The Activities of Recombinant Botulinum Toxin A on Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in a Diabetic Mice Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Body Weight
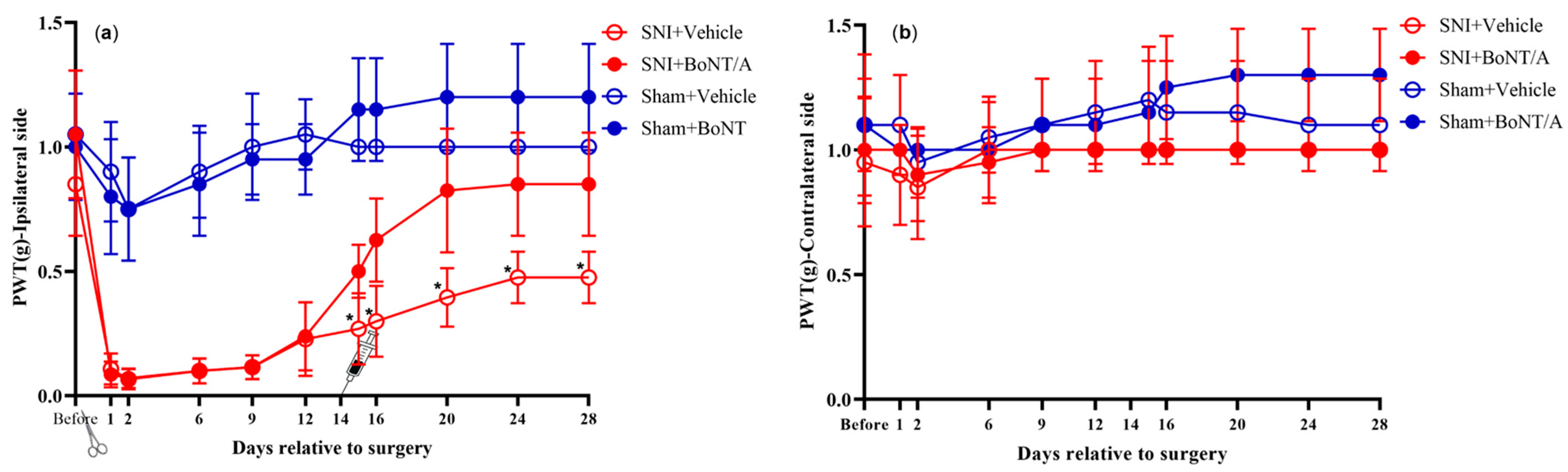
2.2. Von Frey Measurements
2.3. Number Density of Iba1-Marked Cells in the Spinal Cord
2.3.1. Number Density of GFAP-Marked Cells in the Spinal Cord
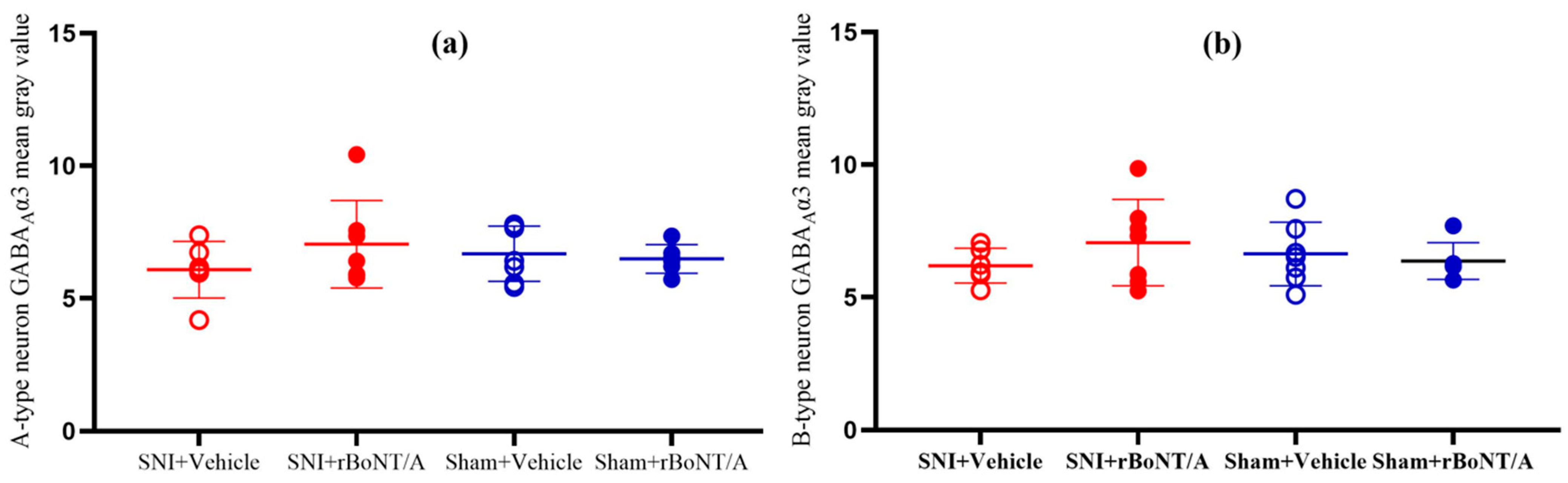
2.3.2. GABAAR Subunits in the Spinal Cord
2.3.3. Axon Area, C-Fiber Diameter, and Myelin Thickness
3. Discussion
3.1. Von Frey Measurements
3.2. Glial Cells
3.3. Axon Diameter, C-Fiber Diameter, and Myelin Thickness
4. Conclusions
5. Materials
5.1. Study Design
5.2. Surgery
5.3. Testing Mechanical Sensitivity
5.4. Tissue Harvesting and Preparation
5.5. Tissue Staining (Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence)
5.5.1. Immunohistochemistry (IBa1 and GFAP)
5.5.2. Immunofluorescence (IB4 and GABAAR)
5.6. Stereological Analysis
5.6.1. Estimating Number Density of Iba1- and GFAP-Marked Cells
5.6.2. Quantifying GABA Intensity
5.6.3. Measuring Sciatic Nerve Parameters Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic neuropathies: Update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Nave, K.-A.; Jensen, T.S.; Bennett, D.L.H. New Horizons in Diabetic Neuropathy: Mechanisms, Bioenergetics, and Pain. Neuron 2017, 93, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zochodne, D.W. Diabetic polyneuropathy: An update. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2008, 21, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Pintos, L.M.; Villegas-Rivera, G.; Rodríguez-Carrizalez, A.D.; Miranda-Díaz, A.G.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G. Diabetic polyneuropathy in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: Inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, C.M.O.; Villar-Delfino, P.H.; Dos Anjos, P.M.F.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Cellular death, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojewska, E.; Piotrowska, A.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Mika, J. Botulinum toxin type A—A modulator of spinal neuron–glia interactions under neuropathic pain conditions. Toxins 2018, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, Y.S.; Hulsebosch, C.E.; Leem, J.W. Neuronal-Glial Interactions Maintain Chronic Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, J.; Zychowska, M.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Rojewska, E.; Przewlocka, B. Importance of glial activation in neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, Y.; Hulsebosch, C. Remote astrocytic and microglial activation modulates neuronal hyperexcitability and below-level neuropathic pain after spinal injury in rat. Neuroscience 2009, 161, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richner, M.; Bjerrum, O.J.; Nykjaer, A.; Vaegter, C.B. The spared nerve injury (SNI) model of induced mechanical allodynia in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, R.-S.; Krug, S.M.; Hackel, D.; Staat, C.; Konasin, N.; Yang, S.; Niedermirtl, B.; Bosten, J.; Günther, R.; Dabrowski, S.; et al. Safety, efficacy, and molecular mechanism of claudin-1-specific peptides to enhance blood–nerve–barrier permeability. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 16, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, M.J.; Quinn, C.P.; Chaddock, J.A.; Purkiss, J.R.; Alexander, F.C.G.; Doward, S.; Fooks, S.J.; Friis, L.M.; Hall, Y.H.J.; Kirby, E.R.; et al. Inhibition of release of neurotransmitters from rat dorsal root ganglia by a novel conjugate of a Clostridium botulinum toxin A endopeptidase fragment and Erythrina cristagalli lectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34846–34852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.M.; Hallett, M.; Ashman, E.J.; Comella, C.L.; Green, M.W.; Gronseth, G.S.; Armstrong, M.J.; Gloss, D.; Potrebic, S.; Jankovic, J.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 86, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périer, C.; Martin, V.; Cornet, S.; Favre-Guilmard, C.; Rocher, M.; Bindler, J.; Wagner, S.; Andriambeloson, E.; Rudkin, B.B.; Marty, R.; et al. Recombinant botulinum neurotoxin serotype A1 in vivo characterization. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, I.; Lacković, Z. Botulinum toxin A, brain and pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 119–120, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, I.; Tékus, V.; Bölcskei, K.; Lacković, Z.; Helyes, Z. Involvement of substance P in the antinociceptive effect of botulinum toxin type A: Evidence from knockout mice. Neuroscience 2017, 358, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucioni, A.; Bales, G.T.; Lotan, T.L.; McGehee, D.S.; Cook, S.P.; Rapp, D.E. Botulinum toxin type A inhibits sensory neuropeptide release in rat bladder models of acute injury and chronic inflammation. BJU Int. 2008, 101, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Khanijou, S.; Rubino, J.; Aoki, K.R. Subcutaneous administration of botulinum toxin A reduces formalin-induced pain. Pain 2004, 107, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Therapeutic use of botulinum toxin in pain treatment. Neuronal Signal. 2018, 2, NS20180058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, I.; Bölcskei, K.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Helyes, Z. Mechanisms of botulinum toxin type A action on pain. Toxins 2019, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.Y.; Sheu, J.J.; Yu, J.M.; Chen, W.T.; Tseng, I.J.; Chang, H.H.; Hu, C.J. Botulinum toxin for diabetic neuropathic pain: A randomized double-blind crossover trial. Neurology 2009, 72, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Ansari, M.; Basiri, K.; Shaigannejad, V. The effects of intradermal botulinum toxin type a injections on pain symptoms of patients with diabetic neuropathy. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.S. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Crunkhorn, S. Silencing chronic pain with botulinum toxin. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeo, G.; Fofi, L.; Barbanti, P. Botulinum Neurotoxin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, F.; De Gregorio, D.; Palazzo, E.; Ricciardi, F.; Boccella, S.; Belardo, C.; Iannotta, M.; Infantino, R.; Formato, F.; Marabese, I.; et al. Behavioral, biochemical and electrophysiological changes in spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Casals-Diaz, L.; Zurawski, T.; Meng, J.; Moriarty, O.; Nealon, J.; Edupuganti, O.P.; Dolly, O. A novel therapeutic with two SNAP-25 inactivating proteases shows long-lasting anti-hyperalgesic activity in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 2017, 118, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, V.; Marinelli, S.