Simple Summary
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. There is proof that interstitial lung disease and lung cancer interact and influence patient outcomes, treatment approaches, and the course of the disease. Common risk factors for both illnesses include smoking, exposure to the environment, and genetic predispositions. When interstitial lung disease is present, lung cancer management is complicated both diagnostically and therapeutically. These challenges include trouble interpreting radiological results and a higher risk of treatment-related toxicities, such as acute exacerbation following surgery and pneumonitis following radiation therapy and immunotherapy. Furthermore, the evidence-based treatment choices for patients with ILDs and lung cancer are still restricted.
Abstract
Lung cancer continues to be one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide. There is evidence of a complex interplay between lung cancer and interstitial lung disease (ILD), affecting disease progression, management strategies, and patient outcomes. Both conditions develop as the result of common risk factors such as smoking, environmental exposures, and genetic predispositions. The presence of ILD poses diagnostic and therapeutic challenges in lung cancer management, including difficulties in interpreting radiological findings and increased susceptibility to treatment-related toxicities, such as acute exacerbation of ILD after surgery and pneumonitis after radiation therapy and immunotherapy. Moreover, due to the lack of large, phase III randomized controlled trials, the evidence-based therapeutic options for patients with ILDs and lung cancer remain limited. Antifibrotic treatment may help prevent pulmonary toxicity due to lung cancer treatment, but its effect is still unclear. Emerging diagnostic modalities and biomarkers and optimizing personalized treatment strategies are essential to improve outcomes in this patient population.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer and interstitial lung diseases (ILD) share distinct biological pathways, even though the precise genetic and cellular mechanisms remain incompletely understood. ILDs can progress to pulmonary fibrosis, which is characterized by progressive scarring and lung tissue thickening, which can lead to impaired lung function []. Numerous signaling pathways and microenvironments have been identified as disruptors of tissue architecture, contributing to dysfunction in both conditions and leading to loss of lung function, impaired gas exchange, and respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea. Despite these commonalities, lung tumorigenesis and fibrosis are characterized by highly heterogeneous behaviors, emphasizing the need for personalized therapeutic approaches tailored to individual patients.
As an example, one of the most progressive forms of ILD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), is influenced by genetic predisposition, aging, and environmental factors. Current evidence indicates that in genetically predisposed individuals, especially those over 60 years of age, environmental exposures lead to alterations in lung epithelium, initiating aberrant cellular activation and localized expansion of fibroblasts, ultimately resulting in fibrotic remodeling, loss of lung architecture, and functional deterioration, with the escalating mechanical stiffness perpetuating the fibrotic response through cell-autonomous and matrix-dependent processes [].
Lung cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lungs by activating various signaling pathways [,]. Although lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis are distinct clinical conditions, evidence suggests shared pathomechanisms, aggravating factors, and signaling pathways between them. Indeed, the coexistence of pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer is not uncommon [,]. The existence of IPF itself causes a 7% to 20% increased risk of lung cancer development []. Also, the prevalence of lung cancer is significantly higher in the ‘combined IPF and emphysema’ (CPFE) cohort as compared with patients with pulmonary fibrosis [].
Moreover, lung transplant patients with IPF exhibit higher rates of lung cancer, suggesting shared molecular connections between the two diseases []. Such shared molecular pathways of established lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis are the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), mesenchymal activation, and SFTPA mutation [].
Also, lung cancer manifests in the peripheral regions of the lungs, where especially fibrotic changes typical of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) are prevalent, and adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the predominant types observed in individuals with IPF []. In more detail, pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer share common risk factors, such as smoking, occupational/environmental exposures (e.g., asbestos, silica), and genetic predisposition. These risk factors may lead to developing both conditions in the same individual, significantly impacting disease survival [].
The global burden of lung cancer and ILDs is increasing [,,]. Since the risk of lung cancer in patients with pulmonary fibrosis is increased, there is growing interest in instituting screening and surveillance programs for this population. The presence of pulmonary fibrosis in individuals with lung cancer has clinical implications, influencing both treatment decisions and prognosis []. The compromised lung function associated with pulmonary fibrosis may limit specific treatment options, and the overall prognosis for individuals with both conditions may be poorer compared to those with lung cancer alone. Early detection of lung cancer is anticipated to facilitate more effective treatment and improve outcomes. This emphasizes the importance of understanding the interplay between pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer for better management and outcomes in affected individuals [,].
As research unravels both conditions’ intricate molecular and cellular landscapes, the prospect of identifying converging points in the pathogenic processes holds promise for innovative and more effective therapeutic interventions. Integrating insights from the research of cancer and fibrosis not only enhances our understanding of these diseases but also offers a potential roadmap for developing targeted therapies that address the unique challenges posed by the heterogeneity observed in lung tumorigenesis and fibrogenesis. Recognizing the commonalities in the underlying pathways between cancer and pulmonary fibrosis opens avenues for the development of novel therapeutic strategies and personalized approaches and may prove essential in optimizing treatment outcomes of individuals with lung cancer and fibrosis.
2. Pathophysiology
Specific pathologic mechanisms and factors have been proposed to contribute to the relationship between ILDs and lung cancer. As indicated by genetic alterations in specific genes and signaling pathways, shared genetic and molecular pathways may contribute to developing both pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer [,,]. This shared susceptibility involves such genetic factors as aberrations in essential genes like TGF-β and p53, with evidence suggesting that specific genetic factors related to lung development, tissue repair, and cell cycle regulation, such as mutations in relevant genes, may play roles in the development of both conditions [].
Specific gene mutations, including those involving microsatellite instability, fragile histidine triads, the oncogene p53, and loss of heterozygosity, are observed in many IPF cases, particularly in the characteristic peripheral lung regions with honeycombing []. Mutations associated with cancer, such as those affecting telomere shortening and telomerase expression, are also found in familial IPF, suggesting shared genetic factors []. Jan kinase and SFTP mutations were found in families with PF and lung cancer.
Chronic inflammation is a common feature in pulmonary fibrosis and tumor development and is associated with the fibrotic process in some ILDs [,]. The inflammatory microenvironment may create conditions that promote the initiation and progression of cancer cells in the lungs []. Furthermore, the fibrotic changes in pulmonary fibrosis involve excessive collagen deposition and other extracellular matrix components, leading to tissue remodeling and scarring []. This altered lung architecture and increased stiffness may create a microenvironment that promotes cancer cell growth [,] and may involve modifications in the extracellular matrix and cytokine profiles [,].
Tyrosine kinases, integral to multiple signaling pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation, adhesion, motility, and cell death, are normally controlled by transmembrane receptors and ligands. However, aberrant kinase activities have been linked to various cancers’ development, progression, and metastasis and some types of ILD []. It is in line with this note that nintedanib, a triple kinase inhibitor, is effective in both lung fibrosis and lung cancer and is authorized for both conditions []. Further, oncogene hypomethylation and tumor suppressor genes’ methylation, which are involved in the pathogenesis of many tumors, are also present in patients with IPF. Recent data show reciprocal changes in global methylation patterns between IPF and lung cancers and hypermethylation of the CD90/Thy-1 promoter region in IPF, contributing to the loss of the glycoprotein Thy-1, associated with invasive cancer behaviors and the transition from fibroblasts to myofibroblasts [].
Fibrosis is intricately linked to the persistent action of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, a regulator of various intracellular mediators and pathways associated with cell growth, organ development, the immune system, metastasis, and cancer progression. The “TGF-β paradox” is observed, according to which TGF-β promotes cellular growth in cancer cells but has the opposite effect in benign cells []. This results from the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway activation in malignant cells and its inactivation in non-cancer cells.
TGF-β, VEGF, PDGF, and FGF are implicated in both lung cancer and lung fibrosis, with VEGF potentially promoting cell survival and proliferation through ERK1/2 and PI3K activation and VEGF mRNA being elevated levels in IPF patient endothelial progenitor cells []. The downregulation of TGF-β receptors is a pivotal event leading to changes in cellular behavior, with low receptor levels promoting metastasis and cancer progression and playing a crucial role in early carcinogenesis []. Lung cancer in individuals with pulmonary fibrosis tends to be more aggressive, with TGF-β playing a critical role by being produced by both pulmonary fibrosis-associated fibroblasts and cancer-derived epithelial cells, promoting myofibroblast recruitment at cancer margins, safeguarding them from apoptosis, and facilitating their invasion through basement membranes and the process of EMT [].
Furthermore, elevated expression of programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is seen in both lung cancer and IPF, where PD-L1, a cell surface protein, interacts with the PD1 receptor on T-cells, leading to immune response suppression and contributing to the pathogenesis of these diseases [].
Additionally, the MET signaling pathway (a receptor tyrosine kinase whose ligand is hepatocyte growth factor), a crucial regulator of cell growth and proliferation activated in response to hypoxia, plays a significant role in both IPF and lung cancer []. Activation of the MET pathway promotes increased cell proliferation, tumor growth, and the expression of genes related to cell proliferation; the upregulation of the MET signaling pathway occurs in fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, contributing to the excessive collagen deposition and tissue fibrosis characteristic of the disease [].
Pulmonary fibrosis is linked to cellular senescence, a state characterized by the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors that promote inflammation and tissue remodeling, potentially contributing to the development of cancer through the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) and the creation of a microenvironment supportive of cancer growth [].
In both cancer and pulmonary fibrosis (particularly IPF), bronchiolar basal cells express molecules, including fascin, laminin, and heat shock protein 27, which are associated with cell migration and invasion, contributing to the invasive front of tumors and expressed in epithelial cells around fibroblast foci []. Additionally, matrix metalloproteases and integrins, known for their role in cell invasion, are strongly linked to the development of stem cell-like properties in cancer cells and, in the context of IPF, promote the initiation, maintenance, and resolution of tissue fibrosis, with clinical trials investigating inhibitors such as the humanized antibody STX-100 and specific antibodies against αvβ6 [].
EMT is a process where epithelial cells undergo changes to become more mesenchymal, and this is implicated in both fibrosis and cancer. The transition of cells from an epithelial to a mesenchymal phenotype can promote tissue remodeling and contribute to cancer progression. EMT is implicated in fibrosis and cancer metastasis. EMT may contribute to tissue remodeling in the lung and create a microenvironment supporting cancer growth [].
