Inferring Snow Water Equivalent for a Snow-Covered Ground Reflector Using GPS Multipath Signals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SWE Estimation
2.1. With a Ground Reflector
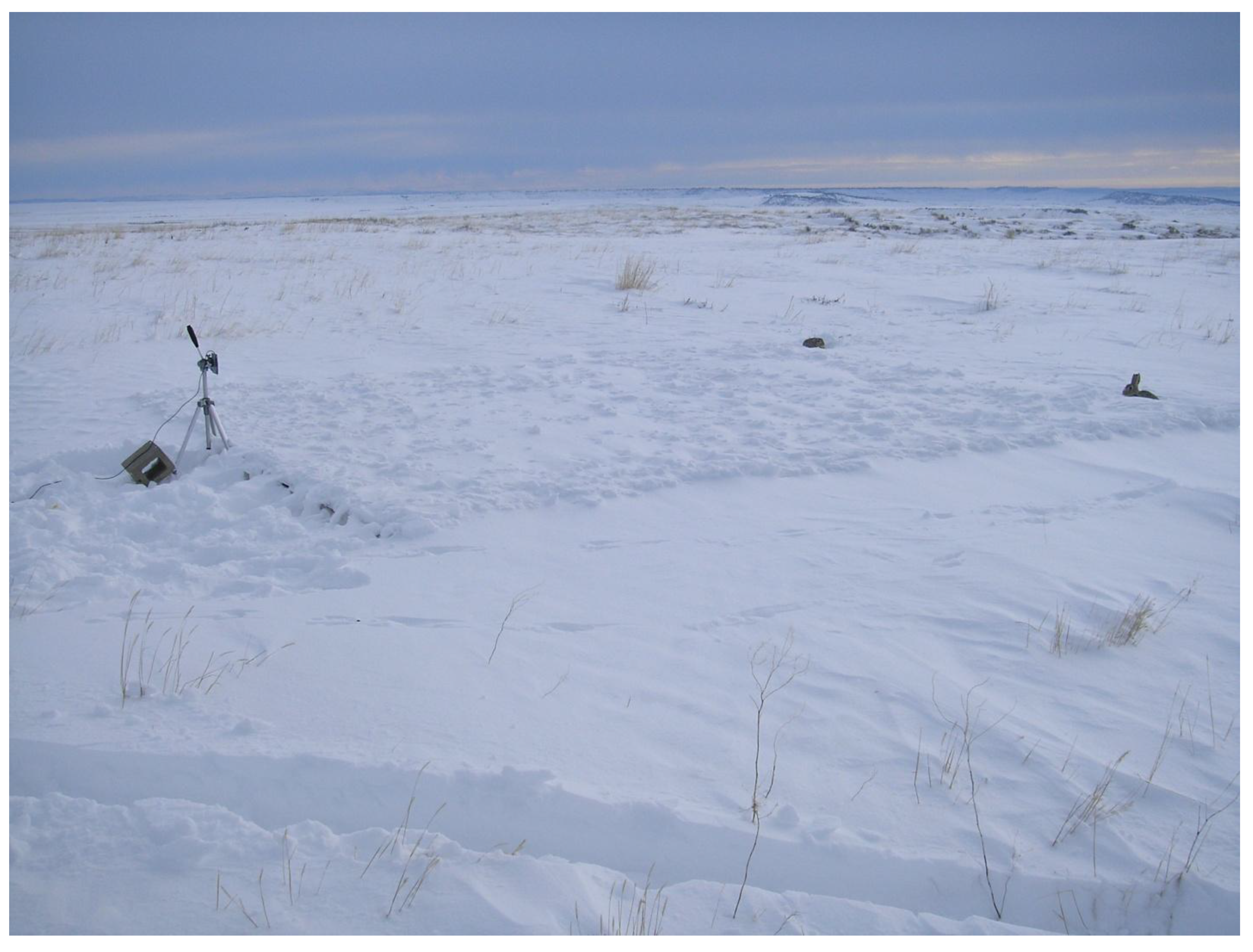
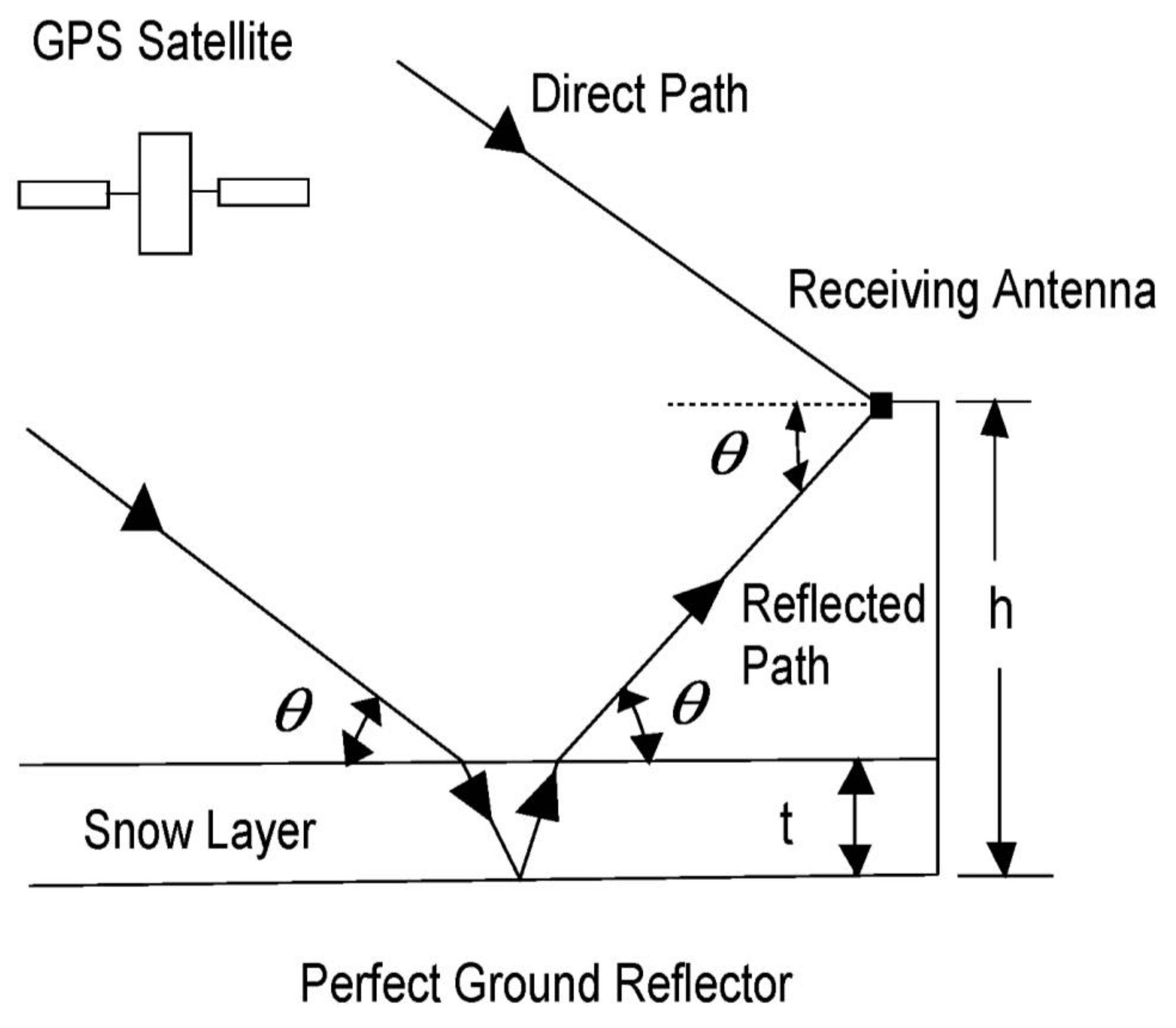

| x, y (m) | (0, 0) | (0, 2.5) | (0, 5) | (2.5, 0) | (2.5,2.5) | (2.5, 5) | (5, 0) | (5, 2.5) | (5, 5) |
| t (cm) | 7.0 | 7.3 | 5.1 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 10.1 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 9.1 |
| INPUT | OUTPUT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (cm) | εsnow | t (cm) | εsnow | ρd (g cm−3) | SE (dB) |
| 2.54 | 1.3 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 2.54 | 1.38 | 3.56 | 1.4 | 0.13 | 1.277 |
| 2.54 | 1.48 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 2.54 | 1.68 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 2.54 | 1.8 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 5.1 | 1.3 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 5.1 | 1.38 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 5.1 | 1.48 | 3.8 | 1.27 | 0.083 | 1.161 |
| 5.1 | 1.68 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 5.1 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 7.6 | 1.3 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 7.6 | 1.38 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 7.6 | 1.48 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 7.6 | 1.68 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 7.6 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 10.1 | 1.3 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 10.1 | 1.38 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 10.1 | 1.48 | 3.4 | 1.3 | 0.13 | 1.334 |
| 10.1 | 1.68 | 3.5 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 1.28 |
| 10.1 | 1.8 | 3.4 | 1.27 | 0.13 | 1.334 |
| 20.0 | 1.3 | 0 | 1.15 | 0.08 | 2.752 |
| 20.0 | 1.38 | 0 | 1.42 | 0.21 | 3.051 |
| 20.0 | 1.48 | 3.4 | 1.28 | 0.14 | 1.349 |
| 20.0 | 1.68 | 0.04 | 1.63 | 0.11 | 1.261 |
| 20.0 | 1.8 | 3.8 | 1.28 | 0.14 | 1.351 |
| 30.0 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 1.15 | 0.074 | 2.411 |
| 30.0 | 1.38 | 11.0 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2.105 |
| 30.0 | 1.48 | 3.4 | 1.28 | 0.14 | 1.349 |
| 30.0 | 1.68 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 30.0 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 40.0 | 1.3 | 27.6 | 1.39 | 0.2 | 3.426 |
| 40.0 | 1.38 | 26.8 | 1.72 | 0.36 | 3.195 |
| 40.0 | 1.48 | 10.5 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2.105 |
| 40.0 | 1.68 | 10.5 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2.105 |
