Co-Supported CeO2Nanoparticles for CO Catalytic Oxidation: Effects of Different Synthesis Methods on Catalytic Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
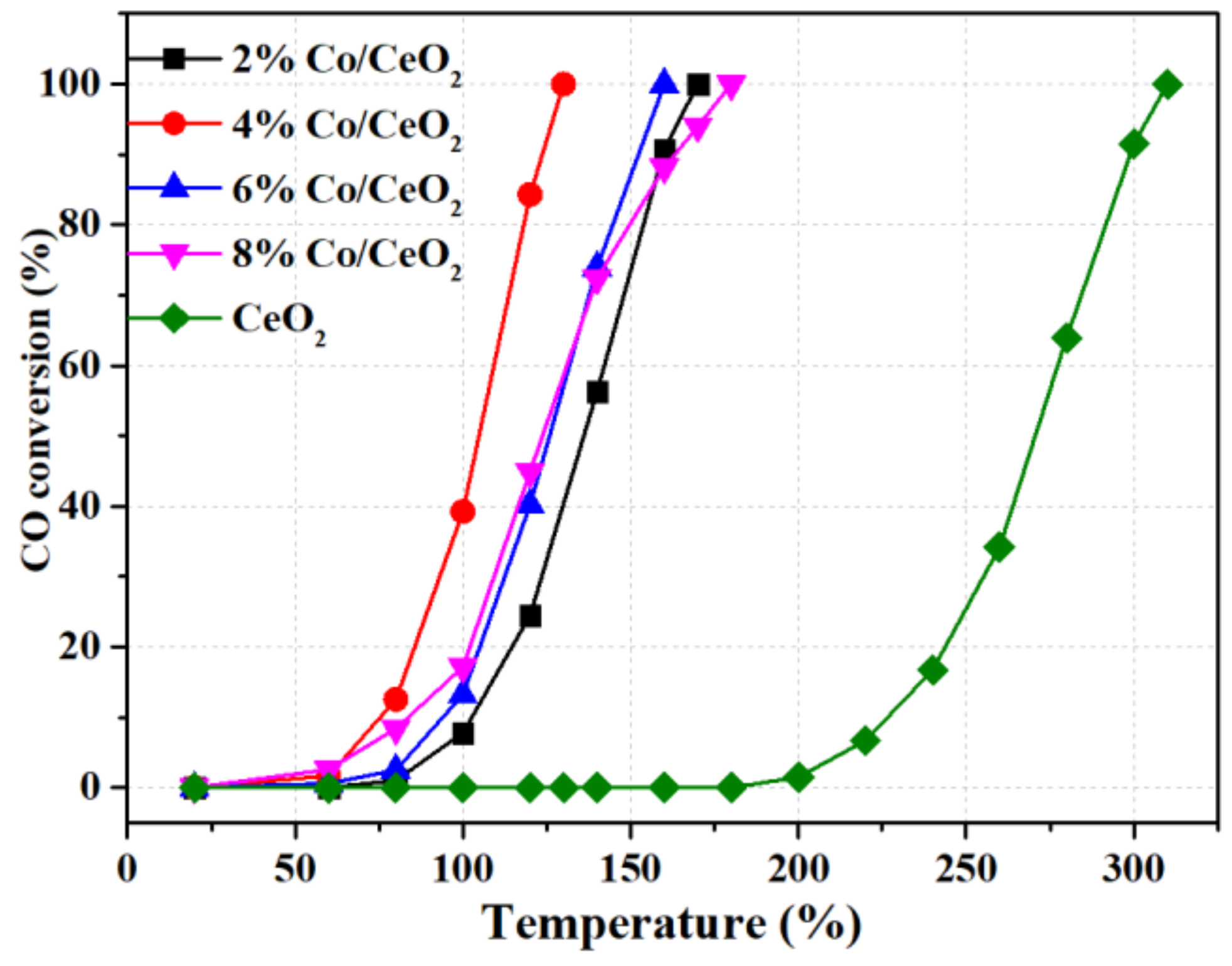
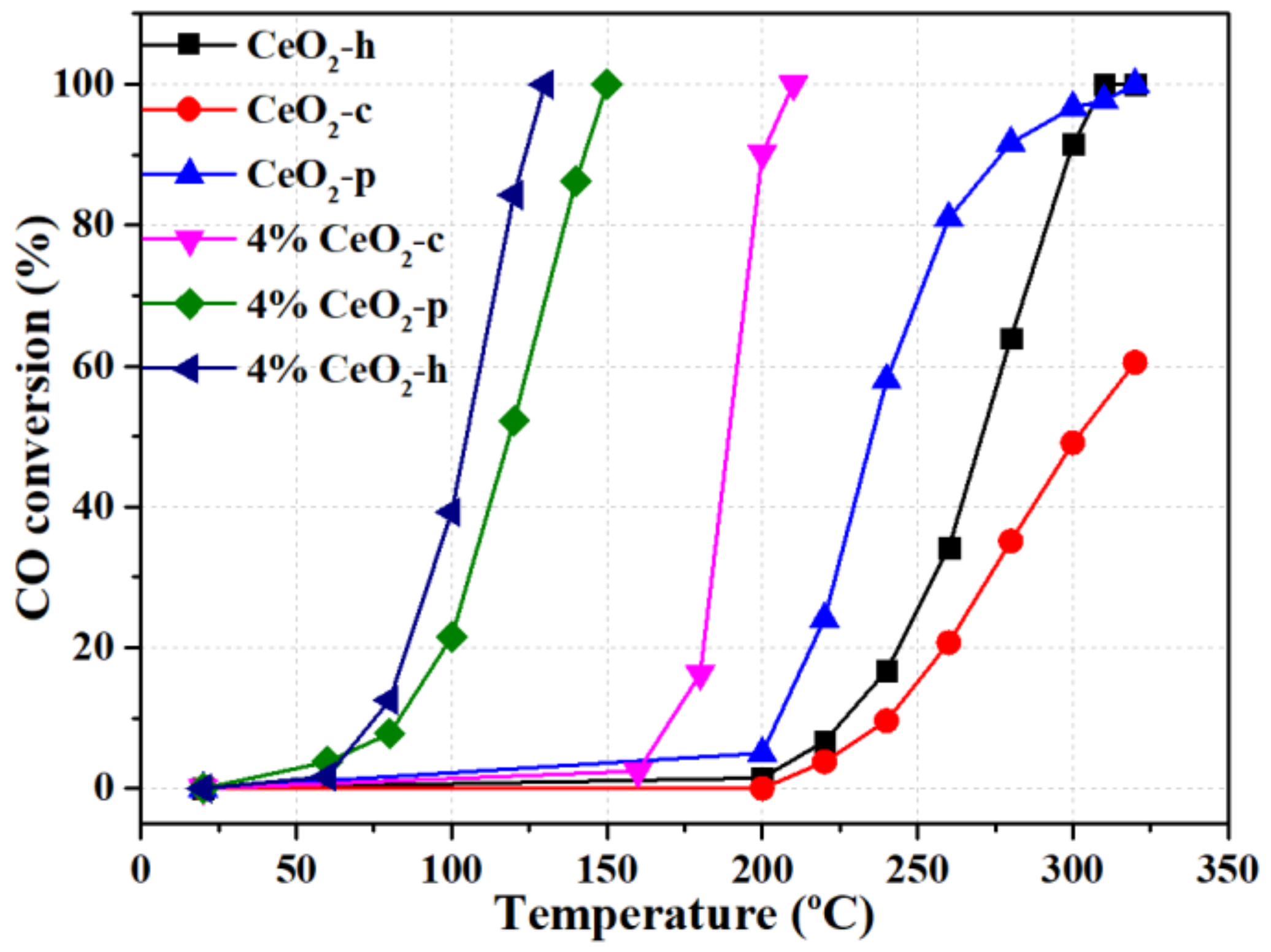
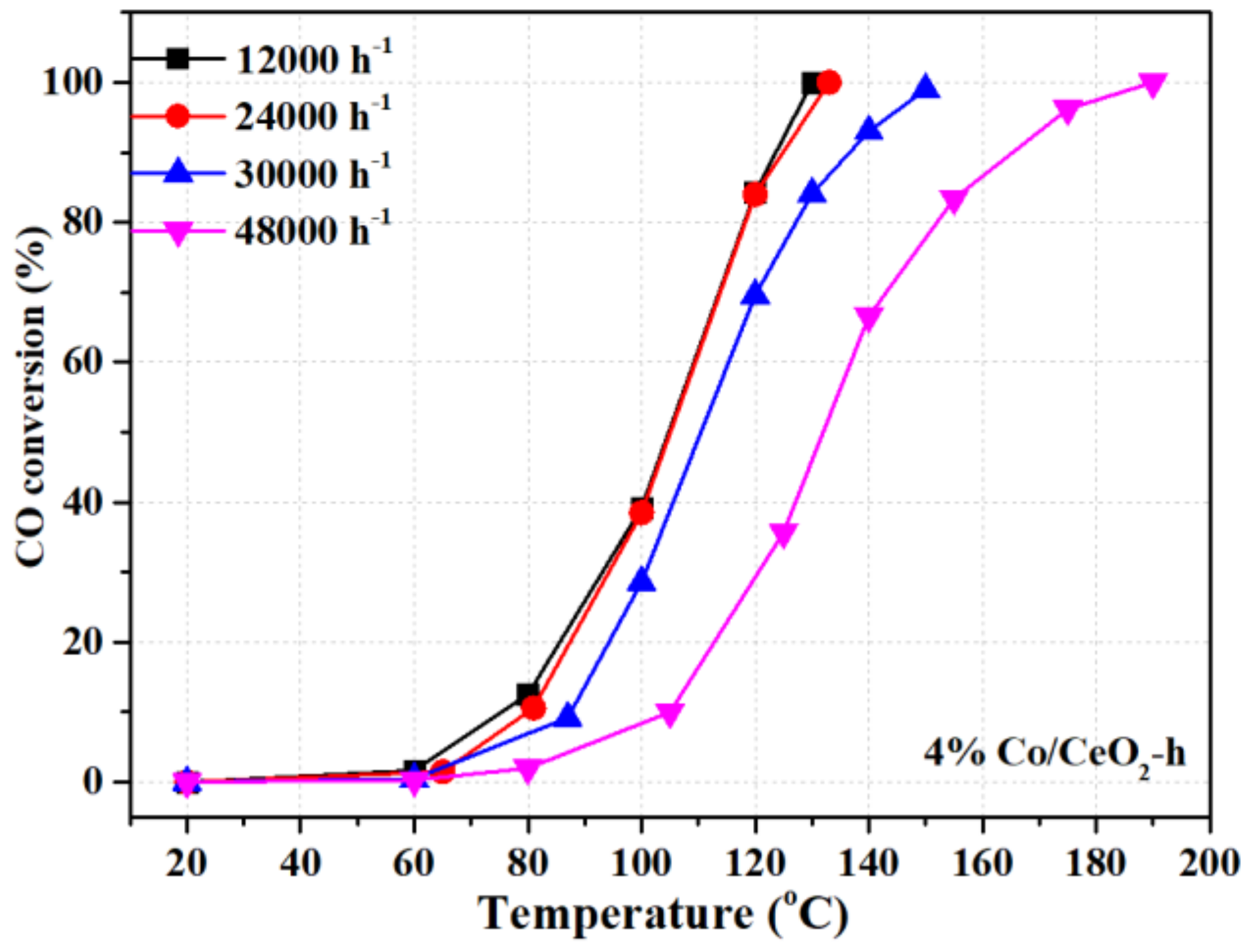
2.1. Catalytic Behavior
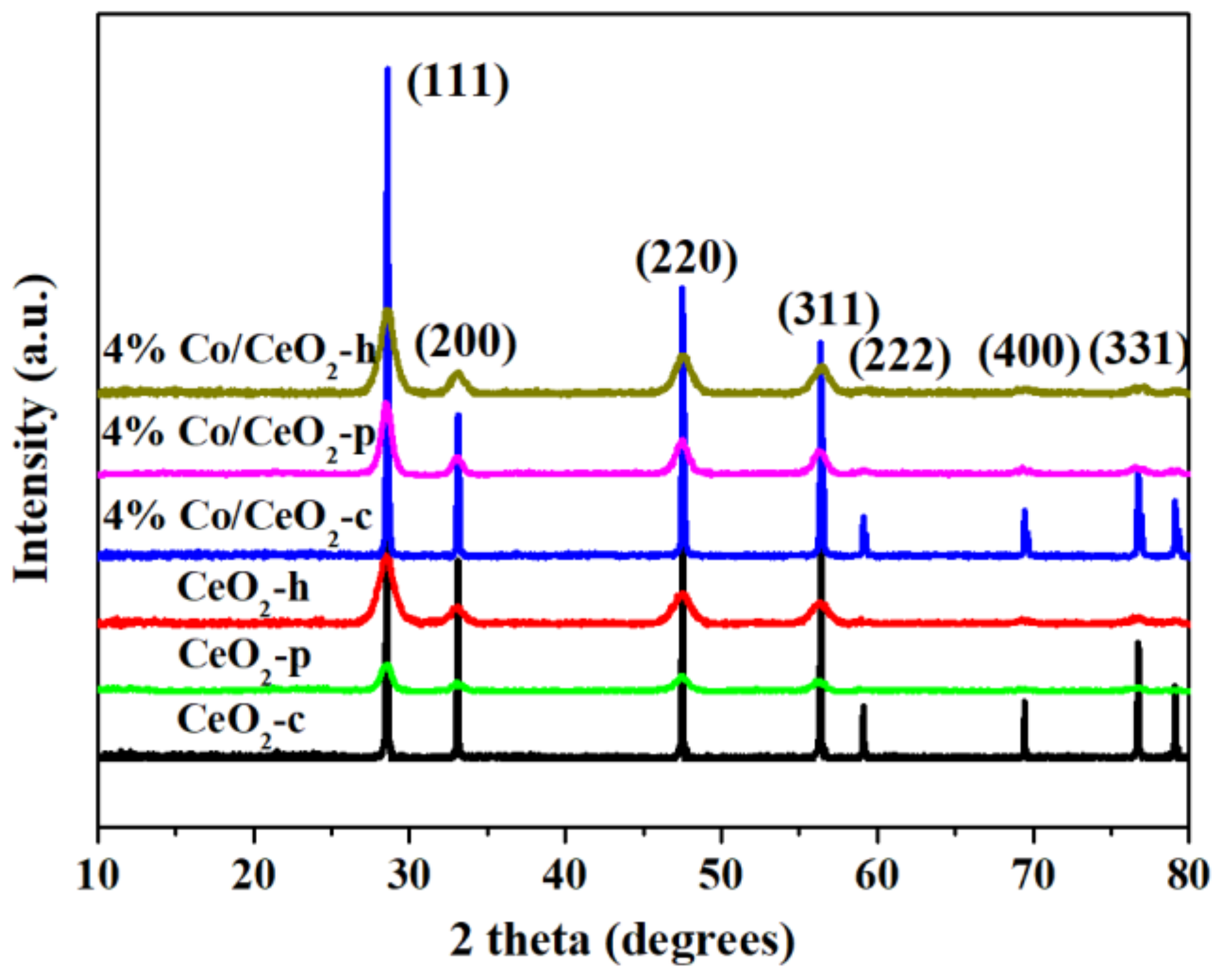
2.2. XRD and BET Analysis
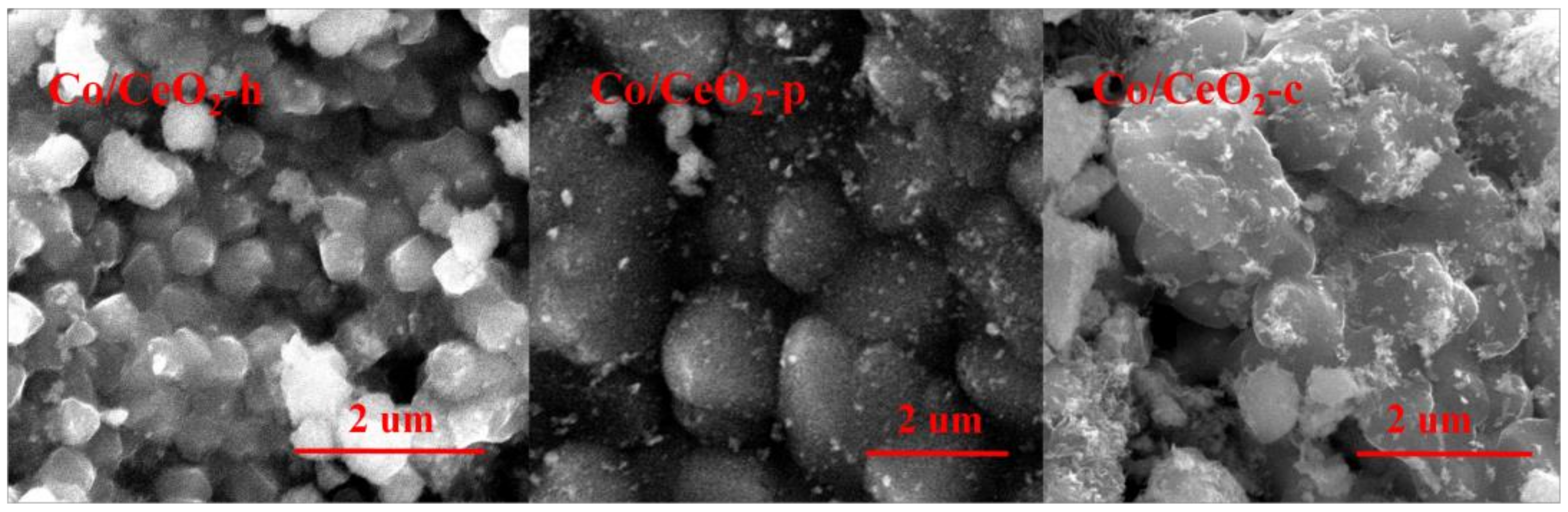
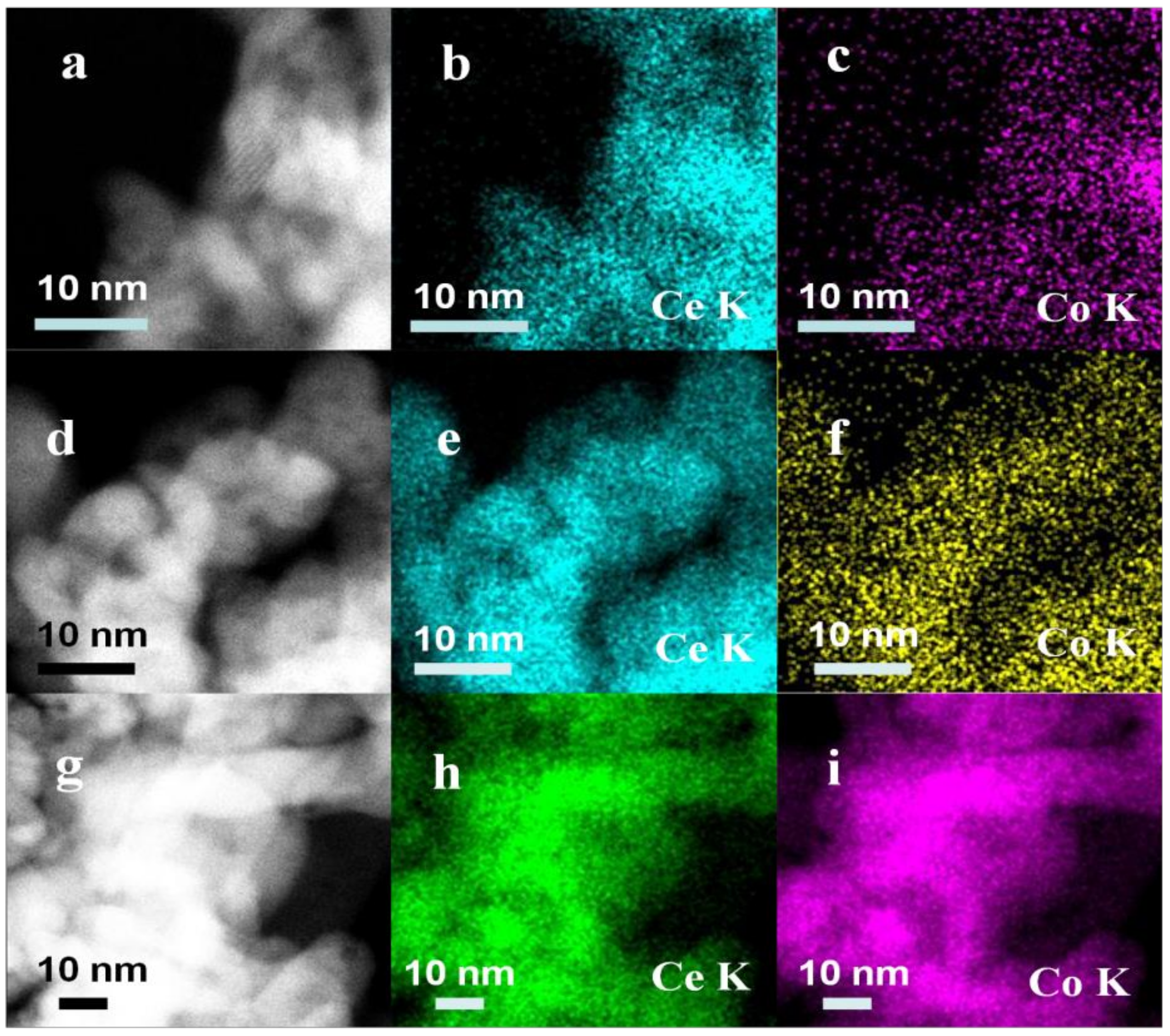
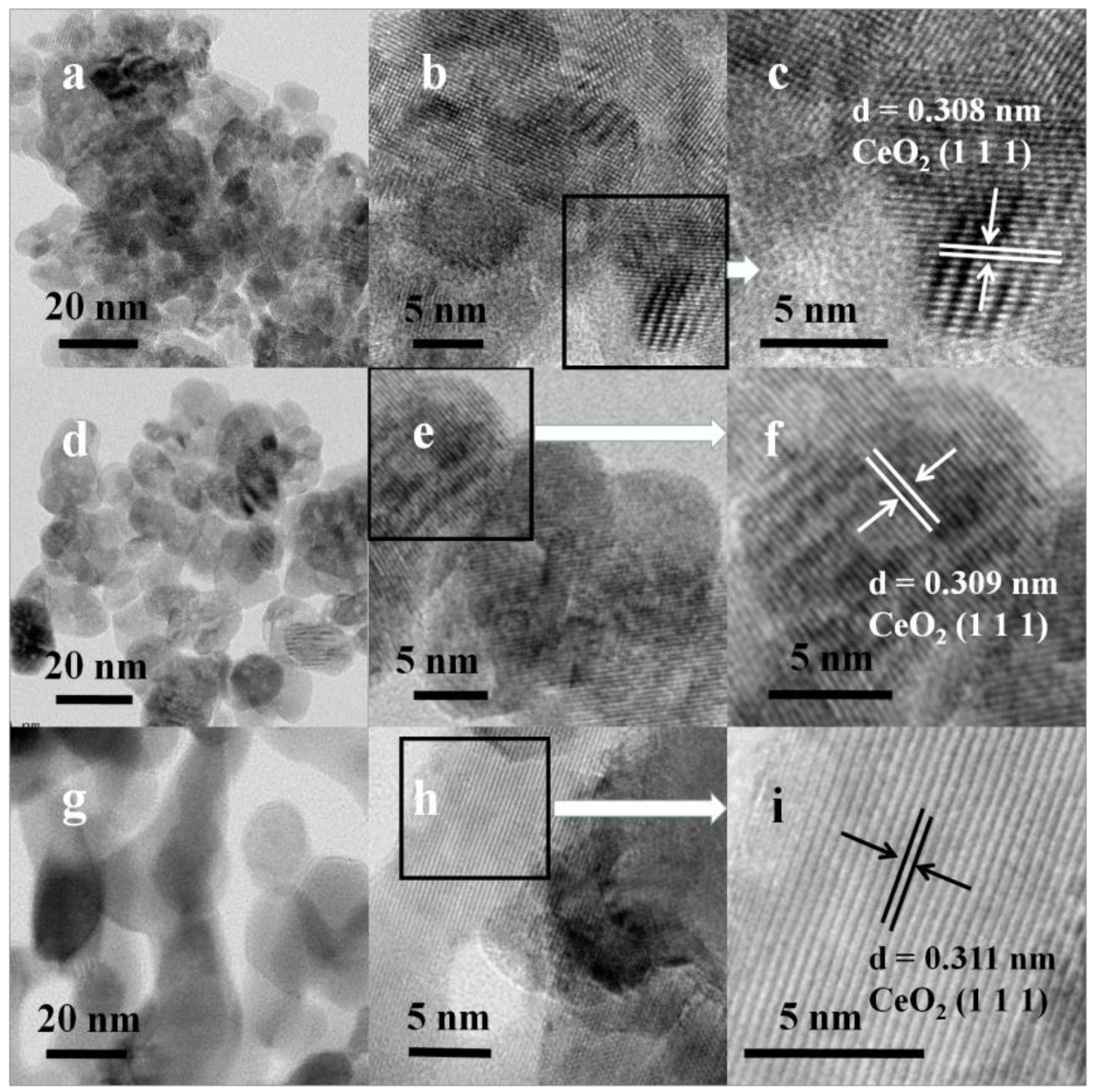
2.3. SEM and TEM Analysis
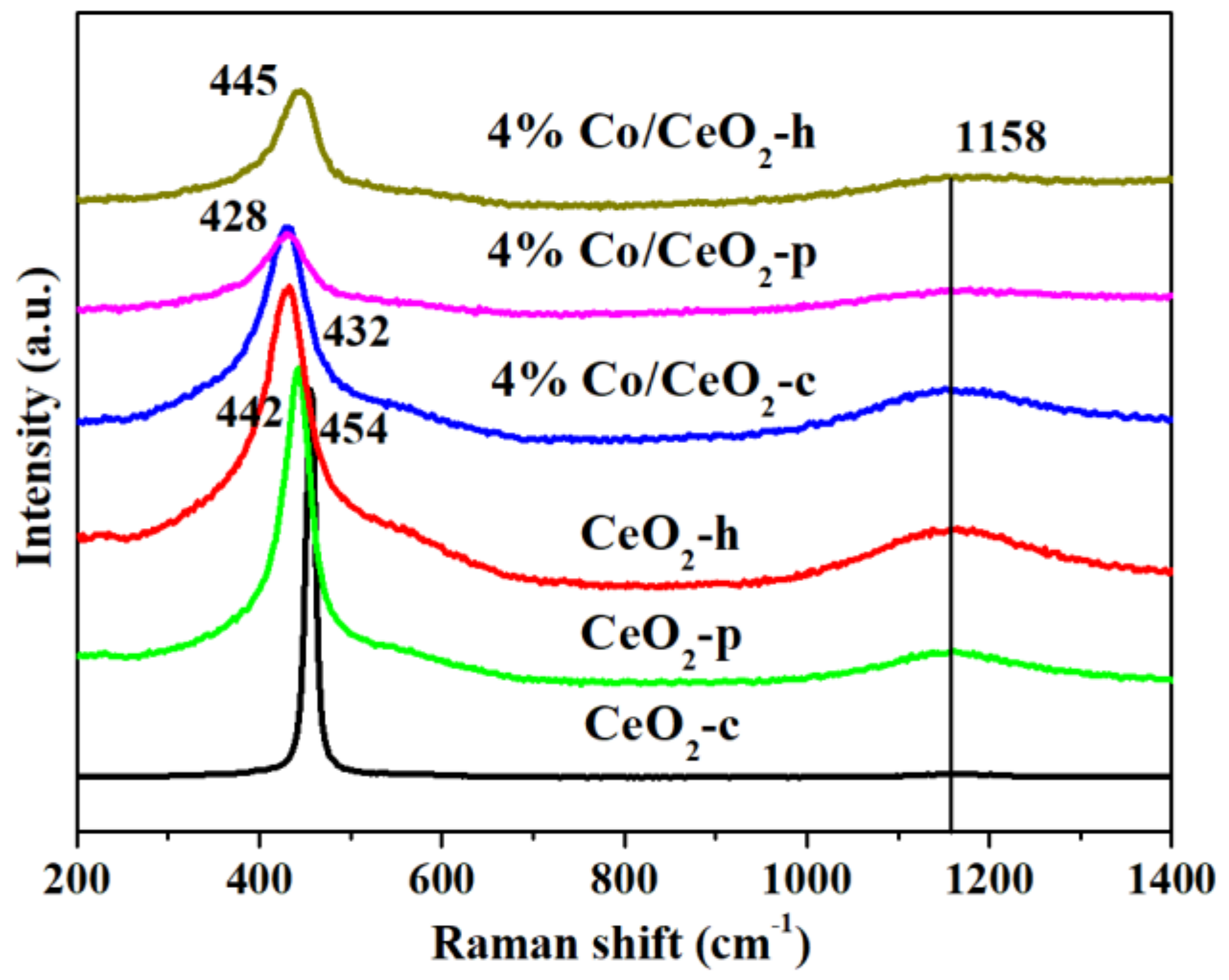
2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
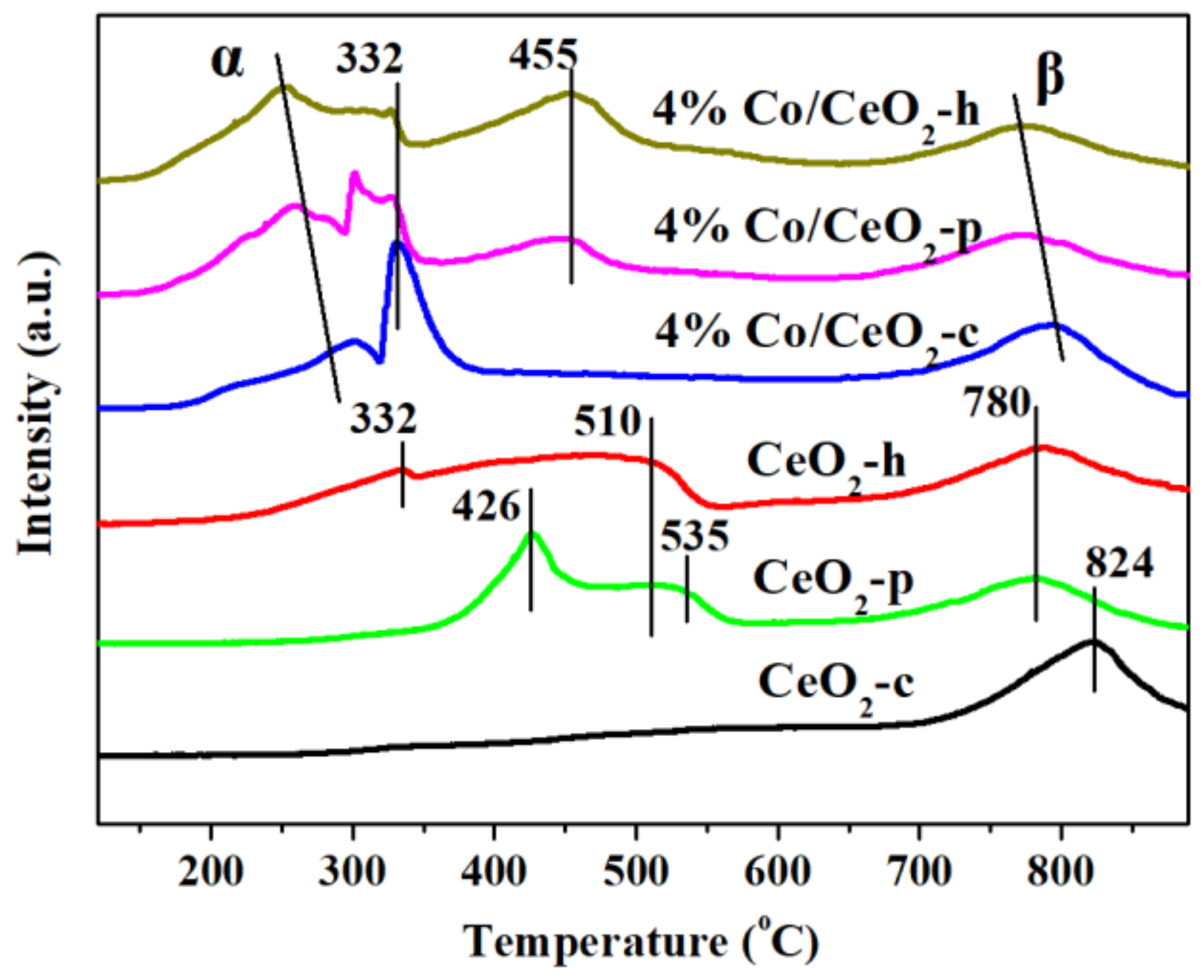
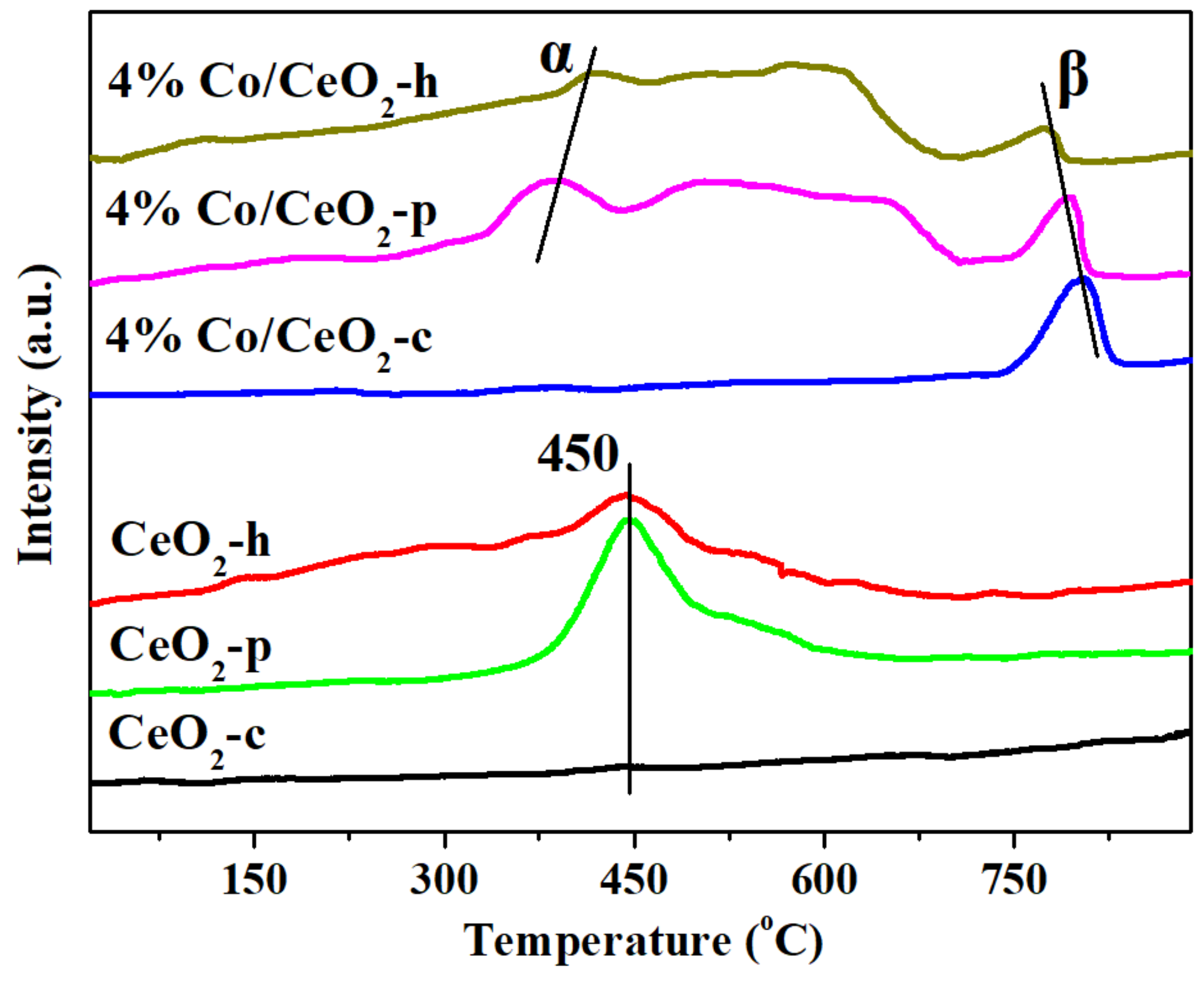
2.5. H2-TPR and O2-TPD Analysis
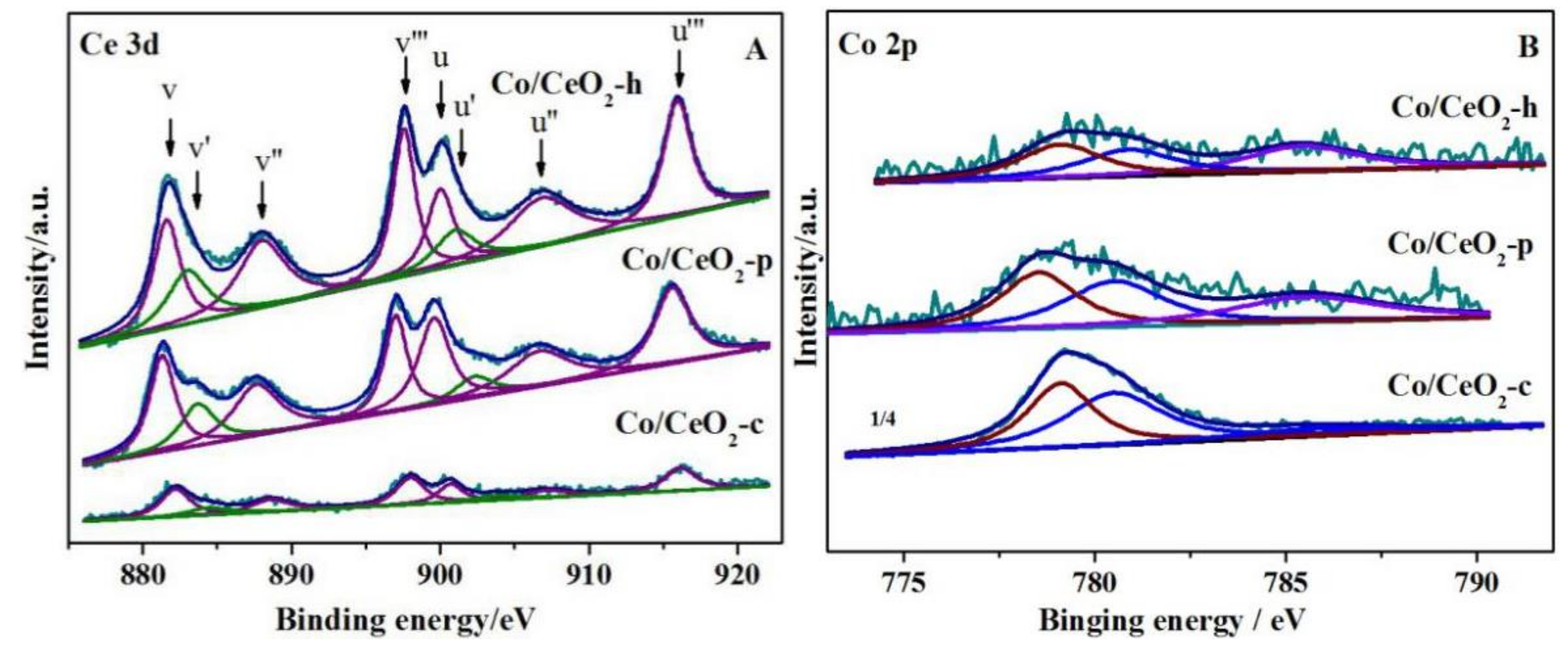
2.6. XPS Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of CeO2Nanoparticles
3.2. Synthesis of Co/CeO2Nanoparticles
3.3. Measurement of CO Oxidation Activity
3.4. Characterization of Materials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan-Hung, L.; Lak, J.H.; Tsai, D.-H. Hydrogen Production via Low-Temperature Steam–Methane Reforming Using Ni–CeO2–Al2O3 Hybrid Nanoparticle Clusters as Catalysts. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 7963–7971. [Google Scholar]
- Bruix, A.; Neyman, K. Modeling Ceria-Based nanomaterials for catalysis and related applications. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 2053–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandro, T.; Jordi, L. Ceria Catalysts at Nanoscale: How Do Crystal Shapes Shape Catalysis? ACSCatal. 2017, 7, 4716–4735. [Google Scholar]
- Divins, N.J.; Angurell, I.; Escudero, C.; Dieste, V.; Liorca, J. Nanomaterials Influence of the support on surface rearrangements of bimetallic nanoparticles in real catalysts. Science 2014, 346, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, Z.; Jiafeng, Y.; Jixin, Z.; Qingjie, G.; Hengyong, X.; Felix, D.; Roland, D.; Jian, S. Tailored metastable Ce–Zr oxides with highly distorted lattice oxygen for accelerating redox cycles. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3386–3394. [Google Scholar]
