Abstract
Sea ice and its surface snow are crucial components of the energy cycle and mass balance between the atmosphere and ocean, serving as sensitive indicators of climate change. Observing and understanding changes in snow depth on Antarctic sea ice are essential for sea ice research and global climate change studies. This study explores the feasibility of retrieving snow depth on Antarctic sea ice using data from the Chinese marine satellite HY-2B. Using generic retrieval algorithms, snow depth on Antarctic sea ice was retrieved from HY-2B Scanning Microwave Radiometer (SMR) data, and compared with existing snow depth products derived from other microwave radiometer data. A comparison against ship-based snow depth measurements from the Chinese 35th Antarctic Scientific Expedition shows that snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR data using the Comiso03 retrieval algorithm exhibits the lowest RMSD, with a deviation of −1.9 cm compared to the Markus98 and Shen22 models. The snow depth derived using the Comiso03 model from HY-2B SMR shows agreement with the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product released by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Differences between the two primarily occur during the sea ice ablation and in the Bellingshausen Sea, Amundsen Sea, and the southern Pacific Ocean. In 2019, the monthly average snow depth on Antarctic sea ice reached its maximum in January (36.2 cm) and decreased to its minimum in May (15.3 cm). Thicker snow cover was observed in the Weddell Sea, Ross Sea, and Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas, primarily due to the presence of multi-year ice, while thinner snow cover was found in the southern Indian Ocean and the southern Pacific Ocean. The derived snow depth product from HY-2B SMR data demonstrates high accuracy in retrieving snow depth on Antarctic sea ice, highlighting its potential as a reliable alternative for snow depth measurements. This product significantly contributes to observing and understanding changes in snow depth on Antarctic sea ice and its relationship with climate change.
1. Introduction
Sea ice is a crucial component of the polar region, characterized by significant variations in its presence on both seasonal and interannual scales, thereby representing a significant feature of the Southern Ocean [,]. Due to its high reflectivity to incoming shortwave radiation, sea ice, along with its surface snow, acts as an insulating layer between the atmosphere and the ocean, playing a vital role in balancing heat exchange and exerting a notable influence on atmospheric circulation and the hydrological cycle, which serves as an essential element of the global climate system [,,]. Snow exerts a pivotal influence on the growth and ablation processes of sea ice. During the growth period, the reduced thermal conductivity of snow slows the growth of sea ice, whereas during the melting period, the high albedo of the snow mitigates the solar radiation absorbed by the sea ice, thereby slowing the ablation process [,]. Snow depth on sea ice is an important parameter that affects the properties of the snow, and it is one of the most challenging variables to measure in the polar climate system [,]. Additionally, snow depth is critical for deriving sea ice thickness from a satellite altimeter, impacting the accuracy of sea ice thickness and volume retrieval [,,]. Consequently, understanding the mechanisms governing sea ice variation and the associated climate implications necessitates the investigation of snow depth on sea ice. However, the harsh climatic conditions prevailing in Antarctica, combined with the scarce field measurements, emphasize the urgent need to enhance research on large-scale variations in snow depth on Antarctic sea ice.
Field observations and airborne snow radar measurements are employed for investigating snow depth on sea ice. Notable data sources include in situ snow depth observations hosted by the Australian Antarctic Data Centre (AADC), ship-based observations from the Antarctic Sea Ice Processes and Climate (ASPeCt) initiative, and airborne measurements collected during Operation IceBridge (OIB) [,,]. However, these data provide localized and time-specific information on snow depth. Hence, passive microwave remote sensing, with the advantages of being low-cost and having daylight and weather-independent observations, has become a preferred method for obtaining long-term, large-scale snow depth variations on Antarctic sea ice [,].
Markus and Cavalieri (1998) first constructed a regression model using the gradient ratio (GR) of the vertically polarized brightness temperature at 19 and 37 GHz measured from the Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) sensor with ship-based snow depth observational data []. Comiso et al. (2003) subsequently adapted the algorithm to passive microwave remote sensing data from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for Earth Observing System (AMSR-E) []. Sturm et al. (2006) identified a robust correlation between surface roughness of sea ice and snow depth []. Worby et al. (2008) and Kern et al. (2015) validated this correlation using ice station measurements and ship-based observations, respectively, on rough sea ice in the Eastern Antarctic and the Bellingshausen Sea, respectively; the AMSR-E snow products underestimate the observed snow depth by a factor of two to four [,]. Markus et al. (1998) also confirmed the impact of surface roughness on snow depth retrieval using ICESat data []. Rostovsky et al. (2018) attempted to use lower frequencies for retrieving deep snow and making the algorithm applicable to multi-year ice in the Arctic, utilizing five years of airborne snow data from OIB []. Shen et al. (2022) analyzed seven-year airborne measured snow depth data from OIB, deriving new coefficients of the regression model to enhance snow depth retrieval using gradient ratios calculated at 7 and 39 GHz in the vertical polarization channels of passive microwave radiometers [].
