Abstract
This work presents the potential of various iron-based catalysts, with an iron content between 10 and 30 wt%, supported on alumina that were explored for pure hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition reaction. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) results indicated that major diffraction peaks associated with the alumina support and iron oxide were found along with fractions of iron aluminate. The reduction profiles from temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) showed that the extent of reduction, number of reducible species, and iron oxide interaction with alumina varied with an increase in iron oxide content, from 10 to 30 wt%, such that an increase in iron oxide loading promoted easier reduction, enhanced reducibility, and improved number of reducible species. Temperature-programmed desorption profiles using hydrogen and nitrogen showed that an increase in iron content increased the amount of hydrogen desorbed; however, nitrogen desorption exhibited a decreasing trend. These factors influenced catalytic activity results and an increase in iron content increased the ammonia conversion. Kinetic data also showed that a higher iron content (30 wt%) demonstrated the lowest apparent activation energy of 48.2 kJ/mol.
1. Introduction
Over the past few years, the liquefaction, purification, and conveyance of ammonia as a hydrogen carrier have become more straightforward [1]. The generation of carbon-neutral hydrogen through ammonia decomposition enables the prospective use of ammonia in hydrogen fuel cell applications [2,3]. Unlike the synthesis of ammonia, its decomposition has garnered significant attention from the scientific community, resulting in intensive research in this domain [2,3,4,5]. Catalysts with high efficiency, such as ruthenium, nickel, iron, and molybdenum, along with their combinations used for ammonia synthesis, typically demonstrate good activity for ammonia decomposition. However, the catalyst that performs optimally for ammonia synthesis may not necessarily exhibit optimal performance for ammonia decomposition. This may result from the reaction kinetics regulated by two competing elementary reactions: (i) the initial removal of hydrogen following the adsorption of ammonia on the surface; and (ii) the desorption of recombinative nitrogen (N) atoms from the surface [6,7,8]. The breakdown rate of ammonia (Scheme 1) is theoretically correlated with the cleavage of the nitrogen–hydrogen (N–H) bond and the recombination of atomic nitrogen (N–N) [8]. Furthermore, N–N recombination restricts the ammonia breakdown rate on metals such as nickel, cobalt, and iron, whereas N–H bond cleavage inhibits the decomposition rate on metals like copper, ruthenium, platinum, and iridium.

Scheme 1.
The steps involved in ammonia decomposition reaction.
The optimal performance of the ruthenium catalyst may primarily result from the favorable equilibrium between competitive N–H bond cleavage and N–N recombination [9,10,11]. A stronger metal–nitrogen bond (M–N) promotes the cleavage of the NHx link, but typically results in a greater barrier for N–N recombination, and vice versa [12]. The elevated N–N recombination barrier in iron catalysts results in their nitridation during the process [13,14]. The outcome of nitridation is not inherently detrimental for the catalysts, as certain iron nitride phases have been documented to exhibit superior catalytic performance compared to pure Fe, despite the reported active phases being notably varied and even conflicting [15,16,17,18,19,20]. Nonetheless, significant safety information can be inferred: the iron catalyst will be compromised by extensive nitridation, and diminishing surface nitrogen atoms may enhance catalytic activity for ammonia breakdown [21,22]. Nitridation and breakdown of iron nitrides occur concurrently during the reaction, ultimately achieving distinct equilibrium states based on the reaction temperature and space velocity employed in the experiment [23]. This implies that the catalyst’s phase during and subsequent to a reaction may merely signify the final stable phase, rather than the most active phase. Identifying and maintaining the most active phase is crucial for the advancement of iron-based catalysts. Consequently, real-time monitoring of the entire reaction process and the structural evolution of the catalysts would be a viable option.
