was reported that ZnO/NiO/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) nanofibers exhibited a high photocatalytic efficacy of a 99% degradation rate of CR under simulated solar illumination within 45 min (Table 1) [52].

Table 1.
A summary of some materials used for dye removal.
Table 1.
A summary of some materials used for dye removal.
| Materials | Compositions | Form | Dye | Removal Method | Efficiency (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCCP | 1. Cerium 2. 2-methylimidazole 3. Chitosan 4. PVA | Fibers | MG | Adsorption | 35.92% (359.2 mg/g) | [46] |
| EPCNFs-10 | 1. Cerium 2. TPA 3. Chitosan 4. PVA | Fibers | CR MB | Adsorption | 74.5% for CR 1543% for MB | [47] |
| ZnO/NiO | 1. ZnO 2. NiO 3. PVP | Fibers | CR | Photocatalysis | 99% | [52] |
| CeTPA | 1. Cerium 2. TPA 3. PMMA | Fibers | CR MB | Catalysis | 60% | Herein |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
PMMA, cerium chloride (CeCl3) anhydrous, Congo red (CR), dimethyl formamide (DMF), methylene blue (MB), and terephthalic acid (TPA) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany).
3.2. Synthesis and Electrospinning of CeTPA Polymers
The CeTPA polymer was synthesized via the solvothermal method. A combination of TPA and CeCl3 (1 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (50 mL) using ultrasonication (30 min, 60 °C). The solution was maintained in an oven at 120 °C for 24 h. The precipitate was then separated via filtration. It was washed with DMF (2 × 10 mL) and water (2 × 10 mL). It was dried at 85 °C in an oven overnight.
The electrospinning process was conducted using a solution of PMMA and CeTPA at concentrations of 2.5%, 5%, and 10 wt.%, achieved by dissolving 3 g of PMMA and CeTPA MOF in 10 mL of DMF. The colloidal solutions were agitated to obtain a uniform spinning solution. The heterogeneous mixture was transferred to the electrospinning device (NANON-01A, MECC, Fukuoka, Japan). The temperature and relative humidity were maintained at 25 °C and 30%, respectively. Electrospinning was conducted by delivering a voltage of 24 kV while maintaining a gap of 15 cm between the collector and the spinneret.
3.3. Characterization
The D8 Advance (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany, Cu Kα radiation) was utilized to acquire XRD patterns. The FT-IR analysis employed an ATR-FTIR (Bruker) instrument. SEM images were obtained using the QUANTA FEG250 (Holland, The Netherlands). DRS spectra were collected using an Evolution 220 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cheshire, UK). Tauc plots were drawn by plotting a relationship between (αE)0.5; where α is Kubelka–Munk, and E (energy) in eV, using Equation 1240/λ, where λ is wavelength in nm.
3.4. Dye Adsorption and Catalysis
A stock solution of organic dyes, CR and MB, was prepared using a stock solution in 100 mL with a concentration of 1 mg/mL. A piece of electrospun CeTPA nanofibers (1 × 1 cm2) was added to a dye solution (100 mL, 1 mg). Then, the dye adsorption was followed by measuring light absorption at 500 nm and 650 nm wavelengths for CR and MB dye using a spectrophotometer (Jenway 73 Series UV/VIS Spectrophotometers, Cole-Parmer 8305816, Thermo Fischer, Waltham, MA, USA).
The catalytic performance for dye degradation was evaluated as mentioned in the adsorption step after adding 5 mL of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30 wt.%). The dye absorption was measured by withdrawing 4 mL of the solution during shaking (5000 rpm) at room temperature. The dye removal efficiency was calculated using the following equation:
A0 and At represent light absorption at a specific wavelength for the dye solution before reaction (A0) and during time (t).
4. Conclusions
We effectively synthesized cerium terephthalate (CeTPA) MOFs and incorporated them into electrospun PMMA nanofibers, resulting in superhydrophobic materials with high catalytic performance. The nanofibers displayed limited adsorption capacity; however, they showed effective catalytic degradation of Congo red (CR) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The selective degrading behavior was ascribed to the structural properties of CR, which promoted oxidation, while methylene blue (MB) exhibited low removal efficiency via adsorption or catalysis with the catalyst. Characterization studies of the fibers after catalysis validated the effective incorporation of CeTPA into the nanofibers without considerable structural damage. The results indicate that CeTPA nanofibers may function as efficient catalytic agents for the selective degradation of organic dyes in wastewater treatment. Future research may investigate optimizing catalytic efficiency and expanding pollutant removal capabilities for improved environmental applications.
