Abstract
This study assesses four Satellite-derived Precipitation Products (SPPs) that are corrected and validated against gauge data such as Soil Moisture to Rain—Advanced SCATterometer V1.5 (SM2RAIN-ASCAT), Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation V2.8 (MSWEP), Global Precipitation Measurement Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM Final run V6 (GPM IMERGF), and Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station (CHIRPS). We evaluate the performance of these SPPs in Nepal’s Myagdi Khola watershed, located in the Kali Gandaki River basin, for the period 2009–2019. The SPPs are evaluated by validating the gridded precipitation products using the hydrological model, Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). The results of this study show that the SM2RAIN-ASCAT and GPM IMERGF performed better than MSWEP and CHIRPS in accurately simulating daily and monthly streamflow. GPM IMERGF and SM2RAIN-ASCAT are found to be the better-performing models, with higher NSE values (0.63 and 0.61, respectively) compared with CHIRPS and MSWEP (0.45 and 0.41, respectively) after calibrating the model with monthly data. Moreover, SM2RAIN-ASCAT demonstrated the best performance in simulating daily and monthly streamflow, with NSE values of 0.57 and 0.63, respectively, after validation. This study’s findings support the use of satellite-derived precipitation datasets as inputs for hydrological models to address the hydrological complexities of mountainous watersheds.
1. Introduction
Precipitation is an important component of the global terrestrial water cycle [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Precipitation data are essential for hydrological modeling [5,7,8], used in hydraulic studies [9], environmental studies [10,11,12], and climate change investigations [5]. Obtaining accurate and reliable precipitation data in remote and rugged areas, such as mountainous regions, is particularly challenging due to the high spatial and temporal variability of data, the sparse and irregular distribution of rain gauge networks, the inadequate spatial representation of in situ measurements, and the failure of climate stations due to natural disasters [7,13,14]. Satellite products have gained popularity for estimating or measuring precipitation and simulating streamflow in recent decades [6,8,15,16,17]. They are not limited by complex terrain and can provide consistent, wider spatial coverage and higher temporal resolution precipitation values compared with gauge-based datasets. Several studies have demonstrated the benefits of satellite products in this regard, including those by [16,18,19,20].
The use of satellite-derived precipitation products (SPPs) is promising for supporting improved water resources management in Nepal, particularly the Himalayan region. The Himalayas make up almost 85% of Nepal’s terrain, and the water reservoirs are the main source of several rivers providing water to millions of people residing in the downstream areas [14,21,22]. Due to Nepal’s complex geography, the summer monsoon system governs most of the country’s precipitation [14,23,24]. The number of rain gauge-based stations in most mountain areas, particularly in high-elevation areas of Nepal, is significantly lower compared with low-elevation areas. This sporadic distribution poses difficulty in conducting hydro-meteorological studies, as noted by [25]. The lack of rain gauge observations hinders the country’s ability to recognize precipitation patterns and conduct comprehensive water management [26]. However, this issue can be solved by utilizing satellite-derived precipitation products. This approach is essential in the case of Nepal, where it can significantly improve the country’s ability to manage water resources effectively.
There are two primary approaches commonly used to evaluate SPP performance: (1) direct comparison of satellite-derived precipitation estimates with in situ precipitation data, and (2) capability assessment of SPPs to simulate streamflow through hydrological models [7,13]. Many researchers have used these approaches to assess various SPPs over different climate regions [3,13,16,17,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. The evaluation and validation of SPPs for a specific area may not apply to others owing to the heterogeneity of the terrain, climate, soil, and land cover [7]. Therefore, a separate evaluation is needed to test the reliability of selected SPPs over any region.
Numerous regional studies have assessed the reliability of SPPs for hydrological simulations [6,34]. Ref. [5] assessed the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) and Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station (CHIRPS) datasets in the catchment of the Gurupura River in India. They simulated streamflow using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model and validated the results against the streamflow simulations using rainfall data from the India Meteorological Department (IMD). Similarly, ref. [16] conducted an assessment of eight gauge-corrected and uncorrected precipitation products, including Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (GPM-IMERG), Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks (PERSIANNs), Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA), and Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation (CHIRP). They combined direct comparison methods with in situ precipitation data and hydrological simulation to comprehensively assess the performance of rainfall products using a hydrological model across six river basins, each representing different climatic regions in Vietnam.
