Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Hyperspectral imagery demonstrated superior performance compared with multispectral data for estimating fire severity across Mediterranean ecosystems.
- Among the hyperspectral vegetation indices, DVIRED, EVI, and CAI achieved the highest correlations across Composite Burn Index (CBI) levels and vegetation types.
What are the implications of the main findings?
- Hyperspectral remote sensing shows strong potential as an accurate, scalable tool for post-fire severity assessment in heterogeneous Mediterranean ecosystems.
- Variations in the performance of hyperspectral vegetation indices among vegetation formations reflect distinct spectral responses associated with differing vegetation structures and burn characteristics.
Abstract
Assessing post-fire disturbance in Mediterranean ecosystems is essential for quantifying ecological impacts and guiding restoration strategies. This study evaluates fire severity following an extreme wildfire event (~28,000 ha) in northwestern Spain using vegetation indices (VIs) derived from PRISMA hyperspectral imagery, validated against field-based Composite Burn Index (CBI) measurements at the vegetation, soil, and site levels across three vegetation formations (coniferous forests, broadleaf forests, and shrublands). Hyperspectral VIs were benchmarked against multispectral VIs derived from Sentinel-2. Hyperspectral VIs yielded stronger correlations with CBI values than multispectral VIs. Vegetation-level CBI showed the highest correlations, reflecting the sensitivity of most VIs to canopy structural and compositional changes. Indices incorporating red-edge, near-infrared (NIR), and shortwave infrared (SWIR) bands demonstrated the greatest explanatory power. Among hyperspectral indices, DVIRED, EVI, and especially CAI performed best. For multispectral data, NDRE, CIREDGE, ENDVI, and GNDVI were the most effective. These findings highlight the strong potential of hyperspectral remote sensing for accurate, scalable post-fire severity assessment in heterogeneous Mediterranean ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Forest fires are the most significant disturbance in Mediterranean ecosystems worldwide, particularly in the Mediterranean basin, where large areas have been burned in recent decades due to abrupt changes in fire regimes caused by climate change and rural land abandonment [1,2,3]. Fires play an essential role in shaping species composition, structure, and dynamics of Mediterranean plant communities [4,5]. Furthermore, fires cause physical, chemical, and biological changes in forest soils [6]. Assessing fire severity is critical for quantifying losses in above- and below-ground biomass [7], evaluating the ecological and socioeconomic impacts of wildfires, and informing evidence-based decision-making in land management [8]. Fire severity is defined as the magnitude of ecological change in a burned area relative to the pre-fire conditions and is measured qualitatively or quantitatively through the effects of fire on vegetation and soils [9,10]. Fire severity can be evaluated in the field through integrative indices such as the Composite Burn Index (CBI) [9]. CBI is considered a well-known field-based fire severity index to calibrate remote sensing products [11]. Its advantages include fast deployment and assessment over large, burned landscapes [12], and strong relationships with field measurements of individual indicators [13] and satellite spectral-based fire severity indices [14]. CBI measurement in the field is based on the visual assessment of several fire severity indicators across the substrate and four vegetation strata in the plots. The individual indicators are rated on a semiquantitative scale between zero (unchanged) and three (highest fire severity), with the indicator scores across strata linearly averaged to procure aggregated fire severity estimates for the substrate, vegetation, and the whole plot (site CBI), which are considered to offer an integrative perspective of the fire-induced ecological impact on ecosystems.
Remote sensing has become a valuable data source for ecological assessment, as it overcomes limitations associated with traditional field-based methods, such as being spatially or temporally limited due to irregular data collection [15]. It is highly effective for assessing fire severity across large, burned landscapes, owing to its favorable cost–benefit ratio and synoptic capabilities [16], as it improves the efficiency, speed, and feasibility of monitoring fire-prone regions [17]. In particular, multispectral data provided by Landsat or Sentinel-2 missions are commonly used in quantitative fire severity assessments [18,19,20,21]. More broadly, multispectral sensors have formed the backbone of operational fire severity mapping for several decades, providing long-term, spatially consistent records that support large-scale fire monitoring [22,23]. For instance, Landsat imagery underpins the Monitoring Trends in Burn Severity (MTBS) program in the United States, which delivers standardized fire severity products for all large wildfires nationwide. Similarly, in Europe, Sentinel-2 data are routinely used within the framework of the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS) to support operational fire damage assessment and post-fire monitoring across member states. These operational applications highlight the central role of multispectral imagery in fire severity assessment at regional to continental scales.
However, while multispectral sensors remain the cornerstone of operational fire severity mapping due to their temporal continuity, spatial coverage, and accessibility, their limited spectral resolution (typically fewer than 15 broad spectral bands) constrains the detection of subtle post-fire changes in vegetation and soil properties [24]. In this context, hyperspectral remote sensing offers a complementary and potentially transformative capability by providing hundreds of contiguous, narrow spectral bands, typically with bandwidths of 5–15 nm [25,26]. The availability of these data has great potential to provide fire severity estimates that are more closely aligned with post-fire management needs, partly by overcoming the suboptimal sensitivity of broadband data to fire effects [18].
Vegetation indices (VIs) calculated from remotely sensed data are critical for conducting post-fire assessments and assisting with spatio-temporal analysis [27]. Indeed, VIs are among the most widely used remote sensing products for evaluating fire severity across large burned landscapes [28]. VIs can capture subtle spectral variations associated with different surface components and provide information on vegetation status, soil conditions, and other land-cover characteristics [29]. VIs are typically defined as linear or nonlinear combination of two or more spectral bands. Traditional multispectral VIs rely on a small number of bands with broad bandwidths and restricted wavelength positions, limiting their capacity to accurately represent biomass changes and thus fire severity. However, hyperspectral VIs may overcome such limitations due to the higher spectral resolution and the availability of spectral information in hundreds of bands [28].
Beyond VIs, physically based approaches have been widely applied to broadband and narrowband satellite data to estimate fire severity, including radiative transfer models (RTMs) and spectral mixture analysis (SMA) techniques. RTMs simulate fire-induced changes in canopy reflectance by explicitly linking biophysical and structural properties of vegetation to observed spectral responses, enabling fire severity to be retrieved along a continuous scale [16,30]. Sub-pixel approaches based on SMA-family techniques, such as Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis (MESMA), provide a physically sound alternative by decomposing pixel reflectance into fractions of char, vegetation, and soil, which are common components of post-fire landscapes at moderate spatial resolutions [18,31]. These methods have demonstrated strong performance for fire severity assessment in heterogeneous environments and are more scalable than RTMs. Nevertheless, despite their physical robustness, both RTM- and MESMA-based approaches involve considerable methodological complexity and computational demands. As a result, their operational implementation by land managers and emergency-response agencies may be constrained, particularly when rapid, transparent, and easily transferable tools are required for post-fire decision-making [32].
In this context, hyperspectral VIs may offer an intermediate and operationally alternative, combining enhanced spectral sensitivity with methodological simplicity. The availability of contiguous narrowbands in imagery from recent spaceborne spectrometer missions such as PRISMA or EnMAP enables a systematic evaluation of a comprehensive battery of VIs across large wildfires, including broadband-adapted, hyperspectral, and multispectral formulations, as well as the exploration of multiple wavelength combinations for each index. While previous studies have largely relied on fixed band definitions [33], only a limited number of works have explicitly explored alternative narrowband combinations, notably the assessment of different near-infrared and shortwave infrared band combinations for a bi-temporal fire severity index, i.e., the differenced normalized burn ratio (dNBR) [24]. This systematic assessment of band combinations, which is uniquely facilitated by hyperspectral data, allows the identification of spectrally optimal and ecologically meaningful indices while maintaining interpretability and transferability to operational fire severity monitoring frameworks. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the performance of an extensive battery of monotemporal VIs, many of which remain largely unexplored for fire severity assessment, computed from post-fire hyperspectral PRISMA data to estimate fire severity across both forest and non-forest ecosystems affected by a large wildfire in northwestern Spain. CBI was assessed at three hierarchical levels—vegetation, soil, and site— to provide field-based reference data. In addition, multispectral VIs derived from Sentinel-2 imagery were computed to benchmark hyperspectral VIs. Finally, fire severity was extrapolated across the entire study site to generate spatially explicit maps for each CBI level.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Study Area
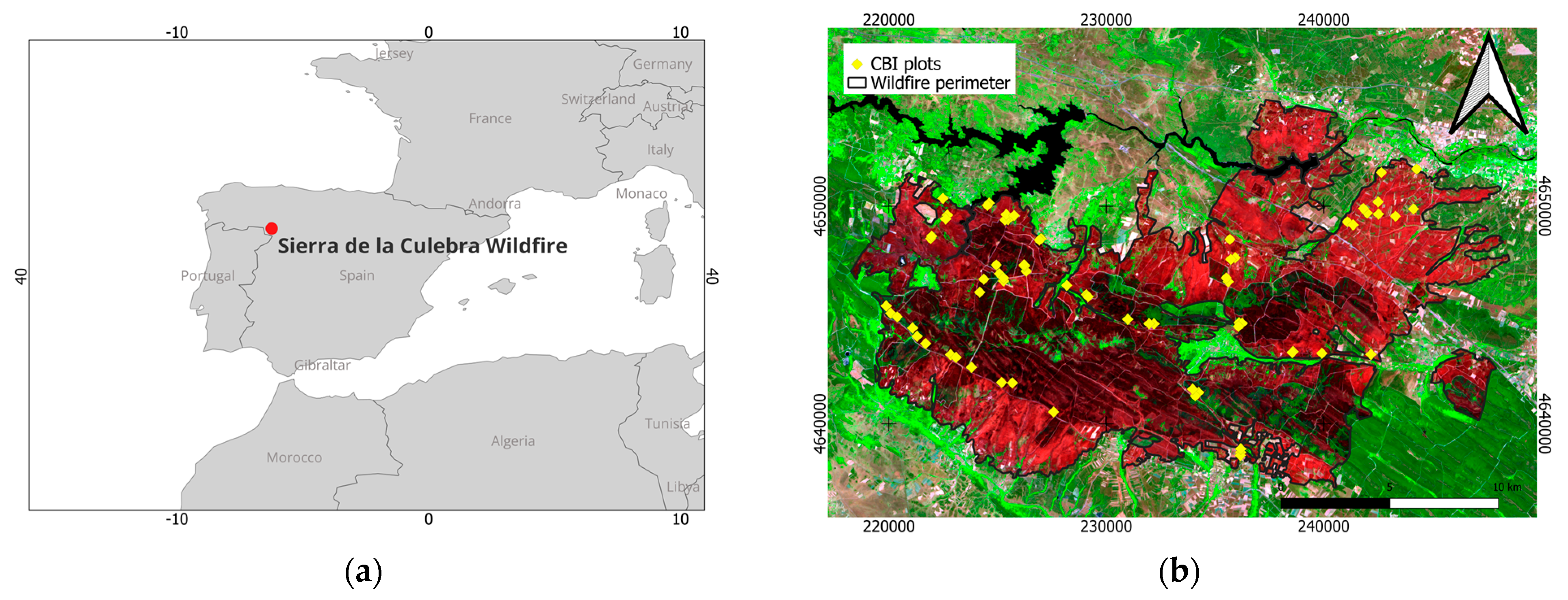
The Sierra de la Culebra wildfire (Figure 1), located in Zamora province, Castilla y León autonomous region (northwest Spain), was the second largest and most destructive fire recorded in the country. This event occurred between 15 June and 19 June 2022, affecting a total area of 28,046 ha. A lightning strike was recorded as the cause of the wildfire, associated with dry storms and a heat wave during that summer period [34]. The Sierra de la Culebra natural area, which is part of the Meseta Ibérica Biosphere Reserve, lost a significant proportion of its high ecological value as a result of this event [23].
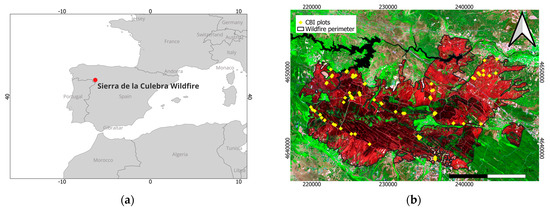
Figure 1.
(a) Location of Sierra de la Culebra wildfire and (b) distribution of Composite Burn Index (CBI) field plots over a Sentinel-2 false color composite—R: band 12; G: band 8A; B: band 4.
