Abstract
The ecological environment of arid and semi-arid regions (ASARs) faces significant challenges, highlighting the need for a robust indicator system to assess ecological environmental quality (EEQ) and sustainability. This study investigates Central Asia (CA) using the Google Earth Engine (GEE) to develop a new remote sensing-based ecological index (ASAEI), assessing EEQ from 2000 to 2022 using the CatBoost–SHAP model. The results reveal a distinct spatial pattern in the ASAEI: the southwestern and southeastern regions face more severe ecological challenges, while the northern and central-southern areas exhibit better ecological conditions. The ASAEI exhibits a strong spatial autocorrelation, with high-value clusters in the northern and central-southern regions, where vegetation is dense, and low-value clusters in the southwestern and southeastern desert and Gobi regions. Over time, we observed that ecological degradation shifts from west to east. Overall, ecological restoration in CA exceeds the extent of degradation. Notably, Kazakhstan is primarily experiencing degradation, while other subregions predominantly show signs of restoration. Our analysis indicates that climate conditions and land use types are the primary factors influencing changes in the ASAEI. Furthermore, we project that 54.5% of the CA region will exhibit an improved EEQ, highlighting the need for restoration efforts in the western areas. The ASAEI offers a novel perspective and methodology for assessing EEQ in ASARs, with significant scientific implications.
1. Introduction
In recent years, climate change and human activities have exerted widespread impacts on global ecosystems [1], with particularly severe ecological challenges observed in ASARs [2]. The ASARs face acute water scarcity, fragile ecosystems, and intensive land use. These factors, compounded by rapid population growth and heavy reliance on agriculture, have accelerated land degradation, desertification, and salinization, posing a significant threat to ecological security [3]. Therefore, accurately understanding the spatial distribution and temporal dynamics of EEQ is crucial for regional ecosystem management, spatial planning, and the pursuit of sustainable development goals [4].
Advances in remote sensing technology have greatly enhanced the efficiency and precision of ecological environment monitoring, particularly in large-scale and time-series ecological assessments [5,6]. The Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI), a comprehensive index integrating greenness (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, NDVI), wetness (soil moisture, WET), heat (land surface temperature, LST), and dryness (Normalized Difference Bare Soil Index, NDBSI), has been widely applied in ecological assessments of urban agglomerations, mountainous areas, and humid regions [7,8]. Its advantages include full reliance on remote sensing data and the absence of manually assigned weights, ensuring strong operability and general applicability. Several studies have introduced diverse modifications to the RSEI, such as incorporating salinity and hydrological network density [9], PM10 concentrations [10], or replacing principal component analysis (PCA) with the entropy weight method [11], to better meet the ecological monitoring needs of specific regions like urban clusters and arid, wind-eroded zones. These efforts have significantly enhanced the RSEI’s regional adaptability in remote sensing-based ecological assessments. These studies typically emphasize the enhanced representation of specific landform types or single environmental factors, thereby improving model performance under particular ecological scenarios. However, the ASARs are characterized by high surface heterogeneity and extensive desertified and bare land cover, leading to ecological response patterns that differ significantly from those in other regions. These unique conditions pose substantial challenges to the applicability of the RSEI in such environments [12]. On one hand, the NDVI has a limited capability in detecting sparse vegetation under strong soil background signals; on the other hand, the original dryness component—NDBSI—includes built-up area information, which can lead to misclassification in regions dominated by desertified grasslands and bare surfaces. Although the aforementioned methods have shown promising results in localized contexts, a systematic assessment framework that effectively captures the distinctive geomorphological and ecological characteristics of ASARs is still lacking.
Based on a systematic analysis of the issues outlined above, this study proposes a novel EEQ assessment framework—the Arid and Semi-Arid Environmental Index (ASAEI)—which introduces three key enhancements to the original RSEI structure. First, to more accurately capture typical ASAR landforms such as bare land, sandy terrain, and surface roughness, we introduce a new dryness component by integrating the Topsoil Grain Size Index (TGSI) and surface albedo. The TGSI characterizes variations in soil particle size at the surface [13], while albedo is widely used to reflect surface conditions and degrees of degradation in ASAR landscapes [14]. Previous studies have shown a high correlation between the TGSI and albedo in desertification processes. Their combined use enhances the stability and ecological relevance of the dryness dimension in ASARs [15] while also mitigating interference from built-up area signals present in the traditional NDBSI. Second, regarding the greenness component, we replace the NDVI with the Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index (MSAVI), which has demonstrated superior performance in identifying vegetation under high soil background interference common in ASAR settings [16]. Third, to improve the regional adaptability of soil salinization detection, we construct an integrated salinity factor (SI) by combining three widely applicable salinity indices. This approach avoids the limitations of any single index in capturing large-scale variations [17], thereby enhancing the model’s robustness and generalizability under complex surface conditions. ASAEI’s indicator selection fully accounts for the disturbance sources and response characteristics of ASAR ecosystems, aiming to achieve a regionally optimized representation of greenness, wetness, heat, and dryness while maintaining the independence of remote sensing data inputs. This model not only addresses the structural limitations of the RSEI in adapting to ASAR environments but also provides a technical foundation for future multi-scale ecological evaluations and dynamic monitoring efforts.
The evolution of EEQ is influenced by a variety of natural and anthropogenic factors, such as climate, moisture conditions, topographic features, and land use changes, that often interact in complex and intertwined ways [18]. Accurately identifying and quantifying the driving patterns and influence intensities of these ecological factors is a critical prerequisite for scientific ecosystem regulation and refined environmental governance. Traditional studies have primarily relied on methods such as regression analysis, trend analysis, or correlation analysis to investigate driving factors [19,20,21]. However, these approaches are generally based on linear assumptions, which limit their ability to capture nonlinear responses and interactions among variables, and often constrain the analysis to a qualitative identification of dominant factors [22]. To overcome these limitations, this study is the first to introduce the highly interpretable CatBoost–SHAP model for identifying the driving factors of EEQ. The CatBoost model offers strong nonlinear fitting capabilities and robust handling of categorical variables, making it well-suited for the heterogeneity inherent in multi-source remote sensing and environmental datasets [23], while the SHAP framework quantitatively elucidates the positive or negative contributions of each driving factor to the model output, as well as their interaction effects [24]. This integrated approach offers a novel technical pathway for unraveling the dominant factors and coupled mechanisms underlying ecological responses in ASARs.
In summary, this study integrates six key remote sensing-based ecological indicators—the Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index (MSAVI), wetness component (WET), land surface temperature (LST), integrated salinity index (SI), surface albedo, and topsoil grain size index (TGSI)—to construct the Arid and Semi-Arid Environmental Index (ASAEI), a comprehensive ecological assessment framework tailored for ASARs. In addition, this study employs the CatBoost–SHAP model to explore the influence, strength, and interaction mechanisms of ecological driving factors in depth. The study area focuses on Central Asia (CA), situated in the core of the world’s largest arid and semi-arid belt. With its diverse ecosystem types and pronounced environmental variability, CA serves as a highly representative case region. The main objectives of this research are (1) to validate the accuracy and reliability of the ASAEI model in assessing EEQ across CA; (2) to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution and inter-country differences in EEQ across CA nations from 2000 to 2022; (3) to identify the primary driving factors influencing ASAEI dynamics and their underlying mechanisms; and (4) to predict future trends in EEQ based on historical data, providing decision support for regional ecological management and policymaking.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
CA is the largest non-zonal arid region in the world (Figure 1a), encompassing Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Xinjiang, China. The region spans latitudes from 34.3°N to 55.4°N and longitudes from 46.5°E to 96.4°E, covering an area of approximately 5.66 million square kilometers. CA is located inland within the Eurasian continent. It served as a key corridor along the ancient Silk Road and remains a crucial node for the westward expansion of the Belt and Road Initiative [25].
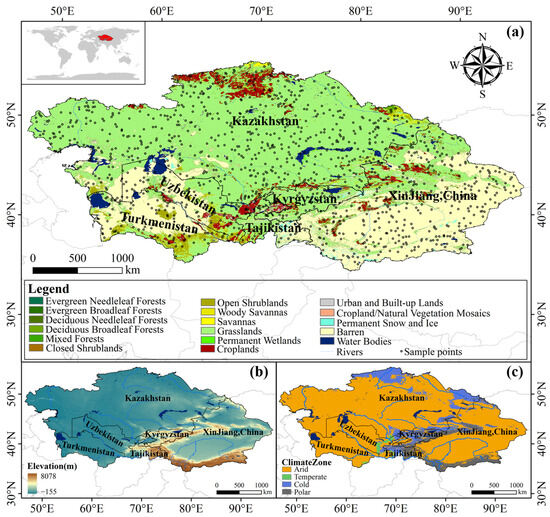
Figure 1.