| 40.0 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 50.0 | 1.3 | 50.4 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 2.845 |
| 50.0 | 1.38 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 50.0 | 1.48 | 52.9 | 1.5 | 0.25 | 2.8 |
| 50.0 | 1.68 | 11.0 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2.105 |
| 50.0 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.146 |
| 100.0 | 1.3 | 86.5 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.972 |
| 100.0 | 1.38 | 3.73 | 1.27 | 0.14 | 1.307 |
| 100.0 | 1.48 | 3.53 | 1.3 | 0.15 | 1.378 |
| 100.0 | 1.68 | 88.2 | 1.87 | 0.44 | 2.761 |
| 100.0 | 1.8 | 89.4 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2.535 |
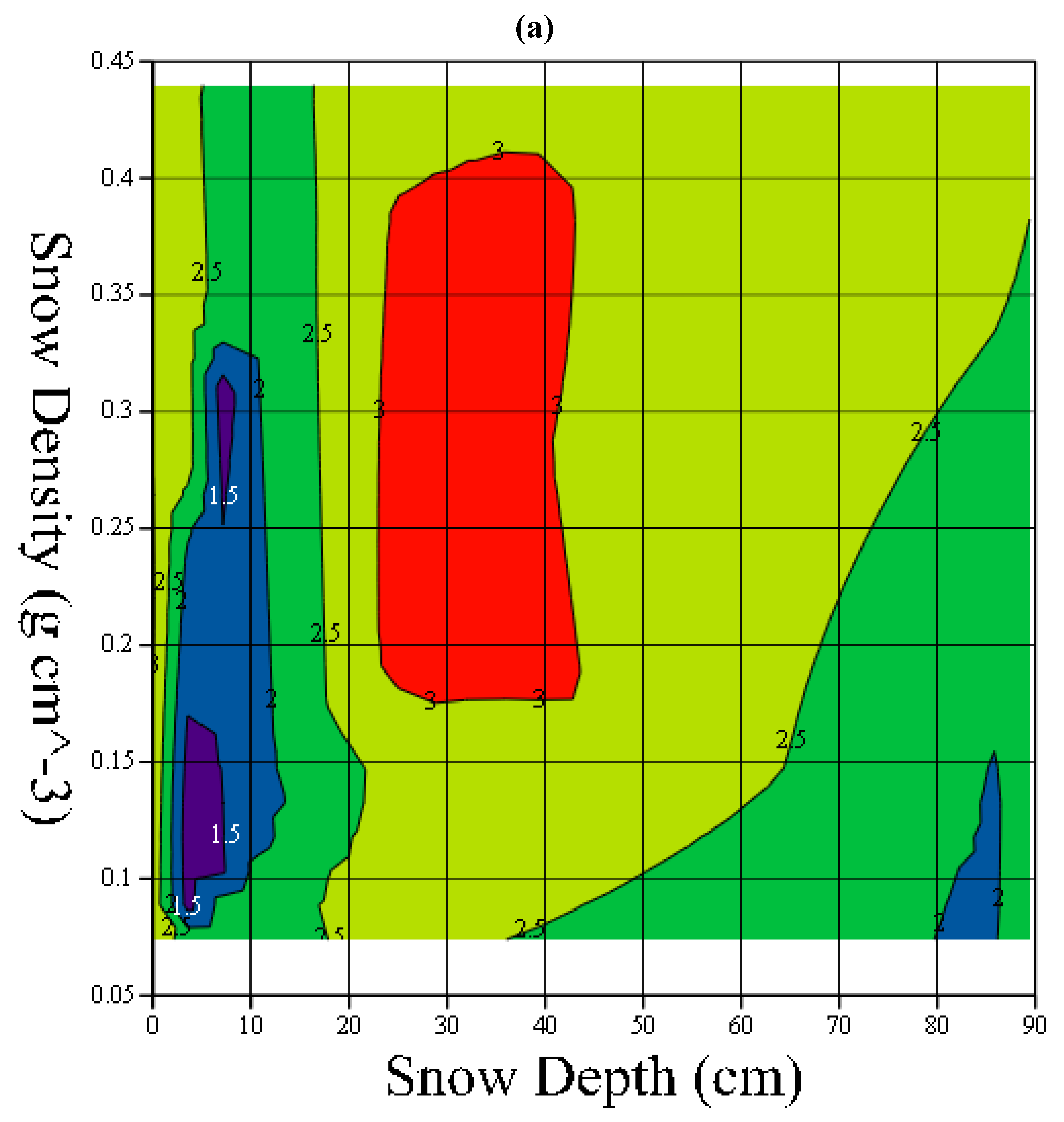
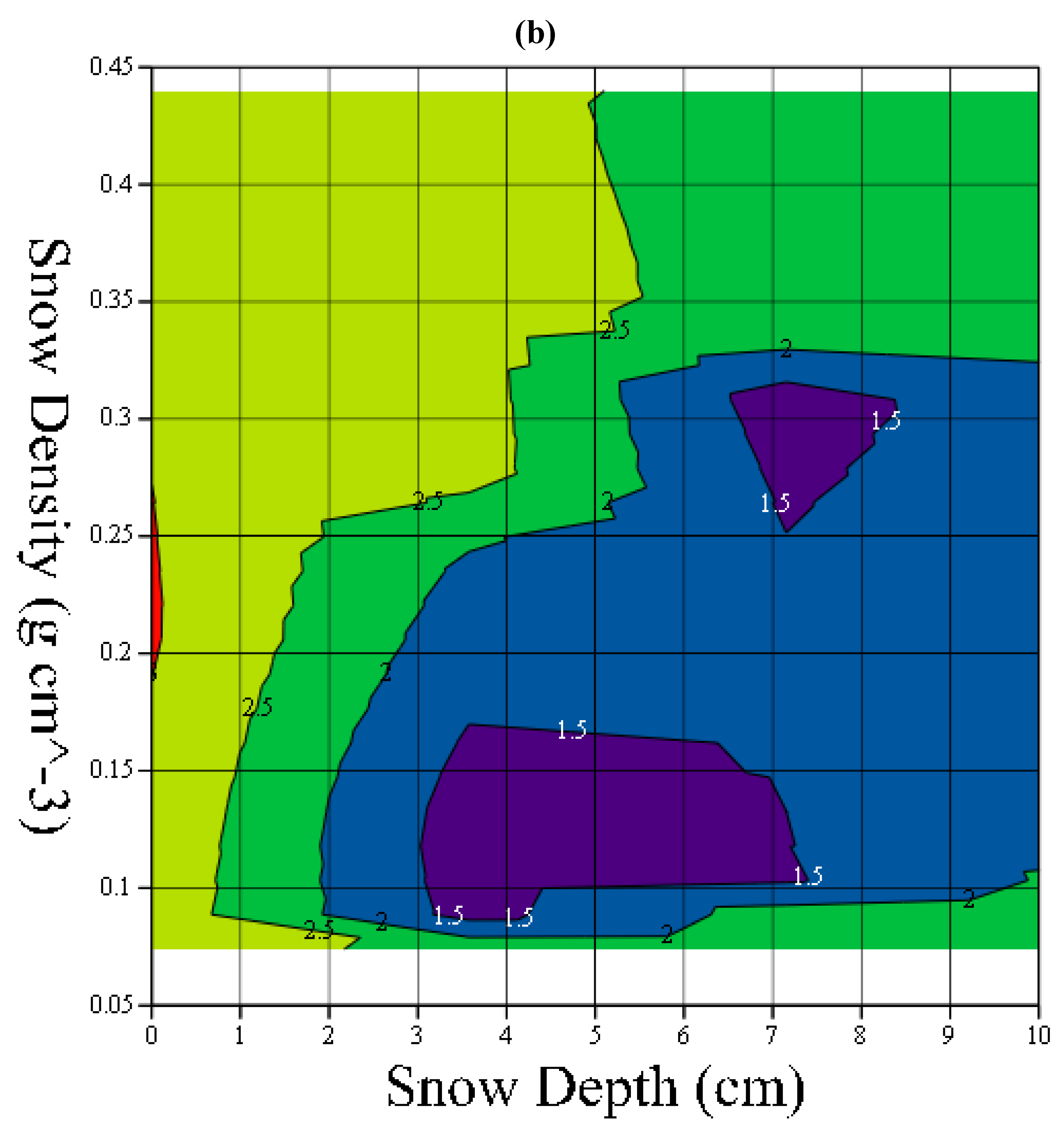
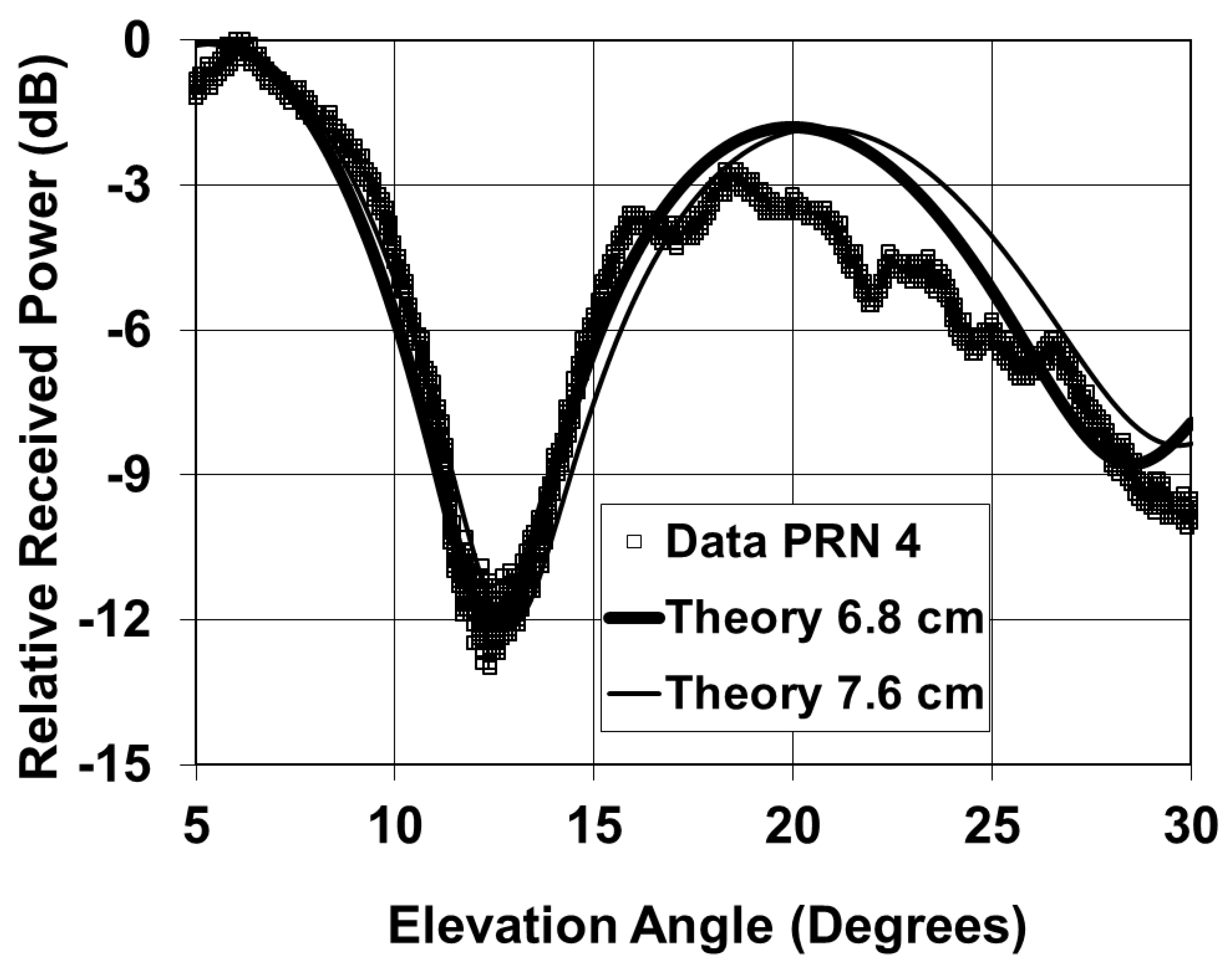
2.2. Without a Ground Reflector
| Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Volumetric Wetness (cm3 cm−3) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Field 1 | 51.5 | 35.1 | 13.4 | 0.24 | 1.54 |
| Field 5 | 5 | 47.6 | 47.4 | 0.36 | 1.42 |
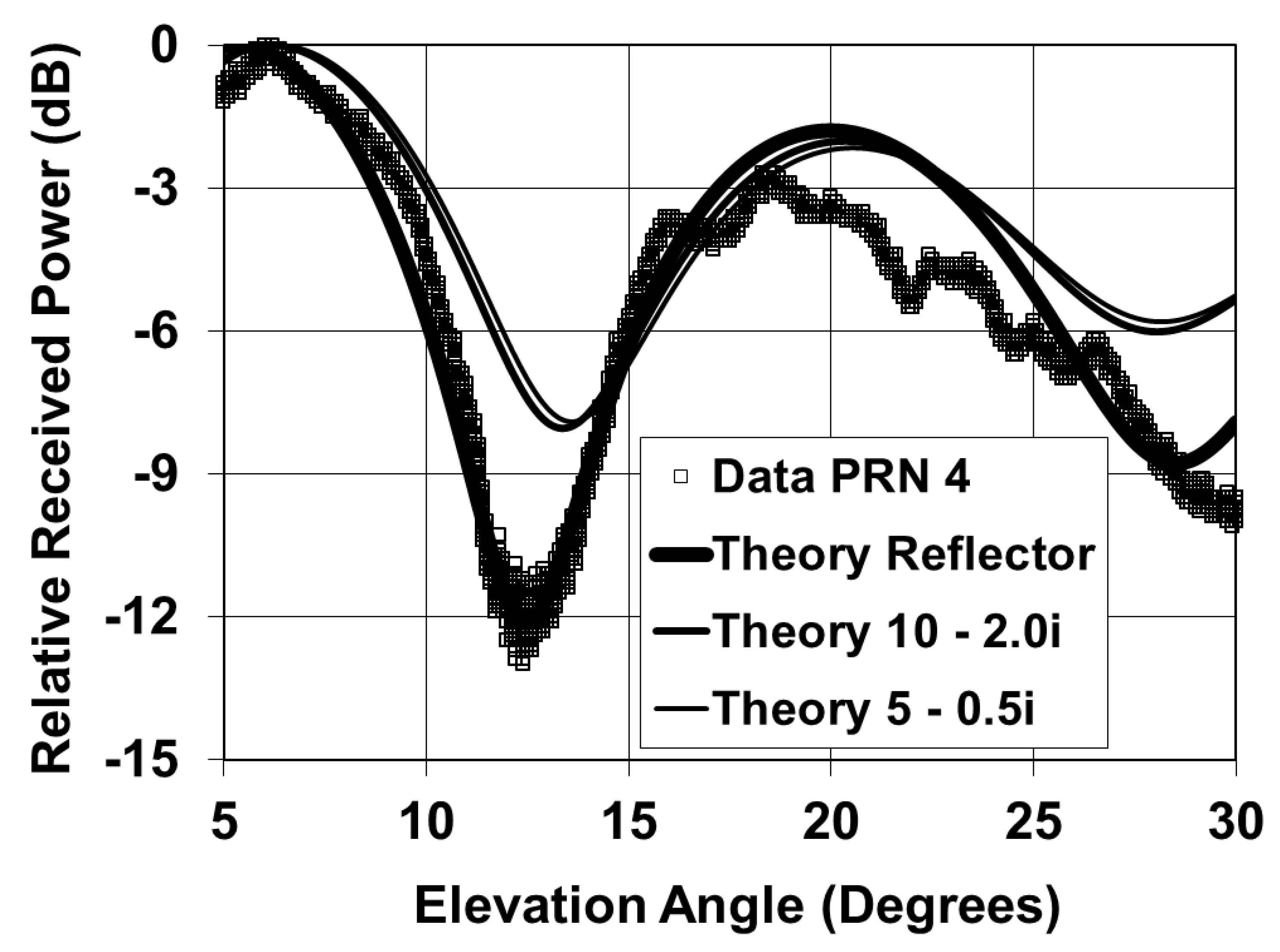
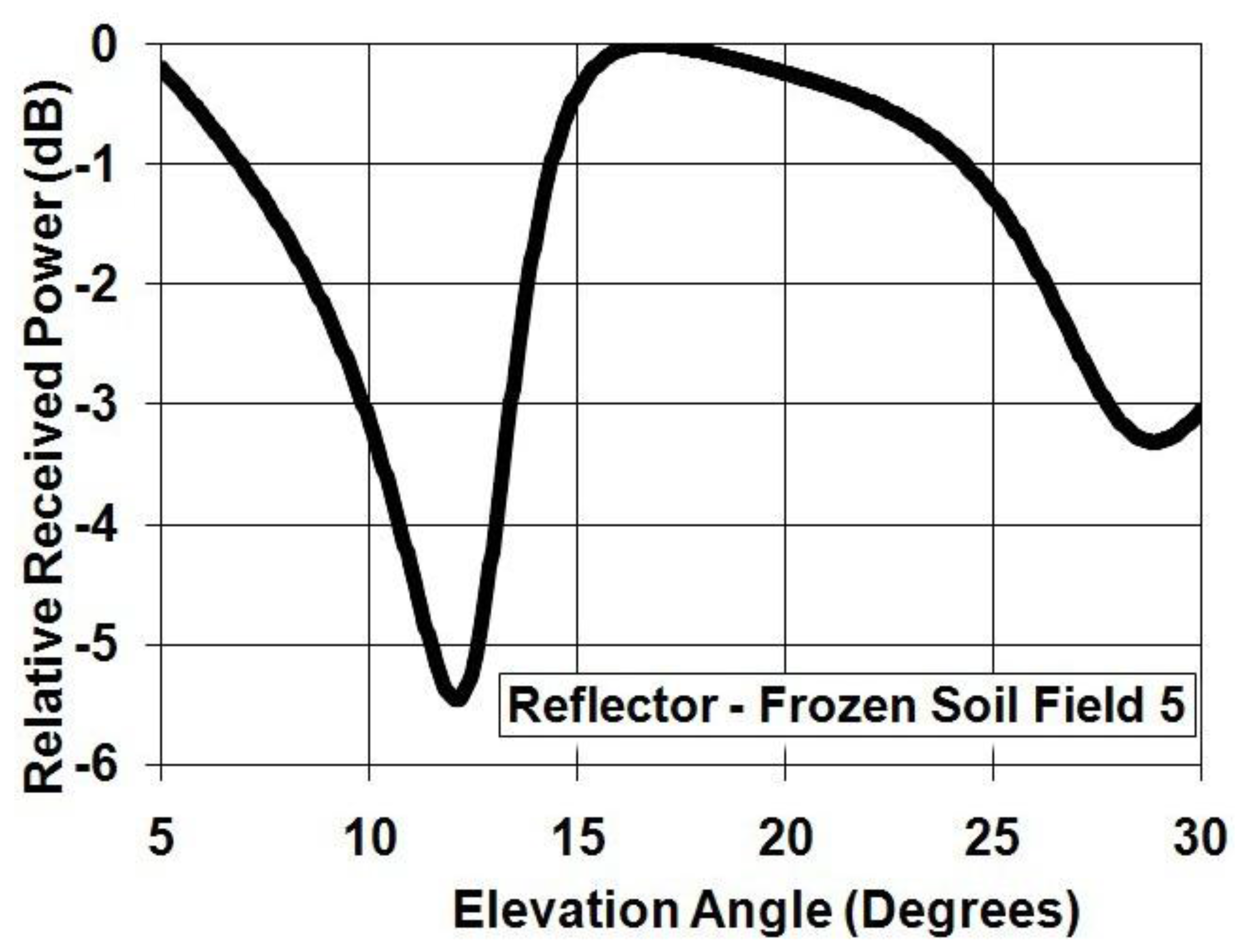
3. Conclusions and Future Research
Acknowledgements
References
- Schaefer, G.L.; Paetzold, R.F. SNOTEL (SNOwpack TELemetry) and SCAN(Soil Climate Analysis Network). In Presented at Automated Weather Stations for Applications in Agriculture and Water Resources Management: Current Use and Future, Lincoln, NE, USA, March 2000; Available online: ftp://ftp.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/downloads/factpub/soils/SNOTEL-SCAN.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2010).
- Serreze, M.C.; Clark, M.P.; Armstrong, R.L.; McGinnis, D.A.; Pulwarty, R.S. Characteristics of the western United States snowpack from Snowpack Telemetry (SNOTEL) data. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2145–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotch, N.P.; Bales, R.C. SNOTEL representatives in the Rio Grande headwaters on the basis of physiographics and remotely sensed snow cover persistence. Hydrol. Processes 2006, 20, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Gutmann, E.; Zavorotny, V.; Braun, J.; Williams, M.; Nievinski, F. Can we measure snow depth with GPS receivers? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.D. Dielectric-covered ground reflectors in GPS multipath reception—Theory and measurement. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.D. Snow-covered lake ice in GPS multipath reception—Theory and measurement. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Komjathy, A. GNSS reflectometry and remote sensing: New objectives and results. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.T.; Kroger, P.; Franklin, G.; LaBerecque, J.L.; Lerma, J.; Lough, M.; Marcin, M.R.; Muellerschoen, R.J.; Spitzmesser, D.; Young, L.E. A delay/doppler- mapping receiver system for GPS-reflection remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 40, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.S.; Acton, S.T.; Katzberg, S.J. Terrain moisture classification using GPS surface-reflected signals. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.; Bilich, A.; Braun, J.; Zavorotny, V.U. Use of GPS receivers as a soil moisture network for water cycle studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, D.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Katzberg, S.J.; Emery, W. GPS signal scattering from land for moisture content determination. In Proceedings of IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; Volume 7, pp. 3090–3092.
