Abstract
Early detection and diagnosis of plant diseases is critical for ensuring global food security and sustainable agricultural practices. This review comprehensively examines latest advancements in crop disease risk prediction, onset detection through imaging techniques, machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and edge computing technologies. Traditional disease detection methods, which rely on visual inspections, are time-consuming, and often inaccurate. While chemical analyses are accurate, they can be time consuming and leave less flexibility to promptly implement remedial actions. In contrast, modern techniques such as hyperspectral and multispectral imaging, thermal imaging, and fluorescence imaging, among others can provide non-invasive and highly accurate solutions for identifying plant diseases at early stages. The integration of ML and DL models, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transfer learning, has significantly improved disease classification and severity assessment. Furthermore, edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) facilitate real-time disease monitoring by processing and communicating data directly in/from the field, reducing latency and reliance on in-house as well as centralized cloud computing. Despite these advancements, challenges remain in terms of multimodal dataset standardization, integration of individual technologies of sensing, data processing, communication, and decision-making to provide a complete end-to-end solution for practical implementations. In addition, robustness of such technologies in varying field conditions, and affordability has also not been reviewed. To this end, this review paper focuses on broad areas of sensing, computing, and communication systems to outline the transformative potential of end-to-end solutions for effective implementations towards crop disease management in modern agricultural systems. Foundation of this review also highlights critical potential for integrating AI-driven disease detection and predictive models capable of analyzing multimodal data of environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, as well as visible-range and thermal imagery information for early disease diagnosis and timely management. Future research should focus on developing autonomous end-to-end disease monitoring systems that incorporate these technologies, fostering comprehensive precision agriculture and sustainable crop production.
1. Introduction
Crop diseases significantly threaten global food security, causing long-standing concern for farmers and agronomists. These diseases contribute to lower crop yields, diminished quality, increased pesticide usage, and substantial economic losses [1,2]. To ensure agricultural sustainability, it is essential to minimize disease-induced damage at the earliest during crop growth and optimize yields. For example, according to the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), wheat rust, a fungal disease affecting wheat and barley, results in global losses of up to $3 billion annually [3]. Consequently, early identification of crop disease risks and the implementation of targeted treatment strategies based on disease severity are crucial for agricultural producers [4]. This plays a key role in protecting yields and maintaining farmers’ profitability. It is also essential that disease control measures are timely and applied in minimal possible amounts such that the farmer’s profitability and environmental sustainability remain unharmed. Leveraging advanced sensing and digital technologies can help in rapid and accurate identification of plant disease and pertaining severity risks for implementing precision crop protection strategies [5,6,7,8]. Over the past few decades, crop disease detection has advanced significantly, evolving from manual scouting and laboratory assays in the 1980s–1990s, to computer vision (CV) and machine learning (ML) approaches with handcrafted features in the 2000s, followed by multispectral and hyperspectral imaging combined with UAV-based monitoring in the 2010s [9]. More recently, the field has shifted toward deep learning (DL) and artificial intelligence (AI), enabling more accurate, scalable, and real-time disease recognition in precision agriculture [9]. This technological progression aligns with increasing global emphasis on sustainable intensification of agriculture. For instance, policy initiatives such as the European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Precision Agriculture initiatives have promoted the adoption of digital farming tools to reduce pesticide use, improve input efficiency, and enhance resilience against crop losses [10,11].
In an ideal situation for zero crop loss from diseases, crop problem assessment should begin at the pre-symptomatic stages and more so ever at the forecast stages. However, conventionally, most of the crop diseases at the earliest are detected at their outbreaks which means that the only opportunity that remains is for minimizing losses through aggressive control measures which may neither be profitable, efficient, or sustainable. Traditional methods for identifying diseases largely rely on farmers’ personal experience, visual scouting, guidance from plant pathologists, or lab-based crop tissue analysis. This approach can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often subjective. Pertinent to visual scouting, symptoms for various biotic or abiotic problems may appear to be very similar, for example, early symptoms of sudden death syndrome, nutrient deficiency, or water stress could appear to be very similar in soybean crops. Such situations combined with the natural illumination variation during the day and inter-human color recognition capacities may introduce significant errors in problem diagnosis hence incorrect management [7,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Lab-based crop tissue evaluation methods are accurate for plant disease diagnosis, but are destructive in nature, limited in sampling accuracy for quantifying in-field spatial variations, and may require extensive experiments, thereby making timely diagnosis impossible [13], especially during the peak growth stages or high workload for experts. This can delay providing results to growers, followed by them missing opportunities for timely implementing remedial measures in the field for minimized crop losses. It must be noted that the efficacy of treatment and dosage of crop protection measures is determinant upon the right identification of crop problem in a high-throughput manner and in real field conditions. Modern techniques such as digital sensing and imaging, data processing, anomaly or similarity identification, and deep learning-based classifications, offer potentially higher efficiency and time saving in early crop disease diagnosis and their precision treatment compared to traditional methods [18,19,20,21,22,23].
Variety of sensing and imaging techniques have emerged over time for detection and identification of plant diseases. These include, Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) or visual range imaging, multispectral, hyperspectral, spectroscopy, thermal, fluorescence, tomography, photoacoustic, magnetic resonance, and time-of-flight, to name a few. While RGB, multispectral imaging (MSI) and hyperspectral imaging (HSI) or spectroscopy analyzes signatures of reflected light mostly in the visible to near-infrared ranges of electromagnetic wavelength spectrum (400–2500 nm) [24], thermal imaging analyzes emissivity of target object (or temperature) within the longwave infrared range (8000–14,000 nm) [25] of the electromagnetic spectrum. Photoacoustic imaging relies on the absorption of light by the object of interest where the resulting pressure distribution is mapped and analyzed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a strong magnetic field to align protons in the tissue, following which radio waves are sent to disrupt the alignment of these protons. When the radio waves are turned off, protons tend to retain their original position by emitting back the radio signals (energy) which are captured to generate an image of internal structures. Fluorescence sensing/imaging is another technique used for plant problem identification wherein the plant tissues are illuminated by fluorescent light leading to electron excitation from the ground state. Since the excited state is unstable, the electrons quickly return to ground state by emitting fluorescence. This emission spectra are captured and analyzed to interpret the health of plant tissue. Among all these sensing/imaging techniques, RGB, multispectral and hyperspectral have emerged as the most adopted ones in the laboratories as well as field-based investigations. Commercial RGB cameras have become inexpensive but lack spectral resolution for identifying the risk or onset of specific diseases beyond the naked eye perspective. This is where MSI and further, HSI find their biggest application scope.
The disease detection methods discussed earlier often rely on laboratory setups, limiting their suitability for real-time applications. Consequently, techniques ranging from traditional to advanced image processing (IP) including ML and DL techniques have emerged as the facilitators of automated identification of crop diseases, quantification of severity and progression, as well as forecasting [26,27]. As the disease outbreaks in plants, they exhibit evolving visual symptoms such as colored spots, lesions, or lines of varying shapes and sizes on stems and other plant parts depending on the type of disease and its progression [12,28]. These visual cues make it possible to automatically detect or identify plant diseases [2,29,30,31]. ML algorithms such as multi-class support vector machines [32], artificial neural network (ANN) [33], radial basis function (RBF) and k-nearest neighbor (KNN) [34] have produced an accuracy of up to 100% in detecting crop disease early or late in the season for a range of cropping systems. The advancements in computing systems, particularly with the development of embedded graphics processing unit (GPU) processors have greatly improved the ability to automatically and rapidly detect crop diseases from imagery datasets. Here, DL [35], a subset of ML and AI, has been widely applied for crop disease identifications. DL leverages multiple layers of non-linear information processing for supervised or unsupervised feature extraction, transformation, pattern recognition, and classification [36]. Among DL architectures, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the most widely used for their efficiency and rapidity of modeling complex processes and identifying patterns in large datasets [7,35]. Some of the widely used CNN-based DL models include YOLO, Inception, Exception, ResNet, GoogleNet, RIC-Net, and MobileNetV2, among others [37].
As previously discussed, plant disease diagnosis generally falls into two primary categories: laboratory-based and field-based methods. Laboratory-based diagnostics employ various specialized techniques to accurately detect the pathogens—whether fungal, bacterial, viral, or other microorganisms—responsible for disease symptoms in plants. This precise identification supports farmers in selecting the most appropriate and effective disease control measures. These diagnostic procedures are typically conducted in controlled settings using more specialized equipment. Established laboratory techniques, including plating, microscopy, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), and polymerase chain reaction (PCR), have significantly enhanced our ability to identify pathogens with high accuracy and sensitivity [38]. Despite remarkable advancements in laboratory-based disease detection, translating these technologies into real-time, field-based applications remains challenging. Field deployments must contend with varying environmental conditions, inconsistent lighting, diverse crop canopies, and limited access to power and computing infrastructure. Nonetheless, recent innovations such as handheld diagnostic tools, smartphone-based platforms, unoccupied aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellites, and unoccupied ground vehicles (UGVs) are helping to bridge the lab-to-field gap. These platforms, when integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) networks, edge computing, and cloud-based architectures, offer a transformative opportunity for real-time, scalable, and end-to-end crop disease monitoring and management. To fully harness these technologies, future research must address several pressing questions:
- How can sensor fusion from multiple platforms (e.g., UGVs, UAVs, satellites) be optimized for accurate field-scale disease mapping?
- What are the most effective models for deploying edge-AI systems that process and act on data locally in resource-limited agricultural environments?
- How can IoT-based disease monitoring networks be designed for long-term scalability and sustainability in smallholder farming systems?
- How can real-time disease forecasts be integrated into automated treatment systems for closed-loop precision crop protection?
By addressing these challenges and exploring such questions, the next generation of digital disease diagnostics can become more accessible, reliable, and impactful across diverse agricultural landscapes. Despite remarkable progress in sensing technologies, imaging systems, and AI-driven analytics, end-to-end solutions for effective crop disease management remain limited in both implementation and research focus. Most existing review studies have primarily examined individual components—such as sensors, imaging modalities, or machine learning techniques—in isolation, without integrating them into a unified framework. This fragmentation creates a gap in understanding how these technologies can collectively function as an efficient, interconnected pipeline for real-time disease detection and management. Motivated by this gap, the present review aims to provide a comprehensive and integrative overview of recent advancements spanning sensors and platforms, imaging technologies, computer vision techniques, edge computing and IoT-based systems. The purpose of this review is to synthesize these components into a cohesive discussion that highlights their interconnections and complementary roles in developing scalable, end-to-end digital disease detection systems. Through this approach, the review seeks to guide future research toward building accessible, reliable, and data-driven solutions for sustainable crop health monitoring and management. Additionally, the review evaluates economic feasibility and provides practical recommendations for adopting emerging technologies to ensure their accessibility, affordability, and scalability across diverse agricultural systems. To support this objective, the paper addresses the following key research questions aimed at clarifying the state-of-the-art developments and their practical implications in agricultural disease monitoring:
- How do the various sensing platforms vary in resolution, scalability, and effectiveness for disease detection above and below the crop canopy?
- How has imaging evolved from 2D to advanced multispectral and 3D methods, and which technique leads in early disease diagnosis?
- How have DL and CNN-based computer vision outperformed traditional methods in automating and improving disease detection accuracy?
- How do IoT and edge computing enable real-time, resource-efficient crop disease detection and decision-making across varied farm settings?
- What are the key economic, infrastructural, and policy factors influencing the adoption and scalability of emerging sensing and AI-driven technologies for end-to-end crop disease diagnosis?
In the rest of the paper, Section 2 describes the methodology of article selection for this review; Section 3 summarizes various case studies on crop disease detection; Section 4 discusses the sensors and platforms employed; Section 5 reviews imaging techniques aiding disease detection; Section 6 explores computer vision methods in disease detection; Section 7 highlights the role of edge computing and IoT in crop disease diagnosis; Section 8 discusses the economic feasibility of adopting crop diagnosis technologies; Section 9 discusses challenges and future prospects in agricultural disease detection; and finally, Section 10 concludes the study. The structure of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
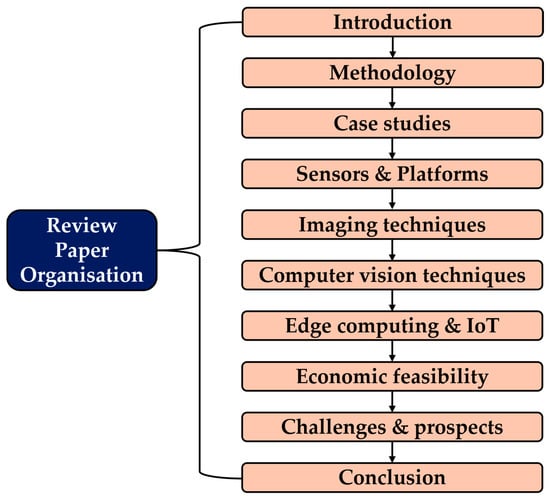
Figure 1.
Review paper structure and organization.
2. Review Methodology and Article Selection
2.1. Article Retrieval Criteria
To ensure a systematic and high-quality review, clear inclusion and exclusion criteria were established to filter studies based on relevance, recency, and research rigor. This review, which explores emerging end-to-end digital technologies for timely crop disease diagnosis and precision crop protection within precision agriculture, applies these criteria to capture a wide scope of existing literature while prioritizing studies with strong experimental or applied contributions.
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
Following criteria were applied to determine studies to be included in this review.
- Relevance to subject of review: A key criterion for inclusion was the study’s alignment with the central theme of plant disease detection and its associated technologies. Selected studies were required to cover at least one relevant aspect of the review, such as sensors and platforms used for plant disease detection, imaging techniques for plant disease detection, development of ML/DL models and computer vision techniques for plant image analysis, or edge-computing and IoT for end-to-end solution for integrated plant disease management systems. Relevance was assessed by reviewing the study’s title, abstract, objectives, and methodology to confirm its consistency with the scope of the paper.
- Publication timeframe: Although the review emphasizes recent innovations and emerging technologies in the field over the past decade, 2015–2025, earlier studies were also examined for a comprehensively understanding advancement over time.
- Article type and subject areas: The literature search for this review primarily targeted review and research articles published in the subject areas of agricultural and biological sciences, computer science, and engineering. The articles selected are comprised of journals, conference papers, thesis and dissertations.
- Language: To maintain consistency and ensure broad accessibility, only English-language publications were considered in this review. This approach supported clarity and uniformity in the analysis of the selected literature.
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
Following criteria were applied to determine studies to be excluded from this review.
- Irrelevance to subject of review: Irrelevant studies such as studies that do not directly address any aspect of the topic of review, were excluded from this research. This was mostly determined by critically examining the study’s abstract.
- Out-of-scope publications: Studies published prior to 2015 were completely excluded from this review, as they do not fall within the scope of the review.
- Non-journal, non-conference paper, non-thesis/dissertation: Articles such as book chapters, editorials, and short communications, which do not have a significant amount of research component, were completely excluded from this review.
- Non-English publications: To maintain consistency and accessibility, studies published in languages other than English were excluded. This also ensured that reviewed literature be accurately interpreted by the broader scientific community.
2.2. Article Selection Process
2.2.1. Database Search
Extensive literature searches were conducted in both ScienceDirect and Google Scholar databases to achieve broad and comprehensive coverage of relevant studies.
2.2.2. Keywords Search
The set of keywords used in the literature search is a combination of the major keywords and their synonyms. Example keywords combinations used are: (i) Machine learning OR Deep learning AND Crop Disease AND Detection OR Classification OR Prediction, (ii) Imaging techniques AND Crop Disease AND Detection AND Agricultural fields, (iii) Image Processing AND Crop Disease AND Detection OR Classification. The keywords used in this study were selected to retrieve research studies related to the advancement of deep learning, machine learning, image processing and imaging technologies for the detection, classification, and prediction of crop diseases.
2.2.3. Initial Screening
The total number of articles gathered from the search on both databases was 3320. Afterwards, initial screening of the papers was conducted based on title and abstract relevance and a total of 629 articles were selected. At this stage, studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. This initial screening step helped narrow down the volume of literature to a more manageable set for in-depth analysis.
2.2.4. Text Evaluation and Final Selection
The shortlisted studies were subjected to full-text evaluation to assess their relevance and contribution to the field. At this stage, detailed inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied, considering each study’s objectives, methods, findings, and overall quality [39]. Finally, based on the relevance of the papers to crop diseases and associated technologies, a total of 356 articles were further selected for analysis in this study.
2.3. Keyword Analysis
The bibliometric networks for the selected papers were constructed and visualized using the VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) software tool (https://www.vosviewer.com/, accessed on 8 August 2024), to represent the data through network, overlay, and density visualizations [40,41]. In this keyword co-occurrence analysis (Figure 2), ten distinct clusters are identified, each represented by different colors—blue, orange, red, green, yellow, purple, pink, brown, turquoise, and light green—comprising a total of 109 keywords meeting the minimum occurrence threshold of three. The node “deep learning” remains the most dominant and central term, underscoring its pivotal role in modern crop disease detection. Closely associated keywords such as “artificial intelligence,” “convolutional neural network,” “computer vision,” and “image processing” (blue—orange clusters) highlight the growing integration of AI-driven models for automated plant disease identification and classification. The green and yellow clusters, which include terms like “plant disease detection,” “hyperspectral imaging,” and “phenotyping,” emphasize the increasing use of imaging and spectral technologies for crop monitoring and trait analysis. Meanwhile, the purple and pink clusters connect keywords such as “internet of things,” “smart agriculture,” and “cloud computing,” revealing the rise in integrated, data-driven frameworks for real-time disease surveillance. Using the association strength method for analysis, collectively, this network structure reflects a multidisciplinary convergence of deep learning, sensing technologies, and IoT-based systems, illustrating the evolving research landscape and the central role of intelligent automation in precision crop protection.
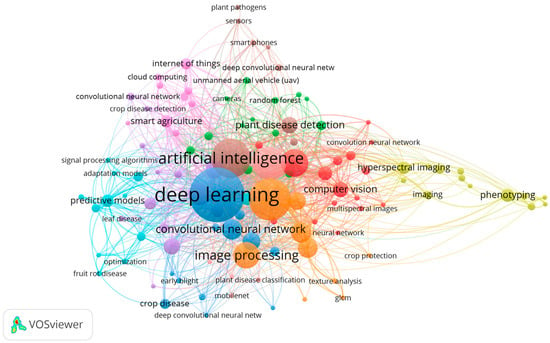
Figure 2.
VOS diagram illustrating the relationships and clusters of keywords derived from the selected papers, providing insights into thematic connections.
The cluster of techniques applied in the reviewed studies (Figure 3) reveals seven interconnected groups representing the diverse analytical and computational approaches employed in crop disease detection. Central to the network are “deep learning” and “machine learning”, which remain the most dominant techniques, closely linked to “artificial intelligence”, “image processing”, and “computer vision”. The strong association between “deep learning”, “convolutional neural networks” (CNNs), “feature extraction”, and “image segmentation” highlights their pivotal role in automating complex visual analysis tasks for early and accurate disease identification. The connections extending toward “hyperspectral imaging”, “feature selection”, and “object detection” demonstrate the integration of data-rich sensing methods with intelligent models to enhance classification precision. Additionally, emerging links to “internet of things” (IoT), “cloud computing”, and “predictive modeling” reflect an increasing shift toward connected, scalable frameworks for real-time disease monitoring and forecasting. Collectively, this methodological landscape underscores the growing convergence of AI-driven techniques with advanced imaging and data-processing tools, marking a progressive trend toward smarter and more autonomous crop protection systems.
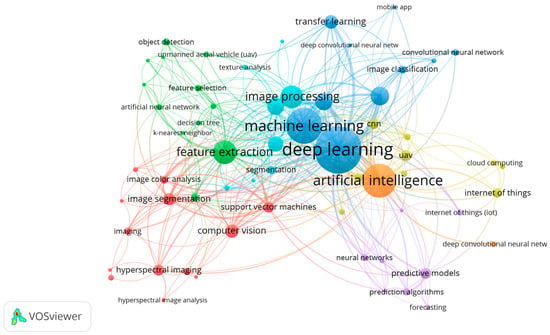
Figure 3.
VOS illustration of relationships and groupings of techniques used in the selected papers, providing an overview of the methodological landscape within the reviewed literature.
3. Case Studies in Crop Disease Detection
One significant role of technology in agriculture is witnessed in effective disease management in preserving the yield and quality of major crops. Key crops like rice, wheat, corn, and high value produce such as tomatoes and bananas are essential for food security and global economic stability. Wheat, rice, and corn make up 80% of global cereal production and supply more than half of the world’s caloric intake, serving as staple foods across numerous cultures [41,42,43]. Wheat is essential in temperate regions, rice is a staple in Asian diets, and corn is important across the Americas and Africa. With population growth and changing diets, global demand for cereal grains continues to increase. Wheat serves as a major food source cultivated across a range of climates, from temperate to subtropical regions, with China, India, Russia, and the United States being leading producers [41]. However, diseases such as rust, septoria, powdery mildew, and Fusarium head blight are prevalent and pose substantial threats to wheat production [44,45]. The most common diseases affecting rice include bacterial blight, leaf blast, brown spot, and tungro [46]. Corn, also known as maize, is an important cereal crop worldwide, serving as a staple food for numerous populations and utilized in diverse ways, including human consumption, livestock feed, and industrial uses like maize syrup and biofuel production [47]. Numerous diseases can impact the growth and productivity of corn crops. Such diseases include leaf blight, maize rust, maize leaf Cercospora leaf spot also known as gray leaf spot and maize mildew, amongst many others.
Advancements in imaging, IP, ML, and DL are enabling more accurate and timely crop disease detection, supporting sustainable farming practices. Table 1 examines case studies that illustrate application of these advanced detection techniques across various crops, highlighting the potential for technology-driven approaches to mitigate the impact of crop diseases effectively. It should be noted that out of the papers analyzed in this study, 55 papers are reported in this section. The selection of these papers was based on studies where authors collected and presented field data. Studies which utilized data from online repositories were not considered in this section.

Table 1.
Summary of crop disease detection case studies.
Figure 4 provides an insightful overview of various crops studied in the past decade alongside the techniques employed for disease detection from the studies reported in this section. Figure 4a captures the range of crops, showing a particular focus on staple crops such as potato, wheat, rice, and corn evident by their percentage distributions of 5%, 7%, 8%, and 11%, respectively, which is more significant compared to other crops studied within this period. This aligns with their global importance for food security. The distribution also highlights increasing interest in high-value crops like tomatoes (12%), bananas (5%), and cucumbers (10%), likely due to their economic significance and susceptibility to various diseases. When compared to global production statistics, these distributions reveal certain mismatches. For example, potato, wheat and rice together account for more than 20% of the global production of primary crops [99] yet represent only 15% of the reviewed studies. Conversely, tomatoes and cucumbers, which occupy less than 5% of global harvested area [99], represent over 22% of research attention. This suggests that research focus may be disproportionately influenced by economic value, disease susceptibility, or ease of imaging experiments rather than global production scale. The distribution of the techniques employed in managing crop diseases during this period is illustrated in Figure 4b. This distribution reveals that most of the studies conducted within this time frame have deployed only DL models in the management of diseases as given by its percentage distribution of 56%. The combination of DL and IP has also seen an increase in recent studies for improved detection of crop diseases. These techniques offer significant improvements over traditional (manual) methods, providing faster and more accurate disease diagnostics.
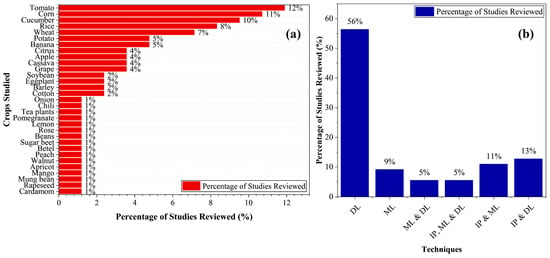
Figure 4.