The region exhibits diverse topography, characterized by steep slopes and broad valleys, with elevations ranging from 747 to 1205 m above sea level. The climate is Mediterranean, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The mean annual temperature is 11 °C, and the mean annual precipitation is 750 mm [35].
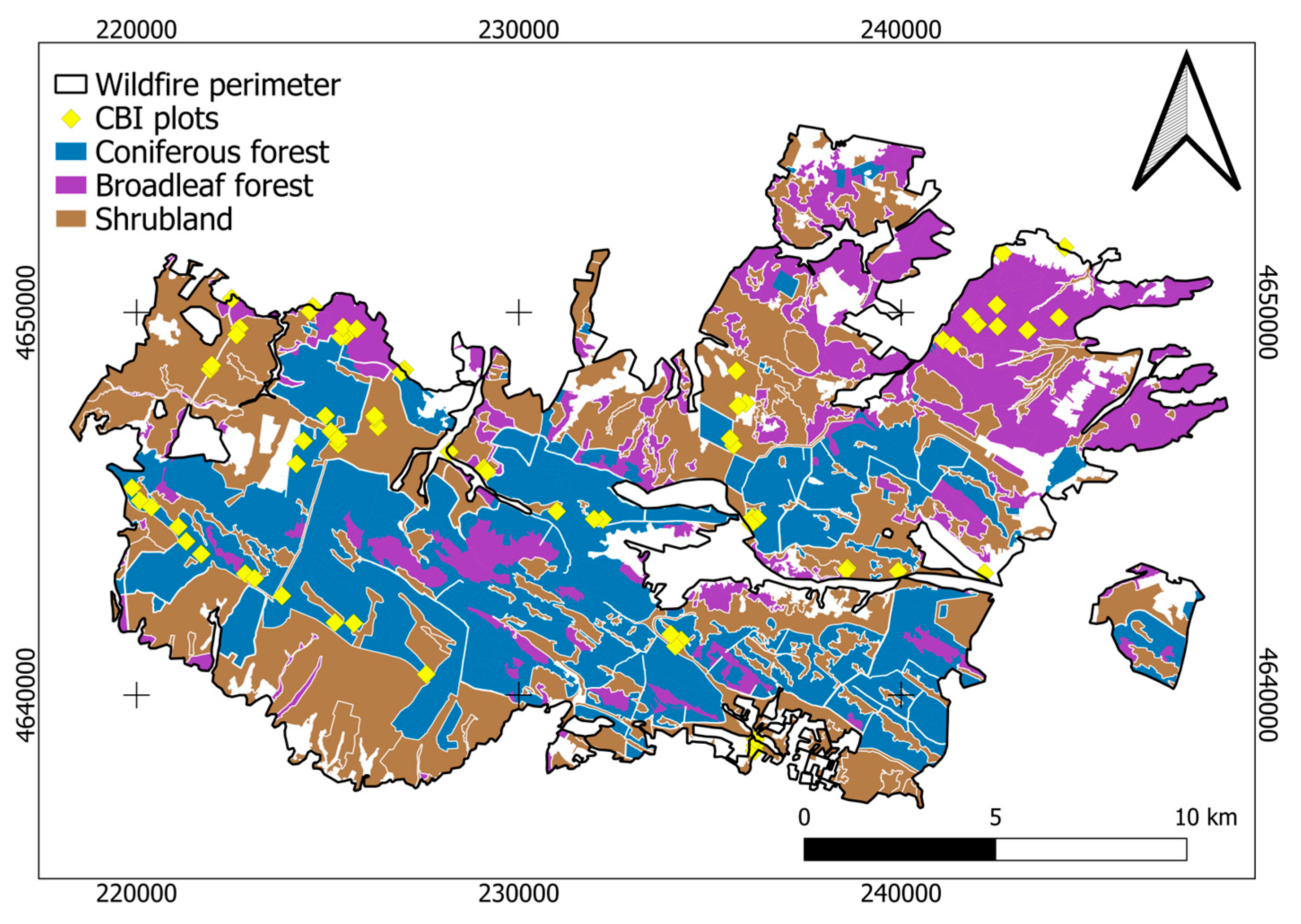
The main vegetation formations present in the study area prior to the fire are shown in Figure 2: (1) coniferous forests, dominated by species such as Pinus sylvestris L. (Scots pine) and Pinus pinaster Ait. (Maritime pine); (2) deciduous and evergreen broadleaf forests, composed of Quercus ilex L. (Holm oak) and Quercus pyrenaica Willd. (European oak); and (3) shrublands dominated by Cistus ladanifer L. (gum rockrose), Pterospartum tridentatum (L.) Willk. (prickled broom), Erica australis L. (Spanish heath) and Halimium lasianthum subsp. Alyssoides (Lam.) Greuter (Lisbon false sunrose), as well as Mediterranean grasslands. The study area comprises 9054 ha of coniferous forests (36.1%), 5380 ha of broadleaf forests (21.4%), and 10,664 ha of shrublands (42.5%).
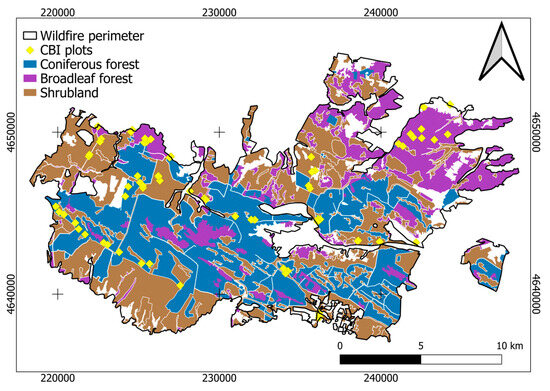
Figure 2.
Vegetation formation in the Sierra de la Culebra wildfire. White areas inside the wildfire perimeter represent grasslands and other non-vegetated surfaces (e.g., buildings and roads).
2.1.2. Field Data
The Composite Burn Index (CBI) is a standardized field metric widely used to validate satellite-derived fire severity estimates [9]. It is based on the visual assessment of post-fire changes across four distinct vegetation and soil strata, providing an integrated measure of fire-induced damage [20]. In this study, post-fire vegetation responses such as changes in species composition were not considered. To ensure consistency and minimize observer bias, each plot was evaluated by at least two trained observers, and only consensus scores were retained for analysis [18]. The CBI system divides the plot into five different strata: (1) substrate stratum, (2) vegetation < 1 m (herbs, low shrubs and tree seedlings), (3) vegetation 1–5 m (tall shrubs and small trees), (4) vegetation 5–20 m (intermediate trees), and (5) vegetation > 20 m (tall trees). From the consensus of the observers, we rated 12 individual CBI attributes across strata.
A total of 70 field plots of 30 m × 30 m were surveyed approximately one month after the wildfire, between 25 June and 25 July 2022 (Figure 1). The sampling design followed a stratified random approach, where strata were defined by dominant vegetation types, excluding Mediterranean grasslands. The final distribution of plots was as follows: 34 in coniferous forests, 20 in broadleaf forests, and 16 in shrublands (Figure 3a).
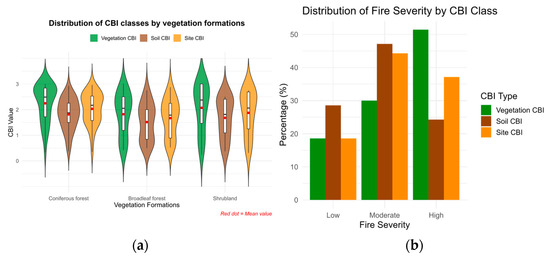
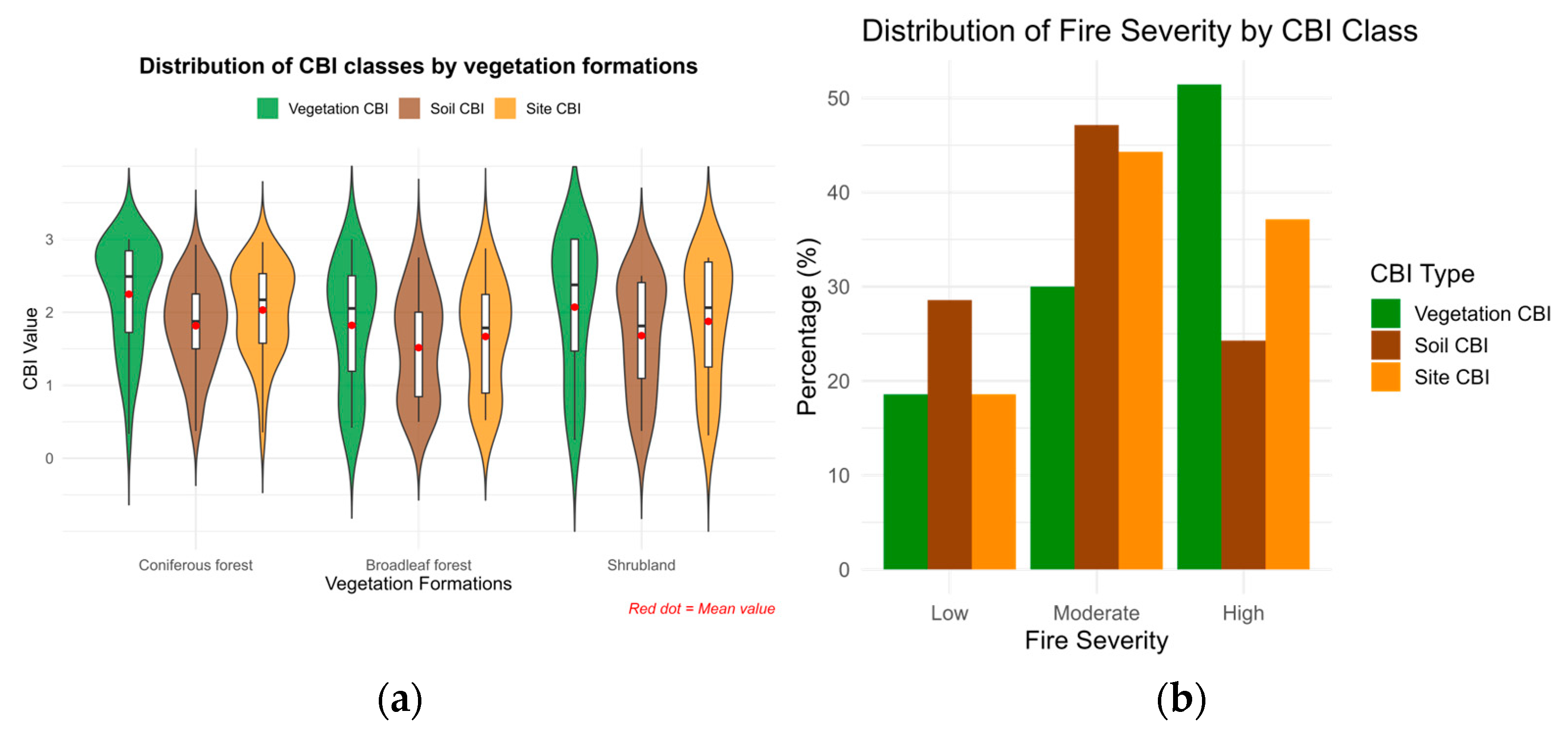
Figure 3.
Distribution of (a) Composite Burn Index (CBI) values by CBI level and vegetation formation, and (b) the percentage of plots by CBI type and fire severity level in the Sierra de la Culebra wildfire.
The site-level CBI for each plot was calculated as the mean CBI score across all strata, while the vegetation CBI was calculated as the mean of the vegetation strata only (excluding substrate). The soil CBI was computed from the substrate stratum alone. Fire severity categories were defined using CBI thresholds: low (CBI < 1.25), moderate (1.25 ≤ CBI ≤ 2.25), and high (CBI > 2.25) [18,36].
As shown in Figure 3b, the proportion of plots within each severity class varies across vegetation types. Fire severity classes correspond to distinct post-fire structural patterns: low severity indicates partial shrub foliage consumption with minimal canopy damage; moderate severity involves substantial understory consumption and partial canopy loss; and high severity denotes nearly complete consumption of both understory and overstory foliage [32]. Figure 3a shows the distribution of CBI values by severity class and vegetation formation.
