Abstract
Accurate quantification of ecosystem water use efficiency (eWUE) over agroecosystems is crucial for managing water resources and assuring food security. Currently, the uncoupled Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) product is the most widely applied dataset for simulating local, regional, and global eWUE across different plant functional types. However, it has been rarely investigated as to whether the coupled product can outperform the uncoupled product in eWUE estimations for specific C4 and C3 crop species. Here, the eWUE as well as gross primary production (GPP) and evapotranspiration (ET) from the uncoupled MODIS product and the coupled Penman–Monteith–Leuning version 2 (PMLv2) product were evaluated against the in-situ observations on eight-day and annual scales (containing 1902 eight-day and 61 annual samples) for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites from the FLUXNET2015 and AmeriFlux datasets. Our results show the following: (1) For GPP estimates, the PMLv2 product showed paramount improvements for C4 maize and slight improvements for C3 soybean, relative to the MODIS product. (2) For ET estimates, both products performed similarly for both crop species. (3) For eWUE estimates, the coupled PMLv2 product achieved higher-accuracy eWUE estimates than the uncoupled MODIS product at both eight-day and annual scales. Taking the result at an eight-day scale for example, compared to the MODIS product, the PMLv2 product could reduce the root mean square error (RMSE) from 2.14 g C Kg−1 H2O to 1.36 g C Kg−1 H2O and increase the coefficient of determination (R2) from 0.06 to 0.52 for C4 maize, as well as reduce the RMSE from 1.33 g C Kg−1 H2O to 0.89 g C Kg−1 H2O and increase the R2 from 0.05 to 0.49 for C3 soybean. (4) Despite the outperformance of the PMLv2 product in eWUE estimations, both two products failed to differentiate C4 and C3 crop species in their model calibration and validation processes, leading to a certain degree of uncertainties in eWUE estimates. Our study not only provides an important reference for applying remote sensing products to derive reliable eWUE estimates over cropland but also indicates the future modification of the current remote sensing models for C4 and C3 crop species.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem water use efficiency (eWUE), the ratio of gross primary production (GPP, the total amount of carbon fixation by vegetation through photosynthesis) and evapotranspiration (ET, the sum of evaporation from soil and transpiration through plant leaves), is a critical indicator connecting the terrestrial carbon and water cycles and reflecting multiple ecosystem functions [1,2]. Cultivated cropland accounts for approximately 12% of the Earth’s non-ice-covered land surface and provides indispensable survival supplements (e.g., food and fiber) for human beings [3,4]. Accurate quantification of eWUE over agroecosystems is therefore pivotal for the management of water resources and assurance of food security.
The satellite-based remote sensing (RS) technique has been recognized as the most practical and feasible means to derive the long-term eWUE at a global scale. With the aid of the RS technique, plenty of eWUE-related research obtained the eWUE at local, regional, and global scales through the free combination of various RS-based GPP and ET products. Essentially, the contemporary GPP and ET products can be categorized into (1) the uncoupled products (e.g., the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) [5], Vegetation Photosynthesis Model (VPM) [6], SatelLite Only Photosynthesis Estimation (SLOPE) [7], FLUXCOM [8] products for GPP estimates, the MODIS [9], Global Land Evaporation Amsterdam Model (GLEAM) [10], Global LAnd Surface Satellite (GLASS) [11], and FLUXCOM [12] products for ET estimates) and (2) the coupled products (e.g., the Penman–Monteith–Leuning version 2 (PMLv2) [13], Boreal Ecosystem Productivity Simulator (BEPS) [14], and Breathing Earth System Simulator (BESS) [15] products for both GPP and ET estimates). The uncoupled products commonly treat vegetation photosynthesis and transpiration as two independent processes and simulate GPP and ET based on various individual algorithms (e.g., the light use efficiency model for GPP estimation and the Penman–Monteith equation for ET estimation). However, the photosynthesis and transpiration of vegetation are intrinsically coupled because the stomata on the surface of plant leaves can simultaneously regulate the exchange of water and carbon in the vegetation–atmosphere interface. Over the past decades, relying on the assumption that the stomatal conductance is positively and linearly correlated with the carbon assimilation rate, mounting stomatal conductance models have been developed, such as the Ball–Berry [16], Ball–Berry–Leuning [17], optimality-based unified stomatal optimization [18], and best-fitted [19] models. Using these stomatal conductance models, the coupled products can couple the estimation of vegetation photosynthesis and transpiration and simulate GPP and ET collectively.
Previous findings revealed that the coupled products outperformed the uncoupled products in both GPP and ET estimations [13,15]. However, the evaluation of eWUE is much more complicated than that of individual GPP or ET, mainly because the error in GPP and ET estimates could be offset or expanded to some extent in the ultimate eWUE estimates (for example, the underestimation of both GPP and ET may lead to an unbiased estimate of eWUE) [2]. Therefore, it is imperative to assess the performance of the coupled and uncoupled products in eWUE estimations. Moreover, the coupled products (i.e., PMLv2 and BESS) have been proven to achieve better results in eight-day and annual eWUE estimations than the uncoupled products (e.g., MODIS) for different plant functional types (PFTs) [2,13]. However, these studies mainly focused on a PFT level, and few evaluations of the performance of the coupled and uncoupled products in eWUE estimations were conducted at a species level (i.e., C4 and C3). Relative to C3 plants, C4 plants are more adaptable to the conditions of high light intensity, high temperature, and low water supplements [20]. On the one hand, C4 plants have more active photosynthesis efficiency and potential production than C3 plants. On the other hand, C4 plants commonly consume less water (through transpiration) when they fix the same amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) as C3 plants. Overall, C4 plants commonly reach a higher eWUE than C3 plants to better survive under a harsh environment. Whereas now, the knowledge on whether the coupled product can better monitor the different magnitudes of eWUE between C4 and C3 than the uncoupled product is still relatively limited and should be drawn more attention.
