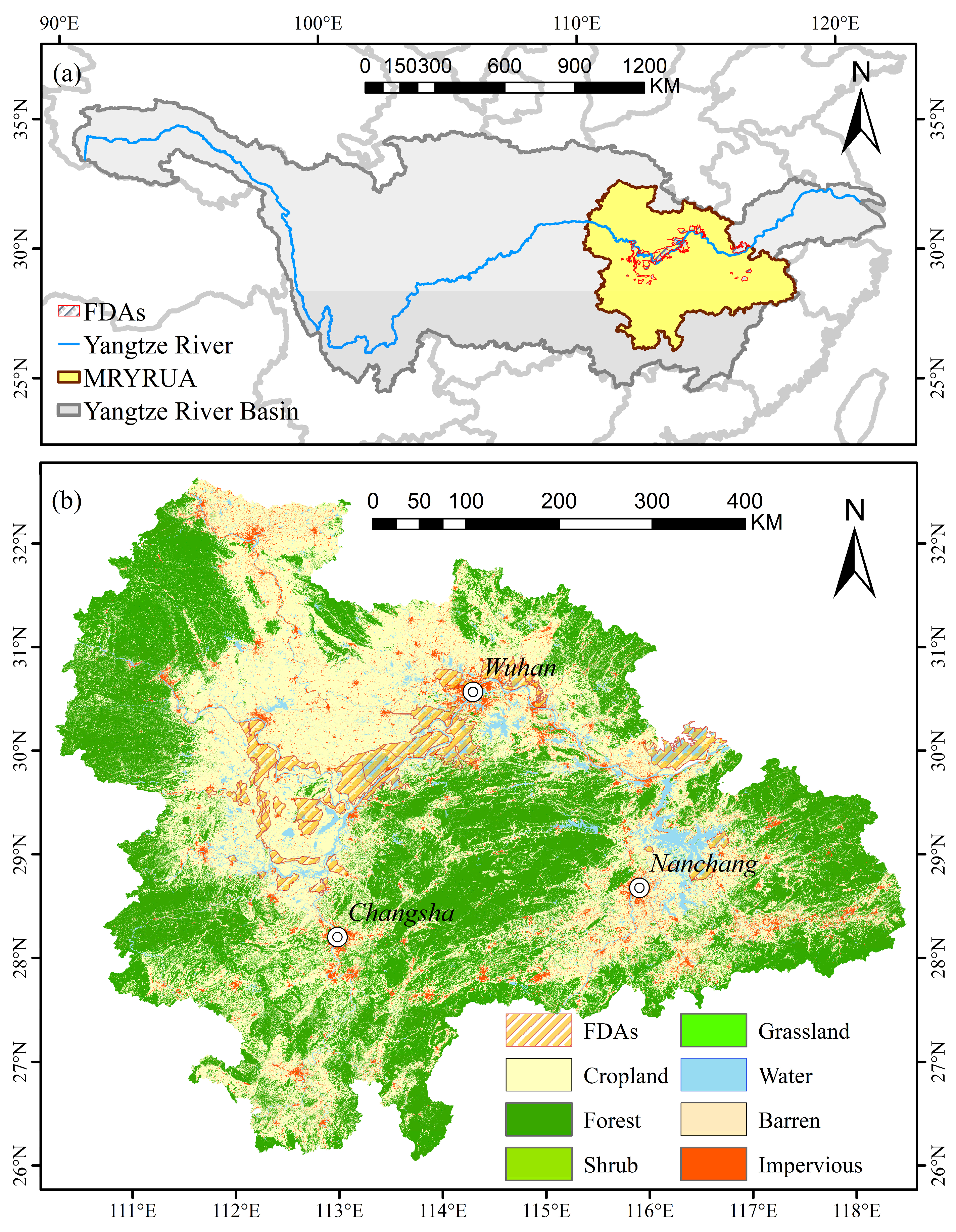
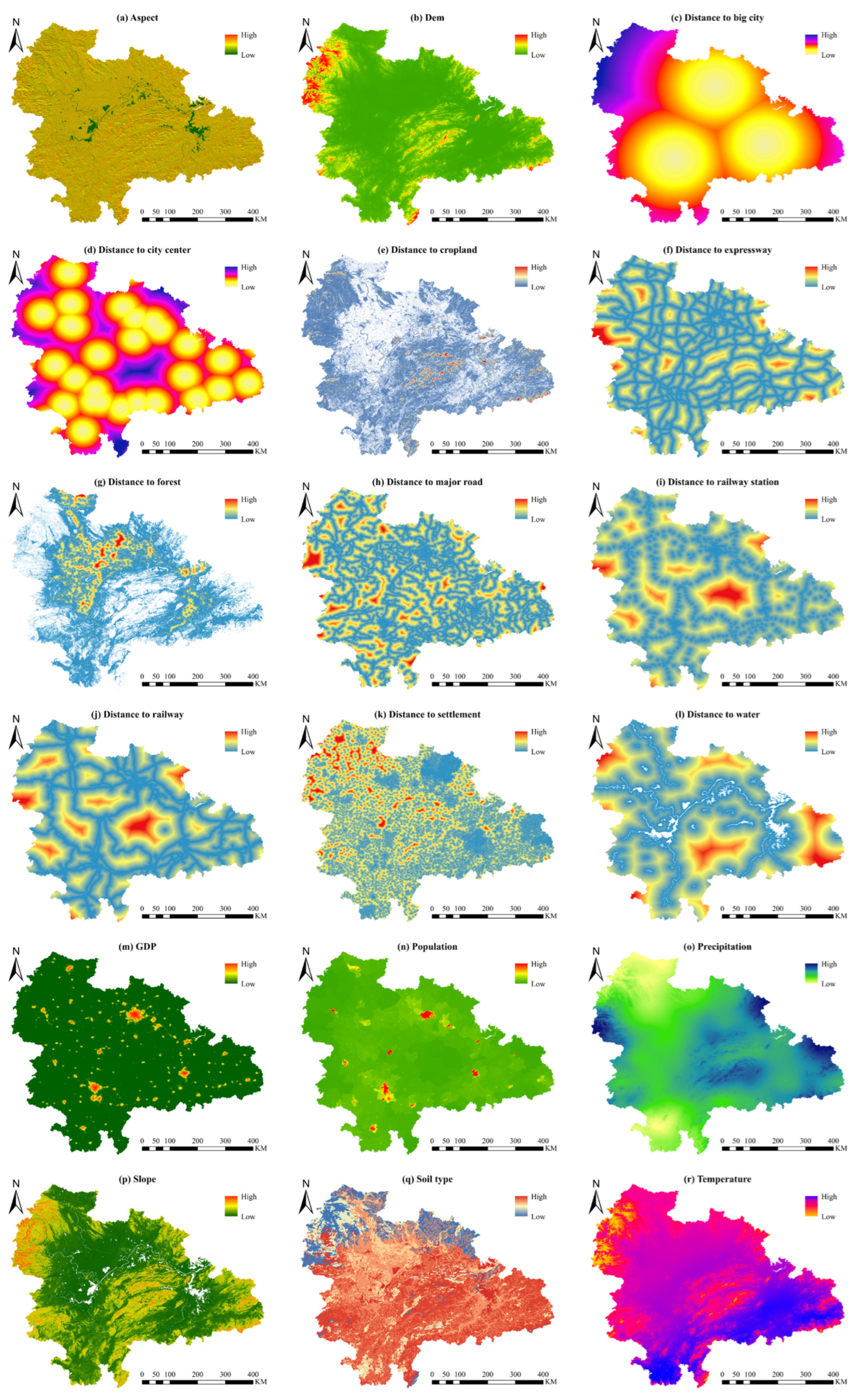
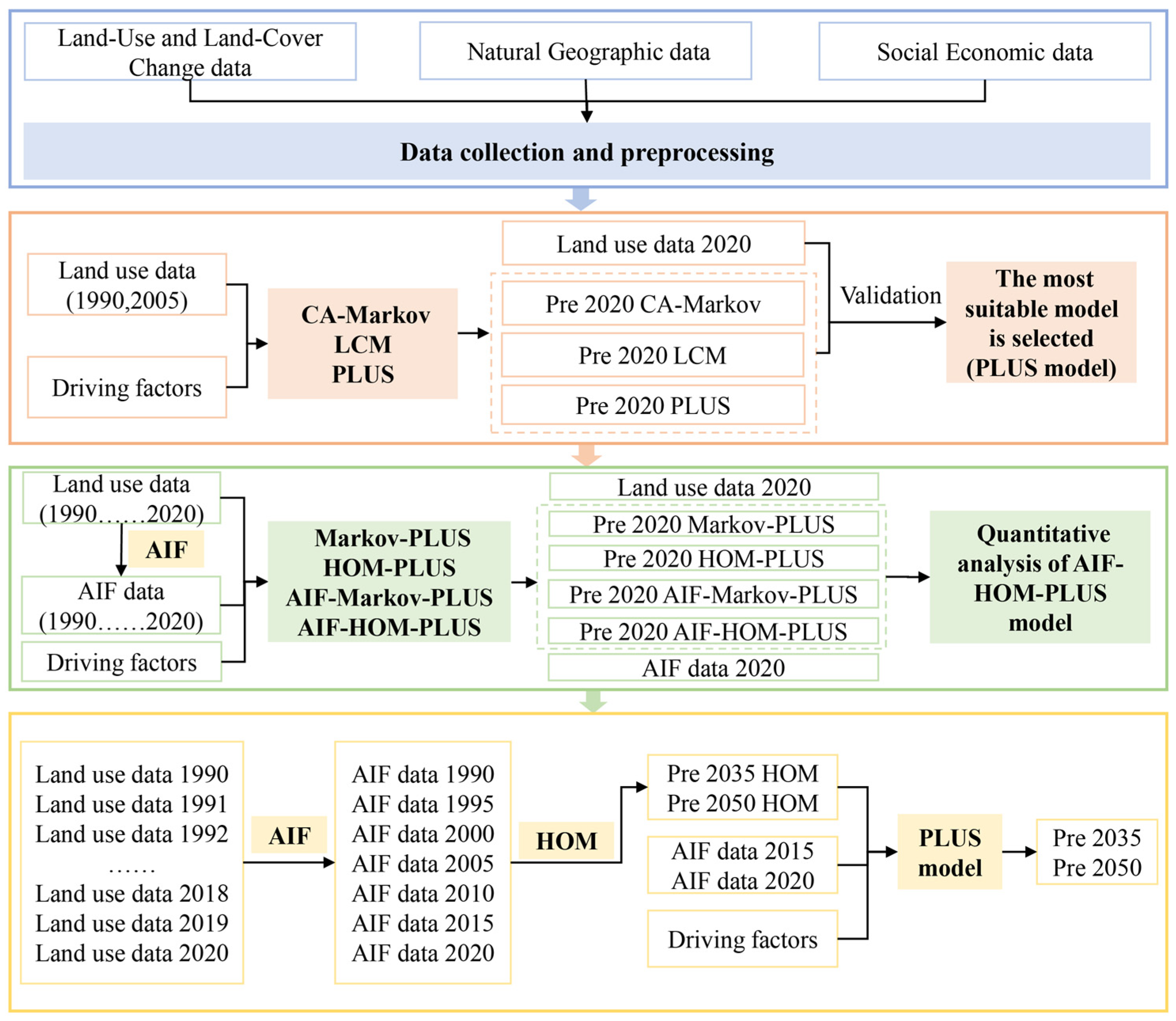
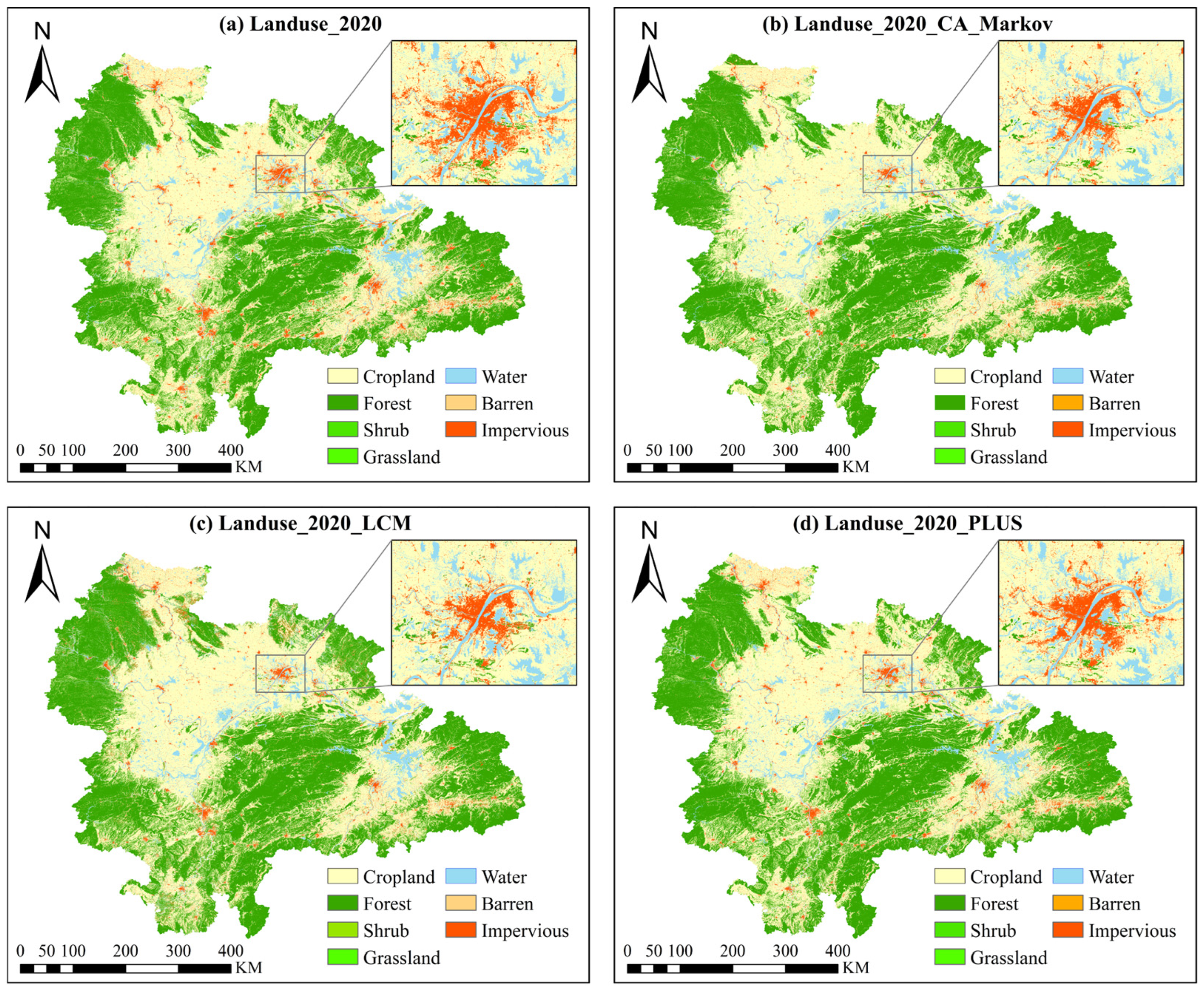
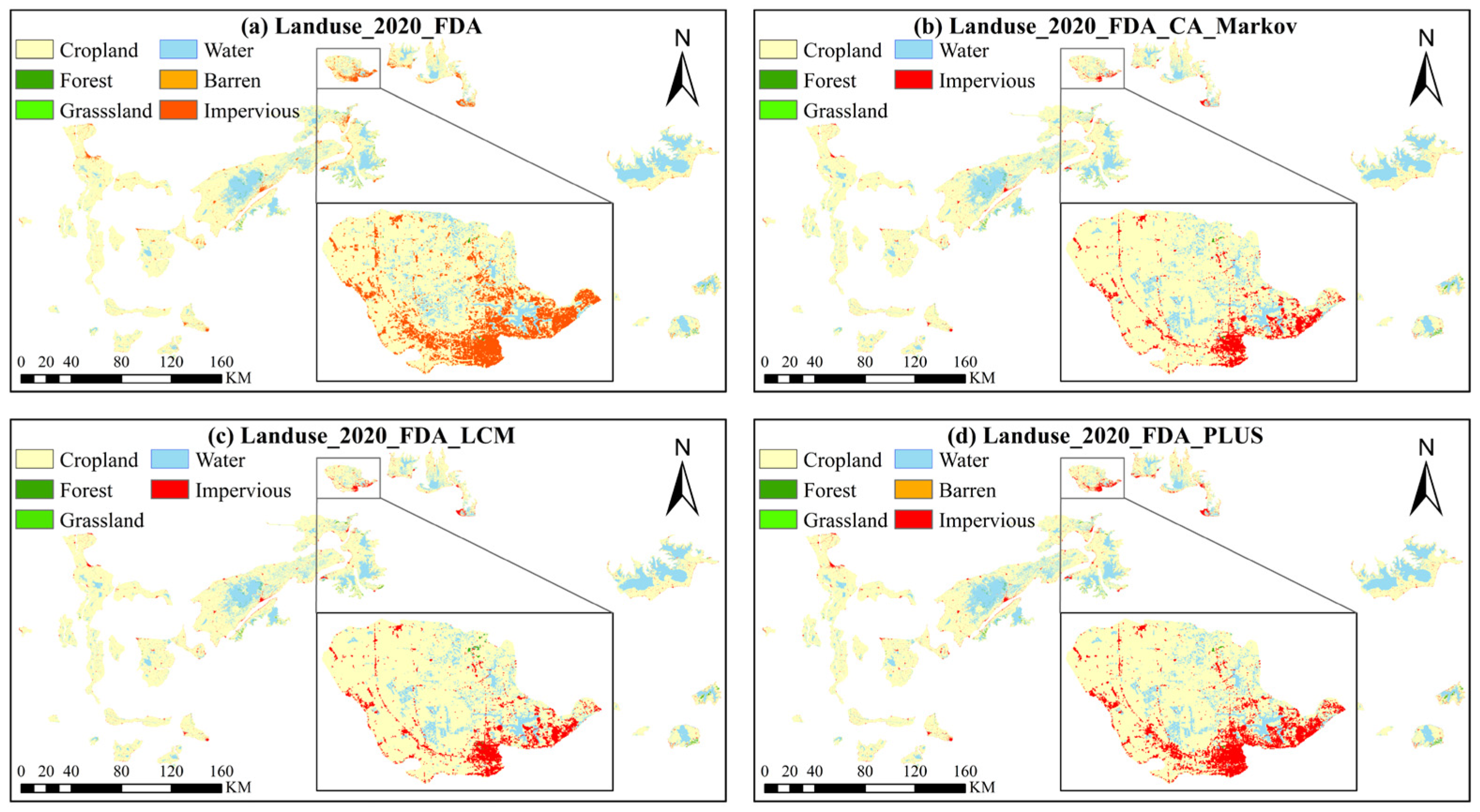
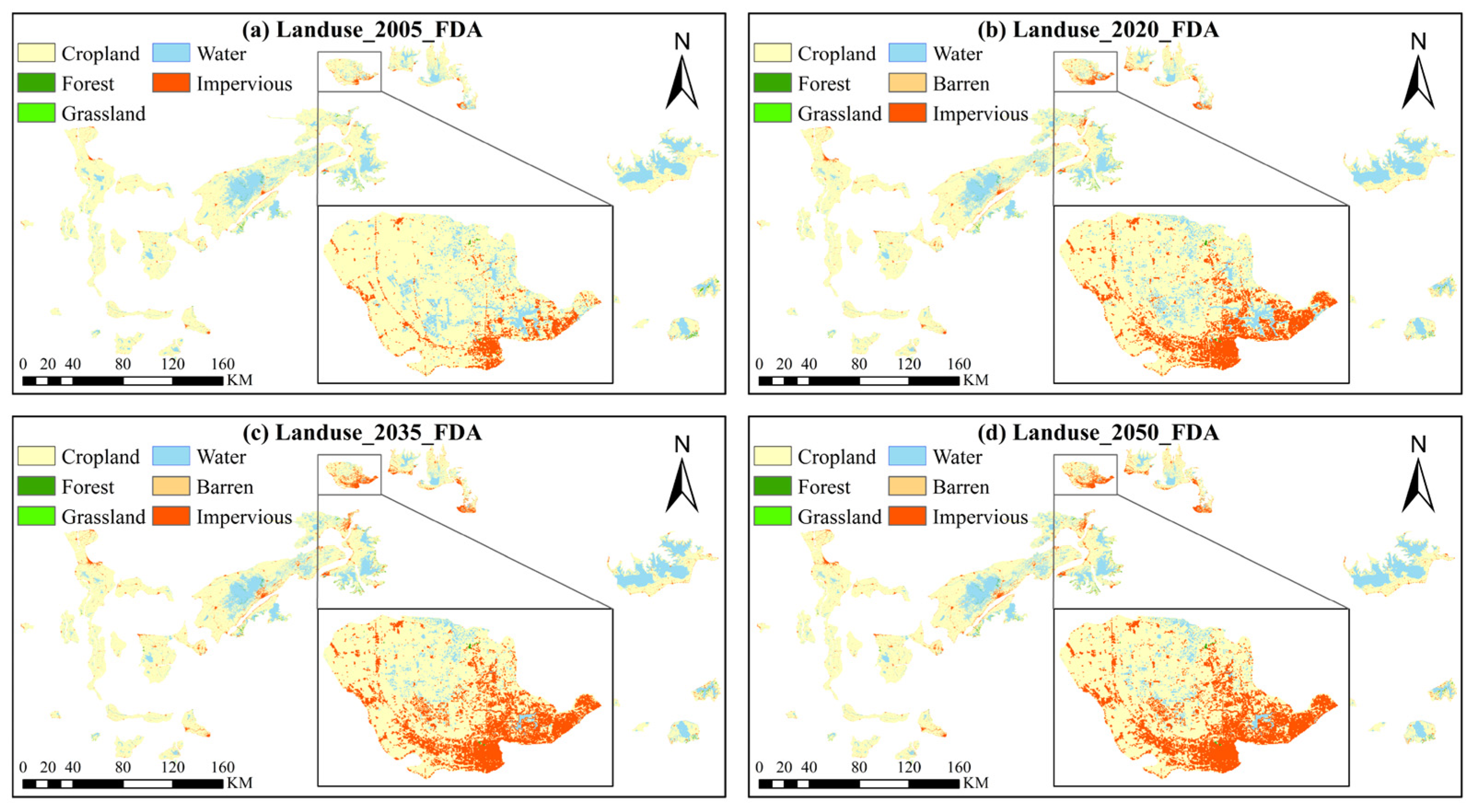
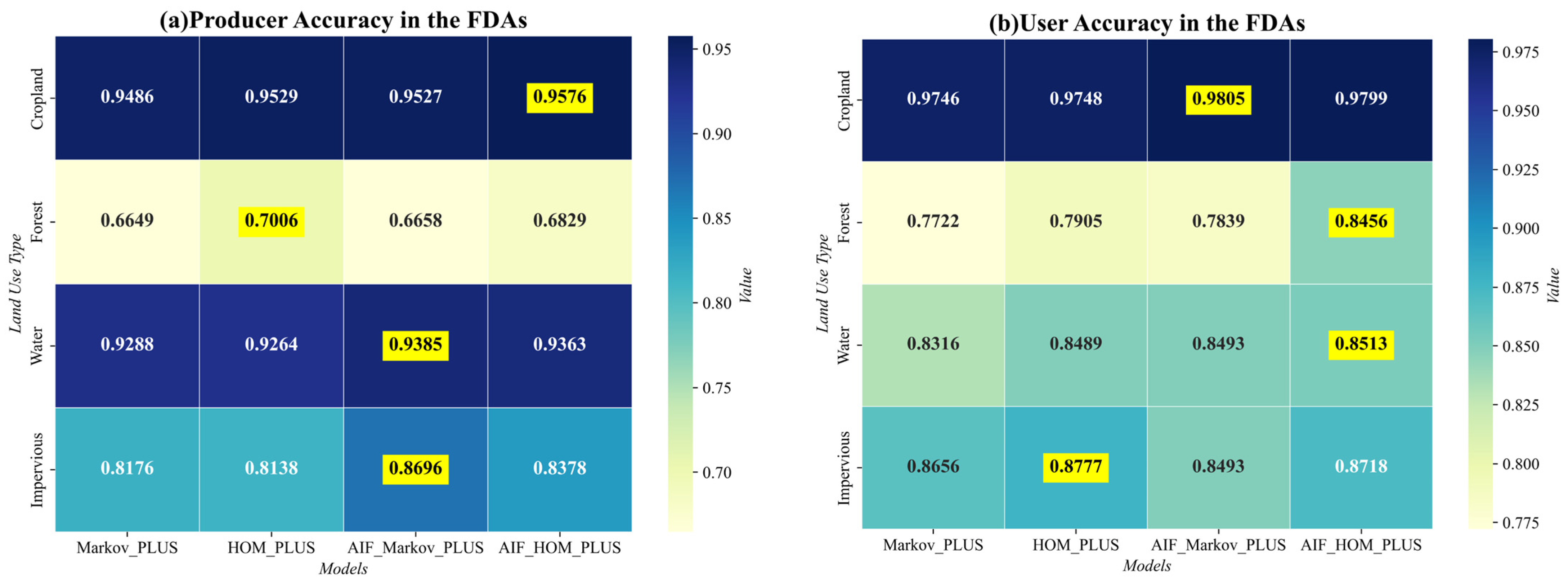
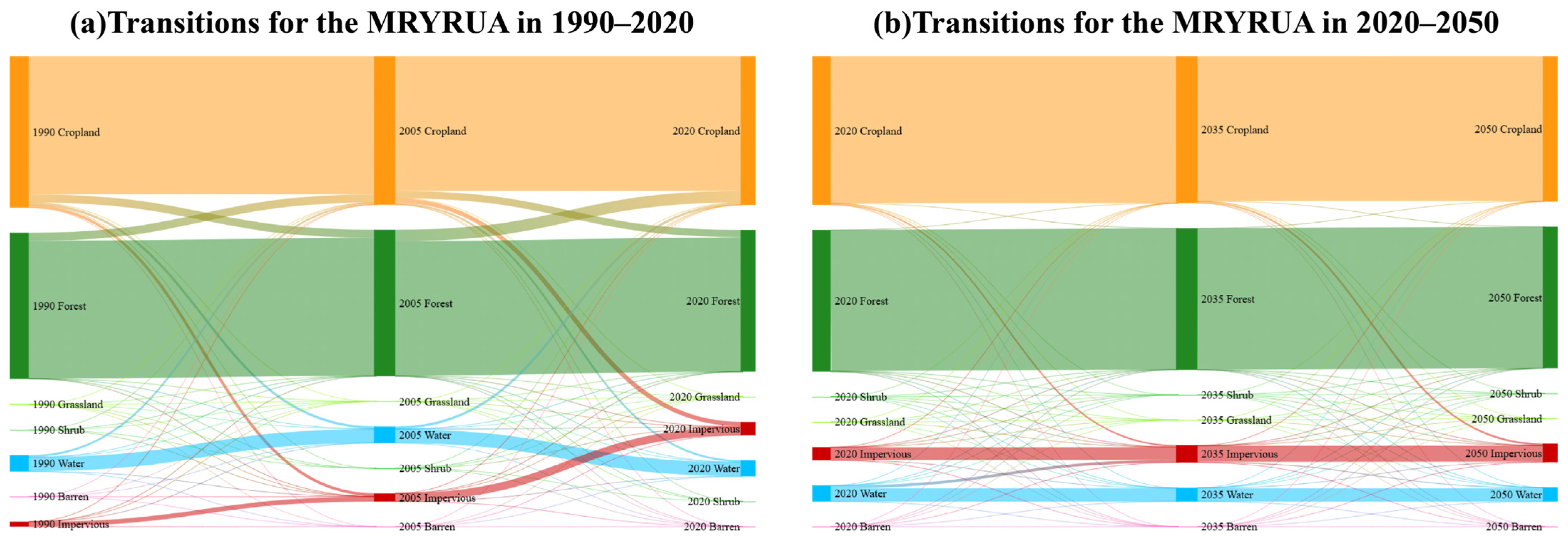
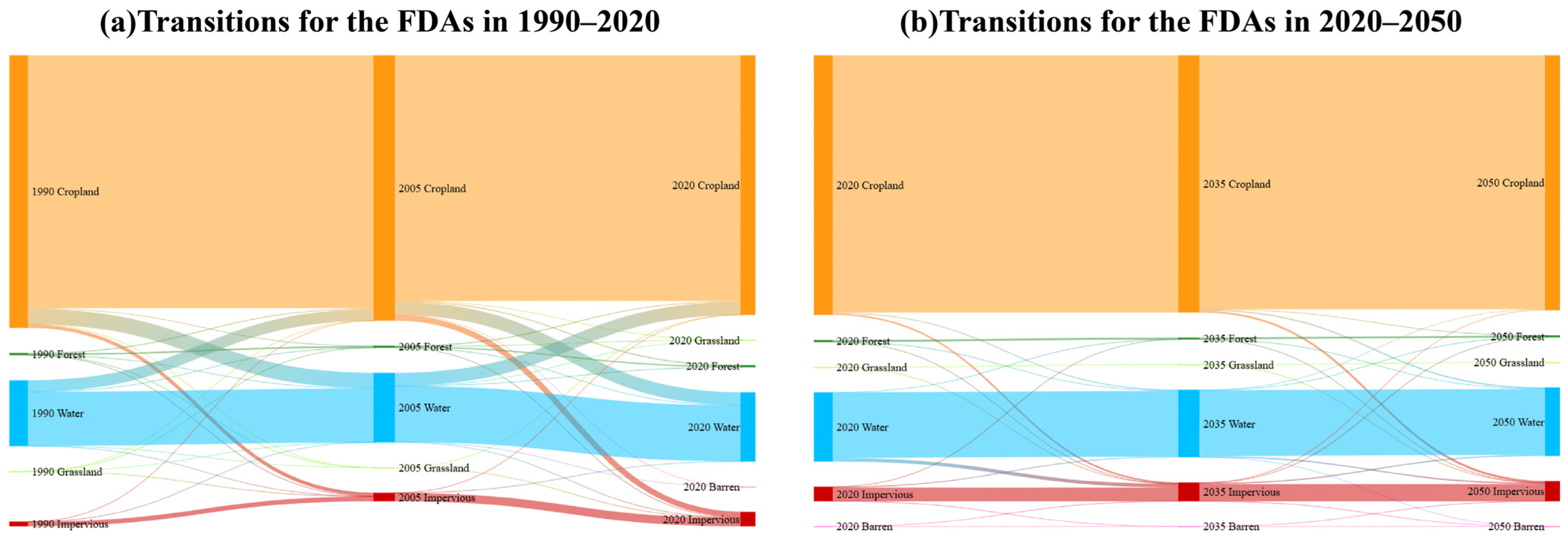
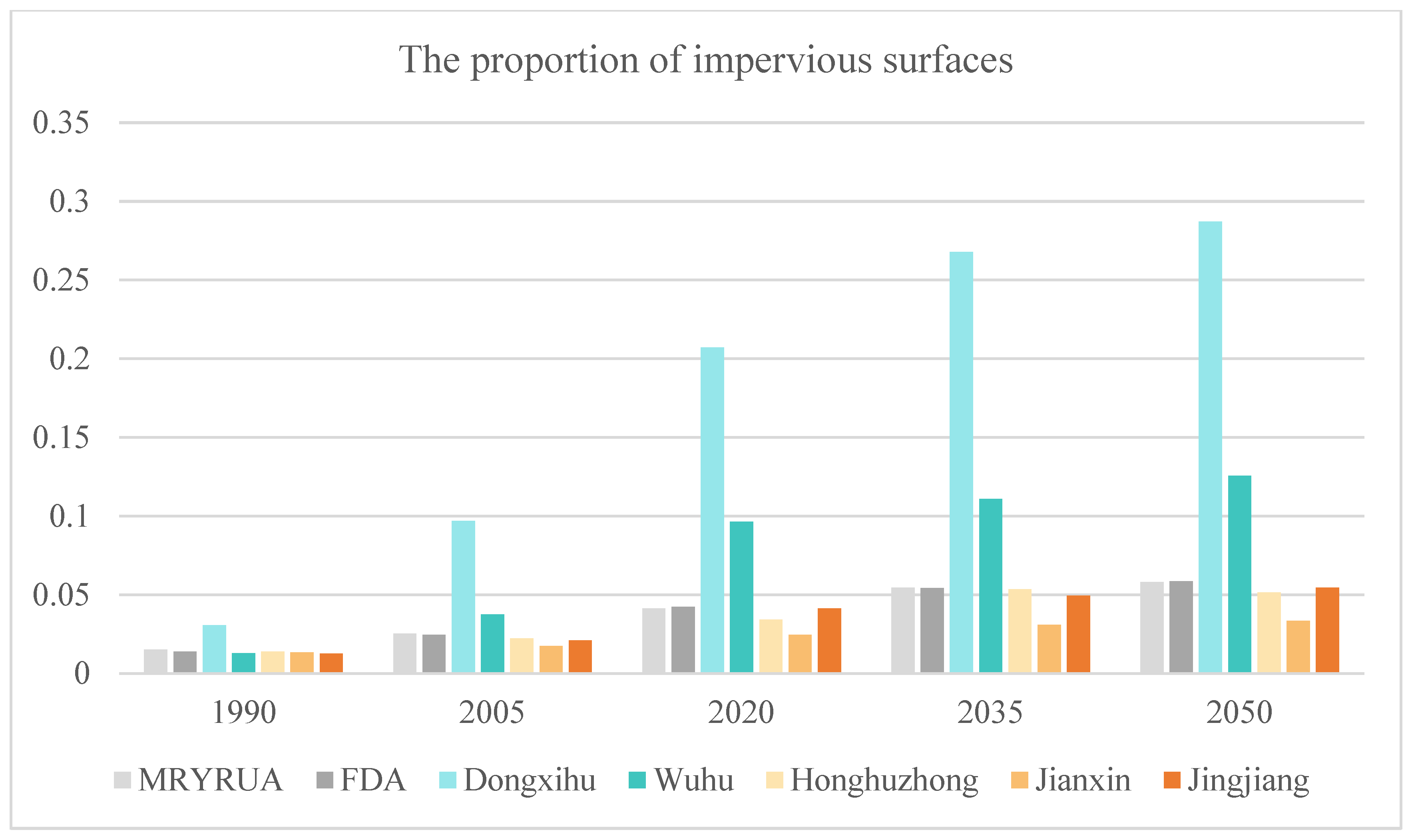
4.3.1. Impact of Land Use Change on Economic Development and Flood Control Policies in FDAs of YRB
FDAs in China exhibit a range of distinctive characteristics that set them apart from conventional land use zones [
5]. Functionally, they serve a dual role—providing emergency flood storage during extreme events, while also supporting agriculture, residential settlements, and, in some cases, industrial activities during normal periods [
1]. This dual-functionality results in inherent policy tensions between flood control objectives and socio-economic development goals [