Ref. [6] thoroughly evaluated three SPPs for a sub-basin in the Mekong River Basin. Additionally, several studies have been performed in Nepal using different SPPs. Ref. [14] evaluated the spatial patterns in satellite-only and gauge-calibrated precipitation products and compared them with 387-gauge measurements in Nepal. Ref. [17] assessed the aptness of four SPPs, PERSIANNs, TMPA, CHIRPS, and Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation (MSWEP), in capturing rainfall attributes across mountainous Himalayan watersheds.
The current literature on the use of SPPs in Nepal has focused on the comparison of different SPPs for discharge simulations in Nepal and its river basins [13,15]. However, due to the challenges associated with obtaining reliable and consistent climate data in the Himalayan region, it is imperative that researchers evaluate various SPPs to assess the performance of streamflow simulation in the Himalayan region of Nepal.
This study aims to evaluate four SPPs for predicting streamflow in the mountainous watersheds of Nepal, where traditional gauge observations are difficult to obtain. This study focuses on the Myagdi Khola watershed, a mountainous watershed that lacks climatic data such as precipitation and temperature. The SPPs used in this study were selected based on data availability, watershed characteristics, and resolution of data. The results of this study fill knowledge gaps in the region and contribute to a better understanding of Nepal’s mountain hydrology via the use of SPPs for streamflow simulation. Insight into the best-performing SPPs will help inform improved water resource management practices in the region by supporting additional hydrological modeling capabilities.
2. Study Area
The Kali Gandaki River originates from the Nhubine Himal Glacier in the Mustang region of Nepal, at an elevation of 6268 m above mean sea level (amsl). The Kali Gandaki River flows south through a steep gorge known as the Kali Gandaki gorge between the Dhaulagiri Mountain range (8167 m amsl to the west) and the Annapurna I Mountain range (8091 m amsl to the east). The Kali Gandaki Gorge is the deepest gorge in the world [35]. Myagdi Khola is one of the main tributaries of the Kali Gandaki River. It is a river with its source at Mount Dhaulagiri, which then passes through the Myagdi district to meet the Kali Gandaki River. The Myagdi Khola watershed was chosen to represent a mountainous watershed (Figure 1) as this watershed has significant variability in terms of elevation, ranging from about 830 to 8130 m amsl (Figure 2). The total area of the watershed is approximately 1100 square kilometers (km2).
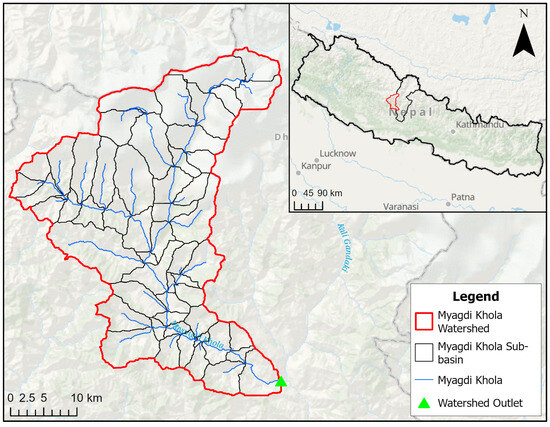
Figure 1.
Map showing the Myagdi Khola watershed (study area) with 55 delineated sub-basins.
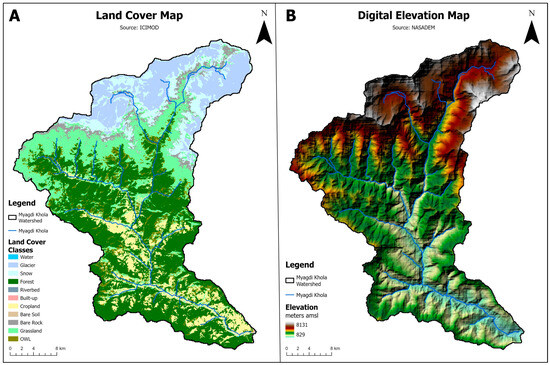
Figure 2.