Location of the study area, the spatial distribution of (a) land types (based on the 2020 International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme Global Vegetation Classification, extracted from the MCD12Q1 dataset), and the distribution of random sampling points for the quantitative analysis, (b) DEM, and (c) Köppen–Geiger climate zones.
The terrain of CA is diverse, with higher elevations in the southeast and lower elevations in the northwest (Figure 1b). The southern part is characterized by deserts, oases, and mountainous areas, while the northern part comprises steppes and plains [26]. The Pamir region in Tajikistan and the Tianshan region in Kyrgyzstan feature high altitudes, while western Kazakhstan lies below sea level. In contrast, Xinjiang exhibits a west-high, east-low topography, with the Altai, Tianshan, and Kunlun Mountains crossing the region, creating a “three mountains enclosing two basins” pattern [27]. CA predominantly has a temperate continental climate characterized by low precipitation, intense evaporation, and significant diurnal temperature variation, with rainfall mainly concentrated in winter and spring (Figure 1c). Mountainous areas are relatively wetter due to topographic influences, while the region around the Aral Sea receives the lowest precipitation [28]. Overall, CA is characterized by arid conditions, low rainfall, intense evaporation, and abundant sunshine, making it one of the driest regions in the world. Therefore, studying the characteristics of ecological changes and their influencing mechanisms is crucial for preserving ecological balance and promoting sustainable development [29].
2.2. Methodology
This study is comprised of four main steps: (1) constructing the ASAEI for the study area from 2000 to 2022 using Google Earth Engine (GEE) (https://code.earthengine.google.com/); (2) analyzing spatiotemporal changes based on the multi-year ASAEI dataset; (3) analyzing the spatial autocorrelation of ASAEI using Moran’s I to identify its spatial clustering pattern; and (4) applying CatBoost–SHAP to determine the response patterns of EEQ to various driving factors and assess their impact intensity. The detailed workflow is presented in Figure 2.
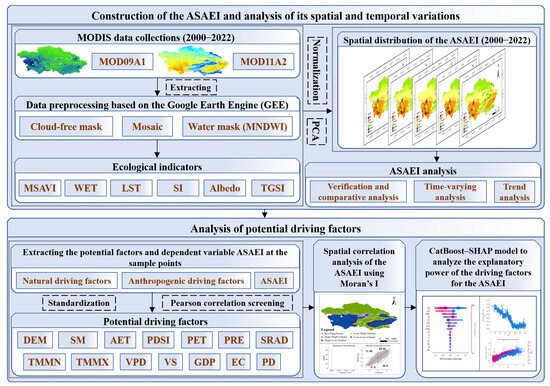
Figure 2.
Research-specific flow chart, including the EEQ assessment and driving factor analysis.
2.3. Data and Pre-Processing
The data used in this study are presented in Table 1. The study period spans from 2000 to 2022. The extraction and construction of ASAEI-related indicators rely primarily on the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) imagery dataset, which provides Earth observation data with high spatial and temporal resolution [30]. Preprocessing was conducted on the GEE platform, utilizing atmospheric correction and other preprocessing methods to improve image quality. Based on prior studies [26,31,32,33], datasets for 15 natural and anthropogenic factors were selected to assess potential influences on the EEQ of the study area. All imagery was resampled to a common spatial resolution of 1000 m to ensure consistency across datasets. For MODIS products sensitive to seasonal variability, the seasonal mean from June to September (summer) was used each year to minimize seasonal effects on the analysis results.

Table 1.
Data types and sources.
2.4. ASAEI Indicator Construction
This study selected the Modified Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (MSAVI) [34], soil moisture (WET), land surface temperature (LST), salinity index (SI), albedo, and Topsoil Granularity Index (TGSI) to develop a remote sensing ecological index for large ASARs. Due to soil background effects in ASARs, NDVI is less effective at reflecting vegetation conditions. Consequently, MSAVI was selected as the greenness indicator in this study because it effectively reduces soil background effects by incorporating the basic soil line [35]. Additionally, WET and LST were used as indicators for humidity and heat. We also selected three commonly used indicators for environmental monitoring in ASARs: a combination of albedo and TGSI to represent land dryness and SI to characterize regional salinization. The remote sensing inversion formulas and corresponding bands for the indicators of the improved ASAEI are as follows:
Among them, RED, BLUE, GREEN, NIR, NIR1, SWIR1, and SWIR2 represent the reflectance in the red, blue, green, near-infrared 1, near-infrared 2, short-wavelength infrared 1, and two short-wavelength infrared bands of MOD09A1, respectively. LST is derived from the MODIS LST product (MOD11A2).
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a multivariate data compression technique that reduces redundancy and multicollinearity among variables while extracting dominant features. It has been widely applied in EEQ assessments [5,36,37]. In this study, PCA was employed to integrate the six ecological indicators. To avoid bias in weighting caused by differences in units, all indicators were first normalized to a [0, 1] scale, as shown in the following formula:
In the formula, denotes the normalized value of the ecological factor, is the original pixel value of the ecological factor, is the global maximum pixel value of the ecological factor, and is the global minimum pixel value of the ecological factor.
In this equation, represents the PCA operation, and represents the obtained principal component. The variables , , , , , and represent MSAVI, WET, LST, SI, albedo, and TGSI as ecological factors, respectively.
Principal components were then extracted, and the first principal component (PC1), which had the highest cumulative variance contribution, was used as the final expression of the ASAEI. PC1 best represents the integrated trend of ecological changes, and its corresponding eigenvector coefficients (loadings) were used as the weights of each factor in the model (Table 2).

Table 2.
Indicator weights for the ASAEI model in CA.
Finally, the ASAEI can be expressed as follows:
where ASAEI represents the improved RSEI model, and to are the weight values corresponding to each indicator. To ensure the comparability of the indicators, the ASAEI was normalized to a range between 0 and 1.
2.5. CatBoost–SHAP Regression Prediction Model
The CatBoostRegressor is a powerful gradient-boosting algorithm designed to efficiently handle categorical features while reducing data bias [38]. Hyperparameters were optimized during model construction using RandomizedSearchCV combined with ten-fold cross-validation, with the primary objective minimization of Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). This approach also assessed the model’s robustness to ensure strong generalization performance. The model was evaluated using metrics such as RMSE, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2), providing a comprehensive assessment of the predictive accuracy and relationships among features [39]. SHAP values were used to explain the model’s decision-making process by analyzing feature contributions, thereby achieving both global and local interpretability. The contribution of each feature to the prediction is quantified through SHAP values. A positive SHAP value indicates a positive influence of the feature on the model output, while a negative value signifies a reduction in the model’s production. Notably, SHAP values are model-agnostic and applicable across various model types, such as tree-based, linear, deep neural networks, and integrated models, allowing for the assessment of each feature’s impact on individual predictions [40]. Additionally, CatBoost adjusts the model parameters by optimizing the following loss function:
In this context, represents the error between the actual value and the predicted value, while is the regularization term used to prevent overfitting.
In each training iteration, the model update formula is
where represents the learning rate and is the regression tree obtained in the t-th iteration of training.
2.6. Coefficient of Variation
The coefficient of variation (CV) is a dimensionless statistical method used to measure the degree of dispersion in a dataset. The calculation formula is
represents the standard deviation of ASAEI, and indicates the mean value of ASAEI. is used to compare the relative dispersion of data with different dimensions. A larger value indicates greater data variability, whereas a smaller value indicates less variability. In this study, is classified into five levels (Table 3).

Table 3.
Coefficient of variation (CV) of the ASAEI.
2.7. Sen’s Slope Estimator and the Mann–Kendall Statistical Test
The Sen slope estimator proposed in [41] is a non-parametric method for estimating the trend rate of a time series. The technique calculates slopes between all pairs of time points and uses the median as the trend slope, making it particularly suitable for analyzing trends in EEQ changes. The calculation formula is as follows:
and represent the ASAEI values for the time series at points and , respectively. The Sen slope estimator can reveal the underlying linear trend in a time series.
