Enhanced De Novo Lipid Synthesis Mediated by FASN Induces Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Public Dataset and Pathway Analysis
2.2. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.3. Gene Silencing and Overexpression with Lentivirus
2.4. Application of Fatty Acid Inhibitors and Palmitate
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT–PCR) and Western Blot Analyses
2.6. The mRNA-Seq and Analysis
2.7. Cell-Viability, Colony-Formation, and Migration Assays
2.8. Quantification of Triacylglycerol and Neutral Lipids
2.9. Cell-Cycle, ROS, and Apoptosis Assays
2.10. In Vivo Studies
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
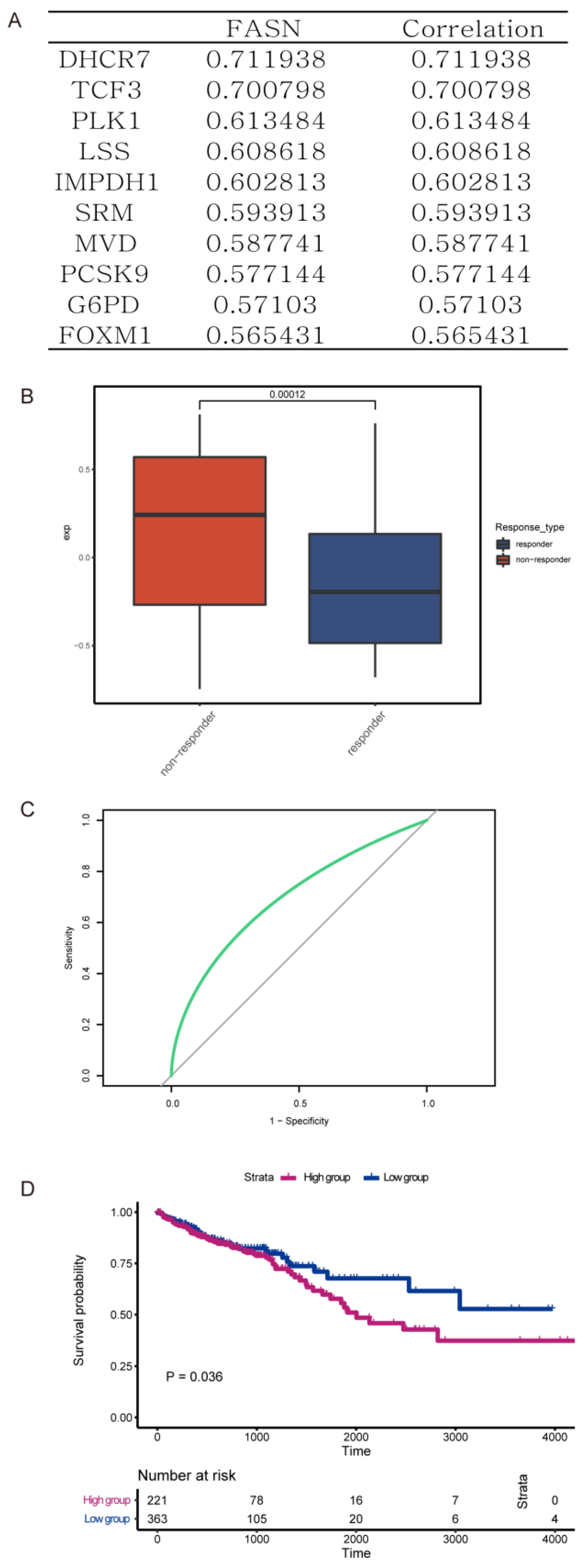
3.1. FASN Expression Was Associated with Worse Prognosis and Poor Oxaliplatin Therapy Response in Colorectal Cancer Patients
3.2. De Novo Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Rescued Colorectal Cancer Cells from Oxaliplatin
3.3. Pharmacological Inhibition of FASN Synergistically Enhanced the Antiproliferative Effect of Oxaliplatin in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
3.4. The Combination of Orlistat and Oxaliplatin Caused Cell-Cycle Arrest and Facilitated Oxaliplatin-Induced Apoptosis
3.5. Orlistat Promoted Oxaliplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity by Inhibiting Phosphorylation of the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT Pathways
3.6. Decreased Tumor Burden in a Xenograft-Implantation Model of Colorectal Cancer by the Sequential Combination of Orlistat and Oxaliplatin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiong, B.H.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, L. XELOX vs. FOLFOX in metastatic colorectal cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Cancer Investig. 2016, 34, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C.C.; Huang, Y.N.; He, M.L.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Molecular mechanisms of chemo- and radiotherapy resistance and the potential implications for cancer treatment. MedComm 2021, 2, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochster, H.S.; Sargent, D.J. One good DNA-damage deserves another: Oxaliplatin in MSI-high colon cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysman, E.; Brusselmans, K.; Scheys, K.; Timmermans, L.; Derua, R.; Munck, S.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Waltregny, D.; Daniëls, V.W.; Machiels, J.; et al. De novo lipogenesis protects cancer cells from free radicals and chemotherapeutics by promoting membrane lipid saturation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8117–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.N.; He, M.M.; Wu, Q.N.; Lu, Y.-X.; Yu, H.-E.; Chen, Z.-H.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Inhibition of fatty acid catabolism augments the efficacy of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. 2020, 473, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Xia, L.; Oyang, L.; Liang, J.; Tan, S.; Wu, N.; Yi, P.; Pan, Q.; Rao, S.; Han, Y.; et al. The POU2F1-ALDOA axis promotes the proliferation and chemoresistance of colon cancer cells by enhancing glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway activity. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1024–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Shan, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Jin, Z. Characterization of the fatty acid metabolism in colorectal cancer to guide clinical therapy. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 20, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakiet, A.; Kobiela, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Sledzinski, T.; Mika, A. Changes in lipids composition and metabolism in colorectal cancer: A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vecchia, S.; Sebastian, C. Metabolic pathways regulating colorectal cancer initiation and progression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, S.; Shukla, S.K.; King, R.J.; Gunda, V.; Vernucci, E.; Abrego, J.; Chaika, N.V.; Lyudmyla, B.; Lazenby, A.J.; Berim, L.; et al. De Novo Lipid Synthesis Facilitates Gemcitabine Resistance through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5503–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.; Augustine, D.; Rao, R.S.; Patil, S.; Awan, K.H.; Sowmya, S.V.; Haragannavar, V.C.; Prasad, K. Lipid metabolism in cancer: A systematic review. J. Carcinog. 2021, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fhu, C.W.; Ali, A. Fatty Acid Synthase: An Emerging Target in Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Lupu, R. Fatty acid synthase (FASN) as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Jian, S.; Ding, Q.; Gu, W.; Yao, Y.; Ma, J.; et al. LYAR Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression by Upregulating FSCN1 Expression and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9979707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xiang, W.; Han, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cai, S.; Xu, Y.; Mo, S.; et al. PTPRO represses colorectal cancer tumorigenesis and progression by reprogramming fatty acid metabolism. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 848–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, C.D.; Hindmarsh, E.J.; Smith, J.W. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis by orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Jin, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, D.; Luo, Q.; Tian, H.; Cai, L.; Meng, L.; Bi, R.; Wang, L.; et al. GLUT5-mediated fructose utilization drives lung cancer growth by stimulating fatty acid synthesis and AMPK/mTORC1 signaling. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e131596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridel, S.J.; Axelrod, F.; Rozenkrantz, N.; Smith, J.W. Orlistat is a novel inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, L. Down-regulation of NTSR3 inhibits cell growth and metastasis, as well as the PI3K-AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Liu, Y.; Gong, T.; Pan, Q.; Xiang, T.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, H.; Han, Y.; Song, M.; et al. Inhibition of DTYMK significantly restrains the growth of HCC and increases sensitivity to oxaliplatin. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, K.; Yao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, R.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L. A miR-567-PIK3AP1-PI3K/AKT-c-Myc feedback loop regulates tumour growth and chemoresistance in gastric cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ali, A.; Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Rahman, F.-U. Inhibition of SREBP-mediated lipid biosynthesis and activation of multiple anticancer mechanisms by platinum complexes: Ascribe possibilities of new antitumor strategies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 227, 113920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, S.; Yang, W.L.; Aziz, M.; Kameoka, S.; Wang, P. Fatty acid synthase inhibitor C75 ameliorates experimental colitis. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, S.; Cox, J.; Cenedella, R.J. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase by Orlistat accelerates gastric tumor cell apoptosis in culture and increases survival rates in gastric tumor bearing mice in vivo. Lipids 2009, 44, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Sheng, L.; Yuan, M.; Hu, J.; Meng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, G.; et al. Orlistat delays hepatocarcinogenesis in mice with hepatic co-activation of AKT and c-Met. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 392, 114918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Bu, X.; Tian, X.; Wu, P.; Yang, L.; Huang, P. Fatty acid synthase regulates proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells via HER2-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnupuri, K.S.; Alvarado, D.M.; Khouri, A.N.; Shabsovich, M.; Chen, B.; Dieckgraefe, B.K.; Ciorba, M.A. IDO1 and Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites Activate PI3K-Akt Signaling in the Neoplastic Colon Epithelium to Promote Cancer Cell Proliferation and Inhibit Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, A.; Duguay, S.R.; Ouellette, R.J.; Surette, M.E. 17beta-estradiol induces stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 expression in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Q.; Sui, F.; Pu, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, S.; Yao, D.; Ji, M.; Hou, P. Vitamin C kills thyroid cancer cells through ROS-dependent inhibition of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways via distinct mechanisms. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4461–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, I.I.C.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Park, Y.; Rivera, K.; Palm, W.; Wilson, J.; Sangar, V.; Hao, Y.; Öhlund, D.; et al. NRF2 Promotes Tumor Maintenance by Modulating mRNA Translation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2016, 166, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Dai, W.; Luo, W.; Ye, L.; Fang, H.; Mo, S.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Cai, G. Enhanced De Novo Lipid Synthesis Mediated by FASN Induces Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030562
Han L, Dai W, Luo W, Ye L, Fang H, Mo S, Li Q, Xu Y, Wang R, Cai G. Enhanced De Novo Lipid Synthesis Mediated by FASN Induces Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030562
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lingyu, Weixing Dai, Wenqin Luo, Li Ye, Hongsheng Fang, Shaobo Mo, Qingguo Li, Ye Xu, Renjie Wang, and Guoxiang Cai. 2023. "Enhanced De Novo Lipid Synthesis Mediated by FASN Induces Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 3: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030562
APA StyleHan, L., Dai, W., Luo, W., Ye, L., Fang, H., Mo, S., Li, Q., Xu, Y., Wang, R., & Cai, G. (2023). Enhanced De Novo Lipid Synthesis Mediated by FASN Induces Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 15(3), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030562