(A) Land cover map and (B) digital elevation map of Myagdi Khola watershed.
The majority of the Myagdi Khola watershed is encompassed by glaciers, snow, forests, and grasslands (Figure 2). In some hilly areas and along the river, the land is used for agricultural purposes, as indicated by cropland. The land cover map reveals a minimal presence of developed (urban) areas in the study area, implying that the watershed is largely in its natural state, except for some agricultural activities initiated by humans.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methodology
This study aims to evaluate the performance of SPPs in the Himalayan region of Nepal by comparing simulated and observed streamflow. The flowchart of the research methodology adopted in this study is shown in Figure 3.
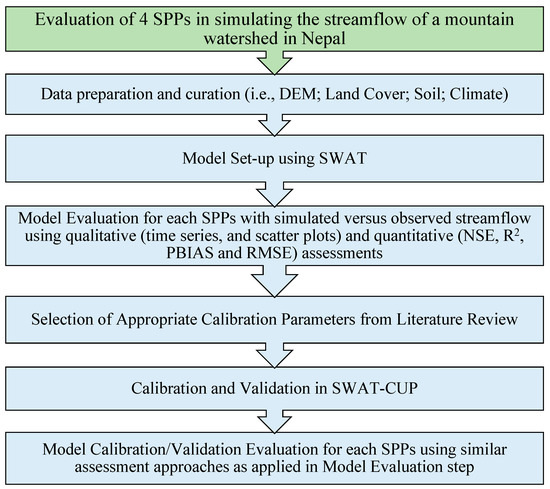
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the research methodology adopted in this study.
First, the Digital Elevation Model (DEM), land cover, soil, and climate data were processed into a suitable format for use as inputs to the hydrological model, SWAT. The domain and inputs for the SWAT model were developed in the second step, and simulation runs were performed using each SPP under consideration.
The third step involved assessing the simulated results from each SPP before the model evaluation process. The quantitative assessment metrics NSE (Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency), RMSE (Root Mean Square Error), PBIAS (Percent Bias), and R2 (Coefficient of Determination) were used to evaluate the models’ performance. Similarly, time series and scatter plots were used for the qualitative assessment.
In the fourth step, appropriate calibration parameters were identified based on parameters commonly used by other modelers for SWAT model calibration in similar regions [35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. Next, the model was calibrated and validated using the SWAT-CUP tool. Lastly, the model for each SPP was calibrated and validated using a similar approach to the model evaluation.
3.2. In Situ Data
This study used daily discharge data of one hydrological gauging station located at the outlet/mouth of the Myagdi Khola, Nepal, from 1 January 2009 to 31 December 2019. The streamflow data were obtained from the Department of Hydrology and Meteorology (DHM), a department under the Nepalese government responsible for gathering and disseminating official climate and hydrological data to the public.
3.3. Spatial Data for SWAT
In this study, NASADEM was chosen as the DEM for SWAT input. This DEM dataset has a spatial resolution of 30 × 30 m (NASA JPL, 2021; accessed on 5 November 2022) (Figure 2). NASADEM is a modernized version of the DEM, generated from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data, and has been used in several studies with SWAT [8,42,43]. The slope was estimated and the watershed boundary was delineated using NASADEM data (https://opentopography.org/, accessed on 5 November 2022). Land cover data at a resolution of 30 × 30 m were obtained from the RDS (Regional Database System) of the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) (http://rds.icimod.org/Home/DataDetail?metadataId=1972729; (FRTC/ICIMOD, 2022) accessed on 5 November 2022). The NLCMS (National Land Cover Monitoring System) has mapped Nepal’s annual land cover from 2000 to 2019. Using a standardized classification method, NLCMS uses remote-sensed Landsat images and applies machine learning techniques in the GEE (Google Earth Engine) environment to generate land cover maps annually (FRTC/ICIMOD, 2022). The NLCMS was devised by the FRTC (Forest Research and Training Centre), Ministry of Forests and Environment, Government of Nepal, with support from the ICIMOD. The land cover data were divided into eleven classes, as shown in Figure 2. The 30 m spatial resolution data related to soil information, which were resampled from the original spatial resolution of 30 arc-s (~1 km), were retrieved from the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) database called Harmonized World Soil Database (FAO, 2009) (https://www.fao.org/; accessed on 5 November 2022). Table 1 describes spatial data used as input in the SWAT model setup. The threshold limit to delineate 55 sub-basins (Figure 1) was 10 km2. The selection of a threshold limit to delineate 55 sub-basins was based on the criterion of achieving an optimal number of sub-basins for the watershed and their centroid points. This approach effectively displayed the spatial distribution of the watershed under study. This choice was also made to facilitate the use of climate data uniformly represented spatially and temporally as input for the model.

