High Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein ITIH5 in Cholangiocarcinomas Correlates with a Favorable Prognosis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Bioprobes/Data Collection
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Reverse Transcription PCR
2.5. Semiquantitative Real-Time PCR
2.6. Pyrosequencing
2.7. In Vitro Demethylation
2.8. Protein Isolation from Cells and Western Blot
2.9. Stable Transfection of EGI-1 and CCC-5 Cells
2.10. XTT Assay
2.11. CFA Assay
2.12. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Expression of ITIH5 Is Strongly Upregulated in Cholangiocarcinoma with Special Emphasis in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (iCCAs)
3.2. Abundant ITIH5 Expression in CCA Is Associated with Favorable Overall Survival
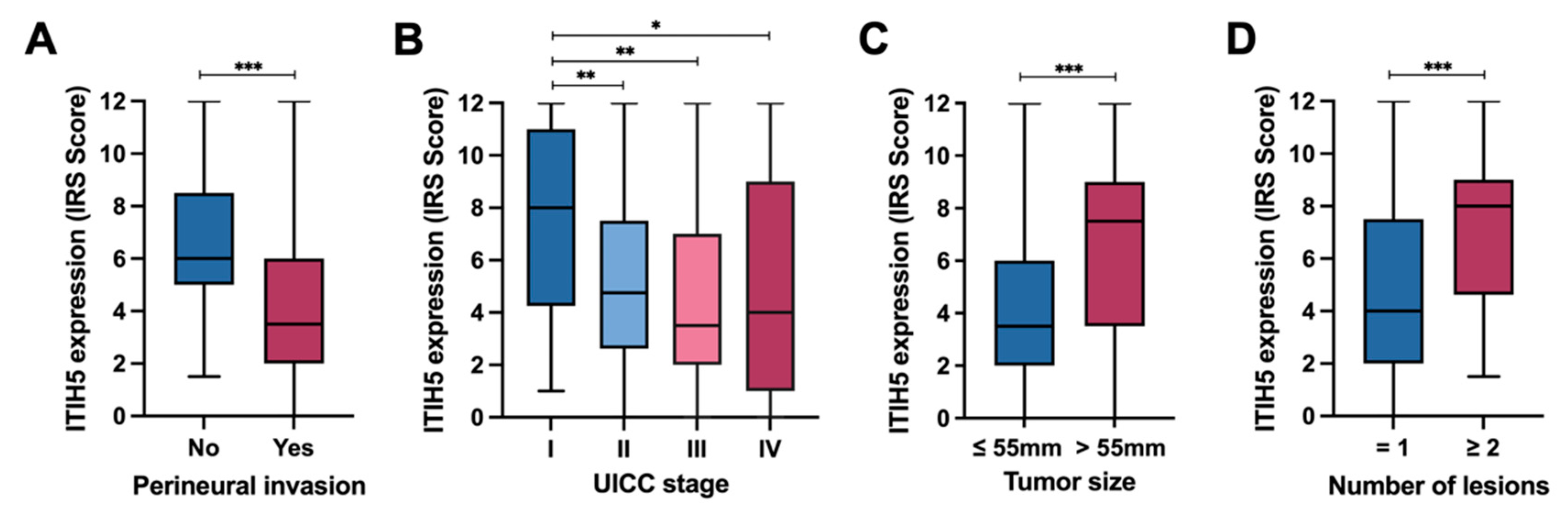
3.3. ITIH5 Expression in CCAs in Relation to Perineural Invasion and UICC Tumor Stages
3.4. ITIH5 Re-Expression in Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines May Impair Colony Growth but Not Cell Proliferation
3.5. ITIH5 mRNA Expression Correlates with Promoter Hypomethylation in CCAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Folseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, S.I.; Khan, S.A.; Hallemeier, C.L.; Kelley, R.K.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma—Evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montal, R.; Sia, D.; Montironi, C.; Leow, W.Q.; Esteban-Fabró, R.; Pinyol, R.; Torres-Martin, M.; Bassaganyas, L.; Moeini, A.; Peix, J.; et al. Molecular classification and therapeutic targets in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, M.J.; DeCarli, K.; Bash, K.; Sun, G.; Almhanna, K. Current and Emerging Therapeutic Targets for the Treatment of Cholangiocarcinoma: An Updated Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blechacz, B. Cholangiocarcinoma: Current Knowledge and New Developments. J. Chest Surg. 2017, 11, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Heij, L.R.; Czigany, Z.; Dahl, E.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Luedde, T.; Neumann, U.P.; Bednarsch, J. The role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in cholangiocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, M.A.; Ptashkin, R.; Jordan, E.; Berger, M.F.; Zehir, A.; Capanu, M.; Kemeny, N.E.; O’Reilly, E.M.; El-Dika, I.; Jarnagin, W.R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Intrahepatic and Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas: Potential Targets for Intervention. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4154–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.I.; Gores, G.J. Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management of Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavolari, S.; Brandi, G. Mutational Landscape of Cholangiocarcinoma According to Different Etiologies: A Review. Cells 2023, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, Y.; Bowlus, C.L.; Yang, G.; Leung, P.S.C.; Gershwin, M.E. Cholangiocarcinoma in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, T.; Hiromichi, I. Biliary Parasitic Diseases Associated with Hepatobiliary Carcinoma. Visc. Med. 2023, 39, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blechacz, B.; Komuta, M.; Roskams, T.; Gores, G.J. Clinical diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.W.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, J.; Woo, S.M.