Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence suggests that the maternal microbiome plays a crucial role in shaping fetal neurodevelopment, immune programming, and metabolic health. Dysbiosis during pregnancy—whether gastrointestinal, oral, or vaginal—can significantly influence pregnancy outcomes and long-term child health. Materials and Methods: The search was performed using databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar including research published from January 2000 to January 2025. The keywords used were “Fetal Programming”, “ Maternal Immune Activation”, “Maternal microbiome”, “Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis”, and “Pregnancy Dysbiosis”. Results: The maternal microbiome undergoes substantial changes during pregnancy, with alterations in microbial diversity and function linked to conditions such as gestational diabetes, obesity, and preeclampsia. Pregnancy-related dysbiosis has been associated with adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes, including an increased risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and cognitive impairments in offspring. Conclusions: Understanding the intricate relationship between maternal microbiota and fetal health is essential for developing targeted interventions. Personalized microbiome-based strategies, including dietary modifications and probiotic supplementation, hold promise in optimizing pregnancy outcomes and promoting health in offspring.
1. Introduction
The gut microbiota represents a complex ecosystem of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, capable of establishing relationships not only between one microorganism and another (cross-feeding mechanisms), but also with the host thanks to symbiotic and commensalism [1]. This large functional unit, defined as the holobiont, not only defines our state of health but also represents the inheritance that can be transmitted in the mother–fetus dyad [2]. Maternal intestinal and vaginal microbiota are currently the focus of several scientific studies intending to better understand how variations in the microbial consortium can determine the state of health and disease in the offspring. Furthermore, there is a strong interest in understanding the role of the maternal microbial consortium in mediating prenatal factors and determining the fertility and implantation of the embryo. This relevance also applies to the paternal side; scientific studies highlight how the seminal microbiota can influence sperm quality and quantity, and how alterations could cause prostatitis and male infertility [3].
Moreover, during pregnancy, physiological hormonal changes aimed at fetal development and growth, such as reduced peripheral sensitivity to insulin, increased gluconeogenesis, and lipolysis, lead to an imbalance in glycemic balance, with an increase in blood glucose levels [4]. At the same time, butyrate-producing bacteria are reduced during the third trimester of pregnancy, and proteobacteria and pro-inflammatory cytokines are increased [5]. This condition leads to increased intestinal permeability, greater diffusion, and loss of compartmentalization of the bacteria in the intestinal epithelium [6,7]. Therefore, pregnancy dysbiosis, not only intestinal but also oral and in the other microbial niches, is little investigated or not promptly assessed. Moreover, oral dysbiosis is a condition of periodontal disease and correlates with adverse obstetric outcomes such as premature birth [8]. Contreras A. and Herrera JA et al. showed how women with preeclampsia had significantly higher rates of periodontal disease and chronic periodontitis (p < 0.001). Furthermore, the bacteria P. gingivalis and E. corrodens were more represented in the group of women with preeclampsia compared to the control group with full-term delivery [9]. Therefore, a study conducted by Vuong et al. on pregnant mouse models has shown how the dysbiotic picture induced by antibiotic therapy leads to a reduced expression of genes related to axogenesis in the offspring [10]. For these reasons, taking care of a pregnant woman who presents a dysbiotic picture is fundamental to ensure an optimal course of pregnancy and the health of the future unborn child.
Particularly in Westernized societies, where people live in urbanized areas, give excessive attention to hygiene practices, and consume a Western-type diet, consisting of excess simple sugars, complex carbohydrates, and reduced intake of fiber and indigestible carbohydrates, as well as where agrochemicals, intensive farming, and livestock farming are excessively used, there has been a progressive distancing from interactions with the environment and the rhizosphere, thus causing a consequent impoverishment of microbial biodiversity [11,12]. Numerous studies indicate that there is a higher prevalence of allergic and immune-related diseases among children today. Additionally, during their reproductive years, including during pregnancy, women are exhibiting increasingly dysbiotic conditions that are frequently associated with health issues such as obesity and gestational diabetes [13,14,15,16].
This review explores the complex interactions in the mother–fetus–microbiota triad and how they can influence health in fetal growth.
2. Materials and Methods
The search was performed using PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases, including studies published from January 2000 to January 2025. The keywords used were “Fetal Programming”, “ Maternal Immune Activation”, “Maternal microbiome”, “Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis”, and “Pregnancy Dysbiosis Boolean operators (AND, OR) were used to refine the search results. The articles included were in English and include meta-analyses, systematic literature reviews, and original articles; articles such as case reports, letters, and commentaries were excluded. Additionally, studies on human cohorts and animals were included. The initial studies included 200 (150 from PubMed, 40 from Google Scholar, and 10 from Scopus). For each keyword, according to our search criteria for “Fetal programming”, we found 20 articles; for the keyword “Maternal Immune Activation”, we found 45 articles; for the keyword “Maternal microbiome”, we found 36 articles; for the keyword “Microbiota–gut–brain axis”, we found 70 articles; and for the keyword “Pregnancy Dysbiosis”, we found 29 articles. Two reviewers independently reviewed abstracts; after checking the texts’ eligibility, discrepancies between reviewers were discussed through engagement and discussion with a third reviewer. Through the implemented search strategy, 200 articles were initially identified. After excluding duplicates and studies with similar content, the final selection of articles included in our review was determined.