Circulating and cell-free DNA, as well as abnormal expression levels of mRNA, are considered diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for both cancer and IPF. The aberrant expression of specific short non-protein-coding RNAs in IPF influences genes associated with fibrosis, ECM regulation, EMT induction, and apoptosis, potentially contributing to functional deterioration in patients with pulmonary fibrosis [,].
Intercellular channels formed by connexins (Cxs) are crucial in cells’ metabolic and electrical coupling. The most abundant Cx on fibroblast membranes is Cx43, which contributes to tissue repair and wound healing; however, the expression of Cx43 in primary lung fibroblasts of IPF patients is reduced, leading to limited intercellular communication. This reflects common defects in contact inhibition and uncontrolled proliferation seen in both IPF and cancer cells [].
The main pathologic mechanisms contributing to the development of lung cancer in pulmonary fibrosis are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main pathologic mechanisms contributing to the development of lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis based on refs. [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. For further explanation, see text.
3. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer in ILD
IPF is an established risk factor for lung cancer. An increased risk of lung cancer in patients with other ILDs has also been reported, although data regarding other ILDs are limited. Even the finding of ILAs in CT screening has been associated with an increased risk of 33% of lung cancer []. Other studies have suggested that the HR of lung cancer diagnosis in patients with ILAs is as high as 2.77 []. Patients with increased risk for lung cancer in ILDs are male patients of older age, decreased lung function with a decline in FVC > 10% per year, low DLCO, and smoking [,]. The risk of lung cancer in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema is nine times higher compared to subjects without underlying disease [,].
Survival outcomes vary based on the ILD subtype, with lung cancer survival being poorer in patients with IPF compared to those with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) or cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) [,,].
Lung cancer in patients with UIP pathological pattern is mainly found in the subpleural areas of the lower lobes (75.5%), a finding consistent with the typical distribution pattern of UIP [,]. Squamous cell carcinoma was the most common cancer type (62.8%) in this group []. In contrast, in patients with ILD and non-UIP histology, lung cancer primarily occurred in the upper lobes (68.1%). Adenocarcinoma was the predominant cancer type and was found in more than half of this group of patients []. In non-IPF lung cancer cases, levels of Krebs von Lungen factor 6 (KL6) have been associated with prognosis []. Data regarding the prevalence, histology, and location of lung cancer in patients with ILDs are shown in Table 2.
An important aspect regarding the epidemiology of lung cancer in patients with ILDs is the establishment of screening programs for lung cancer with low-dose CT (LDCT). LDCT has significantly changed the staging of lung cancer, increased the detection of early-stage cancers, and reduced late-stage diagnoses []. Moreover, LDCT in the setting of lung cancer screening has led to an increased diagnosis of ILAs. Specific guidelines regarding the management of ILAs as an incidental finding have been published []. As described before, ILAs are associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer. Moreover, LDCTs in the setting of a lung cancer screening program are related to the finding of true ILD. In a screening program of 6650 participants, ILDs were first diagnosed in 0.8%, including IPF []. Early findings of ILDs can not only lead to early initiation of appropriate treatment for the ILDs but also identify patients with concomitant lung cancer in an earlier stage, thus increasing the chance of definitive surgical treatment for these patients [].
3.1. IPF
An estimated 17.5-fold greater prevalence of NSCLC among IPF patients compared to the general population has been reported in a large Korean database, even after adjustment for age, smoking history, and sex [].
A study of a large Medicare database of approximately 55,000 patients with NSCLC reported a prevalence of IPF of 1.6% []. Studies from various regions consistently report elevated lung cancer prevalence in IPF patients compared to the general population, with rates ranging from 2.7% to 48%, with a median prevalence of 11.6% in European cohorts of patients with IPF and 15.3% in Asian cohorts []. In Korea, the prevalence of lung cancer in IPF was reported to be 6.4% []. A recently published European large multicenter study of 3178 patients with IPF reported the development of lung cancer in 10.2% of the patients [].
For IPF patients, the cumulative incidence of lung cancer rises significantly, ranging from 1.1% at one year, 8.7% at three years, 15.9% at five years, and 31.1% at ten years of follow-up []. A longitudinal cohort study from Korea showcased a cumulative NSCLC incidence of 3.3%, 15.4%, and 54.7% at 1, 5, and 10 years post-IPF diagnosis, respectively []. In a large European study, the incidence of lung cancer in IPF was 14.1 and 26.6% among patients who were alive upon completion of the three-year and ten-year follow-up, respectively []. The incidence of lung cancer in IPF cases is considerably higher compared to the general population, with reported rates ranging from 3.34 to nearly 5 [,]. In a study of NSCLC in patients with ILD, lung cancer was manifested approximately 2.4 years following ILD diagnosis [].
Among individuals with IPF, the most prevalent histological type is squamous carcinoma, followed by adenocarcinoma, contrary to the general population, in which adenocarcinoma is the most common histological type [,]. Mucinous adenocarcinoma has also been reported to have increased frequency in IPF []. Patients with IPF have a higher frequency of lung cancer occurrence in the lower lobes compared to other ILD patients and to the general population, who have a propensity for the upper lobes [,].
The prognosis for NSCLC patients with concurrent IPF is poorer than for those with either condition alone, persisting even when adjusting for baseline lung function, with a 5-year survival of 14.5% for lung cancer patients with IPF compared to 30.1% for those without []. This difference includes stages I-III of NSCLC, while in stage IV NSCLC and SCLC, the survival difference is similarly low in IPF vs. non-IPF categories [,,]. Reasons for the worse survival of these patients include poor pulmonary status and comorbidities, which exclude many patients with ILDs from surgery as a therapeutic option, treatment complications, such as acute exacerbations perioperatively or due to systemic therapy or pneumonitis due to immunotherapy, the possible detrimental effects of radiation therapy and diagnosis of lung cancer in a more advanced stage, since symptoms of NSCLC and ILDs may overlap [].
3.2. Connective Tissue Disease (CTD)-Related ILD
Patients with connective tissue disease (CTD)-related ILD usually present with different clinical characteristics as patients with IPF: these patients are primarily women and younger than the patients with IPF []. Moreover, the histological pattern of NSIP and not only UIP can be found in many patients with CTD-ILD. Autoimmunity and inflammation play an essential role in the pathogenesis of the CTD. The likelihood of developing lung cancer is almost two times higher in patients with CTD-related ILD compared to ILD patients without CTD. The relative risk is increased from 3.5 to 7.3 for any ILD subtype []. Lung cancer incidence has been reported to be higher in younger patients: the incidence of lung cancer in men with CTD-ILD aged 40–49 years was 3.2 times higher compared to men with ILD of the same age, and the incidence in women with CTD-ILD aged 50–59 years was 2.8 times higher []. Mortality differences have also been reported, with the all-cause mortality rate being higher in older CTD-ILD patients (50 to 79 years old) than in those ILD-only, especially in women [].
Data from a US registry suggest that in individuals with ILD and conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis/dermatomyositis, or systemic sclerosis, the risk was significantly increased, reaching up to 4.95 times higher as compared to the general population []. The prevalence of lung cancer in CTD-ILD was 1.9% []. A Japanese study has reported a prevalence of 9%, with risk factors being male gender, heavy smoking, older age, presence of emphysema, a UIP pattern, and non-receiving immunosuppressive therapy [].
Systemic sclerosis and dermatomyositis/polymyositis with ILD are associated with lung cancer risk: systemic sclerosis was associated with an incidence of 11.1%. In comparison, dermatomyositis/polymyositis and rheumatoid arthritis were associated with an incidence of 4.4% []. In patients with systemic sclerosis, lung cancer has been reported as the most common cancer, with an incidence ranging from 4.9–5.7% [].
In a recently published study of 51,899 patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis, the hazard ratio of developing lung cancer in 4.5 years of follow-up was 1.39. This correlated to male gender and smoking but, surprisingly, not to the presence of ILD []. However, the presence of ILD is a significant risk factor for mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who are also diagnosed with lung cancer: The estimated mortality of lung cancer in patients with chronic ILD with a UIP pattern was five times higher than the general population in a study of 2702 patients with rheumatoid arthritis [].
It seems that chronic inflammation, combined with the detrimental effect of smoking, plays an essential role in the development of lung cancer in patients with CTD-ILDs []
3.3. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP)
HP is caused by exposure to organic antigens. Chronic HP usually presents as progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Differential diagnosis between chronic HP and IPF can be challenging. Kuramochi et al. reported a 10.6% prevalence of lung cancer in HP, with the most common histological type being squamous cell carcinoma in basal, peripheral lung lesions. Interestingly, lung cancer patients with chronic HP had a UIP pathology, suggesting that progressive pulmonary fibrosis and parenchyma distortion due to fibrosis, irrespective of its etiology, contribute to the development of lung cancer []. Other studies have reported that chronic HP contributed to 5.8% of all non-IPF ILD lung cancer cases []. In a prospective database of patients with chronic HP, however, followed up for 32 months, no lung cancer cases were observed [].
3.4. Post-Infectious Fibrosis
In the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic, a pulmonary fibrosis ‘tsunami’ was expected to follow the COVID-19 ‘earthquake’ []. Since fibrosis is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer, an increased incidence of lung cancer might also occur. Luckily, such a ‘tsunami’ did not happen, and an increased incidence of lung fibrosis post-Covid does not seem to be a significant clinical problem at the moment. However, since millions of people were affected by the virus, caution is required to exclude such a relationship in the future [].


Table 2.
Prevalence, histology, and location of lung cancer in patients with ILDs, based on refs. [,,,,,].
Table 2.
Prevalence, histology, and location of lung cancer in patients with ILDs, based on refs. [,,,,,].
| ILD | Prevalence of LC | Most Common LC Histology | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPF | Median 11.6% in European cohorts and 15.3% in Asian cohorts | Squamous cell carcinoma | Lower lobes, fibrotic areas |
| CTD-ILD | 1.9–9% | Adenocarcinoma | Peripheral lung lesions, equal distribution in upper and lower lobes |
| Hypersensitivity pneumonitis | 0–10.6% | Squamous cell carcinoma | Peripheral lung lesions, equal distribution in upper and lower lobes |
LC: lung cancer; IPF: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; CTD-ILD: connective tissue disease-associated ILD.