66]. In addition, FDAs are often spatially fragmented, institutionally regulated at multiple levels, and closely tied to major river systems, making their management highly complex [
3]. These characteristics have profound implications for both land use planning and flood policy design.
Since the 1950s, 42 FDAs have been gradually established in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [
59]. As a crucial component of flood control infrastructure, these FDAs have been repeatedly activated during major flood events. For instance, during the historically significant 1954 flood—the largest in nearly a century—the Jingjiang FDA was activated three times, ensuring the safety of the Jingjiang and southern embankments. However, over the past 70 years, the functional structure of these FDAs has undergone substantial changes.
The results for land use changes from 1990 to 2020 reveal significant cropland loss within the FDAs: from 1990 to 2005, 262.98 km2 of cropland was lost, followed by an additional 209.58 km2 between 2005 and 2020. These combined losses account for 5.4% of the total cropland area within the FDAs, signaling a profound shift in the industrial structure of these agricultural zones, as agricultural activities are gradually being replaced by impervious surfaces and urban expansion. This transformation has not only diminished the flood control capacity of the FDAs but has also altered the region’s economic foundation.
An accompanying challenge is the increased difficulty in activating these FDAs, particularly those that have been converted into economically developed regions. Activating such areas would entail significant economic losses and pose safety risks to the local population. For instance, the Dongxihu FDA near Wuhan has seen its impervious surfaces increase from 3% in 1990 to 21% in 2020 [