The overarching goal of this study was to explore whether the coupled product can outperform the uncoupled product in eWUE estimations for specific C4 and C3 species. To this end, this study applied the widely used coupled PMLv2 and uncoupled MODIS products (both providing GPP and ET estimates with a 500 m spatial resolution and an eight-day temporal resolution) to calculate eWUE. Subsequently, the eWUE as well as GPP and ET from the two products were validated against the observed eWUE at the five cropland sites planted with two major crop species (namely, C4 maize and C3 soybean) from the FLUXNET2015 dataset and AmeriFlux dataset. This study is expected to provide important information on (1) which remote sensing product is more effective for deriving higher-accuracy eWUE for C4 and C3 crop species, and (2) how to further improve the MODIS and PMLv2 products for GPP, ET, and eWUE estimates.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. In-Situ Data
The daily observed GPP and ET data collected from the US-Ne1, US-Ne2, US-Ne3, US-Ro1, and US-Ro5 sites from the FLUXNET2015 dataset (http://fluxnet.fluxdata.org/, accessed on 7 October 2023) and AmeriFlux dataset (https://ameriflux.lbl.gov/, accessed on 7 October 2023), which were planted with C4 maize and C3 soybean, were used for evaluating the GPP, ET, and eWUE estimates from the coupled PMLv2 and uncoupled MODIS products. The sites were selected by the following criteria: (1) the sites planted by C4 maize or C3 soybean or maize–soybean rotation, and (2) the land cover type extracted from the MODIS Land Cover Type Yearly L3 Global 500m product (MCD12Q1) corresponding to the site is croplands, which will affect the coefficients for estimating ET and GPP as well as eWUE. Please see Table 1 and Figure 1 for a detailed description of these five cropland sites. The daily daytime partitioning method-based GPP (termed ‘GPP_DT_VUT_REF’) and daily gap-filled ET using the Marginal Distribution Sampling (MDS) method (termed ‘LE_F_MDS’) were chosen for analysis. The provided daily quality control (QC) flag for observed GPP and ET (termed ‘NEE_VUT_REF_QC’ and ‘LE_F_MDS_QC’, respectively) was used to eliminate the poor-quality in-situ observations. Specifically, the daily GPP and ET were summed up to an eight-day scale, and the daily QC flag for observed GPP and ET (ranging from 0 to 1; the higher QC flag represents that the quality of daily observed GPP and ET data is higher) in every 8 days was averaged. Only the eight-day observed GPP and ET with eight-day average QC flags higher than 0.75 were collected for evaluating the eight-day GPP, ET, and eWUE from the RS products to avoid the uncertainty that might be introduced by the inaccurate in-situ observation as much as possible.

Table 1.
Description of the five cropland sites selected in this study.
Figure 1.
Satellite images over a grid area of 500 m × 500 m centered at five cropland sites accessed through Google Maps.
2.2. Uncoupled MODIS GPP and ET Products
The MOD17A2 GPP and MOD16A2 ET products with an eight-day temporal resolution and a 500 m spatial resolution were downloaded from Level-1 and the Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System Distributed Active Archive Center (LAADS DAAC) (https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/search/order, accessed on 7 October 2023). The MOD17 GPP product relies on the light use efficiency (LUE) scheme (namely, the MOD17 model), which regards the GPP as the product of the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), the fraction of photosynthetically active radiation (FPAR), the maximum LUE, and the environmental scalars [21]. Specifically, the PAR is calculated from the income shortwave radiation provided by the National Center for Environmental Prediction—Department of Energy (NCEP-DOE) Reanalysis II meteorology dataset; the FPAR is directly adopted from the MOD15A2 LAI/FPAR product; the maximum LUE is derived from a PFT-dependent look-up table; and the environmental scalars (representing the hydrological and thermal stresses on photosynthesis efficiency) are calculated by two piecewise linear functions of the vapor pressure deficit (VPD) and air temperature (Ta), respectively. Moreover, the MCD12Q1 land cover type product is used to identify the PFT of each pixel.
The MOD16 ET product is generated by the improved ET algorithm [9] over the previous algorithm [22] based on the Penman–Monteith equation (namely, the MOD16 model). Modified from the Penman equation that assumes ET is controlled by the drying power of the atmosphere (i.e., VPD and wind speed) and the available energy [23], the Penman–Monteith equation further considers the surface control on evaporation and transpiration by using surface conductance and introducing mechanism-based aerodynamic conductance, which is contingent upon wind speed, surface roughness, vegetation height, and atmospheric stability [24]. In the MOD16 model, daily ET is the sum of ET from daytime and nighttime, where daytime is determined by downward solar radiation being above 0. During the daytime, stomatal conductance is assumed to be controlled by vapor pressure deficit and daily minimum air temperature. During the nighttime, the stomata are assumed to be completely closed, leading to zero plant transpiration through the stomata. However, transpiration through the leaf boundary layer and leaf cuticles still occurs. Meanwhile, ET comprises evaporation from wet and moist soil, evaporation from the rainwater intercepted by the canopy, and transpiration through stomata on plant leaves and stems. Canopy conductance for plant transpiration is calculated by using LAI from the combination of MOD15A2H and MCD15A2HCL to scale stomatal conductance up to canopy level, which assumes that leaf area and FPAR do not vary during a given eight-day period. The Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) meteorological forcing dataset is used to drive the MOD16 model, including average and minimum air temperature, incident PAR, and specific humidity.
2.3. Coupled PMLv2 GPP and ET Products
The PMLv2 GPP and ET products with an eight-day temporal resolution and a 500 m spatial resolution were downloaded from the Google Earth Engine (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/CAS_IGSNRR_PMLV2_v017, accessed on 7 October 2023). The PMLv2 product adopts a coupled diagnostic biophysical model to simultaneously estimate GPP and ET (namely, the PMLv2 model). More specifically, a rectangular hyperbola function (for GPP estimation) and the Penman–Monteith equation (for plant transpiration estimation) are connected by a biophysical canopy conductance model [13]. Meanwhile, the Priestley–Taylor equation incorporating a soil evaporation coefficient controlled by precipitation and equilibrium evaporation is employed for estimating soil evaporation, and a revised Gash model is employed for estimating canopy interception. The leaf area index, albedo, and emissivity from the MODIS products and the daily maximum, minimum, and mean air temperature; atmosphere pressure; wind speed; specific humidity; precipitation; and incoming shortwave and longwave solar radiation from the Global Land Data Assimilation System (GLDAS) meteorological forcing dataset is used to drive the PMLv2 model. Readers can refer to the original algorithm articles for the description of the PMLv2 model [25,26].