4. Diagnostic Approach to the Patients with ILD and Suspected Lung Cancer
In individuals with ILD, diagnosis of lung cancer can be difficult since clinical symptoms and functional changes can be attributed to the ILD until lung cancer is suspected. Moreover, suspicious, subtle changes in chest CT may be recognized late and retrospectively due to the existing fibrotic lung alterations (Figure 1) [,]. Careful comparison of CTs to recognize new solitary nodules is important. Since ILDs (particularly IPF) are a risk factor for the development of lung cancer development, annual HRCTs for follow-up of the IPF and eventual development of pulmonary nodules should be strongly considered in these patients []. New pulmonary nodules should be further evaluated according to Fleischner criteria’s high-risk group [,]. It is important to consider that the tumor size may be underestimated by 10% in patients with ILDs []. Additionally, evaluation of mediastinal lymph nodes with CT can be difficult in patients with ILD since reactive mediastinal lymph node enlargement is common in these patients, reducing the specificity of this method for detecting lung cancer [,].
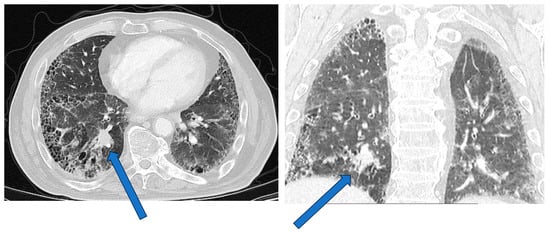
Figure 1.
Lung cancer in a patient with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. The tumor is located in the right lower lobe (arrows).
Most experts would agree that PET-CT can help to identify the malignant character of nodules with a size above 8 mm and provide information for possible extra thoracic lung cancer involvement, which is accessible to biopsy [,,]. Tissue sampling of suspicious mediastinal lymph nodes can be made using endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle biopsy (EBUS-TBNB) and peripheral lesions with radial EBUS []. The latter can be challenging due to fibrotic changes in the surrounding lung [,].
CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy is an alternative, technically more difficult in patients with ILD when the nodule is located in the lower lobes due to motion artifacts and non-diagnostic results due to sampling of fibrotic areas []. Pneumothorax may be a severe complication of CT-guided biopsy and is often associated with poor prognosis in patients with ILDs []. Placement of a tube drainage may be required in 10% of the patients. Factors associated with an increased risk of pneumothorax include lesion size <3 cm, a target lesion depth exceeding 1 cm, longer procedure duration, and honeycombing or emphysema along the needle’s path [,]. Trying to avoid inserting the needle through honeycomb lesions might reduce the risk of pneumothorax, but this cannot be easily achieved. CT-guided biopsy in the prone position is associated with a significantly reduced risk of pneumothorax requiring tube drainage [,]. Immediate manual aspiration of pneumothorax has been reported to be associated with reduced risk of chest tube drainage placement, even for large pneumothoraxes [].
The above approach might be more appropriate for patients with mild to medium lung functional impairment []. The approach to patients with end-stage fibrotic ILD, severely debilitated due to respiratory failure, might be more conservative since therapeutic options in these patients for lung cancer may be limited. A ‘liquid biopsy’ aiming to disclose driver mutations and identify individual treatment in debilitated patients may also be considered. In all cases, shared decision-making should be performed with the patients [].
Limitations of the diagnostic modalities in patients with ILDs suspected of having lung cancer are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Challenges of different modalities for the diagnosis of lung cancer in patients with ILDs based on refs. [,,,,,,,,,].
5. Treatment of NSCLC in Patients with ILDs
5.1. Surgical Therapy
Surgical resections in patients with ILD remain challenging, due to the fact that patients with ILD who are considered for surgical treatment of their malignancy often have an impaired lung function, advanced age, and many comorbidities. Moreover, a surgical procedure is a risk factor for postoperative AE-ILD, which increases the perioperative mortality []. As a result, ILD per se is a risk factor for increased morbidity and mortality after lung resection for lung cancer []. A retrospective cohort analysis of 128,723 patients who underwent lung surgery for NSCLC, among them 1873 with ILD, showed a postoperative mortality of 5.1% in patients with ILD vs. 1.2% in patients without ILD, ARDS 1.9% in ILD vs. 0.5% without ILD and of composite morbidity and mortality of 13.2% in ILD vs. 7.4% without ILD []. ILD remained a predictor of mortality, even after adjustment for lung function, comorbidities, and extent of resection [].
Kumar et al. [] reported an incidence of post-operative AE-ILD of 21%, with a mortality of 80%. The extent of surgical resection was also associated with mortality []. In a study of Park et al., the reported incidence of acute complications (ARDS and ALI) was 28% in 100 patients, with an overall operative mortality of 14%. Pre-existing comorbidities and reduced DLCO were associated with increased risk of AE-ILD in univariate analysis []. In a large, retrospective study from Japan, Sato et al. [] analyzed data of 1763 patients with ILD who underwent pulmonary resections for lung cancer. The study showed an incidence of AE of 9.3% (164 patients) with a mortality rate of 43.9%. AE-ILD was the main cause of 30-day mortality, accounting for 72% of deaths. Risk factors for AE-ILD were male sex and history of previous AE-ILD. A UIP pattern in HRCT and an FVC value of <80% predicted were also identified as risk factors for AE-ILD []. Preoperative steroid use was associated with a 2.86 times increased ratio of AE-ILD. KL-6 serum levels above 1000 U/mL correlated to increased risk of AE-ILD (OR 2.14) []. Patients with CPFE have been reported to have an increased mortality comparable to the patients with emphysema alone. The incidence of AE-ILD was lower as in patients with IPF alone [].
Min Seo Ki et al. [] demonstrated in a propensity score matching study of 104 patients that long-term prognosis is affected negatively in ILD (5-year survival rate 66% vs. 78.8%, p = 0.007). However, there was no difference between groups in postoperative mortality []. Moreover, mortality was significantly higher in patients with a stage III ILD-GAP score []. Ueno et al. also reported a correlation of GAP score with mortality []. In the same study, the degree of fibrosis in HRCT, increased BMI, and a higher CRP were independently associated with mortality [].
Regarding the resection range, most studies report an increased risk of complications, including AE-ILD, with more extensive surgery []. Compared to a wedge resection, performance of lobectomy or segmentectomy had an OR of 3.83 and performance of a pneumonectomy or bilobectomy had an OR of 5.7 of AE-ILD []. Huang et al. also showed that patients who underwent lobectomy or lobectomy had a higher range of complications compared to the patients who underwent sub-lobar resections []. In this study, the AE rate was 15.4%, with a mortality of 9.0%. In the multivariate analysis, however, age, comorbidities, and blood loss but not the extent of surgery were the risk factors for 90-day complications []. Tsutani et al. [], in a study of 107 patients with stage I NSCLC, showed no difference in overall survival between patients who underwent lobectomy and sub-lobar resections. However, the risk of a higher locoregional recovery by very limited resections cannot be ignored. Regarding sub-lobar resections, Motono et al. showed that in patients with ILD and stage IA NSCLC, wedge resection is a poor prognostic factor and that a segmentectomy seems a better option []. Lobectomy is currently compared to segmentectomy and wedge resection in phase III randomized controlled trials examining the clinical effectiveness of each method for early NSCLC with IPF, with the primary endpoint being the overall survival []: a planned total of 430 patients will be enrolled from 50 institutions over five years []. In a recent meta-analysis of 2202 patients with UIP pattern, the overall incidence of AE of UIP postoperatively was 14.6%. Patients who underwent a sub-lobar resection were at significantly lower risk of postoperative AE (OR 0.521) [].
Apart from the extent of the surgical resection, the location of the resected lobe is another important factor regarding the postoperative course of patients with ILDs: Fukui et al. [] studied the difference between upper and lower lobectomy and concluded that there is no statistical difference in mortality and morbidity. This remained after adjusting for the simultaneous presence of emphysema. However, upper lobectomy had a more significant impact on postoperative respiratory function [].
Repeated surgery for lung cancer in patients with ILD is rare and highly challenging. Sato et al. showed in a small sample study (of 13 patients) that repeated surgery was associated with a high percentage of AE-IPF. Still, it could be beneficial in carefully selected patients [].
An important aspect is the prevention of perioperative AE-ILD. Pirfenidone is an antifibrotic agent licensed for the treatment of patients with IPF. In a small phase II trial, administering pirfenidone perioperatively was safe and had promising results in preventing AE-ILD []. In a retrospective study of 100 patients with IPF who were surgically treated for lung cancer, patients treated with pirfenidone had fewer AE-IPF compared to the patients without antifibrotic treatment []. A prospective phase III study examining the effect of pirfenidone in preventing AE-IPF and survival is running [].
5.2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation of the lesions in the lung is an integral part of the therapy in lung cancer. In general, it is indicated for patients with early-stage NSCLC, who are not surgical candidates due to poor lung function or comorbidities, in cases of R1 surgical resection and locally advanced NSCLC combined with chemotherapy [,]. In SCLC, lung radiation therapy is indicated in limited disease []. Moreover, lung radiation therapy is indicated in urgent situations, such as superior vena cava syndrome []. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is the treatment of choice for non-surgical candidates with early-stage disease due to the reduced risk of induced side effects [,]. Radiation therapy, particularly when applied for locally advanced disease, affects larger lung fields and requires higher radiation doses. A well-known side-effect of radiation therapy is radiation pneumonitis []. For this reason, patients with ILDs have been excluded from clinical trials of radiation therapy in patients with lung cancer [].
Retrospective data suggest that the frequency of radiation pneumonitis in patients with ILDs is significantly higher than patients without ILD: A study involving 537 Stage I lung cancer patients treated with SBRT, including 39 patients with ILD-related imaging features, revealed that ILD patients had significantly higher rates of grade ≥2 (20.5% vs. 5.8%) and grade ≥3 (10.3% vs. 1.0%) radiation pneumonitis compared to non-ILD patients []. Moreover, ILD patients exhibited more extensive radiation pneumonitis beyond the radiotherapy treatment fields. Patients with stage I lung cancer and a prior diagnosis of ILD had a significantly higher rate of severe radiation pneumonitis compared to the overall group []. Specifically, 32% of ILD patients experienced grade ≥3 radiation pneumonitis, and 21% had grade 5 radiation pneumonitis []. In an analysis of 66 patients involving treatment with SBRT of primary and metastatic lung tumors, the presence of subclinical ILD was identified as the sole factor significantly linked to the occurrence of grade 2 to 5 radiation pneumonitis [].