67], and it is now a high-tech industrial park, housing numerous businesses and permanent residents. The economic and safety impacts of utilizing this area as an FDA would be substantial, underscoring the need for current policies to account for the emerging risks associated with land use changes in flood management decisions.
Nevertheless, FDAs in the YRB still play a significant role in flood control, particularly during major flood events, where they effectively alleviate flood pressures and reduce flood risks in the middle and lower reaches of the river. However, it has observed that the rate of urban expansion within FDAs is expected to slow down in the future, which will likely reduce the conflict between economic development and flood control functions within these areas. However, numerous challenges still exist within FDAs.
Firstly, among the 42 FDAs in the YRB, most of the flood control infrastructure remains underdeveloped [
3]. For FDAs located farther from urban centers, their primary function is still flood control, and their flood retention capacity can be further enhanced. The “Room for the River” program in the Netherlands serves as a notable example [
68,
69]. This program improves flood discharge capacity by lowering the elevation of floodplain areas, creating water buffer zones, relocating dikes, deepening side channels, and expanding floodways. These measures have enabled the tributaries of the Rhine River to handle floodwaters of up to 16,000 cubic meters per second, while also improving the overall ecological environment of the riverine areas.
For FDAs closer to urban centers, some of these areas have already become important regions for urban expansion. Given the limited feasibility of reverting these areas to flood control facilities, we can draw on the UK’s Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) approach [
70,
71]. The UK government has implemented several tidal FDAs in London [
72], where tidal waters are directed into low-lying areas through sluice gates, thus reducing the flood threat to the city center. This approach is characterized by converting urban green spaces and wetland parks into adaptable FDAs, balancing ecological functions with flood control needs. Additionally, community involvement in co-developing flood management strategies with the government has helped raise public awareness and acceptance of FDAs.
Furthermore, the regions where FDAs are located often contain large areas of wetlands, many of which have been poorly managed during development, leading to resource waste and environmental degradation. In contrast, the United States has a more developed wetland protection policy, which employs market mechanisms such as the Wetland Mitigation Banking Program [
70,
71]. This program involves restoring, creating, or enhancing wetlands to offset unavoidable impacts on other wetlands, thereby promoting the protection and restoration of wetlands and FDAs. The wetland management strategies for FDAs in the YRB can draw on the US wetland mitigation banking policy to encourage the sustainable development of wetland areas.