2.4. Calculation of eWUE
In this study, the eWUE was calculated as follows:
where the GPP and ET are derived from the in-situ observation, the extracted collocated uncoupled MODIS product, and the extracted collocated coupled PMLv2 product. This study evaluated the accuracy of eWUE from the two RS products on both eight-day and annual scales. On an eight-day scale, the eWUE was calculated by following two criteria: (1) only the data with both ET > 1 mm 8d−1 and GPP > 1 g C m−2 8d−1 are used, and (2) only the WUE values smaller than 10 g C Kg−1 H2O are used [2]. On an annual scale, all eight-day GPP and ET were first summed into annual data, and the annual GPP and ET were then used to calculate annual eWUE.
2.5. Evaluation Criteria
Three criteria were employed to evaluate the accuracy of the GPP, ET, and eWUE from the coupled PMLv2 and uncoupled MODIS products against the in-situ observation, including the root mean square error (RMSE), the coefficient of determination (R2), and the average absolute errors (Bias). They are calculated as follows:
where Var represents the variables of GPP, ET, or eWUE; subscript sim represents the GPP, ET, or eWUE estimates from the coupled PMLv2 and uncoupled MODIS products; subscript EC represents the GPP, ET, or eWUE observed by the eddy covariance system; i represents the ith eight-day data; N represents the sample number; and the over-bar represents the mean value.
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy of Eight-Day GPP and ET
Figure 2 shows the comparison of the eight-day observed GPP and RS-based GPP from the PMLv2 and MOD17 products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. For maize, the PMLv2 product could achieve paramount improvements over the MOD17 product in simulating GPP, as indicated by the RMSE reducing from 49.29 g C m−2 8d−1 to 31.68 g C m−2 8d−1, the R2 increasing from 0.72 to 0.86, and the Bias decreasing from −18.88 g C m−2 8d−1 to −6.05 g C m−2 8d−1. It is noteworthy that the PMLv2 product and the MOD17 product both displayed obvious underestimations of medium and high observed GPP and slight overestimations of low observed GPP. These underestimations of medium and high observed GPP found in the MOD17 product could be partially alleviated by the PMLv2 product; however, it is still noticeable. For soybean, the PMLv2 product (with the RMSE = 17.32 g C m−2 8d−1, R2 = 0.81, and Bias = 8.45 g C m−2 8d−1) also outperformed the MOD17 product (with the RMSE = 22.23 g C m−2 8d−1, R2 = 0.62, and Bias = −1.13 g C m−2 8d−1) in reproducing observed GPP. Similar to the result for maize, the MOD17 product still seriously underestimated the medium and high observed GPP and slightly overestimated the low observed GPP for soybean. By contrast, the PMLv2 product presented an overall overestimation of observed GPP.
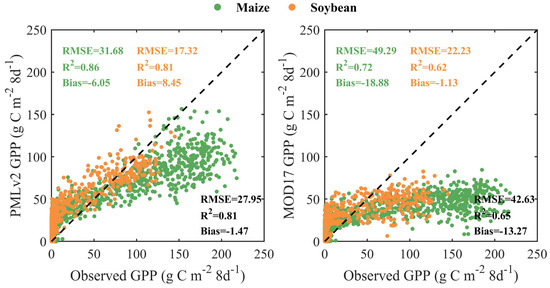
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of the eight-day observed GPP and RS-based GPP from the PMLv2 and MOD17 products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. The statistical metrics with green, orange, and black colors represent the performance of the PMLv2 and MOD17 products for maize, soybean, and both species, respectively.
Figure 3 shows the comparison of the eight-day observed ET and RS-based ET from the PMLv2 and MOD16 products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. Overall, the PMLv2 product exhibited similar performances to the MOD16 product for maize and soybean. Moreover, the PMLv2 and MOD16 products tended to overestimate and underestimate the observed ET for both maize and soybean, respectively. For maize, the PMLv2 product showed a decreased RMSE of 1.05 mm 8d−1, an increased R2 of 0.05, and a decreased absolute Bias of 1.20 mm 8d−1 in comparison to the MOD16 product. For soybean, these two products showed negligible disparities in ET estimations.
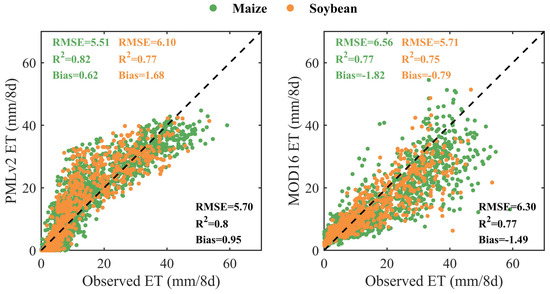
Figure 3.
Scatter plots of the eight-day observed ET and RS-based ET from the PMLv2 and MOD16 products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. The statistical metrics with green, orange, and black colors represent the performance of the PMLv2 and MOD17 products for maize, soybean, and both species, respectively.
3.2. Time Series of Eight-Day GPP and ET
Figure 4 shows the time series of the eight-day observed GPP and RS-based GPP from the PMLv2 and MOD17 products at five cropland sites. Overall, both the PMLv2 and MOD17 products could effectively capture the seasonal variation of observed GPP. Not surprisingly, C4 maize (with a mean of annual maximum observed GPP of 192.93 ± 14.80 g C m−2 8d−1 (mean ± standard deviation)) showed higher photosynthesis capacity than C3 soybean (with a mean of annual maximum observed GPP of 116.14 ± 16.66 g C m−2 8d−1). However, both the PMLv2 and MOD17 products cannot reflect the distinct photosynthesis capacity between C4 and C3 species, where the means of annual maximum GPP from the PMLv2 and MOD17 products for maize (105.98 ± 13.42 g C m−2 8d−1 and 56.74 ± 7.61 g C m−2 8d−1, respectively) were consistent with those for soybean (92.95 ± 16.28 g C m−2 8d−1 and 53.24 ± 10.56 g C m−2 8d−1, respectively). Even worse, in most cases, the severe underestimations for soybean from both the PMLv2 and MOD17 products and the severe underestimations for maize from the PMLv2 product were observed during the peak of growing seasons, while the underestimations for soybean from the PMLv2 product were insignificant. In addition, these underestimations of observed GPP from the MOD17 product were more remarkable than those from the PMLv2 product.