In this article, alumina-supported catalysts with various iron contents (10–30 wt%) were studied for ammonia decomposition reaction in a fixed bed reactor. The catalysts were treated in a reductive environment for an hour at 550 °C before being subjected to reaction. The catalysts were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD) to identify crystalline phase, temperature-programmed reduction to explore reduction behavior, and temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) to quantify the amount of hydrogen and nitrogen desorbed from each catalyst. The characterization results were correlated with the activity profiles.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Fresh Catalysts
The physicochemical properties of iron-based supported catalysts including their specific surface areas, pore sizes, and pore volumes are presented in Table 1. The specific surface area of the fresh alumina support was measured at 73.65 m2/g, while pore volume and pore size were found to be 33.3 cm3/g and 17.7 nm, respectively. Iron sequential doping over alumina indicated a decrease in specific surface area from 73.65 to 55.47 m2/g after 10 wt% iron was doped (F10Al). A further increase in iron loading to 20 (F20Al) and 30 wt% (F30Al) showed further reduction in specific surface area to 42.92 and 25.91 m2/g, respectively. The decline in specific surface area with iron doping could be attributed to the structure breakdown and pore blockage of the alumina support. The average pore sizes of the iron-doped catalysts remained within 2–50 nm assigned to the mesoporous structure, as defined by IUPAC nomenclature [24]. In Figure 1, the hysteresis area decreased with the addition of iron, indicating deteriorated pore structure stability during adsorption–desorption cycles. A smaller hysteresis area suggested lower pore volume, reducing the capacity of the material for gas, which could be crucial for ammonia decomposition activity. The catalyst samples were also analyzed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) to measure the targeted iron loadings between 10 and 30 wt%, and it was found that the theoretical values were achieved.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties and XRF results of iron-based catalysts.

Figure 1.
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of alumina and iron-based supported catalysts.
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) results (Figure 2) were examined to understand the crystalline nature of both the support and iron-doped catalysts. The diffraction pattern of γ-Al2O3 is represented by the black line in Figure 2. After doping Fe2O3, the diffraction intensity of the peaks associated with γ-Al2O3 started to decrease due to iron particle dispersion on the γ-Al2O3. However, a phase transformation of gamma to alpha was found for iron-doped catalysts as indicated by the diffraction peaks corresponding to 2θ = 25.5°, 35.05°, 37.65°, 43.2°, 52.35°, and 57.3° (JCPDS No. 10-0173). The characteristic peaks of iron oxide (Fe2O3) were clearly observed, and the corresponding intensity was also increased with an increase in iron loading from 10 to 30 wt%. Moreover, higher loading catalysts also demonstrated clear diffraction peaks of iron aluminate that results from iron species reacting with the support in the bulk of the sample.

Figure 2.
XRD results of alumina and iron-based supported catalysts. Dashed line is associated with iron aluminate.
Temperature-programmed reduction using hydrogen as a probe gas (H2-TPR) is one of the efficient tools to quantify the number of reducible species on the surface of a catalyst and subsequently analyze their role in ammonia decomposition reaction. Figure 3 shows the H2-TPR profiles of iron-based catalysts in terms of TCD response with respect to temperature. The reduction profiles illustrate the variation in reduction behavior of iron oxide species as the iron content is increased from 10 to 30 wt%. For instance, F10Al showed two reduction peaks with peak maxima at 433 and 619 °C along with an emerging peak close to 1000 °C. The two peaks are assigned to the reduction of Fe2O3 to Fe3O4 followed by Fe3O4 to Fe [25,26], while an emerging peak could be assigned to iron aluminate in line with XRD results (Figure 2). A further increase in iron content to 20 wt% (F20Al) exhibited the first peak at relatively lower temperature with peak maxima at 418 °C, the second peak became broader with two maxima at 593 and 632 °C, and a third peak with maxima at 966 °C. The broader second peak indicates a two-step reduction of Fe3O4 to FeO and FeO to Fe. The F30Al catalyst also demonstrated similar reduction patterns to those of F20Al with the first peak maxima at 405 °C, the second broader peak with maxima at 589 and 641 °C, and the third peak at 952 °C. These results suggest that an increase in iron loading facilitated easier reduction of iron oxide species as indicated by the reduced peak temperatures. The easier reduction has the potential to play a role during reaction, and this correlation is discussed in the catalytic activity section.