2.1.3. Hyperspectral and Multispectral Satellite Data
The hyperspectral imagery was acquired on 13 July 2022 by the PRecursore IperSpettrale della Missione Applicativa (PRISMA) satellite mission (https://prisma.asi.it), developed by the Italian Space Agency (ASI). PRISMA, launched in March 2019, provides spectroscopic data within a spectral range of 400 to 2500 nm, with a spatial resolution of 30 m and a swath width of 30 km. These characteristics render PRISMA a valuable instrument for fire severity assessment [18], particularly due to its sensitivity to post-disturbance spectral changes in vegetation and soil [37].
The multispectral imagery was obtained from the Sentinel-2 satellite mission (level-2A product) on 15 July 2022. The European Space Agency (ESA) operates the Sentinel-2 satellite, which is equipped with a multispectral sensor offering 13 bands with spatial resolutions of 10 m, 20 m, and 60 m, and a swath width of 290 km (https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/). These bands encompass the visible (VIS), red-edge, near-infrared (VNIR), and shortwave infrared (SWIR) regions.
2.2. Methods
The processing of the hyperspectral and multispectral images followed these steps: preprocessing, calculation of VIs, statistical analysis and fire severity mapping. Preprocessing and calculation of VIs were carried out using the Python version 3.11 programming language in Visual Studio Code version 1.108. Image manipulation and VIs calculation were conducted using bespoke libraries such as rasterio version 1.4.3, numpy version 2.4.1, and pandas version 2.3.3.
2.2.1. Image Preprocessing
Hyperspectral bands displaying low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and sensor artefacts were excluded from the analysis to improve the quality of the data. The identification of these bands was carried out in accordance with the recommendations set out by previous studies in post-fire applications [18,38]. Specifically, following the same preprocessing strategy adopted by Quintano et al. [18] for PRISMA hyperspectral data acquired over the same wildfire event, bands in the 400–434 nm, 1345–1459 nm, 1774–1975 nm, 2010–2035 nm, and 2469–2505 nm spectral regions were discarded due to low signal-to-noise ratios and atmospheric absorption features. In addition, an empirical assessment of SNR was performed using visually homogeneous burned and unburned areas within the study scene. A total of three polygons were defined for each condition (burned and unburned), each encompassing at least 100 pixels. Unburned polygons were selected to represent areas with homogeneous vegetation cover. Burned polygons were further constrained to areas affected by comparable fire severity within each polygon to avoid internal heterogeneity. For each spectral band, SNR was estimated as the ratio between mean reflectance and its standard deviation within these homogeneous regions, following the homogeneous area (HA) approach commonly adopted for hyperspectral noise characterization [39]. This empirical analysis confirmed the presence of consistently low SNR values across the same spectral regions identified in previous PRISMA-based studies and considered here. Although the most pronounced SNR minima were generally confined to narrower spectral intervals within these regions, the full wavelength ranges reported in the literature were conservatively retained and excluded to ensure robust data quality control.
The aggregation and renaming of selected hyperspectral bands were conducted according to standard wavelength regions (i.e., blue [400–500 nm], green [500–600 nm], red [600–700 nm], red edge [700–750 nm], near-infrared [NIR; 750–1050 nm] and shortwave infrared [SWIR; 1050–2500 nm]) to facilitate index calculation and enable comparison with multispectral data. Consequently, the number of hyperspectral bands was reduced from 233 to 191, and these bands were labeled with both hyperspectral and multispectral names for the VI computation (Table S1a). The multispectral imagery bands used in this study encompassed the blue (B2), green (B3), red (B4), red edge (B5, B6, B7), near-infrared (B8, B8A), shortwave infrared 1 (B11), and shortwave infrared 2 (B12), with all other bands excluded (Table S1b).
Furthermore, to ensure precise spatial alignment between the PRISMA hyperspectral image and the Sentinel-2 multispectral image, a geometric co-registration procedure was conducted [18]. Well-distributed ground control points (GCPs) were manually selected over invariant landscape features. This step was essential to ensure sub-pixel alignment suitable for pixel-wise analysis and VI computation.
2.2.2. Vegetation Indices Computation
Monotemporal VIs were calculated from both hyperspectral and multispectral imagery to quantify post-fire vegetation and soil changes across the study area. A total of 140 spectral indices were computed, including 40 multispectral and 100 exclusively hyperspectral, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of fire severity (Table S2). The calculation of classical broadband VIs, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) or the Normalized Burn Ratio (NBR), was performed using PRISMA and Sentinel-2 data. In contrast, hyperspectral VIs, such as the Leaf Chlorophyll Index (LCI), the Normalized Difference Nitrogen Index (NDNI), or the Cellulose Absorption Index (CAI), rely on narrow spectral bands that are available only in hyperspectral datasets. These VIs have been specifically designed to discern subtle physiological or structural changes in vegetation, including chlorophyll degradation, variations in nitrogen content, or loss of cellulose [40], which are frequently associated with fire damage. It is noteworthy that the computation of these indices entailed the evaluation of multiple permutations of the VI formula, incorporating several bands situated immediately below and above the target band for each index. The calculation was performed using multiple band combinations within a single formula, with all possible permutations being computed. For instance, the red edge difference vegetation index (DVIRED) was calculated using 32 near-infrared (NIR) and 5 red edge bands from hyperspectral data, yielding 160 VIs; the multispectral data used 2 NIR and 3 red edge bands, yielding 6 VIs.
For the sake of clarity throughout this study, hyperspectral indices refer to indices calculated exclusively from PRISMA hyperspectral data, regardless of whether their original formulation was for hyperspectral or multispectral use. Multispectral indices refer to indices derived from Sentinel-2 multispectral data.
All VIs were computed using a monotemporal post-fire approach for both hyperspectral and multispectral imagery to ensure methodological consistency between sensors. This choice was motivated by the operational constraints of spaceborne hyperspectral missions, such as PRISMA, which operate largely on an on-demand acquisition strategy and rarely provide systematic pre-fire coverage [38]. Under these conditions, monotemporal analyses constitute a realistic and widely used framework for post-fire severity assessment and enable a consistent comparison between hyperspectral and multispectral data [18,41].
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
All hyperspectral and multispectral VIs were extracted at the plot scale (30 m × 30 m) using a regular grid of systematically sampled points within each plot to account for potential mismatches between the pixel grid and field plot boundaries. All statistical analyses were conducted in R version 4.4.2 [42]. Univariate linear regression models were used to evaluate the relationship between each hyperspectral and multispectral VI and fire severity, with VIs treated as independent variables and CBI values at the vegetation, soil, and site levels as dependent variables. This approach allowed the identification of the indices most strongly associated with fire severity, and has been effectively used in previous research [20,32,36,43,44] to analyze relationships between field fire severity assessments and satellite-derived data. Ordinary least squares regression assumptions, including homoscedasticity and normality of residuals, were graphically assessed, confirming that these assumptions were met in all cases. The coefficient of determination (R2) was used to evaluate model performance and the proportion of variability in the CBI data that was explained by each VI. We evaluated model generalization ability within each vegetation formation and CBI level through 10-fold cross-validation (CV) repeated 10 times, using the cross-validated coefficient of determination (CV-R2) and the root mean square error (CV-RMSE) to quantify predictive performance.