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, K.H.; Hwang, J.H. Gemcitabine Plus Cisplatin Chemotherapy Prolongs the Survival in Advanced Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma: A Large Multicenter Study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esnaola, N.F.; Meyer, J.E.; Karachristos, A.; Maranki, J.L.; Camp, E.R.; Denlinger, C.S. Evaluation and management of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer 2016, 122, 1349–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelfarb, M.; Klopocki, E.; Grube, S.; Staub, E.; Klaman, I.; Hinzmann, B.; Kristiansen, G.; Rosenthal, A.; Durst, M.; Dahl, E. ITIH5, a novel member of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain family is downregulated in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2004, 204, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Kloten, V.; Noetzel, E.; Gola, L.; Ehling, J.; Heide, T.; Meurer, S.K.; Gaiko-Shcherbak, A.; Sechi, A.S.; Huth, S.; et al. ITIH5 mediates epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, E.; Villwock, S.; Habenberger, P.; Choidas, A.; Rose, M.; Klebl, B.M. White Paper: Mimetics of Class 2 Tumor Suppressor Proteins as Novel Drug Candidates for Personalized Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Meurer, S.K.; Kloten, V.; Weiskirchen, R.; Denecke, B.; Antonopoulos, W.; Deckert, M.; Knuchel, R.; Dahl, E. ITIH5 induces a shift in TGF-beta superfamily signaling involving Endoglin and reduces risk for breast cancer metastasis and tumor death. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Gaisa, N.T.; Antony, P.; Fiedler, D.; Heidenreich, A.; Otto, W.; Denzinger, S.; Bertz, S.; Hartmann, A.; Karl, A.; et al. Epigenetic inactivation of ITIH5 promotes bladder cancer progression and predicts early relapse of pT1 high-grade urothelial tumours. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyam, K.; Harihar, S. An Overview on the Emerging Role of the Plasma Protease Inhibitor Protein ITIH5 as a Metastasis Suppressor. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, J.; Sechi, A.; Hain, J.; Villwock, S.; Ha, S.A.; Hauschulz, M.; Rose, M.; Steib, F.; Ortiz-Brüchle, N.; Heij, L.; et al. ITIH5 as a multifaceted player in pancreatic cancer suppression, impairing tyrosine kinase signaling, cell adhesion and migration. Mol. Oncol. 2024, 18, 1486–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, O.; Jia, X.; Zhang, H. Long noncoding RNA LINC00261 upregulates ITIH5 to impair tumorigenic ability of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Kurahara, H.; Young, E.D.; Natsugoe, S.; Ijichi, A.; Iwakuma, T.; Welch, D.R. Genome-wide in vivo RNAi screen identifies ITIH5 as a metastasis suppressor in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2017, 34, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.D.; Manley, S.J.; Beadnell, T.C.; Shearin, A.E.; Sasaki, K.; Zimmerman, R.; Kauffman, E.; Vivian, C.J.; Parasuram, A.; Iwakuma, T.; et al. Suppression of pancreatic cancer liver metastasis by secretion-deficient ITIH5. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloten, V.; Rose, M.; Kaspar, S.; von Stillfried, S.; Knüchel, R.; Dahl, E. Epigenetic inactivation of the novel candidate tumor suppressor gene ITIH5 in colon cancer predicts unfavorable overall survival in the CpG island methylator phenotype. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeck, J.; Chorovicer, M.; Naami, A.; Breuer, E.; Zafrakas, M.; Bektas, N.; Durst, M.; Kristiansen, G.; Wild, P.J.; Hartmann, A.; et al. The extracellular matrix protein ITIH5 is a novel prognostic marker in invasive node-negative breast cancer and its aberrant expression is caused by promoter hypermethylation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, S.; Huth, L.; Marquardt, Y.; Fietkau, K.; Dahl, E.; Esser, P.R.; Martin, S.F.; Heise, R.; Merk, H.F.; Baron, J.M. Inter-α-Trypsin Inhibitor Heavy Chain 5 (ITIH5) Is a Natural Stabilizer of Hyaluronan That Modulates Biological Processes in the Skin. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 33, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Midgley, A.; Meran, S.; Woods, E.; Bowen, T.; Phillips, A.O.; Steadman, R. Tumor Necrosis Factor-stimulated Gene 6 (TSG-6)-mediated Interactions with the Inter-α-inhibitor Heavy Chain 5 Facilitate Tumor Growth Factor β1 (TGFβ1)-dependent Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13789–13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Noetzel, E.; Kistermann, J.; Eschenbruch, J.; Rushrush, S.; Gan, L.; Knuchel, R.; Gaisa, N.T.; Dahl, E. The ECM Modulator ITIH5 Affects Cell Adhesion, Motility and Chemotherapeutic Response of Basal/Squamous-Like (BASQ) Bladder Cancer Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Huth, S.; Wiesehöfer, M.; Ehling, J.; Henkel, C.; Steitz, J.; Lammers, T.; Kistermann, J.; Klaas, O.; Koch, M.; et al. ITIH5-Derived Polypeptides Covering the VIT Domain Suppress the Growth of Human Cancer Cells In Vitro. Cancers 2022, 14, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ma, J.; Xie, X.; Su, M.; Zhao, D. Serum ITIH5 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.; Storr, S.J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Rakha, E.A.; Green, A.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Martin, S.G. High nuclear MSK1 is associated with longer survival in breast cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaeteewoottacharn, K.; Pairojkul, C.; Kariya, R.; Muisuk, K.; Imtawil, K.; Chamgramol, Y.; Bhudhisawasdi, V.; Khuntikeo, N.; Pugkhem, A.; Saeseow, O.T.; et al. Establishment of Highly Transplantable Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines from a Patient-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model. Cells 2019, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huth, S.; Heise, R.; Vetter-Kauczok, C.S.; Skazik, C.; Marquardt, Y.; Czaja, K.; Knüchel, R.; Merk, H.F.; Dahl, E.; Baron, J.M. Inter-α-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 5 (ITIH5) is overexpressed in inflammatory skin diseases and affects epidermal morphology in constitutive knockout mice and murine 3D skin models. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmele, W.; Stegner, H.E. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 1987, 8, 138–140. [Google Scholar]
- Meurer, S.K.; Alsamman, M.; Sahin, H.; Wasmuth, H.E.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A.; Trautwein, C.; Weiskirchen, R.; Scholten, D. Overexpression of endoglin modulates TGF-β1-signalling pathways in a novel immortalized mouse hepatic stellate cell line. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelan, R.S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Pisano, M.M.; Greene, R.M. Effects of 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) on gene expression. Drug Metab. Rev. 2018, 50, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.N.; Torrisani, J.; Unterberger, A.; Provençal, N.; Shikimi, K.; Karimi, M.; Ekström, T.J.; Szyf, M. Histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A induces global and gene-specific DNA demethylation in human cancer cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malka, D.; Siebenhüner, A.R.; Mertens, J.C.; Schirmacher, P. The Importance of Molecular Testing in the Treatment of Cholangiocarcinoma. EMJ Oncol. 2020, 8, 82–94. [Google Scholar]