(a) The distribution of crops studied for diseases between 2015 and 2025; (b) The distribution of techniques employed in the study of crop diseases between 2015 and 2025.
Figure 5 illustrates the geographic distribution of research efforts in crop disease detection based on the reviewed case studies. The analysis reveals that India (24.6%), China (15.4%), and the United States (12.3%) collectively account for more than half of the studies analyzed, indicating their leading research engagement in this field. Other notable contributors include Pakistan (7.7%) and several European and African countries with smaller shares. While this distribution reflects strong technological capacity and research infrastructure in these major agricultural economies, it does not necessarily represent their actual contribution to global crop production. According to FAOSTAT [99], India, China, and the United States are also among the top global producers of major primary crops such as wheat, rice, and maize, underscoring their vested interest in advancing disease detection technologies to safeguard yields. However, the limited representation of countries in Africa and South America highlights a regional imbalance in research activity, likely influenced by disparities in funding, technological accessibility, and institutional capacity. This suggests a continued need for broader international collaboration and investment to ensure that emerging disease detection technologies benefit global agriculture equitably.
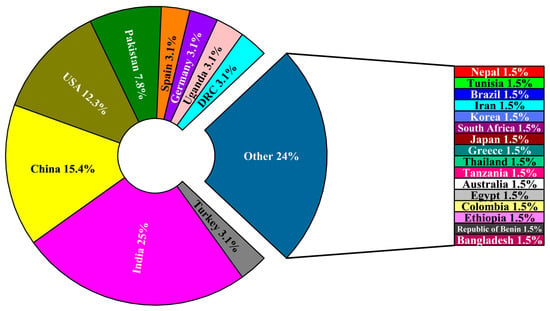
Figure 5.
Geographic distribution of reviewed crop disease detection studies by country. India, China, and the United States account for the largest share of research activity, consistent with their roles as leading global producers of major crops, as reported by FAOSTAT.
4. Sensors and Platforms Used for Crop Disease Detection
Advancements in sophisticated optical sensors and robotic platforms have significantly broadened researchers’ understanding of crop diseases, thereby improving the ability to evaluate them effectively. These sensors, including RGB, spectral, visible shortwave infrared (VIS-SWIR), thermal imaging, and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) systems, provide essential data for monitoring and identifying crop diseases. By deploying these sensors across different platforms, multimodal and multiscale data measurement systems can be developed. Notably, appropriate systems are crucial for accurate crop disease monitoring [100,101]. Depending on specific spatial and spectral resolution, and accuracy required for different tasks, observation platforms (Figure 6) are employed across diverse environments, ranging from laboratory settings such as indoor optical measurement and stereoscopic microscopes to field setups like robots, UGVs, and fixed rail systems, low-altitude platforms such as UAVs and helicopters, and spaceborne platforms including satellites and space shuttles. Hence, enabling researchers to monitor crop diseases at leaf, canopy, and regional scales. The following subsections discuss various platforms used for monitoring and detecting crop diseases.
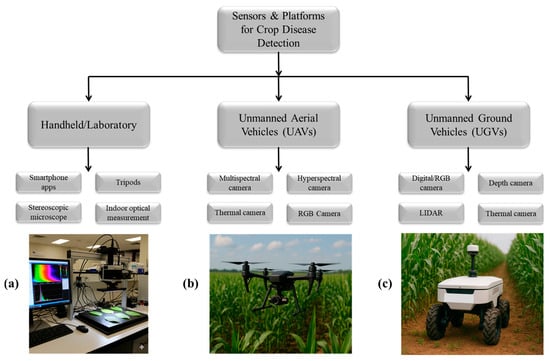
Figure 6.
Sensors and platforms deployed for monitoring and detecting crop diseases: (a) benchtop laboratory setup; (b) UAV for low altitude monitoring and detection; (c) UGV for ground based in-row or in-canopy monitoring and detection.
4.1. Handheld Biosensors and Laboratory Setups
Handheld biosensors/analyzers have emerged as powerful tools for rapid, on-site plant disease diagnostics, offering portability, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness compared to complex imaging or laboratory-based systems. Recent developments in handheld biosensors have broadened their potential by integrating advanced nanomaterials, microfluidics, and smartphone-based readouts to create compact diagnostic systems [38]. These devices are particularly suited for field applications where rapid, real-time decisions are needed, bridging the gap between laboratory precision and practical on-farm disease monitoring. A notable advantage of handheld biosensors is their ability to detect plant pathogens with high sensitivity at the point-of-care, eliminating the delays associated with sample transport and centralized testing facilities. For instance, lateral flow immunoassays (LFIA), handheld electrochemical biosensors, and microfluidic paper-based devices have shown promise for detecting a wide range of pathogens directly in the field [38]. Smartphone-assisted platforms further enhance accessibility by enabling real-time data visualization, geotagging, and wireless transmission of results, making them suitable for integration into digital crop protection frameworks. In practical terms, handheld SPAD chlorophyll meters [102], portable Raman and FTIR spectrometers [103], and compact qPCR devices [104] represent examples of handheld tools already being deployed in crop health monitoring (Figure 7). These advances suggest a paradigm shift towards decentralized, farmer-accessible diagnostic solutions.

Figure 7.
Examples of handheld tools used for crop health monitoring: (a) SPAD 502 chlorophyll meter [102]; (b) BRAVO handheld Raman spectrometer [103]; (c) compact qPCR device (Aurora) [104].
While handheld systems provide portability and rapid results, they face challenges related to sensitivity, specificity under field conditions, and potential interference from environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and dust. Ensuring robustness, user-friendliness, and cost-efficiency remains crucial for their large-scale adoption. Nevertheless, their growing integration with AI-based decision support systems and Internet-of-Things (IoT) networks underscores their importance as scalable components of precision agriculture and digital crop disease management strategies [38]. Using these platforms, researchers can perform analyses at leaf, individual plant, and experimental shed scales under tightly controlled conditions, allowing for high-precision assessments of crop diseases [105]. These tools are specifically used to monitor spectral changes over time to track disease progression. Some researchers have developed and evaluated handheld devices used for assessing crop health status. Wang et al. [106] introduced LeafSpec, a portable and low-cost HSI device designed for accurate corn leaf phenotyping. Using a push-broom HSI camera and touch-based sliding imaging, LeafSpec minimizes noise factors like ambient light and imaging angle. Field and greenhouse tests demonstrated its ability to predict nitrogen content () and relative water content (), outperforming traditional systems in measurement accuracy. Kumari et al. [107] developed a handheld spectral sensor-based device for real-time detection and severity estimation of groundnut bud necrosis virus (GBNV) in tomato plants. Using spectral analysis and a decision tree (DT) ML model, the device achieved high accuracy (93.65%) in classifying disease severity across growth stages. Similarly, Hussain et al. [108] developed a single-tube detection method based on recombinase polymerase amplification combined with CRISPR/Cas12a (Bc-RPA/Cas12a) to detect Botrytis cinerea, a major plant pathogen responsible for gray mold in sweet cherry. Experimental results showed that the Bc-RPA/Cas12a assay demonstrated high specificity and sensitivity, with no cross-reactivity to non-target pathogens. Overall, handheld biosensors represent a critical step toward practical, field-ready solutions that complement laboratory diagnostics in precision crop protection.
While laboratory platforms provide accurate disease analysis, their measurement throughput is limited, making them more suitable for fundamental research within laboratory settings [105]. Disease detection at the tissue scale is limited to laboratory settings, where advanced hyperspectral microscope systems are used. Laboratories offer the most stable conditions for hyperspectral experiments, minimizing the risk of data interferences from ambient conditions such as humidity, temperature, light intensity and direction, thereby eliminating the impacts on outcomes. Measurements at the single plant and canopy levels can be conducted in laboratories, greenhouses, and field settings. Field environments support large-scale applications, whereas greenhouse studies provide a controlled environment with the advantage of high-throughput experimental capability [105].
Despite their growing utility, handheld biosensors and laboratory setups still face limitations that hinder widespread deployment. Many handheld devices suffer from reduced reliability when used across diverse crops, pathogens, or environmental conditions, making their calibration and standardization challenging. Frequent recalibration and operator training are often required, which may reduce ease of adoption by farmers. Laboratory-based platforms, while highly accurate, are constrained by low throughput, high costs, and limited scalability to large production systems. Furthermore, most handheld and lab-based systems remain point-based measurements, restricting their capacity to provide spatially comprehensive disease maps at field scale. Overcoming these limitations may involve integration of handheld sensors with mobile platforms for multi-scale monitoring, improving sensor robustness through adaptive AI calibration models, and promoting low-cost, user-friendly designs tailored to resource-limited agriculture.
4.2. Smartphones and Mobile Apps
Smartphones have become valuable tools in enhancing the accessibility and ease of plant disease detection. A range of mobile applications now utilize smartphone RGB cameras paired with DL models to identify plant infections [109,110]. These tools offer faster diagnosis, lower costs, and reduced reliance on expert knowledge. Notable examples include Plantix, Nuru, Agrio, and Crop Doctor, which have recently gained traction for their practical field use [109,110]. These apps integrate technologies like image processing, AI, ML, and DL to improve diagnostic capabilities [111]. Supported by extensive image databases of plant species and associated diseases, they offer a precise and comprehensive approach to plant disease management [112]. Siddiqua et al. [113] assessed several mobile applications for plant disease detection, including “Plantix,” highlighting the current capabilities of AI technologies in agriculture. Their findings revealed notable deficiencies in the accuracy and dependability on many existing tools, underlining the necessity for further refinement and robust validation to ensure real-world applicability. ViT-SmartAgri, a Vision Transformer-based model, exemplifies progress in this area by utilizing smartphone cameras to capture and analyze leaf images, delivering rapid diagnostic results for diseases such as late blight and mosaic virus [38].
A major limitation with these apps is restricted robustness of imagery data where most images based on which the models are trained are acquired from sample leaves collected from the field and imaged under controlled laboratory conditions. As a result, performance of these apps often declines when confronted with the complex real farm environments, where variable lighting, occlusion from overlapping leaves, dust, and background noise can affect image quality [38]. Moreover, many apps are limited in their ability to detect early or asymptomatic infections, where visual symptoms are either subtle or absent, thereby reducing their practical effectiveness for timely disease management.
To overcome these limitations, future developments must prioritize building large-scale, diverse, and well-annotated field-derived image databases that capture the variability of real-world conditions. Integration with complementary sensing technologies, such as portable biosensors, and coupling with AI-driven decision support systems may also enhance robustness and reliability [38]. Addressing these challenges will be crucial to move beyond proof-of-concept applications and achieve scalable, farmer-friendly solutions. In summary, while smartphone apps hold considerable promise for democratizing plant disease diagnostics, their current limitations highlight the need for continuous refinement, stronger validation, and integration with broader digital agriculture frameworks to ensure consistent and reliable performance in real-world farming systems.
4.3. Unoccupied Aerial Vehicles
UAVs, commonly known as drones, are aerial platforms capable of operating without a human pilot on board. Figure 8 shows the two types of UAVs commonly used in agriculture. These UAVs can either be remotely controlled from afar or autonomously complete planned flight/survey missions using global positioning system (GPS) or AI-powered navigation systems and ground control software. The adoption of agricultural UAVs represents a major advancement in precision agriculture as they are among the most widely used tools for detecting crop diseases. Compared to spaceborne sensors like satellites, which are used for regional scale monitoring, UAVs offer plant to field-scale assessments at lower operating costs and greater flexibility for real-time/on-demand data acquisition, providing notable advantages over satellite platforms [101,114]. UAVs effectively meet the demands for both high spatial/spectral resolution and high throughput. Their mobility and affordability have made them one of the most popular platforms for crop disease detection over the recent decades. UAVs have significantly improved agricultural monitoring at the plot level, including the detection of plant diseases. Equipped with various cameras, UAVs can be deployed in the field to capture images, which are then processed with several algorithms or techniques for rapid and accurate crop health monitoring. As a result, UAVs are increasingly popular, as their spectral sensing capabilities provide essential data on soil and the upper plant canopy across a broad spectrum.
UAV-based disease detection is founded on identifying changes in plants’ optical properties using imaging or non-imaging type sensors, essentially for detecting physiological shifts in plants influenced by biotic or abiotic stress, transpiration rates, morphology, plant density, and variations in solar radiation among plants. This approach enables timely and accurate field-level detection at a much high-throughput rate compared to handheld systems, thereby enhancing disease management capabilities through targeted fungicide applications [115,116]. For the goal of plant disease detection, using UAVs with traditional ML and DL models has seen significant advancement in recent years.
Backpropagation Neural Networks (BPNN) were among the first models used to analyze spectral data from hyperspectral images of tomato plants, estimating infection severity on leaves. A five-stage rating system was implemented to assess the severity of light blight in these images, allowing for the evaluation of BPNN’s effectiveness with this data. The results confirmed the potential of using ANN with backpropagation for spectral predictions in disease diagnosis. Similarly, Al-Saddik et al. [117] employed the Classification and Regression Tree model to detect leafroll disease, based on an analysis of hyperspectral images of grapevine captured by UAVs.
A study by Pande & Moharir [118] utilized high-resolution aerial imaging with UAVs to detect Huanglongbing (HLB), also known as citrus greening disease. By adjusting the flying altitude, a multi-band imaging sensor on the UAVs captured images at the required resolution. The UAV-based sensor data were then compared with those from aircraft-based sensors, which offered lower spatial resolution. The data included seven vegetation indices (VIs) and six spectral bands ranging from 530 to 900 nm. Regression analysis helped extract relevant features from both UAV- and aircraft-based spectral images, demonstrating that high-resolution aerial sensing is an effective method for identifying HLB-infected citrus trees.
UAVs are also employed to monitor physiological stress and disease outbreaks in forest trees. In a study by Dash et al. [119], UAVs were used to observe disease in mature Pinus radiata. A time-series multi-spectral camera, mounted on UAVs, conducted flights over a pine forest area treated with herbicide at regular intervals. Concurrently, a traditional field-based experiment assessed crown and needle discoloration. The findings showed that multi-spectral UAV imagery was highly effective in detecting early physiological stress in mature pine trees, particularly through the red edge and near-infrared bands. Additionally, NDVI proved to be a valuable vegetation index for tracking discoloration resulting from physiological stress over time.
Zhang et al. [120] developed DL-based computer vision models for detecting yellow rust disease to mitigate its impact. Using MSI data from a UAV platform, they proposed a novel semantic segmentation technique, adapted from the U-Net model, to identify areas of wheat crops affected by yellow rust. This enhanced U-Net model, named Ir-Unet, incorporates three key modules: the Irregular Encoder Module (IEM), Irregular Decoder Module (IDM), and Content-aware Channel Re-weight Module (CCRM). The study also examined how different input data formats influenced the model’s accuracy in detecting yellow rust-infected wheat. Their Ir-Unet model achieved a superior F1-score of 96.97%, outperforming the results of Su et al. [121], who reported an F1-score of 92% using all five bands from the RedEdge MSI camera. This accuracy was further improved by incorporating both the raw bands and various measurements of Selected Vegetation Indices (SVIs).
Liu et al. [122] proposed a BPNN model to monitor Fusarium Head Blight through HSI, finding it to be more effective than both SVM and RF models, with an overall accuracy of 98%. In another study, Huang et al. [123] targeted Helminthosporium Leaf Blotch Disease (HLBD) in wheat using RGB images from UAVs, recommending a CNN model based on LeNet to classify HLBD by disease stage. This CNN model achieved a higher accuracy of 91.43% compared to the set of methods and the SVM model. Stewart et al. [124] utilized low-altitude aerial RGB images and employed an instance segmentation technique (Mask R-CNN) to detect Northern Leaf Blight (NLB) disease. Their approach reached an average accuracy of 96% in identifying and segmenting individual lesions.
Despite their wide adoption, UAV-based platforms face limitations that constrain their full potential for crop disease detection. Restricted flight time, payload capacity, and dependence on weather conditions (e.g., wind, rain, cloud cover) limit their ability to provide consistent, long-duration monitoring. Additionally, UAVs are primarily effective for capturing canopy-level information, making it difficult to assess below-canopy plant parts where several diseases initially develop. Regulations on UAV flights, particularly in densely populated or restricted agricultural zones, further add to operational challenges. In contrast, proximal sensing platforms such as UGVs are better suited for capturing high-resolution, close-range data from lower canopy layers or under dense foliage, complementing UAV-based aerial imaging. Therefore, integration of UAVs with UGVs and adaptive AI-driven data fusion models may help overcome these challenges by combining broad spatial coverage with fine-scale, below-canopy disease monitoring.

Figure 8.
Two commonly used UAV types in agriculture: (a) multi rotor UAV; (b) fixed wing UAV (Humpback Whale 360 VTOL fixed wing UAV, Dstechuas) [125].
4.4. Unoccupied Ground Vehicles
UGV is a ground-based vehicle that operates without a human onboard and is remotely controlled, serving as the terrestrial counterpart to UAVs. UGVs are intelligent systems that incorporate capabilities such as environmental perception, localization, navigation, route planning, decision-making, and motion control. These vehicles integrate advanced technologies, including computer science, data fusion, computer vision, and deep learning, to fulfill practical needs and achieve predetermined objectives [126,127]. UGVs typically consist of a mobile frame, robotic arms, end effectors, and environmental sensing systems, with their design tailored to specific operations [128]. Depending on terrain conditions, UGVs for agricultural applications typically deploy wheel-type or track/crawler-type configurations, as illustrated in Figure 9. Environmental perception is a critical technology for UGVs, encompassing both external environment recognition and vehicle state estimation. A high-precision environmental perception system is essential for ensuring safe operation and efficient task performance. To achieve this, UGVs rely on various sensors, such as LiDAR, monocular cameras, and millimeter-wave radar, which provide environmental data inputs for planning, decision-making, and motion control systems [129].
UGVs serve as field platforms and are commonly utilized for small-scale analyses. While field platforms share some similarities with laboratory platforms in certain applications and working conditions, they stand out for maintaining the high spatial resolution of laboratory platforms while significantly enhancing measurement throughput due to being mobile, making them more practical for real-world applications. UGVs are increasingly used in precision agriculture for disease detection [130]. Observing diseases in the upper canopy often indicates that the infection has already spread upward, potentially reflecting a delayed management response. Diagnosing diseases from beneath the crop canopy using UGVs can facilitate early detection when diseases are still in their initial stages. However, UGVs face limitations, including poor signal coverage, latency issues under closed crop canopies, and limited battery life during extensive field scouting across crop rows. Nonetheless, UGVs offer an efficient means of generating systematic agrometeorological datasets using onboard sensors to measure parameters such as temperature, humidity, and more. These measurements can inform risk models that predict the likelihood and severity of future weather-related challenges in agriculture [131]. Notably, UGVs enable continuous operation, including nighttime monitoring, regardless of weather conditions, labor availability, or holidays.
Numerous studies have explored the use of UGVs in detecting crop diseases. Mahmud et al. [132] examined how robots are applied to field tasks like planting, spraying, and harvesting, with a particular focus on crop inspection. They introduced computer vision and ML as essential technologies for the early identification of diseases in both greenhouses and open fields. The authors also provided a comprehensive list of vision schemes used in target detection, outlining their respective functions, benefits, and drawbacks. Menendez-Aponte et al. [133] proposed a collaborative system that integrates aerial and ground robots for identifying diseases in strawberries.
A hybrid UAS-UGV disease management system for corn to detect diseases above and below the canopy using DL was proposed by Ahmad et al. [130]. The UAS captures images from above the canopy, identifying diseases like Gray Leaf Spot (GLS) and Northern Leaf Blight (NLB), while the UGV, equipped with sensors, navigates rows to capture images below the canopy, targeting diseases on lower leaves. The system employs YOLOv7 models to detect disease symptoms, with GPS coordinates tagged for each detection, which are then uploaded to a Google Spreadsheet for real-time disease monitoring. Results showed that the UGV achieved higher accuracy (46.4% mAP@IoU = 0.5) than the UAS (37.6%), suggesting that below-canopy detection is more reliable for early disease diagnosis. This combined approach enhances early and accurate disease management by allowing targeted interventions based on real-time disease data.
In 2021, the robot Icaro X4 was developed by Free Green Nature in Italy as a hybrid UV-C radiation treatment technology for vineyards. Designed to combat diseases, particularly downy mildew and powdery mildew, the robot uses adaptable side panels with UV-C emitters that sterilize fungal pathogens on leaf surfaces. This treatment not only devitalizes surface fungi but also triggers the plant’s natural defenses, helping limit pathogenic spread with fewer chemical applications. While UV radiation is highly effective against powdery mildew, its efficacy for downy mildew is moderate due to the fungus’s deeper penetration, yet it remains valuable in reducing chemical treatments [134].
Sujatha et al. [135] present a UGV equipped with AI-based disease detection for paddy crops, specifically addressing diseases like False Smut, Sheath Blight, Rice Blast, Leaf Scald, Brown Spot, Bacterial Leaf Blight, and Bakane. The UGV, designed for autonomous navigation in polyhouses, integrates sensors for monitoring environmental parameters and uses CNN to detect disease symptoms from images. It incorporates a Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC) to manage navigation across diverse terrains, facilitating efficient data collection and decision-making in challenging conditions. Results demonstrate high detection accuracy, with the AlexNet CNN model achieving up to 99.16% in classifying disease severity, thus effectively aiding in precision agriculture and reducing herbicide usage. Table 2 summarizes case studies on various sensors and platforms adopted for the detection of diseases in agricultural fields.
While UGVs offer unique advantages for proximal sensing and below-canopy disease detection, their operation in unstructured and rough agricultural terrain presents significant challenges. Uneven ground, dense vegetation, and muddy or waterlogged soil can impair locomotion, reduce stability, and complicate autonomous navigation. Weak GNSS signals under dense crop canopy also hinder localization, leading to navigation errors. Battery endurance, high initial costs, and complexity of maintenance further constrain large-scale adoption. Additionally, relatively low field coverage speed of UGVs compared to UAVs makes them less suited for rapid, broad-area assessments. These limitations may be mitigated through adaptive locomotion systems (e.g., hybrid wheel-track platforms), sensor fusion for robust localization (combining RTK-GPS, LiDAR, and vision), and energy-efficient modular designs. Integration of UGVs with UAVs in collaborative frameworks can also compensate for scale limitations by combining UAVs’ aerial view with UGVs’ under-canopy inspection. Together, these strategies can enhance practical deployment of UGVs for reliable disease detection in real-world agricultural settings.

Figure 9.
Two major wheel configurations of UGVs used in agriculture: (a) wheel-type UGV (Atlas 4 × 4 All Terrain Explorer Robot) [136]; (b) track/crawler-type UGV (SuperDroid HD2 Treaded ATR) [137].

Table 2.
Summary of sensors and platforms for crop disease detection.
Table 2.