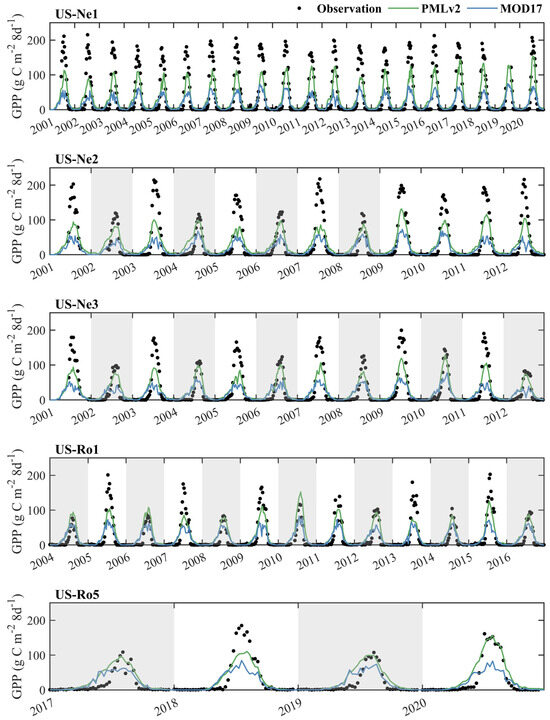
Figure 4.
Time series of the eight-day observed GPP and RS-based GPP from the PMLv2 and MOD16 products at the five cropland sites. The years with white backgrounds represent that C4 maize was planted this year. The years with grey backgrounds represent that C3 soybean was planted this year.
Figure 5 shows the time series of the eight-day observed ET and RS-based ET from the PMLv2 and MOD16 products at the five cropland sites. Overall, both the PMLv2 and MOD16 products also effectively captured the seasonal variation of the observed ET and showed no systematic underestimations or overestimations of observed ET. Unlike the results for GPP, there were marginal differences in the magnitude of observed ET between C4 maize (with a mean of annual maximum observed ET of 45.15 ± 5.64 mm 8d−1) and C3 soybean (with a mean of annual maximum observed ET of 42.23 ± 5.11 mm 8d−1). The PMLv2 and MOD16 products provided relatively consistent ET estimates at all five sites. Additionally, the main disparity between the PMLv2 and MOD16 products was that the PMLv2 product tended to generate higher ET estimates than the MOD16 product at the green-up stage (the period that GPP and ET continuously increased during each growing season) at some growing seasons, while both two products generated consistent ET estimates during the senescence stage (the period that GPP and ET continuously decreased during each growing season).
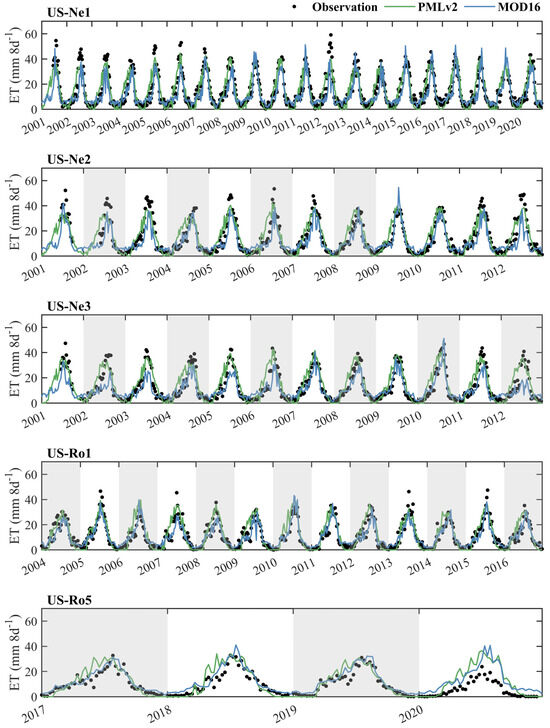
Figure 5.
Time series of the eight-day observed ET and RS-based ET from the PMLv2 and MOD16 products at the five cropland sites. The years with white backgrounds represent that C4 maize was planted this year. The years with grey backgrounds represent that C3 soybean was planted this year.
3.3. Performance of the PMLv2 and MODIS Products in eWUE Estimations
Figure 6 shows the comparison of the eight-day observed eWUE and RS-based eWUE from the PMLv2 and MODIS products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. Overall, the PMLv2 product was able to achieve higher-accuracy eWUE estimates in contrast to the MODIS product, as indicated by the RMSE reducing from 2.14 g C Kg−1 H2O to 1.36 g C Kg−1 H2O and the R2 increasing from 0.06 to 0.52 for maize, with the RMSE reducing from 1.33 g C Kg−1 H2O to 0.89 g C Kg−1 H2O and the R2 increasing from 0.05 to 0.49 for soybean. Moreover, the MODIS product exhibited considerable underestimations and overestimations of high and low observed eWUE for both maize and soybean, respectively. By contrast, the PMLv2 product greatly reduced these above-mentioned biases found in the MODIS product but still showed moderate underestimations of high observed eWUE for maize and slight overestimations of low observed eWUE for both maize and soybean.
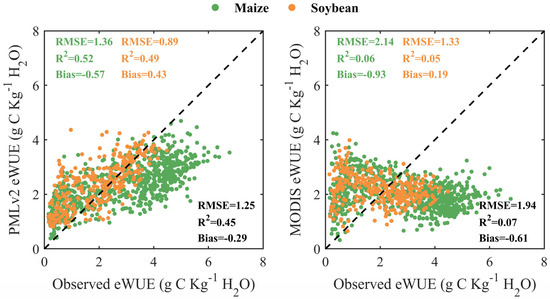
Figure 6.
Scatter plots of the eight-day observed eWUE and RS-based eWUE from the PMLv2 and MODIS products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. The PMLv2 eWUE was calculated as the ratio of GPP and ET from the PMLv2 product. The MODIS eWUE was calculated as the ratio of GPP from the MOD17 product and ET from the MOD16 product.
Figure 7 shows the time series of the eight-day observed eWUE and RS-based eWUE from the PMLv2 and MODIS products at the five cropland sites. Overall, the eWUE calculated from the MODIS product was commonly much lower than the observed eWUE during the peak of growing seasons and much higher than the observed eWUE during the start and end of growing seasons for both maize and soybean. By contrast, the PMLv2 product overall better captured the seasonal variation of observed eWUE compared to the MODIS product. In particular, the eWUE calculated from the PMLv2 product was generally moderately lower than the observed eWUE for maize and was consistent with the observed eWUE for soybean during the peak of growing seasons. Moreover, the eWUE calculated from the PMLv2 product tended to be slightly higher than the observed eWUE for both maize and soybean during the start and end of growing seasons (e.g., the year 2002 at the US-Ne1 and US-Ne2 sites).
