Univariate and Multivariate Pattern Analysis Reveals the Effects of Negative Body Image at Fatness on Food-Related Inhibitory Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Self-Measurements
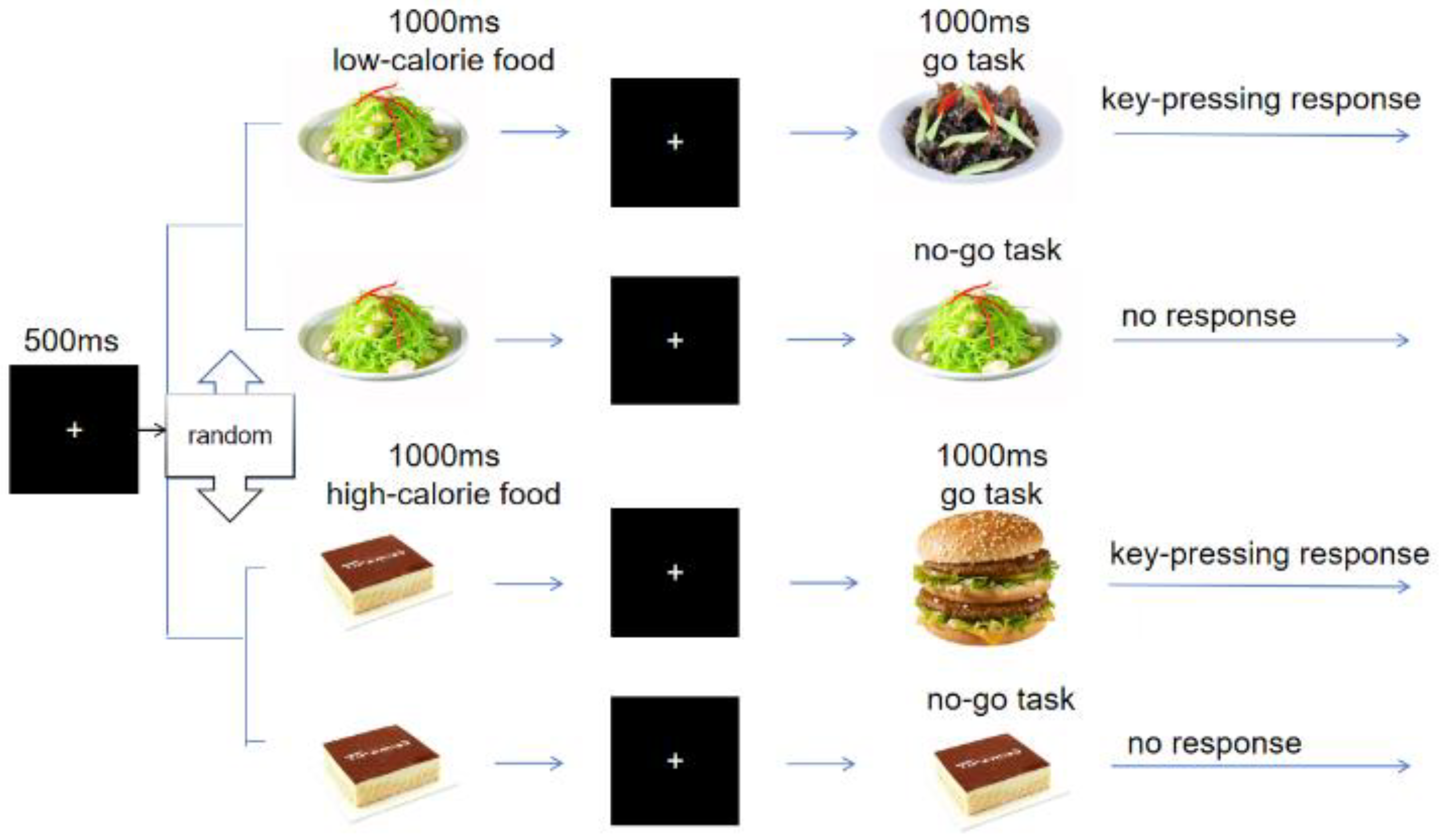
2.2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.3. Data Recording and Analysis
- (1)
- Behavior Analyses
- (2)
- EEG Recording and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Self-Reported Results
3.2. Behavioral Performance
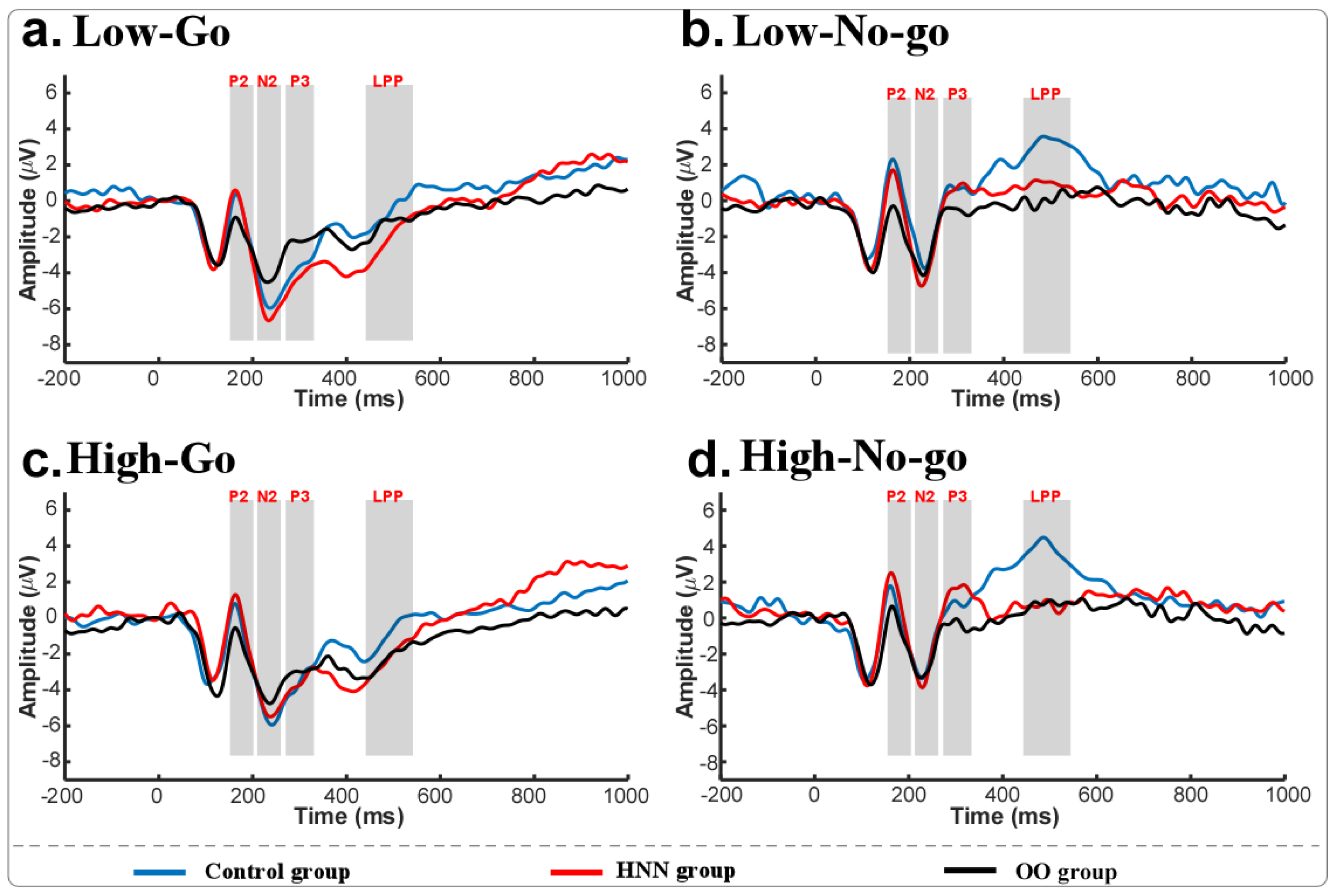
3.3. ERP Results
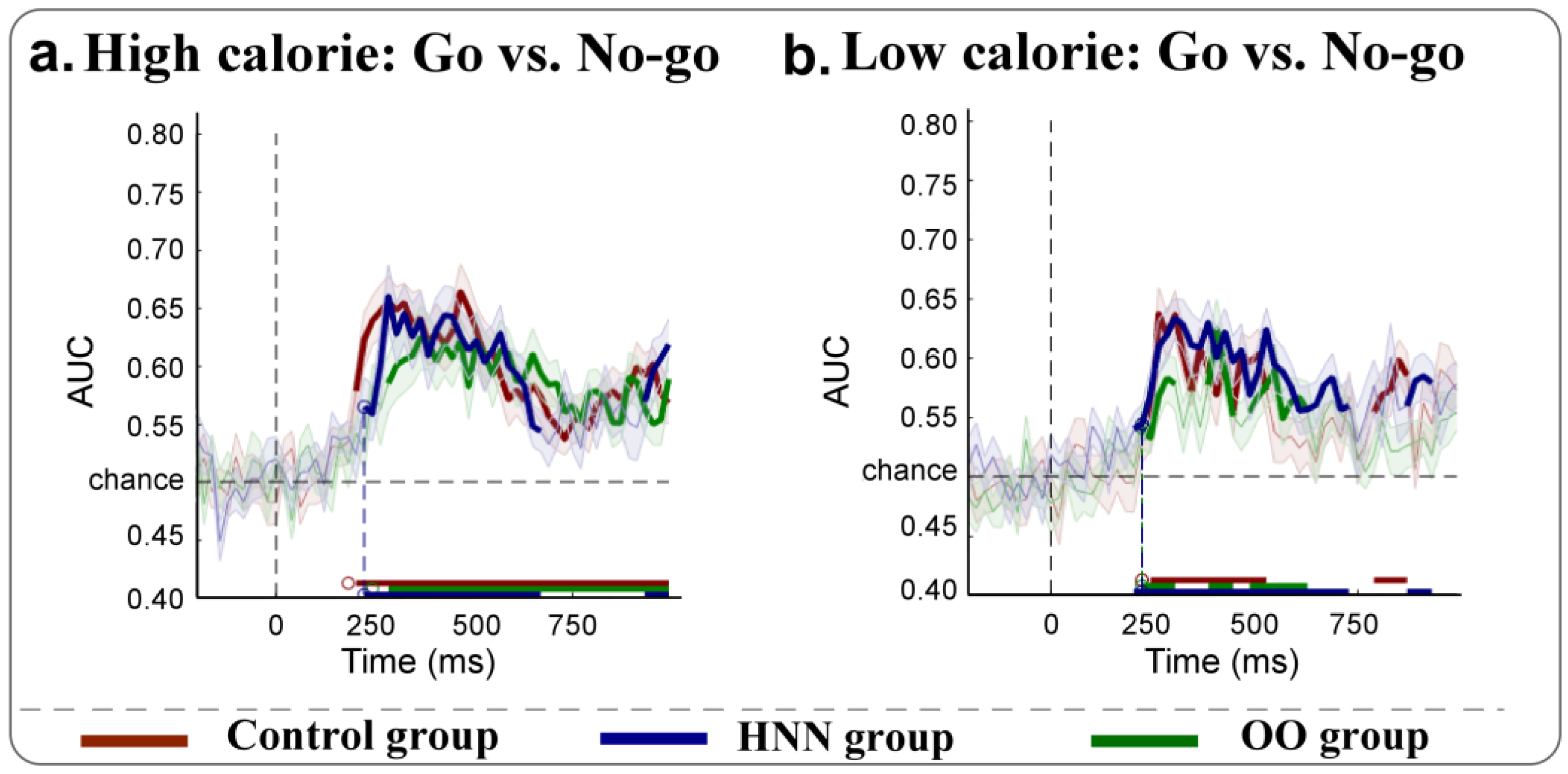
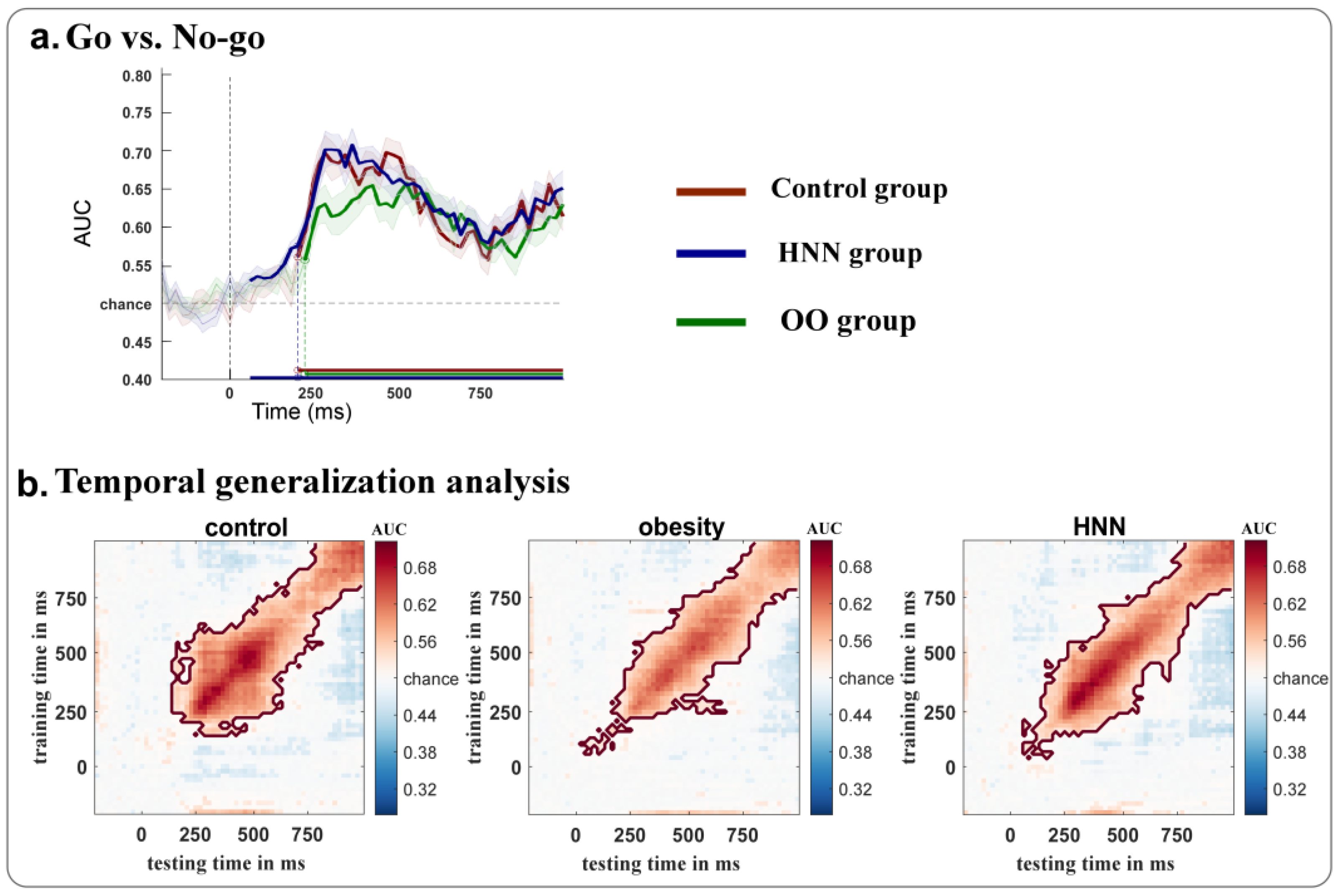
3.4. MVPA Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Distinct ERP Characteristics Among Groups in Response to Food Stimuli
4.2. MVPA Decoding of Neural Dynamics During Food Stimulus Processing
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, G.A.; Kim, K.K.; Wilding, J.P.H. Obese: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World obese Federation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obese in China. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnell, S.; Benson, L.; Pryor, K.; Driggin, E. Appetitive traits from infancy to adolescence: Using behavioral and neural measures to investigate obese risk. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 121, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.R. Metabolic and hedonic drives in the neural control of appetite: Who is the boss? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C. The related metabolic diseases and treatments of obesity. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Long, Z.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y. Alteration of regional heterogeneity and functional connectivity for obese undergraduates: Evidence from resting-state fMRI. Brain Imaging Behav. 2022, 16, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A. Executive functions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Neurocognitive correlates of food-related response inhibition in overweight/obese adults. Brain Topogr. 