2.2.4. Mapping Fire Severity Using CBI Analysis
The assessment of fire severity across the study area was carried out using PRISMA hyperspectral and Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery. VIs were calculated separately for the three dominant vegetation formations: coniferous forests, broadleaf forests, and shrublands. For each vegetation formation, the VI with the highest R2 with the corresponding CBI level was selected for further analysis. The CBI values were classified into three fire severity levels according to the established thresholds. The CBI–VIs relationships were subsequently extrapolated to the entire study area by applying linear model predictions to the respective spectral dataset, thereby producing spatially explicit maps of fire severity for each vegetation formation.
3. Results
3.1. Best Performing Spectral Indices
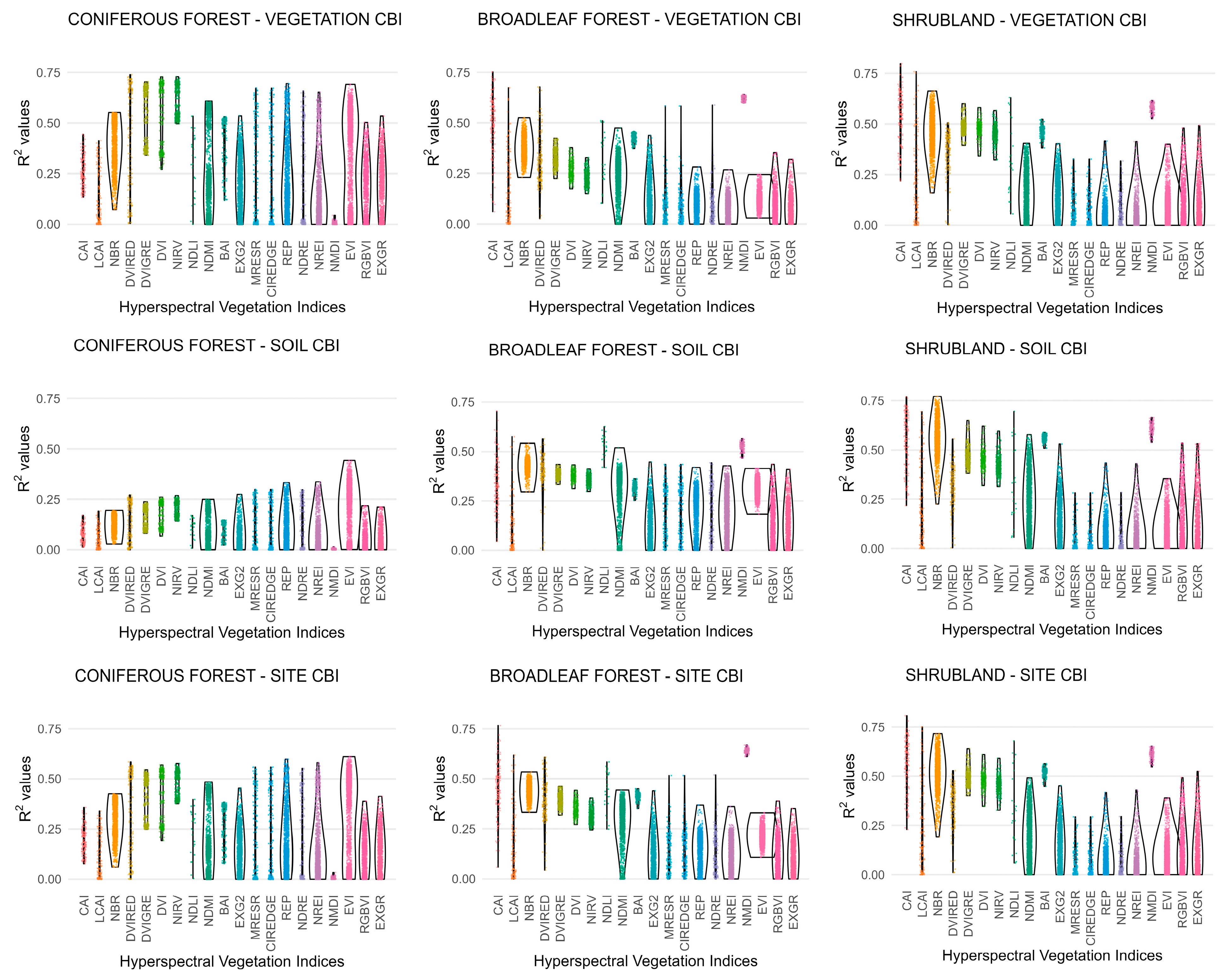
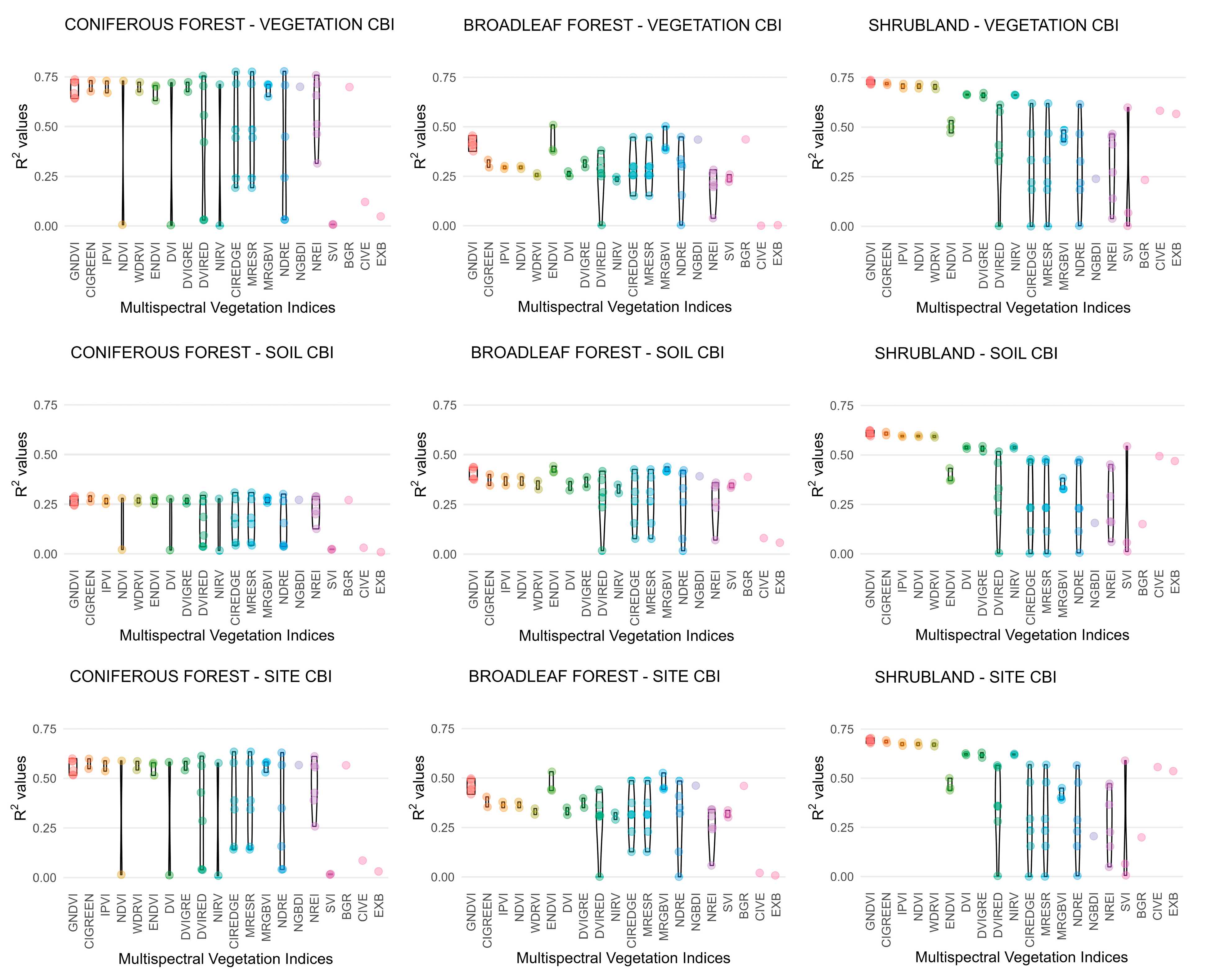
The correlations derived between hyperspectral indices and CBI exhibited considerable variability (Figure 4), ranging, for instance, from 0% to 75% within a single VI formulation. Conversely, some indices displayed a narrow correlation range (i.e., 60–70%), suggesting that these hyperspectral VIs convey similar spectral information. Such variability is expected, as specific VI formulations incorporate spectral bands with a large number of hyperspectral wavelengths (Table S1a). This variability is expected because several VI formulations rely on a broad set of hyperspectral wavelengths (Table S1a), which differ in their sensitivity to fire-induced changes. Consequently, correlation strength depends strongly on the specific band combinations selected, with only a subset producing robust relationships with CBI. Furthermore, the R2 distributions associated with each hyperspectral VI formulation showed marked differences in shape (Figure 4). Uniform, rectangular-shaped envelopes indicate similar explanatory power across band combinations, whereas conical or violin-shaped patterns reveal that only a subset of combinations yields moderate to high correlations with CBI.
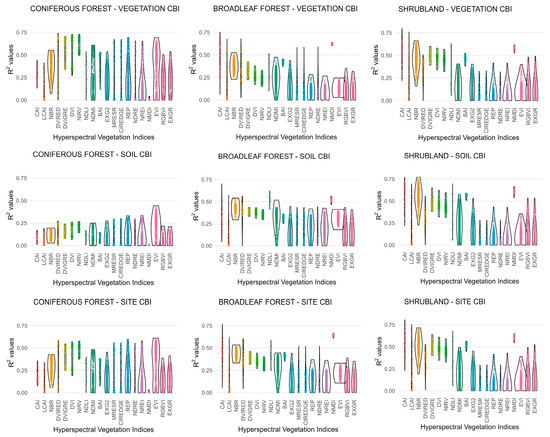
Figure 4.
Distribution of the coefficient of determination (R2) for hyperspectral vegetation indices (Vis) as a function of band combination, vegetation formation, and Composite Burn Index (CBI) level.
By contrast, the correlations obtained from multispectral indices exhibited considerably lower variability within each VI formulation, primarily due to the limited number of spectral bands available in Sentinel-2 imagery (Figure 5). Nonetheless, some multispectral VIs displayed contrasting correlation values, for instance, ranging from 0% to 75%. This marked disparity suggests that certain spectral bands employed in low-performing VIs were suboptimal or unsuitable for those specific formulations. Conversely, a narrow dispersion of R2 values across multispectral VI formulations suggests that these indices respond similarly to fire-induced spectral changes and convey comparable information on fire severity.
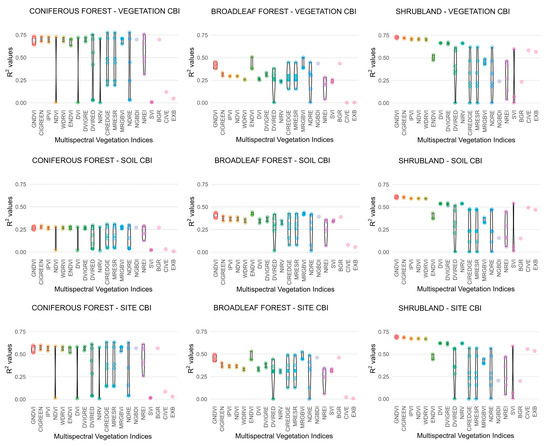
Figure 5.
Distribution of the coefficient of determination (R2) for multispectral vegetation indices (Vis) as a function of band combination, vegetation formation, and Composite Burn Index (CBI) level.
The best-performing VIs demonstrated differences between hyperspectral and multispectral data (Table 1). With respect to the hyperspectral indices, the CAI was identified as the most frequent best-performing VI in broadleaf forests and shrublands. The coniferous forests exhibited the DVIRED and the EVI as the most effective VIs. Among the multispectral VIs, fire effects in coniferous forests are best characterized by the normalized difference red edge (NDRE) and the red edge chlorophyll index (CIREDGE), while fire-induced effects in broadleaf forests are best characterized by the enhanced normalized difference vegetation index (ENDVI) and in shrublands by the GNDVI.

Table 1.
Best-performing hyperspectral and multispectral vegetation indices (VIs) across vegetation formations and Composite Burn Index (CBI) levels evaluated using the cross-validated coefficient of determination (CV-R2) and the root mean square error (CV-RMSE). All the relationships were statistically significant (p-values < 0.001).
Overall, hyperspectral VIs exhibited consistently stronger and more stable relationships with fire severity than multispectral VIs across vegetation formations and CBI levels (Table 1), as reflected by higher CV-R2 and lower CV-RMSE values. This advantage was most pronounced in shrublands and broadleaf forests, where the Cellulose Absorption Index (CAI) repeatedly emerged as the best-performing hyperspectral index across vegetation, soil, and site CBI levels. In coniferous forests, the performance of hyperspectral VIs was more variable across CBI levels, with DVIRED providing the strongest relationships at the vegetation level and EVI performing best at soil and site levels. Although CV-R2 values in coniferous forests were generally lower than those observed in shrublands and broadleaf forests, hyperspectral indices still showed relatively low and stable CV-RMSE values, indicating robust predictive behavior. By contrast, multispectral VIs displayed lower and more heterogeneous performance, consistent with the reduced spectral resolution of Sentinel-2 data. NDRE yielded the strongest relationships in coniferous forests, particularly for vegetation-level CBI, whereas ENDVI and GNDVI performed best in broadleaf forests and shrublands, respectively. Across both sensor types, vegetation-level CBI consistently produced higher CV-R2 values than soil-level CBI, with site-level CBI showing intermediate performance. Collectively, these results emphasize the superior ability of hyperspectral data to resolve post-fire severity patterns, especially in ecosystems characterized by high structural and compositional complexity.
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Fire Severity
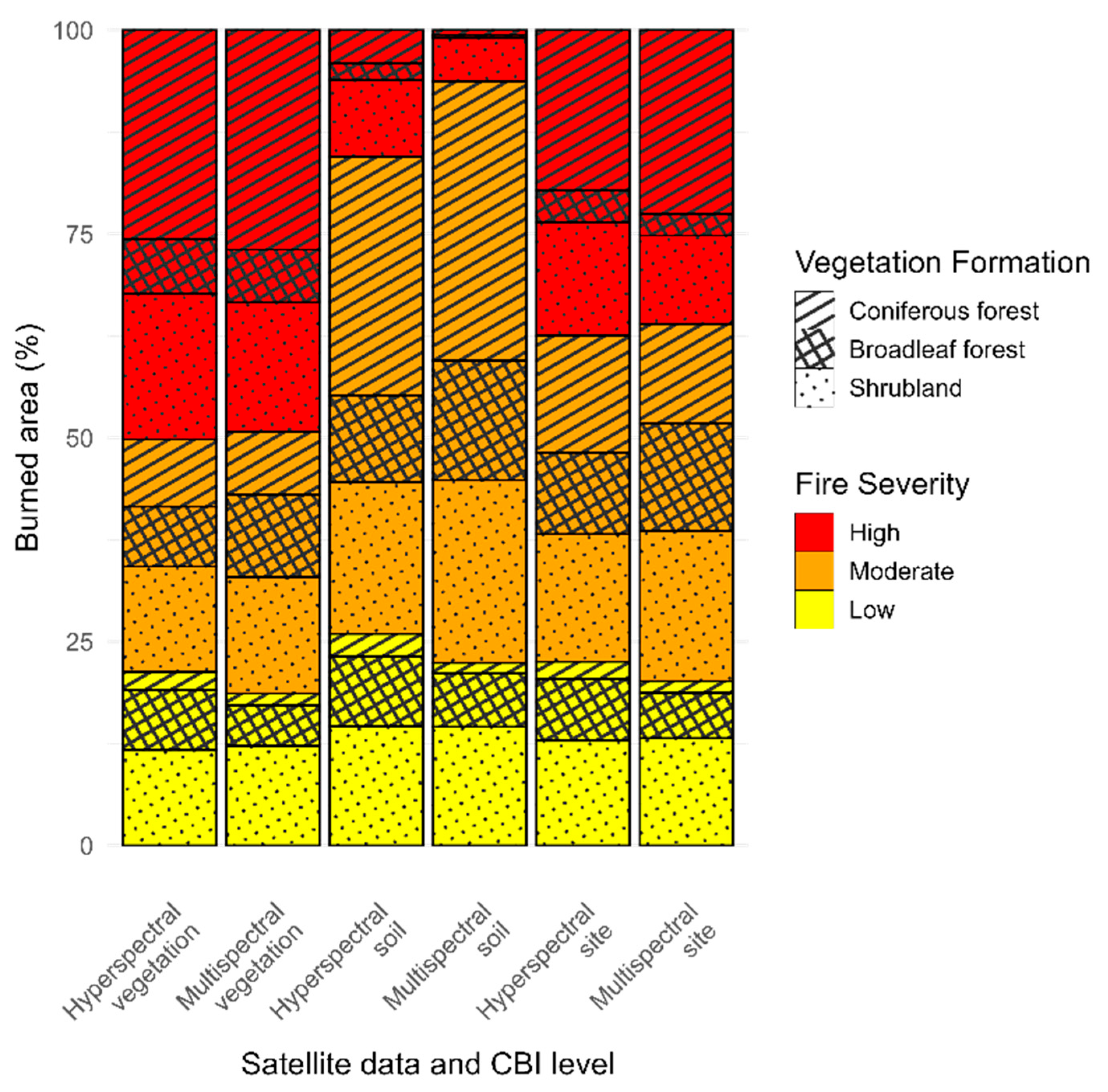
Fire severity at the three CBI levels was spatially mapped within the wildfire perimeter using the best-performing VIs for each sensor type and vegetation formation (Table 1). Overall, both hyperspectral and multispectral data revealed similar spatial patterns (Figure 6), with high fire severity dominating at the vegetation level, affecting approximately half of the study area (hyperspectral: 50.2%; multispectral: 49.2%), followed by moderate (H: 28.5%; M: 32.1%) and low (H: 21.3%; M: 18.3%) fire severity. At the soil level, moderate fire severity prevailed, particularly in the multispectral data (71.3%) compared to hyperspectral imagery (58.5%), while high-severity areas decreased accordingly (H: 15.5%; M: 6.3%). At the site level, moderate fire severity accounted for nearly half of the area (H: 40.0%; M: 43.8%), exceeding both high (H: 37.5%; M: 36.0%) and low severity (H: 22.6%; M: 20.2%) levels. Among vegetation formations, coniferous forests and shrublands were the most affected across all CBI levels. At the vegetation level, coniferous forests (H: 25.6%; M: 26.9%) and shrublands (H: 17.8%; M: 15.8%) exhibited the highest proportions of high-severity burns, while at the soil level, shrublands showed the greatest impact (H: 9.4%; M: 5.4%). Under moderate fire severity, coniferous forests and shrublands again represented the largest affected areas across CBI strata, whereas shrublands maintained a relatively stable proportion of low-severity burns (≈12–15%) across all levels.