The Mann–Kendall (MK) test is a widely used non-parametric statistical method for detecting monotonic trends in time series, and it is especially suitable for ecological data with outliers [42]. The MK test is primarily used to assess the significance of trends and detect increasing or decreasing patterns in the data. The formula for the Mann–Kendall statistic is given below:
n represents the length of the time series, and is used to determine the relative magnitude between and . The standardized Mann–Kendall statistic Z is used to evaluate the significance of the trend, and its formula is as follows:
The method for determining trend significance is presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Mann–Kendall test trend categories.
2.8. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
The global Moran’s I [43] is a widely used indicator for detecting spatial autocorrelation, determining whether similar values are spatially clustered or dispersed [44]. When the data exhibit positive spatial autocorrelation, Moran’s I value approaches 1, indicating the spatial clustering of similar values. Conversely, if the data exhibit negative spatial autocorrelation, Moran’s I value approaches −1, reflecting the spatial dispersion of similar values. If the data are randomly distributed, Moran’s I value approaches 0. The formula for global Moran’s I is given below:
n represents the sample size; and are the ASAEI values for regions i and j, respectively; is the mean ASAEI value; and denotes the spatial weight matrix between regions i and j, typically used to represent adjacency relationships or distance decay.
2.9. Hurst Exponent
The Hurst exponent is a metric that quantifies the long-term dependence of a time series, with values ranging from 0 to 1 [45]. H > 0.5 indicates positive dependence, where the time series exhibits persistence; H = 0.5 signifies a random walk; and H < 0.5 indicates anti-persistence, where the time series tends to reverse its fluctuations. Its calculation is based on the R/S analysis method, with the formula given below:
R represents the range, S denotes the standard deviation, and n is the length of the series.
3. Results
3.1. Validation and Comparative Analysis of the ASAEI Results
Both quantitative and qualitative validation approaches were employed to evaluate whether the ASAEI model is suitable for assessing EEQ in CA (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Since ASAEI is an improved version of RSEI, and RSEI has been widely applied in regional-scale EEQ assessments, we calculated the RSEI and ASAEI for the years 2000 to 2022. These indices were categorized into five levels—poor, fair, moderate, good, and excellent—using intervals of 0.2 [8]. A comparative analysis between the two models was conducted to verify the advantages of the ASAEI in evaluating EEQ in ASARs.
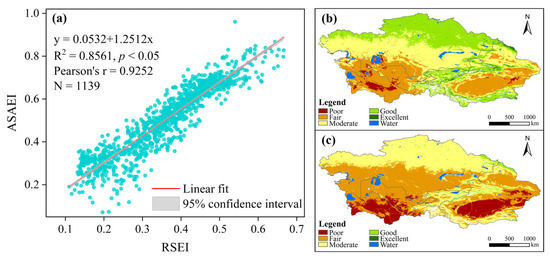
Figure 3.
A comparison of the ASAEI and RSEI models for evaluating EEQ in CA: (a) a scatter plot showing the correlation between the RSEI and ASAEI values, and maps illustrating the distribution of the mean ASAEI (b) and mean RSEI (c) in CA.
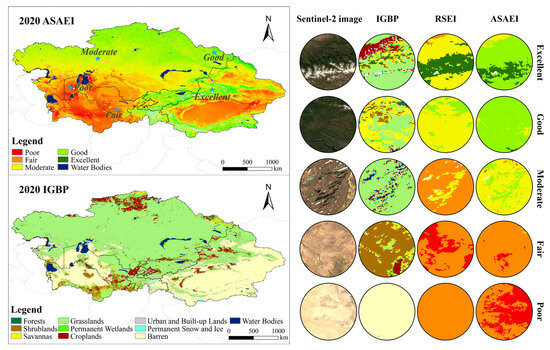
Figure 4.
A comparison of true-color images of the ASAEI across different ecological categories to validate the effectiveness of the ASAEI in the CA region.
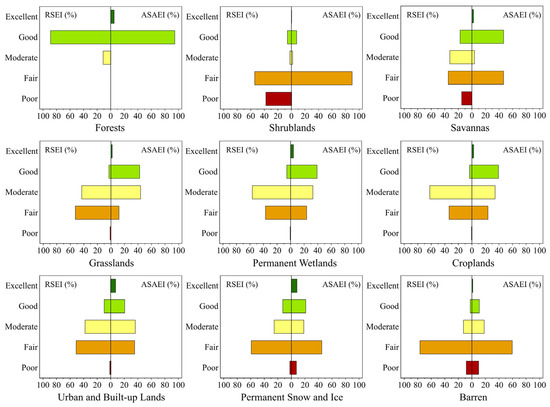
Figure 5.
A comparison of the EEQ results of the RSEI and ASAEI under different IGBP classifications in 2020.
Based on the analysis of randomly generated sample points (Figure 1a), the ASAEI and RSEI exhibit a significant positive correlation, with an R2 value of 0.8561 (p < 0.05; Figure 3a). This result indicates strong consistency between the two indices and confirms their effectiveness in reflecting EEQ across CA. In addition, the multi-year average values of the ASAEI and RSEI demonstrate broadly similar spatial distribution patterns (Figure 3b,c). However, the ASAEI exhibits a noticeably greener landscape than the RSEI, suggesting that the MSAVI is more suitable than the NDVI as a greenness indicator in ASAR environments. Furthermore, at the same spatial resolution, the ASAEI displays finer texture details than the RSEI. This improvement is attributed to the inclusion of SI, albedo, and TGSI—three indicators that are specifically tailored to capture the unique characteristics of ASARs.
To further validate the advantages of the ASAEI in ASARs, five locations representing different EEQ levels were selected in 2020 for verification (Figure 4). High-resolution (10 m) true-color imagery from Sentinel-2 was compared with the IGBP, RSEI, and ASAEI classification results. Compared to the RSEI, the ASAEI more accurately reflects the actual environmental conditions in ASAR landscapes. Across all verification sites, the ASAEI demonstrated greater precision and reliability in identifying texture patterns and EEQ levels, showing superior consistency and spatial continuity. In regions classified as “excellent”, Sentinel-2 imagery captured geomorphological features associated with high vegetation coverage. According to the IGBP classification, land cover in these areas mainly includes forests, savannas, grasslands (the dominant type), and croplands. However, the RSEI results in these regions presented unrealistic discontinuities in ecological grading, with classifications ranging from “excellent” to “moderate” and even “fair”, which deviate notably from the actual vegetation and land cover. Such abrupt classification changes clearly diverge from the region’s actual distribution of vegetation cover and land types. In contrast, the ASAEI accurately captured the ecological characteristics of high vegetation coverage zones, offering improved consistency and spatial continuity in classification. In areas rated as “poor”, the texture features revealed by the ASAEI closely matched the geomorphological patterns visible in the imagery, effectively reflecting the ecological degradation present. Moreover, comparisons of the RSEI and ASAEI results under different IGBP land cover types in 2020 (Figure 5) indicated that the RSEI consistently underestimated the EEQ across various land categories.
3.2. Spatial Distribution of the ASAEI
To quantitatively assess the EEQ of the study area from a spatial perspective, we present the spatial distribution of ASAEI levels in CA during the study period, along with the average ASAEI values for six subregions. The EEQ of CA from 2000 to 2022 shows a clear spatial pattern (Figure 6 and Figure 7). From south to north, the ASAEI values display a fluctuating upward trend, while from west to east, they follow a fluctuating downward trend. EEQ is higher in the northern (Kazakhstan) and central regions (Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan), while the western (Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan) and southeastern regions (localized areas of CNXJ) exhibit a relatively lower EEQ. The overall EEQ level of CA is categorized as moderate. This trend remained stable throughout the study period, although EEQ fluctuated in certain localized areas.
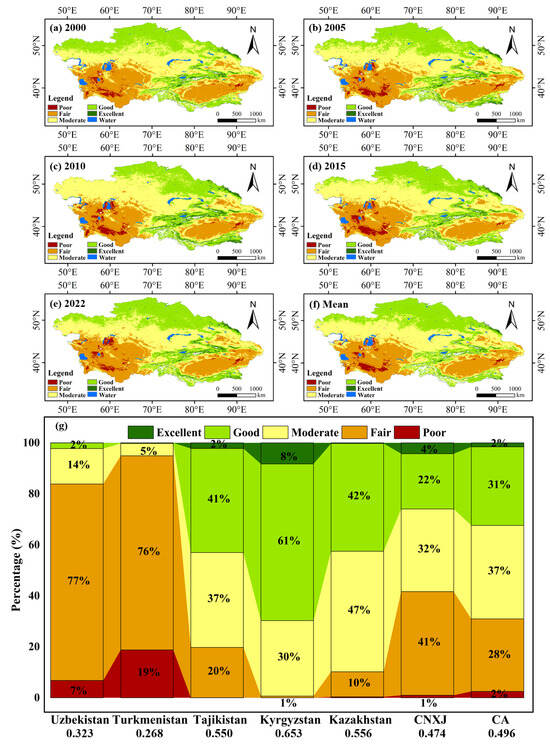
Figure 6.