Figure 3.
H2-TPR results of iron-based supported catalysts.
The number of nitrogen adsorption sites and the metal-to-nitrogen binding energy that influence the catalytic activity of as-synthesized catalysts can be assessed by temperature-programmed desorption using either hydrogen or nitrogen as a probe gas (H2/N2-TPD). Since the mechanism of ammonia cracking reaction necessitates the desorption of hydrogen and nitrogen (more challenging) as a product, the quantity of adsorption sites becomes essential to comprehending ammonia decomposition reactions. Figure 3 and Figure 4 illustrate the hydrogen and nitrogen desorption profiles of iron-based catalysts, respectively.

Figure 4.
H2-TPD results of iron-based supported catalysts.
Figure 4 demonstrates that alumina showed no hydrogen desorption peak, and with an increase in iron content, the amount of hydrogen desorbed, or number of adsorption sites increased. Moreover, two desorption peaks were observed for each catalyst with the first peak maxima appearing at 405, 430, and 390 °C for F10Al, F20Al, and F30Al, respectively, while the second peak maxima remain approximately the same at around 690 °C. This suggests that a broader second peak temperature is independent of iron content, implying that the iron-to-hydrogen bonding strength remains the same. However, this bond is the weakest for F30Al for the low-to-medium temperature desorption peak. The amount of hydrogen desorbed, as shown in Table 2, was also highest for F30Al (0.295 mmol/g), making this catalyst a relatively better candidate to outperform the rest of the catalysts during reaction. Figure 5 presents the nitrogen desorption patterns for various iron-based catalysts. All the catalysts have shown two peaks: the first between a temperature range of 100 and 200 °C and the second between 200 and 700 °C. It is observed that the peak temperatures are insignificantly affected by an increase in iron content; however, the amount of nitrogen desorbed is significantly reduced with an increase in iron content (Table 2). For instance, nitrogen uptake was reduced from 0.511 mmol/g (F10Al) to 0.367 mmol/g when iron content was raised to 30 wt% (F30Al). These findings show either strong bonding or reaction between iron and nitrogen to produce iron nitrides or loss of number of adsorption sites at higher iron loading. The latter is less perceivable, and hence, the probability of iron nitride formation is higher. The difficult nitrogen desorption over the catalyst could play a role during ammonia decomposition reaction.

Table 2.
Quantitative results of temperature-programmed desorption using H2 and N2.

Figure 5.
N2-TPD results of iron-based supported catalysts.
2.2. Activity Performance
The role of varying iron content over alumina was profoundly investigated by the systematic variation in the reaction temperature to obtain the catalytic activity performance of each catalyst, i.e., F10Al, F20Al, and F30Al, during ammonia decomposition reaction. Figure 6a exhibits the activity profiles in terms of ammonia conversion versus temperature. The activity profiles clearly indicate that iron addition to alumina had a positive impact on ammonia decomposition reaction, and ammonia conversion increases with an increase in iron content from 10 to 30 wt%. For instance, ammonia conversion of 52% was found for F10Al at 600 °C, which increased to 58% for F20Al and eventually reached 85% when iron content was increased to 30 wt% (F30Al). To constrain iron particle agglomeration, iron loading was kept at 30 wt%. While studying the ammonia decomposition reaction mechanism, Brauner and Love [27] showed that nitrogen desorption was the rate determining step over iron-based catalysts. However, the rate of reaction is a function of temperature as well as the partial pressure of ammonia and hydrogen. These findings suggest that hydrogen and nitrogen temperature-programmed desorption studies could help in explaining the activity trends in this work. The higher hydrogen desorption value (0.295 mmol/g) in the case of F30Al indicates that this catalyst could outperform the rest of the catalysts. Moreover, the lowest nitrogen desorption (0.367 mmol/g) from this (F30Al) catalyst also shows that this catalyst has promoted reaction between iron and nitrogen, leading to the formation of iron nitrides, which could play a role during reaction. Previously, iron nitride has been reported to have a significant impact on the catalytic performance during ammonia decomposition reaction [4,15,28,29,30]. These reports have discussed the fact that iron nitride could promote activity performance, in agreement with this work where more iron accommodates more nitrogen, facilitating iron nitride formation, which favors ammonia decomposition reaction. This observation is further established by the XRD patterns of spent catalysts (Figure 7) where diffraction peaks of metallic iron, iron nitride, and alpha alumina were obvious. It is noteworthy that specific surface areas of the iron-based catalysts decreased with the increase in the amount of iron; however, no clear correlation could be identified between specific surface areas and activity performance of the catalysts.