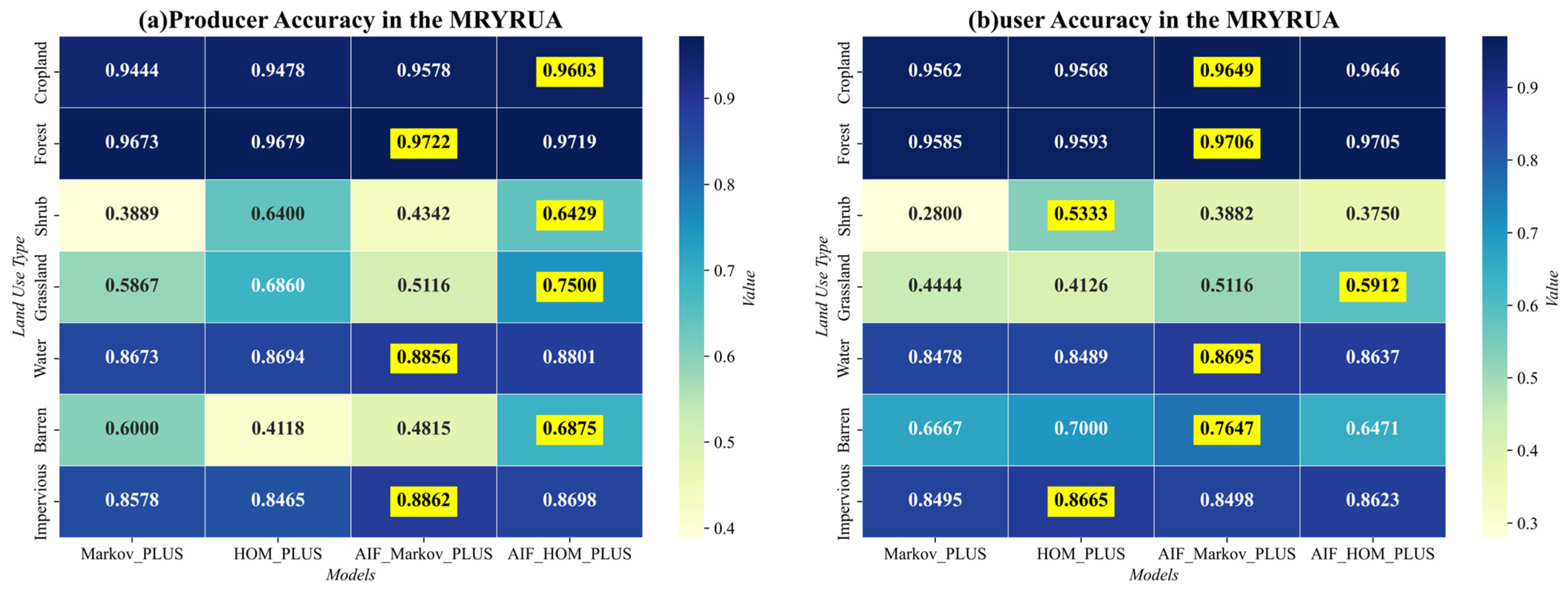
4.3.2. Impact of Land Use Change on Economic Development and Flood Control Policies in MRYRUA
The MRYRUA, covering the provinces of Hubei, Hunan, and Jiangxi, has emerged as a crucial pillar of the Yangtze River Economic Belt since the issuance of the “Development Plan for the Middle Reaches Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration” by the National Development and Reform Commission in April 2015 [
73]. In recent years, with the acceleration of urbanization, land use patterns have undergone significant changes. While this phenomenon has driven economic growth, it has also exerted a profound impact on ecosystems and the hydrological environment.
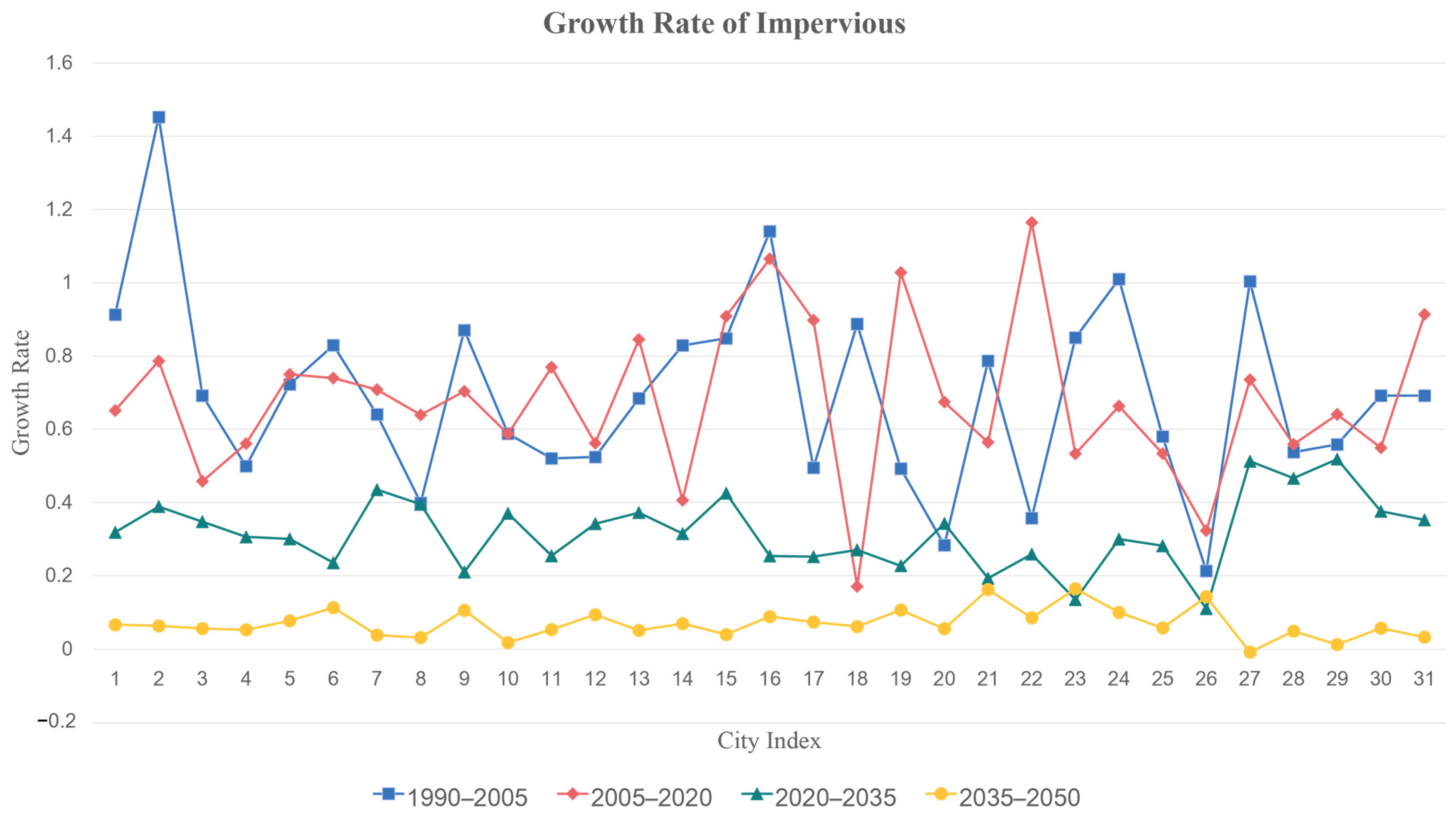
Through an analysis of land use changes in the MRYRUA from 1990 to 2020, we identified two distinct phases of development with this region. From 1990 and 2005, urbanization accelerated significantly, leading to a rapid increase in impervious surfaces, which doubled in area over 15 years. The majority of these impervious surfaces originated from the conversion of cropland. While this large-scale transformation contributed to swift economic growth in the region, it also disrupted the hydrological cycle by reducing rainwater infiltration and increasing surface runoff. Consequently, there was a heightened risk of urban flooding during periods of heavy rainfall, leading to both increased frequency and severity of flood disasters. Furthermore, the decline in cropland resulted in habitat fragmentation that exacerbated ecosystem degradation. The concomitant rise in industrial pollution and urban waste also poses substantial threats to water and air quality.