Author Contributions
H.N.A.: Conceptualization, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—review and editing, Writing—original draft. S.A.S.: Visualization, Validation, Methodology, Investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2502).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Razavi, S.A.A.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H.-C.; Morsali, A. Tuning redox activity in metal–organic frameworks: From structure to application. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 517, 216004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chand, P.; Kaushik, S. A critical review of recent advancements in zinc based metal organic framework nanocomposites and their derivatives for supercapacitor applications with future perspectives and challenges. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Mathew, A. Cellulose-Metal Organic Frameworks (CelloMOFs) Hybrid Materials and their Multifaceted Applications: A Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 451, 214263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, M.N.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Said, A.E.-A.A. Zirconium Oxide Sulfate-Carbon (ZrOSO4@C) Derived from Carbonized UiO-66 for Selective Production of Dimethyl Ether. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Dye encapsulated hierarchical porous zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for carbon dioxide adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Dehydrogenation of sodium borohydride using cobalt embedded zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 297, 122034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Salts Induced Formation of Hierarchical Porous ZIF-8 and Their Applications for CO2 Sorption and Hydrogen Generation via NaBH4 Hydrolysis. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 2000031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; El-Zohry, A.M.; Cong, J.; Thersleff, T.; Karlsson, M.; Kloo, L.; Zou, X. Towards implementing hierarchical porous zeolitic imidazolate frameworks in dye-sensitized solar cells. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H. Cerium-based metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 527, 216405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebenyuk, D.; Shaulskaya, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Zobel, M.; Tedeeva, M.; Kustov, A.; Sadykov, I.; Tsymbarenko, D. Tuning the Cerium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Formation by Template Effect and Precursor Selection. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 48394–48404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, J.; Ienco, A.; D’Amato, R.; Costantino, F.; Stock, N. The chemistry of Ce-based metal–organic frameworks. Dalt. Trans. 2020, 49, 16551–16586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-J.; Yang, Y.-K.; Li, M.-H.; Zou, L.-N.; Zhao, H.-T. Photocatalytic in situ H2O2 production and activation for enhanced ciprofloxacin degradation over CeO2-Co3O4/g-C3N4: Key role of CeO2. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 2695–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Yuan, S.-S.; Yang, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; Zhang, W.-X.; Chen, C.-X.; Zhang, Q.-T.; Ohno, T. Spatially charge-separated 2D homojunction for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 3952–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-Z.; Tian, Q.-H.; Wang, B.-H.; Xu, M.-T.; Jin, Q.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Le, S.-K.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.-C.; Xu, H.-T. Application of modified cerium dioxide for photocatalytic air pollution purification. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 5473–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jia, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S.-Y.; Yuan, S.-S.; Zhang, Q.-T.; Zhang, M.; Ohno, T. Improved photocatalytic performance of acetaldehyde degradation via crystal plane regulation on truncated octahedral CeO2. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Z.; Chen, L.; Yan, G.-Y.; Liang, R.-W.; Ou, H.-H. Post-modification engineering of cerium metal-organic frameworks for efficient visible light-driven water oxidation. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 5802–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.; Tsai, M.-D.; Shen, C.-H.; Huang, C.-W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Kung, C.-W. Cerium-based metal–organic framework-conducting polymer nanocomposites for supercapacitors. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 23, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileep, N.P.; Patel, J.; Pushkar, Y. Evaluation of Ce-MOFs as Photoanode Materials for the Water Oxidation Reaction: The Effect of Doping with [Ru(bpy)(dcbpy)(H2O)2]2+ Catalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 8050–8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.; Andreescu, D.; Andreescu, S. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Stabilized within Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Degradation of Nerve Agents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Chuang, C.-H.; Gu, Y.-J.; Ho, W.H.; Song, Y.-D.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Kung, C.-W. Cerium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Nanocrystals Interconnected by Carbon Nanotubes for Boosting Electrochemical Capacitor Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 16418–16426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kaiser, A. Electrospinning of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Energy and Environmental Applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Molavi, H.; Bahi, A.; Fernández, R.; Alaee, P.; Wu, S.; Wuttke, S.; Ko, F.; Arjmand, M. Metal-Organic Frameworks and Electrospinning: A Happy Marriage for Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Progresses on electrospun metal–organic frameworks nanofibers and their wastewater treatment applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 25, 100974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyamparambil, V.J.; Kandasubramanian, B. A mini-review on the recent advancement of electrospun MOF-derived nanofibers for energy storage. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; He, T. Electrospun metal–organic framework based nanofibers for energy storage and environmental applications: Current approaches and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1642–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabola, K.P.; Mokhena, T.C.; Bambo, M.F.; Mokhothu, T.H.; Modise, J.S.; Mochane, M.J. PVDF-Based Electrospun Nanofibers for Oil/Water Separation: A Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 309, 2300390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Lu, X.; Deka, B.J.; Shang, J.; Wu, H.; Sun, J.; Yi, C.; Farid, M.U.; An, A.K.; Guo, J. Research progress in the preparation of electrospinning MOF nanofiber membranes and applications in the field of photocatalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, J.; Boltes, K.; Aguado, S.; de Villoria, R.G.; Vilatela, J.J.; Rosal, R. Antimicrobial metal–organic frameworks incorporated into electrospun fibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Shen, J.; Qian, Q.; Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Qi, H. Fabrication of Poly(Lactic Acid)@TiO2 Electrospun Membrane Decorated with Metal–Organic Frameworks for Efficient Air Filtration and Bacteriostasis. Polymers 2024, 16, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yang, E.; Liang, Y.; Kim, S.; Byun, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, H. Rational Design of a Necklace-like ZIF-67/Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Electrospun Nanofiber Hybrid Membrane for Simultaneous Removal of PM0.3 and SO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 15348–15361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavani, A.; Mousavi, S.S.; Fakhari, A.R. Electrospun polybenzidine/Zn-MOF-NH2 composite nanofibers as efficient nanosorbent for thin film microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water, tea bag and cereal samples. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.K.; Ravipati, M.; Ray, S.; Badhulika, S. Electrospun Fe/Co Metal–Organic Framework-PVDF Composite Nanofiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Self-Powered Sterilizing Mask. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, 8, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Li, R.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Chai, X.; Ma, N.L.; Naushad, M.; et al. Efficient Cr(VI) remediation by electrospun composite porous nanofibers incorporating biomass with metal oxides and metal-organic framework. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 351, 124026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shi, H.; Gui, D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Enhanced absorption capacity and fundamental mechanism of electrospun MIL-101(Cr)-NH2/PAN nanofibrous membranes for Mo(VI) removal. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 54, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Kulandaivel, S.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Recent trends in superhydrophobic metal–organic frameworks and their diverse applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 518, 216108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalapati, R.; Nandi, S.; Gogoi, C.; Shome, A.; Biswas, S. Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) Derived Recyclable, Superhydrophobic Composite of Cotton Fabrics for the Facile Removal of Oil Spills. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 8563–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Feng, R.; Dong, L.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Superhydrophobic fluorinated metal–organic framework (MOF) devices for high-efficiency oil–water separation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 5636–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, D.A.; Pournara, A.D.; Karagianni, V.I.; Dimitriou, C.; Andreou, E.K.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Armatas, G.S.; Manos, M.J. Just Soaping Them: The Simplest Method for Converting Metal Organic Frameworks into Superhydrophobic Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 12672–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Duan, W.; Yue, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H. Superhydrophobic metal-organic framework layers as multifunctional ion-conducting interfaces for ultra-stable Zn anodes. J. Power Sources 2024, 622, 235364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Helal, M.H.; Alshahrani, W.A.; Alqarni, N.D.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, J.; Luo, H. Superhydrophobic anticorrosive fluoroethylene vinyl ether coating nanocomposited with metal-organic framework derived ferrite nanocapsules and MXene. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.; Bonakala, S.; Adalikwu, S.A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Maji, T.K. Fluorocarbon-Functionalized Superhydrophobic Metal–Organic Framework: Enhanced CO2 Uptake via Photoinduced Postsynthetic Modification. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Su, M.; Liu, H. Liquid Interfacial Gating of Superhydrophobic Plasmonic Metal–Organic Frameworks for Three-in-One Separation, Enrichment, and Recognition in Bacterial Quorum Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32824–32835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Hong, X.; Li, Q.; Rao, R.; Gong, Z.; Zheng, Y. A superhydrophobic zirconium-based metal-organic framework/cellulose fiber composite material. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, M.; Wharmby, M.T.; Smolders, S.; Bueken, B.; Lieb, A.; Lomachenko, K.A.; Vos, D.D.; Stock, N. Cerium-based metal organic frameworks with UiO-66 architecture: Synthesis, properties and redox catalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12578–12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silina, A.; El Achari, A.; Salaün, F. Metal-organic framework electrospun nanofibers in application to dye removal from textile wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatawi, R.A.S. Electrospun nanofiber chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol loaded with metal organic framework nanofiber for efficient adsorption and removal of industrial dyes from waste water: Adsorption isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic, and optimization via Box-Behnken design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tati, A.; Ahmadipouya, S.; Molavi, H.; Mousavi, S.A.; Rezakazemi, M. Efficient removal of organic dyes using electrospun nanofibers with Ce-based UiO-66 MOFs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H.; Salimi, M.S. Green Synthesis of Cerium-Based Metal–Organic Framework (Ce-UiO-66 MOF) for Wastewater Treatment. Langmuir 2023, 39, 17798–17807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Metals Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease. In Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research—Alzheimer Disorders; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2020; pp. 213–235. ISBN 978-981-14-1093-2. [Google Scholar]
- Shamroukh, W.; Abdelhamid, H.N. Fenton-like Cerium Metal–Organic Frameworks (Ce-MOFs) for Catalytic Oxidation of Olefins, Alcohol, and Dyes Degradation. J. Clust. Sci. 2022, 34, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Sharmoukh, W. Intrinsic catalase-mimicking MOFzyme for sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and ferric ions. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Yuan, K.-Z.; Xu, X.-F.; Li, Z.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Long, Y.-Z.; Zhang, H.-D. ZnO/NiO coaxial heterojunction nanofibers with oxygen vacancies for efficient photocatalytic Congo red degradation and hydrogen peroxide production. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 39636–39644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).