- Dvořák, F.; Farnesi, C.M.; Tovt, A.; Tran, N.D.; Negreiros, F.R.; Vorokhta, M. Creating single-atom Pt-ceria catalysts by surface step decoration. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Xiong, H.; Delariva, A.; Peterson, E.; Pham, H.; Challa, S.; Qi, G.; Oh, S.; Wiebenga, M.; Hernandez, X.; et al. Thermally stable single-atom platinum-on-ceriacatalysts via atomtrapping. Science 2016, 353, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, D.; Reddy, L.; Park, S.; Reddy, B. Ceria-zirconia mixed oxides: Synthetic methods and applications. Catal. Rev. 2018, 60, 177–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykaki, M.; Stefa, S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Pandis, P.K.; Stathopoulos, V.N.; Konsolakis, M. Facet-Dependent Reactivity of Fe2O3/CeO2 Nanocomposites: Effect of CeriaMorphology on CO Oxidation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykaki, M.; Pachatouridou, E.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Iliopoulou, E.; Andriopoulou, C.; Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Boghosian, S.; Konsolakis, M. Ceria nanoparticles shape effffects on the structural defects and surface chemistry: Implications in CO oxidation by Cu/CeO2 catalysts. Appl.Catal. B 2018, 230, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalasin, S.; Browne, E.P.; Arcaro, K.F.; Santore, M.M. Surfaces that Adhesively Discriminate Breast Epithelial Cell Lines and Lymphocytes in Buffffer and Human Breast Milk. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17035–17049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigdollers, A.R.; Pacchioni, G. CO Oxidation on Au Nanoparticles Supported on ZrO2: Role of Metal/Oxide Interface and Oxide Reducibility. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Mao, D.; Luo, Z.; Yu, J. CO oxidation on mesoporous SBA-15 supported CuO–CeO2 catalyst prepared by a surfactant-assisted impregnation method. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 27689–27698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junhao, L.; Zhongqi, L.; David, A.C.; Wenhui, H.; Jier, H.; Libo, Y.; Zhenmeng, P.; Peilin, L.; Ruigang, W. Distribution and Valence State of Ru Species on CeO2 Supports: Support Shape Effect and Its Influence on CO Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 11088–11103. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S. A Novel Catalyst for CO Oxidation at Low Temperature. Catal. Lett. 1999, 58, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spezzati, G.; Su, Y.; Hofmann, J.; Benavibez, A.; Delariva, A.; Mccabe, J.; Datye, A.; Hensen, E. Atomically dispersed Pd-O species on CeO2(111) as highly active sites for low-temperature CO oxidation. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaev, R.; Slavinskaya, E.; Novopashin, S.; Smovzh, D.; Zaikovsdii, A.; Osadchii, D.; Bulavchenkoa, O.; Koreven, S.; Boronin, A. Highly active PdCeOx composite catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation, prepared by plasma-arc synthesis. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 147, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarxin, C.; Junxiao, C.; Weiye, Q.; George, C.; Aouine, M.; Vernous, P.; Xingfu, T. Well-Defined Palladium-Ceria Interfacial Electronic Effects Trigger CO Oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10140–10143. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Yang, D.; Dapeng, L.; Xilan, F.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, Z. CO Oxidation Catalyzed by Two-Dimensional Co3O4/CeO2 Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 5769–5778. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. Theoretical investigations of non-noble metal single-atom catalysis: Ni1/FeOx for CO oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1017–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Yao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hong, M.; Zhu, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, J. Transition-Metal Doped Ceria Microspheres with Nanoporous Structures for