Abstract
High-resolution airborne imaging spectroscopy represents a promising avenue for mapping the spread of invasive tree species through native forests, but for this technology to be useful to forest managers there are two main technical challenges that must be addressed: (1) mapping a single focal species amongst a diverse array of other tree species; and (2) detecting early outbreaks of invasive plant species that are often hidden beneath the forest canopy. To address these challenges, we investigated the performance of two single-class classification frameworks—Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM) and Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF)—to estimate the degree of Psidium cattleianum incidence over a range of forest vertical strata (relative canopy density). We demonstrate that both BSVM and MTMF have the ability to detect relative canopy density of a single focal plant species in a vertically stratified forest, but they differ in the degree of user input required. Our results suggest BSVM as a promising method to disentangle spectrally-mixed classifications, as this approach generates decision values from a similarity function (kernel), which optimizes complex comparisons between classes using a dynamic machine learning process.
1. Introduction
Forest ecosystems invaded by exotic plant species can experience changes on native species abundance and richness [1,2], altered ecosystem function [3,4], or economic losses [5]. These and other negative impacts of invasion may also vary as landscapes are gradually invaded [6]. Therefore, our understanding of changes in ecosystem functioning as invasion progresses, especially at the regional scale, depends on spatially-extensive information on species distribution and on accurate assessment of invasion dominance or degree of spread. Consequently, effective methods to map, monitor, and estimate the gradual spread of invasive plant species (invasion dominance) are needed to further understand the impacts of these species and manage their unwanted consequences [7,8].
Remote sensing approaches to map invasive plant species have been assessed for different species, vegetation types, and sources of remotely-sensed data (reviewed in [9,10]). Most previous plant species mapping studies have naturally focused on the upper canopy stratum, as this is the portion of the forest most accessible to remote sensing mapping approaches [11]. However, invasive plant species are often shade tolerant and may grow beneath the canopy of other trees [12]. From a forest management perspective, it is often extremely important to detect species during the early stages of invasion when they might be present only in the forest understory [13]. Despite steady progress in identifying forest canopy attributes with satellite or airborne sensors, methodological approaches to accurately detect plant species predominantly found in the understory of forests remain poorly developed. Therefore, remote detection of such species beneath overlapping tree canopies is a critical bottleneck of invasive species mapping techniques. Because understory spectra represent approximately 20% to 50% of the canopy reflectance, depending on canopy gaps and seasonality [14], the success to detect subcanopy plants may rely on remarkable spectral dissimilarities between the focal species and the host plant community.
Since tree species are commonly mixed with other species or are present beneath the forest canopy, the measured reflectance of a target species by a remote sensor results from the interactions of electromagnetic radiation of multiple constituents [15]. For instance, the near-infrared spectral range (800–1300 nm) shows high photon penetration depth in the forest canopy, which helps nadir-viewing spectrometers to be sensitive to subcanopy properties [16], and yields mixed spectral signatures from different canopy layers. Therefore, spectral unmixing methods are valuable candidates for detection of plant species in a spectrally mixed context [17]. Some recent examples include Spectral Angler Mapper (SAM; [18]) and Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis (MESMA; [19,20,21]). These have been used in species discrimination using these unmixing methods.
However, in tropical forests, species identification using fully supervised spectral unmixing approaches may be hampered by the necessity to collect multiple endmembers (e.g., identification of particular spectral signature of a large number of available species or different patterns of canopy vertical stratification). As an alternative, partial supervised methods (single-class classification approaches) may provide an effective means to overcome such challenges because they require collection of training data (endmembers) solely from the focal class. These methods are designed to increase detection performance of a single focal class, while reducing the requirement for training data collection, often a necessity in multi-class classification methods [22,23]. For example, Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF) focuses on identifying the presence of a single focal class and only requires that training data be collected from the focal class. MTMF is a partial unmixing method that estimates subpixel abundance of a single target material [24]. MTMF estimates the similarity between spectra from given image pixels and the spectra of a target endmember (pure spectral signature from the focal species), estimating subpixel abundance of the target material or the likelihood for the target material is present in a given pixel [25]. Although some prior studies have used MTMF to detect invasive species [26,27,28,29], this technique has been poorly evaluated in ecosystems exhibiting complex canopy structure, such as tropical forests.
Additionally, the Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM) [30] is another single-class classification approach that has been successfully used to identify focal plant species in the upper canopy, including in tropical forests [23,31]. BSVM has the same general architecture as the binary SVM, but the labeled training data used in BSVM come only from the focal class (detailed description available in [31]). Although the BSVM algorithms create binary Boolean classes (i.e., a given pixel may belong or not to the focal class), they compute decision values from support vectors, indicating the degree of similarity between classes [32]. These decision values have rarely been explored for their potential use in focal species mapping with remote sensing (however, see [33]). The ability of BSVM to perform complex comparisons between classes in a dynamic machine learning process may be useful in quantifying the spectral separability of classes. Consequently, BSVM is a strong candidate technique that seems to be particularly well adapted for detecting the presence of a single invasive tree species in spectrally mixed contexts, such as in canopies of tropical forests.
The invasive tree species, Psidium cattleianum, commonly called strawberry guava, is a critically important example of an invader that initially grows in the forest understory. During early stages of its invasion, P. cattleianum is primarily found in the understory, with crowns that are overtopped by, and mixed with, a large diversity of crowns of other tree species [34]. By the time P. cattleianum attains upper-canopy position with fully exposed crowns, it is often well established as the dominant or co-dominant tree in the forest stand. This growth pattern is exhibited by many invasive tree species, and thus detection of invaders in the understory, before maturity, is a key challenge for their effective management.
We aimed to advance remote sensing methods for monitoring invasive species that grow in the subcanopy of tropical forests by comparing the performance of two contrasting single-class classification methods: BSVM and MTMF. We evaluated BSVM and MTMF in mapping P. cattleianum relative canopy density, that is the proportion of the canopy volume occupied by the focal species, in a lowland Hawaiian forest. We implemented the BSVM and MTMF methods using two different classification strategies, a volumetric and a threshold approach. In the volumetric approach, we used the subpixel values of the classifier outputs as a direct estimate of the relative canopy density of P. cattleianum. In the threshold approach, we discretized the continuous subpixel outputs into presence/absence of the focal species, and then we estimated the relative canopy density of the focal species. Through this analysis, we were able to identify effective methods for mapping invasive trees even when they are partially obscured from remote sensing measurements because of overstory trees.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
Our study was conducted in the Wao Kele O Puna Forest Reserve (WKOP), located on the southeast side of Kilauea Volcano on the Island of Hawaii (Figure 1). Mean annual precipitation is approximately 3500 mm·yr−1 and mean annual temperature is 25 °C. WKOP encompasses the last remaining large region of lowland native rainforests in the State. Although the diversity of plant species in the Hawaiian tropical forests is much lower than other tropical regions, the history of biotic invasion throughout Hawaii, and in WKOP in particular, has resulted in a complex mosaic of forest structure and composition [35]. In WKOP, Metrosideros polymorpha ('ohi'a lehua) is the dominant tree species ranging in height from 10–20 m. Other native tree species reaching 10–20 m included Psychotria hawaiiensis, Diospyros sandwicensis, Ilex anamola. Native species reaching 5–10 m included, among others, Cibotium glaucum, Antidesma platyphyllum, and Cheirodendron trigynum. The invasive species, P. cattleianum, is prevalent in the 5–10 m height range. This invasive species may occur as both a subcanopy tree or as a dominant tree stand. Due to its strong competitive capacity and opportunistic colonization of disturbed areas, P. cattleianum is now recognized as one of the most serious threats to native ecosystems of Florida, Puerto Rico, Reunion, Mauritius, Guam, Cook Islands, Fiji, French Polynesia, Palau, Samoa and Norfolk Island [12,36,37]. P. cattleianum was introduced in Hawaii in the early 1800’s [38], and has invaded approximately 384,000 hectares of native forest [39]. In WKOP, this species occurs at a wide range of dominance levels.
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
Imaging spectrometer data for the study area were acquired using the Carnegie Airborne Observatory Beta system (CAO) with an Airborne Visible and Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS; [40]). The imagery was collected in January 2007 and covered 8873 ha of WKOP forest reserve (Figure 1). The CAO was flown at an altitude averaging 2.4 km above ground level (a.g.l.), providing spectroscopic measurements at 2.4 m spatial resolution. The CAO Visible-to-Shortwave Infrared (VSWIR) imaging spectrometer measures spectral radiance in 427 channels spanning the 380–2510 nm wavelength range in 5 nm increments with nominally 6 nm spectral response function (full-width at half-maximum). Additional detector rows are used to monitor the instrument dark signal levels. These spectral data were radiometrically and atmospherically calibrated in the laboratory following flights using ACORN 5LiBatch (Imspec LLC) model, and a MODTRAN look-up table [40]. Water absorption bands near 1450 nm and 1950 nm were removed, resulting in 161 spectral bands for analysis. We were interested in examining only leafy, well-lit vegetation; thus, prior to analysis, we filtered the imagery to include only pixels with a normalized difference vegetation index greater than 0.75 and mean near-infrared (850–1050 nm) reflectance greater than 20%. These leafy pixels represent a controlled set of reflectance signatures that, theoretically, should be most indicative of surfaces containing vegetation.