- Kavak, A.; Xu, G.; Vogel, W.J. GPS multipath fade measurements to determine L-band ground reflectivity properties. In Proceedings of the 20th NASA Propagation Experimenters Meeting, Fairbanks, AK, USA, 4–6 June 1996; pp. 257–263.
- Kavak, A.; Vogel, W.J.; Xu, G. Using GPS to measure ground complex permittivity. Electron. Letters 1998, 34, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzber, S.J.; Torres, O.; Grant, M.S.; Masters, D. Utilizing calibrated GPS reflected signals to estimate soil reflectivity and dielectric constant: Results from SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.B.; Maslanik, J.A.; Axelrad, P. Bistatic scattering of GPS signals off Arctic sea ice. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, D.; Yueh, S.; Chapman, B.; Stankov, B.; Gasiewski, A.; Masters, D.; Elder, K.; Kelly, R.; Painter, T.H.; Miller, S.; Katzberg, S.; Mahrt, L. NASA Cold Land Processes Experiment (CLPX 2002/03): Airborne remote sensing. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komjathy, A.; Maslanik, J.A.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Axelrad, P.; Katzberg, S.J. Towards GPS surface reflection remote sensing of sea ice conditions. In Proceedings of Sixth International Conference on Remote Sensing for the Marine and Coastal Environment, Charleston, SC, USA, 2000; Volume II, pp. 447–456.
- Komjathy, A.; Maslanik, J.A.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Axelrad, P.; Katzberg, S.J. Sea ice remote sensing using surface reflected GPS signals. In Proceedings of IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2000; Volume 7, pp. 2855–2857.
- Gleason, S.; Lowe, S.; Zavorotny, V. Remote sensing using bistatic GNSS reflections. In GNSS Applications and Methods; Gleason, S., Gebre-Egziabher, D., Eds.; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, S. Towards sea ice remote sensing with space detected GPS signals: Demonstration of technical feasibility and initial consistency check using low resolution sea ice information. Remote Sensing 2010, 2, 2017–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, F.; Cardellach, E.; Nogués, O.; Oliveras, S.; Ribó, S.; Rius, A.; Belmonte-Rivas, M. Sea ice remote sensing with GNSS reflections. Instrum. Viewpoint 2009, 8, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Wiehl, M.; Legresy, R.; Dietrich, R. Potential of reflected GNSS signals for ice sheet remote sensing. Progress Electromag. Res. 2003, 40, 177–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herceg, D.; Krejic, N.; Luzanin, Z. Quasi-Newton’s method with correction. Novi Sad J. Math. 1996, 26, 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Stutzman, W.L. Polarization in Electromagnetic Systems; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 188–200. [Google Scholar]
- Beckman, P.; Spizzichino, A. The Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves from Rough Surfaces; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Tiuri, M.E.; Sihvola, A.H.; Nyfors, E.G.; Hallikaiken, M.T. The complex dielectric constant of snow at microwave frequencies. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1984, 9, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dozier, J. Estimation of snow water equivalence using SIR-C/X-SAR, Part I: Inferring snow density and subsurface properties. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing, Active and Passive; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986; Volume III, pp. 2060–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Hallikainen, M.T.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C.; El-Rayes, M.A.; Wu, L.-K. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil—Part I: Empirical models and experimental observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.; Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.; Bilich, A. A physical model for GPS multipath caused by land reflections: Toward bare soil moisture retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Indust. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewchuk, J.R. An Introduction to the Conjugate Gradient Method without the Agonizing Pain; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburg, PA, USA, August 1994; Available online: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~quake-papers/painless-conjugate-gradient.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2010).
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacobson, M.D. Inferring Snow Water Equivalent for a Snow-Covered Ground Reflector Using GPS Multipath Signals. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2426-2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs2102426
Jacobson MD. Inferring Snow Water Equivalent for a Snow-Covered Ground Reflector Using GPS Multipath Signals. Remote Sensing. 2010; 2(10):2426-2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs2102426
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacobson, Mark D. 2010. "Inferring Snow Water Equivalent for a Snow-Covered Ground Reflector Using GPS Multipath Signals" Remote Sensing 2, no. 10: 2426-2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs2102426
APA StyleJacobson, M. D. (2010). Inferring Snow Water Equivalent for a Snow-Covered Ground Reflector Using GPS Multipath Signals. Remote Sensing, 2(10), 2426-2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs2102426