Summary of sensors and platforms for crop disease detection.
| Reference | Technique | Platform/Sensor | Platform Design | Findings | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [138] | Artificial neural network (ANN) | UAV and laboratory setup | (a) DJI Matrice 600 Pro Hexacopter (DJI, Shenzhen, China) with hyperspectral camera, (b) benchtop hyperspectral imaging system | Satisfactory results were obtained in the laboratory and field (UAV-based) conditions top detect diseases | Lack of real time capability as the processing and analysis of data relies solely on computer software |
| [109] | Deep learning and image processing | Smartphone | Smartphone mobile app | The developed model achieved a detection accuracy of 98.79% | High computational resource requirements |
| [111] | Deep learning and image processing | Smartphone | Smartphone mobile app | The developed system achieved high accuracy when tested | Reliance on a relatively small dataset of 659 images |
| [139] | Image processing and deep learning | UAV | Quadcopter UAV with MAPIR Survey2 camera sensor (MAPIR, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) | The proposed method enabled the detection of vine symptoms | Small size training sample which reduced the performance of the model |
| [67] | Deep learning | Smartphone | Smartphone mobile app | The developed system was able to detect and classify diseases with a high confidence score | Low throughput as phone cannot be used to cover large area |
| [140] | Deep multiple instance learning | Smartphone | Smartphone mobile app | Processing speed of 1 s/image based on Mobile 4G service which satisfies real-time application | Inability to handle the high storage and computational demands of DL models. |
| [141] | Deep neural networks | UAS | DJI Mavic 2 Pro (DJI, Shenzhen, China) equipped with ZED depth camera (StereoLabs, San Francisco, CA, USA) and Jetson Nano (NVIDIA, Santa Clara, CA, USA). | Allows for efficient data collection and real-time analysis | Payload constraints, high data bandwidth, and high-power consumption |
| [142] | Machine learning (Random Forest Classifier) | UAV | DJI Spreading Wings S1000 Octocopter (DJI, Shenzhen, China) with multispectral camera | Developed system achieved good performance in distinguishing healthy from infected wheat | Reduced spatial resolution at altitude, reliance on ground calibration, and lack of real-time capability |
| [2] | Deep transfer learning | Handheld | Android-based application | The developed system achieved a recognition accuracy of 99.53% in real time | The developed system was tested based on images collected from laboratory conditions |
5. Imaging Techniques for Crop Disease Detection
Digital imaging has undergone significant evolution over time. The process began with the introduction of 2D RGB image [22]. Subsequently, the adoption of knowledge-based approaches, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) technologies, revolutionized developmental methodologies. This was later followed by advancements of 3D images. Early stages of analyzing digital images utilized digital model-driven techniques, which later transitioned to advanced imaging and computing technologies to achieve more accurate and realistic visualizations tailored to specific needs. For identifying various plant diseases, a range of imaging sensors have been employed to collect data, facilitating the comprehensive assessment of plants from multiple perspectives. Such imaging techniques are utilized for detecting plant diseases, including fluorescence imaging, thermal infrared imaging, MSI, HSI, visible light imaging, and others. Additionally, 3D imaging methods are being explored alongside various other approaches. There are several imaging techniques that have been utilized for detecting plant diseases, and the following subsections provide a detailed explanation of the six imaging techniques for crop disease detection. Figure 10 also shows a schematic of the various imaging techniques discussed in this paper for crop disease detection.
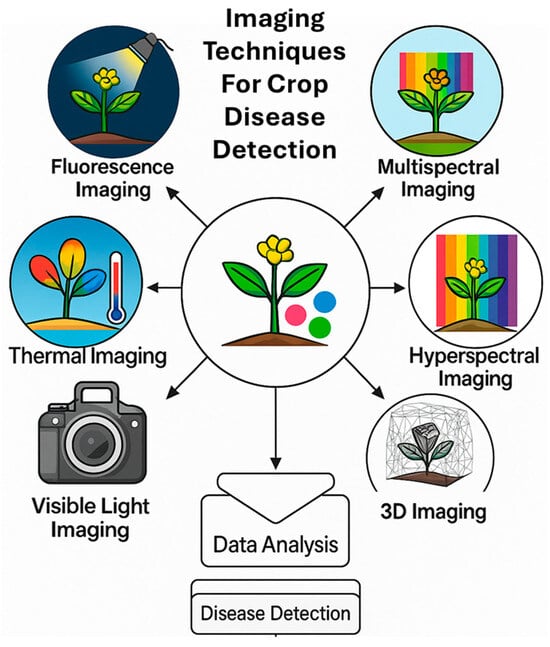
Figure 10.
Schematic representation of different imaging techniques used for crop disease detection.
5.1. Visible Light Imaging
Visible light imaging utilizes digital images designed to replicate human visual perception, serving as a source of data for systems involved in plant phenotyping and trait-based physiological breeding. Its most common application relies on silicon sensors, such as CCD or CMOS arrays, which are sensitive to the visible light spectrum (400–750 nm) and enable two-dimensional imaging. As one of the simplest imaging technologies for plant sensing, it presents raw image data as spatial matrices of intensity values corresponding to photon fluxes in red (~600 nm), green (~550 nm), and blue (~450 nm) spectral bands. Conventional digital cameras, including RGB or CIR cameras, are widely used as visible band cameras due to their ability to provide rapid, cost-effective measurements, making them ideal for plant phenotyping applications.
RGB imaging involves capturing a sequence of photographs through red, green, and blue filters. Similarly to thermography, these images can be compared over time to detect variations in color intensity, which may result from changes in pigment transmittance within plants [143]. Such differences can help identify specific pathogens. Optical RGB cameras typically operate within the 400–750 nm wavelength range, detecting changes in visible light, though slight spectral sensitivity variations can occur across devices, including smartphones [144,145]. These cameras are widely used in plant phenotyping due to their affordability and the extensive availability of image processing tools.
Nonetheless, visible light imaging has several limitations that restrict its effectiveness for early or precise disease detection. RGB sensors capture only the visible spectrum, which means subtle biochemical and structural changes in plants often remain undetected until visible symptoms appear, limiting early diagnosis. Furthermore, image quality is highly sensitive to environmental factors such as lighting, shadows, and background clutter, which can reduce consistency in field applications [144]. Device-dependent variability in sensor quality (e.g., between low-cost cameras and professional imaging systems) also affects accuracy and reproducibility [144]. These challenges may be addressed by integrating RGB imaging with MSI or HSI sensors for improved sensitivity, and by adopting AI-driven image normalization techniques to mitigate environmental variability.
5.2. Multispectral Imaging
Spectral imaging has recently been utilized for phenotyping and non-invasive evaluation of crops’ physiological conditions, improving methods for detecting plant diseases [146,147]. MSI collects data across multiple spectral bands, offering high-resolution spatial information [148]. The Near-Infrared (NIR) spectrum is particularly valuable in plant pathology due to its accuracy in detecting infected leaf areas [149]. Its ability to penetrate deeper into plant tissues enables the identification of physiological changes indicative of disease before visible symptoms emerge. The key distinction between MSI and HSI lies in the range of spectral data captured. MSI records data across a limited number of discrete bands within the electromagnetic spectrum, typically spanning visible to infrared wavelengths [150]. In contrast, HSI collects data across hundreds or even thousands of narrow, contiguous spectral bands, providing significantly higher spectral resolution [151,152]. Figure 11 illustrates the differences in spectral bands captured by the two techniques. MSI cameras are particularly effective in documenting changes from early, minimally visible symptoms to more pronounced, late-stage disease signs, facilitating detailed disease progression analysis under controlled conditions. Such datasets are invaluable for training AI models to detect diseases.
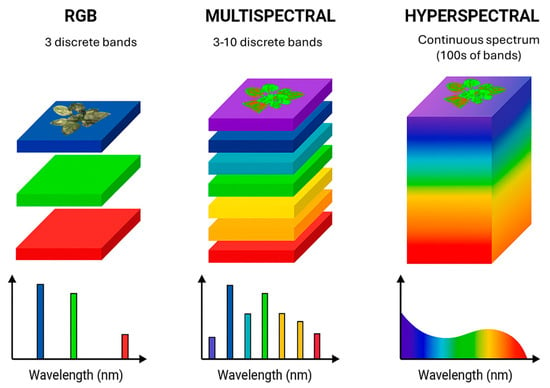
Figure 11.
Schematic spectral sampling and waveband composition difference between RGB, multispectral and hyperspectral imaging cameras.
Compared to traditional and HSI, MSI offers notable advantages in disease detection, including portability, simplified data processing, and lower computational costs, making it a promising tool for crop disease monitoring in field conditions [153]. Furthermore, it includes a red-edge (RE) band situated between the maximum red absorption and the high reflectivity region of the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum. This band is a key spectral feature of vegetation, marking the transition from chlorophyll absorption to cellular scattering [154]. To date, UAV-based MSI has been utilized to estimate chlorophyll content, nitrogen content, biomass, and leaf area index (LAI) [155,156,157,158]. Additionally, it has been employed by various researchers to monitor crop diseases.
Giakoumoglou et al. [159] utilized MSI to improve the detection of gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea. Through controlled inoculation of cucumber leaves, they captured the fungal spectrum across multiple wavelengths, including the near-infrared (NIR) range. The study introduced two annotated datasets, Botrytis-detection and Botrytis-classification, which were used in DL experiments, achieving a classification accuracy of 93% and an F1-score of 0.89. These results highlight the potential of MSI in advancing gray mold detection techniques. Similarly, Fernández et al. [160] were the first to employ close-range MSI to detect cucumber powdery mildew on plants under real commercial conditions. Albetis et al. [161] investigated the effectiveness of UAV-based MSI in identifying both symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevines. Expanding upon their earlier work [162], they collected a more extensive dataset and evaluated 24 variables derived from this new dataset. Among these, the red-green index (RGI) and the green-red vegetation index (GRVI) demonstrated the highest performance.
De Silva & Brown [163] developed a novel MSI dataset using a Canon EOS 800D camera (Canon Inc., Melville, NY, USA) outfitted with four specialized filters: BlueIR, K590, Hot Mirror, and K850, capturing a range of infrared and visible spectrum data. The dataset included images of five fruit plants collected under various weather conditions, with temperatures ranging from 22 °C to 37 °C and exhibited diverse image counts. To identify the most suitable CNN model for the dataset, the study evaluated three established models: Xception, DenseNet-121, and ResNet-50V2. Among these, DenseNet-121 achieved the highest test accuracies across most datasets, with the K850 filter performing the best, reaching a test accuracy of 86.16%. The study also highlighted the impact of weather conditions on data collection, noting that some filters were used on sunny days with clear skies, while others were affected by rain and limited sunlight, resulting in images with water droplets on the leaves.
Lei et al. [164] monitored the severity of yellow leaf disease in areca nuts using vegetation indices (VIs) such as the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and normalized difference red-edge index (NDRE), alongside support vector machine (SVM) and decision tree algorithms. Rodríguez et al. [165] utilized UAV-based MSI with five ML algorithms, including random forest (RF) and a linear support vector classifier, to monitor potato late blight. Additionally, Ye et al. [166] employed artificial neural networks (ANN), RF, and SVM classification algorithms for monitoring banana fusarium wilt using UAV-based MSI. Collectively, these studies highlight high potential of high-resolution UAV-based MSI in agricultural applications.
Despite its promise, MSI is constrained by its limited number of discrete bands [167], which may overlook subtle biochemical variations compared to hyperspectral systems. Many studies rely on vegetation indices or selected filter combinations, which, while effective, can saturate at high canopy densities and are sensitive to environmental noise such as variable sunlight, shadows, or water droplets on leaves [168,169]. UAV-based MSI also introduces challenges related to atmospheric conditions, flight altitude, and sensor calibration, which can impact data consistency. Addressing these limitations requires adaptive calibration protocols, integration of MSI data with complementary sensing modalities such as thermal or HSI, and AI-driven feature extraction methods that move beyond traditional vegetation indices to enhance robustness under field variability.
5.3. Hyperspectral Imaging
HSI is a sophisticated imaging technique designed to capture detailed spectral information about a scene or object. Using a HSI sensor or camera, HSI captures light reflected or emitted in numerous contiguous spectral bands, typically spanning the visible to near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum [170]. This technology enables the identification and characterization of materials and objects that are challenging to discern with the naked eye or traditional imaging methods [171,172]. The enhanced spectral data facilitates more accurate object detection, classification, and improved target identification. HSI integrates optical spectroscopy with image analysis techniques, enabling simultaneous evaluation of both physiological and morphological parameters. This method captures images as a function of wavelength and generates a unique reflectance spectrum for each pixel within an image. Additionally, HSI sensors are applied across various scales, from laboratory analysis of plant tissues and greenhouse screening to open-field applications for detecting and identifying disease infections [105]. HSI sensors utilize high-resolution optical technologies like traditional RGB cameras but with significantly enhanced spectral resolution. Beyond capturing RGB data, HSI can analyze narrow wavebands within the visible (VIS) electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 400 to 700 nm, the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum from 700 to 1000 nm, and the shortwave infrared (SWIR) spectrum from 1000 to 2500 nm ([24], Figure 12).
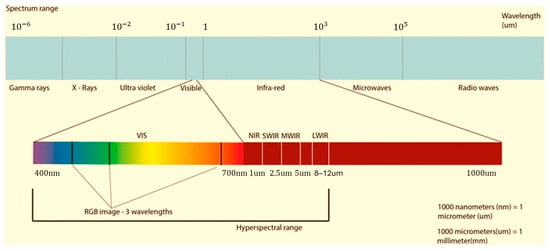
Figure 12.
Electromagnetic spectrum displaying the visible range and infrared ranges.
The narrow wavebands of HSI sensors are highly sensitive to subtle plant changes induced by diseases, enabling differentiation between disease types and facilitating early detection of asymptomatic conditions. HSI remote sensing, encompassing both non-imaging and imaging techniques, has advanced rapidly among various non-invasive methods for monitoring plant diseases and has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in agricultural research [173]. In addition to the general benefits of non-invasive remote sensing methods, HSI can be integrated into automated systems, providing an objective approach that significantly reduces workload [105,174,175]. Applications of HSI technologies span from satellite-level imaging to macroscopic and molecular-level analyses, highlighting their superiority in plant disease monitoring. The use of HIS technology in disease monitoring is particularly promising due to its ability to cover a spectral range of 350–2500 nm with a continuous spectral resolution of less than 10 nm [176,177]. In practice, most hyperspectral imaging systems for agricultural disease monitoring operate between 350 and 2500 nm (VIS–SWIR) [176,178]. Extensions into the MWIR and LWIR (up to 12 µm) exist but are less common [176,178]. These features make it highly effective not only for distinguishing diseases based on subtle variations but also for tracking and analyzing dynamic disease processes, especially during the latent phase before symptoms become visually apparent. A critical factor affecting the information content of HSI is the spatial resolution and the number of mixed pixels [105]. This is heavily influenced by the distance between the sensor and the target object. Consequently, far-range systems, such as airborne or space-borne platforms, have lower spatial resolution compared to near-range or microscopic systems. As spatial resolution decreases, the reliability for detecting individual symptoms or diseased leaves and plants also decreases, making proximal sensing platforms more effective for such applications.
The benefits of HSI have significantly enhanced the feasibility of precision plant protection. Numerous studies have investigated its potential for detecting and classifying crop diseases. Zhang et al. [179] introduced a HSI microscopic image pre-processing framework for extracting kernels infected with Fusarium head blight (FHB). This framework utilized image spectral calibration and normalization through white and dark reference images, followed by conversion to grayscale, image binarization, and threshold segmentation. Couture et al. [180] employed non-imaging hyperspectral data to identify leaves infected with the Potato Y-virus. They utilized a partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) to differentiate infected leaves from healthy ones based on the full-range spectral data, achieving a mean validation kappa of 0.73. Jin et al. [181] applied a deep neural network (DNN) classification algorithm to HSI pixels, enabling accurate identification of Fusarium head blight (FHB) disease regions on wheat ears. More recent studies on HSI techniques reflecting the state-of-the-art in this domain are summarized below.
Ghimire et al. [182] used HSI combined with ML to identify soybean yellow mottle mosaic virus (SYMMV) infection in soybeans at early stage. In here, soybeans were cultivated under two environments: EN I (virus inoculation at V3 stage) and EN II (infected seeds). Spectral data was processed using the information gain method to select characteristic wavelengths, and ML models (SVM, RF, KNN, LR) were used for classification. Continuous wavelengths from 653 to 682 nm were identified as significant while SVM achieved the highest accuracy (>95%), outperforming other models for disease detection, highlighting that HSI combined with ML is effective for early, non-invasive disease detection, even in asymptomatic plants, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods.
A study by Ban et al. [183] assessed disease severity to enable early detection of lettuce downy mildew using HSI combined with biochemical analysis. Two experiments were conducted: one to evaluate disease severity across 150 lettuce accessions and another to detect early infection in susceptible cultivars. HSI captured spectral changes, and ML models (PLS, RF, CNN) were developed for disease index (DI) and biochemical parameter prediction. Significant negative correlations between DI and flavonoid/anthocyanin levels were identified, with specific spectral regions and vegetation indices (e.g., PRI, ARI2) identified as key indicators. RF and CNN models demonstrated high accuracy, and early detection was achieved within 24 h of infection. The study provides tools for disease management and resistance breeding, emphasizing the potential of HSI in plant pathology.
Nguyen et al. [184] developed an early fungal diseases detection model for bok choy using HSI and ML. Hyperspectral data were collected from healthy and infected plants under controlled conditions, and various ML algorithms were tested to train detection models. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) models performed best, achieving 95.9% accuracy and detecting fungal infections with 99% precision within 1–2 days post-inoculation, before visible symptoms appeared. Key wavelengths associated with fungal infection were identified, particularly in the red-edge (719–728 nm) and blue (445–460 nm) regions. The study highlights HSI as a precise tool for early disease detection, addressing challenges in visual inspection and pathogen differentiation.
Liu et al. [185] developed a rapid method for detecting rice blast, a destructive rice disease. Using UAV based HSI, the researchers analyzed spectral and texture features of rice canopies and proposed a novel MS-STNet model combining multi-scale integrator and selective attention mechanisms. The study constructed rice blast texture indices (RBTIs) and combined them with spectral features for disease classification. Field experiments in China demonstrated that the MS-STNet model achieved high accuracy (OA = 96.98%, Kappa = 96.22%) and strong robustness across different environments. Combining spectral and texture features significantly improved classification performance, providing a reliable approach for large-scale rice blast monitoring.
Li et al. [186] developed an efficient method for detecting yellow vein clearing disease (YVCD) in lemons. Using HSI and a novel hybrid 3D-2D-LcNet DL architecture, the study optimized spectral feature extraction and classification. A dataset of 522 lemon leaves was analyzed using ML (SVM, PLS-DA) and CNN models. The hybrid 3D-2D-LcNet achieved the highest accuracy (97.35%) while balancing computational efficiency, outperforming traditional ML methods (accuracy up to 93.52%). The study highlighted the potential of HSI and advanced CNN architectures for precise and scalable plant disease detection, with the SPA-3D-2D-LcNet model offering a practical solution for field applications due to its reduced computational demands.
HSI has proven effective in identifying fungal diseases in winter wheat plants [187], indicating its potential for assessing stem disease expression in winter cereals. For instance, HSI was used to detect head blight caused by F. culmorum in artificially inoculated winter wheat heads at the medium milk stage, based on notable shifts in reflectance within the 680–730 nm and 927–931 nm ranges [188]. These findings collectively highlight HSI’s potential for detecting disease expression triggered by F. pseudograminearum during early vegetative growth. This capability is particularly advantageous for early identification of diseases like crown rot (CR), which target stem bases and often remain asymptomatic until mid to late growth stages. In the absence of visible symptoms, significant time and effort are typically required for specimen collection and visual evaluation [188].
Although HSI offers unmatched spectral detail for distinguishing diseases and detecting asymptomatic infections, its practical use is constrained by high data dimensionality, long processing times, and expensive sensors. Field applications often suffer from environmental variability, illumination changes, and reduced spatial resolution when mounted on aerial platforms, which can introduce noise and mixed-pixel effects. Moreover, the large datasets demand significant storage and computational power, limiting real-time or large-scale use. More feasible solutions include optimizing feature selection to reduce redundancy, developing lightweight DL models tailored for high-dimensional spectral data, improving on-board preprocessing for UAV-mounted sensors, and advancing affordable, miniaturized HSI cameras that maintain accuracy while lowering costs.
5.4. Thermal Imaging
Infrared thermal imaging operates by capturing the infrared radiation emitted from an object’s surface. It facilitates rapid scanning of both stationary objects and dynamic thermal patterns. Known for its high temperature sensitivity and suitability for online detection, this technology has found applications in areas such as defense, electrical and electronics, agricultural pesticide applications, seed germination rate analysis, and several other agricultural production management domains [189,190]. Unlike MSI and HSI, thermal imaging does not rely on a light source [191]. However, its accuracy is significantly influenced by environmental and weather conditions, such as ambient temperature and humidity [192,193]. Consequently, its performance is enhanced in controlled environments. High-end thermal cameras, however, often include real-time calibration systems to account for variations in atmospheric conditions, improving their efficacy.
Infrared thermography (IRT) measures plant temperature, which is linked to plant water status, the microclimate within crop canopies, and variations in transpiration caused by early pathogen infections. Thermographic and infrared cameras detect emitted radiation in the thermal infrared spectrum (Figure 13), producing false-color images where each pixel represents the temperature of the observed object. In plant science, IRT is applicable across various temporal and spatial scales, ranging from aerial surveys to detailed close-range analyses. Leaf temperature is strongly correlated with plant transpiration, which can be influenced by various pathogens in distinct ways. While foliar pathogens, such as leaf spots and rusts, typically cause localized and well-defined alterations, root pathogens like Rhizoctonia solani or Pythium spp. and systemic infections such as those caused by Fusarium spp. often impact the transpiration rate and water movement throughout the entire plant or specific plant organs.
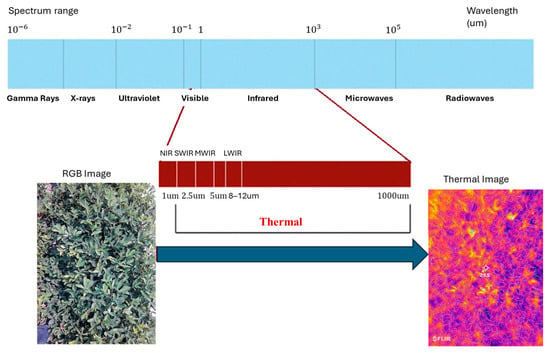
Figure 13.
Thermal infrared spectrum.
Research has demonstrated the effectiveness of thermal imaging in identifying plant diseases at early stages with high accuracy. Yang et al. [194] presented a method for the rapid detection of diseases in tea leaves utilizing infrared thermal imaging technology. The study by Gohad & Khan [195] explores the application of thermal imaging and CNNs for diagnosing leaf health in grape crops. The study used thermal images captured with a Testo 875-2i thermal camera (Testo SE & Co. KGaA, Titisee-Neustadt, Germany) in a Nashik vineyard to identify disease infected and healthy leaves. Preprocessing involved Otsu and binary thresholding, followed by morphological operations and watershed segmentation for isolating regions of interest. A group CNN was developed for classification, incorporating layers for feature extraction, clustering, and softmax-based categorization. The proposed system achieved high accuracy in classifying leaf health based on temperature variations observed in thermal images. The authors emphasized the potential for extending this technique to other crops and diseases.
Zhu et al. [190] investigated thermal imaging for early detection of crop diseases, focusing on tomato mosaic disease and wheat leaf rust. The study employed thermal imaging to monitor temperature variations during the incubation period following inoculation. Maximum Temperature Difference (MTD) was calculated to assess continuous temperature changes. Results showed that MTD for tomato mosaic disease ranged from 0.2 °C to 1.7 °C and for wheat leaf rust from 0.4 °C to 2.0 °C, with increasing trends as the diseases progressed. Symptoms were detected 5 days earlier for tomato mosaic and 7 days earlier for wheat leaf rust compared to visual observation. The study concludes that combining IRT with MTD analysis provides a feasible method for early disease detection and precise pesticide application, offering a theoretical basis for improving crop disease management.
Mastrodimos et al. [196] investigated thermal imaging for early detection of Aspergillus flavus infections in pistachios under controlled conditions. Thermal imaging detected temperature differences between infected and healthy pistachios six hours post-inoculation, earlier than fungal growth visible through RGB imaging. The study utilized Weibull distribution to model temperature variations and fungal growth rates. Results revealed distinct growth rates for A. flavus on pistachios compared to A. carbonarius on grapes. While thermal imaging proved effective, RGB imaging faced challenges due to insufficient color contrast underscoring thermal imaging’s potential for early fungal detection and the influence of environmental and substrate-specific factors. thermal imaging offers several benefits, including clear and intuitive visuals, rapid dynamic response, high precision, and broad detection capabilities. By extending the observational range of the human eye into the infrared spectrum, this technology significantly enhances sensitivity. As a result, infrared thermal imaging holds potential for enabling early diagnosis of crop diseases.