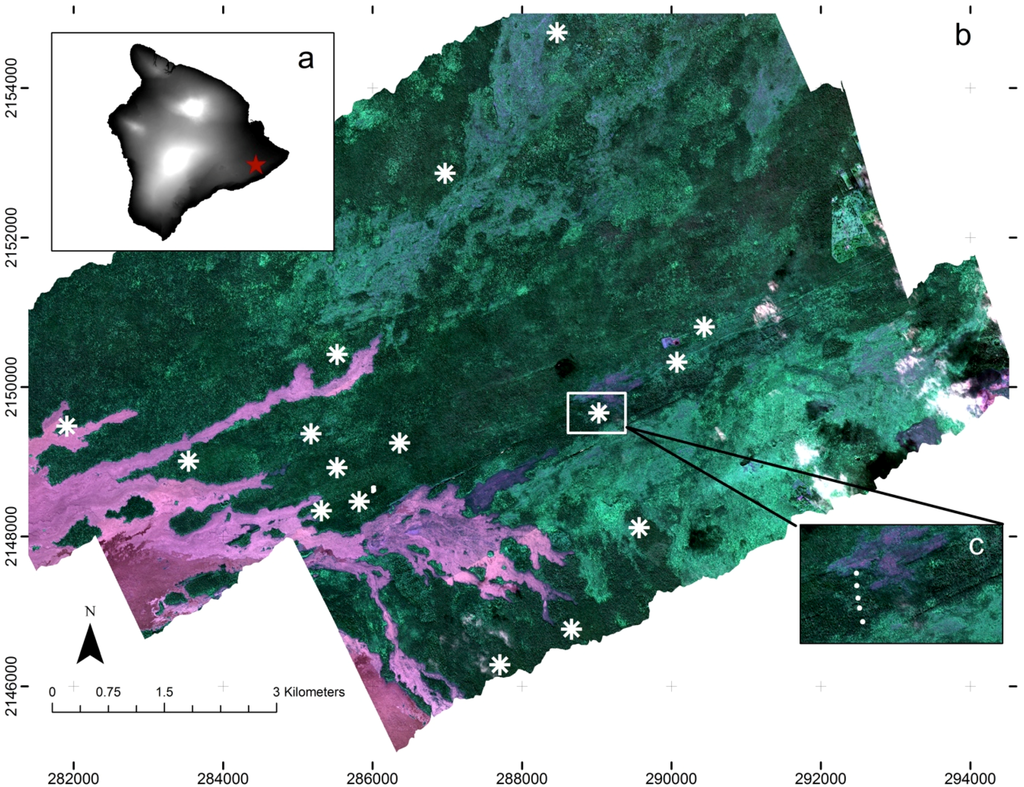
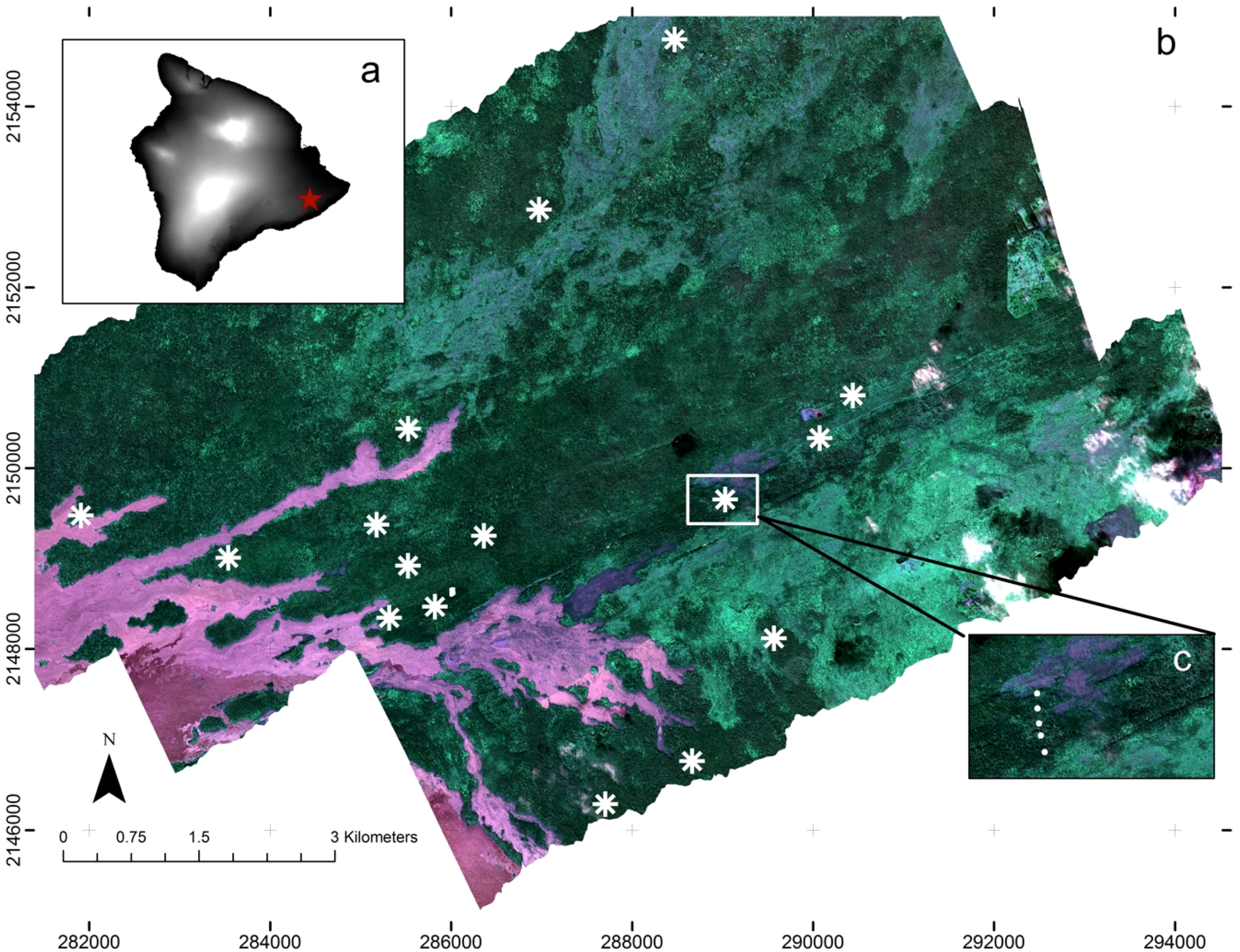
Figure 1.
False color composite map derived from Carnegie Airborne Observatory (CAO) Beta system of the Wao Kele O Puna Forest Reserve on the Island of Hawaii. (a) Island of Hawaii (black to white represents a gradient of elevation from sea level to 4200 m; red star indicates the location of WKOP reserve); (b) Study area and field sites (asterisks represent the spatial distribution of the 16 surveyed sites); (c) Zoom image showing the plot distribution (white points) within each site.
Figure 1.
False color composite map derived from Carnegie Airborne Observatory (CAO) Beta system of the Wao Kele O Puna Forest Reserve on the Island of Hawaii. (a) Island of Hawaii (black to white represents a gradient of elevation from sea level to 4200 m; red star indicates the location of WKOP reserve); (b) Study area and field sites (asterisks represent the spatial distribution of the 16 surveyed sites); (c) Zoom image showing the plot distribution (white points) within each site.
2.3. Field Sampling
We collected two independent field datasets in WKOP: the training and the validation datasets. The training dataset was used to develop the classification models (MTMF and BSVM) to estimate P. cattleianum relative canopy density (invasion dominance), and the validation dataset was used to evaluate the performance of the classifier outputs (Figure 2).
For the training dataset, we identified 50 fully-sunlit exposed crowns of P. cattleianum trees. These trees were selected based on the accessibility of the plants in the ground and for the inclusion of P. cattleianum from different substrate types (lava flow ages), elevations (ranging from 300 m to 600 m above sea level), and flight lines. Each of these 50 P. cattleianum crowns was geo-located in the field based on differentially-corrected GPS (Leica GS-50; Leica Geosystems Inc., St. Gallen, Switzerland). These locations were used to extract from the CAO-AVIRIS a corresponding pixel related to each of the 50 P. cattleianum crowns. We selected one pixel per plant individual because P. cattleianum crowns are small as about 3–4 m in the study area.
For the validation dataset, we collected data on the relative canopy density of P. cattleianum within 52 circular plots (18-m radius) located at 16 sites (Figure 1). These sites were selected based on accessibility and to sample as fully as possible the spectral heterogeneity of the imagery, likely also encompassing a wide range of vegetation types. We distinguished potential differences in vegetation composition and invasion dominance in the study area by assuming that spectral variation within the imagery reflects changes in vegetation structure and composition [41]. We performed a principal components analysis (PCA) on the imagery, and used the first three PC bands to create a composite RGB image. We selected field sites for the validation dataset based on a visual differentiation of contrasting colors (representing contrasting vegetation types) within the image, while being dispersed throughout the study area. This putative vegetation classification was useful as an initial vegetation survey due to the very difficult access to the study area (dense vegetation with many crevasses and hazardous holes due to seismic and volcanic activities).
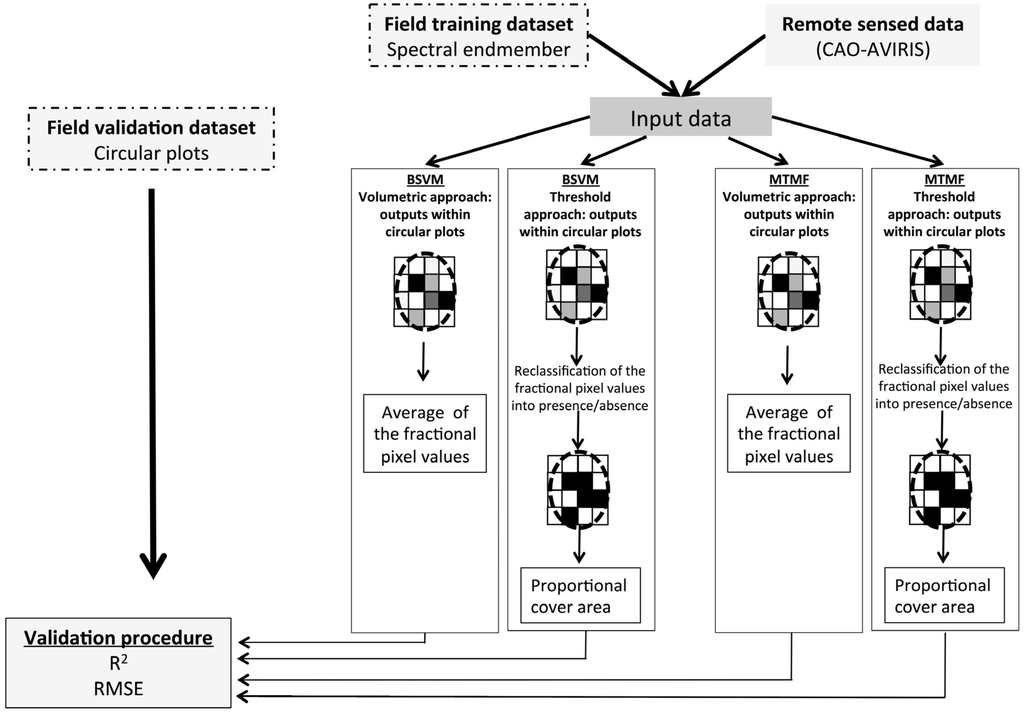
Figure 2.