(a–f) The spatial and temporal distribution of different levels of the ASAEI in CA in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2022 and the average during 2000–2022; (g) percentage of the ASAEI area in different subregions.
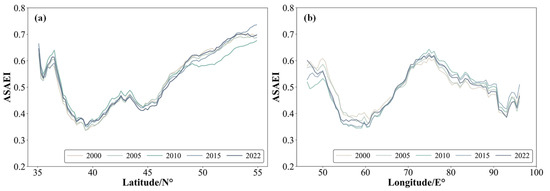
Figure 7.
ASAEI statistics in CA (2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2022). (a) Statistics of the longitude zone and (b) statistics of the latitude zone.
3.3. Volatility of the ASAEI
To further investigate the volatility within specific regions of CA, we analyzed the in the study area from 2000 to 2022 (Figure 8). Table 5 shows the percentage of areas with varying volatility levels. The volatility of the ASAEI in CA is generally low, and a comparison with Figure 6 reveals a strong correlation between ASAEI volatility and its magnitude. Regions with lower ASAEI values typically exhibit higher interannual variability. Areas with moderate to high volatility are primarily located in the southwestern and eastern regions, comprising 10.25% of the total area. In contrast, areas with low to relatively low volatility are mainly concentrated in the northern, northwestern, central, and northeastern regions, covering 89.75% of the total area.
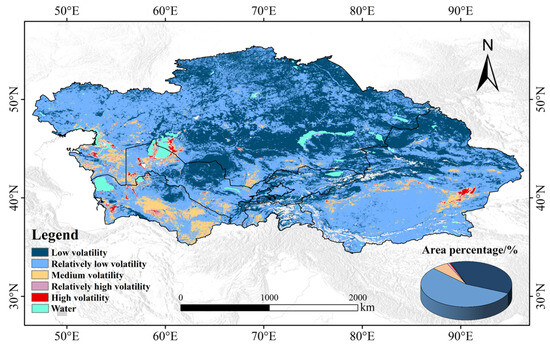
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of the in CA from 2000 to 2022.

Table 5.
Percentages of the areas with different levels of volatility of the ASAEI in CA and its six subregions.
From 2000 to 2022, areas with medium or higher volatility in Turkmenistan accounted for 31.4% of the country’s total area, the highest proportion among the six sub-regions, indicating substantial volatility in the region’s EEQ. In contrast, regions with low or relatively low volatility in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan comprised 96.17%, indicating the most stable EEQ. In CNXJ, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, ASAEI volatility remained relatively stable, with regions exhibiting high or very high volatility comprising less than 2%.
3.4. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the ASAEI
To capture the spatiotemporal variation of ASAEI in CA, we analyzed its changes from 2000 to 2022, along with the transitions in EEQ levels across the six subregions (Figure 9). Changes were classified using the Jenks natural breaks method into three categories: deterioration, stabilization, and recovery. Regions experiencing ecological degradation shifted from west to east over time. From 2000 to 2005, ecological degradation primarily occurred in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, intensifying between 2005 to 2010. From 2010 to 2015, ecological degradation was predominantly observed in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. From 2015 to 2022, regions experiencing ecological degradation shifted to CNXJ. Overall, from 2000 to 2022, ecological restoration in the CA region surpassed degradation, although significant differences existed across geographical subregions: the western part of Kazakhstan primarily experienced degradation, while the eastern part saw restoration. EEQ-level transitions predominantly occurred within the good, moderate, and fair categories. In the other geographical subregions, restoration was the dominant trend. In Turkmenistan, EEQ shifted primarily from poor to fair, while in Kyrgyzstan, it fluctuated predominantly between excellent, good, and moderate levels.
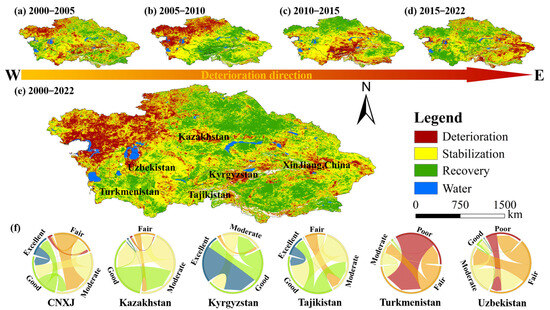
Figure 9.
(a–e) The spatial distribution of EEQ transformation in CA from 2000 to 2005, 2005 to 2010, 2010 to 2015, 2015 to 2022, and 2000 to 2022, respectively. (f) The EEQ level transfer matrix of the six regions in CA from 2000 to 2022.
Spatial trends in ASAEI changes were analyzed using the Sen slope and MK test (Figure 10). From 2000 to 2022, the largest proportion (36.8%) of the CA region exhibited a non-significant increasing trend, primarily in the northern, southern, and eastern areas. Non-significant (30.6%) and slightly significant declining trends (3.2%) were concentrated primarily in the eastern and western regions. Slightly significant (3.2%), significant (4.3%), and extremely significant declining trends (4.8%) were predominantly concentrated in the western part of the study area. The combined proportion of extremely significant, significant, and slightly significant increasing trends was 14.9%, primarily in the central, northeastern, and southwestern regions. These results suggest that, overall, the ASAEI in the study area has shown an increasing trend over the past 23 years, despite declines in some areas.
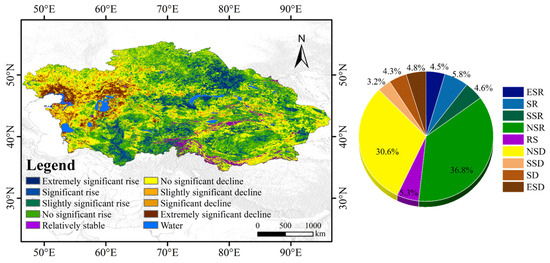
Figure 10.
Distribution of different spatial trends of the ASAEI and the proportion of area occupied by the region.
To further illustrate the ASAEI trend in the CA region, we present the distribution of ASAEI changes across each geographical subregion from 2000 to 2022 (Figure 11). Overall, ASAEI changes in the CA region exhibited an upward trend, with areas showing this trend constituting 54.64% of the total area. Notably, Kazakhstan was the only region exhibiting a downward trend, with the upward trend constituting only 46.55% of its total area. The remaining five geographical subregions, ranked by the proportion of area exhibiting an upward trend, were Tajikistan (79.93%), Kyrgyzstan (66.20%), Turkmenistan (64.34%), Uzbekistan (61.41%), and CNXJ (60.92%).
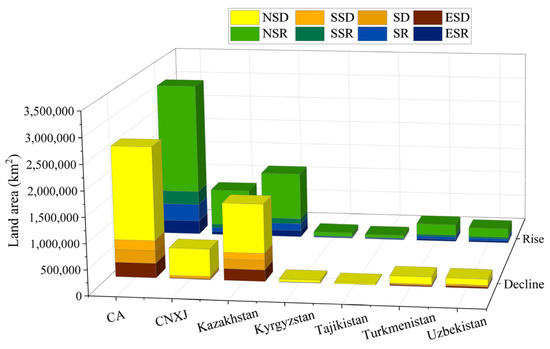
Figure 11.
Distribution of various spatial trends of the ASAEI in the land area of subregions from 2000 to 2022.