While thermal imaging is often effective for detecting early physiological changes linked to diseases, its limited sensitivity to external factors such as ambient temperature, wind, and humidity, can obscure subtle pathogen-induced variations. Many methods depend on temperature difference thresholds or pixel-based segmentation, yet these can produce false positives under fluctuating field conditions or canopy shading. Additionally, thermal cameras with sufficient sensitivity remain expensive, restricting large-scale adoption. Practical solutions include robust correction algorithms to normalize thermal signals against environmental variations, incorporating reference targets in field to improve calibration, and advancing lower-cost sensors with improved stability. Coupling thermal data with automated environmental logging can also enhance reliability, allowing disease-related signals to be distinguished more effectively from background noise.
5.5. Fluorescence Imaging
A plant’s metabolic status can be evaluated through artificial stimulation of its photosystems and observation of their resulting responses, with fluorescence being a critical indicator. Fluorescence is the emission of light triggered by the absorption of shorter wavelength radiation. In plants, the chlorophyll complex is the primary fluorescent component. When chloroplasts are irradiated with blue or actinic light, a portion of the absorbed light is re-emitted by the chlorophyll. The ratio of re-emitted to absorbed light varies based on the plant’s efficiency in metabolizing the harvested light. This fluorescence provides a reliable measure of the plant’s capacity to assimilate actinic light [197]. Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging assesses variations in fluorescence intensity across a plant’s surface or relative to neighboring plants. Under stressful conditions, plant fluorescence generally decreases [16]. This technique is non-invasive and non-destructive; however, it is not confirmatory, as abiotic and biotic stresses can produce similar changes in plant color and texture. Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging devices typically function as active sensors, utilizing LED or laser light sources to evaluate photosynthetic electron transfer [198]. Figure 14 illustrates a standard fluorescence imaging system setup.
Figure 14.
A standard fluorescence imaging system setup.
Fluorescence imaging is one of the primary methods for detecting diseases in leaves, as it monitors the metabolic changes in photosynthesis, respiration, and nutrient flow that are among the earliest processes affected during infection. Due to the high power required for rapid illumination in modulated fluorescence, this technique is typically employed in controlled environments. Fluorescence imaging is highly effective for crop monitoring, enabling early stress detection and significantly reducing yield losses. The limitation of current chlorophyll fluorescence imaging systems is the need for strict plant preparation protocols, making it challenging to apply in typical agricultural greenhouses or field settings. To address this, research has focused on deriving fluorescence parameters from sun-induced reflectance, which shows promise for assessing plant diseases at the canopy or field level [198]. Despite this drawback, chlorophyll fluorescence imaging offers significant advantages by providing physiological insights into plant health, often enabling disease detection before visible symptoms appear. Whether or not this method proves viable for field-based disease monitoring, it still remains a valuable tool for studying plant diseases in controlled laboratory environments [16].
5.6. Three-Dimensional Imaging
In 2D imaging, data is captured in two dimensions, allowing differentiation based on plant characteristics such as development, overall height, and yield estimation. However, the necessity for 3D imaging emerges as crucial for the automatic detection of plant diseases [22]. Three-dimensional imaging includes two primary representations: surface-based and volume-based models. Surface representations provide depth details, surface elements, and spatial coordinates of individual points. Volume representations define the volumetric structure and include a frequency component corresponding to the model’s coordinates. Current imaging sensor technologies for 3D plant mapping primarily include LiDAR or laser scanner sensors, stereo vision, and time-of-flight cameras.
LiDAR is an advanced technique used for active remote sensing. LiDAR is the most widely used and well-regarded sensor for 3D canopy reconstruction due to its robustness, accuracy, and high resolution. It generates accurate and detailed 3D models using structured light projection and laser range scanning. However, LiDAR systems can be costly, complex, and require longer imaging durations. Recently, advanced remote sensing technologies have been developed, such as Multispectral LiDAR (MSL) and Hyperspectral LiDAR (HSL), which simultaneously capture both spectral and structural data [199,200]. LiDAR operates by emitting pulses across the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from ultraviolet to near-infrared wavelengths [201]. These pulses are directed toward Earth’s surface and reflected back to the LiDAR sensor. By measuring the round-trip time of each pulse and utilizing the known speed of light, the sensor calculates elevation data and determines the spatial distance between the transmitter and the reflector. The reflected laser pulses generate point clouds, allowing LiDAR to capture information on the distance, direction, and brightness of objects [201,202]. Figure 15 shows an example of point clouds generated from LiDAR imaging for detecting diseases in plants.

Figure 15.
LiDAR point clouds for analyzing physiology of chestnut trees for detecting blight disease: (a) cluster of point clouds and (b) 3D reconstructed view of the tree.
LiDAR can be used to provide detailed canopy morphology data through point clouds, which allow for the reconstruction of 3D canopy structures (Figure 15). These structures can reveal damage or biomass loss caused by diseases or pests. For instance, plant diseases such as sclerotinia blight in peanuts can cause significant changes in canopy morphology, making them detectable through LiDAR sensors [203]. Analyzing temporal LiDAR data over a crop season could help identify and assess the occurrence and impact of such diseases. Husin et al. [204] applied ground-based LiDAR to analyze oil palm canopy properties to assess the occurrence of basal stem rot (BSR) disease. The study classified oil palm health levels as well as detect BSR disease, using Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) technology. Their technique achieved 86.67% and 80% accuracy for healthy-unhealthy and severity-level classifications, respectively. This novel approach enables early detection of BSR and provides a high-resolution, non-invasive method for oil palm health monitoring.
Although 3D imaging offers detailed structural insights for detecting disease-related canopy changes, its use is hindered by the high cost and complexity of LiDAR systems, long data acquisition times, and the substantial expertise required for processing large point cloud datasets. Methods such as temporal canopy monitoring can be powerful, but they are sensitive to environmental noise, plant movement from wind, and occlusions within dense canopies, which can reduce accuracy. In addition, integration with other remote sensing data is often computationally demanding, limiting scalability for large fields. More practical solutions include improving methods to reduce occlusion effects in dense crop canopies, developing noise-robust algorithms that can account for plant movement caused by wind, and standardizing calibration protocols to ensure consistent results across different field conditions. Advances in automated point cloud annotation and disease-specific feature extraction would also help translate raw 3D data into actionable insights, while integrating temporal 3D datasets into disease progression models could improve early detection and monitoring without excessive manual intervention.
Advanced imaging technologies have proven effective in enhancing disease detection and management capabilities for precision agriculture. Table 3 summarizes applications and methodologies employed by these techniques for crop disease detection and monitoring. Figure 16 shows the trend of the adoption of the various imaging techniques for detecting diseases in crops over the years from 2015 to 2025, based on the papers reviewed in this study. The analysis of studies conducted from 2015 to 2025 highlights the evolving focus on various imaging techniques for crop disease detection. HSI showed a significant increase in studies, peaking in 2024 with seven studies, reflecting its growing adoption due to its ability to capture detailed spectral data. MSI demonstrated steady interest, with the highest activity observed in 2023 (four studies), likely attributed to its cost-effectiveness and broader accessibility. Thermal imaging had limited application, with minimal studies, while spectroscopy, fluorescence, and RGB (visible light) imaging had the least adoption. This trend underscores the increasing recognition of HIS and MSI as prominent tools in plant disease monitoring, while spectroscopy, thermal, fluorescence, and RGB imaging continue to provide complementary insights in specialized contexts.

Table 3.
Summary of various imaging techniques for crop disease detection.
Figure 16.
Adoption trend of various imaging techniques for detecting diseases in crops over the years from 2015 to 2025.
6. Computer Vision Techniques for Crop Disease Detection
AI has become a transformative tool for crop disease detection, leveraging DL and CNNs to achieve significant advancements in early disease detection and classification [240,241]. These AI-driven models automate detection processes, providing efficient and accurate solutions that outperform traditional manual monitoring methods, allowing for timely interventions to minimize disease impacts on crop yields. Among AI technologies, ML is widely used in plant pathology. ML algorithms analyze digital images to classify plant diseases, identifying specific patterns and symptoms, which makes them particularly effective for diagnosing diseases in their early stages [242]. However, traditional ML methods rely on a feature engineering stage, where relevant data features must be manually selected and extracted—a process that is often time-intensive and requires domain expertise [243]. In contrast, DL algorithms can automatically learn and extract features directly from raw data, eliminating the need for manual feature engineering. This capability allows DL to detect subtle disease symptoms that traditional ML and image processing techniques might overlook. By enabling models to learn features directly from raw pixel values, DL has revolutionized the approach to image identification tasks, offering greater efficiency and accuracy.
Computer vision (CV) is another AI technology widely applied in plant pathology. CV algorithms, including object detection and semantic segmentation, enable the identification and localization of specific regions of interest in images, such as plant leaves and disease symptoms [244,245]. The integration of CV with AI has transformed agricultural practices [246,247], particularly in detecting crop diseases [248,249]. Enhanced by DL techniques and advanced imaging, these technologies have significantly improved the accuracy in differentiating healthy plants from diseased ones, enabling targeted interventions to control disease spread [250]. AI-driven methods signify a paradigm shift in crop disease detection, providing effective and robust solutions that contribute to agricultural sustainability. These advancements simplify the disease identification process while equipping farmers with actionable insights to enhance crop health management and strengthen resilience against disease outbreaks [251,252]. Figure 17 depicts the general workflow for executing computer vision tasks. The subsequent subsections delve into the various computer vision techniques employed in detecting crop diseases.
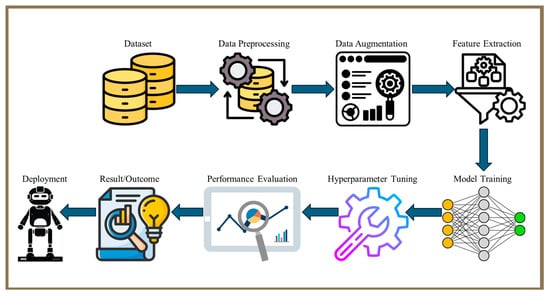
Figure 17.
A general workflow for computer vision applications.
6.1. Traditional Image Processing Techniques
In the dynamic field of agricultural technology, image processing has become a valuable tool for tackling significant challenges, particularly in the detection and management of crop diseases. This technology is advancing rapidly, leveraging diverse tools such as cameras and satellites to capture images for analysis [253]. These images are processed through computer-based analysis techniques to extract meaningful information. Similarly to its impact in other industries, traditional image processing has revolutionized agriculture by simplifying the classification and detection of diseases affecting crops. Image processing enables the identification of affected plant parts, such as leaves, and facilitates the measurement and diagnosis of the diseased areas. It employs various techniques to enhance images, allowing for the extraction of valuable information [254,255]. Multiple images can be generated from a single source, and some may require modifications or enhancements to suit specific applications. Image processing allows for these alterations, improving aspects such as noise reduction, color adjustments, and sharpness. Additionally, it supports image segmentation and feature extraction, further enabling detailed analysis and application.
Detecting diseases in plant leaves requires a systematic approach involving multiple stages [256,257]. These stages include pre-processing, segmentation (disease detection), feature extraction, and classification. The integration of these steps enables a thorough and efficient analysis of infected leaf images, leading to greater accuracy in disease identification and improved agricultural productivity. Image processing and ML offer a range of techniques for each stage of this workflow, effectively supporting disease detection in plants. Pre-processing methods include filtering, contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE), color space transformation, and image resizing. Segmentation techniques comprise thresholding, region growing, clustering, histograms, compression, variational methods, and the watershed algorithm. For feature extraction, approaches such as local binary patterns (LBP), histogram of oriented gradients (HOG), speeded-up robust features (SURF), gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), histogram features, wavelets, and Canny edge detection, Gabor filters, and PCA are employed. Classification methods include support vector machines (SVM), naïve Bayes (NB), decision trees (DT), k-nearest neighbors (K-NN), random forests (RF), AdaBoost, artificial neural networks (ANN), rule-based classifiers, and fuzzy classifiers [258].
Pre-processing phase plays a crucial role in identifying diseases in plant leaves, fruits, and stems, detecting diseased regions, analyzing the shape and color of infected areas, and determining solutions for plant diseases [259]. This step is essential for enhancing the contrast of input images, which are often affected by noise and poor backgrounds when captured using sensors and cameras, thereby reducing segmentation accuracy. Pre-processing techniques refined these raw images, transforming them into a suitable format for subsequent analysis. Numerous studies have utilized image pre-processing methods to prepare their data for effectively detecting abnormalities in plants. Malaisamy & Rethnaraj [260] evaluated additive and perceptual color spaces, concluding that the HSV color space was most effective for isolating leaf spot disease regions in groundnut plants. They further improved segmentation results by using a non-linear noise reduction filter, specifically a median filter, to minimize noise in the images. Similarly, Adem et al. [12] utilized Luv color space transformation to enhance the accuracy of classifying disease severity in sugar beet plant leaves. Additionally, adaptive histogram equalization was employed to improve local contrast within image regions and to enhance edge definition.
Effective image segmentation plays a vital role in distinguishing objects from their background, focusing on isolating regions with abnormalities. This process simplifies the image, making it easier to analyze and enabling clear differentiation between infected and non-infected areas. The choice of threshold is critical to the success of segmentation, as it directly influences accuracy. Grayscale images are often used to highlight specific object features, and a gray histogram is commonly employed to determine the optimal threshold for segmentation [261]. Image segmentation is a foundational aspect of most image processing and computer vision applications, serving as a key technology and a critical issue in image analysis [262,263,264]. Krishnan et al. [265] demonstrated the use of image segmentation techniques for identifying and classifying banana diseases. Similarly, Cui et al. [266] introduced an innovative method for spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification that leveraged spatial autocorrelation within hyperspectral images. This method involved segmenting the hyperspectral image to group pixels into homogeneous regions. Additionally, Singh & Misra [90] proposed an algorithm for the automatic detection and classification of leaf diseases, utilizing a genetic algorithm for segmentation. When tested on various plant leaves, the algorithm produced effective results, proving valuable for early-stage disease detection.
Feature extraction, performed after segmentation, is a crucial step in image processing as it involves identifying relevant attributes that characterize each class. This step is fundamental for constructing classification or recognition models, as the accuracy and computational efficiency of disease detection systems heavily depend on effective feature extraction, the choice of appropriate feature descriptors, and feature selection [267]. Feature descriptors are algorithms or techniques used to generate feature vectors from plant leaf images. Features are extracted based on segmented data and predefined datasets, employing methods such as statistical, structural, fractal, or signal processing techniques. Commonly extracted features include shape, color, texture, size, corners, and edges, which are essential for object recognition. Color, texture, and shape attributes of diseased areas are widely utilized in the literature for detecting and classifying plant diseases. Various feature extraction techniques based on these attributes have been applied in plant disease detection studies. For example, Rachmad et al. [268] used GLCM and K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) for feature extraction in tobacco leaf quality classification, achieving 83.33% accuracy with a neighbor value of 1, a pixel distance of 3, and 2-fold cross-validation. Gabor Filters, which analyze the frequency and orientation components of an image, were employed to extract texture features. These filters effectively capture local texture variations and are applied across multiple scales and orientations to create a detailed feature set [269]. Additionally, Yang et al. [270] introduced a microscopy image detection method for rice diseases that integrates texture and shape features with a decision tree-confusion matrix for comprehensive analysis.
The classification stage is a critical component of plant disease detection using computer vision and image processing. Its effectiveness heavily relies on prior steps, including preprocessing, segmentation of infected regions, and feature selection and extraction. Classifiers, implemented as software routines on computational platforms, are designed to identify specific features necessary for image categorization. The process of classifying plant leaf images based on infections and symptoms utilizes soft computing or ML techniques. Initially, a dataset of leaf images is used to train the ML classifier model, which is then applied to classify or recognize test image sets. The classifier is expected to distinguish between healthy and diseased leaf images and accurately identify specific plant infections [267]. Several plant disease datasets have been created to evaluate the performance of ML classification models, which are trained to learn features extracted from plant leaf images for predicting plant diseases. The next section provides a detailed overview of the various ML models used for detecting and classifying plant diseases.
While image processing has enabled early progress in crop disease detection, its effectiveness is constrained by sensitivity to variations in lighting, background clutter, and imaging conditions, which can lead to inconsistent results in field environments. Many segmentation and feature extraction methods also rely heavily on hand-crafted features, making them less adaptable to new crops, diseases, or symptom variations. Furthermore, traditional pipelines often require substantial manual tuning at each stage, limiting scalability for real-time or large-scale monitoring. More practical directions include developing adaptive pre-processing techniques that can dynamically adjust to field conditions, creating standardized open-access benchmark datasets to improve generalizability, and integrating lightweight hybrid approaches that combine traditional image processing with modern ML/DL for greater robustness without excessive computational cost.
6.2. Classical Machine Learning Techniques
ML, a branch of AI, enables systems to learn and improve from experience without explicit programming, allowing them to make autonomous decisions. ML plays a vital role in precision agriculture, particularly in automating the analysis of visual data for effective disease management. Understanding the distinction between classification and regression tasks in ML is important due to the different outputs they produce. Classification tasks provide qualitative results by categorizing inputs, such as grouping plant leaf diseases [257,271]. In contrast, regression tasks generate numerical outputs, estimating values based on the input data. A range of supervised ML techniques is available for disease detection, each with its strengths and limitations. Popular methods include DT, RF, K-NN, SVM, ANN, NB, linear regression, and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) [272]. These techniques are used to develop models capable of accurately detecting and classifying crop diseases. A key advantage of ML in precision agriculture is its ability to identify diseases in their early stages. By analyzing subtle physiological changes in plants captured through images, ML models can provide early warnings, enabling timely and effective interventions.
ML models are trained using labeled datasets that include images of both healthy and diseased crops. ML techniques are broadly categorized into supervised and unsupervised learning [273]. Supervised methods rely on labeled datasets, while unsupervised methods analyze unlabeled data by inferring patterns without predefined labels during training. Additionally, semi-supervised learning combines both labeled and unlabeled data during the training process. Through this training, ML models learn to identify specific visual indicators of various diseases, enabling accurate and automated disease detection. The literature highlights various classification methods employed for plant disease detection, with SVM, RF, DT, K-NN, NB, and ANN being the most used approaches. These methods are effective in learning features extracted from plant leaves to identify diseases [274]. Additionally, a few studies have explored feature-based, fuzzy logic-based, and vegetation index-based techniques.
The K-NN algorithm is a supervised learning method that operates on the principle that similar or homogeneous items are located near each other [275]. It assigns a class label to a new, unknown data point by evaluating its similarity or closeness to existing labeled data. This similarity is typically measured by calculating the distance between two points on a graph. An artificial neural network ANN is a statistical model inspired by the structure and functionality of the human brain. Similarly to how neurons in the brain learn from past experiences, ANN learns from provided data to classify or predict unknown data [276]. A typical ANN architecture consists of three layers: the input layer, hidden layer, and output layer, each composed of multiple neurons or nodes. The input layer receives the input data, which is passed to the subsequent hidden layer(s). The hidden layer, considered the core of the ANN, processes the data and identifies hidden patterns or features. There can be one or more hidden layers, depending on the complexity of the model. The final layer, which is the output layer, takes processed data from the last hidden layer and generates the output. SVM [277] operates by creating a decision boundary, or hyperplane, that separates n-dimensional space into distinct classes, enabling the classification of new data points into the appropriate categories. It relies on support vectors, or extreme data points, to construct the hyperplane. A DT is a supervised learning algorithm used for both classification and regression tasks, forming a tree-like structure that represents decisions and their possible outcomes. RF, an ensemble learning technique, enhances predictive accuracy and robustness by combining multiple DTs. Each tree independently classifies the input data, and the final classification is determined through majority voting [243].
Numerous studies have investigated the use of ML techniques to detect and manage crop diseases, aiming to enhance agricultural productivity. Saragih et al. [278] evaluated and compared K-NN and a proposed Modified K-NN for identifying diseases in the Jatropha curcas plant. The dataset, comprising 166 values, was split into 60% training and 40% testing data. The Modified K-NN algorithm varied the parameter K (multiples of 5) to assess accuracy, with the highest classification accuracy achieved at K = 10. Similarly, Kumari et al. [279] applied ANN to identify and classify four types of diseases affecting cotton and tomato plants. K-means clustering was used for segmentation, generating three clusters, from which Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) features were extracted from clusters 1 and 3. The proposed ANN-based approach achieved an accuracy of 92.5%. Padol & Yadav [280] analyzed grape leaf images, employing K-means clustering to extract diseased or infected regions of interest and SVM for classifying two types of grape leaf diseases: powdery mildew and downy mildew. Their proposed approach achieved a classification accuracy of 88.89%. Similarly, Bhatia et al. [281] developed a hybrid model incorporating SVM to detect powdery mildew disease in tomato plants.
The study by Ahmed et al. [282] presented a ML-based approach for detecting three common rice leaf diseases: bacterial leaf blight, brown spot, and leaf smut. The study aims to automate disease detection to reduce the time and labor associated with manual methods. A dataset of 480 rice leaf images was used, enhanced through image augmentation and preprocessed using a ColorLayoutFilter for feature extraction, resulting in 35 attributes. Correlation-based feature selection reduced these to five key attributes. The authors applied four ML algorithms: Logistic Regression, K-NN, DT, and NB. Among these, DT performed the best, achieving a 97.92% accuracy on test data following 10-fold cross-validation. The study highlights the potential of ML techniques in improving the efficiency and accuracy of plant disease detection, offering a scalable solution for large-scale rice farming.
The study by Harakannanavar et al. [283] focused on applying ML and image processing techniques to detect tomato leaf diseases. The objective was to automate disease identification and provide an accurate and efficient solution for farmers. A dataset comprising 600 images of tomato leaves with six disorders was used. The methodology involved resizing images, applying histogram equalization for enhancement, and using K-means clustering for segmentation. Key features were extracted using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and GLCM. The extracted features were classified using SVM, K-NN, and CNN. The CNN model achieved the highest accuracy of 99.6%, outperforming SVM (88%) and K-NN (97%). The proposed model demonstrated its effectiveness in early disease detection, significantly reducing manual intervention.
Ahmed & Yadav [284] employed ML techniques for plant disease detection to address agricultural productivity losses caused by diseases. The study leverages datasets of plant images, including greyscale and texture-based images, to develop models for early disease diagnosis. Various ML classifiers such as NB, RF, SVM, ANN, and Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM) were utilized. The methodology involved preprocessing the datasets to enhance image quality, extracting features like texture and color using the GLCM, and classifying plant diseases based on these features. Key performance metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, were used to evaluate the models. The results revealed that RF and NB classifiers achieved high accuracy (97.5%) for texture-based images, outperforming SVM (84.1%). While DL models like CNN and LSTM underperformed with low accuracy due to limited datasets, they demonstrated potential for future improvements with larger datasets. The study highlights the utility of GLCM features in improving classification accuracy and emphasizes the importance of robust ML models in early disease detection for enhanced agricultural outcomes.
The paper by Gali et al. [285] focused on developing an automated system for detecting plant diseases using image processing and ML techniques. The objective was to address challenges in early disease identification to improve agricultural outcomes. The proposed method integrates RGB imaging and ML classifiers, including SVM, K-NN, and CNN. The methodology includes preprocessing plant leaf images using techniques such as Gaussian filtering, K-means clustering, and histogram equalization to enhance image quality and isolate diseased regions. Features like texture, color, and shape are extracted using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and GLCM. These features are then used to train ML classifiers. The CNN model outperformed other methods, achieving classification accuracy between 90% and 100%. The study highlights the potential of combining advanced ML models and image analysis techniques for reliable, efficient plant disease detection, offering significant benefits for precision agriculture.