- Valle, J.W.; Kelley, R.K.; Nervi, B.; Oh, D.Y.; Zhu, A.X. Biliary tract cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cao, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Han, C. ITIH5, a p53-responsive gene, inhibits the growth and metastasis of melanoma cells by downregulating the transcriptional activity of KLF4. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 2168–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithayathil, M.; Khan, S.A. Current epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma in Western countries. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.I.; Affo, S.; Goyal, L.; Lamarca, A.; Sapisochin, G.; Yang, J.D.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma—Novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Sahai, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Vaccaro, G.; Melisi, D.; Al-Rajabi, R.; Paulson, A.S.; Borad, M.J.; Gallinson, D.; Murphy, A.G.; et al. Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavacchi, D.; Caliman, E.; Rossi, G.; Buttitta, E.; Botteri, C.; Fancelli, S.; Pellegrini, E.; Roviello, G.; Pillozzi, S.; Antonuzzo, L. Ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated cholangiocarcinoma: Clinical evaluation and future directions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 237, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Arai, Y.; Totoki, Y.; Shirota, T.; Elzawahry, A.; Kato, M.; Hama, N.; Hosoda, F.; Urushidate, T.; Ohashi, S.; et al. Genomic spectra of biliary tract cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, R. Expression genetics in cancer: Shifting the focus from DNA to RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.Z.; Zhang, B.Y.; Feng, Y.J.; Jia, Z.X.; An, B.; Liu, C.C.; Deng, X.Y.; Kulkarni, A.D.; Lu, Y. Current research in perineural invasion of cholangiocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, X.F.; He, J.; Popescu, I.; Marques, H.P.; Aldrighetti, L.; Maithel, S.K.; Pulitano, C.; Bauer, T.W.; Shen, F.; et al. Prognostic impact of perineural invasion in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Multicentre study. Br. J. Surg. 2022, 109, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapitz, A.; Azkargorta, M.; Milkiewicz, P.; Olaizola, P.; Zhuravleva, E.; Grimsrud, M.M.; Schramm, C.; Arbelaiz, A.; O’Rourke, C.J.; La Casta, A.; et al. Liquid biopsy-based protein biomarkers for risk prediction, early diagnosis, and prognostication of cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaoka, T.; Saito, Y.; Saito, H. Aberrant DNA Methylation as a Biomarker and a Therapeutic Target of Cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickenbach, K.; Galka, E.; Roggin, K.K. Molecular mechanisms of cholangiocarcinogenesis: Are biliary intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct precursors to cholangiocarcinoma? Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 18, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanuma, Y.; Sato, Y.; Ojima, H.; Kanai, Y.; Aishima, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Ariizumi, S.; Furukawa, T.; Hayashi, H.; Unno, M.; et al. Clinicopathological characterization of so-called “cholangiocarcinoma with intraductal papillary growth” with respect to “intraductal papillary neoplasm of bile duct (IPNB)”. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar]