3. How Gut Microbiota Changes During Pregnancy
3.1. Gastrointestinal Microbiota
Scientific studies have shown how fecal microbiota transplantation, typical of the first three months of pregnancy, in germ-free mice induces a significant increase in weight and an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines [17]. In women with overweight and obesity during pregnancy, there is an increase in pro-inflammatory macrophages and in LPS at the level of placental tissue [18]; furthermore, the dysbiosis that characterizes obesity involves an altered production of SCFAs with a reduction in SCFA-producing bacteria (Faecalibacterium prausnitzii), thus compromising the regulation of energy metabolism by worsening insulin resistance and hyperglycemia by triggering fetal metabolic syndrome and impacting fetal brain development [19]. Furthermore, women living in low/middle-income countries, with a high rate of poverty and food insecurity and a higher probability of contracting enteric diseases due to poor environmental hygiene, are more likely to manifest environmental enteric dysfunction (EED), a subclinical syndrome in which there is a compromised intestinal barrier, a high degree of inflammation, and, consequently, malabsorption problems [20]. It has been shown that children born to mothers with EED manifest compromised neurological and immune development, both the result of maternal malnutrition. A study on murine models has shown how a state of malnutrition in future mothers shows a significant correlation with EED in the offspring and an impoverishment of SIgA in both mothers and offspring [21]. A study conducted by Gough EK et al. (2021) has shown that changes in the intestinal microbiota of pregnant women in Zimbabwe are a more accurate predictor of birth weight than gestational age [22].
3.2. Endometrial Microbiota
For decades, it has been claimed that the placenta and endometrium are sterile organs. Today, thanks to next-generation sequencing (NGS) techniques, several studies are in agreement that the dominant species are Lactobacillus (>70%), followed by Bifidobacterium, Corynebacterium, Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus [23]. Furthermore, the endometrium is a site where several players in the immune system work in balance to promote blastocyst implantation during pregnancy [24]. An imbalance in the microbial and immune response in the endometrial niche has been associated with poor obstetric outcomes, including a risk of preterm birth and miscarriage [25]. Moreover, a study by Cicinelli et al. demonstrated that in women with chronic endometritis, there is a reduction in the biodiversity of the endometrial microbial consortium and an increase in pro-inflammatory factors (high TNF-α and IFN-γ levels) [26]. In addition, Yant et al. demonstrated a significant reduction in the rate of preterm birth in pregnant CD1 mice, previously injected intrauterinely with LPS and subsequently administered Lactobacillus rhamnosus peritoneally [27].
3.3. Vaginal Microbiota
The vaginal microbiota accompanies and evolves throughout all phases of a woman’s life, from puberty to pregnancy to menopause [28]. The microbiota in eubiosis in healthy women of Caucasian ethnicity is represented by a prevalence of lactobacilli, which can metabolize glycogen into lactic acid, maintaining the vaginal pH at 3.8–4.4 [29]. In normal pregnancies, the vaginal microbial consortium tends to remain stable except before delivery, when an increase in biodiversity, similar to that in the non-pregnant state, is observed, suggesting that it is a precipitating factor in the onset of labor [30]. However, in cases of vaginal dysbiosis with a microbial imbalance and an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines, it is associated with adverse obstetric outcomes and a risk of preterm birth [31]. Therefore, several studies show that an increase in microbial biodiversity, with low levels of Lactobacillus and an increase in Mycoplasma and Garnerella vaginalis, occurs in women who have experienced a preterm birth; on the contrary, the presence of Lactobacillus crispatus appears to be a protective factor [32].
4. Cross-Talk Between Immune System and Microbiota During Pregnancy
4.1. Maternal Immune Activation and Intestinal Dysbiosis
Changes in the microbial, hormonal, and metabolic cycle during pregnancy can predispose individuals to a non-physiological dysbiotic picture and dysregulation of the immune system; this condition is known as maternal immune activation (MIA).
MIA is a process of activation of the immune system of pregnant women that involves an alteration of cytokine signaling, epigenetic modifications, and changes in placental function (transport of nutrients and oxygen) and has recently been considered a triggering factor in fetal neurodevelopment and the appearance of behavioral disorders in offspring (autism spectrum disorder (ASD), schizophrenia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and cognitive/behavioral impairments) [33,34,35,36]. Moreover, epidemiological and experimental studies in animal models have shown that it is precisely the dysregulated activation of the maternal immune response, and not a specific pathogen, that represents a risk factor for neurodevelopmental disorders [37].