3.5. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of the ASAEI
Moran’s I index was used to analyze the potential spatial clustering of ASAEI distribution in the CA region. The global Moran’s I for the ASAEI during the study period was 0.88. These values passed the 1% significance test, indicating significant spatial autocorrelation of ASAEI at the 99% confidence level and reflecting strong spatial clustering of EEQ in the CA region (Figure 12). Positive Moran’s I values indicated spatial clustering of the ASAEI, revealing significant positive spatial autocorrelation in its distribution. Thus, the geographical distribution of ASAEI highlights a clustering pattern of EEQ rather than a random distribution. Specifically, the clustering patterns of ASAEI over the years were similar and largely consistent with the spatial distribution shown in Figure 6. H-H clusters were concentrated in the western, northern, and eastern regions of Kazakhstan, as well as in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, where EEQ was higher. In contrast, L-L clusters were observed in the southwestern and central-southern regions of Kazakhstan, localized areas of CNXJ, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, with some areas exhibiting no significant spatial patterns. In 2010, the area of H-H clusters in the northern region and L-L clusters in the southwestern region had decreased compared to 2000. In 2022, the area of L-L clusters in the western region had increased compared to 2000, while the area of L-L clusters in the southeastern region had decreased. Additionally, the area of H-H clusters in the central region showed a modest increase. These trends are largely consistent with those shown in Figure 9.
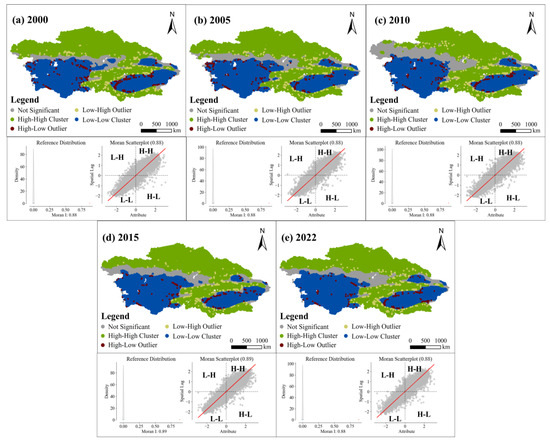
Figure 12.
Spatial clustering distribution of the ASAEI and Moran’s I scatter plot (a–e): 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2022, with the red line indicating the fitted regression line representing the relationship between spatial lag and attribute values.
3.6. Driving Factors of the ASAEI
To investigate the driving factors influencing changes in ASAEI values, 10,000 sampling points were randomly selected within the study area, with a minimum distance of 5 km between adjacent points. The dependent variable (ASAEI) and potential driving factors were extracted from the sampling points. As some datasets were only available until 2020, the years 2000, 2010, and 2020 were selected as samples to analyze the driving factors of the ASAEI. The CatBoost–SHAP regression model was used to identify the driving factors strongly correlated with the ASAEI. The dataset was split into training and test sets in an 80:20 ratio.
Table 6 presents the average results of the CatBoost–SHAP regression model, which was evaluated using 10-fold cross-validation across different years. The evaluation metrics—R2, MAE, and RMSE—consistently performed well across the years, with R2 exceeding 0.921 and the MAE and RMSE below 0.033 and 0.045, respectively. These results suggest that the CatBoost–SHAP regression model demonstrates strong explanatory power and can effectively reveal the relationship between ecological factors and the ASAEI.

Table 6.
Evaluation results of the CatBoost–SHAP regression prediction model using 10-fold cross-validation.
The SHAP value distributions for each variable in different years show their importance in the ASAEI model (Figure 13). They highlight that VPD, IGBP, TMMX, SM, and PET have significant contributions, while TMMN, DEM, SRAD, AET, and VS contribute moderately, and PRE, PDSI, PD, GDP, and EC have low contributions.
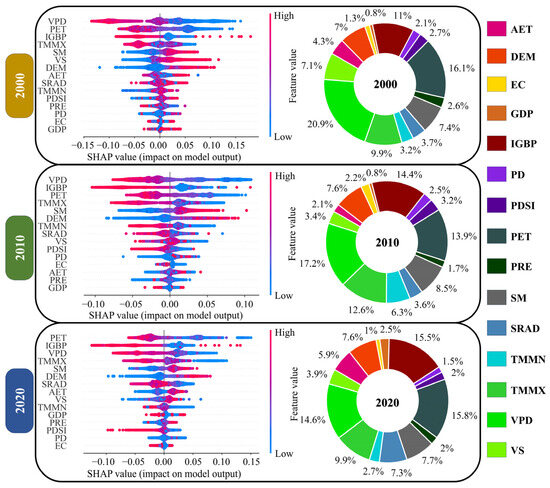
Figure 13.
SHAP waterfall diagrams for the 2000, 2010, and 2020 models (left panels), with color coding indicating feature values from low to high. The horizontal axis shows each feature’s contribution to the model’s output. Mean absolute SHAP value charts for the 2000, 2010, and 2020 models (right panels) represent the relative feature contributions to the overall output.
To further explore the interaction effects among these driving factors, feature elimination was performed to assess their independent impacts on the ASAEI. This analysis was based on the main effects derived from the SHAP evaluation model (Figure 14), with a locally fitted regression trendline shown in the figure. The results show that the positive contributions of VPD, PET, TMMX, and IGBP to the ASAEI diminish progressively as the values of these variables increase. Specifically, once the VPD value reaches 1.5 kPa, the contribution level stabilizes before declining at a steady rate. For PET, the contribution stabilizes gradually when its value reaches 110 mm. When the TMMX value reaches 15 °C, the contribution exhibits a marked, abrupt decrease. As a land cover type variable, IGBP indicates that when the land types are classified as 14 (cropland/natural vegetation mosaics), 15 (permanent snow and ice), and 16 (barren), these land types generally yield negative contributions. The contribution of SM values to the ASAEI is positively correlated. When the SM value reaches 0.10 m3/m3, it begins to contribute positively, with the contribution stabilizing and gradually increasing as the SM value reaches 0.18 m3/m3.
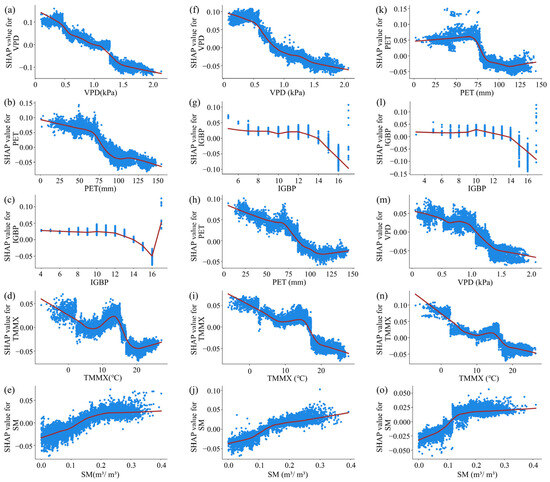
Figure 14.
SHAP main effects of key driving factors on the ASAEI. Panels (a–e) correspond to 2000, (f–j) to 2010, and (k–o) to 2020.
The key driving factors of the ASAEI each year are primarily VPD, IGBP, TMMX, SM, and PET (Figure 13 and Figure 14). Therefore, we superimposed the sampling points from 2000, 2010, and 2020 to investigate the interaction effects between the top five driving factors influencing the ASAEI across these years (Figure 15). These figures facilitate the analysis of how the output of feature A changes in response to feature B. An examination of Figure 14 and Figure 15 reveals the significant coupling and interaction effects between the main driving factors. These effects modify the operating patterns of the features in the model output, resulting in varying degrees of impact.
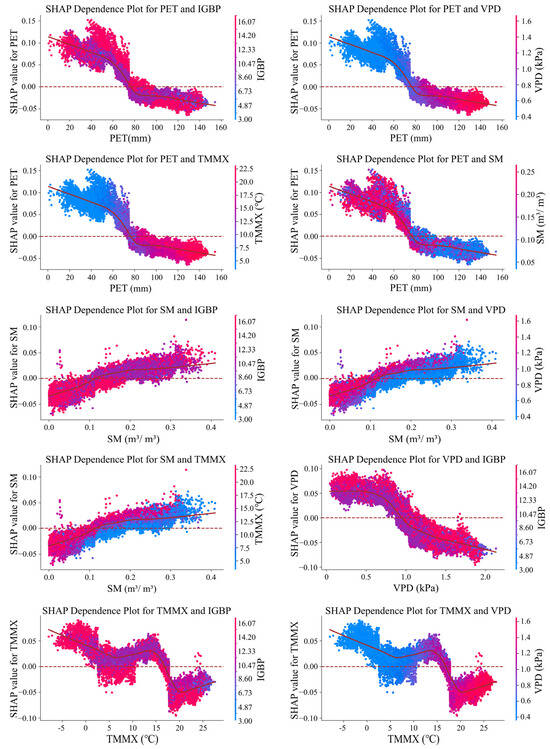
Figure 15.
SHAP Interaction Analysis of Main Drivers Affecting ASAEI.