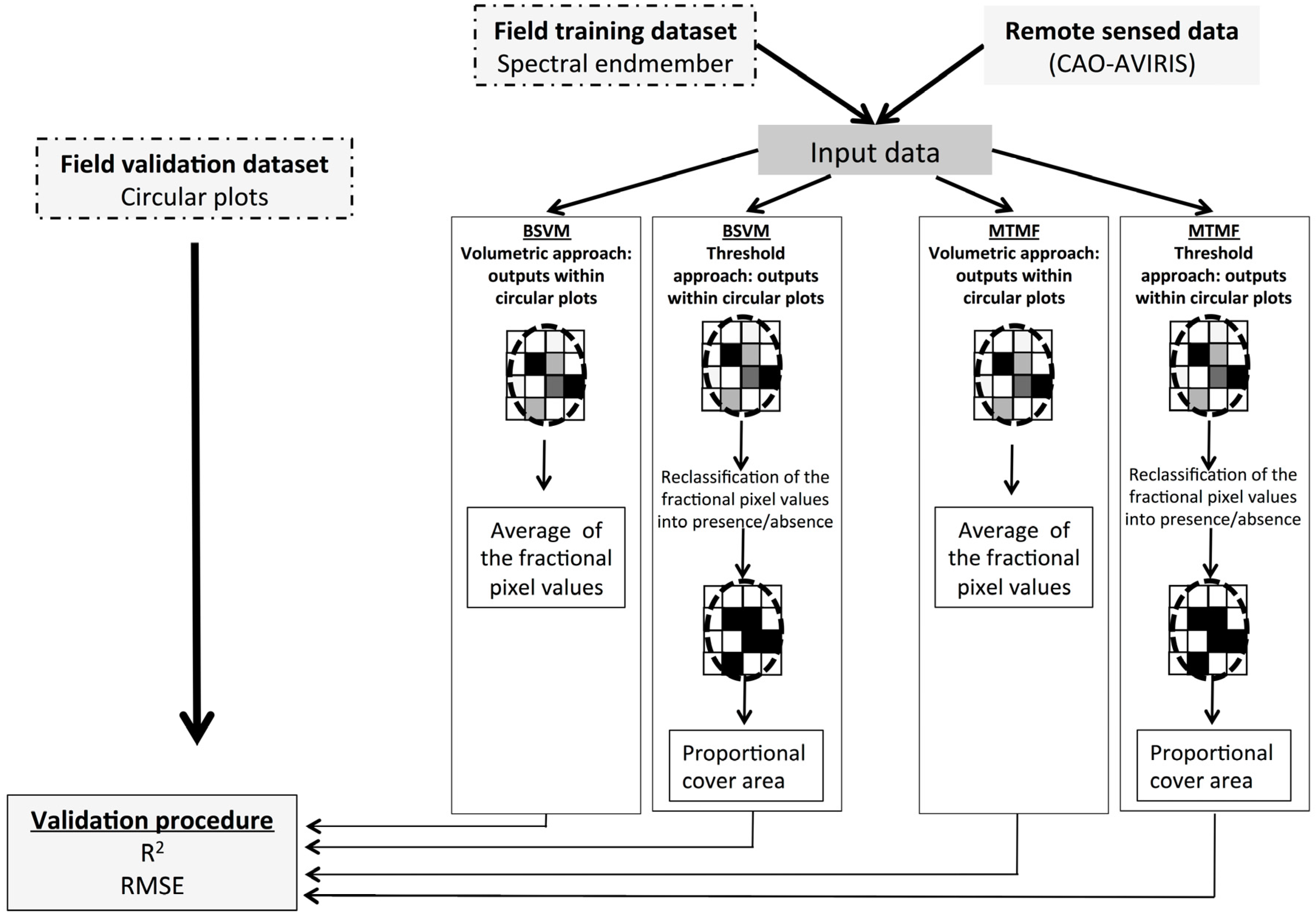
Methodological framework. Field data were used to identify spectral endmembers of the focal species in a high-resolution image (the training dataset). The endmembers were used as training data in two independent classification methods: Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM) and Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF). These methods were performed using both volumetric and threshold approaches. The volumetric approach averages classifier outputs within circular plots. The threshold approach uses threshold values to reclassify outputs as presence/absence and then generates the proportional cover area of the focal species within plots. In the last stage, a validation procedure compares field data and remote sensing estimates.
Figure 2.
Methodological framework. Field data were used to identify spectral endmembers of the focal species in a high-resolution image (the training dataset). The endmembers were used as training data in two independent classification methods: Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM) and Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF). These methods were performed using both volumetric and threshold approaches. The volumetric approach averages classifier outputs within circular plots. The threshold approach uses threshold values to reclassify outputs as presence/absence and then generates the proportional cover area of the focal species within plots. In the last stage, a validation procedure compares field data and remote sensing estimates.
At each of the 16 sites, one to five circular plots were established by delineating an 18-m buffer distance around a central point and the tree species were identified, which further indicated that P. cattleianum occurred in the plots with a large range of invasion dominance. In these plots, we surveyed the P. cattleianum relative canopy density as the proportion of the canopy volume of all vegetation within a plot represented by P. cattleianum. We assessed the canopy volume as the summed canopy cover in six vertical or height layers (Figure 3). These six vertical layers were defined as ground (<1 m from the ground), shrub (1–2 m above ground), H1 (2–5 m above ground), H2 (5–10 m), H3 (10–20 m), and H4 (>20 m). Using a modified Braun-Blanquet method, two field workers independently estimated the proportional area of each vertical layer occupied by the total vegetation community (combining all plant species together) and separately for P. cattleianum. Canopy cover values for each vertical layer were defined after both team members agreed on a unique cover value. We calculated the P. cattleianum relative canopy density within each circular plot as the summed proportion of P. cattleianum cover in the six vertical layers divided by the summed proportion of all vegetation cover in the same vertical layers. Braun-Blanquet sampling procedure provides reliable plant cover estimates that are comparable to other sampling schemes [42]. This methodology depends on visual plant cover observations. Therefore, it is likely to show biases within intermediary plant cover values [42]. To minimize these problems, we used a team of two field workers that independently walked throughout the plots and agreed on a unique cover value. Damgaard [43] also highlights that additional attention should be taken using Braun–Blanquet sampling procedure if the species are highly spatially aggregated within-sites, as it may cause biases in the data analysis. A global positioning system (GPS) location was collected at the center of each circular plot, which was used to transfer the plot locations to the remotely sensed imagery and extract the corresponding CAO-AVIRIS pixels for each plot. Both the field and remotely sensed data at the plot level were then related as described in Section 2.4.
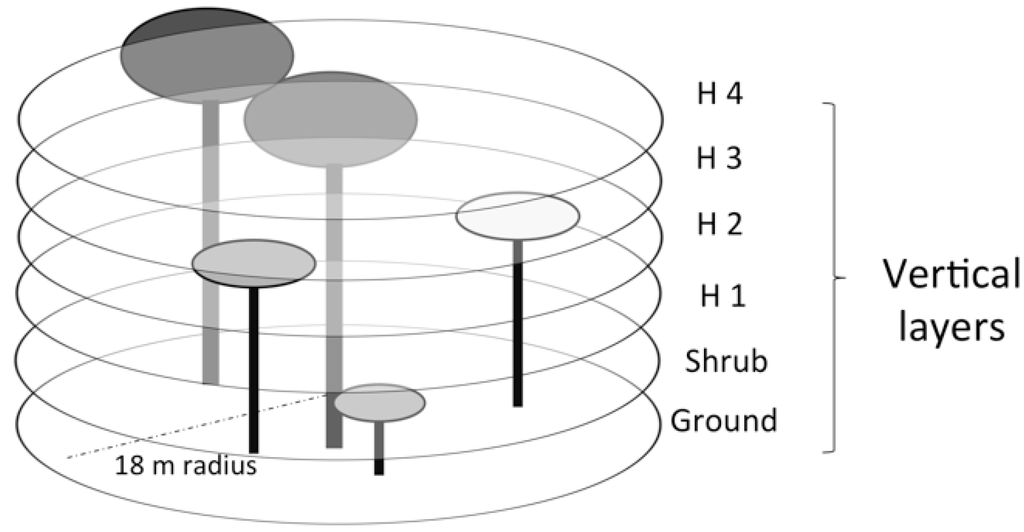
Figure 3.
Schematic of field data collection (canopy volumetric density) using six vegetation height layers.
Figure 3.
Schematic of field data collection (canopy volumetric density) using six vegetation height layers.
2.4. P. cattleianum Classification and Validation
Using the training dataset, we created classification models to quantify P. cattleianum relative canopy density using the MTMF and BSVM methods (Figure 2), as described in detail below (Section 2.4.1 and Section 2.4.2). Each of these methods produce a continuous output variable that scales with the spectral similarity to the target class (here, P. cattleianum). Therefore, we tested the relationships between these continuous classifier outputs and P. cattleianum relative canopy density of the validation datasets, which we call the volumetric approach (Figure 2). We also converted the continuous outputs of MTMF and BSVM to binary variables indicating P. cattleianum presence or absences, which we call the threshold approach (Figure 2). Each model was applied to the imagery and the relative canopy density of P. cattleianum was estimated for each of the field plots in the validation dataset. In both volumetric and threshold approaches, the dominance of the focal invasive plant was assigned at the plot scale (i.e., circular polygons of 18 m radius), with each plot containing approximately 176 pixels from the CAO-AVIRIS imagery. All pixels within the reference field plots (Section 2.3) were integrated as a unique value of relative canopy density of the focal species (see Section 2.4.1 and Section 2.4.2). Therefore, accuracy was evaluated at the plot scale using the R2 and the root mean square error (RMSE) of the relationship between the continuous remote sensing estimates and the plot-based data of P. cattleianum relative canopy density. As an alternative assessment of estimation accuracy in the volumetric approach, we randomly selected 70% of the field circular plots and their related remote sensed estimates to build a predictive logarithmic regression model. We then used this regression model to predict the P. cattleianum relative canopy density of the remaining 30% of the validation plots. We repeated this random selection of plots (70% to build the logarithmic model and 30% to assess prediction accuracies) 100 times and calculated the mean and standard deviation of the RMSE to assess the prediction accuracies. We performed this alternative assessment of accuracy in the volumetric approach when the direct outputs from the classifiers (MTMF and BSVM) did not fit a 1:1 relationship with the field data of the circular plots.
2.4.1. Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering
In the MTMF [24], the reflectance data from the imagery were first transformed by applying minimum noise fraction (MNF) analysis to the data. This data reduction transformation attempts to maximize the spectral variance within a few bands and eliminate bands that are noise dominated [44]. We used the MNF bands as input in the classification. MTMF also requires pure endmembers as reference of the target spectral signature (i.e., P. cattleianum). We therefore used the arithmetic mean of the reflectance of the 50 P. cattleianum pixels from the training dataset. Defining the endmember from the average spectra of the training dataset (as in [18,29,45]) partially accounted for the spectral variability of P. cattleianum trees growing with varying canopy structure, ambient illumination, and at different elevation or substrate characteristics [18].
The MTMF produced two different images as outputs: the matched filtering (MF) and the infeasibility [24]. MF values normally range between 0 and 1, where low values represent background (no target class) and high values contain a fractional target component [45]. Infeasibility values indicate the likelihood that the classified pixel is a false positive [24]. A few pixels received MF values outside the nominal 0–1 range, and we set values >1 to 1 and values <0 to 0. Based on the geographic location of known P. cattleianum and on the range of infeasibility values of these trees, we filtered the MF values for infeasibility values of 0–30. Hereafter, we refer to the filtered MF values as SGuavaMF. MTMF method was performed in the Environment for Visualizing Images (ENVI 4.8; Excelis Corp., Boulder, CO, USA). The MTMF model was applied to all pixels satisfying our well-lit vegetation thresholds in the imagery.
For the MTMF volumetric approach, we estimated P. cattleianum relative canopy density by averaging values of SGuavaMF for pixels within the validation plots (Figure 3). We were also interested in the MTMF threshold approach because previous studies found that spectral unmixing analyses, including MTMF, have a tendency to underestimate fractional cover of a target class within pixels. As a result, it has been suggested that classifier outputs should be interpreted as the likelihood that a target material is contained within a given pixel instead of fractional cover [25,46]. Therefore, our SGuavaMF was assumed to scale with the likelihood of P. cattleianum presence with low values indicating lower likelihood and high values indicating higher likelihood. We reclassified these continuous outputs (SGuavaMF) as a binary “presence/absence” indicator variable of P. cattleianum. Because we did not know the best threshold value to separate presence and absence, we tested five different threshold values of SGuavaMF: 0.75, 0.5, 0.25, 0.10, or 0.05 [47]. We thus produced five different estimates of invasion dominance based on these threshold values. In each of these estimates, we determined the P. cattleianum relative canopy density as the proportion of pixels classified as “presence” within the validation plots.