In addition to an infectious trigger, MIA can also be induced by acute and chronic inflammatory conditions [38,39,40], such as chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), autoimmune diseases, asthma [41], and low-grade systemic inflammation, like excess weight and obesity [42], gestational diabetes [43], and periodontal disease [44], as well as exposure to stress and polluting and toxic environmental factors [45]. Recently, a correlation has also seemed to emerge between MIA and negative outcome on assisted reproductive technology (ART) [46].
All these conditions are united by intestinal dysbiosis which, through an imbalance of bacterial metabolites, in particular short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), plays an essential role with respect to the control of barrier permeability and pro-inflammatory cytokines that can trigger and/or amplify the immune activation of MIA. SCFAs are the main microbial metabolites derived from the fermentation of dietary fiber, and butyrate in particular plays an important role in neuro-immuno-endocrine regulation. Butyrate has local effects in the gut, ranging from maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier to the production of mucus to protection against inflammation [47]. Butyrate is also able to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and modulate neurodevelopment by interacting directly with neuronal and glial cells but also by inhibiting histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity, thus promoting the acetylation of lysine residues present in nucleosomal histones of nervous system cells [48].
Growing evidence suggests that exposure to pro-inflammatory environmental insults in the intrauterine time window, when offspring are particularly vulnerable to neurodevelopmental issues, results in epigenetic changes [49]. Epigenetic changes, through histone modifications, DNA methylation, and microRNA expression, alter the expression of genes involved in the regulation of proper neuronal growth and migration, dendritic development [50], and synapse formation and function [51]. The altered expression in the brain of immune molecules (cytokines and major histocompatibility complex (MHCI)) also modifies synaptic plasticity and connectivity circuits between the various brain areas [52].
MIA is characterized by an increase in pathogen-associated molecular models (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular models (DAMPs) but also microbe-associated molecular models (MAMPs) that activate Toll-like receptors on maternal immune cells and placental cells, leading to a huge production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) precisely in this time window of neuro-fetal vulnerability [53]. Inflammatory cytokines cross the placental barrier and reach the fetus [54]. IL-6 stimulates placental activation of Th17 cells, contributing to placental dysfunction. IL-6, TNF-α, and Th17 activate the immune cells residing at the placental level with a further increase in the inflammatory circulation and transfer of the maternal systemic inflammatory state to the fetus. Finally, inflammatory cytokines in the fetus cross the BBB, causing neuroinflammation and interference with the activation and functional expression of microglial cells [55].
4.2. Maternal Dysbiosis and Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Experimental mouse models of MIA show a close relationship between maternal gut dysbiosis, intestinal barrier permeability, inflammatory status, and altered neurodevelopment in offspring [56]. This may occur because the microbiota and the central nervous system are interconnected through the microbiota–gut–brain axis by means of bacterial metabolites such as tryptophan and SCFAs or MAMPs, which, in addition to modulating the peripheral immune system, also act with respect to the activation of microglia in the developing brain [57].
Microglia are cells of the innate immune system that can act as intermediaries of microbiota. They respond to stimulation by PAMPs, DAMPs, and MAMPS, secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 [58].
Erny D et al. showed that the maternal microbiota is crucial for the maturation and activation of microglia. In fact, they observed that in germ-free mice, microglia show morphological, molecular, and spatial abnormalities with increased density in various brain regions and altered response to proteins involved in the regulation of brain development such as CSF1R, CD31, and the activation marker F4/80 [59].
In addition, the phenotypic and functional changes in microglia are closely linked to SCFAs. In fact, in SPF mice, constitutively lacking the SCFA receptor FFAR2, microglia show an aberrant phenotype like that of germ-free mice or those treated with antibiotics that are known to induce dysbiosis with perturbation of microbial diversity. Vuong, H.E et al. confirm that antibiotic-induced dysbiosis in pregnant mice, as well as pregnancy in germ-free mice, leads to reduced expression of axogenesis-related genes, while microbial consortium colonization is able to prevent such abnormalities [60]. Human studies also confirm that infections and antibiotic use during pregnancy correlate with an increased risk of neurodevelopmental complications in offspring [61].
Moreover, it has also recently been shown that dietary tryptophan is metabolized by the gut microbiota into metabolite agonists of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) that act directly on microglia and astrocytes that express AHR by mimicking inflammation of the central nervous system [62].
Maternal malnutrition, by inducing alteration of the microbiota of pregnant mice, is also associated with a reduction in white matter in the brains of offspring mice, and studies conducted in children have also associated maternal malnutrition during pregnancy with gut dysbiosis and dysregulation of the axogenesis process [63]. Recently, a two-hit theory has been developed (Estes and Mcallister), according to which MIA represents the first hit with respect to the increase in susceptibility to neurodevelopmental disorders in children [64]. According to this theory, neurodevelopment risk can be amplified by the intervention of a second environmental hit that could occur in the postnatal period [65]. We could therefore conclude that an intervention aimed at preserving maternal eubiosis could play a decisive role in calming MIA through the modulation of barrier permeability, inflammatory state, and microglial functional expression, thus preserving fetal neurodevelopment (Figure 1) [66,67,68].