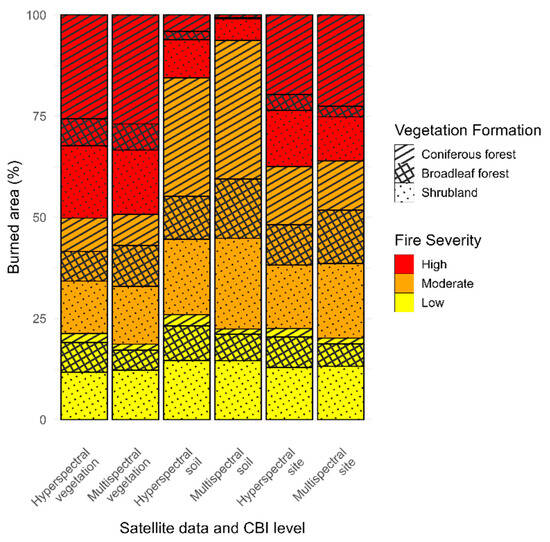
Figure 6.
Percentage of burned area by vegetation formation and fire severity category (low, moderate, and high), shown separately for each CBI level (vegetation, soil, and site) and sensor type (hyperspectral and multispectral).
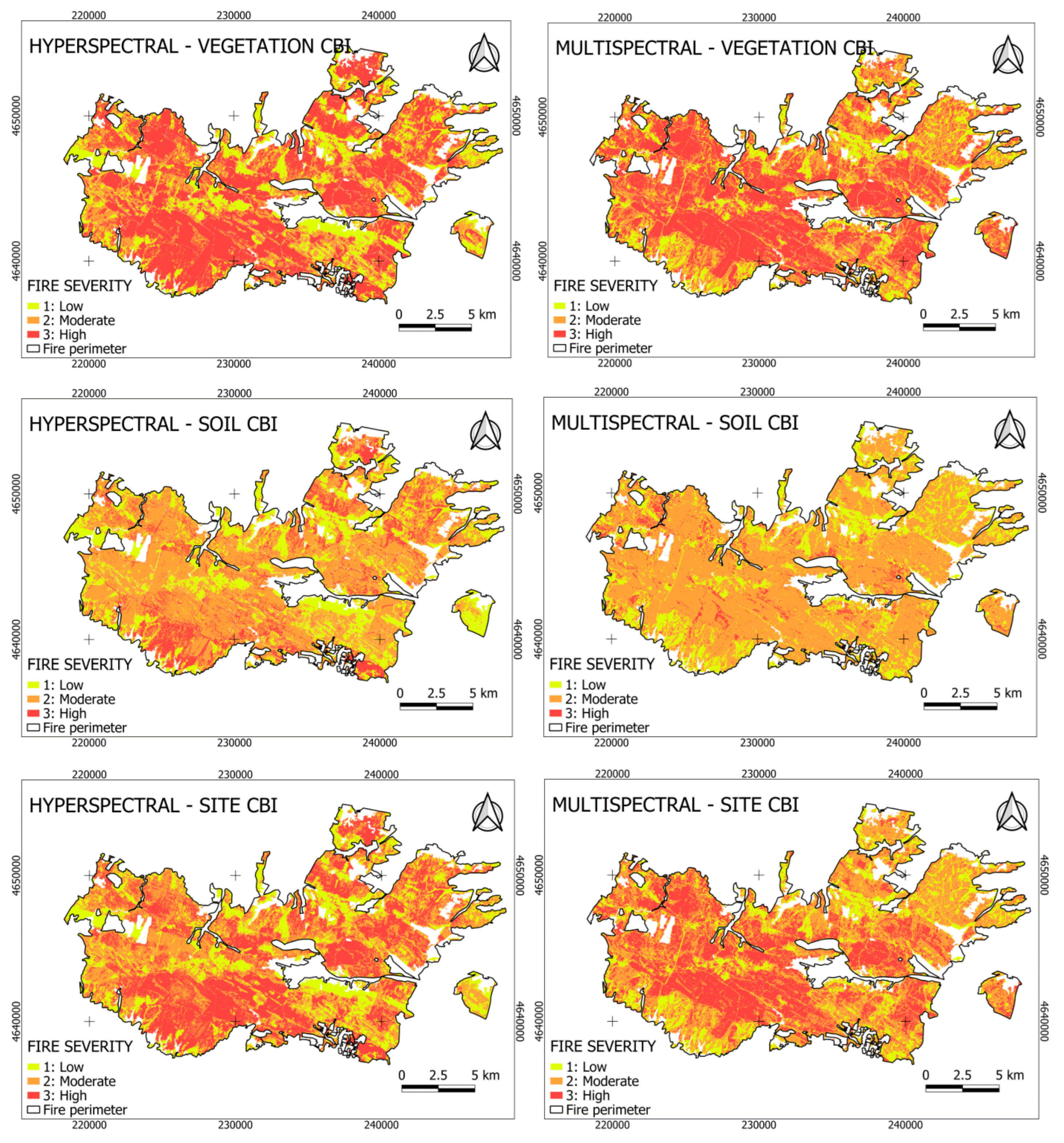
The spatial patterns of fire severity maps highlight a clear aggregation of high-severity areas within the central portion of the wildfire perimeter across vegetation formations and sensor types (Figure 7). Moderate and low fire severity classes appear as more fragmented patches surrounding these core high-severity zones. At the soil level, moderate severity shows a widespread and relatively continuous spatial distribution, whereas high-severity patches remain spatially constrained. At the site level, high-severity areas are spatially concentrated in central regions, while moderate and low severity classes display a more heterogeneous and dispersed distribution across the landscape.
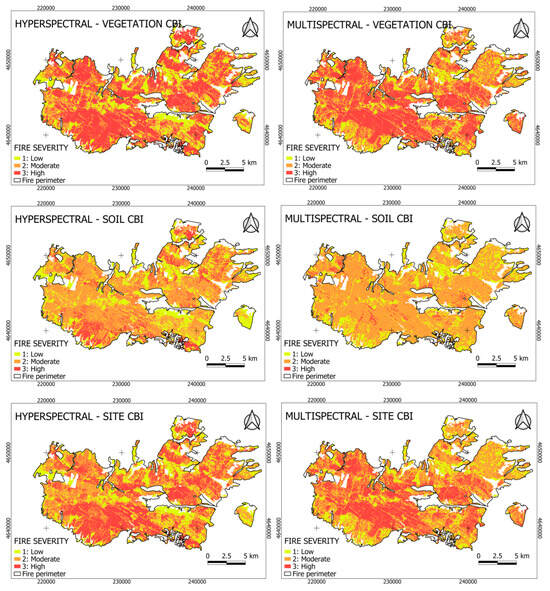
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of fire severity estimates across vegetation formations (coniferous forests, broadleaf forests, and shrublands) using the best-performing hyperspectral and multispectral vegetation indices (VIs) selected for each vegetation formation and Composite Burn Index (CBI) level, as identified in Table 1. Fire severity is shown separately for vegetation, soil, and site CBI levels.
4. Discussion
Hyperspectral VI formulations exhibited R2 distributions that were either narrowly clustered, indicating stable performance across band combinations, or widely dispersed, reflecting strong sensitivity to band selection. As a result, band shifts in the VI formula using adjacent spectral bands exert a substantial influence on hyperspectral index values. This sensitivity is attributed to the availability of narrow, contiguous bands, which allow for more precise detection of biochemical changes in vegetation and soil properties following fire [40]. This pattern is consistent with previous hyperspectral studies showing that distinct index formulations can converge toward comparable explanatory power when sensitive spectral regions are involved [45,46,47]. Indeed, some VI formulations demonstrated high explanatory power for CBI with numerous hyperspectral band combinations, for example, in coniferous forest at the vegetation CBI level and shrubland at the soil CBI level, among others. By contrast, multispectral indices demonstrated reduced variability, attributable to the smaller number of possible band combinations. Additionally, multispectral indices showed lower sensitivity than hyperspectral indices in detecting fine-scale spectral variations, particularly in transition zones between fire severity classes. For instance, several multispectral VI formulations exhibited strong correlations, indicating that multiple indices can effectively characterize fire-induced vegetation damage, such as in coniferous forests at the vegetation-level CBI. In contrast, a similar pattern of consistently weak correlations was observed in the coniferous forests at the soil level.
Hyperspectral VIs showed a stronger correlation with CBI values compared to those derived from multispectral data. For instance, hyperspectral VIs associated with site-level CBI presented a mean correlation of CV-R2 = 0.703, while the corresponding multispectral indices reached a correlation of CV-R2 = 0.594. These results confirm the greater capacity of hyperspectral images to capture finer-scale details in fire severity, in agreement with previous studies that also highlight the superiority of PRISMA images over Sentinel-2 images in landscapes dominated by Mediterranean oak and pine species [18]. The higher sensitivity of the narrow bands of hyperspectral images allows a more precise detection of physical and chemical changes in vegetation [48], making them suitable for fire severity assessment. In addition, visible bands from hyperspectral data are sensitive to soil background effects [45]. Consequently, despite its coarser spatial resolution, PRISMA-derived hyperspectral VIs can achieve higher explanatory power than Sentinel-2 VIs for fire severity estimation, highlighting the dominant role of spectral resolution in this context [18,49]. Advanced modelling techniques, including multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (MESMA) and machine learning algorithms, have also been shown to achieve high predictive performance when exploiting hyperspectral data [18,31]. These approaches can effectively capture complex and nonlinear relationships between spectral responses and fire-induced ecosystem changes. However, their methodological and computational complexity, as well as their reliance on extensive parameterization and model tuning, may limit their operational applicability for rapid and large-scale fire severity mapping, particularly in emergency-response and land management contexts where ease of implementation is critical. In this respect, the results obtained in the present study are consistent with those reported by Quintano et al. [18], while providing complementary insights. Our ecosystem-specific analyses revealed that simpler, index-based approaches can yield comparable performance when applied at the level of individual vegetation formations and CBI components. This finding supports the use of hyperspectral VIs as an operationally efficient alternative for fire severity assessment.