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F. Botulinum toxin A increases analgesic effects of morphine, counters development of morphine tolerance and modulates glia activation and μ opioid receptor expression in neuropathic mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 32, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Luvisetto, S.; Cobianchi, S.; Makuch, W.; Obara, I.; Mezzaroma, E.; Caruso, M.; Straface, E.; Przewlocka, B.; Pavone, F. Botulinum neurotoxin type A counteracts neuropathic pain and facilitates functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury in animal models. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, J.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Korostynski, M.; Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S.; Pavone, F.; Przewlocka, B. The effect of botulinum neurotoxin A on sciatic nerve injury-induced neuroimmunological changes in rat dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord. Neuroscience 2011, 175, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S.; Cobianchi, S.; Pavone, F. Anti-allodynic efficacy of botulinum neurotoxin A in a model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre-Guilmard, C.; Chabrier, P.; Kalinichev, M. Bilateral analgesic effects of abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) following unilateral administration in the rat. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Soria, M.; García-Alloza, M.; Corraliza-Gómez, M. Effects of diabetes on microglial physiology: A systematic review of in vitro, preclinical and clinical studies. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajchgot, T.; Thomas, S.C.; Wang, J.-C.; Ahmadi, M.; Balood, M.; Crosson, T.; Dias, J.P.; Couture, R.; Claing, A.; Talbot, S. Neurons and microglia; A sickly-sweet duo in diabetic pain neuropathy. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.-R.; Liu, J.-T.; Gao, X.-M.; Wang, Q.-F.; Sun, G.-Y.; Su, J.-N.; Zhang, C.; Yu, J.-X.; Yang, Y.-F.; Shi, Y. Effects of liraglutide on astrocyte polarization and neuroinflammation in db/db mice: Focus on iron overload and oxidative stress. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1136070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crown, E.D.; Gwak, Y.S.; Ye, Z.; Johnson, K.M.; Hulsebosch, C.E. Activation of p38 MAP kinase is involved in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 213, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detloff, M.R.; Fisher, L.C.; McGaughy, V.; Longbrake, E.E.; Popovich, P.G.; Basso, D.M. Remote activation of microglia and pro-inflammatory cytokines predict the onset and severity of below-level neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 212, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Pavone, F.; Mika, J. Comparison of the expression changes after botulinum toxin type a and minocycline administration in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat microglial and astroglial cultures. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zychowska, M.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F.; Marinelli, S.; Przewlocka, B.; Mika, J. Participation of pro- and anti-nociceptive interleukins in botulinum toxin A-induced analgesia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 791, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.R.; Cross, J.; Farronay, O.; Ayyar, D.R.; Shebert, R.T.; Bradley, W.G. Demyelinating neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, D.S.; Rosoklija, G.; Hays, A.P.; Trojaborg, W.; Latov, N. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of sural nerve biopsies. Muscle Nerve 1996, 19, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.J.; Waxman, S.G.; Faber, C.G. Small fiber neuropathy. In International Review of Neurobiology; Rosner, J., Karlsson, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; Volume 179, pp. 181–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Sorge, R.; Martin, L.J.; A Isbester, K.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Rosen, S.; Tuttle, A.H.; Wieskopf, J.S.; Acland, E.L.; Dokova, A.; Kadoura, B.; et al. Olfactory exposure to males, including men, causes stress and related analgesia in rodents. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richner, M.; Jager, S.B.; Siupka, P.; Vaegter, C.B. Hydraulic extrusion of the spinal cord and isolation of dorsal root ganglia in rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 55226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandrup, T. A method for unbiased and efficient estimation of number and mean volume of specified neuron subtypes in rat dorsal root ganglion. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 329, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omoniyi, A.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Josefsen, S.; Richner, M.; Lezmi, S.; Vægter, C.B.; Kalinichev, M.; Karlsson, P.; Nyengaard, J.R. The Activities of Recombinant Botulinum Toxin A on Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in a Diabetic Mice Model. Toxins 2025, 17, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110545
Omoniyi AA, Hammer RE, Josefsen S, Richner M, Lezmi S, Vægter CB, Kalinichev M, Karlsson P, Nyengaard JR. The Activities of Recombinant Botulinum Toxin A on Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in a Diabetic Mice Model. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110545
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmoniyi, Akinyemi Ademola, Rasmus Eich Hammer, Sabrina Josefsen, Mette Richner, Stephane Lezmi, Christian Bjerggaard Vægter, Mikhail Kalinichev, Páll Karlsson, and Jens Randel Nyengaard. 2025. "The Activities of Recombinant Botulinum Toxin A on Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in a Diabetic Mice Model" Toxins 17, no. 11: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110545
APA StyleOmoniyi, A. A., Hammer, R. E., Josefsen, S., Richner, M., Lezmi, S., Vægter, C. B., Kalinichev, M., Karlsson, P., & Nyengaard, J. R. (2025). The Activities of Recombinant Botulinum Toxin A on Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in a Diabetic Mice Model. Toxins, 17(11), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110545