Table 1.
Description of spatial data used in the SWAT model setup.
3.4. Satellite-Derived Precipitation Products
Table 2 shows the description of selected SPPs used in this study. Given the relatively small size of the study area (watershed), the SPPs were configured to have a finer spatial and temporal resolution to enhance the efficiency of the analysis and the accuracy of the expected results [6,16,18,19].

Table 2.
Description of the selected SPPs.
3.4.1. GPM IMERGF
GPM IMERG Final run (GPM IMERGF) is a satellite-derived rainfall product that utilizes a set of instructions for estimation and seeks to internally incorporate, interpolate, and calibrate various microwave precipitation estimations [47,51]. GPM IMERGF utilizes analyses from precipitation gaging stations, estimates from calibrated infrared satellites, and other estimators. The IMERGF precipitation data has a 0.1° spatial resolution, is available for areas covering latitudes ranging from 60°S to 60°N, and has a short time interval of about 30 min compared with the TMPA product [47]. This study used the IMERG Final run rather than the Early or Late runs, as many fine-tuning and validation approaches have been considered to generate this dataset. The daily gridded GPM IMERGF dataset was downloaded from the Giovanni website (https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/, accessed on 8 November 2022).
3.4.2. MSWEP
MSWEP is a recently launched global precipitation product with 0.1° spatial resolution and a temporal resolution of 3 h available from 1979 to near real time [48,52]. The MSWEP uniquely combines rain gauge data, satellite data from Global Satellite Mapping and Precipitation Moving Vector with the Kalman filter (GSMaP-MVK), the CPC MORPHing technique (CMORPH), and TMPA 3B42RT, and data from the Japanese 55-year Reanalysis (JRA-55) and European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Re-Analysis (ERA)-Interim to obtain the highest quality precipitation estimates at every location. The Climate Hazards Precipitation Climatology (CHPClim) dataset was used to obtain MSWEP (V1.0) data using long-term average values but was replaced with more precise regional datasets [48,52]. The adjustment for under-catch of gauge and rain shadow effects was first proposed by [3] using average catchment rainfall and streamflow measurements at 13,762 sites globally. Since then, notable changes have been made to MSWEP (V2.8), such as improved finer spatial resolution, corrected frequency for precipitation, different cumulative distribution functions applied, and the use of a satellite-derived thermal infrared imaging estimator to obtain the precipitation estimates. This study obtained the daily gridded MSWEP dataset downloaded from the GloH2O website (http://www.gloh2o.org/mswep/ (accessed on 9 November 2022)).
3.4.3. SM2RAIN-ASCAT
Soil Moisture to Rain—Advanced SCATterometer V1.5 (SM2RAIN-ASCAT) is a newer satellite-derived global precipitation product incorporating soil moisture conditions collected by the operational satellite MetOp from the European Meteorological Satellite (EUMETSAT) Organization (Darmstadt, Germany). This product utilizes an advanced algorithm called SM2RAIN using a bottom-up approach to obtain precipitation estimates using soil moisture data [49,53,54,55]. It was generated using the soil WAter Retrieval Package (WARP) algorithm and ASCAT soil moisture data obtained from MetOp-A and MetOp-B satellites [54]. The 0.125° spatial resolution SM2RAIN–ASCAT daily gridded data were extracted from the link https://zenodo.org/record/6136294 (accessed on 10 November 2022).