Figure 6.
(a) Ammonia conversion versus temperature. (b) Arrhenius plots of iron-based supported catalysts.
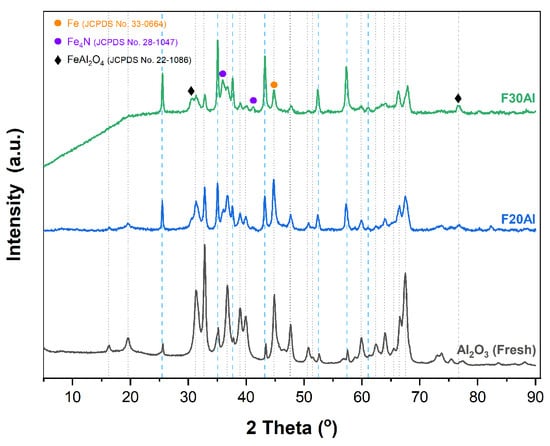
Figure 7.
XRD results of spent iron-based supported catalysts.
The evaluation of apparent activation energy for iron-based catalysts by using the Arrhenius Equation is shown in Figure 6b. The plots of ammonia decomposition reaction rate versus temperature (1/K) yielded activation energies following the order of F30Al (48.2 kJ/mol) < F20Al (89.7 kJ/mol) < F10Al (91.4 kJ/mol). Notably, F30Al presented considerably lower apparent activation energy in comparison with the rest of the catalysts, corresponding to higher activity of this catalyst. The activation energy of iron-based catalysts evaluated for ammonia decomposition reaction with un-nitrided iron species was found to be 160 kJ/mol [4], and the lower activation energies of the catalysts in this work further validate the fact that iron nitride was the major factor behind the catalytic activity trend shown in Figure 6. These findings underscore the significance of iron nitride formation and its impact in revealing the activity performance of these iron-based catalysts during ammonia decomposition, with the F30Al catalyst exhibiting the highest activity.
The comparison of iron-based catalysts of this work with previously reported transition metal-based [4,23,31,32,33,34,35] and Ru-based catalysts [36,37] is presented in Table 3. For the catalysts evaluated under identical operating conditions, these iron-based catalysts have demonstrated either similar or higher ammonia conversions. For instance, the F30Al catalyst with 85% ammonia conversion at 600 °C outperformed iron-based catalysts with higher amounts of iron ≥ 40 wt% supported on SBA-15 [23] and/or alumina [31], where the catalysts showed ammonia conversion of 86% with 90 wt% iron loading [31]. The easily reducible iron species, higher hydrogen desorption, and formation of iron nitride remained the major factors behind the remarkable catalytic performance of these iron-based catalysts. Moreover, these iron-based catalysts have showcased equivalent levels of catalytic performance, facilitating the potential of these catalysts in improving clean hydrogen transport and production.

Table 3.
Literature comparison of iron-based catalysts with previous works.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
Iron-based catalysts were synthesized using incipient wetness impregnation with sequential iron loading. The support was ultra-pure aluminum oxide (Al2O3) from Inframat Advanced Materials (Manchester, CT, USA, 99.99%). The iron precursor solution was made by dissolving Fe(NO3)2·6H2O in deionized water, to achieve 10–30 wt% Fe through successive 5 wt% impregnations. After each step, the catalyst samples were dried at 105 °C for 5 h and calcined at 850 °C for 3 h. The catalyst samples were denoted as FxAl, where x represents the amount of iron, e.g., F10Al catalyst contains 10 wt% iron.