CO Oxidation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Peng, X.; Binder, A.; Chai, S.; Dai, S. Origin of active oxygen in a ternary CuOx/Co3O4-CeO2 catalyst for CO oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 27870–27877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Manos, M. Transition Metal Atoms Embedded in Graphene: How Nitrogen Doping Increases CO Oxidation Activity. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6864–6868. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Di, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of highly efficient α-Fe2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation derived from MIL-100(Fe). J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 247, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, I.; Lokteva, S.; Golubina, E.; Maslakov, K.; Strokova, N.; Chernyak, S.; Lunin, V. Sawdust as an effective biotemplate for the synthesis of Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 and CuO–Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 catalysts for total COE oxidation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 51359–51372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampaiah, D.; Venkataswamy, P.; Coyle, V.E.; Reddy, B.M.; Bhargava, S.K. Low-temperature CO oxidation over manganese, cobalt, and nickel doped CeO2 nanorods. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80541–80548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; An, K. Catalytic CO Oxidation on Nanocatalysts. Top. Catal. 2018, 61, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Li, C.; Zhao, W.; Fan, W. Solubility Product Difference-Guided Synthesis of Co3O4-CeO2 Core-Shell Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7273–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, B.; Mukri, B.; Ghosal, P.; Subrahmanyam, C. Mn Ion substituted CeO2 Nano spheres for Low Temperature CO Oxidation: The Promoting Effect of Mn Ions. Chem. Sel. 2016, 1, 3150–3158. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Chang, S.; Huang, W. Morphology Effect of CeO2 Support in the Preparatport Interaction, and Catalytic Performance of Pt/CeO2 Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 3610–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junemin, B.; Dongjae, S.; Hojin, J.; Beom-Sik, K.; Jeong Woo, H.; Hyunjoo, L. Highly Water-Resistant La-Doped Co3O4 Catalyst for CO Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10093–10100. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Qilei, Y.; Changyu, Z.; Jinlong, Y.; Yue, P.; Junhua, L. Hollow-Structural Ag/Co3O4Nanocatalyst for CO Oxidation: Interfacial Synergistic Effect. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3480–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, M.; Rüsing, M.; Berth, G.; Lischka, K.; Pawlis, A. CuO and Co3O4 Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterizations, and Raman Spectroscopy. J.Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 714853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qin, X. Effect of cobalt oxide on surface structure of alumina supported molybdena catalysts studied by in situ Ramanspectroscopy. Catal. Lett. 1993, 18, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhania, A.; Gupta, S. CeO2-xNx Solid Solutions: Synthesis, Characterization, Electronic Structure and Catalytic Study for CO Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Hildebrandt, E.; Schubert, M.; Boscherini, F.; Zoellner, M.; Alff, L.; Walczyk, D.; Zaumseil, P.; Costina, L.; Wilkens, H.; et al. Oxygen Vacancy Induced Room Temperature Ferromagnetism in Pr-Doped CeO2 Thin Films on Silicon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17496–17505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LEE, Y.; He, G.; Akey, A.J.; Si, R.; Stephanopuulos, M. Raman analysis of mode softening in nanoparticle CeO(2-δ) and Au-CeO(2-δ) during CO oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12952–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvulescu, V.; Tiseanu, C. Local structure in CeO2 and CeO2-ZrO2 nanoparticles probed by Eu luminescence. Catal. Today 