As the research on the retrieval of snow depth from passive microwave data continues to advance, various organizations have released snow depth products. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) released the products of snow depth on Arctic first-year sea ice, which were derived from SSM/I data spanning 1978–2007. The University of Bremen (UB) and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) released snow depth products for 2002–2011 derived from AMSR-E data. Subsequently, the NSIDC released snow depth products from 2011 to the present study using AMSR-2 (Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer 2) data. However, due to the limitations of satellite sensor lifespans, the AMSR-E and AMSR-2 snow depth products are discontinuous in time. It should be noted that there is no Antarctic snow depth product released by Chinese organizations using passive microwave data from Chinese satellite measurements. The Chinese ocean series satellites (HY), launched by the National Satellite Ocean Application Center, include HY-2A (launched on 16 August 2011), an experimental satellite; HY-2B (launched on 25 October 2018), a sun-synchronous orbit satellite; and HY-2C/2D (launched on 21 September 2020 and 19 May 2021, respectively), which are inclined orbit (non-sun-synchronous orbit) satellites. These satellites form a three-star integrated satellite constellation to obtain real-time high-precision ocean dynamic environmental parameters such as global sea surface height, sea surface temperature, and sea surface wind field, supporting efforts to prevent and mitigate marine disasters, as well as to protect and develop marine resources. Currently, HY-2B Scanning Microwave Radiometer (SMR) brightness temperature data are applied to retrieve parameters such as sea ice concentration and sea ice drift. Despite this, the potential of utilizing HY-2B SMR data for the retrieval of snow depth on Antarctic sea ice represents a significant and innovative exploration, holding the promise of advancing our understanding of key polar climatic interactions and sea ice dynamics.
Against this background, this study utilized HY-2B SMR data, combined with the ship-based observational snow depth from the R/V XueLong, to investigate the feasibility of retrieving snow depth on Antarctic sea ice from Chinese HY-2B satellite data based on different snow depth retrieval models. The derived HY-2B snow depth was also compared and evaluated against the AMSR-2 snow depth product released by the NSIDC.
2. Data
2.1. Study Area
The study area in this paper encompasses the ocean surrounding Antarctica, specifically at latitudes above 60°S. Due to the regional influences, sea ice and its surface snow exhibit significantly different characteristics around Antarctica [,]. To better analyze the spatial distribution and the underlying processes, the Antarctic Ocean is commonly divided into five sectors: Weddell Sea (60°W–20°E), Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas (130°–60°W), Ross Sea (160°E–130°W), Southern Indian Ocean (90°–160°E), and the Southern Pacific Ocean (20°–90°E) (Figure 1a). In general, Antarctic sea ice has rapidly decreased in recent years. After breaking low Antarctic sea ice extent records in 2016 and 2022, the extent reached its lowest historical level in the past 40 years in 2023 [,]. In the Antarctic Ocean, sea ice levels fluctuate seasonally; only the coastal regions of the Antarctic continent retain ice during the melting season, whereas the ice cover extends further from the shore during the ice growth season [].
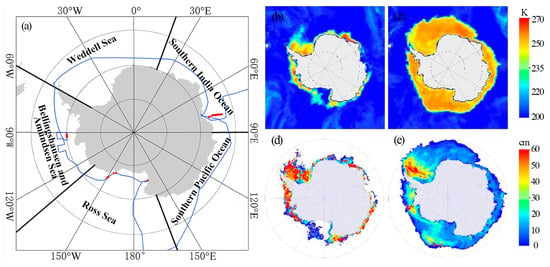
Figure 1.
(a) Five sectors in the Southern Ocean: the blue line represents the R/V XueLong routes during the 35th Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE-35), and the red dots indicate the measurement points of snow depth on sea ice conducted by the ship, (b,c) are the brightness temperature measured by HY-2B SMR at 18.7 GHz on 1 January and 1 July, 2019, respectively, and (d,e) are the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth products released by the NSIDC on 1 January and 1 July, 2019, respectively.
2.2. HY-2B SMR and GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 Brightness Temperature Data
The passive microwave brightness temperature data used in this study were obtained from two sources: HY-2B SMR L2A brightness temperature data from the National Satellite Ocean Application Center (NSOAC) and GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 L3 brightness temperature data from the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Both datasets have a spatial resolution of 25 km with the polar stereographic grid. The HY-2B SMR L2A brightness temperature data include five frequency channels: 6.93, 10.65, 18.7, 23.8, and 37.0 GHz. Except for the 23.8 GHz channel, which has only vertical polarization mode, each frequency channel has both vertical (V) and horizontal (H) polarization modes (Table 1). Prior to using the HY-2B SMR L2A brightness temperature data, geolocation correction, reprojection, and daily synthesis preprocessing were performed. All brightness temperature data measured over one calendar day were processed and mapped onto the polar stereographic grid provided by the NSIDC. (Figure 1b,c). The GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 L3 brightness temperature data consist of six frequency channels: 6.93, 10.65, 18.7, 23.8, 36.5, and 89.0 GHz, all of which have both vertical (V) and horizontal (H) polarization modes. The GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 L3 brightness temperature data are used to analyze the influence of brightness temperature differences observed by different sensors on the retrieval of snow depth on sea ice.

Table 1.
Main characteristics of HY-2B SMR and GCOM-W1 AMSR2.
2.3. NSIDC Snow Depth Data Product and Ship-Based Observational Snow Depth Data
To retrieve the snow depth on sea ice from the HY-2B SMR data and perform a comparative analysis with frequently used snow depth products, the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth data product released by the NSIDC was utilized (Figure 1d,e). The NSIDC AMSR-2 snow depth has a spatial resolution of 25 km and a temporal resolution of 1 day.
