The Inhibitory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Rat Pyloric Smooth Muscle Contractile Response to Substance P In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
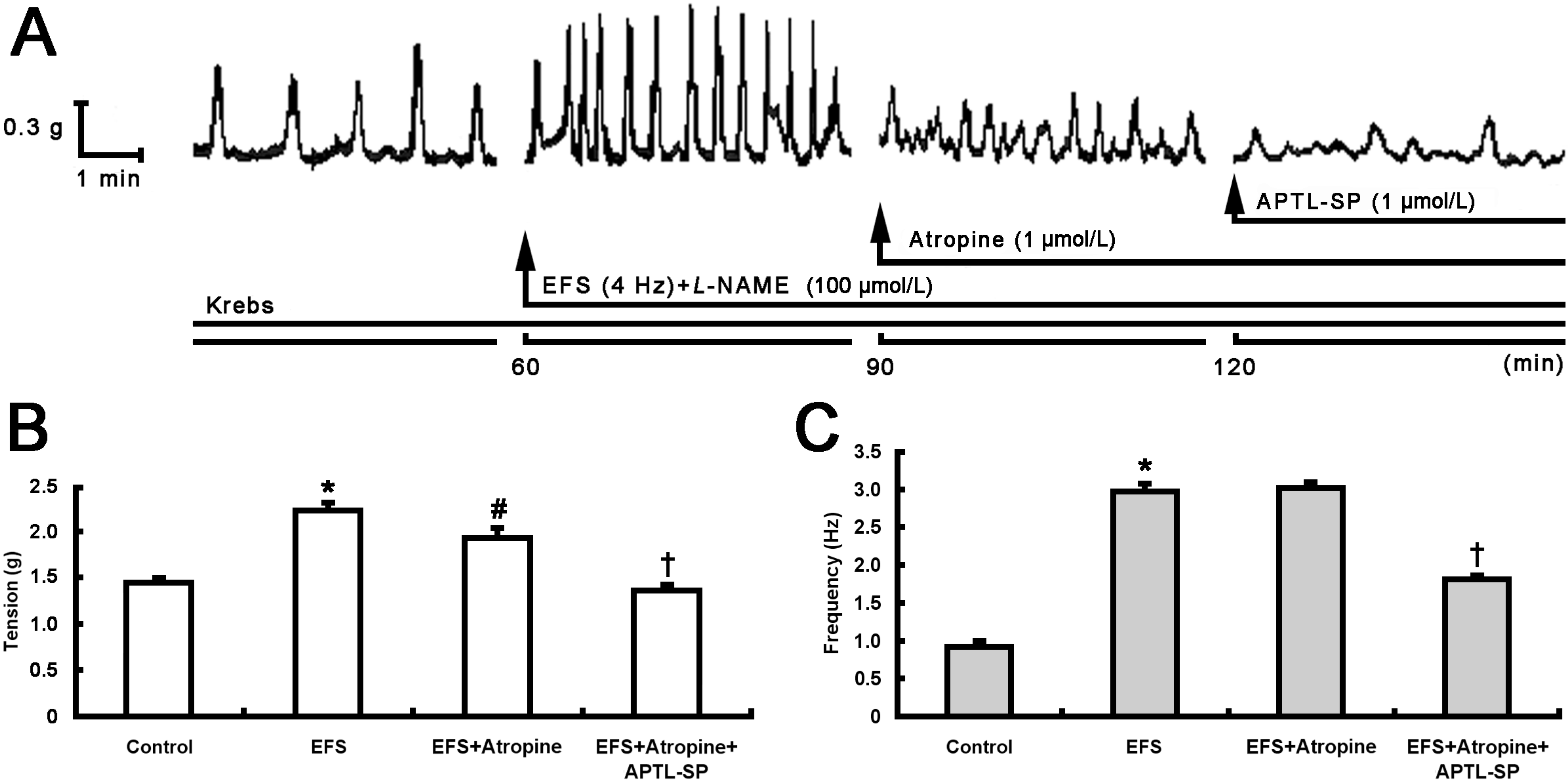
2.1. Inhibitory Effect of BTX-A on Contractile Response to SP Release from Pylorus
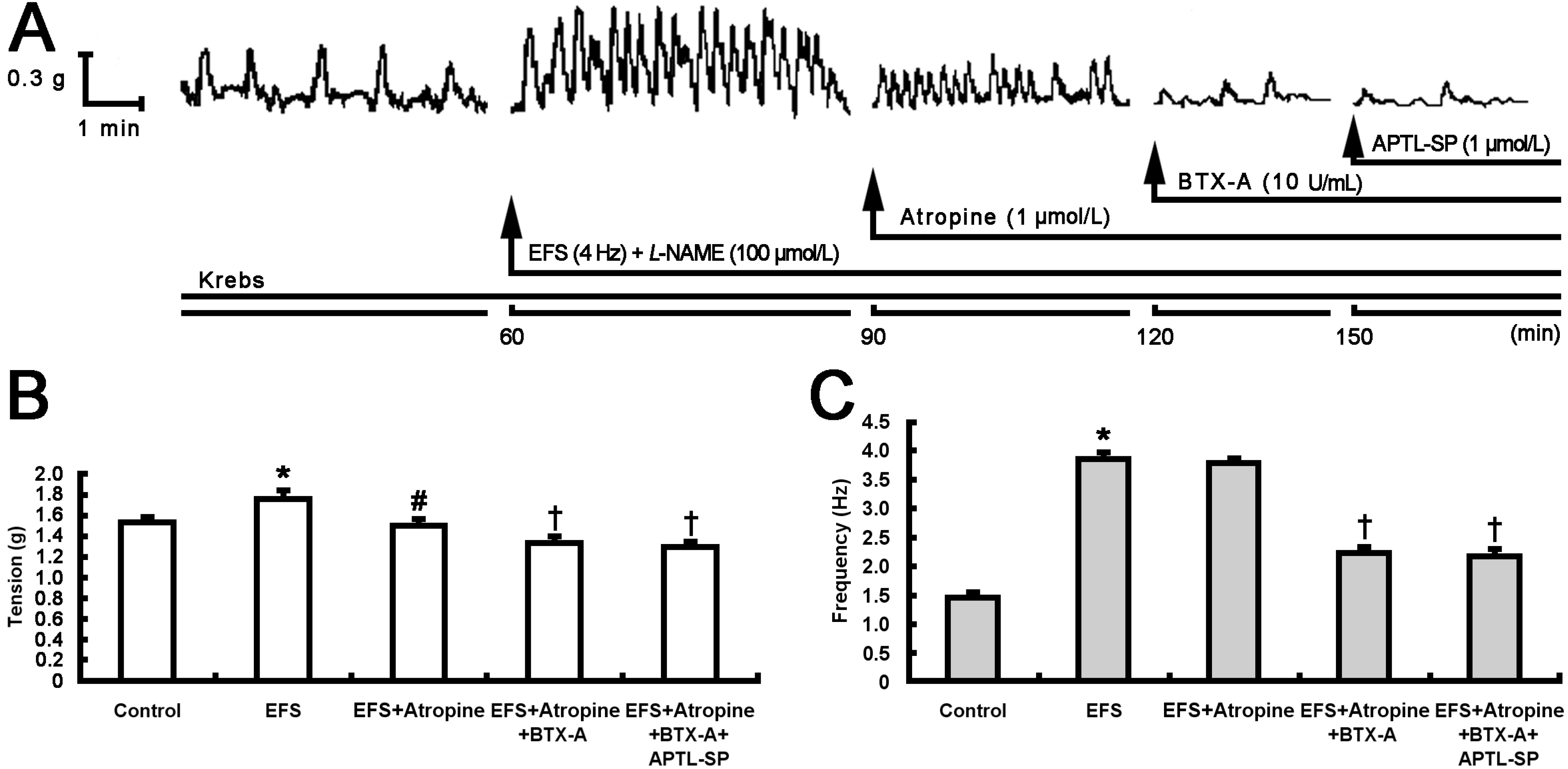
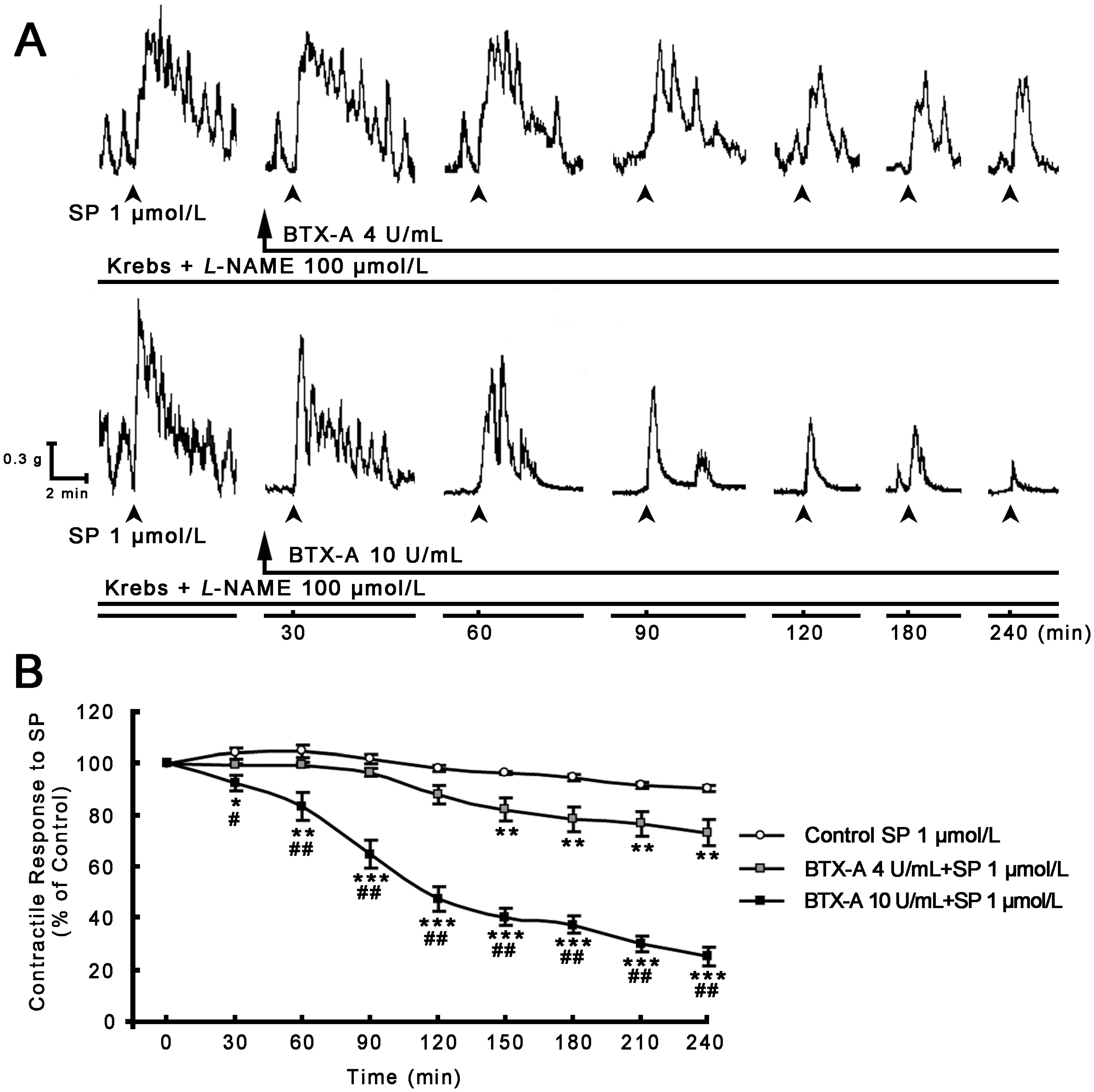
2.2. Inhibitory Effect of BTX-A on SP-induced Contractile Response
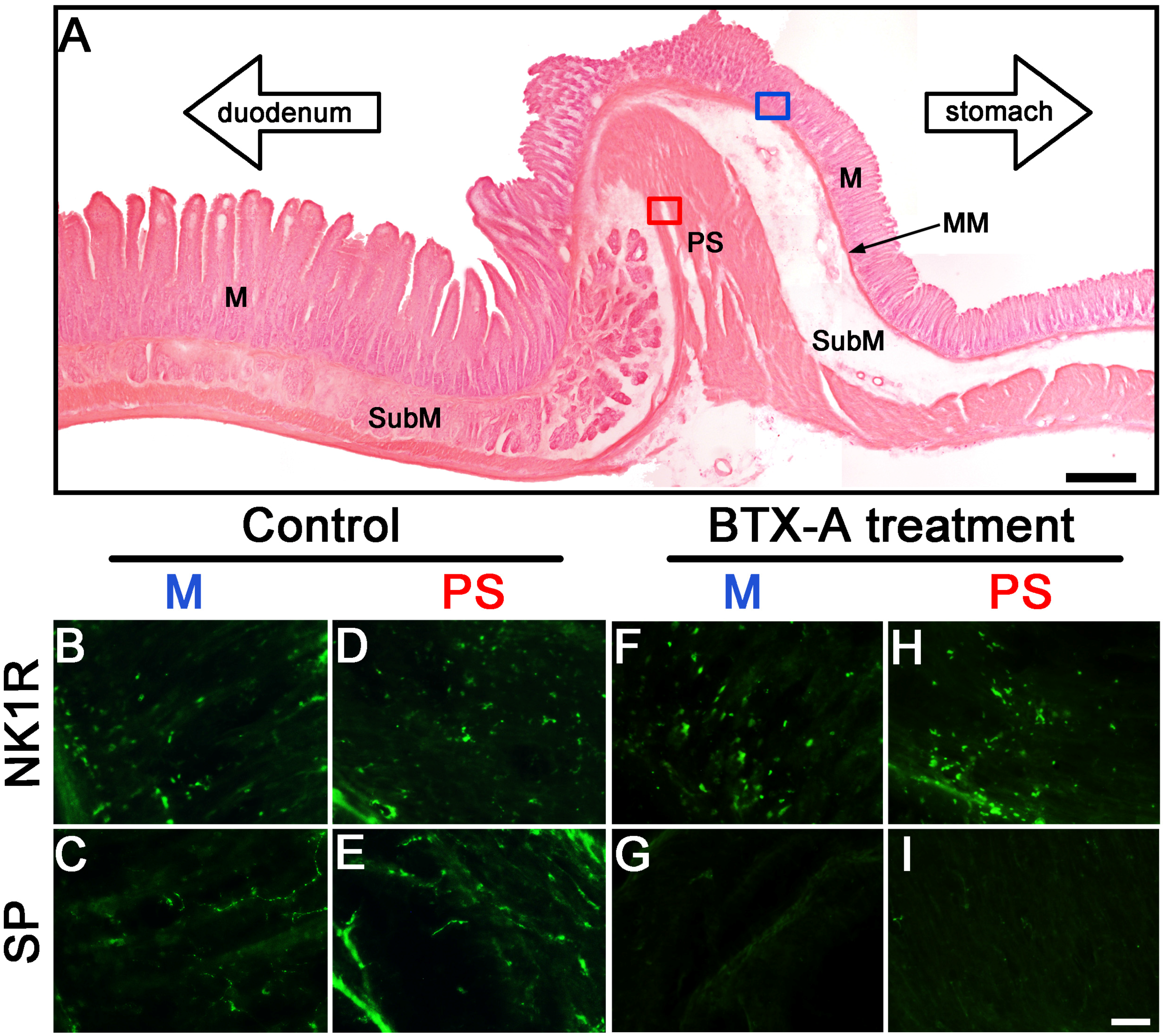
2.3. Distribution of SP- and NK1R-Immunoreactive Expressions in Pylorus without or with BTX-A Treatment
3. Discussion

4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Pyloric Muscle Strip Preparation
4.3. Experimental Protocols
4.4. Identification for the Distribution of SP and NK1R Cells and Fibers in Pylorus
4.5. Data Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simpson, L.L. Molecular pharmacology of botulinum toxin and tetanus toxin. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1986, 26, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonetilleke, A.; Harris, J.B. Clostridial neurotoxins. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75 (Suppl. 3), iii35–iii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslanka, S.E.; Luquez, C.; Dykes, J.K.; Tepp, W.H.; Pier, C.L.; Pellett, S.; Raphael, B.H.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R.; Rao, A.; et al. A novel botulinum neurotoxin, previously reported as serotype h, has a hybrid-like structure with regions of similarity to the structures of serotypes a and f and is neutralized with serotype a antitoxin. J. Infect. Dis. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Brin, M.F. Therapeutic uses of botulinum toxin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D.; Saberi, F.A.; Barbosa, E.R. Botulinum toxin: Mechanisms of action. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2005, 63, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elston, J.S. Botulinum toxin therapy for involuntary facial movement. Eye (Lond. Engl.) 1988, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schantz, E.J.; Johnson, E.A. Properties and use of botulinum toxin and other microbial neurotoxins in medicine. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowe, N.J.; Lowe, P. Botulinum toxins for facial lines: A concise review. Dermatol. Ther. (Heidelb) 2012, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chen, H.X.; Ding, X.D.; Xiao, H.Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Efficacy analysis of ultrasound-guided local injection of botulinum toxin type a treatment with orthopedic joint brace in patients with cervical dystonia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ezzeddine, D.; Jit, R.; Katz, N.; Gopalswamy, N.; Bhutani, M.S. Pyloric injection of botulinum toxin for treatment of diabetic gastroparesis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 55, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, B.E.; Zayat, E.N.; Crowell, M.D.; Schuster, M.M. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of gastroparesis: A preliminary report. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.S.; Szych, G.A.; Kantor, S.B.; Bromer, M.Q.; Knight, L.C.; Maurer, A.H.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Treatment of idiopathic gastroparesis with injection of botulinum toxin into the pyloric sphincter muscle. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, I.; Burnstock, G.; Dolly, J.O. The effects of purified botulinum neurotoxin type a on cholinergic, adrenergic and non-adrenergic, atropine-resistant autonomic neuromuscular transmission. Neuroscience 1982, 7, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.N.; Ryan, J.P.; Parkman, H.P. Inhibitory effects of botulinum toxin on pyloric and antral smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G291–G297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sand, J.; Nordback, I.; Arvola, P.; Porsti, I.; Kalloo, A.; Pasricha, P. Effects of botulinum toxin a on the sphincter of oddi: An in vivo and in vitro study. Gut 1998, 42, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.P.; Song, Y.F.; Zhu, C.M.; Wang, Y.C.; Xie, G.L. Botulinum toxin type a inhibits rat pyloric myoelectrical activity and substance p release in vivo. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 85, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizinga, J.D.; Chang, G.; Diamant, N.E.; El-Sharkawy, T.Y. Electrophysiological basis of excitation of canine colonic circular muscle by cholinergic agents and substance p. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984, 231, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keef, K.D.; Ward, S.M.; Stevens, R.J.; Frey, B.W.; Sanders, K.M. Electrical and mechanical effects of acetylcholine and substance p in subregions of canine colon. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, G298–G307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milenov, K.; Golenhofen, K. Differentiated contractile responses of gastric smooth muscle to substance p. Pflugers Arch. 1983, 397, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.D.; Kannan, M.S.; Brown, D.R.; Turner, T.A.; Trent, A.M. Adrenergic, cholinergic, and nonadrenergic-noncholinergic intrinsic innervation of the jejunum in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1999, 60, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milenov, K.; Oehme, P.; Bienert, M.; Bergmann, J. Effect of substance p on mechanical and myoelectrical activities of stomach and small intestines in conscious dog. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1978, 233, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.D.; Yuan, F.; Wang, J.L.; Hou, Y.P. Botulinum toxin therapy in the ovalbumin-sensitized rat. Neuroimmunomodulation 2007, 14, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Mitsui, Y.; Yoshitomi, T.; Mashimo, K.; Aoki, S.; Mukuno, K.; Shimizu, K. Presynaptic effects of botulinum toxin type a on the neuronally evoked response of albino and pigmented rabbit iris sphincter and dilator muscles. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 44, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, M.J.; Purkiss, J.R.; Foster, K.A. Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2000, 38, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucioni, A.; Bales, G.T.; Lotan, T.L.; McGehee, D.S.; Cook, S.P.; Rapp, D.E. Botulinum toxin type a inhibits sensory neuropeptide release in rat bladder models of acute injury and chronic inflammation. BJU Int. 2008, 101, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, J.M.; Bower, A.L.; Goormastic, M.; Malycky, J.L.; Ponsky, J.L. A comparison of common bile duct pressures after botulinum toxin injection into the sphincter of oddi versus biliary stenting in a canine model. Am. J. Surg. 2001, 181, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Jahromi, B.M.; Bagheri, M.; Borhani Haghighi, A.; Noorafshan, A.; Kumar, P.V.; Omrani, G.R. A pilot study on lipolytic effect of subcutaneous botulinum toxin injection in rabbits. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 2010, 32, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domoto, T.; Yang, H.; Bishop, A.E.; Polak, J.M.; Oki, M. Distribution and origin of extrinsic nerve fibers containing calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance p and galanin in the rat upper rectum. Neurosci. Res. 1992, 15, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindestrom, L.M.; Ekblad, E. Origins and projections of nerve fibres in rat pyloric sphincter. Auton. Neurosci. 2002, 97, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Kimura, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Tamura, K.; Ideno, N.; Aso, T.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ueda, J.; Takahata, S.; et al. Braun enteroenterostomy reduces delayed gastric emptying after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy: A retrospective review. Am. J. Surg. 2015, 209, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Rigoni, M.; Montecucco, C. Different mechanism of blockade of neuroexocytosis by presynaptic neurotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 149, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolly, J.O. Molecular definition of neuronal targets for novel neurotherapeutics: Snares and kv1 channels. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.N.; Kumaran, D.; Binz, T.; Swaminathan, S. Structural analysis of the catalytic domain of tetanus neurotoxin. Toxicon 2005, 45, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, P.; Lehmann, T.E.; Topchiy, E.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Cai, S.; Singh, B.R.; Deshpande, S.; Thyagarajan, B. Effects of enzymatically inactive recombinant botulinum neurotoxin type a at the mouse neuromuscular junctions. Toxicon 2013, 72, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shen, J.; Lee, C.A.; Elsaidi, G.A.; Smith, T.L.; Walker, F.O.; Rushing, J.T.; Tan, K.H.; Koman, L.A.; Smith, B.P. Gene expression of nachr, snap-25 and gap-43 in skeletal muscles following botulinum toxin a injection: A study in rats. J. Orthop. Res. 2005, 23, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, L.L.; Maksymowych, A.B.; Kouguchi, H.; Dubois, G.; Bora, R.S.; Joshi, S. The role of exoproteases in governing intraneuronal metabolism of botulinum toxin. Protein J. 2005, 24, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, J.; Chapman, E.R.; Link, E.; Binz, T.; Yamasaki, S.; De Camilli, P.; Sudhof, T.C.; Niemann, H.; Jahn, R. Botulinum neurotoxin a selectively cleaves the synaptic protein snap-25. Nature 1993, 365, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washbourne, P.; Pellizzari, R.; Baldini, G.; Wilson, M.C.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxin types a and e require the snare motif in snap-25 for proteolysis. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Swaminathan, S. A novel mechanism for clostridium botulinum neurotoxin inhibition. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 9795–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, G.W.; Foran, P.; Oliver Dolly, J. Insights into a basis for incomplete inhibition by botulinum toxin a of ca2+-evoked exocytosis from permeabilised chromaffin cells. Toxicology 2002, 181–182, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niel, J.P.; Bywater, R.A.; Taylor, G.S. Effect of substance p on non-cholinergic fast and slow post-stimulus depolarization in the guinea-pig ileum. J. Auton. Nerv Syst. 1983, 9, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.S.; Bywater, R.A. Antagonism of non-cholinergic excitatory junction potentials in the guinea-pig ileum by a substance p analogue antagonist. Neurosci. Lett. 1986, 63, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn-Smith, I.J.; Furness, J.B.; Gibbins, I.L.; Costa, M. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of enkephalin-, substance p-, and vip-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the circular muscle of the guinea pig small intestine. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 272, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, P.A.; Brookes, S.J.; Costa, M. Immunohistochemical identification of cholinergic neurons in the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 1991, 45, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; Pompolo, S.; Shuttleworth, C.W.; Burleigh, D.E. Light- and electron-microscopic immunochemical analysis of nerve fibre types innervating the taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. Cell Tissue Res. 1992, 270, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.P.; Micci, M.A.; Murthy, K.S.; Pasricha, P.J. Substance P is essential for maintaining gut muscle contractility: A novel role for coneurotransmission revealed by botulinum toxin. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G839–G848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Lau, H.; Sheu, L.; Diamant, N.E.; Gaisano, H.Y. Distinct regional expression of snare proteins in the feline oesophagus. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2002, 14, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Salapatek, A.M.; Lau, H.; Wang, G.; Gaisano, H.Y.; Diamant, N.E. Snap-25, a snare protein, inhibits two types of k channels in esophageal smooth muscle. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.P.; Manns, I.D.; Jones, B.E. Immunostaining of cholinergic pontomesencephalic neurons for alpha 1 versus alpha 2 adrenergic receptors suggests different sleep-wake state activities and roles. Neuroscience 2002, 114, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, A.M.; Hutson, J.M.; Southwell, B.R. Immunohistochemical localization of substance P NK1 receptor in guinea distal colon. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomax, A.E.G.; Bertrand, P.P.; Furness, J.B. Identification of the populations of enteric neurons that have NK1 tachykinin receptors in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 1998, 294, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Y.-F.; Xie, J.-F.; Ren, Y.-X.; Wang, C.; Kong, X.-P.; Zong, X.-J.; Fan, L.-L.; Hou, Y.-P. The Inhibitory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Rat Pyloric Smooth Muscle Contractile Response to Substance P In Vitro. Toxins 2015, 7, 4143-4156. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7104143
Shao Y-F, Xie J-F, Ren Y-X, Wang C, Kong X-P, Zong X-J, Fan L-L, Hou Y-P. The Inhibitory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Rat Pyloric Smooth Muscle Contractile Response to Substance P In Vitro. Toxins. 2015; 7(10):4143-4156. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7104143
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Yu-Feng, Jun-Fan Xie, Yin-Xiang Ren, Can Wang, Xiang-Pan Kong, Xiao-Jian Zong, Lin-Lan Fan, and Yi-Ping Hou. 2015. "The Inhibitory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Rat Pyloric Smooth Muscle Contractile Response to Substance P In Vitro" Toxins 7, no. 10: 4143-4156. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7104143
APA StyleShao, Y.-F., Xie, J.-F., Ren, Y.-X., Wang, C., Kong, X.-P., Zong, X.-J., Fan, L.-L., & Hou, Y.-P. (2015). The Inhibitory Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Rat Pyloric Smooth Muscle Contractile Response to Substance P In Vitro. Toxins, 7(10), 4143-4156. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7104143