3.4.4. CHIRPS
CHIRPS is a quasi-global precipitation dataset, with spatial coverage from 50°S to 50°N and temporal coverage from 1981 to the present. The 0.05° spatial resolution dataset is calibrated and validated using data from rainfall gauges to create gridded precipitation data (Funk et al., 2015). CHIRPS integrates several data sources, including the CHPClim, the TRMM 3B42 from NASA, atmospheric rainfall models from NOAA, Thermal Infrared (TIR) satellite observations, and ground rainfall measurements from various meteorological offices around the globe [50]. This U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) dataset, generated in collaboration with the Climate Hazards Group at the University of California, Santa Barbara, is organized in a grid format. It can be accessed using the link https://data.chc.ucsb.edu/products/CHIRPS-2.0/ (accessed on 12 November 2022).
3.4.5. SWAT Model
SWAT is a semi-distributed physical hydrological model that can incorporate climate data of daily, monthly, and annual time steps to predict streamflow, study sediment movement, and assess water quality of watersheds of any given scale and complexity [56]. The model was developed by the Agriculture Research Service (ARS) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) [57]. SWAT’s small spatial unit is known as the Hydrologic Response Unit (HRU). For estimating streamflow, it is anticipated that runoff will be predicted separately for each Hydrological Response Unit (HRU) with detailed explanation provided by [58]. In recent years, the SWAT tool has become popular in modeling the river basins of the United States, Europe, and other regions [36,37,59] as the model has the capability to handle complex hydrological problems [60]. Other efforts have been made that employed the SWAT model regarding the effects of land use [4,61], climate change impacts [6,43,62], validating DEM products [63], or determining the robustness of SPPs [16,42].
A daily timestep was chosen for the model run with two years (2007–2008) as a period for warm-up over the selected simulation period of 11 years (2009–2019). The calibration period was set between 2009 and 2014 (6 years). The validation period was established between 2015 and 2019 (5 years). Based on the literature review findings on the parameters often used by other modelers to calibrate their SWAT models in similar regions, twenty-nine parameters were selected for calibration and validation as shown in the Supplementary Materials, Table S1, including their short name, methods applied, full name, and their normal range in this study [35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. The number of SWAT parameters for calibration was kept the same for all SPPs to ensure consistency when evaluating the modeled data. The calibration was first run using the range of values in the Supplementary Materials, Table S1 (the SWAT-CUP tool defines the maximum and minimum values for the listed parameters).
After the first calibration run, the newly fitted range for each parameter was used for the final calibration run. The fitted range from the last calibration run was used for validation. The streamflow observed from 2009 to 2019 at the Myagdi Khola station was obtained and used for calibration and validation. The observed streamflow data had several gaps from 2000 to 2008; therefore, the 2009–2019 period was selected for this study. The calibration run was from 2009 to 2014 (6 years), and the validation run was from 2015 to 2019 (5 years). In this study, the calibration and validation were performed using the Sequential Uncertainty Fitting version 2 (SUFI-2) technique and an objective function Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) via SWAT-CUP software (V5.2.1) mentioned by [64,65]. The calibrated parameters used in this study can be found in the Supplementary Materials, Table S1.
3.5. Evaluation Metrics
Table 3 shows the equation and optimal value of the model performance metrics used. The performance of the model, driven by the selected Satellite-derived Precipitation Products (SPPs) for accurate streamflow prediction, was assessed using NSE, PBIAS, RMSE, and R2 [12,66,67]. The R2 values indicate the correlation strength between observed and simulated streamflow values. NSE reflects how well the simulation aligns with the observations. RMSE values indicate the absolute errors of the SPPs. PBIAS assesses the extent to which the simulated streamflow overestimates or underestimates the observations at the gauging station. Specifically, a positive PBIAS value indicates an overestimation relative to the gauging observations, while a negative PBIAS value indicates an underestimation [17].

Table 3.
Performance metrics to evaluate hydrological models.
The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is a popularly used metric to quantify the variations between values predicted by a model and the actual values observed in the modeled environment. RMSE aggregates these individual differences, also referred to as residuals, into a single measure of the model’s predictive capability. It essentially quantifies the discrepancy between two datasets, thus comparing the predicted values with the known or observed values.
The Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) is a normalized metric that measures the difference between the variance in residuals (variance in the model residuals or errors) and the variance in the observed data [68]. It assesses how closely observed vs. simulated data align with the identity (1:1) line. An NSE of 1 denotes a perfect fit between the modeled and the observed data. An NSE between negative infinity and 0 suggests the mean of the observed data is a worthier predictor than the modeled one, while an NSE of 0 indicates that the model’s predictions are as accurate as the mean of the observed data.
Percent bias (PBIAS) measures the bias of the simulated values to be bigger or smaller than their observed counterparts. Low magnitudes of PBIAS indicate a more accurate model simulation, with 0.0 being the optimal value. Negative values of PBIAS signify a bias toward model underestimation, whereas positive values indicate a bias toward model overestimation.
The coefficient of determination (R²) is a value between 0 and 1 that quantifies how well a statistical model predicts an outcome, with the dependent variable in the model representing the outcome. R² can range from as low as 0 to as high as 1. The closer to 1, the more accurate it is. R² is a more refined measure of the goodness of fit of a model. It represents the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that is explained by the model.
4. Results
4.1. Qualitative Assessment
4.1.1. Model Evaluation Results
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the time series plot of daily and monthly mean simulated versus observed streamflow before calibration. The daily simulated streamflow is challenging to interpret against observed data due to the high noise in the streamflow values, leading to many attenuation peaks that impede qualitative assessments and make it harder to identify any discernible patterns or trends. On the other hand, the monthly simulated versus observed streamflow time series is more straightforward to interpret than its daily counterpart. The monthly time series provides a broader and more generalized view of the water flow patterns over a more extended period. The figures below represent an assessment of the quality of model simulation runs for each SPP. Although the simulation failed to capture the flood peak in all SPPs considered for the study, the SM2RAIN-ASCAT and GPM-IMERGF products could simulate higher monthly streamflow than the MSWEP and CHIRPS products. The simulated flood volume is lower than the observed flood volume in all SPPs, leading to the assumption that the model failed to predict the streamflow of the watershed from the model accurately.
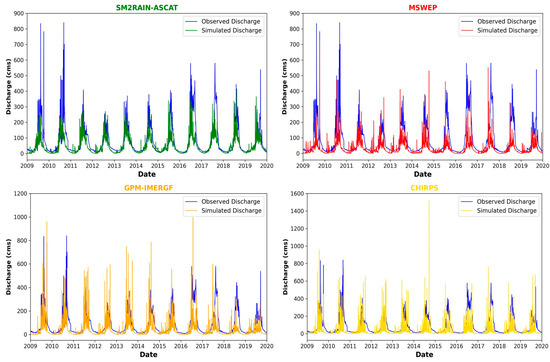
Figure 4.
The comparison of daily simulated vs. observed streamflow for 4 SPPs before calibration.
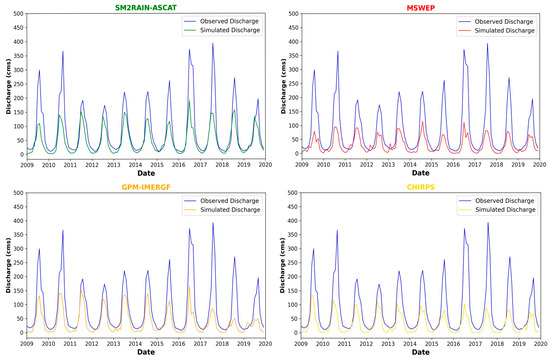
Figure 5.
The comparison of monthly simulated vs. observed streamflow for 4 SPPs before calibration.
Similarly, the simulated low flows are comparable and are somewhat closer to the observed data for each SPP, in contrast to the notable difference observed in the case of simulating peak flows. SM2RAIN-ASCAT can simulate the low flows much better than the other products, as the simulated flows are close to the observed flows.
Furthermore, the models are capable of capturing the seasonality of the flows. It can be inferred that the SPPs considered in this study can simulate the seasonality of streamflow of the watershed but failed to simulate flood peak and volume, which may indicate that the hydrological model has inadequately simulated some key hydrological components. These findings were noted before the calibration process was carried out on the models.