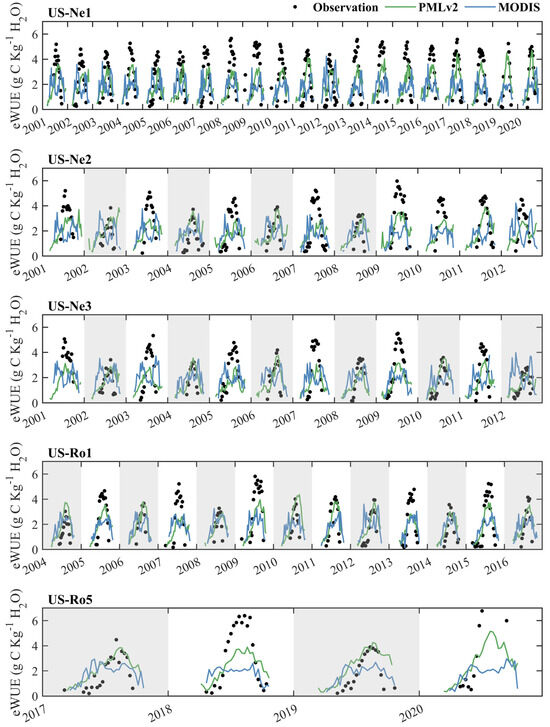
Figure 7.
Time series of the eight-day observed eWUE and RS-based eWUE from the PMLv2 and MODIS products at the five cropland sites. The PMLv2 eWUE was calculated as the ratio of GPP and ET from the PMLv2 product. The MODIS eWUE was calculated as the ratio of GPP from the MOD17 product and ET from the MOD16 product. The years with white backgrounds represent that C4 maize was planted this year. The years with grey backgrounds represent that C3 soybean was planted this year.
Figure 8 shows the comparison of the annual observed GPP, ET, and eWUE and RS-based GPP, ET, and eWUE from the PMLv2 and MODIS products for C4 maize and C3 soybean at the five cropland sites. Overall, the PMLv2 annual GPP, ET, and eWUE performed better than the MODIS annual GPP, ET, and eWUE with lower Bias and RMSE, and higher R2. For GPP and ET estimations, the PMLv2 product with a Bias of −256.3 g C m−2 year−1 and 26.1 mm year−1 and an RMSE of 332.57 g C m−2 year−1 and 76.65 mm year−1 for maize performed better than that with a Bias of 365.36 g C m−2 year−1 and 72.58 mm year−1 and an RMSE of 396.87 g C m−2 year−1 and 82.53 mm year−1 for soybean, respectively. For eWUE estimations, the PMLv2 product for soybean with a Bias of 0.43 g C Kg−1 H2O and an RMSE of 0.52 g C Kg−1 H2O outperformed that for maize with a Bias of −0.55 g C Kg−1 H2O and an RMSE of 0.71 g C Kg−1 H2O. However, the MODIS product for soybean produced better estimates than that for maize for all the GPP, ET, and eWUE at an annual scale, as indicated by the RMSE and Bias reducing from 834.74 g C m−2 year−1 and −799.7 g C m−2 year−1, 126.80 mm year−1 and −76.97 mm year−1, 1.30 g C Kg−1 H2O and −1.18 g C Kg−1 H2O for soybean to 195.85 g C m−2 year−1 and −48.7 g C m−2 year−1, 83.31 mm year−1 and −34.07 mm year−1, 0.29 g C Kg−1 H2O and 0 g C Kg−1 H2O for maize, respectively.
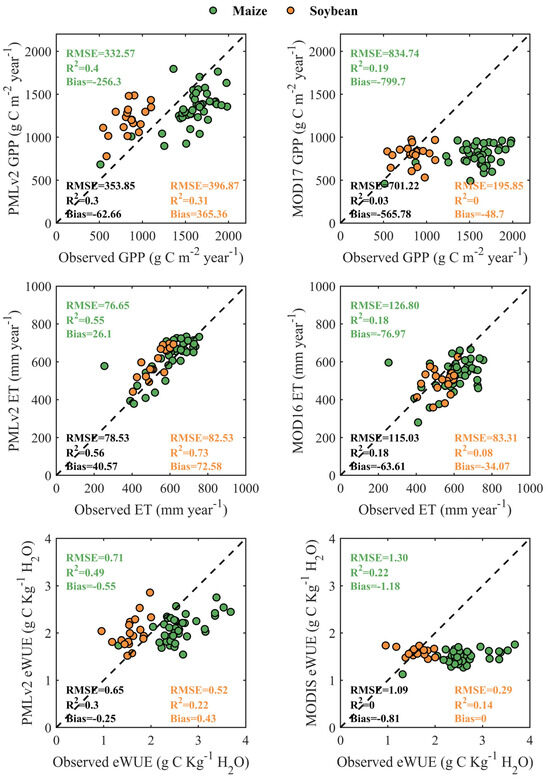
Figure 8.
Scatter plots of the annual observed and RS-based GPP, ET, and eWUE at the five cropland sites from the PMLv2 products (left) and MODIS products (right) for C4 maize and C3 soybean. The PMLv2 eWUE was calculated as the ratio of GPP and ET from the PMLv2 product. The MODIS eWUE was calculated as the ratio of GPP from the MOD17 product and ET from the MOD16 product.