Preliminary data suggest that proton beam therapy (PBT) may be more advantageous than SBRT, particularly for patients with ILDs []. However, PBT is not widely available and large data series regarding its use in ILDs and lung cancer are missing.
A retrospective analysis of 87 patients with subclinical ILD and NSCLC who received conventionally fractionated radiotherapy also examined the impact of radiotherapy on ILD []. Most of the patients had stage III NSCLC and received sequential chemoradiotherapy. Grade ≥2 radiation pneumonitis occurred in 51.7% of patients, while more severe radiation pneumonitis was associated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The mean lung dose, the ILD involvement, and prior gemcitabine use were linked to increased risk of severe pneumonitis []. ILD involvement of >10% of lung field predicted acute development of radiation pneumonitis []. Increased SUV of the fibrotic lung in PET-CT has also been associated with increased frequency of radiation pneumonitis [].
According to a systematic review trying to summarize the above aspects, the overall median incidence of grade ≥3 radiation pneumonitis in patients with ILDs undergoing radiation therapy for lung cancer was 19.7% (range 8–46%). Patients treated with particle beam therapy or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy had a lower incidence (median 12.5%) than those treated with conventional radical radiotherapy (31.8%). Grade 5 radiation pneumonitis occurred with a median rate of 11.9% (range: 0–60%). The existence of ILD independently predicted severe radiation pneumonitis. When idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) or the usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern were present, severe radiation pneumonitis was more common than when these conditions were not [].
Radiotherapy is not commonly used in patients with IPF due to its possible detrimental effects. According to a recently published retrospective, multicenter European study, only a small percentage of 12.5% of patients diagnosed with both IPF and lung cancer underwent radiotherapy []. However, physicians involved in the clinical care of patients with IPF and lung cancer would consider radiotherapy, particularly SBRT in carefully selected patients [].
5.3. Percutaneous Ablation
Percutaneous image-guided ablation is a technique for treating small tumors in early NSCLC, with results like sub-lobar resection and SBRT []. It can be applied as radiofrequency, microwave, or cryoablation [,]. Due to the local effect, this approach might be of value in patients with ILDs [], although data are scarce: mortality rates of 7.1% to 8.7% due to AE-ILD have been reported with a lung toxicity of 25% [,]. Complications, such as pneumothorax, bronchopleural fistula, and pneumonia have been reported [,].
5.4. Systemic Therapy for Lung Cancer in Patients with ILDs
5.4.1. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy plays a cardinal role in the treatment of patients with locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer [,]. Regarding NSCLC, histology and molecular markers are decisive for the appropriate treatment regimen selection. Before the introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), patients typically underwent first-line chemotherapy, often involving a platinum-based doublet regimen [,]. This regimen commonly included either carboplatin or cisplatin along with taxanes, etoposide, or pemetrexed. Patients with ILDs have been mostly excluded from phase III controlled randomized trials examining the effect of systemic therapy in lung cancer. This was due to the possible risk of AE-ILD and drug-induced pneumonitis in patients with ILDs. However, case series, registries, phase II trials, and a phase III trial (J-Sonic trial) have given insight into the effect of chemotherapy on patients with ILDs, particularly IPF [,]. Patients with IPF and SCLC have a significantly higher incidence of AE-IPF than patients with IPF and NSCLC after first-line treatment (31% vs. 63%) []. A recent meta-analysis has shown that AE was significantly more common in IPF than in non-IPF ILD after chemotherapy []. Increased FDG avidity in the contralateral lung on FDG PET/CT has been reported to be correlated with the risk of chemotherapy-related AE and may assist in identifying high-risk patients []. Certain medications increase the risk of pneumotoxicity and AE-ILD. A meta-analysis of 684 patients with ILD who underwent first-line chemotherapy for NSCLC showed a response rate of 43%. AE-ILD was approximately 8% in the context of chemotherapy, with lower rates (5%) observed in regimens containing nab-paclitaxel compared to other regimens (12%) []. For patients receiving docetaxel or gemcitabine, reported ILD exacerbation rates were 28% and 43%, respectively, while vinorelbine was not associated with AE-ILD in a small retrospective study []. Pemetrexed has shown increased toxicity in patients with IPF compared to those with other ILDs and significantly higher compared to patients without underlying ILD [,].
Experimental data suggest an inhibitory effect of pirfenidone on the progression of lung cancer [,,,,]. A small Japanese study of 14 patients with IPF and NSCLC found that the combination of pirfenidone with paclitaxel or S-1 was safe, while no AE-IPF was seen in these patients [].
The above data illustrate the effectiveness of first-line chemotherapy with platinum doublets in patients with NSCLC and ILD []. Although the incidence of AE-ILD was generally less than 10%, some patients died due to AE-ILD [].
5.4.2. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies, such as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors or anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors (ALK), have been associated with pneumotoxicity []. Some studies suggest that targeted therapies might be related to an increased risk of pneumotoxicity in patients with pre-existing ILD []. However, no large studies evaluating these treatments in patients with underlying ILD exist. ILD occurs in up to 5.2% of patients treated with EGFR TKIs for NSCLC, with a grade 3 or higher ILD affecting up to 2.2%. A high mortality in EGFR-TKI-induced ILD has been reported. In a recent meta-analysis, male sex, smoking history, and pre-existing ILDs have been reported as risk factors for EGFR-TKI-induced ILDs. Pre-existing ILD was associated with a six times increased risk of developing EGFR-TKI-induced ILD [,,].
5.4.3. Anti-VEGF Agents
Nintedanib is a tyrosine–kinase inhibitor that exhibits its antiangiogenic properties by targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor, and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor. In combination with docetaxel, it is used as a second-line therapy in patients diagnosed with adenocarcinoma after failure of first-line chemotherapy []. Nintedanib has also been approved for the treatment of IPF, as it was shown that it slows down the progression of the disease and reduces the risk of acute exacerbation at a dose of 150 mg bid [].
There were observations in patients with NSCLC and IPF who received nintedanib to treat the progression of IPF that a reduction of the size of cancerous lesions was achieved as well, while lung function was preserved. The doses used for treatment were 100 to 150 bid [,,,]. In an attempt to examine the optimal therapy for patients with lung cancer and IPF, a randomized phase 3 trial (J-SONIC) compared the efficacy and safety of nintedanib plus chemotherapy to chemotherapy alone []. In this study, the primary end-point, which was exacerbation-free survival, was not met, as there was no significant difference between the two groups. The combination of nintedanib with chemotherapy was well-tolerated and prevented FVC decline at 12 weeks. Overall response rate (ORR) was significantly better for nintedanib plus chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy in nonsquamous NSCLC []. Overall survival was also better in patients with nonsquamous NSCLC and patients with a stage I GAP (gender–age–physiology) [].
The anti-VEGF antibody bevacizumab has been tested in patients with ILD and lung cancer and has been reported to prevent chemotherapy-induced AE-ILD [,].
Since ILD is the most severe complication of EGFR-TKIs, efforts to reduce the risk of pneumotoxicity are of particular importance: a recent meta-analysis examined the effect of anti-VEGF treatment, such as nintedanib, bevacizumab, and ramucirumab, on EGFR-TKI-induced ILD. The authors reported that combining EGFR-TKIs with anti-VEGF agents was associated with a significantly reduced incidence of ILD compared with EGFR-TKI monotherapy. Since nintedanib has been licensed for treating IPF, scleroderma-associated ILD, and progressive pulmonary fibrosis, the combination with EGFR-TKIs may have significant implications for patients with ILD and NSCLC [].
Other reports suggest that nintedanib might reduce the pneumotoxicity of ICIs and slow tumor growth [,].
5.4.4. Immunotherapy
Treating lung cancer in patients with ILD is notably difficult. While the standard of care in patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC is a combination of a platinum-based doublet with immunotherapy [], patients with ILDs are faced with skepticism in the fear of adverse events. Immunotherapy refers to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and includes PD-1 inhibitors (such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab) and PD-L1 inhibitors such as atezolizumab and durvalumab). Adverse events can occur at any time in any organ []. Particularly, ICI-related pneumonitis, which in the context of IPF could be devastating due to their altered lung function, is the reason why patients with IPF are excluded from the majority of the studies. However, in patients without ILDs and NSCLs, immune-related adverse effects correlate to better outcomes []. Patients with ILD and lung cancer have similar levels of PD-L1 compared to the ones without ILD and increased tissue levels of PD-L1 are associated with better outcomes []. Other studies, however, report an increased expression of PD-1 and decreased expression of PD-L1 in mediastinal lymph nodes of patients with IPF compared to patients with lung cancer. The same expression pattern was observed in the lungs of patients with IPF compared to controls []. Mediastinal lymph nodes of bleomycin-treated mice showed increased size and higher PD-1 and PD-L1 mRNA levels than controls, while pembrolizumab attenuated bleomycin-induced fibrosis [].