The research findings indicate that 1. the threshold for the PET value is 78 mm. When the PET value is below 78 mm, lower VPD, lower TMMX, and higher SM values promote an increase in the ASAEI, with the contribution decreasing as the PET value nears the threshold. Possible explanations for this phenomenon are as follows: (1) Lower VPD values indicate that the actual water vapor pressure in the air is close to the saturated vapor pressure, leading to higher relative humidity. Under low evapotranspiration conditions, weaker plant transpiration promotes plant growth [46,47]. (2) Within a specific temperature range, lower TMMX values help reduce water loss from ecosystems due to evapotranspiration [48]. (3) Soil moisture directly influences plant growth and survival, and higher soil moisture better supports plant growth needs [49]. 2. When the SM value is low, higher VPD or TMMX values result in decreased EEQ. Figure 14 shows that the minimum SHAP contribution of the SM value stabilizes at −0.04, whereas under the influence of other factors, it stabilizes around −0.05. This suggests that interactions between factors significantly enhance their explanatory power for the spatial distribution of ASAEI changes in CA. 3. When the IGBP is 12 (croplands) or higher, changes in driving factors such as PET, SM, TMMX, and VPD produce different effects on the numerical changes in the ASAEI. Notably, when the IGBP is 16 (barren), as shown in Figure 14, barren land cover types typically contribute negatively to the ASAEI. However, the contribution can vary between positive and negative when considering the interactions between two factors. This indicates that the influence of potential driving factors on the ASAEI at different spatial scales is not independent or merely additive but is instead the result of interactions among multiple factors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Examination of Future Changes and Their Causes in the ASAEI
The average Hurst index of the ASAEI is 0.43, ranging from 0.05 to 0.99, suggesting that the overall trend of ASAEI changes exhibits a reverse pattern (Figure 16a). In total, 77.22% of the values have a Hurst index of less than 0.5, implying that the future trend of CA will diverge from the pattern observed over the past 23 years. This trend is primarily observed in the southeast and northern regions. In contrast, 22.78% of the values have a Hurst index greater than or equal to 0.5, suggesting that the future trend of CA will align with the pattern observed over the past 23 years, primarily in the central-southern and southwestern regions of CA.
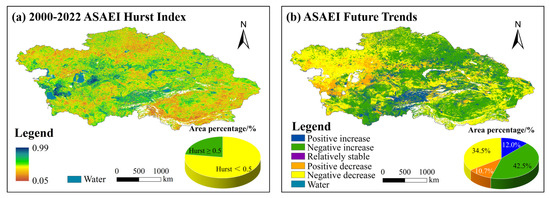
Figure 16.
(a) The spatial distribution of the Hurst exponent of the ASAEI from 2000 to 2022, and (b) the distribution of future trends in the ASAEI.
To further examine the future development trend of CA’s ASAEI, the spatial trends of the ASAEI from 2000 to 2022 (increase, stable, or decrease) were analyzed in conjunction with two sustainability indices (negative and positive), identifying five development trends: two positive trends (positive increase and negative increase), two negative trends (positive decrease and negative decrease), and relative stability [50]. The overall development trend of CA is projected to move in a positive direction, with 54.5% of regions expected to show an increasing trend in the future (Figure 16b). Among regions that previously experienced a decline, 42.5% are expected to experience growth, primarily concentrated in the central and eastern parts of CA (negative increase). In total, 12.0% of regions have experienced sustained growth (positive increase), primarily in the central-southern part of CA. A total of 34.5% of regions that previously experienced growth are projected to undergo a decline in the future (negative decrease), primarily in the western and eastern parts of CA. Only 10.7% of regions show a sustained declining (positive decrease) trend, with these areas being relatively small and primarily concentrated in the western part of CA.
We investigated the underlying causes of these conclusions. Notably, approximately 80% of the southwestern region (Turkmenistan) is desert, though it holds potential for future ecological restoration. This is closely linked to the government’s strong emphasis on environmental protection and the implementation of various policies, including the rational allocation of water resources for irrigated agriculture and the promotion of crop diversification [51]. In the southeast (CNXJ), ecological restoration is also evident, primarily driven by the development of oases. In the oasis regions of Xinjiang, dynamic changes in land use and ecological management practices, such as vegetation restoration and optimized water resource use, play key roles in sustaining the oasis ecosystem [52,53]. However, in the western regions (western Kazakhstan and western Uzbekistan), ecological degradation is more pronounced. The causes, as identified in this investigation, are as follows: First, the overuse and wastage of water resources upstream of the Aral Sea have led to an insufficient water supply, resulting in a dramatic reduction in the Aral Sea’s size, severe salinization and desertification of surrounding areas, and climate change, which further threaten the region’s ecological environment [54]. Additionally, the ecological situation in the northern Caspian Sea is deteriorating, linked to shallow water levels and the accelerated shrinking of the lake due to climate warming [55]. Water resource management and ecological restoration measures have been implemented in CA, but significant challenges remain in preventing further ecological degradation [51].
4.2. Reliability, Applicability, and Scientific Interpretation of the ASAEI Model
To comprehensively evaluate the reliability and applicability of the ASAEI model in ASARs, we conducted a systematic assessment across four dimensions: model accuracy, consistency with the existing literature, ecological and geographical mechanism interpretations, and practical application value.
The ASAEI demonstrated superior performance over the RSEI in identifying EEQ across multiple dimensions. First, the regression analysis of random sample points showed a significant positive correlation between the ASAEI and RSEI (R2 = 0.8561), verifying the effectiveness of the ASAEI in capturing the overall EEQ trends (Figure 3a). However, the ASAEI exhibited finer texture details and clearer boundary features in low-quality ecological areas, such as regions classified as “poor”, showing enhanced sensitivity to ecological degradation zones (Figure 3b,c). Further comparisons with high-resolution Sentinel-2 imagery (Figure 4) revealed that ASAEI’s classifications were more consistent with the actual geomorphological and vegetation conditions, particularly in arid grasslands, croplands, and desert areas (Figure 5). This approach effectively overcame the tendency of the RSEI to underestimate EEQ in ASAR land types.
Moreover, the spatial patterns of EEQ identified by the ASAEI aligned closely with previous research findings, where degradation hotspots were mainly concentrated in the southwestern and southeastern parts of CA [56,57].
From an ecological–geographical perspective, the ASAEI effectively captured the characteristic ecological gradients across CA. For instance, the northern regions (e.g., Kazakhstan), influenced by the westerly circulation, experience relatively humid climates and better ecological conditions, whereas the southwestern and southeastern areas (e.g., Turkmenistan and CNXJ) are constrained by desert geomorphology and arid climates, leading to poorer EEQ (Figure 6). This distribution pattern is consistent with the influence pathways of major climatic control systems, such as the Tibetan Plateau climate system and the westerlies [58], highlighting ASAEI’s strong ecological responsiveness and climatic adaptability at the regional scale.
Regarding dynamic monitoring and practical application, ASAEI demonstrated high stability and sensitivity across both spatial and temporal dimensions. Multi-dimensional analyses, including fluctuation analysis (Figure 8), ecological grade transition trajectories (Figure 9), and trend analyses using Sen’s slope and the Mann–Kendall (MK) test (Figure 10), jointly demonstrated ASAEI’s sensitive response to ecological evolution. Meanwhile, the spatial autocorrelation analysis (Figure 12) revealed significant spatial clustering of the ASAEI results, enabling the effective identification of “high ecological value zones” and “core degradation areas”, thus providing a quantitative basis for ecological risk warning, priority area management, and spatial zoning.
ASAEI exhibits remarkable advantages in indicator design, result reliability, geographical adaptability, and spatial interpretability, establishing itself as an effective tool for ASAR multi-scale EEQ monitoring and management.
4.3. Analysis of the Driving Factors of the ASAEI
Climate change and land use changes are well-established drivers of ecological variations in CA [57,59,60]. The SHAP analysis revealed that variations in the ASAEI are jointly driven by multiple ecological and environmental factors, exhibiting significant nonlinear responses and interactions among variables (Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15). First, regarding the main effects of individual factors (Figure 13 and Figure 14), the key climatic drivers aligned with our established understanding: increases in VPD and potentially PET led to a significant decrease in ASAEI values, with negative SHAP values, indicating that intensified atmospheric dryness strongly suppresses arid region ecosystems. This finding confirms the limiting effect of atmospheric moisture deficits on vegetation productivity, where high evaporative demand and dry atmospheric conditions exacerbate ecosystem water stress, thereby inhibiting ecological vitality [61]. Conversely, increased SM positively influenced the ASAEI (positive SHAP values), highlighting the beneficial role of a sufficient water supply in enhancing the ecosystem status in arid regions. This finding is consistent with the fundamental role of water as the principal limiting resource in arid ecosystems.