Optimal band selection within each VI formulation resulted in high performance for specific vegetation formation–CBI level combinations. However, no single VI demonstrated consistent accuracy across all combinations, highlighting the need to carefully select indices that align with the specific ecological context and analytical objectives. The vegetation-level CBI showed the strongest correlations with spectral indices across all vegetation formations (coniferous forests, broadleaf forests, and shrublands) when using both hyperspectral and multispectral data. This outcome is expected, as the majority of VIs are designed to capture vegetation-related characteristics such as chlorophyll concentration, canopy density, and plant vigor [50]. Moreover, the penetration of optical data into lower strata is enabled by leaf and branch consumption due to fire, which in turn reduces canopy closure [51]. However, the nature of optical satellite data preferentially captures the upper vegetation strata rather than the substrate [52], thereby explaining the superior performance of vegetation-level CBI in comparison to soil-level CBI. These findings reinforce the importance of selecting VIs that are ecologically and structurally meaningful for the vegetation type under analysis. Furthermore, existing fire severity research has yet to incorporate approaches that classify post-fire residual vegetation according to structural attributes, diversity metrics, or pre-fire community composition [24,53]. Additionally, variability in soil properties such as texture, moisture content, organic matter, and ash cover may further contribute to the weaker relationships observed for soil-level CBI, introducing additional spectral heterogeneity that is difficult to capture using VIs [18].
With respect to the vegetation formations under consideration, broadleaf forests and shrublands exhibited the strongest relationships between VIs across all CBI levels, compared with coniferous forests. This pattern is predicated on the notion that distinct plant communities exhibit divergent structural characteristics [51]. Tree density, understory cover, and coarse wood biomass were identified as the most effective predictors of fire severity [52]. As the density of trees and shrubs increases, the extent of canopy damage observed following wildfires also increases [53]. Similarly, variation among vegetation formations can be ascribed to the unique spectral behavior and adaptive traits of plant species within these plant communities. These characteristics include variations in foliar chemistry, moisture content, and post-fire regrowth. These phenomena are more accurately captured by the narrow spectral bands and specific wavelength combinations of hyperspectral sensors [48,54]. The weaker relationships found in coniferous forests may reflect differences in canopy structure and biomass distribution, which have the potential to obscure soil signals and reduce index sensitivity to post-fire changes [55,56,57]. Furthermore, soil composition varies across vegetation formations due to differences in the biomass inputs from plant species, encompassing discrepancies in the mass, volume, and chemical composition of litter such as leaves, needles, and other organic debris [58]. As indicated by the extant literature, factors such as forest density, stem architecture, and remaining biomass influence the sensor detection of exposed soil and ash following fire [59,60]. This further explains the differential performance of spectral indices depending on vegetation formation.
The hyperspectral and multispectral image bands that most frequently appeared in the best-correlated indices with the CBI were the red edge, NIR, and SWIR regions, which are well known for their sensitivity to fire-induced changes in vegetation structure, chlorophyll content, and moisture status [8,61,62]. The normalized burn ratio (NBR) remains one of the most widely used indices for operational fire severity mapping [63]. However, under the monotemporal framework adopted in this study, NBR showed a comparatively limited capacity to correlate with CBI across vegetation formations and CBI levels relative to other VIs tested here. This outcome is consistent with the fact that the performance of NBR may be affected by its sensitivity to differences in canopy structure and vegetation density among ecosystem types as compared to alternative VIs [64,65,66,67]. Moreover, the NBR was initially designed to delimit burned areas, not to assess vegetation biophysical variability as a result of the fire [10,19]. Consequently, the selection of appropriate VIs for fire severity assessment should be guided by the sensor characteristics, data availability, and study objectives, rather than assuming universal applicability across contexts [57]. Looking forward, the increasing availability of on-demand acquisitions and expanding data catalogs from spaceborne hyperspectral missions is expected to facilitate the development of multitemporal fire severity analyses, thereby enabling a more complete characterization of post-fire dynamics in future studies.
Hyperspectral indices such as the red edge difference vegetation index (DVIRED), the enhanced vegetation index (EVI), and the cellulose absorption index (CAI) are particularly effective for assessing fire-induced vegetation damage due to their sensitivity to changes in leaf reflectance, canopy structure, and biomass loss following combustion [68]. This sensitivity is consistent with the strong correlations observed in this study between these indices and CBI-derived fire severity across vegetation formations. DVIRED is especially responsive to reductions in chlorophyll content and canopy disruption in vegetation-covered areas, performing well under heterogeneous post-fire conditions, although its sensitivity decreases over shadowed or sparsely vegetated substrates [69]. EVI, originally designed for high-biomass forests, accounts for canopy saturation and atmospheric effects, making it suitable for capturing fire-driven reductions in canopy density and vigor in forested ecosystems [70]. In contrast, CAI exploits shortwave infrared absorption features around 2100 nm to detect the increased exposure of cellulose- and lignin-rich materials following fire, such as charred litter and woody debris. This response is particularly pronounced under moderate to high fire severity, with coniferous litter exhibiting higher CAI values than deciduous litter, and both exceeding those of bare soil due to the cellulose–lignin absorption feature in the SWIR region [71]. The marked variability in performance observed among hyperspectral band combinations within the same vegetation index formulation reflects the strong sensitivity of post-fire spectral responses to narrow wavelength shifts. Small displacements in red-edge, near-infrared, or shortwave infrared bands can markedly alter index sensitivity to fire-induced changes such as chlorophyll degradation, canopy opening, and the exposure of cellulose- and lignin-rich materials. Hyperspectral sensors allow these fine spectral differences to be resolved, enabling the identification of optimal band combinations that maximize the correspondence with CBI across vegetation formations and severity levels. In contrast, band combinations that partially overlap absorption features or include wavelengths less responsive to post-fire physicochemical changes tend to yield weaker correlations. This mechanistic interpretation explains why optimal hyperspectral band combinations consistently outperform alternative formulations, beyond purely statistical effects.
The most effective Sentinel-2 spectral indices for fire severity assessment were primarily derived from the red-edge (B5) and near-infrared bands (B8/B8A), which are closely linked to variations in chlorophyll content, canopy structure degradation, and biomass loss following fire [9,67]. In this study, multispectral indices such as NDRE, CIREDGE, ENDVI, and GNDVI consistently captured fire-induced changes in vegetation condition, reflecting gradients in chlorophyll concentration, biomass, and vegetation density across ecosystems [72]. NDRE and CIREDGE, both based on red-edge information, proved particularly sensitive to chlorophyll and nitrogen-related responses, whereas ENDVI and GNDVI effectively captured broader vegetation stress and biomass variations. Overall, these results highlight the relevance of red-edge– and NIR-based multispectral indices for fire severity mapping, while also emphasizing that, compared to hyperspectral indices, their performance remains more dependent on vegetation type and structural complexity. In contrast, the identification of optimal hyperspectral indices enables a more precise characterization of post-fire vegetation and soil severity by exploiting narrow spectral features that are not accessible in multispectral data [62,73].
This detailed understanding of vegetation and soil fire severity supports the planning of ecological restoration strategies and post-fire monitoring by enabling the identification of priority areas for management actions [59]. In particular, the estimation of fire severity across the study area based on hyperspectral VIs provided a more detailed and spatially explicit characterization of fire severity patterns across vegetation formations [74]. From an applied perspective, the enhanced spectral sensitivity of hyperspectral data allows a more precise depiction of post-fire damage and recovery processes, thereby supporting land management decisions aimed at ecosystem recovery and resilience. As such, hyperspectral-based fire severity assessments can contribute indirectly to broader policy frameworks, including the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 15 (Life on Land) and SDG 13 (Climate Action), in fire-prone Mediterranean regions [75].
The findings of this study highlight several key directions for future research aimed at refining fire severity assessment methodologies. The development of adaptive algorithms that explicitly incorporate information on vegetation community composition and structure could substantially improve the accuracy and transferability of fire severity estimates [15]. In this context, machine learning-based approaches may offer additional advantages when applied within multivariate frameworks that integrate multiple predictors, allowing complex and nonlinear interactions to be explored. In addition, the timing of image acquisition warrants careful consideration, particularly in the context of hyperspectral data availability, which is often constrained by sensor revisit frequency and tasking priorities. Long post-fire intervals (e.g., one year after the event) may reduce the reliability of severity estimates due to seasonal precipitation patterns and rapid post-fire regrowth of shrubs and grasses, which can partially obscure fire-induced spectral signals [9,76]. To ensure robust model calibration and validation, increasing the number and spatial representativeness of field reference plots remains essential [57], and extending the validation framework to include multiple wildfire events and burned areas would be critical to assess the robustness and generalizability of the proposed approach across contrasting environmental and ecological conditions. Furthermore, the implementation of bitemporal analysis approaches that explicitly compare pre- and post-fire conditions could enhance the isolation of fire-driven vegetation changes, allowing them to be distinguished from pre-existing stressors such as drought or disease outbreaks [57]. Additional research is also required to evaluate the suitability and consistency of alternative hyperspectral imaging sources for operational fire severity assessment. Ultimately, fire severity analyses should be designed with the needs of wildfire management agencies in mind, ensuring that methodological advances translate into timely, reliable, and actionable information for post-fire monitoring and decision-making.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the superior capacity of hyperspectral imagery over multispectral data for estimating fire severity across Mediterranean ecosystems. Hyperspectral VIs showed stronger correlations with field-based CBI measurements, particularly at the vegetation level, due to their enhanced sensitivity to biochemical and structural changes in plant canopies following fire. The most effective spectral regions for assessing fire severity were the red edge, NIR, and SWIR bands. However, no single index achieved consistent performance across all vegetation formations and CBI levels, emphasizing the need for context-specific index selection according to ecosystem structure and spectral characteristics. Broadleaf forests and shrublands exhibited the highest correlations between hyperspectral Vis and CBI levels, reflecting their distinct spectral responses and post-fire regeneration strategies. Overall, these results confirm that hyperspectral remote sensing enables a more detailed and accurate characterization of fire impacts, supporting post-fire ecological restoration and management planning. Methodological improvements should focus on integrating bitemporal analyses, image acquisition timing and expanding field validation. However, it should also be considered that, while hyperspectral imagery provides enhanced spectral detail for fire severity characterization, multispectral missions such as Sentinel-2 still remain essential for operational applications due to their higher revisit frequency, longer temporal coverage, and broader data accessibility.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs18020244/s1, Table S1a: Spectral band alignment of PRISMA based on Sentinel-2 wavelengths; Table S1b: Spectral characteristics of Sentinel-2 bands; Table S2: Formulas, applications, and references for hyperspectral and multispectral vegetation indices. Refs. [29,67,68,70,71,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147] have been cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
J.A.C.-R.: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, C.Q.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition; J.M.F.-G.: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation in the framework of the LANDSUSFIRE project (PID2022-139156OB-C21) within the National Program for the Promotion of Scientific-Technical Research (2021–2023); and by the Regional Government of Castile and León in the framework of the IA-FIREXTCyL project (LE081P23).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Oliveira, S.; Oehler, F.; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Camia, A.; Pereira, J.M.C. Modeling Spatial Patterns of Fire Occurrence in Mediterranean Europe Using Multiple Regression and Random Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 275, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Sousa, A.M.O. The Fire in the Mediterranean Region: A Case Study of Forest Fires in Portugal. In Mediterranean Identities—Environment, Society, Culture; Fuerst-Bjelis, B., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3585-2. [Google Scholar]