2020, 33, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatorre-Cruz, G.C.; Downs, H.; Hagood, D.; Sorensen, S.T.; Williams, D.K.; Larson-Prior, L. Effect of obese on inhibitory control in preadolescents during stop-signal task. An event-related potentials study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 165, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzman, S.L.; Birch, L.L. Low inhibitory control and restrictive feeding practices predict weight outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X. Higher visceral adipose tissue is associated with decreased memory suppression ability on food-related thoughts: A 1-year prospective ERP study. Appetite 2023, 191, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, A.L.; Hetherington, M.M. The thin ideal and body image: An experimental study of implicit attitudes. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2006, 20, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liang, R.; Yu, X.; Shum, D.H.K.; Roalf, D.; Chan, R.C.K. The thinner the better: Evidence on the internalization of the slimness ideal in Chinese college students. PsyCh J. 2020, 9, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Yan, H.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Young adults with negative body image at fatness subscale are more restrained than normal adults during a chocolate discounting task. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wan, X.; Lian, J.; Ma, H.; Dong, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Electrophysiological characteristics of inhibitive control for adults with different physiological or psychological obese. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meule, A.; Lukito, S.; Vögele, C.; Kübler, A. Enhanced behavioral inhibition in restrained eaters. Eat. Behav. 2011, 12, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollitt, S.; Kemps, E.; Tiggemann, M.; Smeets, E.; Mills, J.S. Components of attentional bias for food cues among restrained eaters. Appetite 2010, 54, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polich, J. Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2128–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretié, L.; Mercado, F.; Tapia, M.; Hinojosa, J.A. Emotion, attention, and the ‘negativity bias’, studied through event-related potentials. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2001, 41, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; You, X. Temporal dynamics of hedonic and eudaimonic reward processing: An event-related potentials (ERPs) study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 137, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkers, F.C.L.; van Boxtel, G.J.M. The N2 in go/no-go tasks reflects conflict monitoring not response inhibition. Brain Cogn. 2004, 56, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, S.; Yeung, N.; van den Wildenberg, W.; Ridderinkhof, K. Electrophysiological correlates of anterior cingulate function in a go/no-go task: Effects of response conflict and trial type frequency. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, S.; Peirano, P.; Peigneux, P.; Lozoff, B.; Algrain, C. Inhibitory control in otherwise healthy overweight 10-years-old children. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, E.C. The P300, the LPP, context updating, and memory: What is the functional significance of the emotion-related late positive potential? Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2023, 192, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.R.; Dehaene, S. Characterizing the dynamics of mental representations: The temporal generalization method. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2014, 18, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, M.-Y.; Li, H.; Weng, X.-C. Decoding the representation of cognition: The principles and applications of MVPA. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 18, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, J.; Guo, J.; Dai, X.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lei, X. Decoding the impact of negative physical self-perception on inhibitory control ability from theta and beta rhythms. Cereb. Cortex 2025, 35, bhaf056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/c100122/202505/5163974755e044cfa3883afa80a1f4d0.shtml (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.E.R.; van Staveren, W.A.; Defares, P.B.; Deurenberg, P. The predictive validity of the Dutch Restrained Eating Scale. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.K.; Forbush, K.T.; Hunt, T.K. Are common measures of dietary restraint and disinhibited eating reliable and valid in obese persons? Appetite 2015, 87, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jackson, T.; Huang, X. The Negative Physical Self Scale: Initial development and validation in samples of Chinese adolescents and young adults. Body Image 2006, 3, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnan, S.A.; Mulgrew, K.E.; Lane, B.R. Attention bias modification produces no changes to appearance-related bias, state or trait body dissatisfaction in nonclinical women. Health Psychol. Open 2015, 2, 205510291561431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Han, Y.; Liang, Q.; Yang, X.; Meng, X.; Gao, X. Chinese food image database for eating and appetite studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, H. Overweight adults are more impulsive than normal weight adults: Evidence from ERPs during a chocolate-related delayed discounting task. Neuropsychologia 2019, 133, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, K.; Long, Z. Electroencephalographic oscillations of alpha and beta rhythms during phrase-guessing procedure. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2023, 17, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenfort, J.J.; van Driel, J.; van Gaal, S.; Olivers, C.N.L. From ERPs to MVPA using the Amsterdam Decoding and Modeling Toolbox (ADAM). Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, J.R.; Petten, C.V. Influence of cognitive control and mismatch on the N2 component of the ERP: A review. Psychophysiology 2008, 45, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Asthana, M.K.; Zuo, K.; Comfort, W.E.; Xu, Z. Electrophysiological evidence that release from proactive inhibition reflects late semantic processing. Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turoman, N.; Fiave, P.A.; Zahnd, C.; de Bettencourt, M.T.; Vergauwe, E. Decoding the content of working memory in school-aged children. Cortex 2024, 171, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Langleben, D.D.; O’Brien, C.P.; Childress, A.R.; Wiers, C.E. Multivariate pattern analysis links drug use severity to distributed cortical hypoactivity during emotional inhibitory control in opioid use disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhu, M.; Zhuang, X.; Ma, G. Food word processing in Chinese reading: A study of restrained eaters. Br. J. Psychol. 2023, 114, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbine, K.A.; Muir, A.M.; Allen, W.D.; Le Cheminant, J.D.; Baldwin, S.A.; Jensen, C.D.; Kirwan, C.B.; Larson, M.J. Does inhibitory control training reduce weight and caloric intake in adults with overweight and obesity? A pre-registered, randomized controlled event-related potential (ERP) study. Behav. Res. Ther. 2021, 136, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, L.; Huang, T.; Meng, F.; Yang, Q.; Deng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, P.; Qian, J.; et al. Food-related inhibitory control deficits in young male adults with obesity: Behavioral and ERP evidence from a food-related go/no-go task. Physiol. Behav. 2024, 281, 114573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Tsai, C.-L. Neurocognitive inhibitory control ability performance and correlations with biochemical markers in obese women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables (M ± SD) | Control Group N = 16 | HNN Group N = 17 | OO Group N = 18 | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 19.38 (1.67) | 19.82 (1.47) | 19.78 (1.35) | 0.448 | 0.64 |
| DEBQ-RS *** | 2.41 (0.81) | 3.69 (0.68) | 3.30 (0.82) | 11.86 | <0.001 |
| NPSS-F *** | 1.31 (0.21) | 2.96 (0.33) | 2.97 (0.38) | 151.6 | <0.001 |
| Hunger | 20.63 (16.52) | 32.35 (15.62) | 27.22 (17.76) | 2.04 | 0.14 |
| Thirst | 41.25 (18.57) | 36.47 (10.57) | 32.22 (13.09) | 1.68 | 0.198 |