Ship-based snow depth observational data were used to validate the HY-2B SMR-derived snow depth. These snow depth data were collected during the 35th Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE-35). During CHINARE-35 (from November 2018 to January 2019), a camera and a known-size reference ball were fixed on the R/V XueLong to record sea ice conditions and the snow depth on sea ice along the ship’s track, which followed a standardized photogrammetric method (Figure 2). As the ship sailed through the ice, sea ice bended and reversed, and the process was captured on the camera observing at a frequency of 14 frames per second. Pixel values of snow depth could be obtained from the image. To reduce errors, we selected three places (L12, L34, and L56) and calculated the average value to represent the real pixel value of snow depth. The pixel value of the reference ball diameter was also obtained (LAB). Combined with the actual diameter of the reference ball (Dball = 30 cm), the actual snow depth (Dsnow) could be calculated through the following equation: Dsnow = (L12 + L34 + L56) × . The error of this ship-based observed snow depth was less than 7% []. Due to environmental factors such as photography failure during the ship’s voyage and the quality of the photographic images, a total of 1248 ship-based snow depth measurements, distributed in various sectors of Antarctica, were obtained in this study for evaluating the accuracy of the HY-2B SMR derived snow depth.
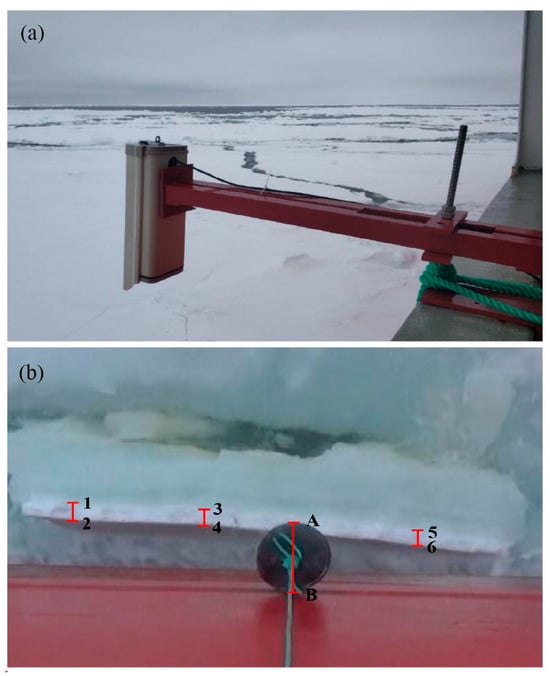

Figure 2.
(a) A measured camera fixed on the R/V XueLong used to record sea ice and snow situation during the 35th Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition and (b) snow depth estimation involving photogrammetric images. The long red line in (b) denotes the reference ball diameter and the short red lines denote snow depth on sea ice.
3. Methods
3.1. Snow Depth Retrieval Model
The snow layer on the sea ice surface scatters the electromagnetic waves emitted by the sea ice [,]. The energy received by the passive microwave sensor is related to the snow depth and the microwave frequency channel. As snow depth and microwave frequency increase, the radiated energy of the sea ice increases due to the scattering by the snow layer. Based on this physical principle, the difference in the scattering of the snow on sea ice at different microwave frequency channels can be used to retrieve snow depth on sea ice [,]. Snow depth can be calculated as follows:
where, SD is the snow depth (in cm), and a and b are the coefficients of the retrieval model. GR represents the gradient ratio of vertical polarization brightness temperature at different frequencies; f1 corresponds to the 37 GHz vertical polarization frequency channel, while f2 corresponds to either the 19 GHz or 7 GHz vertical polarization frequency channel; TB denotes the vertical polarization brightness temperature received by the passive microwave sensor at different frequencies; represents the mean brightness temperature in open water for different frequencies; and C represents the sea ice concentration, obtained from the passive microwave brightness temperatures based on the (NT2) NASA Team 2 algorithm [].
Markus and Cavalieri (1998) pioneered the development of a model for snow depth retrieval using passive microwave SSM/I brightness temperature data, which were derived from SSM/I data spanning 1978–2007 []. This model, referred to as the Markus98 model, has the model coefficients a = −2.3 cm and b = −771 cm. Based on the Markus98 model, Comiso et al. (2003) adapted the algorithm for AMSR-E data and introduced the Comiso03 model, which adjusted the regression coefficients to a = 2.9 cm and b = −782 cm []. Both the Markus98 and Comiso03 models utilized the 37 and 19 GHz frequencies, which have limited penetration capability with an upper limit 60 cm for the retrieval of snow depth on sea ice.
To address the limitations in penetration capability, Shen et al. (2022) employed the lower frequency channel of 7 GHz, which offers better penetration into the snow layer []. The resulting retrieval model, referred to as the Shen22 model, has the coefficients a = −26.7 cm and b = −411 cm. This approach demonstrated improved snow depth estimation, particularly in regions with deep snow. Notably, Equations (1)–(4) established a relationship between snow depth on sea ice and the mean open sea water brightness temperature () at different frequencies, serving as the reference tie point. In this study, a dynamic reference point method [] was applied instead of a fixed reference tie point, enabling more accurate snow depth estimates. Figure 3 shows that the dynamic tie points used for snow depth retrieval were higher than the traditional fixed tie points used at 19 and 37 GHz for . The maximum difference between the dynamic and the fixed tie point for at 19 and 37 GHz was 12.8 and 10.9 K, respectively. The obtained dynamic tie points reflect daily actual changes, thereby benefiting the accuracy of the retrieved snow depth on Antarctic sea ice [].
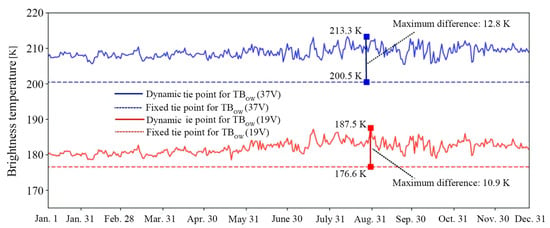
Figure 3.