2015, 253, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Meng, M.; Yao, J.; Li, J.; Zha, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. One-step synthesis of nanostructured Pd-doped mixed oxides MOx-CeO2 (M=Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) for efficient CO and C3H8 total oxidation. Appl.Catal. B 2009, 87, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafeng, C.; Jia, X.; Yun, G.; Jingyue, L. Ultrathin, Polycrystalline, Two-Dimensional Co3O4 for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar]
- Cronauer, D.; Kropf, A.; Marshall, C.; Gao, P.; Hopps, S.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Preconditioning Effects Upon Co-Containing Promoted and Unpromoted Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Rao, K.; Bharali, P. Copper Promoted Cobalt and Nickel Catalysts Supported on Ceria−Alumina Mixed Oxide: Structural Characterization and CO Oxidation Activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 8478–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effect of CeO2 Doping on Structure and Catalytic Performance of Co3O4 Catalyst for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2008, 123, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Qian, X.; Tao, M.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Z. Pt/MOx/SiO2, Pt/MOx/TiO2, and Pt/MOx/Al2O3 Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Catal. 2015, 5, 606–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.; Lu, G.; Wu, G.; Mao, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Promotional role of ceria on cobaltosic oxide catalyst for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Kaidong, W.; Can, W.; Feng, W.; Nan, J.; Guoqiang, J. Co/Co3O4 Nanoparticles Coupled with Hollow Nanoporous Carbon Polyhedrons for the Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18582–18592. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Cao, X.; Lan, J.; Wang, L.; Dai, Q.; Guo, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hu, P.; et al. Ultralow-temperature CO oxidation on an In2O3-Co3O4catalyst: A strategy to tune CO adsorption strength and oxygen activation simultaneously. Chem.Commun. 