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
The iron (Fe) content in the synthesized catalysts was analyzed using Bruker’s M4 Tornado X-ray Fluorescence (XRF, Billerica, MA, USA).
The crystal properties of fresh and spent catalysts were analyzed by XRD using a Rigaku Diffractometer (Akishima, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation at 40 kV and 15 mA. The analysis used a step size of 0.02 over a scan range of 10–80. Crystal phase analysis was conducted using X’pert high score plus software 4.1 and the JCPDS database. All spectra are normalized for clarity.
The textural properties of fresh catalysts were analyzed using the Micromeritics ASAP 2020 instrument (Norcross, GA, USA) with nitrogen as the probe molecule. The Brunauer–Emmet–Teller (BET) method determined the surface area, while the pore volume and diameter were obtained through the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method.
Hydrogen Temperature-Programmed Reduction (H2-TPR) was performed with 0.04 g of the catalyst using a Micromeritics Auto Chem II 2920. The temperature was increased to 1000 °C at 10 °C per minute, with a 10% H2/Ar flow of 50 mL/min. Similarly, Hydrogen/nitrogen Temperature-Programmed Desorption (H2/N2-TPD) was conducted using a specific desorption model to determine the desorption energy. The process involved flowing a 10% H2 and 90% Ar gas mixture at 50 mL/min to the reduced catalyst for 30 min. The temperature was raised to 1000/700 °C (10 °C/min). A TCD analyzed the gas exiting the sample, measuring the hydrogen consumption during TPR and H2/N2 desorption during TPD. All spectra are normalized for clarity.
3.3. Catalyst Evaluation
The experimental configuration for the catalytic decomposition of ammonia employed a fixed-bed stainless steel tubular reactor. The reactor specifications and experimental methodology are available in the previous work [24]. The NH3 conversion experiments were performed at temperatures ranging from 200 to 700 °C and at atmospheric pressure, utilizing 0.3 g of catalyst. An Agilent 7890B gas chromatograph (GC, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) was utilized to quantify NH3 in the effluent gas mixture. The gas chromatograph employed an Agilent J&W HP-PLOT U column, measuring 30 m in length and 0.32 mm in inner diameter. All the experiments were repeated three times, and results were within an error value of ±5%.
The conversion expressed in terms of XNH3 was calculated using the following Equation (1)
4. Conclusions
This work reported the role of iron-based catalysts with various amounts of iron (10–30 wt%) supported over alumina during ammonia decomposition reaction. The catalysts characterized by temperature-programmed reduction, temperature-programmed desorption, and catalytic performance evaluation assisted in deducing the following conclusions:
- ➢
- XRD profiles indicated that iron oxide, i.e., Fe2O3, was found to be the major active component that contributes to catalytic activity performance during ammonia decomposition reaction.
- ➢
- The amount of hydrogen adsorption sites increased with an increase in iron loading, as depicted by H2-TPD results.
- ➢
- The strong affinity of iron for nitrogen leading to iron nitride formation was observed by N2-TPD, where the amount of N2 desorbed decreased with an increase in iron amount.
- ➢
- The increase in iron facilitated an easier reduction in oxides of iron, as demonstrated by H2-TPR.
- ➢
- The specific surface area decreased with iron loading due to the fact that iron blocked pores of the support.
- ➢
- Activity results showed that with the increase in iron from 10 to 30 wt%, ammonia conversion increased, with F30Al outperforming the rest of the catalysts.
- ➢
- The ammonia conversions of iron-based catalysts of this work were both comparable and, in some cases, higher than previously reported catalysts.
- ➢
- The easily reducible iron species, higher hydrogen desorption, and formation of iron nitride remained as the major factors behind the remarkable catalytic performance of iron-based catalysts of this work.