Classical ML approaches have proven effective for plant disease detection, yet their reliance on hand-crafted feature extraction and domain-specific preprocessing limits adaptability to diverse crops, disease types, and field conditions. These methods often require carefully labeled datasets and extensive parameter tuning, which can be time-consuming and may reduce performance when encountering new or variable imaging scenarios. Additionally, small or imbalanced datasets can hinder model generalization and increase susceptibility to overfitting. Given these challenges, DL models are particularly valuable for automating feature extraction, eliminating the need for manual intervention. Techniques such as data augmentation and synthetic image generation help expand training datasets, improving model generalization. Employing lightweight ensemble methods can further enhance robustness while keeping computational demands manageable. Collectively, these strategies increase the scalability and reliability of models across diverse and heterogeneous field conditions.
6.3. Deep Learning Techniques
AI and DL-based approaches are increasingly being adopted in agricultural research due to their capability to automatically extract deep features from image datasets, coupled with their superior accuracy and speed compared to traditional algorithms [67,286]. Unlike ML, DL algorithms have built-in feature extraction capabilities, making them a popular choice among researchers. CNNs are among the most widely used DL architectures, known for their effectiveness in modeling complex processes and identifying patterns in large datasets [35]. DL-based methods excel on autonomously identifying optimal key points from input data, eliminating the need for manual feature selection by human experts. DL frameworks mimic the functioning of the human brain, as they learn to identify and localize objects by observing numerous samples. This process mirrors human objects and pattern recognition. DL architectures deliver more accurate results compared to traditional ML methods, enhancing decision-making capabilities [287]. DL is particularly suited for applications such as image and video recognition, medical image analysis, object detection, flow prediction [288], traffic management [289], healthcare recommendation systems [290], anomaly detection [291], disease recognition [292], weed detection [293], soil monitoring [294], and pest identification [295,296], among others.
DL relies on extensive datasets containing hundreds or thousands of images [297]. In plant disease identification, DL with CNN has become a prominent research focus [298], particularly following the creation of the PlantVillage dataset in 2015 [299]. PlantVillage remains one of the most widely used datasets for disease identification, severity estimation, and the development of various management systems [300]. In recent years, additional publicly available plant disease datasets have been introduced to support DL model training. These include the Digipathos dataset [301], the PlantDoc dataset [302], the Northern Leaf Blight (NLB) dataset [303], the RoCoLe coffee disease dataset [304], the rice disease dataset [77], and the cassava disease dataset [305]. Numerous studies have utilized publicly available datasets to train DL models for identifying crop diseases and addressing yield reduction challenges. Additionally, some research has relied on custom datasets, either manually or automatically collected, tailored to their specific tasks.
DL techniques commonly employed in crop disease diagnosis include using CNNs for image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation. Image classification with DL is particularly popular for agricultural applications, including plant disease identification [306]. This process typically involves supervised training, where labeled image datasets are utilized to classify objects within images, with the softmax activation function in the final output layer determining the most suitable class. Advancements in CNN architectures for image classification, such as LeNet, AlexNet, ZFNet, VGGNet, GoogLeNet, ResNet, DenseNet, CapsNet, and SENet, were highlighted in the study by [307]. While image classification remains the most widely used application of DL in plant disease research, it has limitations in identifying the precise location of disease lesions within images and detecting multiple diseases simultaneously. Object detection, on the other hand, can locate and identify multiple instances of objects in images and videos. This approach relies on supervised training, where images are annotated with bounding boxes to provide ground truth data for DL models. Prominent object detection algorithms include region-based CNN (R-CNN [308], Fast R-CNN [309], Faster R-CNN [310]), you look only once (YOLO [311], and Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) [312]). Object detection based algorithms have been widely applied in plant disease identification, with some studies focusing on detecting entire disease-infected leaves, while others target specific disease lesions [300]. This method shows promise for identifying multiple plant diseases in images and videos. However, objects detected within bounding boxes may include extraneous information beyond the disease-specific features. Semantic segmentation offers a precise method for segmenting disease lesions, allowing the segmented areas to be extracted as regions of interest for further analysis. This approach involves training models to segment entire objects within images, assigning a class label to each pixel based on the training data. Popular semantic segmentation algorithms include Mask R-CNN, U-Net, Deeplab, Enet, and PSPNet. Like other supervised methods, semantic segmentation requires ground truth information during training. Unlike bounding box annotations, the annotations for semantic segmentation are more accurate as they define the exact shape of the object, providing localized details for improved analysis.
DL models are typically trained either from scratch or using transfer learning with pre-trained models. Training a model from scratch with high accuracy requires extensive datasets like ImageNet [313] and MS COCO [314], which contain 3.2 million and 328,000 images, respectively [300]. Transfer learning, on the other hand, involves utilizing pre-trained weights from models trained on similar objects before fine-tuning the model for a specific task. Researchers often use pre-trained weights from the ImageNet dataset to enhance DL model performance, especially when large training datasets are unavailable [306]. This approach has also been shown to achieve higher accuracy in plant disease identification [7,54]. DL models are typically evaluated using training, validation, and testing accuracy, with testing accuracy serving as the key metric for evaluating a model’s ability to identify objects across diverse datasets and conditions. Maximizing testing accuracy on unseen data is essential to ensure robustness. Other metrics frequently used to evaluate DL model performance include precision, recall, and F1-score for image classification; average precision (AP) and mean average precision (mAP) for object detection; and intersection over union (IoU) and mean intersection over union (mIoU) for semantic segmentation. The F1-score is particularly significant in studies where datasets exhibit class imbalance.
To date, numerous researchers have employed various DL architectures for diagnosing plant diseases using images of diseased leaves. The study by Khan et al. [67] focused on developing a mobile-based system for detecting and classifying maize leaf diseases using deep learning. The primary aim was to address the challenges of low yield caused by diseases like blight, sugarcane mosaic virus, and leaf spot. A dataset of 2675 images was collected from a real-field environment, ensuring varied weather and lighting conditions. Data augmentation techniques and expert-annotated labeling were utilized to enhance model performance. Models such as YOLOv3-tiny, YOLOv4, YOLOv5s, YOLOv7s, and YOLOv8n were employed, with YOLOv8n achieving the highest mean Average Precision (mAP) of 99.04%. This model was then integrated into a user-friendly mobile application, enabling real-time disease detection and tracking. This approach demonstrated a significant step towards practical and efficient disease management in maize crops. Yang et al. [2] introduced a mobile-based system leveraging deep transfer learning to estimate crop disease severity using the AI Challenger and PlantVillage datasets. In this study, a novel parallel framework integrating ResNet50 and Xception models, enhanced through transfer learning and deep feature fusion, was proposed. Data imbalance issues were mitigated using techniques like focal loss, achieving 88.58% accuracy on the AI Challenger dataset and 99.53% on PlantVillage.
The study by Albattah et al. [287] introduced an advanced DL framework for the automated detection and classification of plant diseases. The proposed method employs a customized CenterNet architecture enhanced with DenseNet-77 as a feature extractor to improve classification accuracy and computational efficiency. The study uses the PlantVillage dataset, consisting of diverse plant disease images, to evaluate the model. Through robust feature computation and a one-stage detection approach, the framework demonstrated improved localization and classification of 38 plant disease categories, achieving high accuracy even under challenging conditions like variations in color, size, and noise. This approach addresses the limitations of traditional methods and shows promise for real-world applications in agriculture.
Kumar et al. [68] developed and tested a DL model for identifying and classifying seven distinct potato diseases, including early blight, late blight, blackleg, potato virus Y, potato cyst nematode, potato wart disease, and Fusarium dry rot. The model incorporates a complex architecture featuring three convolutional layers, three max-pooling layers, and two fully connected layers. A thorough performance evaluation demonstrated promising results across all disease categories, achieving a weighted average F1-score of 94.81%, highlighting the model’s effectiveness in accurately diagnosing various potato diseases.
Divyanth et al. [58] proposed a novel two-stage semantic segmentation method for detecting corn diseases and estimating their severity, utilizing a custom dataset of handheld images of corn leaves captured in field conditions. The study trained three semantic segmentation models—SegNet, UNet, and DeepLabV3+—for each stage. In the first stage, semantic segmentation extracted corn leaves from complex field backgrounds, while the second stage identified, located, and quantified disease lesions by calculating the percentage of leaf area affected. UNet and DeepLabV3+ emerged as the best-performing architectures for leaf and lesion segmentation, achieving mwIoU scores of 0.9422 and 0.7379, respectively. The model accurately predicted the severity of gray leaf spot (GLS), northern leaf blight (NLB), and northern leaf spot (NLS) with an overall value of 0.96, demonstrating its effectiveness in disease detection and severity estimation.
Rashid et al. [315] developed a CNN-based architecture called the Multi-Model Fusion Network (MMF-Net) for detecting and classifying diseases in precision agriculture, integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technology. MMF-Net combines multi-contextual features through RL-block and PL-blocks 1 and 2, effectively merging multiple model streams trained on diverse datasets. The RL-block processes coarse-grained images to capture local spatial context, while PL-block 1 expands the perceptual area to extract fine-grained global context. PL-block 2 incorporates real-world environmental parameters as features. These features are merged using an ensemble of classifiers at the decision level, employing an adaptive majority voting scheme to generate the final decision probability score. Experimental results demonstrated that MMF-Net with fused features outperformed the non-fused approach, achieving an impressive 99.23% overall accuracy in recognizing corn leaf diseases.
Al-Shahari et al. [316] proposed an automated Plant Disease Detection and Crop Management system, called APDDCM-SHODL, utilizing a spotted hyena optimizer with DL for sustainable agriculture. This approach is designed to detect plant diseases and enhance crop productivity within an IoT-enabled infrastructure. The method employs the Vector Median Filter (VMF) for preprocessing, DenseNet201 for feature extraction, and the Spotted Hyena Optimizer (SHO) for optimal hyperparameter tuning of the DenseNet201 model. For classification, the system uses a recurrent spiking neural network (RSNN). Experimental results demonstrated that the APDDCM-SHODL technique outperformed existing methods, achieving a top accuracy of 98.60%. The study highlights the system’s ability to enable real-time plant health monitoring via interconnected sensors, leveraging DL for swift disease detection and diagnosis. The above studies demonstrate the strength of DL in effective diagnosis of plant health, thereby promoting sustainable agricultural practices and enhancing agricultural productivity. Table 4 summarizes major studies on computer vision for plant disease diagnosis from 2015 to 2025.

Table 4.
Summary of major studies that utilized computer vision techniques for crop disease diagnosis.
DL has significantly advanced crop disease detection by automating feature extraction and achieving high accuracy. However, several challenges persist in the techniques employed. Image classification models, while highly effective for identifying diseased leaves, often struggle with precise lesion localization and multi-disease detection within a single image. Object detection techniques can address this but may include extraneous background information within bounding boxes, reducing feature specificity. Semantic segmentation offers improved lesion localization but requires labor-intensive pixel-level annotations, which are time-consuming and dataset-dependent. Transfer learning mitigates the need for large datasets, yet models trained on generic datasets may underperform under diverse field conditions due to variations in lighting, occlusion, and background complexity. Additionally, multi-stream or multi-context architectures that integrate multiple feature types enhance performance but increase model complexity and computational demands, posing challenges for real-time deployment on resource-limited devices. Addressing these limitations through optimized annotation strategies, lightweight architectures, and robust feature fusion can improve practical applicability and scalability of DL in heterogeneous agricultural environments.
7. Edge Computing and Internet of Things (IoT) for Crop Diagnosis
Transformative technologies for agriculture include the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G cellular technology, cloud computing, and edge computing [325]. Edge computing involves shifting data storage and processing tasks from centralized servers to the edge of the network, closer to end-user devices. This approach minimizes data transfer duration, response latency, and alleviates network bandwidth congestion. Additionally, localized processing at the edge lowers data transmission costs [326]. Edge computing offers a promising solution to address the high latency challenges associated with cloud computing [327,328]. IoT-enabled smart agriculture systems have utilized various wired and wireless technologies, integrating sensors, controllers, and communication tools. This integration facilitates the creation of cost-effective infrastructures for intelligent agriculture.
The integration of edge computing with 5G-enabled IoT offers significant potential to transform agricultural applications [329]. This combination delivers low-latency, high-bandwidth, and real-time capabilities, making it ideal for latency-sensitive smart farming applications [330]. By merging IoT, AI, and edge computing, IoT-enabled technologies have advanced the development of smart agriculture systems capable of real-time monitoring, capturing, and analyzing crop information. These systems support early disease prevention, improved soil monitoring, and efficient crop management. AI enhances the production process by improving crop quality, reducing costs, and minimizing waste. Crop disease identification remains one of the most challenging tasks in smart agriculture, where edge computing plays a vital role. Advanced edge-enabled UAVs, ground vehicles, and imaging systems conduct localized, real-time image analysis of large fields, identifying diseases and pest problems without relying on cloud uploads. This ensures rapid detection and intervention, safeguarding crop health and quality.
Few studies have investigated the potential of edge computing for crop monitoring and disease diagnosis, with key findings summarized as follows. A model called Deep Leaf, designed for timely detection of coffee plant diseases to prevent their spread, was introduced by De Vita et al. [331]. This edge computing-based detector targets major biotic stresses affecting crops. It employs a dynamic compression algorithm using K-means to reduce the CNN model’s footprint, enabling it to operate on devices with limited hardware capabilities. Similarly, the study by Gu et al. [332] proposed an IoT monitoring framework for identifying tomato diseases. Initially, a pretraining model was developed on the cloud using VGG networks. To adapt the model for embedded mobile platforms, a depth-wise separable convolutional network was utilized to minimize parameters and optimize the feature extractor. Experimental results demonstrated that the framework accurately detects crop diseases in less time. Zhang & Li [333] proposed an edge computing-based adaptive sensing strategy for the crop life cycle. Using Gath—Geva fuzzy clustering, crop growth stages are divided for sensing nodes, while data-driven algorithms optimize key parameters by reducing redundancy and improving data correlations. A neural network model is then applied to predict crop growth stages.
8. Economic Feasibility, Accessibility, and Recommendations for Emerging End-to-End Solutions for Crop Disease Diagnosis
Technologies for crop disease diagnosis (sensors such as RGB, multispectral, hyperspectral, thermal and LiDAR; platforms such as UAVs, UGVs, handheld devices and lab platforms; and computational options from edge devices to cloud servers) offer strong technical capability but present a wide range of economic and accessibility trade-offs that shape real-world adoption. High capital expenditure (sensor + platform), recurring operational costs (maintenance, batteries, data processing, licenses), and human capacity needs are repeatedly identified in the literature as primary barriers, especially for smallholders in low- and middle-income countries [334,335]. Policy, infrastructure (electricity, broadband), finance (credit/subsidies), and regulation (UAV flight rules) further affect affordability and scalability [336].
The economic feasibility of adopting these technologies for crop disease diagnosis largely depends on the trade-off between performance, scalability, and affordability [337]. While advanced systems such as hyperspectral and robotic platforms provide superior diagnostic capabilities, their high capital and operational costs limit accessibility for smallholders and research programs in developing regions [338]. More affordable options like multispectral and RGB systems offer practical scalability but may compromise on early detection precision. Similarly, computational strategies involve cost-performance tradeoffs: edge computing enhances real-time analysis, data privacy, and autonomy but requires greater upfront hardware investment and local energy support, whereas cloud computing reduces local hardware needs but adds recurring data transfer and subscription costs [334]. Consequently, hybrid architectures that combine on-device preprocessing with cloud analytics are increasingly viewed as the most cost-effective and technically balanced approach, optimizing resource use while maintaining analytical accuracy and timeliness [334].
To provide a concise overview of the economic considerations associated with implementing different sensing, platform, and computational technologies for crop disease diagnosis, Table 5 presents a comparative summary of their relative cost ranges, computational requirements, adoption barriers, and potential solutions. This synthesis highlights the trade-offs between affordability, technical performance, and accessibility, offering a practical perspective on how these technologies can be deployed effectively across varying scales of agricultural operations.

Table 5.
A comparative summary of cost ranges, computational requirements, adoption barriers, and potential solutions for emerging digital technologies for end-to-end crop diagnosis.
Figure 18 depicts a recommendation matrix for selecting different technology combinations for crop disease diagnosis. The matrix synthesizes the suitability of various technology combinations (vertical axis) for different crops (horizontal axis), marked by a recommendation level (high, medium, or low) and a core advantage. For example, UGV + HSI + DL offers below-canopy high-res data, which is highly recommended for wheat and corn but less suitable (low) for soybean and other crops. Conversely, UAV + MSI + ML is rated as a high recommendation across the board, providing field-scale mapping, which is practical and scalable, aligning with the need for cost-effective systems that avoid the high capital and operational costs of more advanced platforms. The overall goal is to offer a quick technical selection reference, balancing the superior diagnostic capabilities of high-end, often costly systems (like those involving hyperspectral or thermal sensors for early detection and confirmatory tests) with more affordable, scalable options (like RGB and MSI) that still provide valuable data like low-cost imaging and rich feature extraction. It should be noted that these recommendations are based on the articles analyzed in this study and are meant to be flexible and not “hard-coded”. Special situations may require setups tailored specifically to the user’s needs and availability of resources.
Figure 18.
Recommendation matrix for technical selection in crop disease diagnosis. This matrix compares the suitability of various technology combinations (platforms, sensors, and computational methods) across major crop types. The color-coded cells indicate the recommendation level and state the core advantage of that combination, providing a quick-reference guide for practitioners to balance diagnostic performance, scalability, and affordability.
9. Challenges and Prospects
Addressing the challenges posed by plant diseases requires innovative and sustainable approaches. Integrating precision tools, such as UAVs, UGVs, and advanced computations has emerged as an effective strategy. These technologies complement each other for enhanced accuracy in disease detection while promoting sustainability by reducing environmental impact and reliance on agrochemicals. The shift from traditional methods to integrated precision disease management represents a much-awaited transformation. Advanced technologies in agriculture have demonstrated great potential in improving disease control. UAVs, UGVs, and advanced imaging sensors facilitate comprehensive monitoring and early disease detection, enabling timely and targeted interventions. Additionally, ML and DL algorithms strengthen these capabilities by analyzing vast datasets and providing actionable insights. Despite their promise, challenges such as data quality, high computational demands, and the need for diverse datasets to train reliable models remain as critical obstacles that must be addressed. Over the past decade, advancements in computer vision and ML have significantly enhanced the ability to detect and classify plant diseases from images. However, a key challenge remains the lack of high-quality labeled datasets that adequately represent real-world scenarios and provide sufficient examples of various plant diseases [344]. These datasets are crucial for enabling ML algorithms to learn accurate patterns and features from images [345]. Without them, detection and classification models face limitations in accuracy and reliability, potentially leading to misdiagnoses and financial losses for farmers [274,346]. The labeling process itself is labor-intensive and time-consuming, further complicating dataset generation. Additionally, plant diseases often exhibit variability depending on the type of disease, contamination stage, plant growth stage, and environmental conditions. The presence of multiple infections on a single plant adds to the complexity of accurate diagnosis [198]. High-quality images capturing symptoms across different disease stages are essential for reliable diagnosis and classification [347,348,349]. Achieving this requires specialized equipment such as high-resolution cameras, proper lighting, and advanced lenses, which can be costly and difficult to obtain in remote regions.
Although image processing techniques perform well under controlled laboratory conditions, their effectiveness diminishes significantly in outdoor environments [350]. This decline is largely attributed to the variability of color under natural lighting conditions, which complicates image analysis. Limited technical expertise further exacerbates these challenges, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate image processing techniques and classification strategies for optimal computer vision system performance [351]. Common issues include oversized sample sets, overfitting, and insufficient technical details in some studies, making validation difficult. The similarity of visual symptoms among different diseases adds to the complexity, such as Cercospora leaf spot may closely mimic other diseases like Ramularia leaf spot, bacterial blight, and Phoma leaf spot, or abiotic stressors, leading to misdiagnoses and reduced system accuracy [352]. Environmental variability across regions further complicates the development of universal models that can work across all plants and conditions. Innovative approaches are needed beyond visual inspection, incorporating genetic markers or crop-specific indicators to improve diagnostic accuracy [243]. Additionally, the lack of standardized data collection methods poses a significant challenge, as inconsistent procedures across researchers lead to variations in datasets, hindering the development of reliable predictive models [351].
Deploying DL for plant disease detection on edge devices poses challenges due to resource limitations. Edge computing processes data near its source rather than relying entirely on centralized cloud servers, enabling faster and more efficient analysis. However, this approach requires balancing computational performance with energy efficiency. DL models, which demand extensive data and processing power, are often constrained by the limited storage and battery life of edge devices. This challenge is particularly relevant for real-time plant disease detection in fields or greenhouses, where models must operate efficiently under resource constraints. Research has shown that pruning models can reduce their size by up to 90% without substantial accuracy loss [353]. Such optimization facilitates practical deployment on edge devices while minimizing energy consumption and costs. Although optimized models offer promising solutions, further advancements are needed to fully address these challenges. Additional considerations include limitations of the techniques used within deep learning, such as bounding box-based object detection including extraneous information, and semantic segmentation requiring precise and labor-intensive annotations. Emerging solutions like attention-based or transformer object detection for better localization, instance segmentation, weakly- or semi-supervised learning, and synthetic data generation with domain adaptation can address these constraints while improving robustness and reducing the annotation burden. A detailed comparison of different sensors, analytical algorithms, and their performances for efficient crop disease identification is provided in Table 3, Table 4 and Figure 18. Insights from these tables can be utilized to develop new methods or explorations for new disease identification as well as in new crops that have not yet been evaluated, especially when additional diseases are emerging in agricultural systems.
Early prediction of plant disease occurrence represents one of the most critical yet challenging aspects of crop protection. Since visual symptoms often appear only after significant physiological damage has occurred, predictive modeling that leverages environmental and weather-related data is essential for timely intervention. Integrating AI with time-series models, and meteorological parameters (e.g., temperature, humidity, solar radiation) can enable forecasting of disease risk before visible onset, allowing for preventive management rather than reactive control. Such predictive capabilities not only improve the efficiency and precision of disease management decisions but also reduce yield losses, input costs, and environmental impact. Therefore, advancing the robustness and generalizability of early disease risk prediction models remains a key research frontier for achieving sustainable, data-driven crop protection systems. A growing number of studies have investigated predictive modeling frameworks capable of estimating plant disease risk based on environmental, climatic, and crop-related factors. For example, Wagle et al. [354] proposed a hybrid Bilinear Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) model optimized with Gaussian Bayesian optimization (BLSTM_bayOpt) to predict tomato disease risk using weather parameters such as temperature and relative humidity. The study achieved high accuracy () and a 40.67% improvement in mean squared error (MSE) for relative humidity prediction. Similarly, Guo et al. [355] developed a hybrid CNN-LSTM model enhanced with a Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) attention mechanism to predict peanut leaf spot disease using multi-year meteorological and survey data. The optimized model achieved high accuracy (), demonstrating strong potential for timely and precise disease management. Using Z-score standardized datasets, Alzakari et al. [356] developed a CNN-LSTM model for detecting major potato diseases, including late and early blight. A reported accuracy of 97.1% demonstrates the model’s effectiveness in early disease detection. Collectively, these studies, which make use of open-field meteorological data, underscore the growing potential of AI-driven, weather-informed predictive models as powerful tools for enabling proactive, precise, and sustainable crop disease management.
While open-field, weather-based monitoring provides valuable insights for disease risk forecasting at regional or field scales, it often overlooks the distinct microclimatic variations that exist within crop canopies. For most crops, the initial stages of pathogenic growth occur beneath the canopy, where environmental conditions—characterized by lower temperature, higher relative humidity, and reduced solar radiation—create favorable habitats for disease development. Consequently, relying solely on data from open-field weather stations may lead to generalized predictions that fail to accurately capture these localized microclimate dynamics. To address this limitation, a promising future direction involves developing autonomous, below-canopy monitoring systems powered by edge computing and IoT technologies. Such systems could integrate localized sensor networks with AI-driven predictive models to continuously capture temperature, humidity, and light intensity data within the canopy microenvironment. By analyzing these parameters in real time, the system could more precisely identify areas at higher risk of pathogenic proliferation, enabling farmers to implement preventive measures before visible disease symptoms emerge. This microclimate-focused approach represents a critical advancement toward more spatially precise, early-warning frameworks for crop disease management and improved field-level decision support.