2.4.2. Biased Support Vector Machine
Biased support vector machine (BSVM) is a partially supervised classification [30], consisting of a binary classifier that finds the optimal separation between two classes in a transformed hyperspace. However, as stated before, in BSVM the only labeled training data used come from the focal class (P. cattleianum). The P. cattleianum training data were contrasted against a random selection of 5000 “background” pixels from the total pool of pixels meeting the NDVI and NIR reflectance filters described above. The BSVM model was tuned using a grid search over the following values for three parameters: γ {e−7, e−6, . . . , e−0}, wc {0.01, 0.02, . . . , 0.1, 0.15, . . . , 0.6}, and C {e5, e6, . . . , e15}. The γ parameter determines the width of the kernel function used to transform the feature space, wc parameter defines the relative cost of errors occurring within the “focal” or the “background” class, and the C parameter determines the penalty associated with misclassification errors [30]. Because the “background” class may contain samples from the focal class (P. cattleianum), the potential models are more penalized with the cost parameter C for errors occurring within the labeled focal class than for errors within the “background” class. We built a model for each combination of values of model parameters (γ, wc, C), and calculated the model performance via the r2/P[ƒ(x) = 1] criterion proposed by [48], where r is the sensitivity of the focal class (recall accuracy) and P[ƒ(x) = 1] is the probability that a sample is assigned to the focal class. The optimal combination of the BSVM model parameters was identified as the model with higher performance via the r2/P[ƒ(x) = 1] criterion. We built the BSVM models in R [49] using the package “e1071” [50].
We were interested in the ability of BSVM to identify the focal species in mixed pixels rather than its ability to classify a pixel as either the focal or non-focal class. For this we extracted the continuous decision values [51,52] of the best BSVM model selected above, which scale with the degree of spectral similarity between a pixel and the focal species. To convert BSVM decision values into probability attributes (or degree of certainty), a sigmoidal function is fit to the relationship between the decision values and the input data attributes that is equivalent to fitting a logistic regression model to the estimated decision values [51,53]. This resulted in a value that we call SGuavaBSVM, which is a number between 0 and 1 that indicates the spectral similarity of a pixel to P. cattleianum.
For the BSVM volumetric approach (Figure 2), we estimated P. cattleianum relative canopy density by averaging values of SGuavaBSVM of pixels within the validation plots. For the BSVM threshold approach, we reclassified the SGuavaBSVM continuous values as a binary presence/absence indicator variable using the same five threshold values that were tested for the MTMF threshold approach. For each threshold value, we determined the P. cattleianum relative canopy density as the proportion of pixels classified as “presence” within the validation field plots.
3. Results
Figure 4 shows maps of the output values of MTMF (SGuavaMF) and BSVM (SGuavaBSVM). Overall, MTMF and BSVM methods performed well in estimating P. cattleianum relative canopy density (invader dominance). MTMF showed better performance using a threshold mapping approach than a volumetric approach, and the opposite occurred with BSVM. The relationship between field and remote sensing estimates were slightly better using the MTMF—threshold approach (R2 = 0.86; RMSE = 0.9) than BSVM—volumetric approach (R2 = 0.85; RMSE = 0.10). These results indicate the capability of remote sensing data to estimate the location of invasive trees in both upper canopy and subcanopy positions, and they highlight the potential use of this BSVM as a spectral unmixing method.
Using the volumetric mapping approach, where the classifier outputs were averaged and directly used to estimate P. cattleianum dominance within the canopy and subcanopy, MTMF and BSVM produced outputs (SGuavaMF and SGuavaBSVM, respectively) that were positively related to the field data collected in different canopy vertical layers (Figure 5). MTMF consistently underestimated P. cattleianum dominance (Figure 5a). BSVM overestimated P. cattleianum dominance in plots with low invader abundance and underestimated in plots with high invader abundance (Figure 5b). However, when we applied a logarithmic regression between field and remotely sensed estimates of relative canopy cover (SGuavaMF and SGuavaBSVM), the BSVM method (R2 = 0.85; Table 1 and Figure 5b) performed better than MTMF in predicting P. cattleianum dominance using the volumetric approach (R2 = 0.83; Figure 5a).
Using the threshold mapping approach, MTMF and BSVM models yielded different accuracies in estimating invasion dominance. The most accurate estimate was obtained by the MTMF method (R2 = 0.86 with a threshold value of SGuavaMF > 0.10; Figure 6). This low threshold value indicates that P. cattleianum may be present in a given pixel, even when the spectral similarity between this pixel and the focal endmember is low. The best estimate of the BSVM using threshold approach was obtained with the threshold of 0.5 (R2 = 0.80; Figure 7). A SGuavaMF threshold of 0.01 overestimated P. cattleianum relative canopy density by two-fold, but the same threshold for SGuavaBSVM overestimated relative canopy density by about eight-fold in areas with low invasion spread. A threshold of 0.05 also showed similar patterns, although the degree of overestimation was lower than models using the 0.01 threshold. Overall, both types of models (MTMF and BSVM) underestimated relative canopy density when threshold values were high.
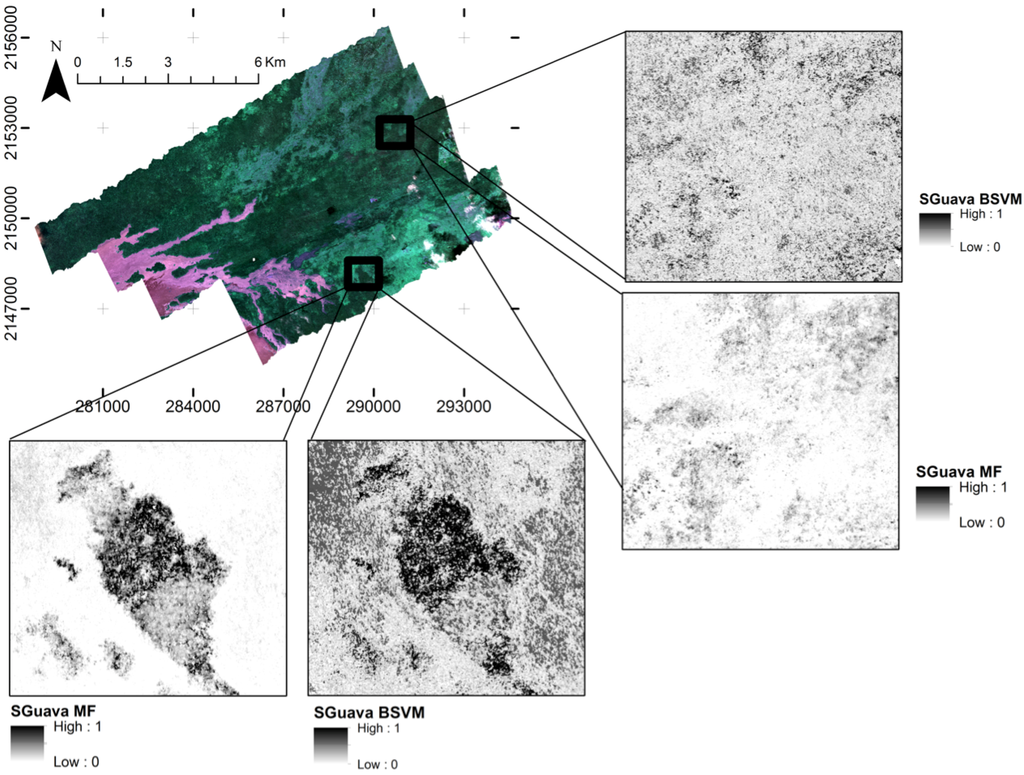
Figure 4.
Maps in the study area for P. cattleianum dominance using Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF; Sguava MF) and Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM; Sguava BSVM). False color composite map derived from Carnegie Airborne Observatory (CAO) Beta system of the Wao Kele O Puna Forest Reserve on the Island of Hawaii.
Figure 4.
Maps in the study area for P. cattleianum dominance using Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF; Sguava MF) and Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM; Sguava BSVM). False color composite map derived from Carnegie Airborne Observatory (CAO) Beta system of the Wao Kele O Puna Forest Reserve on the Island of Hawaii.
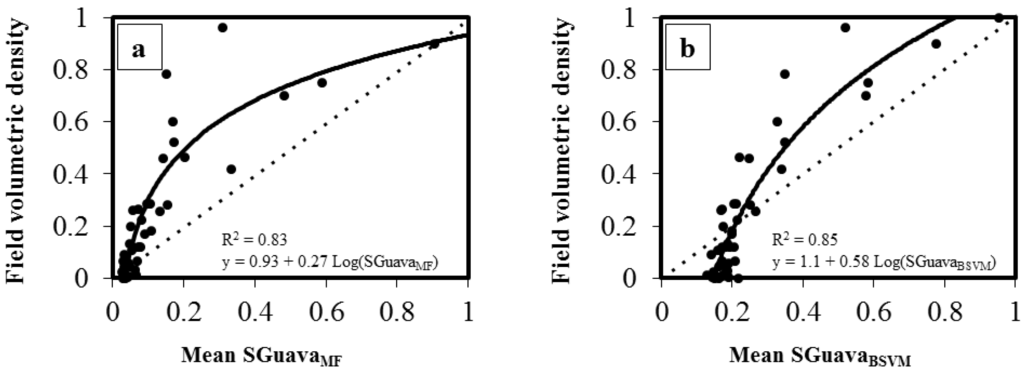
Figure 5.
Relationships between field dataset (P. cattleianum relative canopy density) and classifier outputs using the volumetric approach (SGuavaMF or SGuavaMTMF pixel values were averaged within plots). (a) MTMF outputs; (b) BSVM outputs. Dotted lines represent the 1:1 relationship. Black lines represent the logarithmic model.
Figure 5.
Relationships between field dataset (P. cattleianum relative canopy density) and classifier outputs using the volumetric approach (SGuavaMF or SGuavaMTMF pixel values were averaged within plots). (a) MTMF outputs; (b) BSVM outputs. Dotted lines represent the 1:1 relationship. Black lines represent the logarithmic model.