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainty of RS-Based GPP, ET, and eWUE Estimations
Undoubtedly, the accuracy of RS-based eWUE is tightly related to the performance of individual GPP and ET products. Overall, the PMLv2 product could provide higher-accuracy GPP estimates than the MOD17 product for maize and soybean. From the perspective of model structure, the MOD17 and PMLv2 products adopt the LUE model and the light response curve (i.e., the rectangular hyperbola function), respectively, which are established on different theoretical bases. The LUE model, which assumes the GPP is equal to the product of APAR and LUE, has the advantage of ease of use and few model inputs/parameters [3]. However, some limitations in the LUE model still exist. First, the LUE scheme lacks a solid mechanism explanation in comparison to the process-based model. Second, no consensus has been reached on which formulas of FPAR and environmental scalar are the most effective in the LUE scheme. Third, different environmental stress factors may have interactions among themselves [27]. The abovementioned issues can reduce the accuracy of the LUE model. In addition, the light response curve, which reveals a rectangular hyperbola function between light saturation and photosynthesis [28], has been recognized as one of the reliable methods to partition GPP from net ecosystem exchange (NEE) and simulate GPP [25,29,30,31]. Despite the better performance of the PMLv2 product than the MOD17 product, neither model exhibited sufficiently satisfying accuracy in GPP estimation over cropland, which could further introduce large errors in eWUE estimation. One common weakness of the PMLv2 and MOD17 products is that both two products cannot accurately reflect the distinct photosynthesis capacity between C4 and C3 crop species (see Figure 2), primarily because both two products fail to differentiate C4 and C3 crop species in their model calibration and validation processes [5,13]. In reality, the carbon assimilation capacity of different crop species (C4 vs. C3) varies largely. A previous manuscript found that the calibrated maximum LUE of C4 maize was significantly larger than that of C3 soybean in the MOD17 model [4]. Moreover, another study revealed that the best-fitted maximum LUE of C4 maize was 1.69–2.63 times higher than that of six other C3 crop species (namely, potato, winter wheat, rape, paddy rice, soybean, and winter barley) in the MOD17 model [32]. However, the current MOD17 model simply assumes that C4 and C3 crop species have the same maximum LUE [5] and thus cannot well monitor the different magnitudes of GPP between C4 maize and C3 soybean. A similar issue can be also found in the PMLv2 product. Moreover, the MOD17 product severely underestimated the observed GPP during the peak of growing seasons for both maize and soybean (see Figure 4), which is consistent with the previous findings [4,33,34]. These biases in the MOD17 product predominantly stem from the underestimation of the maximum LUE, which is obtained from a simple Biome-specified Parameters Look-Up Table (BPLUT). A recent study applied the Bayesian inference in conjunction with the Markov chain Monte Carlo approach to re-calibrate the free parameter (including but not limited to the maximum LUE) in the MOD17 model at globally distributed flux sites and further substantiated that the updated BPLUT could benefit the performance of the MOD17 model [33]. In addition, one possible explanation for the better performance of the PMLv2 product for C3 soybean than C4 maize is that the most of the in-situ data at 11 cropland sites used for the model calibration were collected for C3 species, and therefore the PMLv2 product may achieve an overall high retrieval accuracy as much as possible.
In comparison to the result of GPP estimation, the PMLv2 and MOD16 products showed more consistent accuracy of ET estimates, whereas the PMLv2 only slightly outperformed the MOD16 product (see Figure 3). Their almost consistent performance in ET estimations could be attributed to the fact that two products calculate ET based on the Penman–Monteith algorithm logic. However, the PMLv2 and MOD16 products systematically overestimated and underestimated the observed ET, respectively. One possible reason may be that the two products use different meteorological datasets to drive the model. Take the MOD16 product for example, the MOD16 product using the GMAO meteorological inputs shows a more significant underestimation of observed ET than that using tower-based meteorological inputs [9]. The VPD from the GMAO meteorological data (with a coarse spatial resolution) may inadequately monitor water stress over smaller subregions, leading to uncertainty in the MOD16 product [35]. In addition, some previous studies attributed the general underestimation of ET in Continental U.S. (CONUS) croplands from the MOD16 product to model parameterization uncertainty [36,37]. Re-calibrating the model parameters according to C3 and C4 crop species could enhance the accuracy of the MOD16 algorithm in CONUS croplands [38]. Note that all these problematic issues in the MOD16 product may also occur in the PMLv2 product in ET estimation.
The PMLv2 product has been proven to outperform the MODIS product in eight-day eWUE estimations for both C4 maize and C3 soybean (see Figure 6). The MODIS product commonly exhibited noticeable overestimations and underestimations under low and high observed eWUE for both maize and soybean, respectively. During the peak of growing seasons (characterized by high observed eWUE), both the MOD17 and MOD16 products underestimated observed GPP and ET, respectively; however, the degree of underestimations of the observed GPP was larger than that of the observed ET. Therefore, the eWUE calculated from the MODIS product was still lower than the observed eWUE. During the start and end of growing seasons (characterized by low observed eWUE), the MOD17 and MOD16 products overestimated and underestimated observed GPP and ET, respectively, thus leading to the overestimations of observed eWUE. By contrast, the PMLv2 product achieved significantly more satisfactory performance in eWUE estimations and only slightly underestimated the observed eWUE during the peak of growing seasons for maize and slightly overestimated the observed eWUE during the start and end of growing seasons for both maize and soybean. The underestimations of observed eWUE for maize mainly stem from the underestimation of GPP from the PMLv2 product, which has been discussed above. The slight overestimations of observed eWUE for soybean can be explained by that the overestimations of GPP were more pronounced than that of ET and the small value of ET.
4.2. Implications and Future Work
This study first evaluated the performance of the coupled PMLv2 and uncoupled MODIS products in the eight-day and annual GPP, ET, and eWUE estimations for C4 maize and C3 soybean and subsequently analyzed the uncertainty in the RS-based GPP, ET, and eWUE estimates. To acquire high-accuracy eWUE based on the widely used RS-based GPP and ET products over cropland, some modifications for the RS-based products should be implemented to eliminate those systematic biases of eWUE: (1) the PMLv2 and MODIS products are expected to separately calibrate the model free parameter over cropland by differentiating C4 and C3 crop species to better reflect their different photosynthesis and transpiration; (2) the MOD17 product should be re-parameterized to eliminate the severe systematic underestimations of observed GPP; and (3) both two products should be calibrated and validated at more cropland sites to enhance their feasibility.