Economic feasibility and accessibility remain major challenges in the large-scale adoption of emerging sensing and computational technologies for end-to-end crop disease diagnosis. While advanced systems such as hyperspectral imaging, UAV/UGV platforms, and AI-driven analytics demonstrate exceptional technical performance, their high capital costs, maintenance demands, and energy or connectivity requirements limit accessibility—particularly for smallholder farmers in low- and middle-income regions. Bridging this gap requires strategies such as promoting low-cost modular sensors, shared equipment or leasing models, open-source computational frameworks, and supportive policy interventions to subsidize technology deployment and enhance rural infrastructure. Addressing these economic and operational barriers will be critical for translating technical feasibility into practical, scalable, and inclusive disease management solutions.
Finally, as agriculture modernizes through data-driven solutions, cyber threat risks also persist that may compromise data and decision quality acquired from vulnerable devices and systems. Eventually, these can compromise crop input applications to damage productivity and economic returns. Research and development targeting cybersecurity in agriculture that include attack-resistant electronic communication devices and protocols, regular data security audits of farm data, and other related measures need to be adopted.
10. Conclusions
This review highlights transformative role of advanced technologies and end-to-end solutions for real-time diagnosis of crop diseases, addressing critical challenges in agriculture such as yield reduction, economic losses, and environmental sustainability. Techniques spanning from sensing technologies such as HSI and MSI, thermal imaging, visible light imaging, and fluorescence imaging have collectively broadened the toolkit for early disease detection, offering non-invasive, rapid, and highly sensitive approaches capable of capturing both physiological and structural changes in crops. Moreover, the integration of ML and DL technologies has significantly enhanced disease identification processes, enabling automated systems that reduce human error, accelerate detection, and optimize decision-making. Approaches like CNNs, object detection, semantic segmentation, transfer learning, and ensemble methods have demonstrated efficacy in diverse applications, including disease classification, lesion localization, and severity assessment, underscoring their growing potential in modern precision agriculture. Emerging techniques, such as attention mechanisms, weakly supervised learning, and synthetic data generation, further address limitations associated with annotation burden and extraneous information in DL-based models, enhancing model robustness, scalability, and applicability under heterogeneous field conditions.
Overall, the articles analyzed in this study reveal clear trends driving the evolution of crop disease detection. First, the convergence of imaging systems and AI has been central to improving diagnostic precision and operational efficiency, establishing a foundation for scalable digital disease management. Second, edge computing and IoT integration have enabled near real-time processing of sensor data, paving the way for autonomous field monitoring systems that are both cost-effective and energy efficient. Third, AI-driven predictive modeling—particularly hybrid frameworks combining CNNs, LSTMs, and meteorological data—has shown strong potential for early disease risk prediction, moving crop protection from a reactive to a preventive paradigm. Together, these developments illustrate the shift towards providing complete end-to-end solutions for practical implementations that can adapt dynamically to environmental variability and disease pressure.
The review also emphasizes the importance of deploying innovative and integrated sensors and platforms, including UAVs, UGVs, and IoT-enabled edge computing systems, for end-to-end scalable and real-time disease monitoring. Integration of microclimate sensing (temperature, humidity, solar radiation) beneath crop canopies alongside advanced imaging can enable proactive interventions before disease onset, offering a shift from reactive to predictive disease management. These systems, when combined with DL models, can provide farmers with actionable insights in near real-time, improving both efficiency and sustainability.
From a scientific perspective, these advancements offer new pathways for interdisciplinary research combining plant pathology, computer vision, and data science to develop interpretable and generalizable models. For industry, the growing availability of low-cost sensors, portable imaging systems, and embedded AI processors opens opportunities for developing commercial decision-support tools and automated platforms for large-scale disease monitoring. Technology providers can leverage these findings to design modular, interoperable systems that integrate seamlessly with existing agricultural machinery and digital farm management platforms. Collectively, these applications demonstrate how research progress can translate into tangible innovations that enhance productivity, reduce agrochemical use, and improve sustainability across global agricultural systems.
Despite significant advancements, challenges remain. These include ensuring affordability and accessibility, cybersecurity, managing vast and diverse datasets, addressing environmental and inter-disease variability, and overcoming practical deployment constraints such as computational resource limitations and annotation requirements. Future research should also focus on developing standardized data collection protocols, lightweight and interpretable models suitable for edge devices, and frameworks capable of integrating multiple sensing modalities to deliver holistic crop health monitoring. By fostering collaboration between researchers, technologists, and agricultural stakeholders, these advancements can revolutionize disease management practices. Leveraging integrated AI-driven frameworks, precision sensing, and predictive modeling can support sustainable crop production through minimized agrochemical use and ultimately contribute to global food security. These efforts represent a critical step towards a more resilient, data-driven, and environmentally responsible agricultural ecosystem.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.N. and A.K.C.; methodology, C.L.N. and A.K.C.; validation, C.L.N. and A.K.C.; formal analysis, C.L.N.; investigation, C.L.N.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.N.; writing—review and editing, A.K.C.; visualization, C.L.N. and A.K.C.; supervision, A.K.C.; project administration, A.K.C.; funding acquisition, A.K.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in parts by the Virginia Tech College and Agricultural and Life Sciences through faculty startup funds, hatch projects VA-160181, VA-136412, VA-136438, and VA-136452 funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the author(s) used [ChatGPT, GPT-5] and [Gemini, 2.5 Flash] for the purpose of generating some graphics used in this manuscript. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the authors and should not be construed to represent any official USDA or U.S. Government determination or policy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mohanty, S.P.; Hughes, D.P.; Salathé, M. Using Deep Learning for Image-Based Plant Disease Detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 215232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Seklouli, A.S.; Ren, L.; He, Y.; Yu, X.; Ouzrout, Y. A New Mobile Diagnosis System for Estimation of Crop Disease Severity Using Deep Transfer Learning. Crop Prot. 2024, 184, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Singh, P.K.; Rutkoski, J.; Hodson, D.P.; He, X.; Jørgensen, L.N.; Hovmøller, M.S.; Huerta-Espino, J. Disease Impact on Wheat Yield Potential and Prospects of Genetic Control. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Q.; Deng, Z. Multi-Label Learning for Crop Leaf Diseases Recognition and Severity Estimation Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 15327–15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampatzidis, Y.; De Bellis, L.; Luvisi, A. iPathology: Robotic Applications and Management of Plants and Plant Diseases. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.C.; Luvisi, A.; De Bellis, L.; Ampatzidis, Y. X-FIDO: An Effective Application for Detecting Olive Quick Decline Syndrome with Deep Learning and Data Fusion. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Du, K.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Z.; Sun, Z. A Recognition Method for Cucumber Diseases Using Leaf Symptom Images Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 154, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qi, F. Tomato Diseases Recognition Based on Faster RCNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Qingdao, China, 23–25 August 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 772–776. [Google Scholar]
- George, R.; Thuseethan, S.; Ragel, R.G.; Mahendrakumaran, K.; Nimishan, S.; Wimalasooriya, C.; Alazab, M. Past, Present and Future of Deep Plant Leaf Disease Recognition: A Survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 234, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Precision Agriculture in Crop Production|NIFA. Available online: https://www.nifa.usda.gov/grants/programs/precision-geospatial-sensor-technologies-programs/precision-agriculture-crop-production (accessed on 3 October 2025).
- European Commission. The Farm to Fork Strategy|Fact Sheets on the European Union|European Parliament. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/factsheets/en/sheet/293547/the-farm-to-fork-strategy (accessed on 3 October 2025).
- Adem, K.; Ozguven, M.M.; Altas, Z. A Sugar Beet Leaf Disease Classification Method Based on Image Processing and Deep Learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 12577–12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, X.; Fu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhang, L. A Fuzzy Clustering Segmentation Method Based on Neighborhood Grayscale Information for Defining Cucumber Leaf Spot Disease Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Pierro, R.; Materazzi, A.; Panattoni, A.; De Bellis, L.; Luvisi, A. Detection of Grapevine Yellows Symptoms in Vitis vinifera L. with Artificial Intelligence. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Guo, W.; Han, X.; Chen, C.; Wu, H. EFDet: An Efficient Detection Method for Cucumber Disease under Natural Complex Environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutka, A.M.; Bart, R.S. Image-Based Phenotyping of Plant Disease Symptoms. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chan, S.S.F.; Cham, W.-K.; Chu, L.M. Plant Identification Using Leaf Shapes—A Pattern Counting Approach. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 3203–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Shekhawat, R.S. Review of Image Processing Approaches for Detecting Plant Diseases. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, M.A.; AL-Tuwaijari, J.M. Plant Leaf Diseases Detection and Classification Using Image Processing and Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (CSASE), Duhok, Iraq, 16–18 April 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraju, M.; Chawla, P. Systematic Review of Deep Learning Techniques in Plant Disease Detection. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2020, 11, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasubramanian, K.; Jones, S.; Singh, A.K.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, A.; Ganapathysubramanian, B. Plant Disease Identification Using Explainable 3D Deep Learning on Hyperspectral Images. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S. A Review of Imaging Techniques for Plant Disease Detection. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Wu, X. Northern Maize Leaf Blight Detection Under Complex Field Environment Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 33679–33688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.; Harrison, N.; French, A.P. Hyperspectral Image Analysis Techniques for the Detection and Classification of the Early Onset of Plant Disease and Stress. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujić, K. A Review of Thermal Spectral Imaging Methods for Monitoring High-Temperature Molten Material Streams. Sensors 2023, 23, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, Z.; Ozguven, M.M.; Yanar, Y. Determination of Sugar Beet Leaf Spot Disease Level (Cercospora beticola Sacc.) with Image Processing Technique by Using Drone. Curr. Investig. Agric. Curr. Res. 2018, 5, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguven, M.M.; Altas, Z. A New Approach to Detect Mildew Disease on Cucumber (Pseudoperonospora cubensis) Leaves with Image Processing. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 104, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguven, M.M. Deep Learning Algorithms for Automatic Detection and Classification of Mildew Disease in Cucumber. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 7081–7087. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Hu, Y.; Coppola, G.; Zhang, D.; Sun, W. PD2SE-Net: Computer-Assisted Plant Disease Diagnosis and Severity Estimation Network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Du, P.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, H. A Cucumber Leaf Disease Severity Classification Method Based on the Fusion of DeepLabV3+ and U-Net. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y. Cucumber Leaf Disease Identification with Global Pooling Dilated Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, K.R.; Raja, P.; Mukesh, K.V.; Aniirudh, R.; Ashiwin, R.; Szczepanski, C. Disease Classification in Maize Crop Using Bag of Features and Multiclass Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 January 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1191–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal, P.; Patel, S.C. Pattern Recognition Method to Detect Two Diseases in Rice Plants. Imaging Sci. J. 2008, 56, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulridha, J.; Batuman, O.; Ampatzidis, Y. UAV-Based Remote Sensing Technique to Detect Citrus Canker Disease Utilizing Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi Anari, M. A Hybrid Model for Leaf Diseases Classification Based on the Modified Deep Transfer Learning and Ensemble Approach for Agricultural AIoT-Based Monitoring. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 6504616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, E.C.; Yujian, L.; Njuki, S.; Yingchun, L. A Comparative Study of Fine-Tuning Deep Learning Models for Plant Disease Identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 161, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, J. RIC-Net: A Plant Disease Classification Model Based on the Fusion of Inception and Residual Structure and Embedded Attention Mechanism. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Yadav, K. Portable Solutions for Plant Pathogen Diagnostics: Development, Usage, and Future Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1516723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Chandel, N.S.; Singh, K.P.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Nandede, B.M.; Kumar, M.; Subeesh, A.; Upendar, K.; Salem, A.; Elbeltagi, A. Deep Learning and Computer Vision in Plant Disease Detection: A Comprehensive Review of Techniques, Models, and Trends in Precision Agriculture. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwini, C.; Sellam, V. EOS-3D-DCNN: Ebola Optimization Search-Based 3D-Dense Convolutional Neural Network for Corn Leaf Disease Prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 11125–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, A.; Nehra, A.; Joshi, K.; Kumar, A.; Tuteja, N.; Varshney, R.K.; Gill, S.S.; Gill, R. Exploration of Machine Learning Approaches for Automated Crop Disease Detection. Curr. Plant Biol. 2024, 40, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, K.S.; Kårlund, A.O.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Johansson, D.P.; Scheers, N.M.; Marklinder, I.M.; Eriksen, A.K.; Silventoinen, P.C.; Nordlund, E.; Sozer, N.; et al. Grains—A Major Source of Sustainable Protein for Health. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 1648–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldamichael, F.G.; Debelee, T.G.; Schwenker, F.; Ayano, Y.M.; Kebede, S.R. Machine Learning in Cereal Crops Disease Detection: A Review. Algorithms 2022, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; An, D. Identification of an Elite Wheat-Rye T1RS·1BL Translocation Line Conferring High Resistance to Powdery Mildew and Stripe Rust. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2940–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I.; Tyagi, B.S.; Singh, G.; Venkatesh, K.; Gupta, O.P. Enhancing Wheat Production- A Global Perspective. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 85, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhesh, K.M.; Sowmya, V.; Sainamole Kurian, P.; Sikha, O.K. AI Based Rice Leaf Disease Identification Enhanced by Dynamic Mode Decomposition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Marwaha, S.; Deb, C.K.; Nigam, S.; Arora, A. Recognition of Diseases of Maize Crop Using Deep Learning Models. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 7407–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Shrestha, B.; Baiju, B.; Saban Kumar, K.C. Tomato Plant Diseases Detection System Using Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 1st KEC Conference on Engineering and Technology, Lalitpur, Nepal, 27 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, J.; Bouaziz, B.; Algergawy, A. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for Banana Leaf Diseases Classification. In Proceedings of the Datenbanksysteme für Business, Technologie und Web (BTW 2017)-Workshopband, Stuttgart, Germany, 6–10 March 2017; Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V.: Hamburg, Germany, 2017; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Arnal Barbedo, J.G. Plant Disease Identification from Individual Lesions and Spots Using Deep Learning. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 180, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashourloo, D.; Aghighi, H.; Matkan, A.A.; Mobasheri, M.R.; Rad, A.M. An Investigation Into Machine Learning Regression Techniques for the Leaf Rust Disease Detection Using Hyperspectral Measurement. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4344–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, A.; Sundaresan, P.; Bhavsar, A.; Mattu, M.; Kavitha, M.S.; Shaik, A. Tea Leaf Disease Detection Using Segment Anything Model and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhange, M.; Hingoliwala, H.A. Smart Farming: Pomegranate Disease Detection Using Image Processing. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 58, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Nanehkaran, Y.A. Using Deep Transfer Learning for Image-Based Plant Disease Identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yin, H.; Zhang, D. A Self-Adaptive Classification Method for Plant Disease Detection Using GMDH-Logistic Model. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2020, 28, 100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chug, A.; Bhatia, A.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, D. A Novel Framework for Image-Based Plant Disease Detection Using Hybrid Deep Learning Approach. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 13613–13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChant, C.; Wiesner-Hanks, T.; Chen, S.; Stewart, E.L.; Yosinski, J.; Gore, M.A.; Nelson, R.J.; Lipson, H. Automated Identification of Northern Leaf Blight-Infected Maize Plants from Field Imagery Using Deep Learning. Phytopathology 2017, 107, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divyanth, L.G.; Ahmad, A.; Saraswat, D. A Two-Stage Deep-Learning Based Segmentation Model for Crop Disease Quantification Based on Corn Field Imagery. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.C.; Park, D.S. A Robust Deep-Learning-Based Detector for Real-Time Tomato Plant Diseases and Pests Recognition. Sensors 2017, 17, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridasan, A.; Thomas, J.; Raj, E.D. Deep Learning System for Paddy Plant Disease Detection and Classification. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, A.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Peng, N.; Yan, N.; Jiang, C. Tomato Leaf Disease Detection System Based on FC-SNDPN. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 2121–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaye, F.O.; Olusanya, M.O.; Akinyelu, A.A. A Multi-Class Hybrid Variational Autoencoder and Vision Transformer Model for Enhanced Plant Disease Identification. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2025, 26, 200490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; He, D.; Liang, C. Real-Time Detection of Apple Leaf Diseases Using Deep Learning Approach Based on Improved Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59069–59080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Rajni; Sivia, J.S. Development of Deep and Machine Learning Convolutional Networks of Variable Spatial Resolution for Automatic Detection of Leaf Blast Disease of Rice. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Uga, H.; Kagiwada, S.; Iyatomi, H. Basic Study of Automated Diagnosis of Viral Plant Diseases Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advances in Visual Computing; Bebis, G., Boyle, R., Parvin, B., Koracin, D., Pavlidis, I., Feris, R., McGraw, T., Elendt, M., Kopper, R., Ragan, E., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 638–645. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.I.; Quadri, S.M.K.; Banday, S.; Latief Shah, J. Deep Diagnosis: A Real-Time Apple Leaf Disease Detection System Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Zafar, N.; Tahir, M.N.; Aqib, M.; Waheed, H.; Haroon, Z. A Mobile-Based System for Maize Plant Leaf Disease Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1079366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Jain, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Jain, N.; Das, P.; Sahni, P. Advanced Deep Learning Model for Multi-Disease Prediction in Potato Crops: A Precision Agriculture Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Information Technology, Electronics and Intelligent Communication Systems (ICITEICS), Bangalore, India, 28–29 June 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Yi, S.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Identification of Rice Diseases Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Neurocomputing 2017, 267, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahum, R.; Munir, H.; Mughal, Z.-U.-N.; Awais, M.; Sher Khan, F.; Saqlain, M.; Mahamad, S.; Tlili, I. A Novel Framework for Potato Leaf Disease Detection Using an Efficient Deep Learning Model. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2023, 29, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, M.T.; Biswas, S.; Das, A.K.; Saha, H.N.; Chakrabarti, A.; Deb, N. Deep Learning Based Automated Disease Detection and Pest Classification in Indian Mung Bean. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 12017–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.B.; Senapati, B.; Zaidi, A.; Maaliw, R.R.; Sudman, M.S.I.; Das, D.; Almeida, F.; Sakr, H.A. Detecting Three Different Diseases of Plants by Using CNN Model and Image Processing. J. Electr. Syst. 2024, 20, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazi, X.E.; Moshou, D.; Tamouridou, A.A. Automated Leaf Disease Detection in Different Crop Species through Image Features Analysis and One Class Classifiers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, J.; Mishra, K.; Ratha, A.K.; Behera, S.K.; Sethy, P.K.; Nanthaamornphong, A. Enhancing Paddy Leaf Disease Diagnosis—A Hybrid CNN Model Using Simulated Thermal Imaging. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picon, A.; Seitz, M.; Alvarez-Gila, A.; Mohnke, P.; Ortiz-Barredo, A.; Echazarra, J. Crop Conditional Convolutional Neural Networks for Massive Multi-Crop Plant Disease Classification over Cell Phone Acquired Images Taken on Real Field Conditions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picon, A.; Alvarez-Gila, A.; Seitz, M.; Ortiz-Barredo, A.; Echazarra, J.; Johannes, A. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Capture Device-Based Crop Disease Classification in the Wild. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 161, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, H.B.; Shah, J.P.; Dabhi, V.K. Detection and Classification of Rice Plant Diseases. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2017, 11, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Imran, H.M.; Hossain, A.; Siddiqui, I.H.; Sakib, A.H. Explainable Vision Transformers for Real-time Chili and Onion Leaf Disease Identification and Diagnosis. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2025, 15, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.U.; Alam, F.; Ahmad, N.; Arshad, S. Image Processing Based System for the Detection, Identification and Treatment of Tomato Leaf Diseases. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 9431–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcharan, A.; Baranowski, K.; McCloskey, P.; Ahmed, B.; Legg, J.; Hughes, D.P. Deep Learning for Image-Based Cassava Disease Detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, A.K.; Purushothaman, R.; Prabhakar, M.; Szczepański, C. Crop Identification and Disease Classification Using Traditional Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 228–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Diepeveen, D.; Laga, H.; Gupta, S.; Jones, M.G.K.; Sohel, F. A Transformer-Based Few-Shot Learning Pipeline for Barley Disease Detection from Field-Collected Imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 109751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.H.; Salman, A.E. A Plant Disease Classification Using One-Shot Learning Technique with Field Images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 58935–58960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivam, G.; Opiyo, G.D. A Predictive Machine Learning Application in Agriculture: Cassava Disease Detection and Classification with Imbalanced Dataset Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Egypt. Inform. J. 2021, 22, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, M.G.; Vergara, A.; Ruiz, H.; Safari, N.; Elayabalan, S.; Ocimati, W.; Blomme, G. AI-Powered Banana Diseases and Pest Detection. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Selvaraj, M.; Vergara, A.; Montenegro, F.; Alonso Ruiz, H.; Safari, N.; Raymaekers, D.; Ocimati, W.; Ntamwira, J.; Tits, L.; Omondi, A.B.; et al. Detection of Banana Plants and Their Major Diseases Through Aerial Images and Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study in DR Congo and Republic of Benin. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Azam, M.F.; Lali, M.I.U.; Javed, M.Y. Detection and Classification of Citrus Diseases in Agriculture Based on Optimized Weighted Segmentation and Feature Selection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Berwal, Y.P.S.; Ghai, W. Performance Analysis of Deep Learning CNN Models for Disease Detection in Plants Using Image Segmentation. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovon, M.S.H.; Mozumder, S.J.; Pal, O.K.; Mridha, M.F.; Asai, N.; Shin, J. PlantDet: A Robust Multi-Model Ensemble Method Based on Deep Learning For Plant Disease Detection. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 34846–34859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Misra, A.K. Detection of Plant Leaf Diseases Using Image Segmentation and Soft Computing Techniques. Inf. Process. Agric. 2017, 4, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Chouhan, S.S.; Jain, S.; Jain, S. Multilayer Convolution Neural Network for the Classification of Mango Leaves Infected by Anthracnose Disease. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 43721–43729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, R.; Chatterjee, J.M.; Jhanjhi, N.; Brohi, S.N. Performance of Deep Learning vs Machine Learning in Plant Leaf Disease Detection. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 80, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, C.K.; Jaidhar, C.D.; Patil, N. Cardamom Plant Disease Detection Approach Using EfficientNetV2. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoğlu, M.; Hanbay, D. Plant Disease and Pest Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Features. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 27, 1636–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J. Vegetable Disease Detection Using an Improved YOLOv8 Algorithm in the Greenhouse Plant Environment. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cao, B.; Zhao, F.; Ning, S.; Xu, P.; Zhang, W.; Hou, X. Wheat Leaf Disease Identification Based on Deep Learning Algorithms. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 123, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; You, Z.; Zhang, L. Leaf Image Based Cucumber Disease Recognition Using Sparse Representation Classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 134, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; You, Z. Plant Diseased Leaf Segmentation and Recognition by Fusion of Superpixel, K-Means and PHOG. Optik 2018, 157, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. World Food and Agriculture—Statistical Yearbook 2024; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 978-92-5-139255-3. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Chen, W.-H. AI Meets UAVs: A Survey on AI Empowered UAV Perception Systems for Precision Agriculture. Neurocomputing 2023, 518, 242–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cai, Y.; Zhuang, P.; Li, J. Remotely Sensed Crop Disease Monitoring by Machine Learning Algorithms: A Review. Unmanned Syst. 2024, 12, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konica Minolta. Chlorophyll Meter. Available online: https://sensing.konicaminolta.eu/products/colour-measurement/chlorophyll-meter (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Bruker. BRAVO. Handheld Raman Spectrometer. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/en/products-and-solutions/raman-spectroscopy/raman-spectrometers/bravo-handheld-raman-spectrometer.html (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Aurora QPCR Device–UltraFast (FQ-8A). Aurora Biomed. Available online: https://www.aurorabiomed.com/product/ultrafast-qpcr-fq-8a/ (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Thomas, S.; Kuska, M.T.; Bohnenkamp, D.; Brugger, A.; Alisaac, E.; Wahabzada, M.; Behmann, J.; Mahlein, A.-K. Benefits of Hyperspectral Imaging for Plant Disease Detection and Plant Protection: A Technical Perspective. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2018, 125, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Rehman, T.U.; Ma, D.; Carpenter, N.R.; Tuinstra, M.R. LeafSpec: An Accurate and Portable Hyperspectral Corn Leaf Imager. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Parray, R.; Basavaraj, Y.B.; Godara, S.; Mani, I.; Kumar, R.; Khura, T.; Sarkar, S.; Ranjan, R.; Mirzakhaninafchi, H. Spectral Sensor-Based Device for Real-Time Detection and Severity Estimation of Groundnut Bud Necrosis Virus in Tomato. J. Field Robot. 2025, 42, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Zhao, B.-Y.; Aarti, A.; Yin, W.-X.; Luo, C.-X. A Single Tube RPA/Cas12a-Based Diagnostic Assay for Early, Rapid, and Efficient Detection of Botrytis Cinerea in Sweet Cherry. Plant Dis. 2025, 109, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, R.S.; Babatunde, A.N.; Ogundokun, R.O.; Yusuf, O.K.; Sadiku, P.O.; Shah, M.A. A Novel Smartphone Application for Early Detection of Habanero Disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xia, T.; Wang, H.; Tu, Z.; Tarkoma, S.; Han, Z.; Hui, P. Smartphone App Usage Analysis: Datasets, Methods, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 937–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakakis, P.; Papadopoulou, G.; Mikos, G.; Kalogiannidis, N.; Ioannidis, D.; Tzovaras, D.; Pechlivani, E.M. Smartphone-Based Citizen Science Tool for Plant Disease and Insect Pest Detection Using Artificial Intelligence. Technologies 2024, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Tzovaras, D. Generate-Paste-Blend-Detect: Synthetic Dataset for Object Detection in the Agriculture Domain. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqua, A.; Kabir, M.A.; Ferdous, T.; Ali, I.B.; Weston, L.A. Evaluating Plant Disease Detection Mobile Applications: Quality and Limitations. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, G.; Tewolde, H. Multisource Remote Sensing Field Monitoring for Improving Crop Production Management. In Proceedings of the 2021 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Virtual, 12–16 July 2021; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Alami, M.M.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Abbas, Q.; Naqvi, S.A.H.; Rao, M.J.; Mosa, W.F.A.; Abbas, Q.; et al. Drones in Plant Disease Assessment, Efficient Monitoring, and Detection: A Way Forward to Smart Agriculture. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbedo, J.G.A. Factors Influencing the Use of Deep Learning for Plant Disease Recognition. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saddik, H.; Laybros, A.; Simon, J.C.; Cointault, F. Protocol for the Definition of a Multi-Spectral Sensor for Specific Foliar Disease Detection: Case of “Flavescence Dorée”. In Phytoplasmas: Methods and Protocols; Musetti, R., Pagliari, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 213–238. ISBN 978-1-4939-8837-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, C.B.; Moharir, K.N. Application of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Role in Precision Farming and Sustainable Agriculture Under Climate Change: A Review. In Climate Change Impacts on Natural Resources, Ecosystems and Agricultural Systems; Pande, C.B., Moharir, K.N., Singh, S.K., Pham, Q.B., Elbeltagi, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 503–520. ISBN 978-3-031-19059-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, J.P.; Watt, M.S.; Pearse, G.D.; Heaphy, M.; Dungey, H.S. Assessing Very High Resolution UAV Imagery for Monitoring Forest Health during a Simulated Disease Outbreak. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Su, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.-H.; Li, J. Ir-UNet: Irregular Segmentation U-Shape Network for Wheat Yellow Rust Detection by UAV Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yi, D.; Su, B.; Mi, Z.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Chen, W.-H. Aerial Visual Perception in Smart Farming: Field Study of Wheat Yellow Rust Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Huang, W.; Du, X.; Ma, H. Monitoring Wheat Fusarium Head Blight Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Deng, J.; Lan, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Detection of Helminthosporium Leaf Blotch Disease Based on UAV Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.L.; Wiesner-Hanks, T.; Kaczmar, N.; DeChant, C.; Wu, H.; Lipson, H.; Nelson, R.J.; Gore, M.A. Quantitative Phenotyping of Northern Leaf Blight in UAV Images Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dstechuas. Humpback Whale 360 VTOL FIXED WING UAV. Available online: https://www.dstechuas.com/Humpback-Whales-320-VTOL-p3595339.html (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Farella, A.; Paciolla, F.; Quartarella, T.; Pascuzzi, S. Agricultural Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV): A Brief Overview. In Farm Machinery and Processes Management in Sustainable Agriculture; Lorencowicz, E., Huyghebaert, B., Uziak, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Recent Advancements in Autonomous Robots and Their Technical Analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6634773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Actuators and Sensors for Application in Agricultural Robots: A Review. Machines 2022, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Yuan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X. Review on Vehicle Detection Technology for Unmanned Ground Vehicles. Sensors 2021, 21, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Aggarwal, V.; Saraswat, D.; Johal, G.S. UAS and UGV-Based Disease Management System for Diagnosing Corn Diseases Above and Below the Canopy Using Deep Learning. J. ASABE 2024, 67, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agelli, M.; Corona, N.; Maggio, F.; Moi, P.V. Unmanned Ground Vehicles for Continuous Crop Monitoring in Agriculture: Assessing the Readiness of Current ICT Technology. Machines 2024, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.S.A.; Abidin, M.S.Z.; Emmanuel, A.A.; Hasan, S. Robotics and Automation in Agriculture: Present and Future Applications. Appl. Model. Simul. 2020, 4, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Menendez-Aponte, P.; Garcia, C.; Freese, D.; Defterli, S.; Xu, Y. Software and Hardware Architectures in Cooperative Aerial and Ground Robots for Agricultural Disease Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS), Orlando, FL, USA, 31 October–4 November 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Quartarella, T.; Farella, A.; Paciolla, F.; Pascuzzi, S. UVC Rays Devices Mounted on Autonomous Terrestrial Rovers: A Brief Overview. In Farm Machinery and Processes Management in Sustainable Agriculture; Lorencowicz, E., Huyghebaert, B., Uziak, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 609, pp. 378–386. ISBN 978-3-031-70954-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sujatha, K.; Reddy, T.K.; Bhavani, N.P.G.; Ponmagal, R.S.; Srividhya, V.; Janaki, N. UGVs for Agri Spray with AI Assisted Paddy Crop Disease Identification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 230, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JSUMO. ATLAS All Terrain Robot 4x4 Explorer Robot Kit (UGV Robot)|JSumo. Available online: https://www.jsumo.com/atlas-4x4-robot-mechanical-kit (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- SuperDroid. Configurable-HD2 Treaded ATR Tank Robot Platform. Available online: https://www.superdroidrobots.com/store/product=789 (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Abdulridha, J.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Kakarla, S.C.; Roberts, P. Detection of Target Spot and Bacterial Spot Diseases in Tomato Using UAV-Based and Benchtop-Based Hyperspectral Imaging Techniques. Precis. Agric. 2020, 21, 955–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkech, M.; Hafiane, A.; Canals, R. Vine Disease Detection in UAV Multispectral Images Using Optimized Image Registration and Deep Learning Segmentation Approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Hu, J.; Zhao, G.; Mei, F.; Zhang, C. An In-Field Automatic Wheat Disease Diagnosis System. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 142, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P. Disease Detection in Plants Using UAS and Deep Neural Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Tennessee State University, Nashville, TN, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Liu, C.; Coombes, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, L.; Chen, W.-H. Wheat Yellow Rust Monitoring by Learning from Multispectral UAV Aerial Imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 155, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, C.; Mahnke, M.; Sanchez, L.; Kurouski, D. Advanced Spectroscopic Techniques for Plant Disease Diagnostics. A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatabadian, A.; Neik, T.X.; Danilevicz, M.F.; Upadhyaya, S.R.; Batley, J.; Edwards, D. Image-Based Crop Disease Detection Using Machine Learning. Plant Pathol. 2025, 74, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, S.; Nishi, S.; Ohtera, R. Measurement and Estimation of Spectral Sensitivity Functions for Mobile Phone Cameras. Sensors 2021, 21, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Kalogeropoulou, E.; Klaridopoulos, C.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Christakakis, P.; Markellou, E.; Frangakis, N.; Tzovaras, D. Early Detection of Botrytis Cinerea Symptoms Using Deep Learning Multi-Spectral Image Segmentation. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terentev, A.; Dolzhenko, V.; Fedotov, A.; Eremenko, D. Current State of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Early Plant Disease Detection: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechlivani, E.M.; Papadimitriou, A.; Pemas, S.; Giakoumoglou, N.; Tzovaras, D. Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging Device for Portable Remote Sensing. Instruments 2023, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrentrapp, J.; Ria, F.; Geilhausen, M.; Panassiti, B. Detection of Gray Mold Leaf Infections Prior to Visual Symptom Appearance Using a Five-Band Multispectral Sensor. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Multispectral Imaging for Plant Food Quality Analysis and Visualization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, M.; Brown, D. Tomato Disease Detection Using Multispectral Imaging with Deep Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD), Port Louis, Mauritius, 1–2 August 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gewali, U.B.; Monteiro, S.T.; Saber, E. Machine Learning Based Hyperspectral Image Analysis: A Survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1802.08701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ji, X.; He, Q.; Gong, Z.; Sun, H.; Wen, T.; Guo, W. Monitoring of Wheat Fusarium Head Blight on Spectral and Textural Analysis of UAV Multispectral Imagery. Agriculture 2023, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Huang, W.; Du, X.; Ren, B.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, H. A Disease Index for Efficiently Detecting Wheat Fusarium Head Blight Using Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 52181–52191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, F.; Yang, H.; Feng, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhao, C.; Yang, G. Monitoring Key Wheat Growth Variables by Integrating Phenology and UAV Multispectral Imagery Data into Random Forest Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Du, T. Inversion of Winter Wheat Growth Parameters and Yield Under Different Water Treatments Based on UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 609876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Q.; Lu, J.S.; Zhang, N.; Yang, T.C.; He, J.Y.; Yao, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.X.; Tian, Y.C. Inversion of Rice Canopy Chlorophyll Content and Leaf Area Index Based on Coupling of Radiative Transfer and Bayesian Network Models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, W.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. A Comparative Assessment of Different Modeling Algorithms for Estimating Leaf Nitrogen Content in Winter Wheat Using Multispectral Images from an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumoglou, N.; Pechlivani, E.M.; Sakelliou, A.; Klaridopoulos, C.; Frangakis, N.; Tzovaras, D. Deep Learning-Based Multi-Spectral Identification of Grey Mould. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.I.; Leblon, B.; Wang, J.; Haddadi, A.; Wang, K. Detecting Infected Cucumber Plants with Close-Range Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albetis, J.; Duthoit, S.; Guttler, F.; Jacquin, A.; Goulard, M.; Poilvé, H.; Féret, J.-B.; Dedieu, G. Detection of Flavescence Dorée Grapevine Disease Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albetis, J.; Jacquin, A.; Goulard, M.; Poilvé, H.; Rousseau, J.; Clenet, H.; Dedieu, G.; Duthoit, S. On the Potentiality of UAV Multispectral Imagery to Detect Flavescence Dorée and Grapevine Trunk Diseases. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, M.; Brown, D. Early Plant Disease Detection Using Infrared and Mobile Photographs in Natural Environment. In Intelligent Computing; Arai, K., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 307–321. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, S.; Luo, J.; Tao, X.; Qiu, Z. Remote Sensing Detecting of Yellow Leaf Disease of Arecanut Based on UAV Multisource Sensors. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Lizarazo, I.; Prieto, F.; Angulo-Morales, V. Assessment of Potato Late Blight from UAV-Based Multispectral Imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 184, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Huang, W.; Huang, S.; Cui, B.; Dong, Y.; Guo, A.; Ren, Y.; Jin, Y. Identification of Banana Fusarium Wilt Using Supervised Classification Algorithms with UAV-Based Multi-Spectral Imagery. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucasbosch Spectral Sampling Rgb Multispectral Hyperspectral Imaging.Svg 2021. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Spectral_sampling_RGB_multispectral_hyperspectral_imaging.svg (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Zou, X.; Mõttus, M. Sensitivity of Common Vegetation Indices to the Canopy Structure of Field Crops. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, O.; Masenyama, A.; Sibanda, M. Spectral Saturation in the Remote Sensing of High-Density Vegetation Traits: A Systematic Review of Progress, Challenges, and Prospects. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 198, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Srivastava, S.; Jaiswal, G.; Sharma, A. Detecting Document Forgery Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. In Computer Vision and Image Processing; Raman, B., Murala, S., Chowdhury, A., Dhall, A., Goyal, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Adetutu, A.E.; Bayo, Y.F.; Emmanuel, A.A.; Opeyemi, A.-A.A. A Review of Hyperspectral Imaging Analysis Techniques for Onset Crop Disease Detection, Identification and Classification. J. For. Environ. Sci. 2024, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, G.; Rani, R.; Mangotra, H.; Sharma, A. Integration of Hyperspectral Imaging and Autoencoders: Benefits, Applications, Hyperparameter Tunning and Challenges. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2023, 50, 100584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Zou, M.; Liu, X.; Du, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Prediction of Cadmium Concentration in Brown Rice before Harvest by Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Hammersley, S.; Oerke, E.-C.; Dehne, H.-W.; Goldbach, H.; Grieve, B. Supplemental Blue LED Lighting Array to Improve the Signal Quality in Hyperspectral Imaging of Plants. Sensors 2015, 15, 12834–12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlet, N.; Sabermanesh, K.; Sadeghi-Tehran, P.; Hawkesford, M.J. Field Scanalyzer: An Automated Robotic Field Phenotyping Platform for Detailed Crop Monitoring. Funct. Plant Biol. 2017, 44, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yang, G.; Pan, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, C. A Review of Advanced Technologies and Development for Hyperspectral-Based Plant Disease Detection in the Past Three Decades. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, P. Early Plant Disease Detection Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Machine Learning and IoT. Available online: https://research.csiro.au/robotics/early-plant-disease-detection-using-hyperspectral-imaging-combined-with-machine-learning-and-iot/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Adão, T.; Hruška, J.; Pádua, L.; Bessa, J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J. Hyperspectral Imaging: A Review on UAV-Based Sensors, Data Processing and Applications for Agriculture and Forestry. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Pan, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Ding, C.; Yang, G. Development of Fusarium Head Blight Classification Index Using Hyperspectral Microscopy Images of Winter Wheat Spikelets. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 186, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, J.J.; Singh, A.; Charkowski, A.O.; Groves, R.L.; Gray, S.M.; Bethke, P.C.; Townsend, P.A. Integrating Spectroscopy with Potato Disease Management. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Jie, L.; Wang, S.; Qi, H.; Li, S. Classifying Wheat Hyperspectral Pixels of Healthy Heads and Fusarium Head Blight Disease Using a Deep Neural Network in the Wild Field. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, A.; Lee, H.S.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, Y. Prediction of Soybean Yellow Mottle Mosaic Virus in Soybean Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Plant Methods 2025, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, S.; Tian, M.; Hu, D.; Xu, M.; Yuan, T.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Wei, S. Evaluation and Early Detection of Downy Mildew of Lettuce Using Hyperspectral Imagery. Agriculture 2025, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.D.; Tan, A.J.H.; Lee, R.; Lim, W.F.; Wong, J.Y.; Suhaimi, F. Monitoring of Plant Diseases Caused by Fusarium Commune and Rhizoctonia Solani in Bok Choy Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qi, Y.; Yang, F.; Yi, X.; Guo, S.; Wu, P.; Yuan, Q.; Xu, T. Early Detection of Rice Blast Using UAV Hyperspectral Imagery and Multi-Scale Integrator Selection Attention Transformer Network (MS-STNet). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 231, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, F.; Wei, Z.; Han, G. Identification of Yellow Vein Clearing Disease in Lemons Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and Deep Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1554514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoujahed, M.B.; Rangarajan, A.K.; Whetton, R.L.; Vincke, D.; Eylenbosch, D.; Vermeulen, P.; Mouazen, A.M. Detection of Fusarium Head Blight in Wheat under Field Conditions Using a Hyperspectral Camera and Machine Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Plett, D.; Liu, H. The Promise of Hyperspectral Imaging for the Early Detection of Crown Rot in Wheat. AgriEngineering 2021, 3, 924–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.Z.; Wu, W.B.; Zheng, W.G.; Dong, D.M. The Infrared Thermal Image-Based Monitoring Process of Peach Decay under Uncontrolled Temperature Conditions. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015, 25, 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, H.; Ciechanowska, I.; Spaner, D. Application of Infrared Thermal Imaging for the Rapid Diagnosis of Crop Disease. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-118-34328-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda, M.; Barón, M.; Pérez-Bueno, M.-L. Thermal Imaging for Plant Stress Detection and Phenotyping. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Johnson, M.A.; Langston, D.B.; Mehl, H.L.; Li, S. Identifying Optimal Wavelengths as Disease Signatures Using Hyperspectral Sensor and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Yuan, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Mao, H. Tea Diseases Detection Based on Fast Infrared Thermal Image Processing Technology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3459–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohad, P.R.; Khan, S.S. Diagnosis of Leaf Health Using Grape Leaf Thermal Imaging and Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Kedah, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrodimos, N.; Lentzou, D.; Templalexis, C.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Xanthopoulos, G. Thermal and Digital Imaging Information Acquisition Regarding the Development of Aspergillus Flavus in Pistachios against Aspergillus Carbonarius in Table Grapes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidekker, M.A.; Dong, K.; Mattos, E.; van Iersel, M.W. A Very Low-Cost Pulse-Amplitude Modulated Chlorophyll Fluorometer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.-K. Plant Disease Detection by Imaging Sensors—Parallels and Specific Demands for Precision Agriculture and Plant Phenotyping. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Mali, P.; Arthur, L.; Molaei, F.; Atsyo, S.; Geng, J.; He, L.; Ghatrehsamani, S. Advanced Technologies for Precision Tree Fruit Disease Management: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 109704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, J.; Xu, H.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H. Evaluating the Potential of Airborne Hyperspectral LiDAR for Assessing Forest Insects and Diseases with 3D Radiative Transfer Modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 297, 113759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, C.; Rani, V.; Kumar, M. Advance Remote Sensing Technologies for Crop Disease and Pest Detection. In Hyperautomation in Precision Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 181–190. ISBN 978-0-443-24139-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.Y.; Shaker, A.; El-Ashmawy, N. Urban Land Cover Classification Using Airborne LiDAR Data: A Review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Pu, R.; Gonzalez-Moreno, P.; Yuan, L.; Wu, K.; Huang, W. Monitoring Plant Diseases and Pests through Remote Sensing Technology: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husin, N.A.; Khairunniza-Bejo, S.; Abdullah, A.F.; Kassim, M.S.M.; Ahmad, D.; Azmi, A.N.N. Application of Ground-Based LiDAR for Analysing Oil Palm Canopy Properties on the Occurrence of Basal Stem Rot (BSR) Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.; Zhou, J.; Bhuiyan, S.A.; Adhikari, P.; Tuxworth, G.; Ford, R.; Gao, Y. Early Detection of Sugarcane Smut and Mosaic Diseases via Hyperspectral Imaging and Spectral-Spatial Attention Deep Neural Networks. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, I.; Phadikar, S.; Majumder, K.; Mukherjee, H.; Sau, A. A Novel Plant Disease Prediction Model Based on Thermal Images Using Modified Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenkamp, D.; Behmann, J.; Mahlein, A.-K. In-Field Detection of Yellow Rust in Wheat on the Ground Canopy and UAV Scale. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenkamp, D.; Kuska, M.T.; Mahlein, A.-K.; Behmann, J. Hyperspectral Signal Decomposition and Symptom Detection of Wheat Rust Disease at the Leaf Scale Using Pure Fungal Spore Spectra as Reference. Plant Pathol. 2019, 68, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; De Silva, M. Plant Disease Detection on Multispectral Images Using Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the 25th Irish Machine Vision and Image Processing Conference (IMVIP), Galway, Ireland, 30 August–1 September 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, D.; Zhang, H.; Pérez, J.A.S.; Yang, X.; Li, M. Early Diagnosis of Greenhouse Cucumber Downy Mildew in Seedling Stage Using Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging Technology. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 242, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, K.; Yadav, S.A.; Kansal, L.; Adilakshmi, J.; Kaliyaperumal, G.; Albawi, A. Fusion of Hyperspectral Imaging and Convolutional Neural Networks for Early Detection of Crop Diseases in Precision Agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Communication, Computer Sciences and Engineering (IC3SE), Gautam Buddha Nagar, India, 9–11 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1172–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Hong, D.; Li, C.; Yao, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chanussot, J. RustQNet: Multimodal Deep Learning for Quantitative Inversion of Wheat Stripe Rust Disease Index. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, H.; Lv, X.; Yang, L.; Shang, J.; Sun, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, B.; Wu, J.; et al. Applying Convolutional Neural Networks for Detecting Wheat Stripe Rust Transmission Centers under Complex Field Conditions Using RGB-Based High Spatial Resolution Images from UAVs. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, I.; Khan, M.A.; Nazir, M.; Hamza, A.; Alqahtani, O.; Alouane, M.T.-H.; Masood, A. Crops Leaf Disease Recognition From Digital and RS Imaging Using Fusion of Multi Self-Attention RBNet Deep Architectures and Modified Dragonfly Optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 7260–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win Kent, O.; Weng Chun, T.; Lee Choo, T.; Weng Kin, L. Early Symptom Detection of Basal Stem Rot Disease in Oil Palm Trees Using a Deep Learning Approach on UAV Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkech, M.; Hafiane, A.; Canals, R. Deep Leaning Approach with Colorimetric Spaces and Vegetation Indices for Vine Diseases Detection in UAV Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 155, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.H.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Cao, A.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Cheng, T.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; et al. Early Detection of Powdery Mildew Disease and Accurate Quantification of Its Severity Using Hyperspectral Images in Wheat. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, U.; Matros, A.; Petrovic, T.; Zanker, T.; Scott, E.S.; Seiffert, U. Improved Classification Accuracy of Powdery Mildew Infection Levels of Wine Grapes by Spatial-Spectral Analysis of Hyperspectral Images. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, L.; Lee, H.S.; Tayade, R.; Ghimire, A.; Chung, Y.S.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, Y. Evaluation of Soybean Wildfire Prediction via Hyperspectral Imaging. Plants 2023, 12, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucker, M.; Wahabzada, M.; Kersting, K.; Peter, M.; Beyer, W.; Steiner, U.; Mahlein, A.-K.; Oerke, E.-C. Hyperspectral Imaging Reveals the Effect of Sugar Beet Quantitative Trait Loci on Cercospora Leaf Spot Resistance. Funct. Plant Biol. 2016, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Huang, W.; Dong, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, A. Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery to Detect Winter Wheat Fusarium Head Blight. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Alisaac, E.; Al Masri, A.; Behmann, J.; Dehne, H.-W.; Oerke, E.-C. Comparison and Combination of Thermal, Fluorescence, and Hyperspectral Imaging for Monitoring Fusarium Head Blight of Wheat on Spikelet Scale. Sensors 2019, 19, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Kuska, M.T.; Thomas, S.; Bohnenkamp, D.; Alisaac, E.; Behmann, J.; Wahabzada, M.; Kersting, K. Plant Disease Detection by Hyperspectral Imaging: From the Lab to the Field. Adv. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 8, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, P.; Ward, D.; Goan, E.; Jayawardena, S.; Sikka, P.; Hernandez, E. Plant Disease Detection Using Hyperspectral Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Sydney, Australia, 29 November–1 December 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, C.; Sagan, V.