| Desire to eat | 25.00 (18.26) | 30.59 (17.13) | 24.44 (19.17) | 0.594 | 0.56 |
| PAS | 2.98 (0.73) | 2.72 (0.58) | 3.00 (0.61) | 0.969 | 0.387 |
| NAS | 1.84 (0.72) | 1.96 (0.70) | 1.86 (0.63) | 0.149 | 0.862 |
| BMI *** | 20.30 (1.38) | 21.40 (1.44) | 26.82 (1.88) | 83.13 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Control Group (M ± SD) N = 16 | HNN Group (M ± SD) N = 17 | OO Group (M ± SD) N = 18 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT_high | 466.20 (55.81) | 478.68 (72.43) | 472.43 (56.48) |
| RT_low | 474.13 (54.86) | 486.12 (74.02) | 479.90 (60.99) |
| ACC_low_nogo | 0.877 (0.069) | 0.929 (0.046) | 0.910 (0.052) |
| ACC_low_go | 0.989 (0.011) | 0.977 (0.022) | 0.983 (0.016) |
| ACC_high_nogo | 0.915 (0.051) | 0.936 (0.046) | 0.922 (0.045) |
| ACC_high_go | 0.991 (0.012) | 0.989 (0.019) | 0.994 (0.008) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Han, J.; Sun, L.; Lian, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Univariate and Multivariate Pattern Analysis Reveals the Effects of Negative Body Image at Fatness on Food-Related Inhibitory Control. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152555
Xu Z, Xu Y, Han J, Sun L, Lian J, Li Z, Liu Y, Zhao J. Univariate and Multivariate Pattern Analysis Reveals the Effects of Negative Body Image at Fatness on Food-Related Inhibitory Control. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152555
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zihan, Yuchan Xu, Junyao Han, Lechang Sun, Junwei Lian, Zhifang Li, Yong Liu, and Jia Zhao. 2025. "Univariate and Multivariate Pattern Analysis Reveals the Effects of Negative Body Image at Fatness on Food-Related Inhibitory Control" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152555
APA StyleXu, Z., Xu, Y., Han, J., Sun, L., Lian, J., Li, Z., Liu, Y., & Zhao, J. (2025). Univariate and Multivariate Pattern Analysis Reveals the Effects of Negative Body Image at Fatness on Food-Related Inhibitory Control. Nutrients, 17(15), 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152555