Additionally, the effect of TMMX on the ASAEI exhibited a nonlinear threshold pattern: at low to moderate temperature ranges, increases in TMMX had a relatively mild and occasionally slightly positive impact; however, beyond a certain threshold, further warming significantly reduced the ASAEI. Enhanced transpiration and heat stress at high temperatures led to sharp declines in the ASAEI (Figure 14). This nonlinear relationship illustrates the “double-edged sword” effect of temperature on ecosystems: moderate warming may yield positive effects, whereas extreme heat results in net negative impacts [62]. Different IGBP vegetation types exhibited varying baseline ASAEI levels and sensitivities. For instance, forest ecosystems typically maintained higher baseline ASAEI values, while desert shrublands exhibited lower baselines; moreover, the magnitude of their responses to climatic factors varied considerably. These patterns reflect the role of plant functional traits, such as rooting depth and water use efficiency, in modulating ecosystem responses to climatic variability.
Interactions between driving factors further deepened the understanding of ASAEI variation mechanisms (Figure 15). The bivariate dependency analysis revealed that when two factors change simultaneously, their combined impact on the ASAEI is not merely additive but often exhibits synergistic or offsetting nonlinear effects. For example, the interaction between PET and VPD showed a pronounced synergistic effect: under extreme atmospheric dryness (high VPD), further increases in PET resulted in sharper declines in the ASAEI, indicating that the co-occurrence of a high evaporative demand and strong atmospheric aridity significantly exacerbates ecosystem water stress, leading to a greater decline than either factor would cause individually. Previous studies have similarly found that when high temperature and drought occur simultaneously, the suppression of vegetation growth is significantly greater than under either stressor alone [63]. Moreover, the interaction between PET and SM displayed a buffering effect: under sufficient SM conditions, even high PET levels resulted in less severe declines in the ASAEI than under dry soil conditions. This suggests that adequate soil water can substantially mitigate drought stress caused by a high evaporative demand [64]. In other words, improved moisture conditions can partially offset the negative ecological impacts of climate-induced aridity under drought scenarios.
Similarly, when soils are dry, even moderate warming can significantly reduce the ASAEI; in contrast, ecosystems exhibit higher thermal tolerance under moist soil conditions, and the negative effects of heat are greatly diminished. In addition, interactions between vegetation types and climatic factors further illustrated the heterogeneity of ecological responses. The response magnitude of the ASAEI to changes in PET or VPD varied significantly among different IGBP types. Forest and shrubland ecosystems showed relatively moderate ASAEI changes under the same climatic conditions, whereas other types (those with IGBP class numbers greater than seven) exhibited much more pronounced fluctuations. These differences may stem from the varying tolerance of plant functional types to hydrothermal changes. For example, deep-rooted species can access subsoil moisture to alleviate drought stress, while shallow-rooted vegetation is more prone to functional decline during soil water shortages.
The variation in the ASAEI results from the intertwined nonlinear interactions among multiple climatic and ecological factors, rather than from the linear influence of any single factor. Each driving factor affects the ASAEI both through its main effects and through interaction effects that either reinforce or offset one another. In some cases, their impacts amplify one another, such as concurrent atmospheric drought and heat intensifying ecological stress, while in other cases, they partially counteract each other, as when adequate soil moisture mitigates the adverse effects of heat and drought. Therefore, adopting an integrated perspective that simultaneously considers the combined effects of multiple factors is essential for understanding ecosystem dynamics in arid regions. The application of the SHAP analysis, which quantifies both main and interaction effects of driving factors, provides an effective approach to unraveling these complex relationships. This approach not only deepens our understanding of the dynamic mechanisms underlying ASAEI variations but also offers a scientific basis for future assessments of the combined impacts of climate change and human activities on dryland ecosystems.
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
This study developed an EEQ evaluation framework tailored to ASARs, assessing the EEQ of CA from multiple perspectives. However, several limitations remain that should be addressed in future research. (1) While the ASAEI model demonstrates better applicability than the RSEI in ASARs, uncertainties related to the natural environmental complexity of the study area persist. Therefore, future research should focus on integrating additional ecological assessment data, incorporating regional dimensions to develop a more comprehensive ecological evaluation system. (2) The ASAEI model relies on remote sensing imagery, and its accuracy is constrained by the image quality and spatial resolution, which may introduce errors in EEQ assessments. Future work should enhance model accuracy by integrating multi-source, high-resolution imagery (e.g., Sentinel-2 and Landsat series) and standardizing the seasonal time window annually to reduce cloud cover and extreme weather interference. (3) Climate factors are the primary drivers of ASAEI changes. This study employed the CatBoost–SHAP model to explore the interaction directions, boundaries, and thresholds of the driving factors influencing ASAEI spatial heterogeneity. Still, it did not examine the mechanisms by which climate factors drive changes in EEQ. Future research should focus on understanding the mechanisms underlying these driving factors. (4) Although 10-fold cross-validation was applied during model training to mitigate the risk of overfitting and ensure stable predictions across years, the inherent complexity of the CatBoost algorithm and the high dimensionality of remote sensing variables still pose a risk of limited model generalization. Future work could incorporate cross-regional datasets to validate model transferability or further adopt ensemble modeling strategies to enhance the assessment framework’s robustness and adaptability.
5. Conclusions
This study developed a Remote Sensing Ecological Assessment Index (ASAEI) tailored for ASARs. It systematically revealed the spatial patterns, temporal dynamics, and future trends of EEQ in CA from 2000 to 2022. The results demonstrated that the ASAEI outperformed traditional models in ecological identification accuracy, geomorphological adaptability, and spatiotemporal stability, effectively delineating ecological degradation and recovery areas. Overall, the regional ecological condition exhibited fluctuating improvements, with high-value areas concentrated in the northern zones and mountain–oasis belts, while low-value areas were primarily located in the desert and Gobi regions. The CatBoost–SHAP model identified key climatic factors, such as VPD, PET, and SM, along with land use types, as dominant variables. Their nonlinear interactions played a significant role in modulating ecological responses. The future trend analysis suggests that approximately half of the region is expected to experience continued ecological improvement, while certain areas, particularly in the west, remain under degradation pressure and require targeted attention. This study broadens the application scope of remote sensing-based ecological indices for regional-scale monitoring, offering theoretical insights and a technical pathway for understanding ecosystem responses and implementing integrated management in ASARs.