- Boer, M.M.; Nolan, R.H.; Resco De Dios, V.; Clarke, H.; Price, O.F.; Bradstock, R.A. Changing Weather Extremes Call for Early Warning of Potential for Catastrophic Fire. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, N.; Sapir, Y.; Wittenberg, L.; Greenbaum, N. Recovery of Mediterranean Vegetation after Recurrent Forest Fires: Insight from the 2010 Forest Fire on Mount Carmel, Israel. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Calvo, L. Modeling Pinus Pinaster Forest Structure after a Large Wildfire Using Remote Sensing Data at High Spatial Resolution. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 446, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelides, C.; Nobajas, A. Red-Edge Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI705) from Sentinel-2 Imagery to Assess Post-Fire Regeneration. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 17, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.E. Fire Intensity, Fire Severity and Burn Severity: A Brief Review and Suggested Usage. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Roberts, D.A. Can Landsat-Derived Variables Related to Energy Balance Improve Understanding of Burn Severity from Current Operational Techniques? Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape Assessment (LA): Sampling and Analysis Methods. In FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System; USDA Forest Service: Manchester, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lentile, L.B.; Smith, A.M.S.; Hudak, A.T.; Morgan, P.; Bobbitt, M.J.; Lewis, S.A.; Robichaud, P.R. Remote Sensing for Prediction of 1-Year Post-Fire Ecosystem Condition. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.W.; Harvey, B.J.; Kane, V.R.; Moskal, L.M.; Alvarado, E. Different Approaches Make Comparing Studies of Burn Severity Challenging: A Review of Methods Used to Link Remotely Sensed Data with the Composite Burn Index. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2023, 32, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, S.; Holsinger, L.; Koontz, M.; Collins, L.; Whitman, E.; Parisien, M.-A.; Loehman, R.; Barnes, J.; Bourdon, J.-F.; Boucher, J.; et al. Giving Ecological Meaning to Satellite-Derived Fire Severity Metrics across North American Forests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.J.; Agne, M.C.; Harvey, B.J. Do You CBI What I See? The Relationship between the Composite Burn Index and Quantitative Field Measures of Burn Severity Varies across Gradients of Forest Structure. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2022, 31, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, N.H.F.; Kasischke, E.S.; Hall, R.J.; Murphy, K.A.; Verbyla, D.L.; Hoy, E.E.; Allen, J.L. Using Landsat Data to Assess Fire and Burn Severity in the North American Boreal Forest Region: An Overview and Summary of Results. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E.; Mouillot, F.; Van Der Werf, G.R.; San Miguel, J.; Tanase, M.; Koutsias, N.; García, M.; Yebra, M.; Padilla, M.; Gitas, I.; et al. Historical Background and Current Developments for Mapping Burned Area from Satellite Earth Observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; He, B.; Yebra, M.; Quan, X.; Edwards, A.C.; Liu, X.; Liao, Z. Improving Burn Severity Retrieval by Integrating Tree Canopy Cover into Radiative Transfer Model Simulation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atun, R.; Kalkan, K.; Gürsoy, Ö. Determining the Forest Fire Risk with Sentinel 2 Images. Turk. J. Geosci. 2020, 1, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Quintano, C.; Calvo, L.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Fernandes, P.M.; Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M. First Evaluation of Fire Severity Retrieval from PRISMA Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Boschetti, L.; Trigg, S.N. Remote sensing of fire severity: Assessing the performance of the normalized burn ratio. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, V.; Santamarta, M.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Marcos, E.; Calvo, L. Burn severity metrics in fire-prone pine ecosystems along a climatic gradient using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcourt, C.J.F.; Combee, A.; Izbicki, B.; Mack, M.C.; Maximov, T.; Petrov, R.; Rogers, B.M.; Scholten, R.C.; Shestakova, T.A.; van Wees, D.; et al. Evaluating the Differenced Normalized Burn Ratio for Assessing Fire Severity Using Sentinel-2 Imagery in Northeast Siberian Larch Forests. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotte, J.J.; Bhattarai, K.; Howard, D.; Lecker, J.; Epting, J.; Quayle, B.; Benson, N.; Nelson, K. Changes to the Monitoring Trends in Burn Severity program mapping production procedures and data products. Fire Ecol. 2020, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Calvo, L. Fire severity shows limited dependence on fuel structure under adverse fire weather conditions: A case study of two extreme wildfire events. Fire Ecol. 2025, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gerrevink, M.J.; Veraverbeke, S. Evaluating the Hyperspectral Sensitivity of the Differenced Normalized Burn Ratio for Assessing Fire Severity. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, A.F.H. Three Decades of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of the Earth: A Personal View. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transon, J.; D’Andrimont, R.; Maugnard, A.; Defourny, P. Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysafis, I.; Mallinis, G.; Tsakiri, M.; Patias, P. Evaluation of Single-Date and Multi-Seasonal Spatial and Spectral Information of Sentinel-2 Imagery to Assess Growing Stock Volume of a Mediterranean Forest. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 77, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dai, D.; Yu, D.; Gao, W.; Feng, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Tu, L.; Cao, D.; Huang, C.; et al. The Variation in Climate Conditions and Fire-Related Traits across Pinus (Pinaceae) Species. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 54, e03152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yuan, X.; Gan, S.; Luo, W.; Bi, R.; Li, R.; Gao, S. A New Vegetation Index Based on UAV for Extracting Plateau Vegetation Information. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 128, 103668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E.; Vaughan, P.J. Short-term assessment of burn severity using the inversion of PROSPECT and GeoSail models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Roberts, D.A. Burn severity analysis in Mediterranean forests using maximum entropy model trained with EO-1 Hyperion and LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 155, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Fernandes, P.M.; Marcos, E.; Beltrán-Marcos, D.; Sarricolea, P.; Farris, M.; Calvo, L. Caution is needed across Mediterranean ecosystems when interpreting wall-to-wall fire severity estimates based on spectral indices. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 546, 121383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wagtendonk, J.W.; Root, R.R.; Key, C.H. Comparison of AVIRIS and Landsat ETM+ detection capabilities for burn severity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Cunill Camprubí, À.; Balaguer-Romano, R.; Coco Megía, C.J.; Castañares, F.; Ruffault, J.; Fernandes, P.M.; Resco De Dios, V. Drivers and Implications of the Extreme 2022 Wildfire Season in Southwest Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninyerola, M.; Pons, X.; Roure, J.M. Atlas Climático Digital de La Península Ibérica. In Metodología y Aplicaciones En Bioclimatología y Geobotánica; Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.D.; Thode, A.E. Quantifying burn severity in a heterogeneous landscape with a relative version of the delta Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, S.; Piscini, A. Exploring PRISMA Scene for Fire Detection: Case Study of 2019 Bushfires in Ben Halls Gap National Park, NSW, Australia. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tane, Z.; Roberts, D.; Veraverbeke, S.; Casas, Á.; Ramirez, C.; Ustin, S. Evaluating Endmember and Band Selection Techniques for Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis Using Post-Fire Imaging Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Du, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yang, W.; Wu, Y. A comparative study on linear regression-based noise estimation for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Clark, D.B. Hyperspectral Discrimination of Tropical Rain Forest Tree Species at Leaf to Crown Scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraverbeke, S.; Stavros, E.N.; Hook, S.J. Assessing fire severity using imaging spectroscopy data from the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS) and comparison with multispectral capabilities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E. GeoCBI: A modified version of the Composite Burn Index for the initial assessment of the short-term burn severity from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintano, C.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Calvo, L.; Marcos, E.; Valbuena, L. Land surface temperature as potential indicator of burn severity in forest Mediterranean ecosystems. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D. Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices and Novel Algorithms for Predicting Green LAI of Crop Canopies: Modeling and Validation in the Context of Precision Agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Miller, J.R.; Morales, A.; Berjón, A.; Agüera, J. Hyperspectral Indices and Model Simulation for Chlorophyll Estimation in Open-Canopy Tree Crops. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Di, L.; Zhang, L.; Deng, M.; Qin, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lin, H. Estimation of Crop LAI Using Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices and a Hybrid Inversion Method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Identification and Mapping of Wetland Vegetation: A Review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, T.; Gu, X.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mi, X.; Cao, W.; Li, J. The Impact of Spatial Resolution on the Classification of Vegetation Types in Highly Fragmented Planting Areas Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Zhao, F. Remote Sensing of Fire Effects: A Review for Recent Advances in Burned Area and Burn Severity Mapping. In Remote Sensing of Hydrometeoroloical Hazards; CRC Press: Boca Rarton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 261–283. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Calvo, L. Radar and Multispectral Remote Sensing Data Accurately Estimate Vegetation Vertical Structure Diversity as a Fire Resilience Indicator. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 9, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braziunas, K.H.; Abendroth, D.C.; Turner, M.G. Young Forests and Fire: Using Lidar–Imagery Fusion to Explore Fuels and Burn Severity in a Subalpine Forest Reburn. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, B.; Reilly, S.; Clark, M.; Ferrell, R.; Kelly, A.; Krause, P.; Matley, C.; O’Neil, M.; Villasenor, M.; Disney, M.; et al. Comparing Remote Sensing and Field-Based Approaches to Estimate Ladder Fuels and Predict Wildfire Burn Severity. Front. For. Glob. Change 2022, 5, 818713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Trejo, D.A.; Fulé, P.Z. Fire Ecology of Mexican Pines and a Fire Management Proposal. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2003, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, M.A.; Martínez, G. Mapeo del daño en bosques incendiados de Chile central, mediante el modelado de índices espectrales ex-ante y ex-post. Bosque 2021, 42, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana, C.; Revilla, M.; Gonzales, J.; Saavedra, Y.; Moncada, W.; Maicelo, J. Relación de firmas espectrales para la identificación de bosque seco en imágenes de satélite Sentinel 2, cuenca baja del río Chira, Región Piura. Rev. Teledetec. 2020, 56, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Rodríguez, A.G.; Flores-Garnica, J.G.; González-Eguiarte, D.R.; Gallegos-Rodríguez, A.; Zarazúa-Villaseñor, P.; Mena-Munguía, S. Análisis Comparativo de Índices Espectrales Para Ubicar y Dimensionar Niveles de Severidad de Incendios Forestales. Investig. Geográficas 2021, 106, e60396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, L.; Santalla, S.; Marcos, E.; Valbuena, L.; Tárrega, R.; Luis, E. Regeneration after Wildfire in Communities Dominated by Pinus Pinaster, an Obligate Seeder, and in Others Dominated by Quercus Pyrenaica, a Typical Resprouter. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 184, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Llamas, P.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Taboada, A.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Fernández-García, V.; Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Marcos, E.; Calvo, L. Environmental Drivers of Fire Severity in Extreme Fire Events That Affect Mediterranean Pine Forest Ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, P.R.; Lewis, S.A.; Laes, D.Y.M.; Hudak, A.T.; Kokaly, R.F.; Zamudio, J.A. Postfire Soil Burn Severity Mapping with Hyperspectral Image Unmixing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E.; Riaño, D.; Danson, F.M.; Martin, P. Use of a Radiative Transfer Model to Simulate the Postfire Spectral Response to Burn Severity. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, G04S09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Ramírez, F.; Marques Da Silva, J.R.; Agüera-Vega, F.; Martínez-Carricondo, P.; Serrano, J.; Moral, F.J. Evaluation of Fire Severity Indices Based on Pre- and Post-Fire Multispectral Imagery Sensed from UAV. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.A.; Robichaud, P.R.; Hudak, A.T.; Strand, E.K.; Eitel, J.U.H.; Brown, R.E. Evaluating the Persistence of Post-Wildfire Ash: A Multi-Platform Spatiotemporal Analysis. Fire 2021, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulino, L.; Rita, A.; Migliozzi, A.; Maffei, C.; Allevato, E.; Garonna, A.P.; Saracino, A. Detecting Burn Severity across Mediterranean Forest Types by Coupling Medium-Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery and Field Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viedma, O.; Chico, F.; Fernández, J.J.; Madrigal, C.; Safford, H.D.; Moreno, J.M. Disentangling the Role of Prefire Vegetation vs. Burning Conditions on Fire Severity in a Large Forest Fire in SE Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Llamas, P.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Calvo, L. Evaluation of Fire Severity in Fire Prone-Ecosystems of Spain under Two Different Environmental Conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Manso, A.; Fernández-Manso, O.; Quintano, C. SENTINEL-2A Red-Edge Spectral Indices Suitability for Discriminating Burn Severity. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Tang, W.; Gao, D.; Zhao, R.; An, L.; Li, M.; Sun, H.; Song, D. UAV-Based Chlorophyll Content Estimation by Evaluating Vegetation Index Responses under Different Crop Coverages. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, J.; Yue, H. Comprehensive Evaluation of Sentinel-2 Red Edge and Shortwave-Infrared Bands to Estimate Soil Moisture. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7448–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A Feedback Based Modification of the NDVI to Minimize Canopy Background and Atmospheric Noise. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; Goward, S.N. Plant Litter and Soil Reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 71, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.A.; Gianelle, D.; Rocchini, D.; Dalponte, M.; Martín, M.P.; Sakowska, K.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Vescovo, L. VIS-NIR, Red-Edge and NIR-Shoulder Based Normalized Vegetation Indices Response to Co-Varying Leaf and Canopy Structural Traits in Heterogeneous Grasslands. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, A.T.; Morgan, P.; Bobbitt, M.J.; Smith, A.M.S.; Lewis, S.A.; Lentile, L.B.; Robichaud, P.R.; Clark, J.T.; McKinley, R.A. The Relationship of Multispectral Satellite Imagery to Immediate Fire Effects. Fire Ecol. 2007, 3, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, F.; Qin, X.; Huang, S.; Meng, F.; Yu, L. Exploration of Suitable Spectral Bands and Indices for Forest Fire Severity Evaluation Using ZY-1 Hyperspectral Data. Forests 2025, 16, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.J. Sustainable Development Goals and the Forest Sector—A Complex Relationship. Forests 2019, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornacca, D.; Ren, G.; Xiao, W. Evaluating the Best Spectral Indices for the Detection of Burn Scars at Several Post-Fire Dates in a Mountainous Region of Northwest Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Ranjbar, H.; Sekandari, M.; Abd El-Wahed, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Hashim, M.; Yousefi, M.; Zoheir, B.; Wambo, J.D.T.; Muslim, A.M. Remote Sensing for Mineral Exploration. In Geospatial Analysis Applied to Mineral Exploration; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 17–149. ISBN 978-0-323-95608-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS; NASA Goddard Space Flight Cent. 3d ERTS-1 Symp Pap.-A20; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; Volume 1, pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- García, M.L.; Caselles, V. Mapping Burns and Natural Reforestation Using Thematic Mapper Data. Geocarto Int. 1991, 6, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, G. New Spectral Metrics for Mangrove Forest Identification. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.F. Derivation of Leaf-Area Index from Quality of Light on the Forest Floor. Ecology 1969, 50, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Viña, A.; Ciganda, V.; Rundquist, D.C.; Arkebauer, T.J. Remote Estimation of Canopy Chlorophyll Content in Crops. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 2005GL022688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gritz, Y.; Merzlyak, M.N. Relationships between Leaf Chlorophyll Content and Spectral Reflectance and Algorithms for Non-Destructive Chlorophyll Assessment in Higher Plant Leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar, M.T.; Chen, X. Land Degradation Assessment with the Aid of Geo-information Techniques. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hao, D.; Badgley, G.; Damm, A.; Rascher, U.; Ryu, Y.; Johnson, J.; Krieger, V.; Wu, S.; Qiu, H.; et al. Estimating Near-Infrared Reflectance of Vegetation from Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Willis, P.; Mueller, R. Impact of Band-Ratio Enhanced AWIFS Image to Crop Classification Accuracy; USDA/NASS/R&D Division: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, N.S.; Qin, W. Influences of Canopy Architecture on Relationships between Various Vegetation Indices and LAI and Fpar: A Computer Simulation. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 10, 309–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A. Wide Dynamic Range Vegetation Index for Remote Quantification of Biophysical Characteristics of Vegetation. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Miao, Y.; Feng, G.; Yuan, F.; Yue, S.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Ustin, S.L.; Chen, X. Improving Estimation of Summer Maize Nitrogen Status with Red Edge-Based Spectral Vegetation Indices. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ye, S.; Bai, Z.; Nedzved, A.; Tuzikov, A. Moderate Red-Edge Vegetation Index for High-Resolution Multispectral Remote Sensing Images in Urban Areas. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallik, L.; Kuusk, A.; Lang, M.; Kuusk, J. Reflectance Properties of Hemiboreal Mixed Forest Canopies with Focus on Red Edge and Near Infrared Spectral Regions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Pan, Y.; Ren, S.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, G. Accurate Vegetation Destruction Detection Using Remote Sensing Imagery Based on the Three-Band Difference Vegetation Index (TBDVI) and Dual-Temporal Detection Method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woebbecke, D.M.; Meyer, G.E.; Von Bargen, K.; Mortensen, D.A. Color Indices for Weed Identification under Various Soil, Residue, and Lighting Conditions. Trans. ASAE 1995, 38, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silleos, N.G.; Alexandridis, T.K.; Gitas, I.Z.; Perakis, K. Vegetation Indices: Advances Made in Biomass Estimation and Vegetation Monitoring in the Last 30 Years. Geocarto Int. 2006, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Merzlyak, M.N. Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll Concentration in Higher Plant Leaves. Adv. Space Res. 1998, 22, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traba, J.; Gómez-Catasús, J.; Barrero, A.; Bustillo-de La Rosa, D.; Zurdo, J.; Hervás, I.; Pérez-Granados, C.; García De La Morena, E.L.; Santamaría, A.; Reverter, M. Comparative Assessment of Satellite- and Drone-based Vegetation Indices to Predict Arthropod Biomass in Shrub-steppes. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Cunha, M.; Jayavelu, S.; Cammarano, D.; Fu, Y. Machine Learning-Based Approaches for Predicting SPAD Values of Maize Using Multi-Spectral Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diker, K.; Bausch, W.C. Potential Use of Nitrogen Reflectance Index to Estimate Plant Parameters and Yield of Maize. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 85, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W.; De Jong, S.M.; Epema, G.F.; Van Der Meer, F.; Bakker, W.H.; Skidmore, A.K.; Addink, E.A. MERIS and the Red-Edge Position. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2001, 3, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.E.; Neto, J.C. Verification of Color Vegetation Indices for Automated Crop Imaging Applications. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 63, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, M.; Pajares, G.; Riomoros, I.; Herrera, P.J.; Burgos-Artizzu, X.P.; Ribeiro, A. Automatic Segmentation of Relevant Textures in Agricultural Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 75, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamon, J.A.; Surfus, J.S. Assessing Leaf Pigment Content and Activity with a Reflectometer. New Phytol. 1999, 143, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaro, R.; Crepy, M.; Trupkin, S.A.; Karayekov, E.; Buchovsky, A.S.; Rossi, C.; Casal, J.J. Cryptochrome as a Sensor of the Blue/Green Ratio of Natural Radiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, E.R.; Cavigelli, M.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; Mcmurtrey, J.E.; Walthall, C.L. Evaluation of Digital Photography from Model Aircraft for Remote Sensing of Crop Biomass and Nitrogen Status. Precis. Agric. 2005, 6, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, J.; Yu, K.; Aasen, H.; Bolten, A.; Bennertz, S.; Broscheit, J.; Gnyp, M.L.; Bareth, G. Combining UAV-Based Plant Height from Crop Surface Models, Visible, and near Infrared Vegetation Indices for Biomass Monitoring in Barley. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhaichi, M.; Borman, M.M.; Johnson, D.E. Spatially Located Platform and Aerial Photography for Documentation of Grazing Impacts on Wheat. Geocarto Int. 2001, 16, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Kaneko, T.; Okamoto, H.; Hata, S. Crop Growth Estimation System Using Machine Vision. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM 2003), Kobe, Japan, 20–24 July 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. b1079–b1083. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Su, B. Significant Remote Sensing Vegetation Indices: A Review of Developments and Applications. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, J.E.; Rock, B.N.; Moss, D.M. Red Edge Spectral Measurements from Sugar Maple Leaves. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowski, S.; Pushnik, J.; Zarcotejada, P.; Ustin, S. Simple Reflectance Indices Track Heat and Water Stress-Induced Changes in Steady-State Chlorophyll Fluorescence at the Canopy Scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birth, G.S.; McVey, G.R. Measuring the Color of Growing Turf with a Reflectance Spectrophotometer. Agron. J. 1968, 60, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, E., Jr.; Rock, B. Detection of Changes in Leaf Water Content Using Near- and Middle-Infrared Reflectances. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 30, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Wang, X.Q. An Application of Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data in Vegetation Identification and Extraction of Vegetation Information. Resour. Sci. 2008, 30, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Zhen, J.; Miao, J.; Zhao, D.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, J.; Gao, C.; Wu, G.; Wang, J. Newly-Developed Three-Band Hyperspectral Vegetation Index for Estimating Leaf Relative Chlorophyll Content of Mangrove under Different Severities of Pest and Disease. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Gamon, J.A.; Fredeen, A.L.; Merino, J.; Field, C.B. Reflectance Indices Associated with Physiological Changes in Nitrogen- and Water-Limited Sunflower Leaves. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Lloret, P.; Muñóz, F.; Vilajeliu, M. Reflectance Assessment of Mite Effects on Apple Trees. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, N.; Delegido, J.; Van Wittenberghe, S.; Verrelst, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Moreno, J. Retrieval of Canopy Water Content of Different Crop Types with Two New Hyperspectral Indices: Water Absorption Area Index and Depth Water Index. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 67, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, P.E.; Roberts, D.A. Daytime Fire Detection Using Airborne Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Merzlyak, M.N. Spectral Reflectance Changes Associated with Autumn Senescence of Aesculus Hippocastanum L. and Acer Platanoides L. Leaves. Spectral Features and Relation to Chlorophyll Estimation. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 143, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.M.; Clarke, T.R.; Richards, S.E.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Haberland, J.; Kostrzewski, M.; Waller, P.; Choi, C.; Riley, E. Coincident Detection of Crop Water Stress, Nitrogen Status, and Canopy Density Using Ground-Based Multispectral Data; ASA-CSSA-SSSA: Madison, WL, USA, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Galvão, L.S.; Formaggio, A.R.; Tisot, D. Discrimination of Sugarcane Varieties with Hyperspectral Data from the Hyperion/EO-1 Sensor. Rev. Bras. Cartogr. 2005, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Hardisky, M.A.; Klemas, V.; Smart, R.M. The Influence of Soil Salinity Growth Form and Leaf Moisture on the Spectral Radiance of Spartina Alterniflora Canopies. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1983, 49, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Fiodortsev, R.V.; Silie Cuenca, A.R.; Kozhevnikov, D.A.; Medina, V.M.; Delgado, R. Application of Satellite Image Processing Methods for Hydrocarbon Field Search. Devices Methods Meas. 2019, 10, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.U.; Liu, L. The Potential of the MERIS Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index for Crop Yield Prediction. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, B. Remote Sensing of Water Content in Eucalyptus Leaves. Aust. J. Bot. 1999, 47, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Huang, K.; Sun, W.; Meng, X.; Mao, D.; Ge, Y. Enhanced Mangrove Vegetation Index Based on Hyperspectral Images for Mapping Mangrove. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 189, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between Leaf Pigment Content and Spectral Reflectance across a Wide Range of Species, Leaf Structures and Developmental Stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.-L.; Breon, F.-M. Estimating PAR Absorbed by Vegetation from Bidirectional Reflectance Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M. Evaluation of Vegetation Indices and a Modified Simple Ratio for Boreal Applications. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 22, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Niu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Huang, W. Estimating Chlorophyll Content from Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices: Modeling and Validation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeaux, G.; Steven, M.; Baret, F. Optimization of Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripada, R.P. Determining In-Season Nitrogen Requirements for Corn Using Aerial Color-Infrared Photography. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Cen, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, D.; Weng, H.; He, Y. Combining UAV-Based Vegetation Indices, Canopy Height and Canopy Coverage to Improve Rice Yield Prediction under Different Nitrogen Levels. In Proceedings of the 2019 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 7–10 July 2019; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.M.; Zheng, N.S.; Qi, Y.; Chen, S. Using GPS-R Remote Sensing Technology to Invert Vegetation Biomass. Surv. Mapp. Bull. 2018, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W. Intelligent Monitoring and System Development of Diagnostic Index of the Wheat Seedling Growth. Master’s Thesis, YangZhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R.; Rundquist, D. Novel Algorithms for Remote Estimation of Vegetation Fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Merzlyak, M.N. Use of a Green Channel in Remote Sensing of Global Vegetation from EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, P.E. Fire Detection in Imaging Spectrometer Data Using Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Absorption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzlyak, M.N.; Gitelson, A.A.; Chivkunova, O.B.; Rakitin, V.Y. Non-destructive Optical Detection of Pigment Changes during Leaf Senescence and Fruit Ripening. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 106, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Merzlyak, M.N.; Chivkunova, O.B. Optical Properties and Nondestructive Estimation of Anthocyanin Content in Plant Leaves. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 74, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Stark, R.; Grits, U.; Rundquist, D.; Kaufman, Y.; Derry, D. Vegetation and Soil Lines in Visible Spectral Space: A Concept and Technique for Remote Estimation of Vegetation Fraction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2537–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, L.; Peñuelas, J.; Ustin, S.L. Remote Sensing of Nitrogen and Lignin in Mediterranean Vegetation from AVIRIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughtry, C.S.T.; Hunt, E.R., Jr.; Doraiswamy, P.C.; Mcmurtrey, I. Remote Sensing the Spatial Distribution of Crop Residues. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.J. NMDI: A Normalized Multi-band Drought Index for Monitoring Soil and Vegetation Moisture with Satellite Remote Sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 2007GL031021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.