2014, 50, 6835–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezhi, L.; Jianjun, C.; Yue, P.; Weichen, L.; Tao, Y.; Junhua, L. The relationship between surface open cells ofa-MnO2 and CO oxidation ability from a surface point of view. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 20911–20921. [Google Scholar]
- Hyunwoo, H.; Sinmyung, Y.; Kwangjin, A.; Hyun, Y.K. Catalytic CO Oxidation over Au Nanoparticles Supported on CeO2 Nanocrystals: Effect of the Au–CeO2 Interface. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11491–11501. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Liu, F.; He, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C. A superior Ce-W-Ti mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 115, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Structure–activity relationship of VOx/CeO2 nanorod for NO removal with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, G.; Wu, G.; Mao, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Effect of TiO2 crystal structure on the catalytic performance of Co3O4/TiO2 catalyst forlow-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanyi, J.; Xijun, W.; Wenhui, Z.; Zhunzhun, W.; Oleg, V.P.; Yi, L.; Jun, J. Catalytic Chemistry Predicted by a Charge Polarization Descriptor: Synergistic O2 Activation and CO Oxidation by Au–Cu Bimetallic Clusters on TiO2(101). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9629–9640. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Superior activity of MnOx-CeO2/TiO2 catalyst for catalytic oxidation of elemental mercury at low flue gas temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 111, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Ke, J.; Xiao, H.; Lv, X.; Liu, S.; Tade, M.; Wang, S. Mwchanistic investigation of the enhanced NH3-SCR on cobalt-decorated Ce-Ti mixed oxide: In situ FTIR analysis for structure-activity aorrelation. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 300, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Catalysts | Particle Size a(nm) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | O2 Desorption b (mmol/g) | H2Consumption c (mmol/g) | H/Htheoretical d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2-h | 10.0 | 128.1 | 0.82 | 1.19 | 0.59 |
| CeO2-p | 14.6 | 65.1 | 0.50 | 0.88 | 0.57 |
| CeO2-c | >100 | 40.6 | 0 | 0.07 | 0.24 |
| 4%Co/CeO2-h | 8.9 | 96.4 | 1.08 | 2.01 | 0.92 |
| 4%Co/CeO2-p | 12.5 | 56.1 | 0.94 | 1.58 | 0.91 |
| 4%Co/CeO2-c | >100 | 43.8 | 0 | 1.11 | 0.74 |
| CeO2-c | CeO2-p | CeO2-h | Co/CeO2-c | Co/CeO2-p | Co/CeO2-h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D/F2g (%) | 77.96 | 82.46 | 97.42 | 74.68 | 78.9 | 80.74 |
| Catalysts | Atomic Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Ce3+/Ce | Co3+/Co | |
| 4% Co/CeO2-h | 16.58 | 52.84 |
| 4% Co/CeO2-p | 13.50 | 48.53 |
| 4% Co/CeO2-c | 11.89 | 45.72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sui, C.; Xing, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M. Co-Supported CeO2Nanoparticles for CO Catalytic Oxidation: Effects of Different Synthesis Methods on Catalytic Performance. Catalysts 2020, 10, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020243
Sui C, Xing L, Cai X, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Li M. Co-Supported CeO2Nanoparticles for CO Catalytic Oxidation: Effects of Different Synthesis Methods on Catalytic Performance. Catalysts. 2020; 10(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleSui, Chao, LeHong Xing, Xue Cai, Yang Wang, Qi Zhou, and Minghao Li. 2020. "Co-Supported CeO2Nanoparticles for CO Catalytic Oxidation: Effects of Different Synthesis Methods on Catalytic Performance" Catalysts 10, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020243
APA StyleSui, C., Xing, L., Cai, X., Wang, Y., Zhou, Q., & Li, M. (2020). Co-Supported CeO2Nanoparticles for CO Catalytic Oxidation: Effects of Different Synthesis Methods on Catalytic Performance. Catalysts, 10(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020243