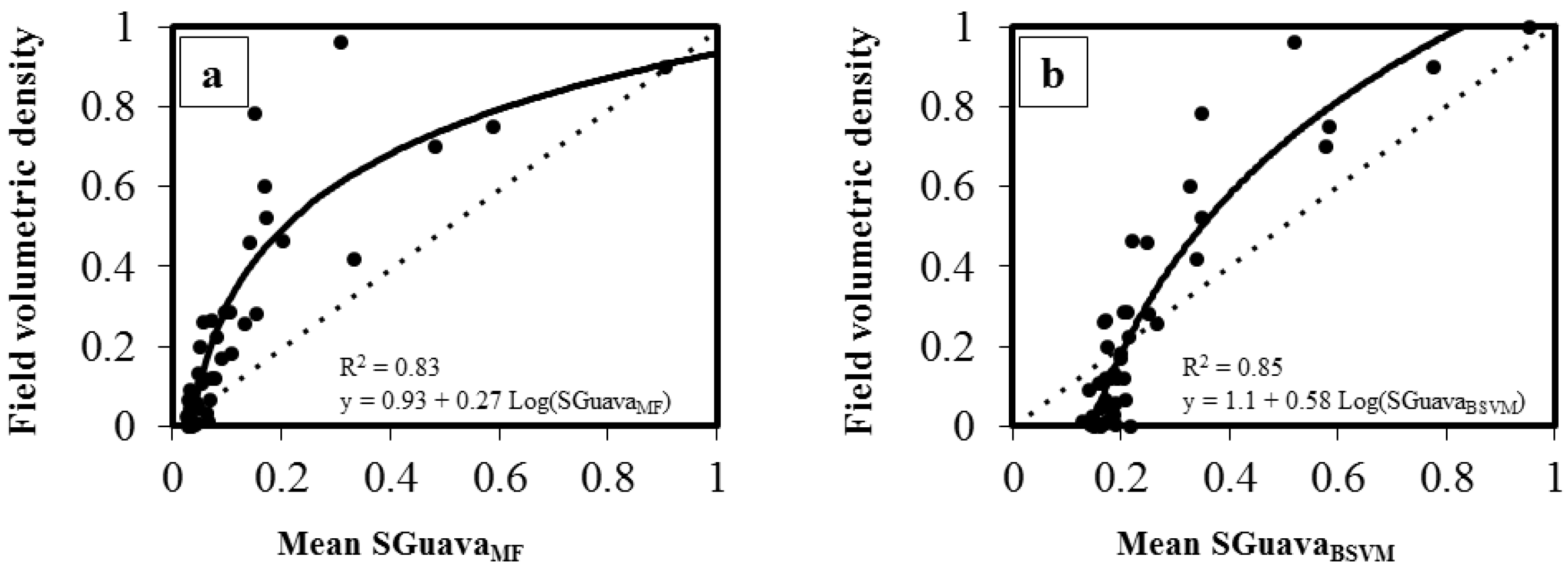
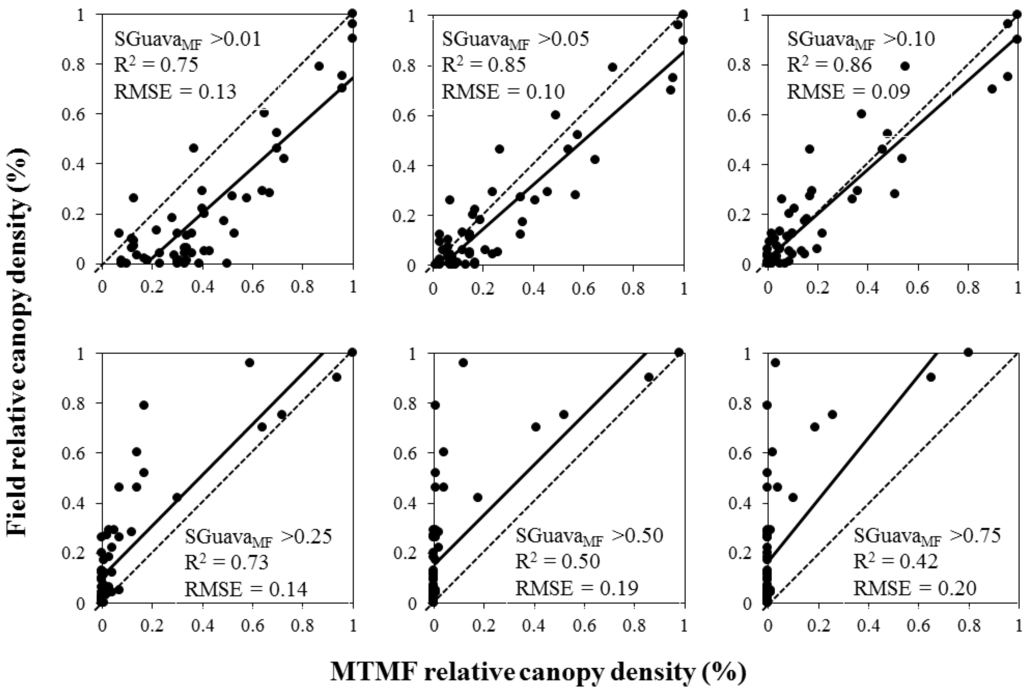
Figure 6.
Relationship between field data (P. cattleianum relative canopy density) and Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF) outputs using the threshold approach (SGuavaMF). Dotted lines represent the 1:1 relationship. Black lines represent the linear regression. R2 = square root. RMSE = root mean square error.
Figure 6.
Relationship between field data (P. cattleianum relative canopy density) and Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (MTMF) outputs using the threshold approach (SGuavaMF). Dotted lines represent the 1:1 relationship. Black lines represent the linear regression. R2 = square root. RMSE = root mean square error.
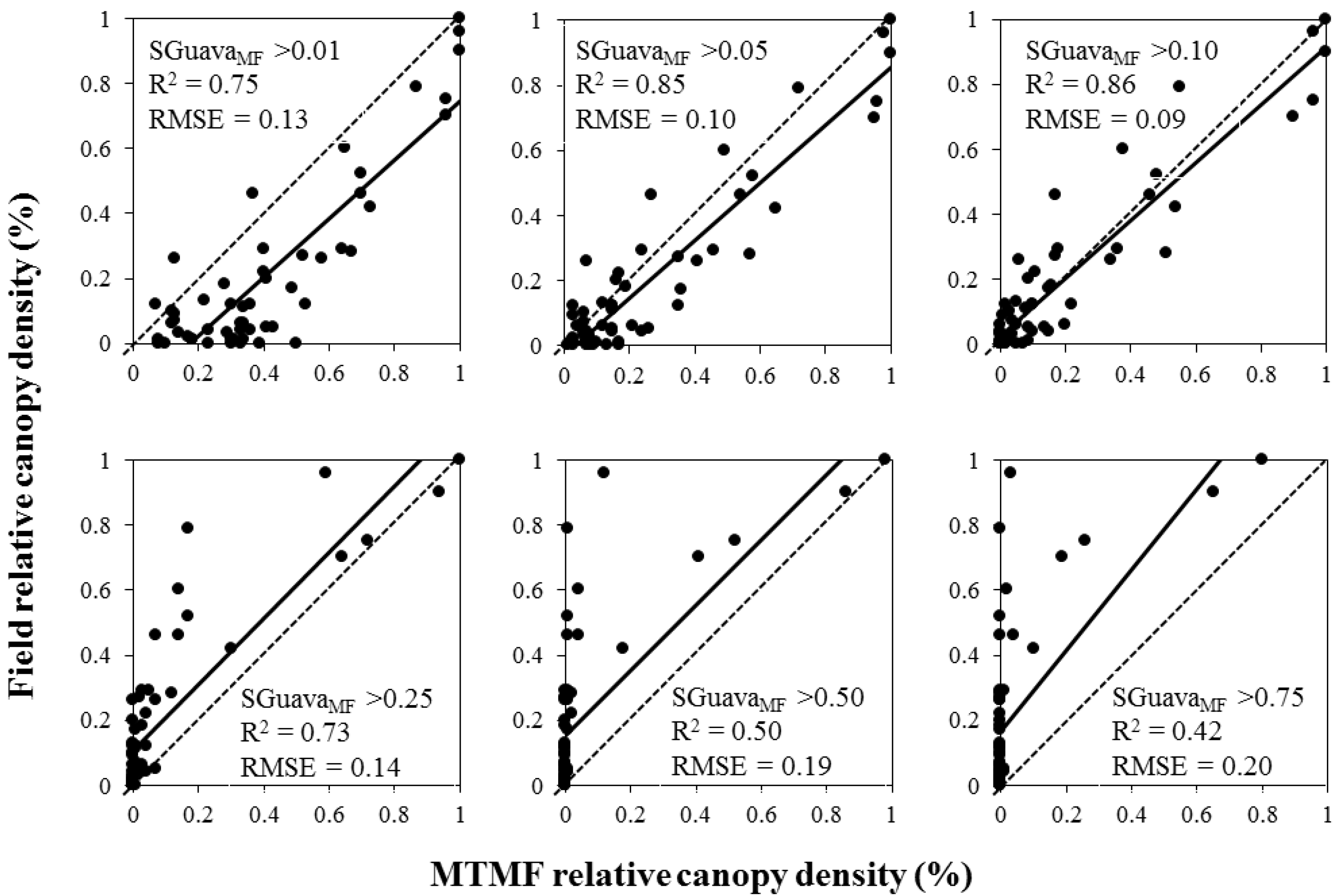
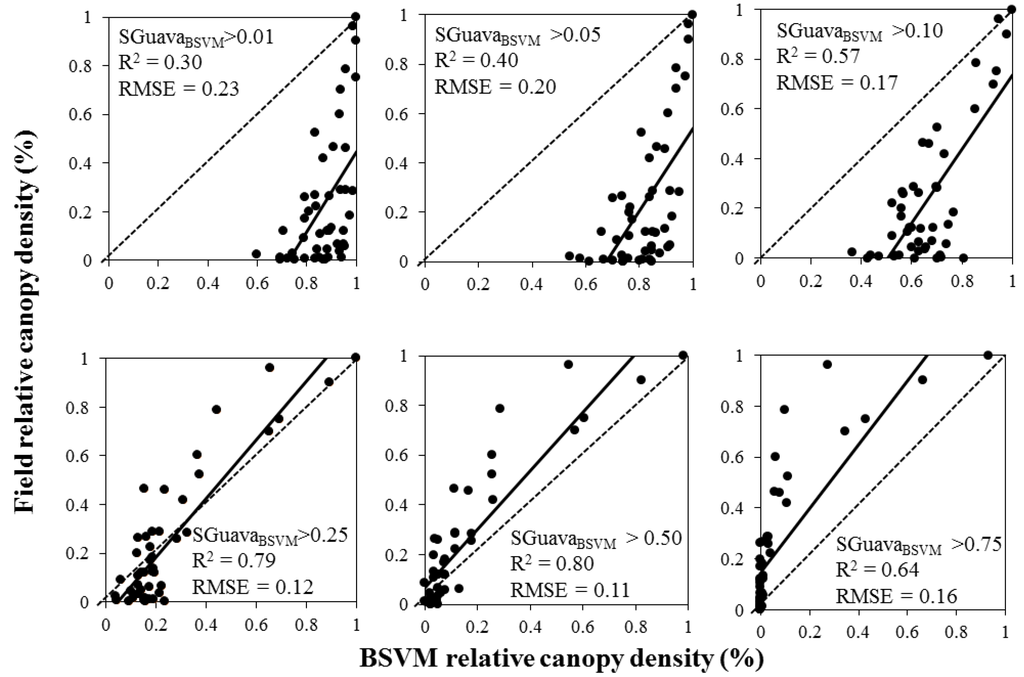
Figure 7.
Relationship between field data (relative canopy density) and Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM) outputs using the threshold approach (SGuavaBSVM). Dotted lines represent the 1:1 relationship. Black lines represent the linear regression. R2 = square root. RMSE = root mean square error.