Comparison of fixed (traditional method) and dynamic (this study) tie points calculated from the HY-2B SMR measured brightness temperature at 19 and 37 GHz for open sea water in 2019.
Additionally, it is important to consider the effects of day-time melt and nightly freeze of the snow on sea ice. Consequently, a highly scattering layer is created, leading to an overestimation of the snow depth on sea ice []. Snow-covered ice can be re-covered by new snow. Additionally, the melt–refreeze phenomenon alters snow properties, including changes in snow grain size and density. These factors contribute to an overestimation of the snow depth on sea ice during the remote sensing retrieval from passive microwave data []. To mitigate the impact of these uncertainties on snow depth retrieval from HY-2B SMR data, this study employs a sliding 5-day box window for the retrieved snow depth [,].
3.2. Comparison and Accuracy Evaluation
To evaluate the differences in accuracy of the retrieved snow depth among different models and compare the retrieved HY-2B SMR snow depth with the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product, we used three statistical parameters: mean deviation (MD), mean absolute deviation (MAD), and root mean square deviation (RMSD), as defined in Equations (5)–(7). These parameters are commonly used in the field due to their effectiveness in quantifying the dispersion of data points around the mean (Smith et al., 2000). They provide a comprehensive measure of the model’s performance by evaluating the bias, precision, and overall error, respectively [].
where, represents the snow depth on sea ice retrieved from HY-2B SMR data, refers to the average snow depth obtained from in situ observations conducted by the R/V Xuelong after spatial and temporal matching, or the snow depth product from GCOM-W1 AMSR-2, and n represents the number of pixels involved in the comparison.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Assessment of the Retrieved HY-2B SMR Snow Depth Based on Different Models
Based on commonly used remote sensing models for the retrieval of snow depth on sea ice, namely Markus98 [], Comiso03 [], and Shen22 [], this study employed HY-2B SMR data to retrieve the snow depth for Antarctic sea ice. Figure 4 presents the snow depth retrievals based on the three different models, with each model’s results indicated by a separate trace (taking 1 February, 14 February, and 28 February in 2009 as examples). Generally, the retrieved snow depth retrieved from HY-2B based on Markus98, Comiso03, and Shen22 models has similar spatial distribution, with thicker snow concentrated in the Weddell Sea and Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas, which are mainly in multi-year ice areas []. Due to the melting sea ice season in February, only thin snow existed on the remaining sea ice in the Southern Indian and Southern Pacific oceans. Among the differences in snow depth derived from the three models, the snow depth retrieved from HY-2B SMR data based on the Comiso03 model was relatively thicker than that retrieved using the Shen22 and Markus98 models.
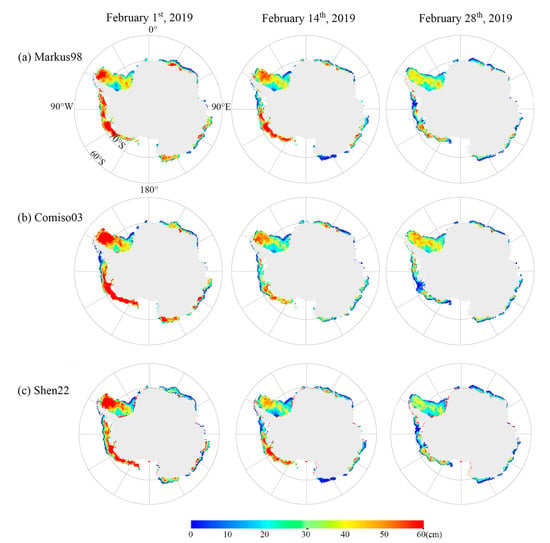
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of the retrieved HY-2B snow depth based on the Markus98 model (a), Comiso03 model (b), and Shen22 model (c).
The retrieved snow depths were compared and validated against ship-based observational snow depths during the 35th Chinese Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE-35), with the assessment results presented in Table 2. Compared to the ship-based snow depth measurements, the retrieved HY-2B SMR snow depth using the three models exhibited a certain negative deviation. This finding is consistent with previous studies that reported an underestimation of snow depth using the AMSR-E brightness temperature data [,]. This underestimation phenomenon is influenced by a myriad of factors, including sensor performance, data processing strategies, and environmental conditions. When employing passive microwave remote sensing techniques to retrieve snow depth on Antarctic sea ice, the physical properties of snow, such as grain size and moisture content, significantly affect the penetration and scattering of microwave signals, posing challenges to the accurate determination of snow depth [].

Table 2.
Comparison of snow depths retrieved from HY-2B SMR using different snow depth models against ship-based snow depth measurements.
In comparison of the accuracy of snow depth retrieval based on the three models, it was observed that the Comiso03 model exhibited a better performance relative to the Markus98 and Shen22 models, with the smallest MD of −1.9 cm and the lowest MAD and RMSD. Therefore, given its feasibility, we applied the Comiso03 model to retrieve the snow depth on Antarctic sea ice from HY-2B SMR passive microwave data for the entire year of 2019.