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Bhadra, S.; Kwasniewski, M.T. Early Detection of Plant Viral Disease Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Ji, S.; Xuan, G.; Ren, Y.; Feng, W.; Jia, H.; Wang, Q.; He, S. Detection and Analysis of Chili Pepper Root Rot by Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Agronomy 2024, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Zhang, L.; Tian, J.; Yu, Q.; Lang, C. ToT-Net: A Generalized and Real-Time Crop Disease Detection Framework via Task-Level Meta-Learning and Lightweight Multi-Scale Transformer. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 12, 101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásconez, J.P.; Vásconez, I.N.; Moya, V.; Calderón-Díaz, M.J.; Valenzuela, M.; Besoain, X.; Seeger, M.; Auat Cheein, F. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Visual Symptoms of Bacterial Wilt Disease Caused by Ralstonia Solanacearum in Tomato Plants. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, R.; Balaji, G.N. Balancing Composite Motion Optimization Using R-ERNN with Plant Disease. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 154, 111288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Song, Z.; Xie, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Q. Detection of Rice Leaf SPAD and Blast Disease Using Integrated Aerial and Ground Multiscale Canopy Reflectance Spectroscopy. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Lv, J.; Cen, H.; He, M.; Zeng, Y.; Hua, S.; Li, H.; Meng, Y.; Fang, H.; He, Y. Hyperspectral Reflectance Imaging Combined with Carbohydrate Metabolism Analysis for Diagnosis of Citrus Huanglongbing in Different Seasons and Cultivars. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 275, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterich, C.B.; de Oliveira Neves, R.F.; Belasque, J.; Marcassa, L.G. Detection of Citrus Canker and Huanglongbing Using Fluorescence Imaging Spectroscopy and Support Vector Machine Technique. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetterich, C.B.; de Oliveira Neves, R.F.; Belasque, J.; Ehsani, R.; Marcassa, L.G. Detection of Huanglongbing in Florida Using Fluorescence Imaging Spectroscopy and Machine-Learning Methods. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Plett, D.; Evans, M.; Garrard, T.; Butt, M.; Clarke, K.; Liu, H. Hyperspectral Imaging Detects Biological Stress of Wheat for Early Diagnosis of Crown Rot Disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Fang, X.; Yang, W.; Xu, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Y. Multiple Light Sources Excited Fluorescence Image-Based Non-Destructive Method for Citrus Huanglongbing Disease Detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Camino, C.; Beck, P.S.A.; Calderon, R.; Hornero, A.; Hernández-Clemente, R.; Kattenborn, T.; Montes-Borrego, M.; Susca, L.; Morelli, M.; et al. Previsual Symptoms of Xylella Fastidiosa Infection Revealed in Spectral Plant-Trait Alterations. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, F.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Detection of Wheat Powdery Mildew by Differentiating Background Factors Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Huang, W.; Cui, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L. New Spectral Index for Detecting Wheat Yellow Rust Using Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Elazab, A.; Bort, J.; Vergara, O.; Serret, M.D.; Araus, J.L. Low-Cost Assessment of Wheat Resistance to Yellow Rust through Conventional RGB Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 116, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran Pandiri, D.N.; Murugan, R.; Goel, T.; Sharma, N.; Singh, A.K.; Sen, S.; Baruah, T. POT-Net: Solanum Tuberosum (Potato) Leaves Diseases Classification Using an Optimized Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Imaging Sci. J. 2022, 70, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Shah, B.; Hussain, T.; Ali, A.; Ullah, A.; Alenezi, F.; Gechev, T.; Ali, F.; Syed, I. A Deep Learning-Based Model for Plant Lesion Segmentation, Subtype Identification, and Survival Probability Estimation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1095547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Shah, B.; EI-Sappagh, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, A.; Alenezi, F.; Gechev, T.; Hussain, T.; Ali, F. An Advanced Deep Learning Models-Based Plant Disease Detection: A Review of Recent Research. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1158933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, S.A.A.; Huang, N.-F.; Wani, T.M.; Bhat, S.A. Advances and Challenges in Computer Vision for Image-Based Plant Disease Detection: A Comprehensive Survey of Machine and Deep Learning Approaches. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 2639–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmi, Y.; Gangwar, S. A Leaf Image Localization Based Algorithm for Different Crops Disease Classification. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 456–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y. Leaf Disease Image Retrieval with Object Detection and Deep Metric Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 963302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülmez, B. A Novel Deep Learning Model with the Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm for Cotton Disease Detection. JUCS-J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2023, 29, 595–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülmez, B. Advancements in Rice Disease Detection through Convolutional Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-Y.; Lin, I.-A.; Yu, J.-Y.; Yang, J.; Chang, Y.-C. High Efficiency Disease Detection for Potato Leaf with Convolutional Neural Network. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafik, W.; Tufail, A.; Namoun, A.; De Silva, L.C.; Apong, R.A.A.H.M. A Systematic Literature Review on Plant Disease Detection: Motivations, Classification Techniques, Datasets, Challenges, and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 59174–59203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Conrad, A.O.; Flower, C.E.; Pinchot, C.C.; Hayes-Plazolles, N.; Chen, Z.; Song, Z.; Fei, S.; Jin, J. Machine Learning-Based Spectral and Spatial Analysis of Hyper- and Multi-Spectral Leaf Images for Dutch Elm Disease Detection and Resistance Screening. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2023, 10, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, J.; Khan, I.; Ali, G.; Almotiri, S.H.; AlGhamdi, M.A.; Masood, K. Multi-Level Deep Learning Model for Potato Leaf Disease Recognition. Electronics 2021, 10, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheed, K.; Qureshi, I.; Abbas, F.; Jabbar, S.; Abbas, Q.; Ahmad, H.; Sajid, M.Z. EfficientRMT-Net—An Efficient ResNet-50 and Vision Transformers Approach for Classifying Potato Plant Leaf Diseases. Sensors 2023, 23, 9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoubi, S.; Jawarneh, M.; Bsoul, Q.; Keshta, I.; Soni, M.; Khan, M.A. An Advanced Approach for Fig Leaf Disease Detection and Classification: Leveraging Image Processing and Enhanced Support Vector Machine Methodology. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Cao, H. Rice Blast Disease Recognition Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvanshi, A.; Singh, U.K.; Sajja, G.S.; Pallathadka, H.; Asenso, E.; Kamal, M.; Singh, A.; Phasinam, K. Intrusion Detection Using Machine Learning for Risk Mitigation in IoT-Enabled Smart Irrigation in Smart Farming. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 3955514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kaur, R. Plant Disease Detection Using Image Processing—A Review. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 124, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, V.; Mall, A.K. Harnessing Image Processing for Precision Disease Diagnosis in Sugar Beet Agriculture. Crop Des. 2024, 3, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothen, M.E.; Pai, M.L. Detection of Rice Leaf Diseases Using Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Fourth International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 11–13 March 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Shah, J.H.; ur Rehman, M.H.; Javed, K. An Automated Detection and Classification of Citrus Plant Diseases Using Image Processing Techniques: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 153, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisamy, J.; Rethnaraj, J. Disease Segmentation in Groundnut Crop Leaves Using Image Processing Techniques. In Proceedings of the Innovations and Advances in Cognitive Systems; Ragavendiran, S.D.P., Pavaloaia, V.D., Mekala, M.S., Cabezuelo, A.S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Elaziz, M.A.; Oliva, D.; Ewees, A.A.; Xiong, S. Multi-Level Thresholding-Based Grey Scale Image Segmentation Using Multi-Objective Multi-Verse Optimizer. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 125, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.S.; Singh, U.P.; Jain, S. Applications of Computer Vision in Plant Pathology: A Survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 611–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesejo, P.; Ibáñez, Ó.; Cordón, Ó.; Cagnoni, S. A Survey on Image Segmentation Using Metaheuristic-Based Deformable Models: State of the Art and Critical Analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 44, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitoun, N.M.; Aqel, M.J. Survey on Image Segmentation Techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 65, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.G.; Deepa, J.; Rao, P.V.; Divya, V.; Kaviarasan, S. An Automated Segmentation and Classification Model for Banana Leaf Disease Detection. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Ma, X.; Xie, X.; Ren, G.; Ma, Y. Classification of Visible and Infrared Hyperspectral Images Based on Image Segmentation and Edge-Preserving Filtering. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 81, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, V.K.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, B. Plant Disease Detection Using Computational Intelligence and Image Processing. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2021, 128, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmad, A.; Hapsari, R.K.; Setiawan, W.; Indriyani, T.; Rochman, E.M.S.; Satoto, B.D. Classification of Tobacco Leaf Quality Using Feature Extraction of Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (GLCM) and K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN). In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Neural Networks and Machine Learning 2022 (ICONNSMAL 2022); Agustin, I.H., Ed.; Advances in Intelligent Systems Research. Atlantis Press International BV: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 177, pp. 30–38, ISBN 978-94-6463-173-9. [Google Scholar]
- Muzaffar, A.W.; Riaz, F.; Abuain, T.; Abu-Ain, W.A.K.; Hussain, F.; Farooq, M.U.; Azad, M.A. Gabor Contrast Patterns: A Novel Framework to Extract Features From Texture Images. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 60324–60334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Qian, Y.; EL-Mesery, H.S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, A.; Tang, J. Rapid Detection of Rice Disease Using Microscopy Image Identification Based on the Synergistic Judgment of Texture and Shape Features and Decision Tree–Confusion Matrix Method. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6589–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Hussain, T.; Shah, B.; Ullah, I.; Shah, S.M.; Ali, F.; Park, S.H. Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Classification of Leaf Images for Detection of Tomato Plant Disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1031748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linardatos, P.; Papastefanopoulos, V.; Kotsiantis, S. Explainable AI: A Review of Machine Learning Interpretability Methods. Entropy 2020, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Pandey, S.; Goel, S. Plants Disease Identification and Classification Through Leaf Images: A Survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 507–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, S.M.; Banakar, A.; Rahnama, K.; Vakilian, K.A.; Ampatzidis, Y. Feature Engineering to Identify Plant Diseases Using Image Processing and Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, L.; Nagpal, J. A Systematic Review of Recent Machine Learning Techniques for Plant Disease Identification and Classification. IETE Tech. Rev. 2023, 40, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakate, M.; Ingole, A.B. Diagnosis of Pomegranate Plant Diseases Using Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fifth National Conference on Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Image Processing and Graphics (NCVPRIPG), Patna, India, 16–19 December 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, M.; Deisy, C. Disease Detection and Classification in Agricultural Plants Using Convolutional Neural Networks—A Visual Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 7–8 March 2019; pp. 1063–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Saragih, T.H.; Fajri, D.M.N.; Rakhmandasari, A. Comparative Study of Decision Tree, K-Nearest Neighbor, and Modified K-Nearest Neighbor on Jatropha Curcas Plant Disease Identification. Kinet. Game Technol. Inf. Syst. Comput. Netw. Comput. Electron. Control 2020, 5, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, C.U.; Jeevan Prasad, S.; Mounika, G. Leaf Disease Detection: Feature Extraction with K-Means Clustering and Classification with ANN. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 27–29 March 2019; pp. 1095–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Padol, P.B.; Yadav, A.A. SVM Classifier Based Grape Leaf Disease Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Advances in Signal Processing (CASP), Pune, India, 9–11 June 2016; pp. 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, A.; Chug, A.; Singh, A.P. Hybrid SVM-LR Classifier for Powdery Mildew Disease Prediction in Tomato Plant. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 27–28 February 2020; pp. 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahidi, T.R.; Irfanul Alam, S.M.; Momen, S. Rice Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 4.0 (STI), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 24–25 December 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Harakannanavar, S.S.; Rudagi, J.M.; Puranikmath, V.I.; Siddiqua, A.; Pramodhini, R. Plant Leaf Disease Detection Using Computer Vision and Machine Learning Algorithms. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2022, 3, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Yadav, P.K. Plant Disease Detection Using Machine Learning Approaches. Expert Syst. 2023, 40, e13136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, B.; Jaina, T.; Katpally, G.; Kankipati, G.; Rajyalakshmi, C. Image Based Plant Disease Detection Using Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2024 Fourth International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Computing, Communication and Sustainable Technologies (ICAECT), Bhilai, India, 11–12 January 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, R.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, S.; Zou, X. Plant Disease Recognition Model Based on Improved YOLOv5. Agronomy 2022, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albattah, W.; Nawaz, M.; Javed, A.; Masood, M.; Albahli, S. A Novel Deep Learning Method for Detection and Classification of Plant Diseases. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglani, A.; Kumar, N. Deep Learning Models for Traffic Flow Prediction in Autonomous Vehicles: A Review, Solutions, and Challenges. Veh. Commun. 2019, 20, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, V.; Bedi, P. High Performance Adaptive Traffic Control for Efficient Response in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 16, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.G.; Suresh Kumar, B.; Narang, G. Recommender System for Health Care Analysis Using Machine Learning Technique: A Review. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2022, 23, 613–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kaur, K.; Kumar, N.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Hybrid Deep-Learning-Based Anomaly Detection Scheme for Suspicious Flow Detection in SDN: A Social Multimedia Perspective. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astani, M.; Hasheminejad, M.; Vaghefi, M. A Diverse Ensemble Classifier for Tomato Disease Recognition. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Zafar, N.; Tahir, M.N.; Aqib, M.; Saleem, S.; Haroon, Z. Deep Learning-Based Approach for Weed Detection in Potato Crops. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 23, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Arrouays, D.; Leatitia Mulder, V.; Poggio, L.; Minasny, B.; Roudier, P.; Libohova, Z.; Lagacherie, P.; Shi, Z.; Hannam, J.; et al. Digital Mapping of GlobalSoilMap Soil Properties at a Broad Scale: A Review. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Shi-Quan, S.; Wei, G. Maize Seedling and Weed Detection Based on MobileNetv3-YOLOv4. In Proceedings of the 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC), Beijing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 5679–5683. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.-L.; Chuang, T.-C.; Liao, Y.-C. Application of Transfer Learning and Image Augmentation Technology for Tomato Pest Identification. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2022, 33, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, G. Deep Learning: A Critical Appraisal. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.00631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Li, Y. Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Symmetry 2017, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.P.; Salathe, M. An Open Access Repository of Images on Plant Health to Enable the Development of Mobile Disease Diagnostics. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.08060. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Saraswat, D.; El Gamal, A. A Survey on Using Deep Learning Techniques for Plant Disease Diagnosis and Recommendations for Development of Appropriate Tools. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbedo, J.G.A.; Koenigkan, L.V.; Halfeld-Vieira, B.A.; Costa, R.V.; Nechet, K.L.; Godoy, C.V.; Junior, M.L.; Patricio, F.R.A.; Talamini, V.; Chitarra, L.G.; et al. Annotated Plant Pathology Databases for Image-Based Detection and Recognition of Diseases. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2018, 16, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Jain, N.; Jain, P.; Kayal, P.; Kumawat, S.; Batra, N. PlantDoc: A Dataset for Visual Plant Disease Detection. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM IKDD CoDS and 25th COMAD, Hyderabad, India, 5–7 January 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner-Hanks, T.; Stewart, E.L.; Kaczmar, N.; DeChant, C.; Wu, H.; Nelson, R.J.; Lipson, H.; Gore, M.A. Image Set for Deep Learning: Field Images of Maize Annotated with Disease Symptoms. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parraga-Alava, J.; Cusme, K.; Loor, A.; Santander, E. RoCoLe: A Robusta Coffee Leaf Images Dataset for Evaluation of Machine Learning Based Methods in Plant Diseases Recognition. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewola, D.O.; Dada, E.G.; Misra, S.; Damaševičius, R. Detecting Cassava Mosaic Disease Using a Deep Residual Convolutional Neural Network with Distinct Block Processing. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Deep Learning in Agriculture: A Survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, F.; Sufian, A.; Dutta, P. Advancements in Image Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Research in Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (ICRCICN), Kolkata, India, 22–23 November 2018; pp. 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9905, pp. 21–37. ISBN 978-3-319-46447-3. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8693, pp. 740–755. ISBN 978-3-319-10601-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, R.; Aslam, W.; Aziz, R.; Aldehim, G. An Early and Smart Detection of Corn Plant Leaf Diseases Using IoT and Deep Learning Multi-Models. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 23149–23162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahari, E.A.; Aldehim, G.; Aljebreen, M.; Alqurni, J.S.; Salama, A.S.; Abdelbagi, S. Internet of Things Assisted Plant Disease Detection and Crop Management Using Deep Learning for Sustainable Agriculture. IEEE Access 2024, 13, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamasneh, A.R.; Ibrahim, R.W. Classification of Tomato Leaf Images for Detection of Plant Disease Using Conformable Polynomials Image Features. MethodsX 2024, 13, 102844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhwaiti, Y.; Khan, M.; Asim, M.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Ishaq, M.; Alruwaili, M. Leveraging YOLO Deep Learning Models to Enhance Plant Disease Identification. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwinkumar, S.; Rajagopal, S.; Manimaran, V.; Jegajothi, B. Automated Plant Leaf Disease Detection and Classification Using Optimal MobileNet Based Convolutional Neural Networks. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Devendran, V. A Novel Framework for Semi-Automated System for Grape Leaf Disease Detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 50733–50755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Meng, W.; Zhou, X. SerpensGate-YOLOv8: An Enhanced YOLOv8 Model for Accurate Plant Disease Detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1514832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivya Lakshmi, R.T.; Katiravan, J.; Visu, P. CoDet: A Novel Deep Learning Pipeline for Cotton Plant Detection and Disease Identification. Automatika 2024, 65, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, L.N.B.; Bharathy, A.M.V.; Ramakuri, S.K.; Sethy, A.; Kumar, R. An Optimized Machine Learning Framework for Crop Disease Detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, P.; Tyagi, A.K.; N, K. A Crop Disease Severity Index Derived from Transfer Learning and Feature Fusion Using Enhanced OPTICS Algorithm. Int. J. Hybrid Intell. Syst. 2024, 20, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Rubio, V.; Rovira-Más, F. From Smart Farming towards Agriculture 5.0: A Review on Crop Data Management. Agronomy 2020, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Chen, J. A Survey of Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence, and Edge Computing for Web 3.0. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2024, 54, 100667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makondo, N.; Kobo, H.I.; Mathonsi, T.E.; Mamushiane, L. A Review on Edge Computing in 5G-Enabled IoT for Agricultural Applications: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET), Cape Town, South Africa, 16–17 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sucharitha, V.; Prakash, P.; Iyer, G.N. Agrifog—A Fog Computing Based IoT for Smart Agriculture. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 7, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Liyanage, M.; Porambage, P.; Ding, A.Y.; Kalla, A. Driving Forces for Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) IoT Integration in 5G. ICT Express 2021, 7, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, F.; Nocera, G.; Bruneo, D.; Tomaselli, V.; Giacalone, D.; Das, S.K. Porting Deep Neural Networks on the Edge via Dynamic K-Means Compression: A Case Study of Plant Disease Detection. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2021, 75, 101437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Li, K.-C.; Li, Z.; Han, Q.; Fan, W. Recognition of Crop Diseases Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution in Edge Computing. Sensors 2020, 20, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, X. Edge Computing Driven Data Sensing Strategy in the Entire Crop Lifecycle for Smart Agriculture. Sensors 2021, 21, 7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizik, T. How Can Precision Farming Work on a Small Scale? A Systematic Literature Review. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 384–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundal, G.S.; Laux, C.M.; Buckmaster, D.; Sutton, M.J.; Langemeier, M. Exploring Barriers to the Adoption of Internet of Things-Based Precision Agriculture Practices. Agriculture 2023, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbi, N.; Gumbi, L.; Twinomurinzi, H. Towards Sustainable Digital Agriculture for Smallholder Farmers: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP. Precision Agriculture for Smallholder Farmers. Available online: https://www.undp.org/publications/precision-agriculture-smallholder-farmers (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Bahmutsky, S.; Grassauer, F.; Arulnathan, V.; Pelletier, N. A Review of Life Cycle Impacts and Costs of Precision Agriculture for Cultivation of Field Crops. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 52, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebsi, R.; Mami, S.; Chokmani, K. Drones in Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Review of Applications, Technologies, and Challenges. Drones 2024, 8, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPH. Engineering Hyperspectral Cameras and Drones: A Practical Guide. Available online: https://www.sphengineering.com/news/hyperspectral-cameras-and-drones-a-practical-guide (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Candrone Buy Multispectral Sensors & Cameras For Drones. Available online: https://candrone.com/collections/multispectral-sensors (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Ouster. Digital Lidar Sensors for Automation, Drones & Robotics|Ouster. Available online: https://ouster.com/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Agrawal, J.; Arafat, M.Y. Transforming Farming: A Review of AI-Powered UAV Technologies in Precision Agriculture. Drones 2024, 8, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClearPath Robotics Warthog Unmanned Ground Vehicle Robot—Clearpath. Available online: https://clearpathrobotics.com/warthog-unmanned-ground-vehicle-robot/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Javidan, S.M.; Banakar, A.; Vakilian, K.A.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Rahnama, K. Diagnosing the Spores of Tomato Fungal Diseases Using Microscopic Image Processing and Machine Learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 67283–67301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, X. An Approach for Validating Quality of Datasets for Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 December 2018; pp. 2795–2803. [Google Scholar]
- Dhiman, P.; Kukreja, V.; Manoharan, P.; Kaur, A.; Kamruzzaman, M.M.; Dhaou, I.B.; Iwendi, C. A Novel Deep Learning Model for Detection of Severity Level of the Disease in Citrus Fruits. Electronics 2022, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulridha, J.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Qureshi, J.; Roberts, P. Identification and Classification of Downy Mildew Severity Stages in Watermelon Utilizing Aerial and Ground Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 791018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo Da Cunha, V.A.; Hariharan, J.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Roberts, P.D. Early Detection of Tomato Bacterial Spot Disease in Transplant Tomato Seedlings Utilising Remote Sensing and Artificial Intelligence. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 234, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B. Plant Disease Detection and Classification by Deep Learning—A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 56683–56698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguven, M.M.; Yanar, Y. The Technology Uses in the Determination of Sugar Beet Diseases. In Sugar Beet Cultivation, Management and Processing; Misra, V., Srivastava, S., Mall, A.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 621–642. ISBN 978-981-19273-0-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ouhami, M.; Hafiane, A.; Es-Saady, Y.; El Hajji, M.; Canals, R. Computer Vision, IoT and Data Fusion for Crop Disease Detection Using Machine Learning: A Survey and Ongoing Research. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallau, L.; Neumann, M.; Klatt, B.; Kleinhenz, B.; Klein, T.; Kuhn, C.; Röhrig, M.; Bauckhage, C.; Kersting, K.; Mahlein, A.-K.; et al. Automated Identification of Sugar Beet Diseases Using Smartphones. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bhatele, A. Exploiting Sparsity in Pruned Neural Networks to Optimize Large Model Training; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Wagle, S.A.; Harikrishnan, R.; Kotecha, K. Bilinear LSTM with Bayesian Gaussian Optimization for Predicting Tomato Plant Disease Using Meteorological Parameters. Ingénierie Systèmes Inf. 2024, 29, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Chi, Y.; Shi, D. Construction and Validation of Peanut Leaf Spot Disease Prediction Model Based on Long Time Series Data and Deep Learning. Agronomy 2024, 14, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzakari, S.A.; Alhussan, A.A.; Qenawy, A.-S.T.; Elshewey, A.M. Early Detection of Potato Disease Using an Enhanced Convolutional Neural Network-Long Short-Term Memory Deep Learning Model. Potato Res. 2025, 68, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).