Potentiation by Protein Synthesis Inducers of Translational Readthrough of Pathogenic Premature Termination Codons in PTEN Isoforms
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of PTC Distribution (PTCome)
2.2. Cell Culture, Transfections, and Reagents
2.3. Plasmids and Mutagenesis
2.4. Immunoblot and PTEN Functional Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
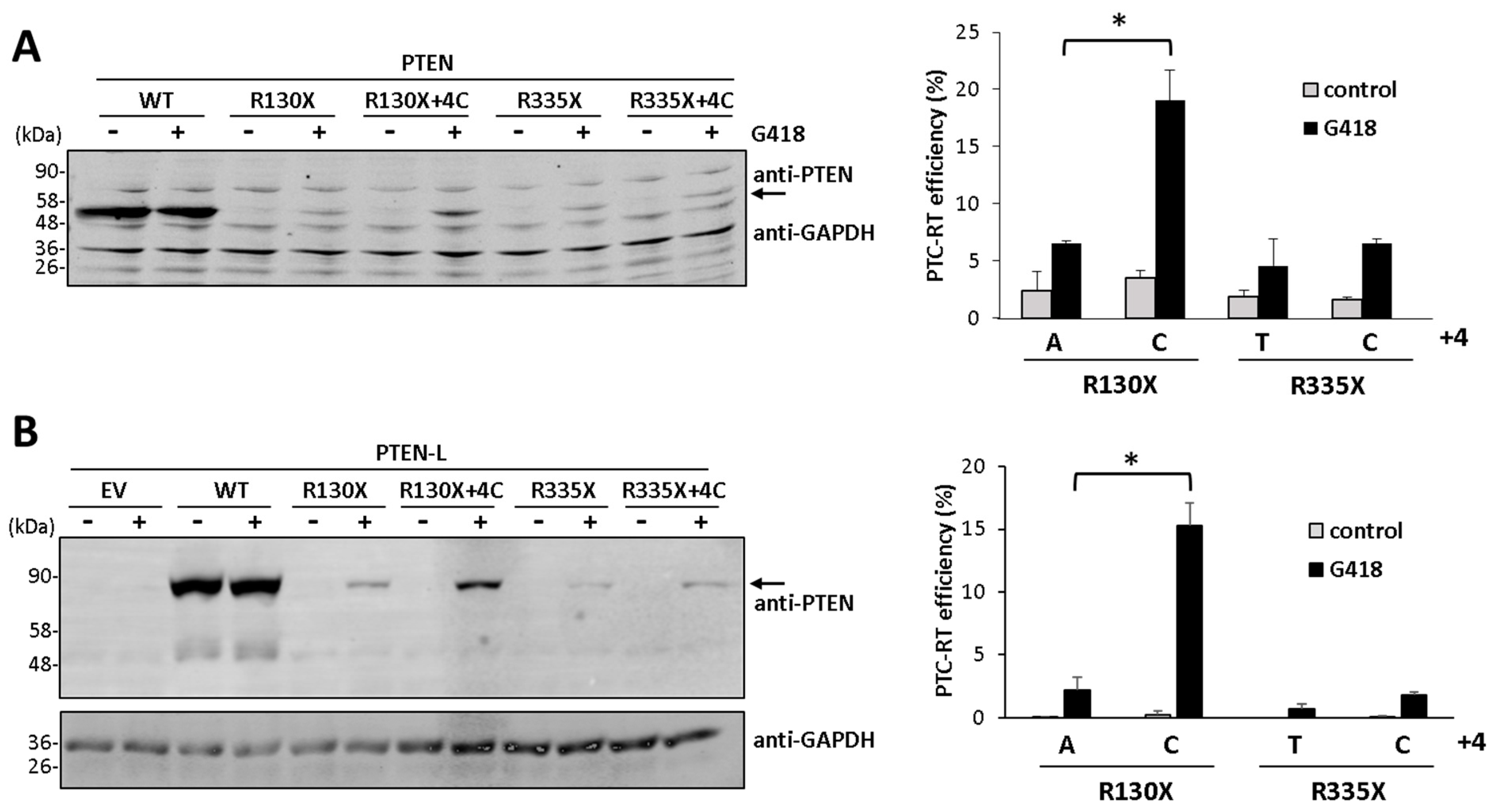
3.1. Distribution of Premature Termination Codons and Translational Readthrough of PTEN-L
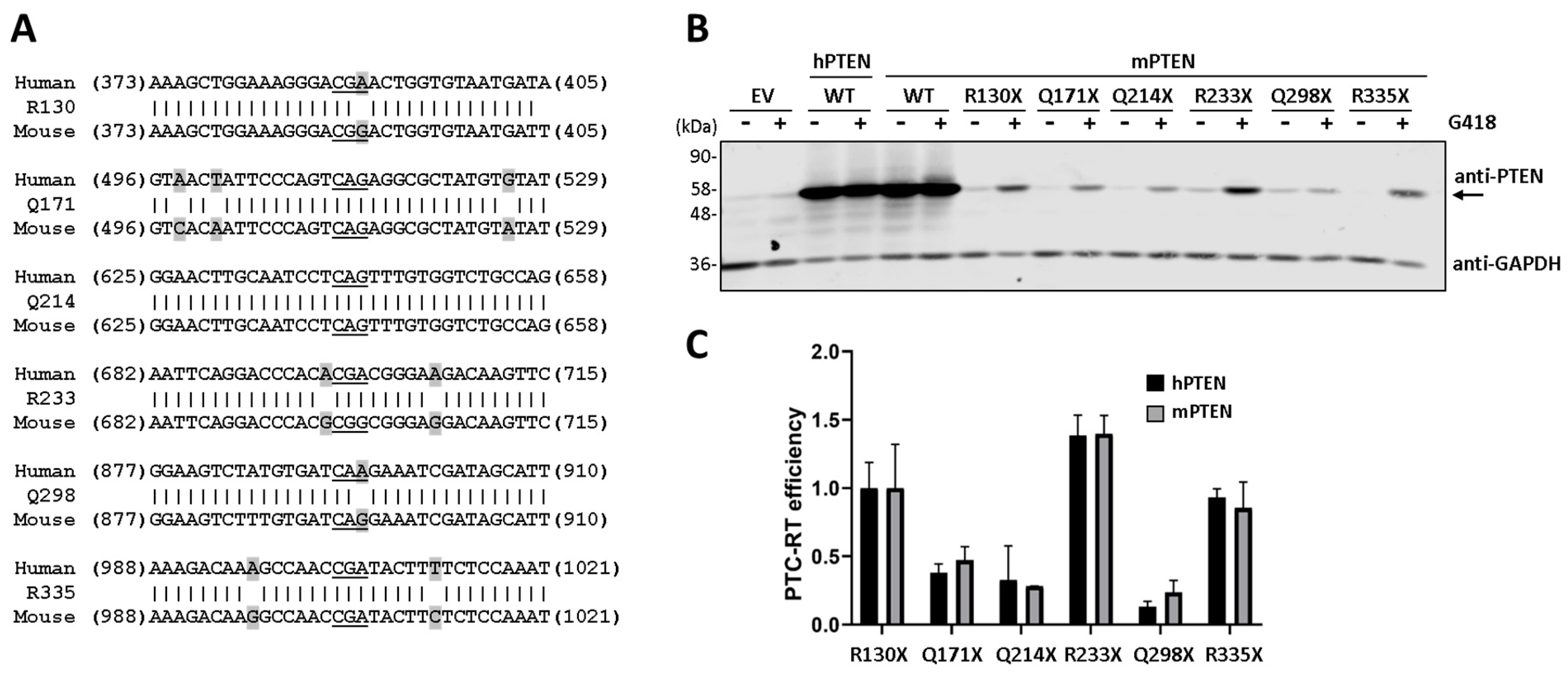
3.2. Nucleotide Context and Readthrough Efficiency in Human and Mouse PTEN
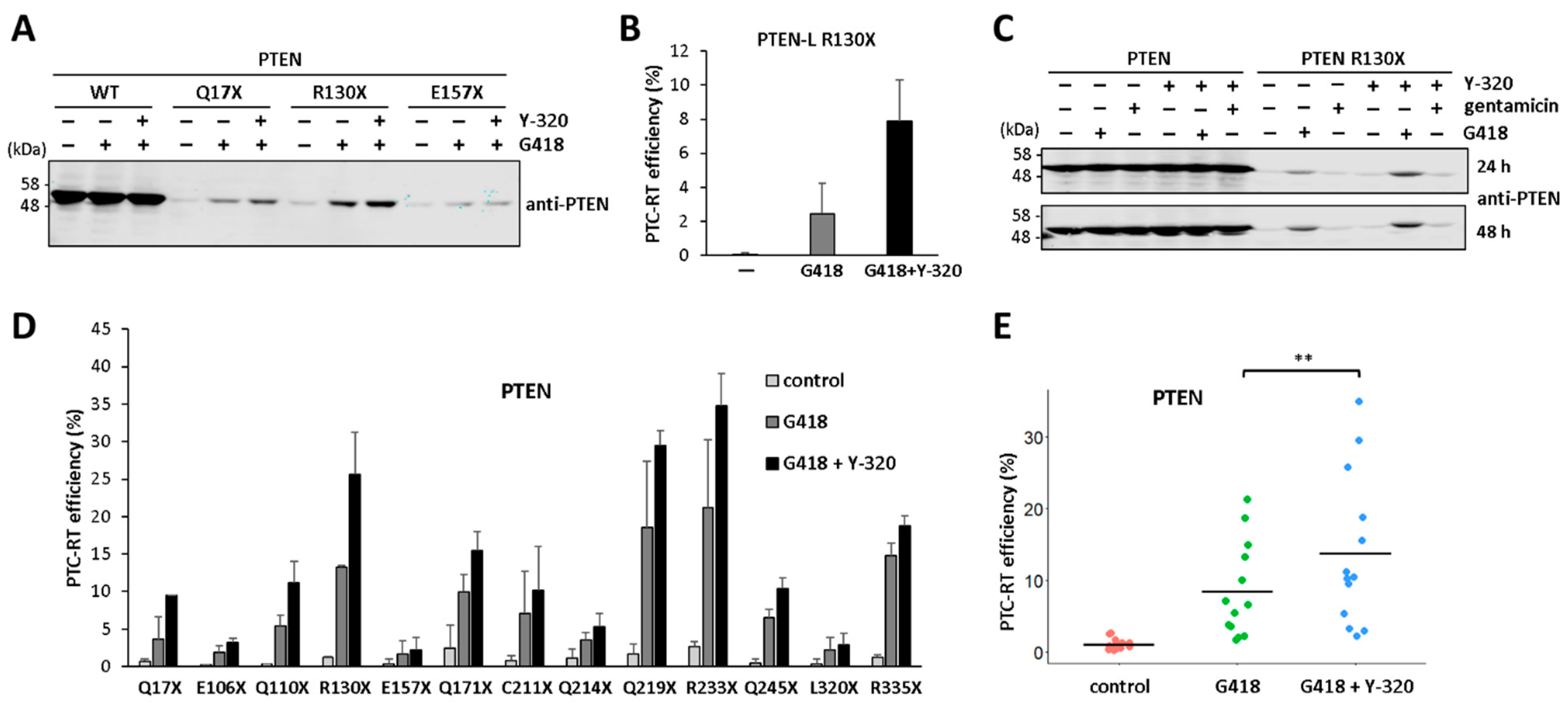
3.3. Protein Synthesis Rate Affects PTEN Readthrough Efficiency
3.4. Potentiation of PTEN Readthrough by Y-320
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, M.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: New modes and prospects. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maehama, T.; Dixon, J.E. PTEN: A tumour suppressor that functions as a phospholipid phosphatase. Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, R. PTEN: A yin-yang master regulator protein in health and disease. Methods 2015, 77–78, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Ghosh, G.; Chowdhury, S.G.; Karmakar, P. Non-canonical function of nuclear PTEN and its implication on tumorigenesis. DNA Repair 2021, 107, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. Phosphatase-independent functions of the tumor suppressor PTEN. In Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases in Cancer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Garcia, V.; Tawil, Y.; Wise, H.M.; Leslie, N.R. Mechanisms of PTEN loss in cancer: It’s all about diversity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, R.; Mingo, J.; Gaafar, A.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Luna, S.; Torices, L.; Angulo, J.C.; Lopez, J.I. Precise Immunodetection of PTEN Protein in Human Neoplasia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a036293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Parada, L.F. PTEN signaling in autism spectrum disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Fine, B.; Steinbach, N.; Dendy, M.; Rapp, Z.; Shaw, J.; Pappas, K.; Yu, J.S.; Hodakoski, C.; Mense, S.; et al. A secreted PTEN phosphatase that enters cells to alter signaling and survival. Science 2013, 341, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; He, S.; Yang, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, X.; McNutt, M.A.; Shen, W.H.; et al. PTENalpha, a PTEN Isoform Translated through Alternative Initiation, Regulates Mitochondrial Function and Energy Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, R.; Baker, S.J.; Barata, J.T.; Carracedo, A.; Cid, V.J.; Chin-Sang, I.D.; Dave, V.; den Hertog, J.; Devreotes, P.; Eickholt, B.J.; et al. A Unified Nomenclature and Amino Acid Numbering for Human PTEN. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, pe15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzani, I.; Ivanov, I.P.; Andreev, D.E.; Dmitriev, R.I.; Dean, K.A.; Baranov, P.V.; Atkins, J.F.; Loughran, G. Systematic analysis of the PTEN 5′ leader identifies a major AUU initiated proteoform. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 150203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngeow, J.; Eng, C. PTEN in Hereditary and Sporadic Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a036087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehia, L.; Keel, E.; Eng, C. The Clinical Spectrum of PTEN Mutations. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torices, L.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Mingo, J.; Luna, S.; Erramuzpe, A.; Cortes, J.M.; Pulido, R. Induction of Translational Readthrough on Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases Targeted by Premature Termination Codon Mutations in Human Disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2743, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supek, F.; Lehner, B.; Lindeboom, R.G.H. To NMD or Not To NMD: Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay in Cancer and Other Genetic Diseases. Trends Genet. TIG 2021, 37, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, M.; Bukowy-Bieryllo, Z.; Zietkiewicz, E. Advances in therapeutic use of a drug-stimulated translational readthrough of premature termination codons. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, K.M.; Xue, X.; Gunn, G.; Bedwell, D.M. Therapeutics based on stop codon readthrough. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2014, 15, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Dias, P.; Romao, L. Nonsense suppression therapies in human genetic diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2021, 78, 4677–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beryozkin, A.; Nagel-Wolfum, K.; Banin, E.; Sharon, D. Factors Affecting Readthrough of Natural Versus Premature Termination Codons. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1415, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, M.; Bukowy-Bieryllo, Z.; Zietkiewicz, E. Translational readthrough potential of natural termination codons in eucaryotes--The impact of RNA sequence. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ma, F.