Monotherapy with ICIs for patients with NSCLC without ILD has an incidence of pneumonitis between 3–6%, which rises to 10% when ICIs are combined []. The incidence of pneumonitis in IPF is estimated to be between 7.3% and 42.9%, according to data from retrospective studies, including patients with NSCLC and IPF or ILA []. As was shown in a retrospective study with 123 patients with NSCLC treated with nivolumab and pembrolizumab, when the fibrosis score, defined visually in CT-scan according to the classification of Kazerooni et al. [], increased from zero to >/1, the incidence of pneumonitis increased from 5.8% to 35.1% []. Increased fibrosis score and ground glass opacities are reported as risk factors for developing ICI-related pneumonitis in some studies [,,]. A multicenter retrospective study from Japan, which included 200 patients with chronic interstitial pneumonia who were treated with ICIs, showed pneumonitis grades 3–5 in 15.5% and death in 4.5% of the patients. Pneumonitis manifested radiologically preferentially as organizing pneumonia (OP) (47.5%), while diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) was reported in more than 30% of the patients; DAD was associated with significantly worse survival compared to other histological patterns. Almost half of the patients suffered immune-related adverse events. Patients with adverse effects had a substantially better prognosis than those without, with a median PFS of 200 days versus 77 days and a median OS of 597 days versus 390 days. The objective response and disease control rates were 41.3% and 68.5%, respectively []. A meta-analysis of 179 patients in 10 studies with pre-existing ILD treated with ICIs for NSCLC showed that compared to patients without ILD, patients with pre-existing ILD had a substantially higher (almost double) overall response rate. The disease-control rate and progression-free survival in patients with preexisting ILD were similar to those without ILD. Patients with pre-existing ILD and NSCLC had a significantly higher incidence rate of any grade and grade 3 or higher CIP than those with NSCLC and without ILD (OR, 3.23; OR, 2.91) [].
Case reports and a pilot study where nivolumab was administered as second-line therapy to patients with lung cancer and concomitant IPF after first-line chemotherapy failed suggested that nivolumab might be safely used in these patients. No signs of pneumonitis were observed during 12 weeks of treatment and efficacy showed partial response or stable disease [,]. A multicenter open-label single-arm phase II trial followed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of nivolumab in patients with mild IPF and NSCLC: grade 2 pneumonitis was seen in 11% of the patients. The six-month PFS rate was 56%, the response rate was 39%, and the disease control rate was 72% []. These results are corroborated by another retrospective study with 461 patients (412 without ILD and 49 with ILD) who were treated with nivolumab or pembrolizumab, which showed that despite the increased frequency of pneumonitis, the response rate (RR), the disease control rate (DCR), the progression-free survival (PFS), and the overall survival (OS) were non-inferior in the ILD-NSCLC group than the patients with NSCLC without pre-existing ILD [].
Most of the published case reports and original studies included Asian populations. In these patients, an increased risk of AE-ILD and chemotherapy-associated toxicity, including EGFR and TKI treatment, has been reported []. Therefore, additional studies in populations of other ethnic origins are helpful for comparison and extrapolation of the previously reported results. In a retrospective French study of 10,452 patients with advanced NSCLC who were treated with nivolumab, the effect of immunotherapy was examined in 148 patients (1.4%) with ILD. The overall survival time and the time-to-treatment duration were similar between patients with and without ILDs []. Survival was comparable in patients with idiopathic ILD, autoimmune/granulomatous ILD, and ILDs of other known causes. However, the results should be interpreted cautiously due to the small numbers in the different groups [].
Although hesitancy to use immunotherapy in this group of patients is explained by the minimal, mostly retrospective research into the field, ICIs can be used in this population after assessing risks and benefits, so that therapy is tailored to the individual patient.

Table 4.
Proposed treatment for patients with NSCLC and ILDs based on refs. [,,,]. Decisions to be taken by the oncology board, considering the patient’s wishes, comorbidities, NSCLC stadium, and ILD stadium. Oncologic outcomes and preservation of lung function to be considered. Close monitoring for AE-ILD and pneumonitis required.

Table 5.
Systemic treatment considerations for patients with ILD and advanced (stage IV) NSCLC, based on refs. [,].
6. Treatment Options for SCLC Patients with ILD
SCLC is less common than NSCLC in patients with ILDs, accounting for approximately 20% of lung cancers []. Most reports suggest that patients with SCLC and ILD, particularly IPF, have reduced overall survival [,,,]. Individuals diagnosed with SCLC and ILD exhibit similar responses to standard treatment to the general population, provided they tolerate chemotherapy [,,]. Pneumonitis was more often seen in patients with ILD and was associated with worse survival [,].
A phase II study of 33 participants with unresectable SCLC and IPF examined the effect of carboplatin, etoposide, and nintedanib combination: the incidence of AE-IPF after chemotherapy was 3% with an ORR of 68.8%, PFS of 4.2 months, and overall survival of 13.4 months, suggesting a role for nintedanib in preventing AE-IPF due to chemotherapy [].
Immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy has become the standard of care in extensive SCLC. Immunotherapy-induced interstitial lung disease incidence in large clinical trials is between 2.6 and 4%. Other studies have reported an incidence in Japanese patients up to 15.7%. Interestingly, the onset of immunotherapy-induced pneumonitis correlated to the presence of ILAs. These results suggest that the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in patients with ILDs and SCLC should be used with extreme caution and an individualized approach should be practiced [].
7. Palliative Care
Patients with fibrotic ILDs, and particularly IPF, have a dismal prognosis. The combination of fibrotic ILDs with lung cancer is a difficult situation for the patient, as well as for the treating physician. Impaired lung function, the risk of AE and pneumonitis, and comorbidities make many patients unfit or too frail for the usual therapeutic choices in the general population. The results of the DIAMORFOSIS study underline this problem []. Palliative treatment refers not only to pre-mortal interventions. Palliative treatment can greatly help alleviate patient’s symptoms in an early stage, particularly dyspnea, cough, and pain. Therefore, open discussion with the patients and their families is of paramount importance for improving their quality of life.
8. Conclusions
The relationship between lung cancer and ILD underscores the complexity of treatment decisions and potential complications. Retrospective studies have revealed varying rates of pneumonitis, including AE-ILD, in patients with ILD undergoing different therapeutic approaches for lung cancer. Factors such as the extent of ILD involvement, surgical resection, radiation dose, and specific chemotherapy agents have been identified as significant contributors to the mortality risk due to complications in these patients. These findings emphasize the need for careful consideration of treatment modalities and personalized approaches for individuals with both lung cancer and ILD. Future research and prospective studies are essential to refine treatment guidelines and enhance our understanding of the optimal management strategies for this complex patient population.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.S. and F.D.; writing—original draft preparation, all authors; writing—review and editing, P.S., A.G. and F.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Suzuki, A.; Maher, T.M. Interstitial lung diseases. Lancet 2022, 400, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, A.; Selman, M. The Interplay of the Genetic Architecture, Aging, and Environmental Factors in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Liang, C.; Hua, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.; et al. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts: Recent advances and future perspectives. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Tzilas, V.; Tringidou, R.; Steiropoulos, P.; Aidinis, V.; Papiris, S.A.; Bouros, D.; Tzouvelekis, A. Lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, C.E.; Jett, J.R. Does interstitial lung disease predispose to lung cancer? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2005, 11, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archontogeorgis, K.; Steiropoulos, P.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Nena, E.; Bouros, D. Lung cancer and interstitial lung diseases: A systematic review. Pulm. Med. 2012, 2012, 315918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Tomassetti, S.; Tsitoura, E.; Vancheri, C. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2015, 21, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Drent, M.; van Haren, E.H.J.; Verschakelen, J.A.; Verleden, G.M. Lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients diagnosed during or after lung transplantation. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2012, 5, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Gomatou, G.; Bouros, E.; Trigidou, R.; Tzilas, V.; Bouros, D. Common Pathogenic Mechanisms Between Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Chest 2019, 156, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, M.; Li, P.; Su, Z.; Gao, P.; Zhang, J. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis will increase the risk of lung cancer. Chin Med. J. 2014, 127, 3142–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer, C.; Kocarnik, J.M.; Compton, K.; Dean, F.E.; Fu, W.; Gaw, B.L.; Harvey, J.D.; Henrikson, H.J.; Lu, D.; Pennini, A.; et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups From 2010 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol 2022, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.C.R.D. Global burden of chronic respiratory diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: An update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 59, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, N.; Song, H.; Lu, T.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of lung cancer patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 13 studies. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 5322–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, N.W.; Luzina, I.G.; Atamas, S.P. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2012, 5, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.L.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips, J.A.; et al. Telomerase Mutations in Families with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, K.; Arvanitis, D.A.; Vassilakis, D.A.; Siafakas, N.M.; Spandidos, D.A. MYCL1, FHIT, SPARC, p16 INK4 and TP53 genes associated to lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2002, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chung, M.J.; Ullenbruch, M.; Yu, H.; Jin, H.; Hu, B.; Choi, Y.Y.; Ishikawa, F.; Phan, S.H. Telomerase activity is required for bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Role of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: From innocent targets to serial killers. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, D.S.; O’Donnell, D.; O’Connell, F.; O’Byrne, K.J. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 2024–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.G.; Simpson, J.K.; Saini, G.; Bentley, J.H.; Russell, A.-M.; Braybrooke, R.; Molyneaux, P.L.; McKeever, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Flynn, A.; et al. Longitudinal change in collagen degradation biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An analysis from the prospective, multicentre PROFILE study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, I.E.; Eickelberg, O. The Impact of TGF-β on Lung Fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.s.; Thannickal, V.J.; Pardo, A.; Zisman, D.A.; Martinez, F.J.; Lynch, J.P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Drugs 2004, 64, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomidi, I.; Burbridge, E.; Cavadas, M.; Sullivan, G.; Collis, B.; Naegele, H.; Clancy, D.; Brezinova, J.; Hu, T.; Bileck, A.; et al. iTAP, a novel iRhom interactor, controls TNF secretion by policing the stability of iRhom/TACE. eLife 2018, 7, e35032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimminger, F.; Schermuly, R.T.; Ghofrani, H.A. Targeting non-malignant disorders with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, E.I.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Steinfeld, I.; Gibson, K.F.; Pandit, K.V.; Yu, G.; Yakhini, Z.; Kaminski, N. Global Methylation Patterns in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, N.; Lee, C. Mysteries of TGF-b Paradox in Benign and Malignant Cells. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malli, F.; Koutsokera, A.; Paraskeva, E.; Zakynthinos, E.; Papagianni, M.; Makris, D.; Tsilioni, I.; Molyvdas, P.A.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Daniil, Z. Endothelial Progenitor Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Evolving Concept. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Qubo, A.; Numan, J.; Snijder, J.; Padilla, M.; Austin, J.H.M.; Capaccione, K.M.; Pernia, M.; Bustamante, J.; O’Connor, T.; Salvatore, M.M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer: Future directions and challenges. Breathe 2022, 18, 220147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Goto, T. Molecular Mechanisms of Pulmonary Fibrogenesis and Its Progression to Lung Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsoukis, N.; Wang, Q.; Strauss, L.; Boussiotis, V.A. Revisiting the PD-1 pathway. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organ, S.L.; Tsao, M.-S. An overview of the c-MET signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, G.M.; Gentile, A.; Balderacchi, A.; Meloni, F.; Milan, M.; Benvenuti, S. Ockham’s razor for the MET-driven invasive growth linking idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuwano, K.; Araya, J.; Hara, H.; Minagawa, S.; Takasaka, N.; Ito, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakayama, K. Cellular senescence and autophagy in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Respir. Investig. 2016, 54, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research, N. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidera, Y.; van Tsubaki, M.; Yamazoe, Y.; Shoji, K.; Nakamura, H.; Ogaki, M.; Satou, T.; Itoh, T.; Isozaki, M.; Kaneko, J.; et al. Reduction of lung metastasis, cell invasion, and adhesion in mouse melanoma by statin-induced blockade of the Rho/Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.K.; Kugler, M.C.; Wolters, P.J.; Robillard, L.; Galvez, M.G.; Brumwell, A.N.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. Alveolar epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13180–13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovat, F.; Valeri, N.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2011, 38, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.B.; Pantel, K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato-Salinaro, A.; Trovato-Salinaro, E.; Failla, M.; Mastruzzo, C.; Tomaselli, V.; Gili, E.; Crimi, N.; Condorelli, F.D.; Vancheri, C. Altered intercellular communication in lung fibroblast cultures from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker Brown, S.A.; Padilla, M.; Mhango, G.; Powell, C.; Salvatore, M.; Henschke, C.; Yankelevitz, D.; Sigel, K.; de-Torres, J.P.; Wisnivesky, J. Interstitial Lung Abnormalities and Lung Cancer Risk in the National Lung Screening Trial. Chest 2019, 156, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, G.T.; Putman, R.K.; Aspelund, T.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Hida, T.; Araki, T.; Nishino, M.; Hatabu, H.; Gudnason, V.; Hunninghake, G.M.; et al. The associations of interstitial lung abnormalities with cancer diagnoses and mortality. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1902154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Jeong, B.H.; Chung, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Chung, M.P. Risk factors and clinical characteristics of lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Saeki, K.; Waseda, Y.; Murata, A.; Takato, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Yasui, M.; Kimura, H.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Matsushita, T.; et al. Lung cancer in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Clinical features and impact on outcomes. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y. Meta-analysis: Clinical features and treatments of lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2023, 40, e2023045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.J.; Do, K.H.; Lee, J.B.; Alblushi, S.; Lee, S.M. Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Homma, S.; Sano, A.; Sakai, T.; Koezuka, S.; Otsuka, H.; Tochigi, N.; Kishi, K.; Iyoda, A. Impact of accurate diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases on postoperative outcomes in lung cancer. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 71, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Kanzaki, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Isaka, T.; Oyama, K.; Murasugi, M.; Onuki, T. Effect of collagen vascular disease-associated interstitial lung disease on the outcomes of lung cancer surgery. Surg. Today 2017, 47, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kreuter, M.; Ehlers-Tenenbaum, S.; Schaaf, M.; Oltmanns, U.; Palmowski, K.; Hoffmann, H.; Schnabel, P.A.; Heussel, C.P.; Puderbach, M.; Herth, F.J.; et al. Treatment and outcome of lung cancer in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2015, 31, 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kawabata, Y.; Koyama, N.; Ikeya, T.; Hoshi, E.; Takayanagi, N.; Koyama, S. A clinicopathological study of surgically resected lung cancer in patients with usual interstitial pneumonia. Respir. Med. 2017, 129, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Spagnolo, P.; Mogulkoc, N.; Wuyts, W.A.; Tomassetti, S.; Bendstrup, E.; Molina-Molina, M.; Manali, E.D.; Unat, O.S.; Bonella, F.; et al. Lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective multicentre study in Europe. Respirology 2023, 28, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Kim, H.H.; Hyun, D.G.; Ji, W.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, H.C. Clinical characteristics and outcome of lung cancer in patients with fibrosing interstitial lung disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, E.L.; Tietzova, I.; Bartlett, E.; Devaraj, A.; Biederer, J.; Brambilla, M.; Brunelli, A.; Chorostowska, J.; Decaluwe, H.; Deruysscher, D.; et al. ERS/ESTS/ESTRO/ESR/ESTI/EFOMP statement on management of incidental findings from low dose CT screening for lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 64, ezad302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upperton, S.; Beirne, P.; Bhartia, B.; Boland, A.; Bradley, C.; Crosbie, P.A.J.; Darby, M.; Eckert, C.; Gabe, R.; Hancock, N.; et al. Diagnoses and treatments for participants with interstitial lung abnormalities detected in the Yorkshire Lung Screening Trial. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, R.J.; Bartlett, E.C.; Ganatra, R.; Butt, H.; Kouranos, V.; Chua, F.; Kokosi, M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Desai, S.R.; Wells, A.U.; et al. Lung cancer screening provides an opportunity for early diagnosis and treatment of interstitial lung disease. Thorax 2022, 77, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.I.; Park, J.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Park, B.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.H.; Choi, W.I.; Lee, C.W. Prevalence of lung cancer in patients with interstitial lung disease is higher than in those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Medicine 2018, 97, e0071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker Brown, S.A.; Padilla, M.; Mhango, G.; Taioli, E.; Powell, C.; Wisnivesky, J. Outcomes of Older Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.W.; Dobelle, M.; Padilla, M.; Agovino, M.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Hashim, D.; Boffetta, P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.S.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.C. A nationwide population-based study of incidence and mortality of lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, Y.; Suda, T.; Naito, T.; Enomoto, N.; Hashimoto, D.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Nakamura, H.; Chida, K. Cumulative incidence of and predictive factors for lung cancer in IPF. Respirology 2009, 14, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Nouraie, M.; Chen, X.; Zou, R.H.; Sellares, J.; Veraldi, K.L.; Chiarchiaro, J.; Lindell, K.; Wilson, D.O.; Kaminski, N.; et al. Characteristics of lung cancer among patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial lung disease–analysis of institutional and population data. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Jeune, I.; Gribbin, J.; West, J.; Smith, C.; Cullinan, P.; Hubbard, R. The incidence of cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barczi, E.; Nagy, T.; Starobinski, L.; Kolonics-Farkas, A.; Eszes, N.; Bohacs, A.; Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Muller, V. Impact of interstitial lung disease and simultaneous lung cancer on therapeutic possibilities and survival. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassetti, S.; Gurioli, C.; Ryu, J.H.; Decker, P.A.; Ravaglia, C.; Tantalocco, P.; Buccioli, M.; Piciucchi, S.; Sverzellati, N.; Dubini, A.; et al. The impact of lung cancer on survival of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2015, 147, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masai, K.; Tsuta, K.; Motoi, N.; Shiraishi, K.; Furuta, K.; Suzuki, S.; Asakura, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Sakurai, H.; Watanabe, S.I.; et al. Clinicopathological, Immunohistochemical, and Genetic Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma Occurring in the Setting of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.; Song, J.W. Impact of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis on clinical outcomes of lung cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauclet, C.; Dupont, M.V.; Roelandt, K.; Regnier, M.; Delos, M.; Pirard, L.; Vander Borght, T.; Dahlqvist, C.; Froidure, A.; Rondelet, B.; et al. Treatment and Prognosis of Patients with Lung Cancer and Combined Interstitial Lung Disease. Cancers 2023, 15, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomaish, H.; Ung, Y.; Wang, S.; Tyrrell, P.N.; Zahra, S.A.; Oikonomou, A. Survival analysis in lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Antoniou, K.; Kreuter, M.; Evison, M.; Blum, T.G.; Poletti, V.; Grigoriu, B.; Vancheri, C.; Spagnolo, P.; Karampitsakos, T.; et al. The DIAMORFOSIS (DIAgnosis and Management Of lung canceR and FibrOSIS) survey: International survey and call for consensus. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00529-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.I.; Lee, D.Y.; Choi, H.G.; Lee, C.W. Lung Cancer development and mortality in interstitial lung disease with and without connective tissue diseases: A five-year Nationwide population-based study. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, Y.; Inui, N.; Yoshimura, K.; Nishimoto, K.; Mori, K.; Kono, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Enomoto, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Iwashita, T.; et al. Lung cancer development in patients with connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease: A retrospective observational study. Medicine 2016, 95, e5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, J.M.; Gibiot, Q.; Monnet, I.; Antoine, M.; Wislez, M.; Chouaid, C.; Cadranel, J. Lung cancer and interstitial lung disease: A literature review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3829–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.H.; Cho, J.H.; Eun, Y.; Han, K.; Jung, J.; Cho, I.Y.; Yoo, J.E.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Risk of Lung Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakutani, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Tominaga, A.; Kodama, K.; Nogi, S.; Tsuno, H.; Ogihara, H.; Nunokawa, T.; Komiya, A.; Furukawa, H.; et al. Related factors, increased mortality and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramochi, J.; Inase, N.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kawachi, H.; Takemura, T.; Yoshizawa, Y. Lung cancer in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respiration 2011, 82, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walscher, J.; Gross, B.; Morisset, J.; Johannson, K.A.; Vasakova, M.; Bruhwyler, J.; Kreuter, M. Comorbidities and survival in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udwadia, Z.F.; Koul, P.A.; Richeldi, L. Post-COVID lung fibrosis: The tsunami that will follow the earthquake. Lung India 2021, 38, S41–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chan, B.C.; Zhang, B.; Wong, K.C.; Kan, L.L.; Wong, C.K. Dark under the Lamp: Neglected Biological Pollutants in the Environment Are Closely Linked to Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Spagnolo, P.; Bonella, F.; Vancheri, C.; Tzilas, V.; Crestani, B.; Kreuter, M.; Bouros, D. Patients with IPF and lung cancer: Diagnosis and management. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.; Landeras, L.; Chung, J.H. Updated Fleischner Society Guidelines for Managing Incidental Pulmonary Nodules: Common Questions and Challenging Scenarios. Radiographics 2018, 38, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgalla, G.; Larici, A.R.; Golfi, N.; Calvello, M.; Farchione, A.; Del Ciello, A.; Varone, F.; Iovene, B.; Manfredi, R.; Richeldi, L. Mediastinal lymph node enlargement in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Relationships with disease progression and pulmonary function trends. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Galaris, A.; Chrysikos, S.; Papaioannou, O.; Vamvakaris, I.; Barbayianni, I.; Kanellopoulou, P.; Grammenoudi, S.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Stratakos, G.; et al. Expression of PD-1/PD-L1 axis in mediastinal lymph nodes and lung tissue of human and experimental lung fibrosis indicates a potential therapeutic target for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, T.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Yi, C.A.; Chung, M.P.; Kwon, O.J.; Kim, B.T.; Shim, Y.M. Incremental value of PET/CT Over CT for mediastinal nodal staging of non-small cell lung cancer: Comparison between patients with and without idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Sung, C.; Lee, H.S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, J.S.; Song, J.W.; Kim, M.Y.; Ryu, J.S. Is (18)F-FDG PET/CT useful for the differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Fukui, M.; Hattori, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Takamochi, K.; Suzuki, K. Diagnostic Value of Nodal Staging of Lung Cancer With Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Using PET. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 114, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Seol, H.Y.; Chung, H.S.; Mok, J.; Lee, G.; Jo, E.J.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.U.; et al. Safety and Diagnostic Yield of Radial Probe Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy for Peripheral Lung Lesions in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Respiration 2022, 101, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogawa, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Tsuchida, T. Diagnostic usefulness of bronchoscopy for peripheral pulmonary lesions in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 6304–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J.; Yun, G.; Yoon, S.H.; Song, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, K.H. Accuracy and complications of percutaneous transthoracic needle lung biopsy for the diagnosis of malignancy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9000–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, H.; Tsukahara, Y.; Sato, S.; Ohta, H.; Kida, G.; Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Kawabe, R.; Oba, T.; Akasaka, K.; et al. Impact of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD) in ILD patients complicated with secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2022, 38, e2021042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.V.; Afraz, Z.; Huo, Y.R.; Kandel, S.; Rogalla, P. Manual aspiration of a pneumothorax after CT-guided lung biopsy: Outcomes and risk factors. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drumm, O.; Joyce, E.A.; de Blacam, C.; Gleeson, T.; Kavanagh, J.; McCarthy, E.; McDermott, R.; Beddy, P. CT-guided Lung Biopsy: Effect of Biopsy-side Down Position on Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Placement. Radiology 2019, 292, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Sun, Y.G.; Ma, C.; Jiao, P.; Wu, Q.J.; Tian, W.X.; Yu, H.B.; Tong, H.F. Surgical outcomes and perioperative risk factors of patients with interstitial lung disease after pulmonary resection. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axtell, A.L.; David, E.A.; Block, M.I.; Parsons, N.; Habib, R.; Muniappan, A. Association Between Interstitial Lung Disease and Outcomes After Lung Cancer Resection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 116, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Goldstraw, P.; Yamada, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M.; Dubois, R.M.; Ladas, G. Pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer: Risk and benefit analysis of pulmonary resection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 125, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Shim, Y.M.; Choi, Y.S. Prediction of acute pulmonary complications after resection of lung cancer in patients with preexisting interstitial lung disease. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 59, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Teramukai, S.; Kondo, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ebina, M.; Kishi, K.; Fujii, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Maniwa, T.; et al. Impact and predictors of acute exacerbation of interstitial lung diseases after pulmonary resection for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1604–1611.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, H.; Sugino, K.; Hata, Y.; Makino, T.; Koezuka, S.; Isobe, K.; Tochigi, N.; Shibuya, K.; Homma, S.; Iyoda, A. Clinical features and outcomes of patients with lung cancer as well as combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.H. Clinical Outcomes and Prognosis of Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease Undergoing Lung Cancer Surgery: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, e27–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, F.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Shiina, T.; Asaka, S.; Yasuo, M.; Wada, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Yoshizawa, A.; Hanaoka, M. The Interstitial Lung Disease-Gender-Age-Physiology Index Can Predict the Prognosis in Surgically Resected Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease and Concomitant Lung Cancer. Respiration 2020, 99, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutani, Y.; Mimura, T.; Kai, Y.; Ito, M.; Misumi, K.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, M. Outcomes after lobar versus sublobar resection for clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer in patients with interstitial lung disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 1089–1096.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motono, N.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwai, S.; Iijima, Y.; Uramoto, H. Interstitial lung disease and wedge resection are poor prognostic factors for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Tsutani, Y.; Wakabayashi, M.; Mizutani, T.; Aokage, K.; Miyata, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Saji, H.; Watanabe, S.I.; Okada, M.; et al. Sublobar resection versus lobectomy for patients with resectable stage I non-small cell lung cancer with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A phase III study evaluating survival (JCOG1708, SURPRISE). Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 50, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.J.; Walters, G.I.; Watkins, S.; Rogers, V.; Fallouh, H.; Kalkat, M.; Naidu, B.; Bishay, E.S. Lung cancer resection in patients with underlying usual interstitial pneumonia: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, M.; Takamochi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Hotta, A.; Ando, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Oh, S.; Suzuki, K. Lobe-specific outcomes of surgery for lung cancer patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 68, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Goto, T.; Kitahara, A.; Koike, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Watanabe, T.; Tsuchida, M. Survival after repeated surgery for lung cancer with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Yoshino, I.; Yoshida, S.; Ikeda, N.; Tsuboi, M.; Asato, Y.; Katakami, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Okami, J.; et al. A phase II trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of perioperative pirfenidone for prevention of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in lung cancer patients undergoing pulmonary resection: West Japan Oncology Group 6711 L (PEOPLE Study). Respir Res 2016, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanayama, M.; Mori, M.; Matsumiya, H.; Taira, A.; Shinohara, S.; Kuwata, T.; Imanishi, N.; Yoneda, K.; Kuroda, K.; Tanaka, F. Perioperative pirfenidone treatment for lung cancer patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Surg. Today 2020, 50, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakairi, Y.; Yoshino, I.; Iwata, T.; Yoshida, S.; Kuwano, K.; Azuma, A.; Sakai, S.; Kobayashi, K. A randomized controlled phase III trial protocol: Perioperative pirfenidone therapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer combined with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis to confirm the preventative effect against postoperative acute exacerbation: The PIII-PEOPLE study (NEJ034). J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remon, J.; Soria, J.C.; Peters, S. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: An update of the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines focusing on diagnosis, staging, systemic and local therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, A.C.; Fruh, M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Besse, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Hendriks, L.E.; Lantuejoul, S.; Peters, S.; Reguart, N.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanic, S.; Paulus, R.; Timmerman, R.D.; Michalski, J.M.; Barriger, R.B.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.M.; Bradley, J. No clinically significant changes in pulmonary function following stereotactic body radiation therapy for early- stage peripheral non-small cell lung cancer: An analysis of RTOG 0236. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Dickinson, P.; Shrimali, R.K.; Salem, A.; Agarwal, S. Is Thoracic Radiotherapy an Absolute Contraindication for Treatment of Lung Cancer Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease? A Systematic Review. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2022, 34, e493–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, D.; Lyen, S.; Kandel, S.; Shapera, S.; Le, L.W.; Lindsay, P.; Wong, O.; Bezjak, A.; Brade, A.; Cho, B.C.J.; et al. Impact of Pretreatment Interstitial Lung Disease on Radiation Pneumonitis and Survival in Patients Treated With Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e219–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahig, H.; Filion, E.; Vu, T.; Chalaoui, J.; Lambert, L.; Roberge, D.; Gagnon, M.; Fortin, B.; Beliveau-Nadeau, D.; Mathieu, D.; et al. Severe radiation pneumonitis after lung stereotactic ablative radiation therapy in patients with interstitial lung disease. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, M.; Itonaga, T.; Saito, T.; Shiraishi, S.; Mikami, R.; Nakayama, H.; Sakurada, A.; Sugahara, S.; Koizumi, K.; Tokuuye, K. Predicting risk factors for radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary or metastatic lung tumours. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Pyo, H.; Noh, J.M.; Lee, W.; Park, B.; Park, H.Y.; Yoo, H. Preliminary result of definitive radiotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer who have underlying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Comparison between X-ray and proton therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Liang, S.; Xu, Y. Risk factors for radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer patients with subclinical interstitial lung disease after thoracic radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, Y.; Abe, T.; Omae, M.; Matsui, T.; Kato, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Enomoto, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Inui, N.; Yamada, K.; et al. Impact of Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease on Acute, Extensive Radiation Pneumonitis: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.; Pham, N.; Ansari, S.; Meshkov, D.; Castillo, S.; Li, M.; Olanrewaju, A.; Hobbs, B.; Castillo, E.; Guerrero, T. Pre-radiotherapy FDG PET predicts radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Huang, Y.Y.; Wang, T. Sublobar resection versus ablation for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, D.E.; Fernando, H.C.; Hillman, S.; Ng, T.; Tan, A.D.; Sharma, A.; Rilling, W.S.; Hong, K.; Putnam, J.B. Radiofrequency ablation of stage IA non-small cell lung cancer in medically inoperable patients: Results from the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z4033 (Alliance) trial. Cancer 2015, 121, 3491–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Bie, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Li, X. Safety and efficacy of CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer in patients with comorbid idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 4708–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashima, M.; Yamakado, K.; Takaki, H.; Kodama, H.; Yamada, T.; Uraki, J.; Nakatsuka, A. Complications after 1000 lung radiofrequency ablation sessions in 420 patients: A single center’s experiences. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, W576–W580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Senan, S.; Nossent, E.J.; Boldt, R.G.; Warner, A.; Palma, D.A.; Louie, A.V. Treatment-Related Toxicity in Patients With Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Coexisting Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Bie, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Synchronous percutaneous core-needle biopsy and microwave ablation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer in patients with Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Initial experience. Int. J. Hyperth. 2023, 40, 2270793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Jaiyesimi, I.A.; Ismaila, N.; Leighl, N.B.; Mamdani, H.; Phillips, T.; Owen, D.H. Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Without Driver Alterations: ASCO Living Guideline, Version 2023.1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, e51–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Jaiyesimi, I.A.; Ismaila, N.; Leighl, N.B.; Mamdani, H.; Phillips, T.; Owen, D.H. Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer With Driver Alterations: ASCO Living Guideline, Version 2023.1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, e42–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, K.; Kishimoto, J.; Ando, M.; Kenmotsu, H.; Minegishi, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Kato, T.; Ichihara, E.; Kondo, M.; Atagi, S.; et al. Nintedanib plus chemotherapy for nonsmall cell lung cancer with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A randomised phase 3 trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2200380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Naito, T.; Kimura, M.; Ono, A.; Shukuya, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuya, A.; Kaira, K.; Murakami, H.; Takahashi, T.; et al. The risk of cytotoxic chemotherapy-related exacerbation of interstitial lung disease with lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Jiao, G. Risk factors for acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease during chemotherapy for lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1250688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, K.; Saruwatari, K.; Matsushima, R.; Fujino, K.; Morinaga, J.; Oda, S.; Takahashi, H.; Shiraishi, S.; Okabayashi, H.; Hamada, S.; et al. Clinical impact of SUV(max) of interstitial lesions in lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease who underwent pulmonary resection. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y. The Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Chemotherapy in Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Kuroki, T.; Hayama, N.; Shiraishi, Y.; Amano, H.; Nakamura, M.; Hirano, S.; Tabeta, H.; Nakamura, S. Pemetrexed Plus Platinum for Patients With Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease. In Vivo 2019, 33, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Shukuya, T.; Takahashi, F.; Mori, K.; Suina, K.; Asao, T.; Kanemaru, R.; Honma, Y.; Muraki, K.; Sugano, K.; et al. Pemetrexed for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yano, Y.; Kuge, T.; Okabe, F.; Ishijima, M.; Uenami, T.; Kanazu, M.; Akazawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Mori, M. Safety and effectiveness of pirfenidone combined with carboplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, K.W.; Pyo, J.; Hatabu, H.; Nishino, M. The incidence of ALK inhibitor-related pneumonitis in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2019, 132, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johkoh, T.; Sakai, F.; Kusumoto, M.; Arakawa, H.; Harada, R.; Ueda, M.; Kudoh, S.; Fukuoka, M. Association between baseline pulmonary status and interstitial lung disease in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib—A cohort study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Tanaka, A.; Sagara, H. Risk factors for interstitial lung disease in patients with non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Investig. 2024, 62, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X. Pulmonary Toxicities of Gefitinib in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2016, 95, e3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Kishi, N.; Alerasool, P.; Rohs, N.C. Adverse Event Profile of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: An Updated Meta-analysis. Target. Oncol. 2024, 19, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S. Nintedanib: A Review of Its Use as Second-Line Treatment in Adults with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabholkar, S.; Gao, B.; Chuong, B. Nintedanib-A case of treating concurrent idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and non-small cell lung cancer. Respirol. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e0902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, T.; Tanaka, H.; Tabe, C.; Tsuchiya, J.; Ishioka, Y.; Itoga, M.; Taima, K.; Takanashi, S.; Tasaka, S. Effect of nintedanib on non-small cell lung cancer in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A case report and literature review. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1720–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, K.; Yokoe, S.; Kawashima, S.; Uchida, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Nakano, Y. Nintedanib prevented fibrosis progression and lung cancer growth in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirol. Case Rep. 2018, 6, e00363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Fukuoka, A.; Hontsu, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; Muro, S. Remarkable response of non-small cell lung cancer to nintedanib treatment in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, S.; Ichiyasu, H.; Ikeda, T.; Inaba, M.; Kashiwabara, K.; Sadamatsu, T.; Sato, N.; Akaike, K.; Okabayashi, H.; Saruwatari, K.; et al. Protective effect of bevacizumab on chemotherapy-related acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, X.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Y. Anti-Angiogenic Drugs Inhibit Interstitial Lung Disease Progression in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 873709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Chen, H.L.; Tsai, M.J.; Yang, C.J. EGFR-TKI plus antiangiogenic agent combination therapy may reduce the incidence of EGFR-TKI-associated interstitial lung disease in Asian. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Shimizu, J.; Shigematsu, F.; Watanabe, N.; Hasegawa, T.; Horio, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Fujiwara, Y. Atezolizumab and nintedanib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and interstitial lung disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 3371–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Oba, T.; Ohta, H.; Tsukahara, Y.; Kida, G.; Tsumiyama, E.; Nishizawa, T.; Kawabe, R.; Sato, S.; Akasaka, K.; et al. Nintedanib allows retreatment with atezolizumab of combined non-small cell lung cancer/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis after atezolizumab-induced pneumonitis: A case report. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, K.; Meti, N.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Hudson, M. Adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment for cancer. CMAJ 2019, 191, E40–E46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Kudo, K.; Yonesaka, K.; Kato, R.; Kaneda, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Takeda, M.; et al. Association of Immune-Related Adverse Events With Nivolumab Efficacy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibaki, R.; Murakami, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Goto, Y.; Kanda, S.; Horinouchi, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Motoi, N.; Kusumoto, M.; et al. Tumor expression and usefulness as a biomarker of programmed death ligand 1 in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with preexisting interstitial lung disease. Med. Oncol. 2019, 36, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duitman, J.; van den Ende, T.; Spek, C.A. Immune Checkpoints as Promising Targets for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, A.J.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Dobre, I.A.; Tait, S.; Schumacher, L.; Fintelmann, F.J.; Fingerman, L.M.; Keane, F.K.; Montesi, S.B. Management of Lung Cancer in the Patient with Interstitial Lung Disease. Oncologist 2023, 28, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazerooni, E.A.; Martinez, F.J.; Flint, A.; Jamadar, D.A.; Gross, B.H.; Spizarny, D.L.; Cascade, P.N.; Whyte, R.I.; Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Toews, G. Thin-section CT obtained at 10-mm increments versus limited three-level thin-section CT for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Correlation with pathologic scoring. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 169, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Shimizu, J.; Hasegawa, T.; Horio, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Hida, T. Pre-existing pulmonary fibrosis is a risk factor for anti-PD-1-related pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis. Lung Cancer 2018, 125, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Masuda, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Horimasu, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Tsutani, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Fujitaka, K.; et al. Pre-existing interstitial lung abnormalities are risk factors for immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced interstitial lung disease in non-small cell lung cancer. Respir. Investig. 2019, 57, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Honda, T.; Sema, M.; Kawahara, T.; Jin, Y.; Natsume, I.; Chiaki, T.; Yamashita, T.; Tsukada, Y.; Taki, R.; et al. The utility of ground-glass attenuation score for anticancer treatment-related acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease among lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Tomii, K.; Takimoto, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Sugino, K.; Ichikado, K.; Moriguchi, S.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with lung cancer having chronic interstitial pneumonia. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00981-2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, K.; Cheng, Y. Clinical Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Preexisting Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2022, 161, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunger, M.; Velcheti, V. A Case of a Patient with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis with Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Nivolumab. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, e96–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, M.; Tanaka, K.; Sunami, S.; Asoh, T.; Maeyama, T.; Tsuruta, N.; Nakanishi, Y.; Okamoto, I. Durable response to nivolumab in a lung adenocarcinoma patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 1519–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, D.; Yomota, M.; Sekine, A.; Morita, M.; Morimoto, T.; Hosomi, Y.; Ogura, T.; Tomioka, H.; Tomii, K. Nivolumab for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with mild idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: A multicenter, open-label single-arm phase II trial. Lung Cancer 2019, 134, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaka, Y.; Honda, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Tsutsui, T.; Saito, H.; Watabe, H.; Shimaya, K.; Mochizuki, A.; Tsuyuki, S.; Kawahara, T.; et al. Non-inferior clinical outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease. Lung Cancer 2021, 155, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudoh, S.; Kato, H.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Nakata, K.; Ichinose, Y.; Tsuboi, M.; Yokota, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Suga, M.; et al. Interstitial lung disease in Japanese patients with lung cancer: A cohort and nested case-control study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assie, J.B.; Chouaid, C.; Nunes, H.; Reynaud, D.; Gaudin, A.F.; Grumberg, V.; Jolivel, R.; Jouaneton, B.; Cotte, F.E.; Duchemann, B. Outcome following nivolumab treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and comorbid interstitial lung disease in a real-world setting. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2023, 15, 17588359231152847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Guidelines Version 7.2024 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1450 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Bando, M.; Homma, S.; Date, H.; Kishi, K.; Yamauchi, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Miyamoto, A.; Goto, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Azuma, A.; et al. Japanese guidelines for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 2023:Revised edition. Respir. Investig. 2024, 62, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JafariNezhad, A.; YektaKooshali, M.H. Lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwabara, K.; Semba, H.; Fujii, S.; Tsumura, S.; Aoki, R. Difference in benefit of chemotherapy between small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial pneumonia and patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2015, 35, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Togashi, Y.; Masago, K.; Handa, T.; Tanizawa, K.; Okuda, C.; Sakamori, Y.; Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Mishima, M. Prognostic significance of preexisting interstitial lung disease in Japanese patients with small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kanaji, N.; Shimizu, J.; Sakai, K.; Ueda, Y.; Miyawaki, H.; Watanabe, N.; Uemura, T.; Hida, T.; Inoue, T.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Clinical features of patients with small cell lung cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis treated with chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620963866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, N.; Iwai, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Aoshiba, K.; Nakamura, H. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in small cell lung cancer as a predictive factor for poor clinical outcome and risk of its exacerbation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K.; Niho, S.; Umemura, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; Ohe, Y. Safety and efficacy of platinum agents plus etoposide for patients with small cell lung cancer with interstitial lung disease. Anticancer. Res. 2013, 33, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakao, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Horimasu, Y.; Masuda, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Nakashima, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Fujitaka, K.; Hamada, H.; et al. Chemotherapy-associated Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease Shortens Survival Especially in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 5725–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Ogura, T.; Kato, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Agemi, Y.; Tokito, T.; Ito, K.; Isomoto, K.; Takiguchi, Y.; Yoneshima, Y.; et al. Nintedanib plus Chemotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer with Comorbid Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2024, 21, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Ozguroglu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).