However, between 2005 and 2020, the pace of urbanization experienced a deceleration. While the growth of impervious surfaces primarily stemmed from agricultural land and forested areas, it is noteworthy that the total area of cropland actually increased during this period. This trend suggests that effective implementation and enforcement of cropland protection policies occurred within the MRYRUA. Between 1999 and 2001, China experienced three consecutive years of declining grain production, which failed to meet domestic demand. In response to this challenge, in 2005, the State Council issued the “Provincial Government Cropland Protection Responsibility Assessment Guidelines”, linking cropland protection policies directly to the performance evaluations of local officials. This mechanism facilitated the effective implementation of cropland protection policies. Although the expansion of cropland played a positive role in ensuring food security, it often resulted in significant conversion of forestland. The substantial reduction in forestland weakened the resilience of the regional ecosystem, diminished the ecological functions of forests in climate regulation, water conservation, and wind and sand prevention, and increased the risk of soil erosion. Consequently, despite rapid economic development in this region, both flood control capacity and ecological functions are now at significant risk of degradation.
Subsequently, through predictions of land use changes in the MRYRUA from 2020 to 2050, it is found that the area of impervious surfaces is expected to continue increasing. However, this growth will occur at a significantly slower rate compared to the past three decades. This trend suggests that the ongoing implementation of cropland protection policies has led to an increase in cropland that aligns with expectations, while the growth of impervious surfaces has kept pace with economic development. As China transitions from a phase of rapid economic growth to high-quality development, the pace of economic development is gradually decelerating, which suggests that the expansion of impervious surfaces will similarly slow down. Nevertheless, it is important to note that the continued growth in both cropland and impervious surfaces comes at a cost: reductions in forestland and water bodies persist. This situation poses challenges for ecosystem resilience and necessitates further enhancement of regional flood control capacities.
In response to the hydrological impacts caused by the expansion of urban impervious surfaces, the State Council of China issued the “Guidelines for Promoting Sponge City Construction” in 2015, signifying the comprehensive implementation of sponge city development. The initiative aims to enhance urban stormwater management and improve the urban water environment through natural infiltration, storage, purification, and the efficient use of rainwater [
74,
75]. Given the frequent flooding, rapid urban expansion, and ecosystem degradation in the MRYRUA, this region has become a critical area for the application of sponge city construction.
In the MRYRUA, cities such as Wuhan and Nanchang have been designated as pilot cities for sponge city development [
76]. This initiative has catalyzed the implementation of various measures, including rain gardens, permeable pavements, and ecological green spaces. For instance, in Wuhan, sponge city construction has been carried out in the Qingshan pilot area, where green infrastructure such as lakes is utilized for stormwater retention, and the role of blue-green infrastructure, including source control facilities and natural lake systems, has been strengthened. Model evaluations indicate that the proportion of the sewer network capable of accommodating a rainfall event with a return period of three years has increased from the current 17% to approximately 50% [
77]. In Nanchang, leveraging the Poyang Lake Ecological Zone, the city has effectively mitigated urban flooding and improved water resource efficiency through the renovation of the urban drainage system, the establishment of an ecological water network, and the promotion of sponge-type buildings and green spaces. Since being successfully selected as one of the “Second Batch of Systematic and Comprehensive Sponge City Construction Demonstration Cities” in May 2022, Nanchang has developed a total sponge city area of 159.96 square kilometers by the end of 2023, increasing the proportion of the impervious surfaces area meeting sponge city standards from 21.5% to 42.5% (Source: Nanchang City government, China, 1 February 2025).
Although the concept of sponge cities has been implemented in the MRYRUA, it continues to encounter numerous challenges, including high governance costs [
78], difficulties in policy coordination [
79], lack of public participation, and unreasonable spatial distribution of structural practices [
80]. To advance a more scientific and systematic model for urban water management, international experiences are essential. Globally, countries adopt various approaches to urban flood management. Developed countries such as Germany, Australia, and Singapore possess extensive expertise in managing urban flooding.
In Germany, the concepts of compact cities and Low-Impact Development (LID) are actively promoted [
81]. The focus of these concepts is on curbing urban sprawl, encouraging land-intensive use, and increasing urban green space. Additionally, ecological drainage is also employed, with measures such as green roofs, permeable roads, and sunken green spaces to reduce stormwater runoff. Furthermore, rainwater storage facilities are constructed to improve urban water resource recycling and alleviate flood control pressure.
Australia has adopted the Water-Sensitive City model in urban construction [
82], which integrates water resource management with urban planning, as well as addressing social and environmental needs. This approach aims to tackle challenges such as urban flooding, drought, and water scarcity. The concept emphasizes the comprehensive management of urban water resources, optimizing water cycle systems, and using green infrastructure to cope with the water resource pressures brought about by urbanization. It has been widely implemented in cities such as Melbourne and Perth [
83].
The urban development process of Singapore promotes the “ABC Waters Programme” (Active, Beautiful, Clean Waters) (Sources: PUB Singapore—ABC Waters Programme, 1 February 2025). The Programme integrates urban landscape design, ecological restoration, and water resource management [
84]. The primary measures include establishing an urban water cycle system, optimizing rainwater collection, treatment, and reuse to improve water resource efficiency; creating waterfront spaces, enhancing shoreline landscapes, and achieving coordination between ecological protection and urban development; and implementing rainwater management zoning, developing differentiated strategies for rainwater management based on various land use types, and enhancing the adaptability of drainage systems.
The MRYRUA encounters various challenges, including land use changes, water resource management issues, and ecosystem degradation amid urban expansion and economic development. Drawing on successful international experiences such as the compact city model in Germany, the water-sensitive city model in Australia, and the ABC Waters Programme in Singapore, the MRYRUA can enhance its flood control capacity, optimize land use, and promote sustainable urban development. This can be achieved through compact city planning, green infrastructure, smart water resource management, cross-regional ecological governance, and policy innovation. In the future, through collaborative efforts among the government, markets, and society, the MRYRUA has the potential to transition toward a greener, smarter, and more resilient urban development path.
In addition to providing policy recommendations for the YRB and the MRYRUA, this study also contributes to the broader discourse on integrating land change science with floodplain governance [
85]. By aligning empirical prediction models with real-world planning instruments, future research can help bridge the gap between environmental modeling and spatial policy implementation [
86]. The experience gained from FDAs can be further extended to other transitional land systems—such as peri-urban wetlands and multifunctional floodplains—in developing countries [
87]. Strengthening this link between spatial data analytics and adaptive land governance will be crucial for advancing interdisciplinary approaches in land system science and sustainable urbanization [
88].