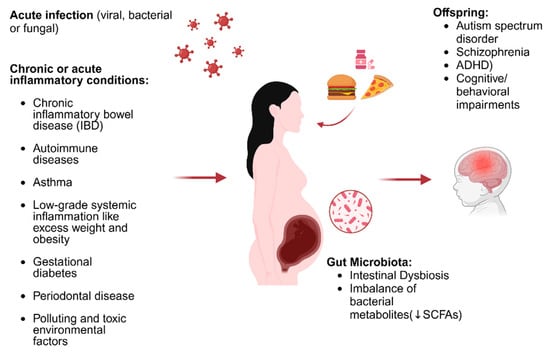
Figure 1.
Illustration of the triggers of MIA and how these affect neurodevelopment (edited using biorender.com). ↓: decrease.
4.3. Diet During Pregnancy and Practical Applications of Clinical Microbiomics
Nutrition during pregnancy is a fundamental element that not only ensures correct fetal growth and maternal well-being but also drives the enrichment (or otherwise) of the intestinal microbiota of the mother and the newborn [69]. Heather A. Paul et al. demonstrated that in mouse models fed a high-fat/sucrose diet for 10 weeks, females were significantly heavier than in the lean control group, showed higher plasma glucose and insulin levels, and showed significantly lower levels of peptide-YY (PYY) [70]. In addition, the gut microbiota resulted in a lower relative abundance of fecal Bifidobacterium spp. and a higher abundance of Clostridium [71]. Furthermore, because of HFD and maternal dysbiosis, molecular changes may occur at the fetal level and in the brain of the offspring, such as a reduction in the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); the latter promotes neuronal differentiation and regulates learning, memory, and behavior [70]. On the contrary, a diet rich in fiber and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in obese women during pregnancy is associated with an improvement in the microbial community, better bacterial biodiversity, and a reduction in serum zonulin [72]. Moreover, in the MAMI-MED cohort study, conducted by an Italian research group, the dietary patterns of 667 pregnant women were investigated to evaluate their association with birth weight for gestational age. The group of women with a dietary pattern based on ultra-processed foods, such as French fries, sauces, and sweets and an excess of refined complex carbohydrates, showed a greater probability of large-for-gestational-age (LGA) births compared to women belonging to the group with a healthy diet based on fish, white meat, and abundant quantities of fruits and vegetables (OR = 2.213; 95%CI = 1.047–4.679; p = 0.038) [73]. Moreover, the SPRING (PRobiotics IN Gestational Diabetes) randomized controlled trial study showed that a cohort of pregnant women with a vegetarian diet had an abundance of Holdemania, Roseburia, and Lachnospiraceae, which are among the major strains producing SCFAs [74]. Furthermore, a cross-sectional study by M. Selma-Royo et al. showed that a maternal diet rich in saturated (SFAs) and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) was positively associated with an increase in Firmicutes in the neonatal microbiota and inversely related to a diet rich in fiber and plant proteins [75].
Following what has been reported, a paradigm shift is therefore necessary in addressing the issue of maternal diet; to date, in line with the present scientific evidence on the importance of microbiota in pregnancy, it is insufficient to adopt the same dietary patterns for all women. An individualized and personalized approach is necessary with the possibility of investigating intestinal microbiota in the first months of pregnancy to be able to act in terms of real health prevention [76]. It will therefore be useful to reduce simple sugars by favoring complex carbohydrates, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals [77,78], unsaturated fats and fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, tempeh, and kimchi, which can improve microbial biodiversity, to enable a butyrate-producing microbial profile [79,80].
4.4. New Frontiers in Probiotic and Prebiotic Supplementation
The use of supplements during pregnancy is not to be considered the only therapeutic alternative for women with pregnancy dysbiosis but is a useful aid once an individualized nutritional plan has been implemented. Therefore, many probiotics are useful not only for the treatment of intestinal dysbiosis but also as mood modulators [81]. Tian et al. showed that in mouse models, supplementation of B. longum subsp. infantis E41 and B. breve M2CF22M7 significantly improved 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) secretion, with a positive impact on the regulation of mood and depressive behavior in pregnancy [82]. Moreover, in rats, the administration of L. farciminis appears to have a modulatory effect on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA), with downregulation of circulating ACTH and consequently glucocorticoids such as cortisol [83]. Cortisol, in addition to being known as the “stress hormone”, increases intestinal permeability [84,85]. Meanwhile, Akkermansia muciniphila instead forfeits intestinal permeability in favor of the turnover of the mucolayer and contrasts a migration of LPS with a mechanism of metabolic endotoxemia; this Gram-negative bacterium belongs to the phylum Verrucomicrobia and has the task of degrading intestinal mucus. This activity overstimulates goblet cells to produce more mucus, favoring their turnover [86,87,88]. Furthermore, studies in the literature have shown how in murine models, A. muciniphila, thanks to its wall component Amuc1100, can interact with the Toll-like receptor (TLR) found at the apical level of enterocytes; this bacterium–receptor relationship favors the expression of genes that transcribe for proteins that favor tight junctions (occludin and claudin), thus promoting intestinal barrier activity [89]. Therefore, A. muciniphila and its metabolites (butyrate and propionate) have been shown to significantly improve the symptoms of preeclampsia in rat models by promoting trophoblast invasion and M2 polarization of macrophages in the placenta [90]. Moreover, Carole Brosseau et al. demonstrated how in pregnant mice, inulin and galactooligosaccharide (GOS) supplementation during gestation increased the Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio in favor of Bacteroidetes, resulting in increased production of acetate detectable in amniotic fluid, and following prebiotic supplementation, B and T cells increased in the fetus and remained in later stages of life also [91].