4.2. Comparison of HY-2B SMR Snow Depth with GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 Snow Depth Product
The retrieved snow depth on Antarctic sea ice using HY-2B SMR presents a similar trend to the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product (Figure 5), primarily due to the utilization of the same snow depth retrieval model (Comsio03 model) for both. Overall, the snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR was higher than that from GCOM-W1 AMSR-2. This disparity could be attributed to differences in brightness temperatures observed by the SMR and AMSR-2 sensors. Specifically, the average difference between the HY-2B SMR measured brightness temperature at 18.7 GHz (36.5 GHz) and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 measured brightness temperature is −5.1 K (−6.8 K). Table 3 shows the monthly snow depth differences between HY-2B SMR and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2. Significant differences were mainly observed during the sea ice ablation period (November to March), with the MD ranging from 5.2 cm to 11.1 cm. During the sea ice melting season, snow on sea ice undergoes phase changes, melting during the day and refreezing at night. These phase changes result in variations in microwave emissivity measured by different passive microwave sensors [,], such as SMR and AMSR-2, which have different measured brightness temperature sensitivities (Table 1). This leads to differences in the derived snow depth. The differences were relatively small during spring, autumn, and winter, with the difference being below 2.4 cm (Table 3). During the freeze-up period (April to October), the difference between the snow depth obtained from HY-2B SMR and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 product were relatively small, with a MD of 1.0 cm and a RMSD of 7.4 cm. However, during the melt period (November to March), the snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR was significantly higher than the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product exhibited larger differences compared to the sea ice growth period, with a MD of 5.0 cm and RMSD of 14.4 cm. The SMR-derived snow depth exhibits a high-frequency variability compared to the AMSR-2-derived snow depth. This could be attributed to the different brightness temperature sensitivity between SMR and AMSR-2 that was affected by synoptic-scale meteorological factors, such as water vapor and heat.
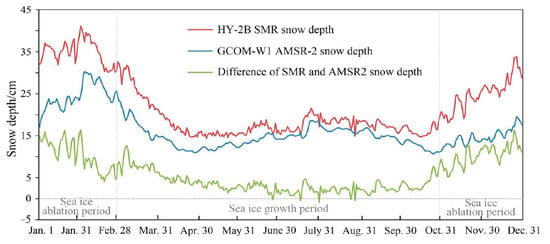
Figure 5.
Daily spatial average differences of HY-2B SMR snow depth and GCOM-W1 AMSR2 snow depth on Antarctic sea ice in 2019.

Table 3.
Comparison of snow depths retrieved from HY-2B SMR using different snow depth models against ship-based snow depth measurements in different months.
To further analyze the spatiotemporal differences between the snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product, we conducted a statistical analysis of the differences in snow depth between the two across different Antarctic seas and seasons (Table 4). Except for the Weddell Sea during winter, the snow depth obtained from HY-2B SMR was consistently higher than that of the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 product. The differences between the two were relatively small during spring (September to October), autumn (March to May), and winter (June to August), but exhibited significant disparities during summer (December to February), with the snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR being considerably higher than the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 product. This snow depth discrepancy in summer could be attributed to the unstable snow phase on sea ice due to high summer air temperatures, resulting in different brightness temperatures observed by different passive microwave sensors. The spatial distribution of the HY-2B SMR snow depth and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth is generally consistent, with thick snow mainly distributed in the Weddell Sea, and thin snow depth primarily distributed in East Antarctica sea areas. However, some localized differences were observed in different sea areas, particularly in the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas, where the RMSD between the two was 13.2 cm. This finding is consistent with the validation results obtained by Kern et al. (2011), who utilized ship-based snow depth observations at the Bellingshausen Sea in 2006 to validate the AMSR-E snow depth product, which underestimated the actual snow depth by up to 20 cm []. Considering the underestimation of GCOMW1 snow depth product on Antarctic sea ice [,], the HY-2B SMR retrieved snow depth, which is thicker than the GCOMW1 snow depth in this study, which is closer to the true snow depth situation.

Table 4.
Differences between HY-2B SMR snow depth and GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth products across different Antarctic seas and different seasons in 2019.
4.3. Spatiotemporal Variations of Snow Depth on Antarctic Sea Ice in 2019
Figure 6 displays the spatial distribution of monthly snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR in 2019. During the Antarctic summer season (December to February), thinner sea ice and its surface snow gradually melt as temperatures increase, leading to the minimum extent of sea ice coverage []. A small amount of thicker snow was distributed on the remnants of multi-year ice in the Weddell Sea and Bellingshausen Sea, as well as in nearshore regions of other Antarctic sea areas. In January, the average snow depth reaches its maximum at 36.2 cm. As temperatures decrease, the sea ice growth period begins in March, and, along with the growth of new ice [], the spatial average snow depth on sea ice gradually decreases, reaching its lowest average value of 15.3 cm in May. During the Antarctic winter, snow continues to accumulate on the newly formed ice, with thicker snow accumulation observed in the northwest regions of the Weddell Sea and the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas []. In early spring, the sea ice continues to grow until October, reaching its peak extent, and the snow accumulation rate slows down, leading to a decrease in snow depth on Antarctic sea ice. However, as temperatures rise again, both the snow and sea ice decay and melt, causing an increase in the remaining snow depth on the thicker Antarctic sea ice surviving in November and beyond.