- ➢
- The scientific findings and insights of this work could provide a guideline for designing an efficient iron-based catalyst in future research and development advancing the field of hydrogen production and transport.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.H., W.U.K., A.F.P.P. and H.A.; formal analysis, W.U.K. and A.F.P.P.; investigation, W.U.K., H.A. and A.F.P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.H., W.U.K. and A.F.P.P.; writing—review and editing, M.M.H., W.U.K. and H.A.; supervision, M.M.H.; project administration, M.M.H.; funding acquisition, M.M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Interdisciplinary Research Center for Refining & Advanced Chemicals (IRCRAC) at King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM), grant number INRC 2507.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by the IRCRAC at KFUPM for facilitating this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lamb, K.E.; Dolan, M.D.; Kennedy, D.F. Ammonia for Hydrogen Storage; A Review of Catalytic Ammonia Decomposition and Hydrogen Separation and Purification. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3580–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, S.-U.; Kim, J.-R.; Kim, T.-W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chae, H.-J. Ru-Supported Lanthania-Ceria Composite as an Efficient Catalyst for COx-Free H2 Production from Ammonia Decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Devaguptapu, S.V.; Sviripa, A.; Lund, C.R.F.; Wu, G. Low-Temperature Ammonia Decomposition Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabczyk, W.; Zamlynny, J. Study of the Ammonia Decomposition over Iron Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 1999, 60, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarçay, Ö.; Kurtoğlu, S.F.; Uzun, A. Ammonia Decomposition on a Highly-Dispersed Carbon-Embedded Iron Catalyst Derived from Fe-BTC: Stable and High Performance at Relatively Low Temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 28664–28681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Ma, D.; Yang, Z. Adsorption and Dissociation of Ammonia on Small Iron Clusters. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzani, G.; Laasonen, K. NH3 Adsorption and Dissociation on a Nanosized Iron Cluster. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6571–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, J.C.; Thomas, F.S.; Seebauer, E.G.; Masel, R.I. A Priori Catalytic Activity Correlations: The Difficult Case of Hydrogen Production from Ammonia. Catal. Lett. 2004, 96, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-C.; Fu, X.-P.; Wang, W.-W.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; Si, R.; Ma, C.; Jia, C.-J.; Yan, C.-H. Ceria-Supported Ruthenium Clusters Transforming from Isolated Single Atoms for Hydrogen Production via Decomposition of Ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Liu, L.; Yu, P.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Wu, G.; Chen, P. Mesoporous Ru/MgO Prepared by a Deposition-Precipitation Method as Highly Active Catalyst for Producing COx-Free Hydrogen from Ammonia Decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 211, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, D.; Hu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Feng, G. Ru/La2O3 Catalyst for Ammonia Decomposition to Hydrogen. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 476, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Shi, C. An Investigation of the Thermal Stability, Crystal Structure and Catalytic Properties of Bulk and Alumina-Supported Transition Metal Nitrides. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 464, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabczyk, W.; Zamłynny, J.; Moszyński, D. Kinetics of Nanocrystalline Iron Nitriding. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2010, 12, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.J.; Makepeace, J.W.; David, W.I.F. Neutron Diffraction and Gravimetric Study of the Iron Nitriding Reaction under Ammonia Decomposition Conditions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 27859–27865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelka, R.; Moszyńska, I.; Arabczyk, W. Catalytic Ammonia Decomposition Over Fe/Fe4N. Catal. Lett. 2008, 128, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelka, R.; Arabczyk, W. Studies of the Kinetics of Reaction Between Iron Catalysts and Ammonia—Nitriding of Nanocrystalline Iron with Parallel Catalytic Ammonia Decomposition. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelka, R.; Kiełbasa, K.; Arabczyk, W. Catalytic Ammonia Decomposition during Nanocrystalline Iron Nitriding at 475 °C with NH3/H2 Mixtures of Different Nitriding Potentials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6178–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.C.; Han, S.S.; Lee, H.M. Mechanistic Investigation of the Catalytic Decomposition of Ammonia (NH3) on an Fe(100) Surface: A DFT Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5309–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Gong, W.; Guo, H. Plasma Driven Ammonia Decomposition on a Fe-Catalyst: Eliminating Surface Nitrogen Poisoning. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Wen, J.; Ren, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Highly Efficient COx-Free Hydrogen Evolution Activity on Rod Fe2N Catalysts for Ammonia Decomposition. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 18277–18284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H. NH3 Decomposition for H2 Generation: Effects of Cheap Metals and Supports on Plasma–Catalyst Synergy. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4167–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.E.; Torrente-Murciano, L. H2 Production via Ammonia Decomposition Using Non-Noble Metal Catalysts: A Review. Top. Catal. 2016, 59, 1438–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, J.-C.; Gu, D.; Pistidda, C.; Horstmann, C.; Dornheim, M.; Ternieden, J.; Weidenthaler, C. Tracking the Active Catalyst for Iron-Based Ammonia Decomposition by In Situ Synchrotron Diffraction Studies. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 4465–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAmoudi, O.M.; Ullah Khan, W.; Hantoko, D.; Bakare, I.A.; Ali, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic Activity of Co/γ-Al2O3 Catalysts for Decomposition of Ammonia to Produce Hydrogen. Fuel 2024, 372, 132230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.; Bianchi, C.L.; Di Michele, A.; Vitali, S.; Ragaini, V. Fischer Tropsch and Water Gas Shift Chemical Regimes on Supported Iron-Based Catalysts at High Metal Loading. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Fakeeha, A.H.; Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Abasaeed, A.E.; Khan, W.U. Methane Decomposition over Iron Catalyst for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 7593–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Love, K.S.; Keenan, R.G. Adsorption of Nitrogen and the Mechanism of Ammonia Decomposition Over Iron Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1942, 64, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, Q.; Ren, S.; Arshid, M.A.; Chu, W.; Chen, C. Implication of Iron Nitride Species to Enhance the Catalytic Activity and Stability of Carbon Nanotubes Supported Fe Catalysts for Carbon-Free Hydrogen Production via Low-Temperature Ammonia Decomposition. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Li, L.; Ren, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H. Ammonia Decomposition over Iron-Based Catalyst: Exploring the Hidden Active Phase. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 314, 121475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcel, M.; Berendts, S.; Bonati, L.; Perego, S.; Müller, A.; Lerch, M.; Parrinello, M.; Muhler, M. Iron Nitride Formation and Decomposition during Ammonia Decomposition over a Wustite-Based Bulk Iron Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 13947–13957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroyama, H.; Saburi, C.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. Ammonia Decomposition over Ni/La2O3 Catalyst for on-Site Generation of Hydrogen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 443–444, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzut, B.; Montini, T.; Bevilacqua, M.; Fornasiero, P. FeMo-Based Catalysts for H2 Production by NH3 Decomposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Yan, Z.F.; Lu, G.Q.; Rintoul, L. Catalytic Ammonia Decomposition over Ru/Carbon Catalysts: The Importance of the Structure of Carbon Support. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 320, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Gong, Q.; Luo, J.; Lin, R.; Xin, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Peng, Q.; et al. Sub-Nm Ruthenium Cluster as an Efficient and Robust Catalyst for Decomposition and Synthesis of Ammonia: Break the “Size Shackles”. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4774–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-C.; Wang, W.-W.; Jin, Z.; Wang, X.; Si, R.; Jia, C.-J. Transition Metal Nanoparticles Supported La-Promoted MgO as Catalysts for Hydrogen Production via Catalytic Decomposition of Ammonia. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 38, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-Q.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, R.-J.; Zheng, M.-J.; Guo, Y.-M.; Song, Q.-S.; Jia, C.-J. Transition Metal Nanoparticles Dispersed in an Alumina Matrix as Active and Stable Catalysts for COx-Free Hydrogen Production from Ammonia. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17172–17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henpraserttae, S.; Charojrochkul, S.; Klysubun, W.; Lawtrakul, L.; Toochinda, P. Reduced Temperature Ammonia Decomposition Using Ni/Zr-Doped Al2O3 Catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).