Figure 7.
Relationship between field data (relative canopy density) and Biased Support Vector Machine (BSVM) outputs using the threshold approach (SGuavaBSVM). Dotted lines represent the 1:1 relationship. Black lines represent the linear regression. R2 = square root. RMSE = root mean square error.
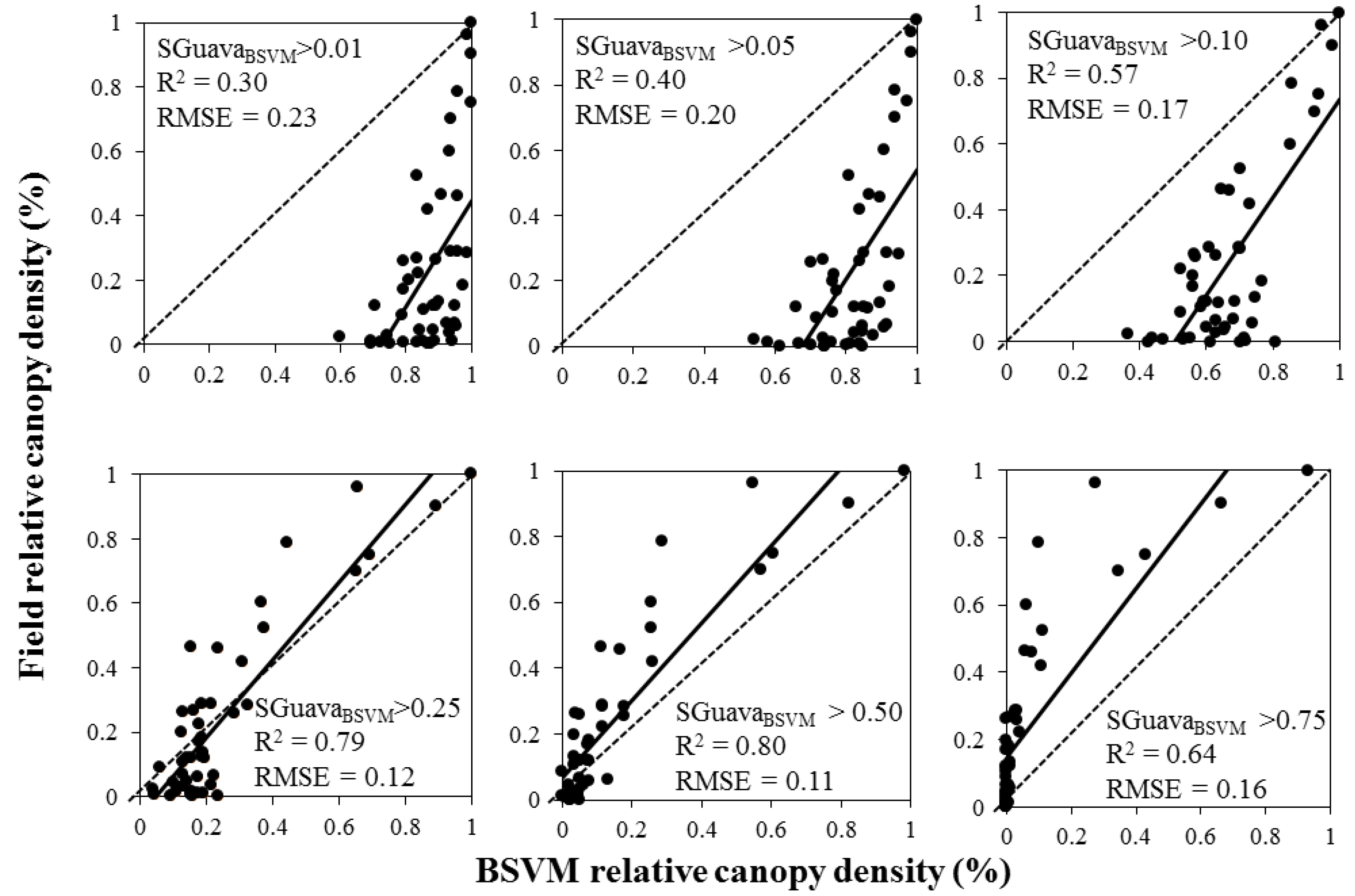

Table 1.
Summary of parameters and suitability of the logarithmic regression models for estimating P. cattleianum relative canopy density using the volumetric approach. BSVM = Biased support vector machine. MTMF = Mixture tuned matched filtering. Adj. R2 = adjusted coefficient of determination; RMSE = root mean square error calculated from the comparison between field and predicted data; SD = standard deviation.
| Model | Fitting Parameters | Regression Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | Equation | p-Level | |
| BSVM | 0.85 | 0.10 (SD = 0.025) | 1.1 + 0.58 Ln(SGuavaBSVM) | <0.001 |
| MTMF | 0.83 | 0.14 (SD = 0.019) | 0.93 + 0.27 Ln(SGuavaMF) | <0.001 |
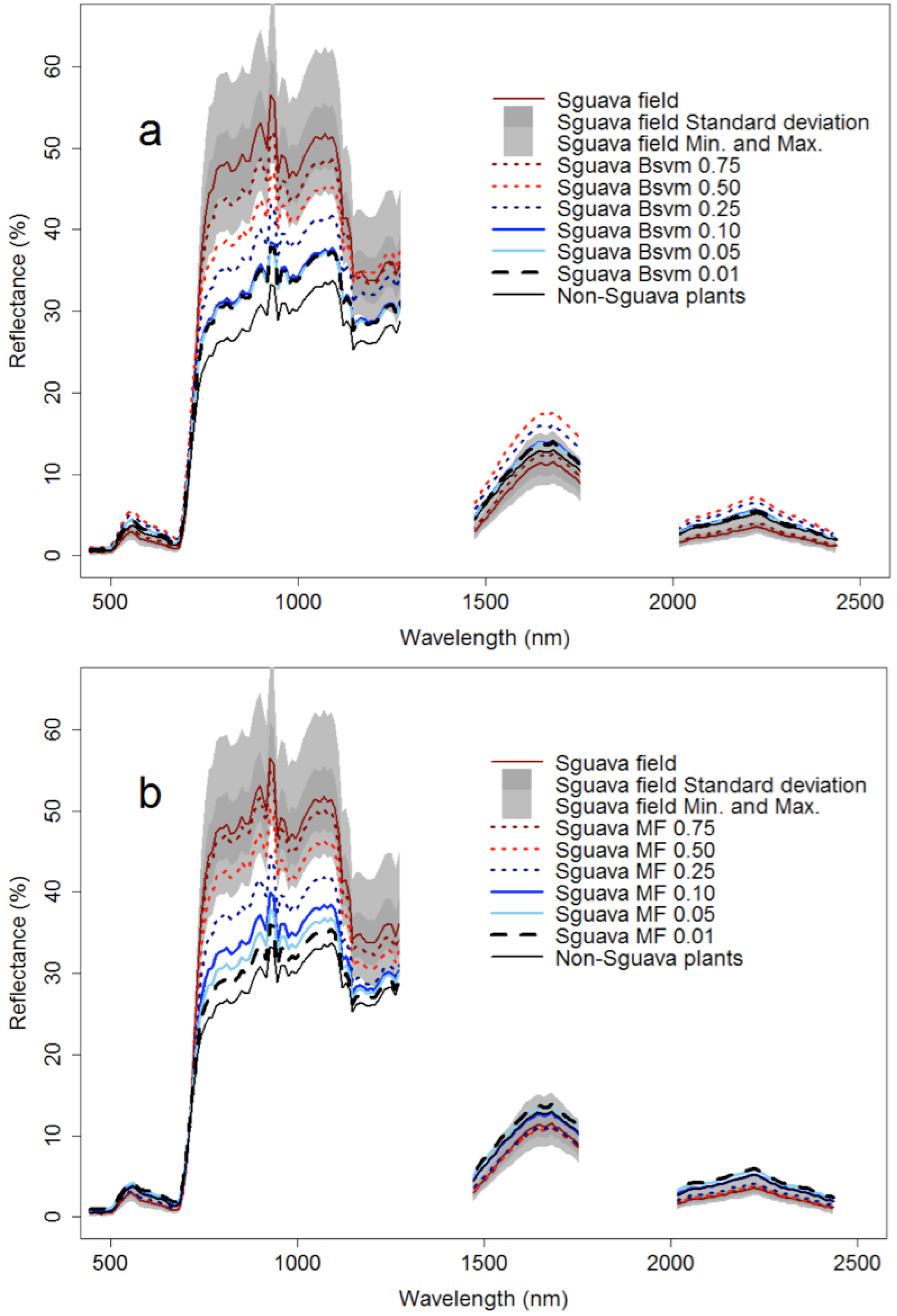
Reflectance of pixels classified as P. cattleianum using different methods (BSVM or MTMF) showed distinctive patterns (Figure 8), mainly within the near-infrared (800–1300 nm) spectral range. However, classifier outputs from both methods displayed a gradual increase in spectral similarity with the P. cattleianum endmembers as the threshold increased, which indicate that both methods are similar, but not identical, in measuring the level of spectral correspondence between target pixels and endmembers. In Figure 4, the spectra for non-P. cattleianum trees were obtained from five field plots where the tree species within these plots comprised 77% of the total number of trees (13 species) found within all study plots. Mean reflectance of BSVM outputs overlapped in the near-infrared range when we used thresholds between 0.01 and 0.10; however, reflectance of MTMF outputs exhibited a gradual increase in this threshold range. Using threshold values between 0.25 and 0.75, the reflectance pattern from MTMF and BSVM outputs exhibited greater similarity to P. cattleianum endmembers than when using low threshold values (i.e., <0.25). However, MTMF outputs approached the minimum and maximum reflectance of the focal species endmembers across a wider spectral range than did the BSVM approach. In the visible and shortwave infrared spectral regions (400–700 nm and >1300 nm, respectively), the differences between field data and classifier output (BSVM and MTMF) were not as large as in the near-infrared range (700–1300 nm).