The coupled product can effectively avoid internal inconsistencies between ET and GPP from the uncoupled product and therefore could provide higher-accuracy eWUE estimates [13]. Over the years, a large amount of eWUE-related research (e.g., the spatial and temporal variation of eWUE, the response of eWUE to drought and natural and human activities, and the driver of eWUE changes [1,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]) has been conducted for various PFTs (including but not limited to cropland); however, most of these studies calculated eWUE based on the MODIS product, whose accuracy is strongly queried by this study as well as previous studies [2,13,49]. This study indicates that the coupled product is more suitable and effective to be applied in the eWUE-related research for different crop species to reduce the uncertainty from the inaccurate RS-based eWUE estimates from the uncoupled products. In future work, more coupled products (e.g., BESS and BEPS) and those high-accuracy uncoupled products (e.g., GLASS and FLUXCOM) could be further validated for more various crop species (e.g., barley, rape, and wheat) to explore the best combination of GPP and ET products for eWUE estimations. Note that some uncertainties may be caused by the imperfect match between 500 m remote sensing pixels and in-situ observations. For the sites with homogeneous landscapes (such as the US-Ne1, US-Ne2, and US-Ne3 sites, please see Figure 1), the in-situ observations could be treated as the relative truth to validate the remote sensing data collected at the collocated pixels, and the evaluation is more reliable. However, for the sites with less homogeneous landscapes (such as the US-Ro1 and US-Ro5 sites), the mismatch issue may not be negligible and reduce the reliability of the evaluation. Take the US-Ro5 site for example, a few trees that fall within 500 m of the site may lead to a certain degree of errors in eWUE estimates from the MODIS and PMLv2 products, since the remote sensing products treat the underlying surface of the 500 m pixel as the homogeneous cropland. However, it is difficult to quantitatively explore the uncertainty without a specific and sophisticated C4 and C3 species map. In future work, more attempts should be implemented to address this issue.
5. Summary and Conclusions
This study evaluated the eight-day and annual GPP, ET, and eWUE from the uncoupled MODIS product and the coupled PMLv2 product against the in-situ observations for C4 maize and C3 soybean at five cropland sites from the FLUXNET2015 and AmeriFlux datasets. The main conclusion of this study can be drawn as follows: (1) For GPP estimates, the PMLv2 product showed paramount improvements for C4 maize and slight improvements for C3 soybean, relative to the MODIS product. (2) For ET estimates, the PMLv2 product exhibited similar performances to the MOD16 product for C4 maize and C3 soybean. (3) For eWUE estimates, the coupled PMLv2 product could achieve higher-accuracy eWUE estimates than the uncoupled MODIS product at both eight-day and annual scales. Taking the result at an eight-day scale for example, compared to the MODIS product, the PMLv2 product could reduce the RMSE from 2.14 g C Kg−1 H2O to 1.36 g C Kg−1 H2O and increase the R2 from 0.06 to 0.52 for C4 maize, as well as reduce the RMSE from 1.33 g C Kg−1 H2O to 0.89 g C Kg−1 H2O and increase the R2 from 0.05 to 0.49 for C3 soybean. (4) Despite the outperformance of the PMLv2 product, both two products failed to differentiate C4 and C3 crop species in their model calibration and validation processes, leading to a certain degree of uncertainties in eWUE estimates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.H., M.L. and N.Y.; methodology, L.H.; software, L.H.; validation, L.H. and N.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, L.H.; writing—review and editing, L.H., M.L. and N.Y.; visualization, L.H. and N.Y.; supervision, M.L.; funding acquisition, M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Projects for High-Resolution Earth Observation Systems (No. 09-Y30F01-9001-20/22), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42001310, 42371401), and the China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely appreciate the staff members from the FLUXNET2015 and AmeriFlux network for providing meteorological and flux data and the MODIS and PMLv2 data teams for providing the GPP and ET products.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Chao, L.; Ezaz, G.T.; Li, X.; Forzieri, G. Recent Seasonal Variations in Ecosystem Water Use Efficiency in China’s Key Tropical-Subtropical Transitional Zones in Response to Climate Change. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2022, 36, e2022GB007635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Yao, F.; Guo, H. The Potential of Remote Sensing-Based Models on Global Water-Use Efficiency Estimation: An Evaluation and Intercomparison of an Ecosystem Model (BESS) and Algorithm (MODIS) Using Site Level and Upscaled Eddy Covariance Data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 287, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lin, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Tang, R. A Two-Stage Light-Use Efficiency Model for Improving Gross Primary Production Estimation in Agroecosystems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 104021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Cai, W.; Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Fang, H.; Suyker, A.E.; Chen, Y.; Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Uncertainty in Simulating Gross Primary Production of Cropland Ecosystem from Satellite-Based Models. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 207, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Improvements of the MODIS Terrestrial Gross and Net Primary Production Global Data Set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wu, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J. A Global Moderate Resolution Dataset of Gross Primary Production of Vegetation for 2000–2016. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Guan, K.; Wu, G.; Peng, B.; Wang, S. A Daily, 250 m and Real-Time Gross Primary Productivity Product (2000–Present) Covering the Contiguous United States. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Schwalm, C.; Migliavacca, M.; Walther, S.; Camps-Valls, G.; Koirala, S.; Anthoni, P.; Besnard, S.; Bodesheim, P.; Carvalhais, N.; et al. Scaling Carbon Fluxes from Eddy Covariance Sites to Globe: Synthesis and Evaluation of the FLUXCOM Approach. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 1343–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, B.; Miralles, D.G.; Lievens, H.; van der Schalie, R.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Fernández-Prieto, D.; Beck, H.E.; Dorigo, W.A.; Verhoest, N.E.C. GLEAM v3: Satellite-Based Land Evaporation and Root-Zone Soil Moisture. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2017, 10, 1903–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Fisher, J.B.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Bayesian Multimodel Estimation of Global Terrestrial Latent Heat Flux from Eddy Covariance, Meteorological, and Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4521–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Koirala, S.; Weber, U.; Ichii, K.; Gans, F.; Camps-Valls, G.; Papale, D.; Schwalm, C.; Tramontana, G.; Reichstein, M. The FLUXCOM Ensemble of Global Land-Atmosphere Energy Fluxes. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Gan, R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Coupled Estimation of 500 m and 8-Day Resolution Global Evapotranspiration and Gross Primary Production in 2002–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Liu, J.; Cihlar, J.; Goulden, M.L. Daily Canopy Photosynthesis Model through Temporal and Spatial Scaling for Remote Sensing Applications. Ecol. Model. 1999, 124, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ryu, Y. Multi-Scale Evaluation of Global Gross Primary Productivity and Evapotranspiration Products Derived from Breathing Earth System Simulator (BESS). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 528–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.T.; Woodrow, I.E.; Berry, J.A. A Model Predicting Stomatal Conductance and Its Contribution to the Control of Photosynthesis under Different Environmental Conditions. In Progress in Photosynthesis Research; Biggins, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 221–224. ISBN 978-94-017-0521-9. [Google Scholar]