| Variable | N | ITIH5 Low | ITIH5 High | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 175 | 137 | 38 | |||
| Gender | Male | 93 | 74 | 19 | 0.8946 |
| Female | 80 | 63 | 17 | ||
| Unknown | 2 | - | - | ||
| Age | ≤Median (68 y) | 92 | 72 | 20 | 0.9933 |
| >Median (68 y) | 83 | 65 | 18 | ||
| Tumor type | iCCA | 93 | 61 | 32 | <0.0001 *** |
| pCCA | 79 | 75 | 4 | ||
| Mixed type | 2 | - | - | ||
| GBC excluded | 1 | - | - | ||
| Tumor size | ≤Median (55 mm) | 87 | 79 | 8 | <0.0001 *** |
| >Median (55 mm) | 82 | 52 | 30 | ||
| Unknown | 6 | - | - | ||
| Number of lesions | 1 | 143 | 118 | 25 | 0.0041 ** |
| ≥ 2 | 32 | 19 | 13 | ||
| Lymph node invasion | Yes | 49 | 41 | 8 | 0.2708 |
| No | 112 | 85 | 27 | ||
| Unknown | 14 | - | - | ||
| Vascular invasion | Yes | 59 | 52 | 7 | 0.0411 * |
| No | 107 | 80 | 27 | ||
| Unknown | 9 | - | - | ||
| Perineural invasion | Yes | 79 | 71 | 8 | 0.0359 * |
| No | 31 | 23 | 8 | ||
| Unknown | 65 | - | - | ||
| Liver cirrhosis | Yes | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0.5867 |
| No | 170 | 132 | 38 | ||
| Tumor Grade | G1 + G2 | 113 | 88 | 25 | 0.3696 |
| G3 + G4 | 50 | 42 | 8 | ||
| Unknown | 12 | - | - | ||
| UICC Tumor stage | I | 37 | 23 | 14 | 0.0074 ** |
| II + III + IV | 138 | 114 | 24 | ||
| Resection margin | R0 | 136 | 107 | 29 | 0.7366 |
| R1 + R2 | 23 | 18 | 5 | ||
| Unknown | 16 | - | - | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dreyer, V.J.; Shi, J.-X.; Rose, M.; Onyuro, M.T.; Steib, F.; Hilgers, L.; Seillier, L.; Dietrich, J.; Riese, J.; Meurer, S.K.; et al. High Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein ITIH5 in Cholangiocarcinomas Correlates with a Favorable Prognosis. Cancers 2024, 16, 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213647
Dreyer VJ, Shi J-X, Rose M, Onyuro MT, Steib F, Hilgers L, Seillier L, Dietrich J, Riese J, Meurer SK, et al. High Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein ITIH5 in Cholangiocarcinomas Correlates with a Favorable Prognosis. Cancers. 2024; 16(21):3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213647
Chicago/Turabian StyleDreyer, Verena J., Jia-Xin Shi, Michael Rose, Maureen T. Onyuro, Florian Steib, Lars Hilgers, Lancelot Seillier, Jana Dietrich, Janik Riese, Steffen K. Meurer, and et al. 2024. "High Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein ITIH5 in Cholangiocarcinomas Correlates with a Favorable Prognosis" Cancers 16, no. 21: 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213647
APA StyleDreyer, V. J., Shi, J.-X., Rose, M., Onyuro, M. T., Steib, F., Hilgers, L., Seillier, L., Dietrich, J., Riese, J., Meurer, S. K., Weiskirchen, R., Neumann, U., Heij, L., Luedde, T., Loosen, S. H., Lurje, I., Lurje, G., Gaisa, N. T., Jonigk, D., ... Brüchle, N. O. (2024). High Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Protein ITIH5 in Cholangiocarcinomas Correlates with a Favorable Prognosis. Cancers, 16(21), 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213647