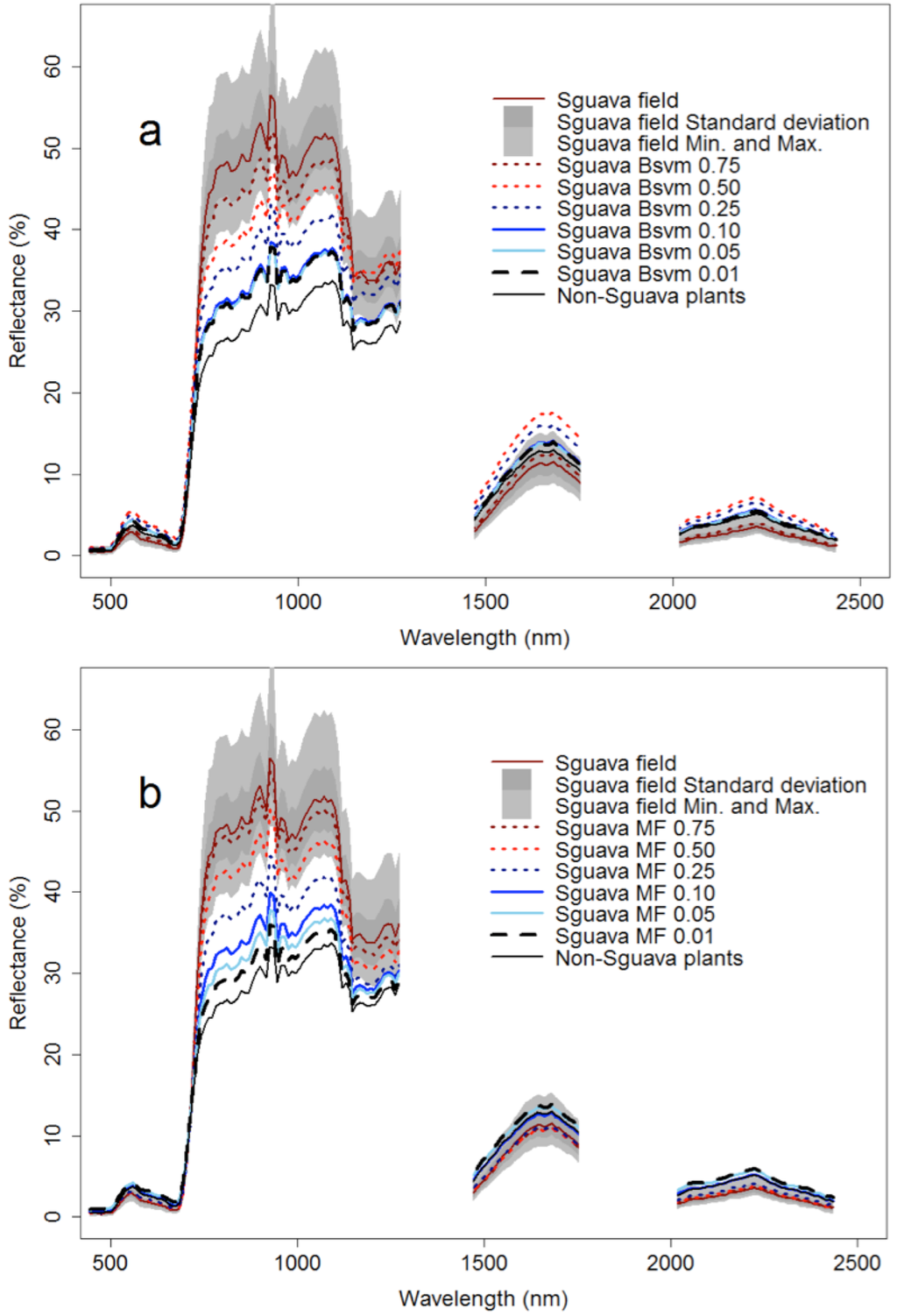
Figure 8.
Mean reflectance by wavelength of pixels selected using field data, and pixels classified as P. cattleianum using the threshold classification approach. (a) Biased Support Vector Machine (SGuavaBSVM); (b) Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (SGuavaMF). SGuava field is the mean reflectance of pixels where P. cattleianum was identified in the field and Non-SGuava plant is the mean reflectance of pixels where P. cattleianum was absent in the field. SGuava BSVM or MF between 0.01 and 0.75 indicate thresholds used to perform the pixel reclassification as P. cattleianum presence/absence.
Figure 8.
Mean reflectance by wavelength of pixels selected using field data, and pixels classified as P. cattleianum using the threshold classification approach. (a) Biased Support Vector Machine (SGuavaBSVM); (b) Mixture Tuned Matched Filtering (SGuavaMF). SGuava field is the mean reflectance of pixels where P. cattleianum was identified in the field and Non-SGuava plant is the mean reflectance of pixels where P. cattleianum was absent in the field. SGuava BSVM or MF between 0.01 and 0.75 indicate thresholds used to perform the pixel reclassification as P. cattleianum presence/absence.
4. Discussion
Using an airborne high-resolution imaging spectrometer, we successfully detected P. cattleianum crowns even when the plant was mixed with other species, a situation that poses challenges to remote detection of plant species. MTMF and BSVM enabled us to estimate the proportion of canopy vertical layers occupied by Psidium cattleianum (relative canopy density), which helped us to determine areas with low to high dominance of this species. Previous studies have also mapped invasive species distribution using MTMF (e.g., [18,28]), among others spectral unmixing methods [17,19,21]. However, here, we first use this methodological approach to estimate invader fractional abundance within different canopy vertical layers.
To our knowledge, BSVM has not yet been proposed for mapping invasive species or estimating crown volumetric density of focal plant species. BSVM and other variants of the support vector machine are flexible and distribution-free modeling approaches, which are based on the principles of structural risk minimization theory, i.e., a machine learning procedure that balances model complexity and efficiency based on the success of fitting the training data [54]. BSVM is a partially supervised and non-parametric classification method that researchers have recently increased its use in for remote sensing applications [31,33,55]. Our results suggest BSVM as a promising method to disentangle spectrally-mixed classifications, as this approach generates decision values from a similarity function (kernel), which optimize complex comparisons between classes in a dynamic machine learning process.
Tropical forests often exhibit complex and vertically stratified canopy structure, with individual trees expressing their morphologies (i.e., crown position and volume) in response to life cycle, specific environmental conditions, and biological interactions [56]. Thus, the remote detection of overlapping and hidden crowns relies on a limited signal in the spectra from material below the canopy [14,57]. Our results suggest MTMF and BSVM were sensitive to the subtle spectral signature of P. cattleianum crowns present in different vertical canopy layers (Figure 3 and Figure 5). These methods were able to detect the focal species when relative canopy density was as low as 10%–20%. It should be noted that in Hawaii, native ohia trees (Metrosideros polymorpha) often constitute the overstory canopy [58]. Structurally, ohia trees often exhibit clumped leaves, with significant canopy gaps around one another. This permits deeper penetration of light within the canopy [59] and likely aids detection of P. cattleianum growing in the subcanopy.
Although fully supervised classifiers have a demonstrable capability to map tree species in tropical forest via high resolution imaging spectrometry, partially supervised methods such as MTMF and BSVM may be suitable alternatives because they greatly reduce the amount of training data required [22,31,60]. This is important in high-diversity or structurally-complex ecosystems, where species express varying spectral signatures under different conditions [34]. Here, we limited the training and validation data collection to the focal species, rather than labeling all species or collecting data from all potential combinations of overlapping plant species. However, lack of labeled training data may constrain the utility and effectiveness of partially supervised methods for assessing commission errors [48]. To overcome this limitation, we indirectly assessed the “background” information (non P. cattleianum trees) in the validation dataset as the proportion of the canopy volume not occupied by the focal species.
The inclusion of the covariance structure of endmembers in spectral unmixing methods can improve classification accuracy when species display similar spectra [60,61]. BSVM uses the full spectral variability of the focal species to generate decision values and to create complex boundaries between classes. On the contrary, MTMF uses a static analysis of the endmember spectra (i.e., arithmetic mean); therefore, MTMF may not incorporate the full variability of the endmember spectral signatures in the classification of target species [60]. In our study area, the spectra of P. cattleianum are strongly different from other species [62], which may have minimized potential constrains in the MTMF performance to estimate the invader dominance. Because MESMA is a classification method that accounts for spectral variability of endmembers on a per-pixel basis when solving spectrally unmixing problems [17], this method has the potential to also be tested in future studies using our methodological framework. Previous studies have suggested that the efficacy of spectral unmixing methods may be species- and site-specific [28], may depend on seasonality [19] or on the source of remote sensing data [9,10]. Therefore, we suggest that our methodological approach (i.e., vertically stratified field sampling, MTMF-threshold approach or BSVM-volumetric approach) be further evaluated in other classification conditions. Our mapping procedures worked well in our study area, a Hawaiian lowland tropical forest, where plant species diversity is not as high as in other tropical forests. Future studies may elucidate the accuracy of these classification methods in other forests.
BSVM performed better in detecting P. cattleianum dominance using a volumetric approach combined with a logarithmic regression model between field data and classifier outputs (i.e., decision values). In contrast, MTMF performed better using a threshold approach, which performs a threshold reclassification creating discretizing maps of presence/absence of the focal species in pixels located within given plots. It is important to note that the field plot data were needed to model relative canopy density from the raw model outputs; thus, these methods were not able to estimate relative canopy density from only the spectral endmembers. However, efforts related to these additional steps (regression or search for the best threshold) are comparable to other procedures required to determine best modeling parameters. It is also important to note that, when P. cattleianum shows full horizontal cover in the overstory of a plot, this plot may show higher “relative canopy density” than another plot where this invasive species shows full horizontal cover in the understory. A few native species in Hawaii grows beneath P. cattleianum, but this invasive species often grows in the subcanopy. Therefore, P. cattleianum may only share the canopy volumetric space with other species in the case where this invader is growing in the subcanopy, which leads us to assume that these two scenarios represent different ecological conditions.
In the present study, we used an image with fine spatial resolution. Small pixel size may increase the occurrence of shadowed crowns and exposed substrate within the canopy area. To minimize this problem, we masked our imagery to leafy and well-lit pixels. The contribution of understory to forest reflectance (in nadir viewing) can range between approximately 20% to 50% [14]. Therefore, we assumed that the detection of understory flora might be more effective using our masking procedure as the sunlight may penetrate deeper in the sub-canopy in well-lit pixels. Pixels not meeting this masking requirement for leafy or well-lit conditions were left unanalyzed. The exclusion of these pixels in the classification might increase false-negative presence of the focal species, although it does not seem to be a problem in areas with low or high invader dominance (Figure 5). Images with coarse spatial resolution may show increased spectral mixture among canopies and non-photosynthetic materials within pixels. Therefore, small patches of P. cattleianum may become even more diffuse and difficult to detect. However, by spatially aggregating fine resolution airborne AVIRIS data, Roth et al. [63] also show that coarser spatial resolution images may improve classification accuracies due to a reduction of within-class spectral variance of target classes, and accuracy may also increase when coarser pixels closely approximate class patch size. This suggests that our methodological framework may work on images with coarser pixel sizes when invader dominance is medium to high.
5. Conclusions
Management programs for controlling invasive species are in need of methods to map and monitor the spread of target plants. Remote species detection using imaging spectroscopy takes advantage of the spectral traits produced by biochemical and structural properties of the canopies, but translating that to species abundance or degree of infestation in tropical forests requires understanding of spectral patterns in a mixed canopy context. We tested different methodological approaches with the aim of assessing the subpixel abundance of P. cattleianum based on the presence of the species in different canopy vertical layers. When these results were aggregated to the plot level (approximately 1000 m2), both MTMF and BSVM approaches were useful in assessing the degree of species invasion across the landscape. Our results suggest BSVM as a promising method to disentangle spectrally-mixed classifications, as this approach generates decision values from a similarity function. This study helps to bridge the gap between remote species detection of plants located in the canopy and in the subcanopy using high-resolution imaging spectroscopy, which is critical in the face of the current effort to map species over large spatial scales. Future studies that link spatially-explicit estimates of invader dominance and climatic conditions may help us to understand how the environment determines species abundance in the particular landscapes.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation and a grant from the USDA 2014-67013-21603. Carnegie Airborne Observatory data collection and mapping was funded privately by the William Hearst III and the Carnegie Institution for Science. The Carnegie Airborne Observatory is made possible by the Avatar Alliance Foundation, Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, W. M. Keck Foundation, Margaret A. Cargill Foundation, Grantham Foundation for the Protection of the Environment, Mary Anne Nyburg Baker and G. Leonard Baker Jr., and William R. Hearst III. All authors agree with the contents of the manuscript and its submission to the journal.