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Xie, X. Pharmaceuticals Promoting Premature Termination Codon Readthrough: Progress in Development. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spelier, S.; van Doorn, E.P.M.; van der Ent, C.K.; Beekman, J.M.; Koppens, M.A.J. Readthrough compounds for nonsense mutations: Bridging the translational gap. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Farahabadi, S.; Baradaran-Heravi, A.; Zimmerman, C.; Choi, K.; Flibotte, S.; Roberge, M. Small molecule Y-320 stimulates ribosome biogenesis, protein synthesis, and aminoglycoside-induced premature termination codon readthrough. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittenstein, A.; Caspi, M.; Rippin, I.; Elroy-Stein, O.; Eldar-Finkelman, H.; Thoms, S.; Rosin-Arbesfeld, R. Nonsense mutation suppression is enhanced by targeting different stages of the protein synthesis process. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, S.; Torices, L.; Mingo, J.; Amo, L.; Rodriguez-Escudero, I.; Ruiz-Ibarlucea, P.; Erramuzpe, A.; Cortes, J.M.; Tejada, M.I.; Molina, M.; et al. A global analysis of the reconstitution of PTEN function by translational readthrough of PTEN pathogenic premature termination codons. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, M.J.; Chitipiralla, S.; Brown, G.R.; Chen, C.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; Kaur, K.; Liu, C.; et al. ClinVar: Improvements to accessing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D835–D844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Chapman, M.; Evans, K.; Azevedo, L.; Hayden, M.; Heywood, S.; Millar, D.S.; Phillips, A.D.; et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD((R))): Optimizing its use in a clinical diagnostic or research setting. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Andrés-Pons, A.; Fernández, E.; Valiente, M.; Torres, J.; Cervera, J.; Pulido, R. Nuclear localization of PTEN by a Ran-dependent mechanism enhances apoptosis: Involvement of an N-terminal nuclear localization domain and multiple nuclear exclusion motifs. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 4002–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingo, J.; Rodriguez-Escudero, I.; Luna, S.; Fernandez-Acero, T.; Amo, L.; Jonasson, A.R.; Zori, R.T.; Lopez, J.I.; Molina, M.; Cid, V.J.; et al. A pathogenic role for germline PTEN variants which accumulate into the nucleus. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2018, 26, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.; Torres, J.; Torres, M.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.; Macia, M.; Carracedo, A.; Pulido, R. A novel loss-of-function mutation (N48K) in the PTEN gene in a Spanish patient with Cowden disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torices, L.