- Leuning, R. A Critical Appraisal of a Combined Stomatal-Photosynthesis Model for C3 Plants. Plant Cell Environ. 1995, 18, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlyn, B.E.; Duursma, R.A.; Eamus, D.; Ellsworth, D.S.; Colin Prentice, I.; Barton, C.V.M.; Crous, K.Y.; de Angelis, P.; Freeman, M.; Wingate, L. Reconciling the Optimal and Empirical Approaches to Modelling Stomatal Conductance. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Gentine, P.; Huang, Y.; Guan, K.; Kimm, H.; Zhou, S. Diel Ecosystem Conductance Response to Vapor Pressure Deficit Is Suboptimal and Independent of Soil Moisture. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 250–251, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guan, L.; Liu, X. Directly Estimating Diurnal Changes in GPP for C3 and C4 Crops Using Far-Red Sun-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S.W.; Nemani, R.R.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Reeves, M.; Hashimoto, H. A Continuous Satellite-Derived Measure of Global Terrestrial Primary Production. BioScience 2004, 54, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a Global Evapotranspiration Algorithm Based on MODIS and Global Meteorology Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Natural Evaporation from Open Water, Bare Soil and Grass. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Monteith, J.L. Solar Radiation and Productivity in Tropical Ecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 1972, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Eamus, D.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Yu, Q. Use of Satellite Leaf Area Index Estimating Evapotranspiration and Gross Assimilation for Australian Ecosystems: Coupled Estimates of ET and GPP. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, N.; Tian, J.; Kong, D.; Liu, C. A Daily and 500 m Coupled Evapotranspiration and Gross Primary Production Product across China during 2000–2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 5463–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Doughty, R.; Yang, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X. Evolution of Light Use Efficiency Models: Improvement, Uncertainties, and Implications. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 317, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Berry, J.A.; Baldocchi, D.D. What Is Global Photosynthesis? History, Uncertainties and Opportunities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, J.; He, L.; Arain, M.A.; Thomas, S.C.; Murphy, J.G.; Geddes, J.A.; Black, T.A. Inverting the Maximum Carboxylation Rate (V Cmax) from the Sunlit Leaf Photosynthesis Rate Derived from Measured Light Response Curves at Tower Flux Sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 236, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Yin, G.; Nan, X. Derivation of Temporally Continuous Leaf Maximum Carboxylation Rate (V) from the Sunlit Leaf Gross Photosynthesis Productivity through Combining BEPS Model with Light Response Curve at Tower Flux Sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasslop, G.; Reichstein, M.; Papale, D.; Richardson, A.D.; Arneth, A.; Barr, A.; Stoy, P.; Wohlfahrt, G. Separation of Net Ecosystem Exchange into Assimilation and Respiration Using a Light Response Curve Approach: Critical Issues and Global Evaluation: Separation of NEE into GPP and RECO. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhao, L.; Liang, C.; Cui, N.; Gong, D.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Zou, Q. Comparison of Satellite-Based Models for Estimating Gross Primary Productivity in Agroecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 297, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, M. Improving the Global MODIS GPP Model by Optimizing Parameters with FLUXNET Data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 300, 108314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ma, M.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Yang, H. The Uncertainty Analysis of the MODIS GPP Product in Global Maize Croplands. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pan, M.; Mu, Q.; Shi, X.; Mao, J.; Brümmer, C.; Jassal, R.S.; Krishnan, P.; Li, J.; Black, T.A. Comparing Evapotranspiration from Eddy Covariance Measurements, Water Budgets, Remote Sensing, and Land Surface Models over Canada. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1540–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velpuri, N.M.; Senay, G.B.; Singh, R.K.; Bohms, S.; Verdin, J.P. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Two MODIS Evapotranspiration Products over the Conterminous United States: Using Point and Gridded FLUXNET and Water Balance ET. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinukollu, R.K.; Wood, E.F.; Ferguson, C.R.; Fisher, J.B. Global Estimates of Evapotranspiration for Climate Studies Using Multi-Sensor Remote Sensing Data: Evaluation of Three Process-Based Approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kimball, J.S.; Yi, Y.; Running, S.W.; Guan, K.; Moreno, A.; Wu, X.; Maneta, M. Satellite Data-Driven Modeling of Field Scale Evapotranspiration in Croplands Using the MOD16 Algorithm Framework. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 230, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Manevski, K.; Yi, S.; Zhao, X. Variation of Gross Primary Production, Evapotranspiration and Water Use Efficiency for Global Croplands. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 287, 107935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; He, B.; Han, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z. A Global Examination of the Response of Ecosystem Water-Use Efficiency to Drought Based on MODIS Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhai, P.; Piao, S. Divergent Responses of Ecosystem Water Use Efficiency to Drought Timing over Northern Eurasia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 045016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Assessing the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Water Use Efficiency across China and the Response to Natural and Human Activities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Fan, B.; Li, L.; Tan, B.; Jin, Z.; Lu, H.; Liu, T. Spatial Responses of Ecosystem Water-Use Efficiency to Hydrothermal and Vegetative Gradients in Alpine Grassland Ecosystem in Drylands. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe Terán, C.; Naz, B.S.; Graf, A.; Qu, Y.; Hendricks Franssen, H.-J.; Baatz, R.; Ciais, P.; Vereecken, H. Rising Water-Use Efficiency in European Grasslands Is Driven by Increased Primary Production. Commun Earth Env. 2023, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Cropland Ecosystem Water-Use Efficiency and the Responses to Agricultural Water Management in the Shiyang River Basin, Northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Qu, H.; Xing, W.; Zhou, C.; Tu, Y.; He, Z. Spatial and Temporal Drought Characteristics in the Huanghuaihai Plain and Its Influence on Cropland Water Use Efficiency. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.-L.; Guo, Q.; Otto, A.; Xiao, J.; Tao, S.; Li, L. Global Patterns, Trends, and Drivers of Water Use Efficiency from 2000 to 2013. Ecosphere 2015, 6, art174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, T.; Xiao, J.; Liu, S.; Mao, K.; Song, L.; Yao, Y.; He, X.; Feng, H. Responses of Water Use Efficiency to Drought in Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Contrasting Trends in Water Use Efficiency of the Alpine Grassland in Tibetan Plateau. JGR Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD036919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).