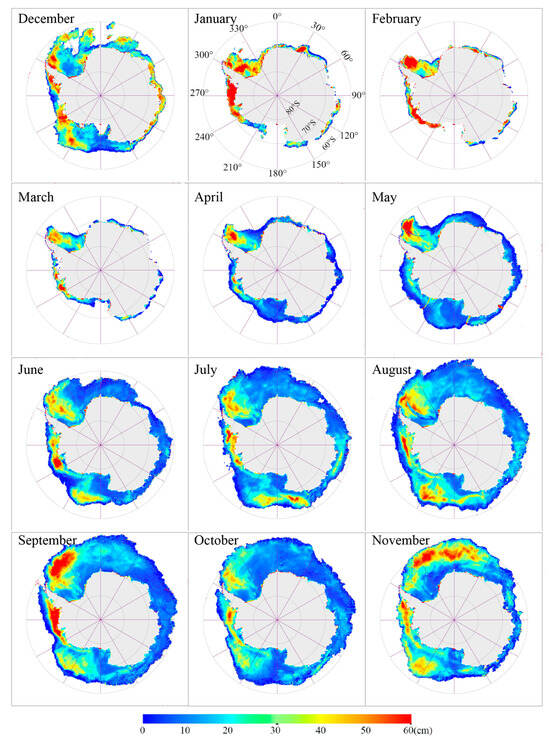
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of HY-2B SMR derived monthly snow depth in 2019.
The time-series snow depth on sea ice in the Antarctic Ocean and its various sea areas were plotted in Figure 7. It can be observed that the variation trends in snow depth were generally consistent across different sea areas and the entire Antarctic Ocean. Throughout the summer season, except for the Weddell Sea, the daily snow depth exhibits significant variations. This phenomenon may be attributed to the frequent occurrence of melt–refreeze processes caused by the diurnal temperature difference in Antarctica. Consequently, the brightness temperature observed by passive microwave sensors undergoes substantial daily fluctuations, thereby affecting the retrieved snow depth based on the passive microwave data []. Unlike other sea areas, the snow depth on sea ice in the Ross Sea exhibits a significant increasing trend towards the end of summer. During the spring, changes in wind speed in the Ross Sea promote the early melting and reduction of sea ice thickness, thereby increasing the absorption rate of solar radiation. These changes significantly impact the autumn sea ice cover five months later, primarily manifesting as a reduction in sea ice area, which creates a precondition for the increase in snow depth at the end of the summer. This series of changes reveals the key driver behind the increase in late-summer snow depth in the Ross Sea region, highlighting the complex interplay between atmospheric conditions and sea ice dynamics []. Thick snow (over 30 cm) is primarily found in the Weddell Sea, Bellingshausen Sea, Amundsen Sea, and Ross Sea. During the autumn season, the snow depth decreases in all Antarctic sea areas; however, the rate of decline slows down gradually. In winter, the snow depth continues to rise in the southwestern Antarctic sea areas (Bellingshausen Sea, Amundsen Sea, and Ross Sea), which could be due to frequent cyclonic activity and higher precipitation, whereas the eastern Antarctic sea areas (Southern Indian and Southern Pacific oceans) experience relatively thinner snow depths due to the growth of new ice []. With the arrival of spring, snow depth decreases in the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas, initially declines then increases in the Weddell and Ross seas, and steadily rises in the Southern Indian and Pacific oceans. Regional and seasonal changes in snow depth are affected by multiple factors, such as snowfall, rainfall, and wind-derived blowing snow []. Based on the HY-2B derived snow depth on Antarctic sea ice, it is possible to conduct an in-depth analysis of the impact mechanism of changes in snow depth and the related meteorological and climatic indicators in future work.
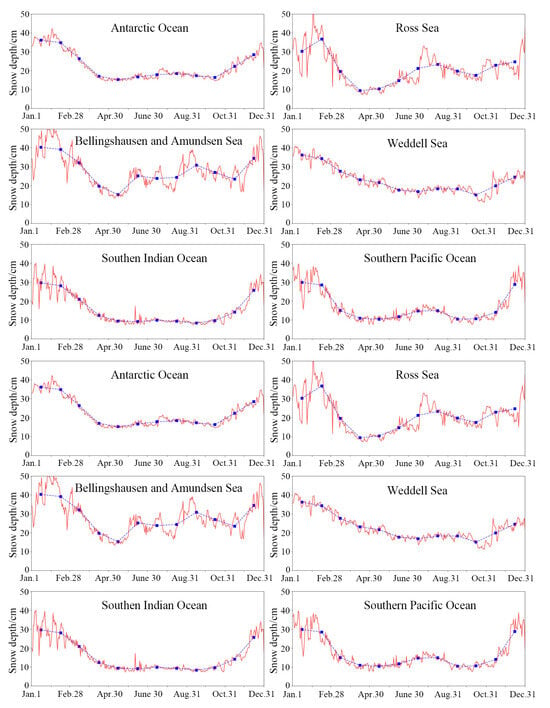
Figure 7.
Time-series of snow depth on Antarctic sea ice and its various sea areas derived from HY-2B SMR data in 2019. The red solid line is the daily HY-2B SMR snow depth and the blue dashed line is the monthly average HY-2B SMR snow depth.
5. Conclusions
The investigation of retrieving snow depth on Antarctic sea ice using passive microwave data is of significant importance for observing Antarctic sea ice and snow variations in the context of global warming. In this study, we explored the retrieval of snow depth on Antarctic sea ice using HY-2B SMR data based on three snow depth retrieval models (the Markus98 model, Comiso03 model, and Shen22 model). The accuracy of these models was verified using the ship-based snow depth observational data of the Chinese 35th Antarctic Scientific Expedition. The retrieved HY-2B SMR snow depths were compared with the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product, followed by an analysis of the spatiotemporal distribution of snow depth on Antarctic sea ice in 2019.
The utilization of passive microwave remote sensing data from HY-2B SMR demonstrates a certain feasibility in retrieving snow depths on Antarctic sea ice. Compared to the Markus98 and Shen22 models, the Comiso03 model produces a relatively better performance for snow depth retrieval on Antarctic sea ice.