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Lopez, J.I.; Pulido, R. Novel anti-PTEN C2 domain monoclonal antibodies to analyze the expression and function of PTEN isoform variants. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torices, L.; de Las Heras, J.; Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Cortes, J.M.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Pulido, R. MMADHC premature termination codons in the pathogenesis of cobalamin D disorder: Potential of translational readthrough reconstitution. Mol. Genet Metab. Rep. 2021, 26, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Pulido, R. The tumor suppressor PTEN is phosphorylated by the protein kinase CK2 at its C terminus. Implications for PTEN stability to proteasome-mediated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingo, J.; Erramuzpe, A.; Luna, S.; Aurtenetxe, O.; Amo, L.; Diez, I.; Schepens, J.T.; Hendriks, W.J.; Cortes, J.M.; Pulido, R. One-Tube-Only Standardized Site-Directed Mutagenesis: An Alternative Approach to Generate Amino Acid Substitution Collections. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingo, J.; Luna, S.; Gaafar, A.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Torices, L.; Mosteiro, L.; Ruiz, R.; Guerra, I.; Llarena, R.; Angulo, J.C.; et al. Precise definition of PTEN C-terminal epitopes and its implications in clinical oncology. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, S.J. Signal transduction mechanisms in the regulation of protein synthesis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 1994, 19, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, R.E. Regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis by initiation factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 3017–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, M.A.; Esmaili, M.; Hassan, M.; Ragheb, M.A. The Role of PTEN-L in Modulating PINK1-Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Parsons, R.E. Molecular pathways: Intercellular PTEN and the potential of PTEN restoration therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5379–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, G.; Shen, H.M. The Long and the Short of PTEN in the Regulation of Mitophagy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Vanaja, K.G.; Boyer, J.A.; Gadal, S.; Solomon, H.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Levchenko, A.; Rosen, N. Regulation of PTEN translation by PI3K signaling maintains pathway homeostasis. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 708–723 e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, V.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Viollet, L.; Wall, C.; King, W.; Al-Dahhak, R.; Lewis, S.; Shilling, C.J.; Kota, J.; Serrano-Munuera, C.; et al. Gentamicin-induced readthrough of stop codons in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peled, A.; Samuelov, L.; Sarig, O.; Bochner, R.; Malki, L.; Pavlovsky, M.; Pichinuk, E.; Weil, M.; Sprecher, E. Treatment of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp with topical gentamicin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Renouil, M.; Fajac, A.; Bidou, L.; Parbaille, B.; Pierrot, S.; Davy, N.; Bismuth, E.; Reinert, P.; Lenoir, G.; et al. In vitro prediction of stop-codon suppression by intravenous gentamicin in patients with cystic fibrosis: A pilot study. BMC Med. 2007, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahi-Birjand, M.; Yaghoubi, S.; Abdollahpour-Alitappeh, M.; Keshtkaran, Z.; Bagheri, N.; Pirouzi, A.; Khatami, M.; Sineh Sepehr, K.; Peymani, P.; Karimzadeh, I. Protective effects of pharmacological agents against aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity: A systematic review. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, A.; Cancer, M.; Palomar-Siles, M.; Ohlin, S.; Zhang, M.; Sun-Zhang, A.; Mariani, A.; Liu, J.; Bykov, V.J.N.; Wiman, K.G. Novel compounds that synergize with aminoglycoside G418 or eRF3 degraders for translational readthrough of nonsense mutant TP53 and PTEN. RNA Biol. 2023, 20, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torices, L.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Pulido, R. Potentiation by Protein Synthesis Inducers of Translational Readthrough of Pathogenic Premature Termination Codons in PTEN Isoforms. Cancers 2024, 16, 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162836
Torices L, Nunes-Xavier CE, Pulido R. Potentiation by Protein Synthesis Inducers of Translational Readthrough of Pathogenic Premature Termination Codons in PTEN Isoforms. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162836
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorices, Leire, Caroline E. Nunes-Xavier, and Rafael Pulido. 2024. "Potentiation by Protein Synthesis Inducers of Translational Readthrough of Pathogenic Premature Termination Codons in PTEN Isoforms" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162836
APA StyleTorices, L., Nunes-Xavier, C. E., & Pulido, R. (2024). Potentiation by Protein Synthesis Inducers of Translational Readthrough of Pathogenic Premature Termination Codons in PTEN Isoforms. Cancers, 16(16), 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162836