Author Contributions
Jomar M. Barbosa designed the study, performed data analysis and wrote the manuscript. Gregory P. Asner designed the study, collected remote sensing and field data, wrote the manuscript, and acquired funding for the project. Claire A. Baldeck provided analytical methods and assisted with the manuscript. Roberta E. Martin collected field data and assisted with the manuscript. Flint Hughes and Tracy Johnson provided scientific support and acquired funding for the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript: |
| MTMF: | Mixture tuned matched filtering |
| BSVM: | Biased support vector machine |
| CAO: | Carnegie Airborne Observatory |
| AVIRIS: | Airborne Visible and Infrared Imaging Sectrometer |
| VSWIR: | Visible-to-Shortwave Infrared |
| SAM: | Spectral angler mapper |
| MESMA: | Multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis |
| RMSE: | root mean square error |
| SD: | standard deviation |
| SGuavaMF: | continuous output of the MTMF classificaiton |
| SGuavaBSVM: | continuous output of the BSVM classification |
References
- Sax, D.F.; Gaines, S.D. Species invasions and extinction: The future of native biodiversity on islands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11490–11497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, K.I.; Chase, J.M.; Knight, T.M. Invasive plants have scale-dependent effects on diversity by altering species-area relationships. Science 2013, 339, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenfeld, J.G. Ecosystem consequences of biological invasions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.F.; Asner, G.P.; Mascaro, J.; Uowolo, A.; Baldwin, J. Carbon storage landscapes of lowland Hawaii: The role of native and invasive species through space and time. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, D.; Zuniga, R.; Morrison, D. Update on the environmental and economic costs associated with alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 52, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohlgren, T.J.; Rejmanek, M. No universal scale-dependent impacts of invasive species on native plant species richness. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20130939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chornesky, E.A.; Bartuska, A.M.; Aplet, G.H.; Britton, K.O.; Cummings-Carlson, J.; Davis, F.W.; Eskow, J.; Gordon, D.R.; Gottschalk, K.W.; Haack, R.A.; et al. Science priorities for reducing the threat of invasive species to sustainable forestry. Bioscience 2005, 55, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E. Weed risk assessment: A way forward or a waste of time? J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.S.; Rocchini, D.; Neteler, M.; Nagendra, H. Benefits of hyperspectral remote sensing for tracking plant invasions: Plant invasion and hyperspectral remote sensing. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Asner, G.P. Applications of remote sensing to alien invasive plant studies. Sensors 2009, 9, 4869–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asner, G.P. Organismic remote sensing for tropical forest ecology and conservation. Ann. Mol. Bot. Gard. 2015, 100, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueffer, C.; Daehler, C.C.; Torres-Santana, C.W.; Lavergne, C.; Meyer, J.-Y.; Otto, R.; Silva, L. A global comparison of plant invasions on oceanic islands. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 12, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheley, R.L.; Krueger-Mangold, J. Principles for restoring invasive plant-infested rangeland. Weed Sci. 2003, 51, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautiainen, M.; Lukeš, P. Spectral contribution of understory to forest reflectance in a boreal site: An analysis of EO-1 Hyperion data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshava, N.; Mustard, J.F. Spectral unmixing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P. Hyperspectral remote sensing of canopy chemistry, physiology, and biodiversity in tropical rainforests. In Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Tropical and Sub-Tropical Forests; Kalacska, M., Sanchez-Azofeifa, A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 261–295. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, B.; Asner, G.P.; Tits, L.; Coppin, P. Endmember variability in spectral mixture analysis: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, J.; Glenn, N.; Weber, K.; Prather, T.; Lass, L.; Pettingill, J. Discrimination of hoary cress and determination of its detection limits via hyperspectral image processing and accuracy assessment techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Asner, G.P. Multi-temporal hyperspectral mixture analysis and feature selection for invasive species mapping in rainforests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bue, B.D.; Thompson, D.R.; Sellar, R.G.; Podest, E.V.; Eastwood, M.L.; Helmlinger, M.C.; McCubbin, I.B.; Morgan, J.D. Leveraging in-scene spectra for vegetation species discrimination with MESMA-MDA. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.H.; Roberts, D.A.; Almeida, T.I.R.; Souza Filho, C.R. Mapping invasive species and spectral mixture relationships with neotropical woody formations in southeastern Brazil. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Atkinson, P.M.; Gething, P.W.; Ravenhill, N.A.; Kelly, C.K. Identification of specific tree species in ancient semi-natural woodland from digital aerial sensor imagery. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldeck, C.A.; Asner, G.P.; Martin, R.E.; Anderson, C.B.; Knapp, D.E.; Kellner, J.R.; Wright, S.J. Operational tree species mapping in a diverse tropical forest with airborne imaging spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boardman, J.W.; Kruse, F.A.; Green, R.O. Mapping target signatures via partial unmixing of AVIRIS data. In Fifth JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1995; Volume 95, pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.J.; Glenn, N.F. Subpixel abundance estimates in mixture-tuned matched filtering classifications of leafy spurge (Euphorbia esula L.). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6099–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.B.; Root, R.R.; Kokaly, R.F.; Anderson, G.L. Increased spatial and temporal consistency of leafy spurge maps from multidate AVIRIS imagery: A modified, hybrid linear spectral mixture analysis/mixture-tuned matched filtering approach. In Proceedings of the 13th JPL Airborne Earth Sciences Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 31 March–2 April 2004.
- Glenn, N.F.; Mundt, J.T.; Weber, K.T.; Prather, T.S.; Lass, L.W.; Pettingill, J. Hyperspectral data processing for repeat detection of small infestations of leafy spurge. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.; Ustin, S. The role of environmental context in mapping invasive plants with hyperspectral image data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4301–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulam, A.; Porton, I.; Freeman, K. Detecting subcanopy invasive plant species in tropical rainforest by integrating optical and microwave (InSAR/PolInSAR) remote sensing data, and a decision tree algorithm. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Lee, W.S.; Yu, P.S. Building text classifiers using positive and unlabeled examples. In Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Melbourne, FL, USA, 19–22 November 2003; pp. 179–186.
- Baldeck, C.A.; Asner, G.P. Single-Species detection with airborne imaging spectroscopy data: A comparison of support vector techniques. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Weng, R.C. Simple Probabilistic Predictions for Support Vector Regression; National Taiwan University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrakoudis, D.; Dragozi, E.; Gitas, I.; Karydas, C. Decision fusion based on hyperspectral and multispectral satellite imagery for accurate forest species mapping. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6897–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Hughes, R.F.; Vitousek, P.M.; Knapp, D.E.; Kennedy-Bowdoin, T.; Boardman, J.; Martin, R.E.; Eastwood, M.; Green, R.O. Invasive plants transform the three-dimensional structure of rain forests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4519–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loope, L.L.; Mueller-Dombois, D. Characteristics of invaded islands, with special reference to Hawaii. In Biological Invasions: A Global Perspective; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 257–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lorence, D.H.; Sussman, R.W. Exotic species invasion into Mauritius wet forest remnants. J. Trop. Ecol. 1986, 2, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunison, T. Element Stewardship Abstratct for Psidium Cattleianum—USDA Forest Service. Available online: http://www.invasive.org/weedcd/pdfs/tncweeds/psidcat.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2015).
- Wagner, W.L.; Herbst, D.R.; Sohmer, S.H. Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawaii; University of Hawaii Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- State of Hawaii. Final Environmental Assessment: Biocontrol of Strawberry Guava by Its Natural Control Agent for Preservation of Native Forests in the Hawaiian Islands; The Environmental Notice: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2011.
- Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Kennedy-Bowdoin, T.; Jones, M.O.; Martin, R.E.; Boardman, J.; Field, C.B. Carnegie airborne observatory: In-flight fusion of hyperspectral imaging and waveform light detection and ranging for three-dimensional studies of ecosystems. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 013536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldeck, C.; Asner, G. Estimating vegetation beta diversity from airborne imaging spectroscopy and unsupervised clustering. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2057–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, C. Estimating mean plant cover from different types of cover data: A coherent statistical framework. Ecosphere 2014, 5, art20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, C. Hierarchical and spatially aggregated plant cover data. Ecol. Inform. 2013, 18, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.A.; Berman, M.; Switzer, P.; Craig, M.D. A transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, J.T.; Streutker, D.R.; Glenn, N.F. Partial unmixing of hyperspectral imagery: Theory and methods. In Proceedings of the American Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Tampa, FL, USA, 7–11 May 2007.
- Heinz, D.C.; Chang, C.-I. Fully constrained least squares linear spectral mixture analysis method for material quantification in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.E.; Wang, L. Characterizing spatial patterns of invasive species using sub-pixel classifications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Liu, B. Learning with positive and unlabeled examples using weighted logistic regression. In Procedings of the 20th International Conference Machine Learning, Washington, DC, USA, 21–24 August 2003; Volume 3, pp. 448–455.
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computer: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, D.; Dimitriadou, E.; Hornik, K.; Weingessel, A.; Leisch, F.; Chang, C.; Lin, C. Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics, Probability Theory Group (Formerly: E1071), TU Wien. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/e1071/e1071.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2015).
- Lin, H.-T.; Lin, C.-J.; Weng, R.C. A note on Platt’s probabilistic outputs for support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2007, 68, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Meyer, D.; Karatzoglou, A. Support vector machines in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2006, 15, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J. Probabilistic outputs for support vector machines and comparison to regularized likelihood methods. In Advances in large Margin Classifiers; Smola, A., Bartlett, P., Schölkopf, B., Schuurmans, D., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. Principles of risk minimization for learning theory. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrija-Trejos, E.; Pérez-García, E.A.; Meave, J.A.; Bongers, F.; Poorter, L. Functional traits and environmental filtering drive community assembly in a species-rich tropical system. Ecology 2010, 91, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asner, G.; Vitousek, P. Remote analysis of biological invasion and biogeochemical change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4383–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemmermann, L. Ecological studies of Hawaiian Metrosideros in a successional context. Pac. Sci. 1983, 37, 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ollinger, S.V. Sources of variability in canopy reflectance and the convergent properties of plants: Tansley review. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGwire, K.C.; Minor, T.B.; Schultz, B.W. Progressive discrimination: An automatic method for mapping individual targets in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2674–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, C.; Asner, G.P.; Wessman, C. Endmember bundles: A new approach to incorporating endmember variability into spectral mixture analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Kennedy-Bowdoin, T.; Jones, M.O.; Martin, R.E.; Boardman, J.; Hughes, R.F. Invasive species detection in Hawaiian rainforests using airborne imaging spectroscopy and LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1942–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Peterson, S.H.; Alonzo, M. The impact of spatial resolution on the classification of plant species and functional types within imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