There is good consistency between the snow depth derived from HY-2B SMR and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product. However, notable differences primarily occur during the melting sea ice season, with a deviation of 5.0 cm. The spatial differences mainly concentrate in the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas and the Southern Pacific Ocean. Overall, the snow depth on Antarctic sea ice derived from HY-2B SMR tends to be higher than the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 product, which mitigates the underestimation phenomenon for the retrieval of snow depth on sea ice from passive microwave data in previous studies.
In 2019, the monthly snow depth on Antarctic sea ice reached its peak in January (36.2 cm) and decreased to its lowest in May (15.3 cm). Snow depth on Antarctic sea ice is influenced by both seasonal and geographical regions. Thicker snow cover throughout the year was primarily distributed in the Weddell, Bellingshausen, Amundsen, and Ross seas, while thinner snow on sea ice was found in the Southern Indian Ocean and the Southern Pacific Ocean.
This study presents a potential possibility for applying HY-2B SMR data to retrieve snow depths on Antarctic sea ice, which is significant for observing the long-term variations of Antarctic sea ice and its surface snow. It should be noted that the preferred Comiso03 model for HY-2B SMR data in this study is also the retrieval model used in the AMSR-2 snow depth product released by the NSIDC. However, it should be underscored that the AMSR-2 sensor aboard the GCOM-W1 satellite, while instrumental to the snow depth retrieval, has been operational for over 12 years, exceeding the designed lifespan of the satellite, which may impact the reliability of its data for long-term continuous observing purposes. Additionally, the retrieval capability of the Comiso03 model is limited to deep snow (greater than 60 cm). Thus, the snow depth retrieval model for the passive microwave data still needs to be improved. In future work, it is recommended to explore the construction of a novel model for retrieving snow depths on Antarctic sea ice using HY-2B satellite data both from high and low-frequency channels, which have better penetration capabilities for detecting thick snow. Additionally, the deep learning techniques could be applied to construct a more efficient and accurate snow depth retrieval model. This would provide long-term information on the snow depth on Antarctic sea ice, thereby supporting continuous observing of Antarctic sea ice and its surface snow changes in the context of global warming.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.J.; methodology, Q.J. and N.L.; software, M.Y. and Z.X.; analysis, Q.J. and X.P.; writing, Q.J. and N.L.; visualization, Z.Z. and M.Y.; and funding acquisition, Q.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 42076235, the Excellent Teacher Training Program of Anhui Province under Grant No. YQZD2023009, and the Quality Engineering Project for Anhui Higher Education Universities under Grant No. 2023jyxm0164.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available to readers by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Chinese National Satellite Ocean Application Service (NSOAS) and the U.S. National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) for providing HY-2B SMR brightness temperature data and the GCOM-W1 AMSR-2 snow depth product used in this study. We acknowledgement the Chinese Arctic and Antarctic Administration and the Polar Research Institute, as well as the members of the R/V Xuelong of the 35th Chinese Antarctic Expedition for their great support and assistance during the Antarctic sea ice and snow in situ survey.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Massom, R.A.; Stammerjohn, S.E. Antarctic Sea ice change and variability-physical and ecological implications. Polar Sci. 2010, 4, 149–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmich, K.; Vancoppenolle, M.; Madec, G.; Sallée, J.-B.; Holland, P.R.; Lebrun, M. Drivers of Antarctic sea ice advance. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, J.A.; Schramm, J.L.; Ebert, E.E. Sea ice-albedo climate feedback mechanism. J. Clim. 1995, 8, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.G. Remote Sensing of Snow and Ice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, M.A.; Gerland, S.; Holland, M.; Hunke, E.; Kwok, R.; Lecomte, O.; Massom, R.; Perovich, D.; Sturm, M. Snow in the changing sea-ice systems. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.A.; Rigor, I.G.; Nghiem, S.V.; Kurtz, N.T.; Farrell, S.L.; Perovich, D.K.; Sturm, M. Interdecadal changes in snow depth on Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2014, 119, 5395–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Kacimi, S. Three years of sea ice freeboard, snow depth, and ice thickness of the Weddell Sea from Operation IceBridge and CryoSat-2. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 2789–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, M.; Hoppmann, M.; Arndt, S.; Hendricks, S.; Katlein, C.; Nicolaus, A.; Rossmann, L.; Schiller, M.; Schwegmann, S. Snow depth and air temperature seasonality on sea ice derived from snow buoy measurements. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 655446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, S.; Khvorostovsky, K.; Skourup, H.; Rinne, E.; Parsakhoo, Z.S.; Djepa, V.; Wadhams, P.; Sandven, S. The impact of snow depth, snow density and ice density on sea ice thickness retrieval from satellite radar altimetry: Results from the ESA-CCI Sea Ice ECV Project Round Robin Exercise. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Kacimi, S.; Webster, M.A.; Kurtz, N.; Petty, A. Arctic snow depth and sea ice thickness from ICESat-2 and CryoSat-2 freeboards: A first examination. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2020, 125, 2019JC016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Q.; Li, G.; Shi, L.; Lan, M.; Liang, Z. An improved algorithm for the retrieval of the Antarctic sea ice freeboard and thickness from ICESat-2 altimeter data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpan, P.; Meiners, K.M.; Langhorne, P.J.; Heil, P.; Smith, I.J.; Leonard, G.H.; Massom, R.A.; Clementson, L.A.; Haskell, T.G. Estimation of Antarctic land-fast sea ice algal biomass and snow depth from under-ice radiance spectra in two contrasting areas. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2018, 123, 1907–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, S.R.