Future studies will have to follow an approach that is now commonly known as precision medicine. The key today is not a “one-size-fits-all” approach but rather the individualization of pro/pre/postbiotics starting from an accurate analysis of the clinical history, nutritional regime, and enterotype.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, numerous scientific studies have shown that the gestation period is associated with multiple immunological, metabolic, and hormonal changes. These changes are accompanied by alterations in the intestinal microbial consortium of the pregnant woman. To date, however, the processes underlying these changes are not yet well understood. Therefore, new studies are needed to expand our knowledge on how to best preserve health in the maternal–fetal dyad, starting with a consideration of pre- and perinatal factors. Studying the interactions between the microbiota and pregnant women could open new avenues for the identification of early biomarkers of neonatal health.
Funding
The study was supported by National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), project MNESYS (PE0000006)—A Multiscale integrated approach to the study of the nervous system in health and disease (DN. 1553 11.10.2022). IRCCS ‘G. Gaslini’ is a member of ERN-Epicare.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Postler, T.S.; Ghosh, S. Understanding the Holobiont: How Microbial Metabolites Affect Human Health and Shape the Immune System. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, S. Maternal gut microbiota in the health of mothers and offspring: From the perspective of immunology. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1362784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, F.T.L.; Viana, M.C.; Cariati, F.; Conforti, A.; Alviggi, C.; Esteves, S.C. Effect of environmental factors on seminal microbiome and impact on sperm quality. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1348186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, F.; Fenizia, C.; Introini, A.; Zavatta, A.; Scaccabarozzi, C.; Biasin, M.; Savasi, V. The pathophysiological role of estrogens in the initial stages of pregnancy: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications for pregnancy outcome from the periconceptional period to end of the first trimester. Hum. Reprod. Update 2023, 29, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Feng, P.; Zhang, S.; Peng, L.; Xing, S.; Li, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhou, L.; Goswami, S.; Xiao, M.; et al. Maternal gut microbiota influence stem cell function in offspring. Cell Stem Cell 2025, 32, 246–262.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, L. The impact of gut microbiota on autoimmune thyroiditis and relationship with pregnancy outcomes: A review. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1361660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Makhlouf, Z.; Alharbi, A.M.; Alfahemi, H.; Khan, N.A. The Gut Microbiome and Female Health. Biology 2022, 11, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioli, V.; Sortino, V.; Falsaperla, R.; Striano, P. Role of Human Milk Microbiota in Infant Neurodevelopment: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Child 2024, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.A.; Parra, B.; Herrera, E.; Botero, J.E.; Arce, R.M.; Contreras, A.; López-Jaramillo, P. Periodontal disease severity is related to high levels of C-reactive protein in pre-eclampsia. J. Hypertens. 2007, 25, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, H.E.; Pronovost, G.N.; Williams, D.W.; Coley, E.J.L.; Siegler, E.L.; Qiu, A.; Kazantsev, M.; Wilson, C.J.; Rendon, T.; Hsiao, E.Y. The maternal microbiome modulates fetal neurodevelopment in mice. Nature 2020, 586, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioli, V.; Volpedo, G.; Riva, A.; Mainardi, P.; Striano, P. From Birth to Weaning: A Window of Opportunity for Microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Soil microbiomes and one health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhle, S.; Muir, A.; Woolcott, C.G.; Brown, M.M.; McDonald, S.D.; Abdolell, M.; Dodds, L. Maternal pre-pregnancy obesity and health care utilization and costs in the offspring. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, S.; Paparo, L.; Bedogni, G.; Nocerino, R.; Costabile, D.; Cuomo, M.; Chiariotti, L.; Carucci, L.; Agangi, A.; Napolitano, M.; et al. Effects of Mediterranean diet during pregnancy on the onset of overweight or obesity in the offspring: A randomized trial. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 49, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Elhaj, D.A.I.; Ibrahim, I.; Abdullahi, H.; Al Khodor, S. Maternal microbiota and gestational diabetes: Impact on infant health. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekema, L.; Schoenmakers, S.; Schenkelaars, N.; Laskewitz, A.; Huurman, R.H.; Liu, L.; Walters, L.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Faas, M.M. Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice Affects the Maternal Gut Microbiota and Immune Response in Mid-Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.M.; Khatiwada, S.; Morris, M.J.; Maloney, C.A. Effects of paternal overnutrition and interventions on future generations. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiex, N.W.; Chames, M.C.; Loch-Caruso, R.K. Tissue-specific cytokine release from human extra-placental membranes stimulated by lipopolysaccharide in a two-compartment tissue culture system. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, K.F.; Flanagan, J.P.; Sones, J.L. Microbiome and pregnancy: Focus on microbial dysbiosis coupled with maternal obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowardin, C.A.; Syed, S.; Iqbal, N.; Jamil, Z.; Sadiq, K.; Iqbal, J.; Ali, S.A.; Moore, S.R. Environmental enteric dysfunction: Gut and microbiota adaptation in pregnancy and infancy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perruzza, L.; Rezzonico Jost, T.; Raneri, M.; Gargari, G.; Palatella, M.; De Ponte Conti, B.; Seehusen, F.; Heckmann, J.; Viemann, D.; Guglielmetti, S.; et al. Protection from environmental enteric dysfunction and growth improvement in malnourished newborns by amplification of secretory. IgA. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, E.K.; Edens, T.J.; Geum, H.M.; Baharmand, I.; Gill, S.K.; Robertson, R.C.; Mutasa, K.; Ntozini, R.; Smith, L.E.; Chasekwa, B.; et al. Maternal fecal microbiome predicts gestational age, birth weight and neonatal growth in rural Zimbabwe. eBioMedicine 2021, 68, 103421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Goodrich, J.K.; Cullender, T.C.; Spor, A.; Laitinen, K.; Bäckhed, H.K.; Gonzalez, A.; Werner, J.J.; Angenent, L.T.; Knight, R.; et al. Host remodeling of the gut microbiome and metabolic changes during pregnancy. Cell 2012, 150, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.G.; Bellissimo, C.J.; Yeo, E.; Xia, Y.F.; Petrik, J.J.; Surette, M.G.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Sloboda, D.M. Obesity during pregnancy results in maternal intestinal inflammation, placental hypoxia, and alters fetal glucose metabolism at mid-gestation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-N.; Liu, X.-T.; Liang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicinelli, E.; De Ziegler, D.; Nicoletti, R.; Tinelli, R.; Saliani, N.; Resta, L.; Bellavia, M.; De Vito, D. Poor reliability of vaginal and endocervical cultures for evaluating microbiology of endometrial cavity in women with chronic endometritis. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2009, 68, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inversetti, A.; Zambella, E.; Guarano, A.; Dell’Avanzo, M.; Di Simone, N. Endometrial Microbiota and Immune Tolerance in Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolfaroli, I.; Monzó Miralles, A.; Hidalgo-Mora, J.J.; Marcos Puig, B.; Rubio Rubio, J.M. Impact of Endometrial Receptivity Analysis on Pregnancy Outcomes In Patients Undergoing Embryo Transfer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2023, 40, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Louwers, Y.V.; Laven, J.S.E.; Schoenmakers, S. Clinical Relevance of Vaginal and Endometrial Microbiome Investigation in Women with Repeated Implantation Failure and Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicinelli, E.; Vitagliano, A.; Loizzi, V.; De Ziegler, D.; Fanelli, M.; Bettocchi, S.; Nardelli, C.; Trojano, G.; Cicinelli, R.; Minervini, C.F.; et al. Altered Gene Expression Encoding Cytochines, Grow Factors and Cell Cycle Regulators in the Endometrium of Women with Chronic Endometritis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, W.; Challis, J.R.G.; Reid, G.; Kim, S.O.; Bocking, A.D. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 supernatant prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm birth and reduces inflammation in pregnant CD-1 mice. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 44.e1–44.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, N.; Singh, J.; Kaur, M. Microbiota in vaginal health and pathogenesis of recurrent vulvovaginal infections: A critical review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, W.J.Y.; Chew, S.Y.; Than, L.T.L. Vaginal microbiota and the potential of Lactobacillus derivatives in maintaining vaginal health. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayar, E.; Bennett, P.R.; Chan, D.; Sykes, L.; MacIntyre, D.A. The pregnancy microbiome and preterm birth. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, V.S.; Sheikh, S.A.; Ahmad, A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Bokhari, H.; Javed, S. Vaginal microbiome: Normalcy vs dysbiosis. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3793–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettweis, J.M.; Serrano, M.G.; Brooks, J.P.; Edwards, D.J.; Girerd, P.H.; Parikh, H.I.; Huang, B.; Arodz, T.J.; Edupuganti, L.; Glascock, A.L.; et al. The vaginal microbiome and preterm birth. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gars, A.; Ronczkowski, N.M.; Chassaing, B.; Castillo-Ruiz, A.; Forger, N.G. First Encounters: Effects of the Microbiota on Neonatal Brain Development. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 682505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borre, Y.E.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: Implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawadzka, A.; Cieślik, M.; Adamczyk, A. The Role of Maternal Immune Activation in the Pathogenesis of Autism: A Review of the Evidence, Proposed Mechanisms and Implications for Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliry, A.; Pereira, E.N.G.d.S. Role of Maternal Microbiota and Nutrition in Early-Life Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, H.; Gressens, P.; Mallard, C. Inflammation during fetal and neonatal life: Implications for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disease in children and adults. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Nielsen, T.C.; Mohammad, S.S.; Hofer, M.J.; Gold, W.; Brilot, F.; Lain, S.J.; Nassar, N.; et al. Maternal acute and chronic inflammation in pregnancy is associated with common neurodevelopmental disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, M.L.; McAllister, A.K. Maternal immune activation: Implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Science 2016, 353, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-K.; Choi, G.B.; Huh, J.R. Maternal inflammation and its ramifications on fetal neurodevelopment. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, J.M.; Osman, H.C.; Schwartzer, J.J.; Ashwood, P. The influence of asthma on neuroinflammation and neurodevelopment: From epidemiology to basic models. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 116, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbonaite, G.; Knyzeliene, A.; Bunn, F.S.; Smalskys, A.; Neniskyte, U. The impact of maternal high-fat diet on offspring neurodevelopment. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 909762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biete, M.; Vasudevan, S. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Impacts on fetal neurodevelopment, gut dysbiosis, and the promise of precision medicine. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1420664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madianos, P.N.; Bobetsis, Y.A.; Offenbacher, S. Adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) and periodontal disease: Pathogenic mechanisms. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84 (Suppl. S4), S170–S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, M.D.; Graham, A.M.; Feczko, E.; Miranda-Dominguez, O.; Rasmussen, J.M.; Nardos, R.; Entringer, S.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Buss, C.; Fair, D.A. Maternal IL-6 during pregnancy can be estimated from newborn brain connectivity and predicts future working memory in offspring. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kissin, D.M.; Schieve, L.A.; Jamieson, D.J.; Rice, C.; Bearman, P. Association between assisted reproductive technology conception and autism in California, 1997–2007. Am J Public Health 2015, 105, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Z.-R.; Green, R.S.; Holzman, I.R.; Lin, J. Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilling, R.M.; van de Wouw, M.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The neuropharmacology of butyrate: The bread and butter of the microbiota-gut-brain axis? Neurochem. Int. 2016, 99, 110–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehler, M.F. Epigenetic principles and mechanisms underlying nervous system functions in health and disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 86, 305–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundakovic, M.; Jaric, I. The Epigenetic Link between Prenatal Adverse Environments and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Genes 2017, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengeler, K.E.; Lukens, J.R. Innate immunity at the crossroads of healthy brain maturation and neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, E.D.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. Activity-dependent suppression of miniature neurotransmission through the regulation of DNA methylation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, R.M.; Lorusso, J.M.; Fletcher, J.; ElTaher, H.; McEwan, F.; Harris, I.; Kowash, H.M.; D’Souza, S.W.; Harte, M.; Hager, R.; et al. Maternal immune activation and role of placenta in the prenatal programming of neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuronal Signal. 2023, 7, NS20220064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-L.; Hsiao, E.Y.; Yan, Z.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Patterson, P.H. The placental interleukin-6 signaling controls fetal brain development and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Haq, R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Glass, C.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiome-microglia connections via the gut-brain axis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossad, O.; Erny, D. The microbiota-microglia axis in central nervous system disorders. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thion, M.S.; Low, D.; Silvin, A.; Chen, J.; Grisel, P.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Blecher, R.; Ulas, T.; Squarzoni, P.; Hoeffel, G.; et al. Microbiome Influences Prenatal and Adult Microglia in a Sex-Specific Manner. Cell 2018, 172, 500–516.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Reyes, T.M. Offspring neuroimmune consequences of maternal malnutrition: Potential mechanism for behavioral impairments that underlie metabolic and neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2017, 47, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atladóttir, H.Ó.; Henriksen, T.B.; Schendel, D.E.; Parner, E.T. Autism after infection, febrile episodes, and antibiotic use during pregnancy: An exploratory study. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1447–e1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhammer, V.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Bunse, L.; Takenaka, M.C.; Kenison, J.E.; Mayo, L.; Chao, C.-C.; Patel, B.; Yan, R.; Blain, M.; et al. Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrig, J.L.; Venkatesh, S.; Chang, H.-W.; Hibberd, M.C.; Kung, V.L.; Cheng, J.; Chen, R.Y.; Subramanian, S.; Cowardin, C.A.; Meier, M.F.; et al. Effects of microbiota-directed foods in gnotobiotic animals and undernourished children. Science 2019, 365, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, J.R.; Eskandar, S.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Scherjon, S.A. Microglia, the missing link in maternal immune activation and fetal neurodevelopment; and a possible link in preeclampsia and disturbed neurodevelopment? J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 126, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.G.; Ciesla, A.A. Maternal Immune Activation Hypotheses for Human Neurodevelopment: Some Outstanding Questions. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2022, 7, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastenbroek, L.J.M.; Kooistra, S.M.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Prins, J.R. The role of microglia in early neurodevelopment and the effects of maternal immune activation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2024, 46, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, H.A.; Bomhof, M.R.; Vogel, H.J.; Reimer, R.A. Diet-induced changes in maternal gut microbiota and metabolomic profiles influence programming of offspring obesity risk in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borge, T.C.; Aase, H.