Author Contributions
Y.L.: research, conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. J.W. and J.D.: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, and project administration. Z.Z. (Zipeng Zhang) and Z.L.: research and methodology. Z.Z. (Zihan Zhang), J.Z. and L.S.: supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Key Program of the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U2003202), The Technology Innovation Team (Tianshan Innovation Team), Innovative Team for Efficient Utilization of Water Resources in Arid Regions (NO. 2022TSYCTD0001), The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41961059), and The National Natural Science Foundation of China (42171269).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EEQ | Ecological environmental quality |
| ASAEI | Arid and Semi-Arid Environmental Index |
| MSAVI | Modified Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index |
| WET | Wetness component |
| LST | Land surface temperature |
| SI | Composite salinity index |
| TGSI | Topsoil Grain Size Index |
| RSEI | Remote Sensing Ecological Index |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| NDBSI | Normalized Difference Bare Soil Index |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| ASARs | arid and semi-arid regions |
| CA | Central Asia |
| CNXJ | Xinjiang, China |
| DEM | Digital elevation model |
| IGBP | International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme |
| SM | 1 km surface soil moisture |
| AET | Actual evapotranspiration |
| PDSI | Palmer drought severity index |
| PET | Reference evapotranspiration |
| PRE | Precipitation accumulation |
| SRAD | Downward surface shortwave radiation |
| TMMN | Minimum temperature |
| TMMX | Maximum temperature |
| VPD | Vapor pressure deficit |
| VS | Wind speed |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| EC | Electricity consumption |
| PD | Population density |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| MK | Mann–Kendall |
| ESR | Extremely significant rise |
| SR | Significant rise |
| SSR | Slightly significant rise |
| NSR | No significant rise |
| RS | Relatively stable |
| NSD | No significant decline |
| SSD | Slightly significant decline |
| SD | Significant decline |
| ESD | Extremely significant decline |
References
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Xin, Q. Ecological responses to climate change and human activities in the arid and semi-arid regions of Xinjiang in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, G.; Guo, M. “Dry gets drier, wet gets wetter”: A case study over the arid regions of central Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 1072–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morante-Carballo, F.; Montalván-Burbano, N.; Quiñonez-Barzola, X.; Jaya-Montalvo, M.; Carrión-Mero, P. What do we know about water scarcity in semi-arid zones? A global analysis and research trends. Water 2022, 14, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.; Bashari, H.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Jafari, R. Assessing the impacts of land use and land cover changes on soil functions using landscape function analysis and soil quality indicators in semi-arid natural ecosystems. Catena 2019, 177, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; He, J. Spatial and temporal variation of ecological quality in northeastern China and analysis of influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Du, P.; Guo, S.; Lin, C.; Zheng, H.; Fu, P. Enhanced remote sensing ecological index and ecological environment evaluation in arid area. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 27, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; She, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, C. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Ecological Environment Quality in Ningxia Based on Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Ecol. Environ. 2024, 33, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.-L.; Wang, Z.-W.; Tian, S.-F.; Liu, Y.-T.; Sun, M.-Y.; Yang, Y.-M. Evaluation of eco-environmental quality in Mentougou District of Beijing based on improved remote sensing ecological index. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 1177. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, C.; Marinello, F. Instability of remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) and its improvement for time series analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Altansukh, O.; Chuluun, T. Spatial-temporal pattern of desertification in the Selenge River Basin of Mongolia from 1990 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1125583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinove, C.J. Space platform albedo measurements as indicator,,,s of change in arid lands. Adv. Space Res. 1983, 2, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamchin, M.; Lee, W.-K.; Jeon, S.W.; Lee, J.-Y.; Song, C.; Piao, D.; Lim, C.H.; Khaulenbek, A.; Navaandorj, I. Correlation between desertification and environmental variables using remote sensing techniques in Hogno Khaan, Mongolia. Sustainability 2017, 9, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F. Spectral vegetation indices performance evaluated for Cholistan Desert. J. Geogr. Reg. Plan. 2012, 5, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Ding, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Sensitivity analysis of soil salinity and vegetation indices to detect soil salinity variation by using Landsat series images: Applications in different oases in Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5007–5022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.; Lv, T. Identifying regional eco-environment quality and its influencing factors: A case study of an ecological civilization pilot zone in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Yu, W.; Zhou, L.; Liang, C. Atmospheric and surface-condition effects on CO2 exchange in the Liaohe Delta Wetland, China. Water 2017, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, D.; Hua, T.; Marchi, M.; Urrego, J.P.F.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F. Changes in multiple ecosystem services and their influencing factors in Nordic countries. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Zhai, J. Spatio-temporal variation of potential evapotranspiration and climatic drivers in the Jing-Jin-Ji region, North China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Bi, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in Central Asia’s arid regions: A case study in Altay Prefecture, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Hu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Han, B.; Wang, H. Spatial patterns of residents’ daily activity space and its influencing factors based on the catboost model: A case study of nanjing, china. Front. Arch. Res. 2022, 11, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, Y. Spatial distribution and source identification of potentially toxic elements in Yellow River Delta soils, China: An interpretable machine-learning approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Fu, W.; Lu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, G. Space recognition of eco-environment global change response of arid and semi-arid region of the Silk Road Economic Belt. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2016, 31, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Han, L.; Wang, R.; Qin, S. Central Asia’s desertification challenge: Recent trends and drives explored with Google Earth Engine. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Yang, Q. Hydro-climatic changes and their impacts on vegetation in Xinjiang, Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.-Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.-W.; Dilinuer, T.; Mao, W.-Y. Stationarity in the variability of arid precipitation: A case study of arid Central Asia. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate change on key soil ecosystem services and interactions in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Angal, A.; Chang, T.; Chiang, K.; Lei, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Twedt, K.; Wu, A. MODIS and VIIRS calibration and characterization in support of producing long-term high-quality data products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Altansukh, O.; Chuluun, T. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving mechanisms of desertification on the Mongolian Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Li, L.; Yan, M.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. Thirty years’ spatio-temporal evolution of desertification degrees and driving factors in Turpan–Hami Basin, Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Marin, D.; Dash, J.; Ogutu, B. The use of remote sensing for desertification studies: A review. J. Arid. Environ. 2022, 206, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, A.; Boulghobra, N.; Allache, F.D. Assessment. Multi-temporal Landsat imagery and MSAVI index for monitoring rangeland degradation in arid ecosystem, case study of Biskra (southeast Algeria). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Guo, B.; Zang, W.; Ge, D.; Luo, W.; Zhao, H. Natural Hazards; Risk. Desertification detection model in Naiman Banner based on the albedo-modified soil adjusted vegetation index feature space using the Landsat8 OLI images. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, T.; Zhen, N.; Niu, R. Monitoring the effects of open-pit mining on the eco-environment using a moving window-based remote sensing ecological index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15716–15728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Bentéjac, C.; Csörgő, A.; Martínez-Muñoz, G. A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1937–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Cui, W.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, W. A hybrid strategy of AutoML and SHAP for automated and explainable concrete strength prediction. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T.; Kahya, E. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Application of improved Moran’s I in the evaluation of urban spatial development. Spat. Stat. 2023, 54, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-term storage capacity of reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitrano, C.; Arena, C.; Rouphael, Y.; De Pascale, S.; De Micco, V. Vapour pressure deficit: The hidden driver behind plant morphofunctional traits in controlled environments. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2019, 175, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yao, J.; Zheng, J. Spatio-temporal changes in atmospheric aridity over the arid region of Central Asia during 1979–2019. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Yu, X.; Tian, R.; Han, W.; Guan, J. Increasing influence of minimum temperature on grassland spring phenology in arid Central Asia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 355, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Guan, J.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Strong positive direct impact of soil moisture on the growth of central asian grasslands. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, H.; Shao, H.; Li, A.; Li, S.; Fan, W. Temporal and spatial variations in the leaf area index and its response to topography in the Three-River Source Region, China from 2000 to 2017. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Usman, M.; Morper-Busch, L.; Schönbrodt-Stitt, S. Remote sensing-based assessments of land use, soil and vegetation status, crop production and water use in irrigation systems of the Aral Sea Basin. A review. Water Secur. 2020, 11, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; He, H.; Zong, R.; Wang, D.; Jia, Z.; Wen, Y. Experiences and challenges of agricultural development in an artificial oasis: A review. Agric. Syst. 2021, 193, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuti, T.; Luo, G. Analysis of land cover change and its driving forces in a desert oasis landscape of Xinjiang, northwest China. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Shrinking of Aral Sea: An environmental disaster in Central Asia. Int. J. Humanit. Arts Soc. Sci. 2020, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koriche, S.A.; Singarayer, J.S.; Cloke, H.L. The fate of the Caspian Sea under projected climate change and water extraction during the 21st century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 094024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.-Q.; Chen, Y.-N.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ding, J.-L. Spatiotemporal changes in ecological quality and its associated driving factors in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, M. Spatial characteristics and trade-offs of ecosystem services in arid central asia. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zou, S.; Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y. Spatiotemporal variability in extreme precipitation and associated large-scale climate mechanisms in Central Asia from 1950 to 2019. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, X.; Qin, Y.; Xu, F. Spatiotemporal differentiation and mechanisms of ecological quality in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushanjiang, A.; Zhang, F.; Tan, M.L. Spatial-temporal characteristics of ecosystem health in Central Asia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.; Ma, S.; Verfaillie, J. On the inter-and intra-annual variability of ecosystem evapotranspiration and water use efficiency of an oak savanna and annual grassland subjected to booms and busts in rainfall. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhou, W.; Liang, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Yang, Q.; et al. Transcriptome and metabolite reveal the inhibition induced by combined heat and drought stress on the viability of silk and pollen in summer maize. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 226, 120720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Piao, S.; Chen, A.; Huntingford, C.; Fu, B.; Li, L.Z.; Huang, J.; Sheffield, J.; Berg, A.M.; Keenan, T.F.; et al. Multifaceted characteristics of dryland aridity changes in a warming world. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Mao, J.; Bachmann, C.M.; Hoffman, F.M.; Koren, G.; Chen, H.; Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Tao, J.; Tang, J.; et al. Soil moisture controls over carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas emissions: A review. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).