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Toro, M.; Hultstrand, D.M. Mapping snow cover and snow depth across the Lake Limnopolar watershed on Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island, Maritime Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2013, 25, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwok, R.; Haas, C. Effects of radar side-lobes on snow depth retrievals from Operation IceBridge. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Cavalieri, D.J. Snow depth distribution over sea ice in the Southern Ocean from satellite passive microwave data. Antarct. Sea Ice Phys. Process. Interact. Var. 1998, 74, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, T.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Gasiewski, A.J.; Klein, M.; Maslanik, J.; Powell, D.; Stankov, B.; Stroeve, J.; Sturm, M. Microwave signatures of snow on sea ice: Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Cavalieri, D.J.; Markus, T. Sea ice concentration, ice temperature, and snow depth using AMSR-E data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Maslanik, J.A.; Perovich, D.; Stroeve, J.; Richter-Menge, J.; Markus, T.; Holmgren, J.; Heinrichs, J.; Tape, K. Snow depth and ice thickness measurements from the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas collected during the AMSR-Ice03 campaign. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3009–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worby, A.P.; Markus, T.; Steer, A.D.; Lytle, V.I.; Massom, R.A. Evaluation of AMSR-E snow depth product over East Antarctic Sea ice using in situ measurements and aerial photography. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2008, 113, C05S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, S.; Ozsoy-Cicek, B.; Willmes, S.; Nicolaus, M.; Haas, C.; Ackley, S. An intercomparison between AMSR-E snow-depth and satellite C-and Ku-band radar backscatter data for Antarctic Sea ice. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Massom, R.; Worby, A.; Lytle, V.; Kurtz, N.; Maksym, T. Freeboard, snow depth and sea-ice roughness in East Antarctica from in situ and multiple satellite data. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostosky, P.; Spreen, G.; Farrell, S.L.; Frost, T.; Heygster, G.; Melsheimer, C. Snow depth retrieval on Arctic sea ice from passive microwave radiometers—Improvements and extensions to multiyear ice using lower frequencies. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 7120–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ke, C.Q.; Li, H. Snow depth product over Antarctic Sea ice from 2002 to 2020 using multisource passive microwave radiometers. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worby, A.P.; Geiger, C.A.; Paget, M.J.; Van Woert, M.L.; Ackley, S.F.; DeLiberty, T.L. Thickness distribution of Antarctic Sea ice. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2008, 113, C05S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Cavalieri, D.J. Interannual and regional variability of Southern Ocean snow on sea ice. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 44, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raphael, M.N.; Handcock, M.S. A new record minimum for Antarctic sea ice. Nat. Rev. Earth Env. 2022, 3, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.; Holmes, C. 2023’s Antarctic sea ice extent is the lowest on record. Weather 2024, 79, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.; Sinha, N. Sea Ice: Physics and Remote Sensing; American Geophysical Union: Washington DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.E.; Chang, A.T.; Tsang, L.; Foster, J. A prototype AMSR-E global snow area and snow depth algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Cavalieri, D.J. The AMSR-E NT2 sea ice concentration algorithm: Its basis and implementation. J. Remote Sens. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 29, 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lavergne, T.; Sørensen, A.M.; Kern, S.; Tonboe, R.; Notz, D.; Aaboe, S.; Bell, L.; Dybkjær, G.; Eastwood, S.; Gabarro, C.; et al. Version 2 of the EUMETSAT OSI SAF and ESA CCI sea-ice concentration climate data records. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Kern, S.; Qu, M.; Ji, Q.; Fan, P.; Liu, Y. Sea ice concentration derived from FY-3D MWRI and its accuracy assessment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willatt, R.C.; Giles, K.A.; Laxon, S.W.; Stone-Drake, L.; Worby, A.P. Field investigations of Ku-band radar penetration into snow cover on Antarctic Sea ice. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Johnson, R.; Williams, C. Statistical evaluation of model performance. J. Hydro.-Environ. Res. 2000, 231, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Lv, T.; Sun, Q.; Ding, Z.; Shen, H.; Gao, Y.; He, Y.; Fu, M.; Li, C. Analysis of spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors of sea ice extent in the Arctic and Antarctic. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Massonnet, F.; Goosse, H.; Luo, H.; Barthélemy, A.; Yang, Q. Synergistic atmosphere-ocean-ice influences have driven the 2023 all-time Antarctic sea-ice record low. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Markus, T.; Ivanoff, J.A.; Miller, J.A.; Brucker, L.; Sturm, M.; Maslanik, J.A.; Heinrichs, J.F.; Gasiewski, A.J.; Leuschen, C.; et al. Comparison of snow depth on sea ice retrievals using airborne altimeters and an AMSR-E simulator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 50, 3027–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Q.; Wang, K. Recent changes in pan-Antarctic region surface snowmelt detected by AMSR-E and AMSR2. Cryosphere 2022, 14, 3811–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, S.; Ozsoy-Cicek, B. An attempt to improve snow depth retrieval using satellite microwave radiometry for rough Antarctic sea ice. Remote Sens. 2009, 11, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.L.; Chang, A.; Rango, A.; Josberger, E. Snow depths and grain-size relationships with relevance for passive microwave studies. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 17, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.M.; Landrum, L.; Raphael, M.; Stammerjohn, S. Springtime winds drive Ross Sea ice variability and change in the following autumn. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, S.L.; Tripoli, G.J.; Thom, J.E.; Weidner, G.A. The influence of blowing snow and precipitation on snow depth change across the Ross Ice Shelf and Ross Sea regions of Antarctica. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 1306–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).