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Biele, G. The importance of maternal diet quality during pregnancy on cognitive and behavioural outcomes in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, G.; Ronchi, F.; Conrad, M.L. Nutrition during pregnancy: Influence on the gut microbiome and fetal development. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 91, e13802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, H.L.; Gomez-Arango, L.F.; Wilkinson, S.A.; McIntyre, H.D.; Callaway, L.K.; Morrison, M.; Dekker Nitert, M. A Vegetarian Diet Is a Major Determinant of Gut Microbiota Composition in Early Pregnancy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma-Royo, M.; García-Mantrana, I.; Calatayud, M.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Collado, M.C. Maternal diet during pregnancy and intestinal markers are associated with early gut microbiota. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Magnano San Lio, R.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Favara, G.; Ferrante, G.; Galvani, F.; Pappalardo, E.; Ettore, C.; Ettore, G.; et al. The Effect of Maternal Dietary Patterns on Birth Weight for Gestational Age: Findings from the MAMI-MED Cohort. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, G.L.; Castro-Rodríguez, D.C.; Zambrano, E. Pregnancy and Lactation: A Window of Opportunity to Improve Individual Health. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1735, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza-Martí, A.; Ruiz-Ródenas, N.; Herranz-Chofre, I.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; de la Delgado, V.C.S.; Hurtado-Sánchez, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Pregnancy and Its Benefits on Maternal-Fetal Health: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 813942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Gaskins, A.J.; Li, L.-J.; Huang, Z.; Eriksson, J.G.; Hu, F.B.; Chong, Y.S.; Zhang, C. Mediterranean diet and female reproductive health over lifespan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 229, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, M.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Gänzle, M.; Arrieta, M.C.; Cotter, P.D.; De Vuyst, L.; Hill, C.; Holzapfel, W.; Lebeer, S.; Merenstein, D.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on fermented foods. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erçelik, H.C.; Kaya, V. The effects of fermented food consumption in pregnancy on neonatal and infant health: An integrative review. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2024, 75, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonstein, J.S.; Meinhardt, T.A.; Pavlidi, P.; Kokras, N.; Dalla, C.; Charlier, T.D.; Pawluski, J.L. Maternal probiotic Lactocaseibacillus rhamnosus HN001 treatment alters postpartum anxiety, cortical monoamines, and the gut microbiome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2024, 165, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium with the role of 5-hydroxytryptophan synthesis regulation alleviates the symptom of depression and related microbiota dysbiosis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 66, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Durand, H.; Cartier, C.; Chaumaz, G.; Eutamene, H.; Ferrier, L.; Houdeau, E.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L.; Theodorou, V. Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute psychological stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, J.A.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.R. Signalling cognition: The gut microbiota and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Weerth, C. Do bacteria shape our development? Crosstalk between intestinal microbiota and HPA axis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 83, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, V.F.; Elias-Oliveira, J.; Pereira, Í.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Barbosa, S.C.; Machado, M.S.G.; Carlos, D. Akkermansia muciniphila and Gut Immune System: A Good Friendship That Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Obesity, and Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Kaicen, W.; Bian, X.; Yang, L.; Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhuge, A.; Li, L. Akkermansia muciniphila alleviates high-fat-diet-related metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota and bile acids. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 1924–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ou, Z.; Pang, M.; Tao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Wen, D.; Li, Q.; Zhou, R.; Chen, P.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Akkermansia muciniphila promote placentation and mitigate preeclampsia in a mouse model. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Gao, L.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, J.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Promotes Preeclampsia by Regulating Macrophages and Trophoblasts. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anhê, F.F.; Marette, A. A microbial protein that alleviates metabolic syndrome. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosseau, C.; Selle, A.; Duval, A.; Misme-Aucouturier, B.; Chesneau, M.; Brouard, S.; Cherbuy, C.; Cariou, V.; Bouchaud, G.; Mincham, K.T.; et al. Prebiotic Supplementation During Pregnancy Modifies the Gut Microbiota and Increases Metabolites in Amniotic Fluid, Driving a Tolerogenic Environment In Utero. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 712614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).