Figure 6 and Figure 7 depict the scatter plots that compare daily and monthly simulated versus observed streamflow for the four SPPs before the calibration process. The poor correlation between the simulated and observed data in the figures is primarily attributed to the inability of the models to simulate flood volume and capture peak flows accurately. Additionally, the plots highlight notable differences in simulated and observed streamflow for all four SPPs. However, SM2RAIN-ASCAT shows a relatively better correlation with an R2 value of 0.53 in daily flows compared with other products. Although the value of 0.53 is lower than the optimal value of 1, it demonstrates a relatively better correlation than other products. An interesting observation is that MSWEP exhibits a better correlation coefficient value of 0.36 than GPM-IMERGF (R2 = 0.27). Referring to Figure 5, GPM-IMERGF produces better-simulated results, with better-predicted flow peaks than those from the MSWEP product. However, the scatter plot shows that MSWEP exhibits more consistent and comparable simulated values than GPM-IMERGF. Meanwhile, CHIRPS demonstrates a very low correlation coefficient value (R2 = 0.14) between simulated and observed streamflow.
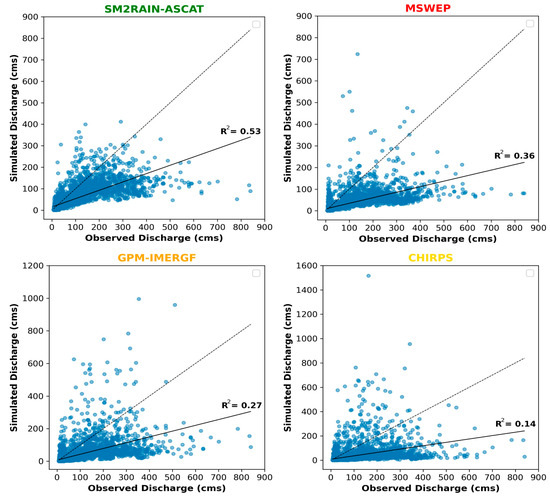
Figure 6.
Daily simulated vs. observed streamflow scatter plot before calibration for 4 SPPs with a trend line showing R2 values and a 1:1 linear line (dashed line) drawn as a reference line.
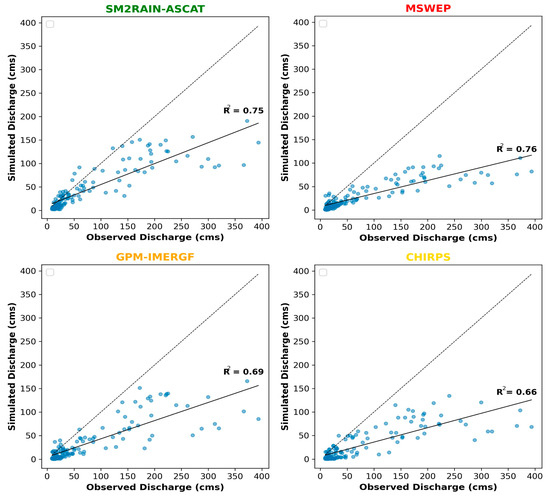
Figure 7.
Monthly simulated vs. observed streamflow scatter plot before calibration for 4 SPPs with a trend line showing R2 values and a 1:1 linear line (dashed line) drawn as a reference line.
The correlation coefficient values are higher for monthly flows compared with daily flows. The values increased for all SPPs. Monthly data are aggregated and averaged over the daily data, resulting in significantly lesser variability in daily flows while aggregating into monthly flows, as observed in Figure 7. MSWEP showed the highest correlation coefficient value of 0.76, followed by SM2RAIN-ASCAT, with a correlation value 0.75. GPM-IMERGF and CHIRPS correlation coefficient values significantly increased to 0.69 and 0.66, respectively.
Furthermore, while aggregating the daily flows into monthly flows, the uncertainty associated with daily flows significantly decreases, resulting in a significant increase in the correlation coefficient values. Aggregating the data produced better results and facilitated the interpretation of findings in this study.
4.1.2. Streamflow Evaluation
This study re-evaluated the model performance by examining the peak flow, low flows, time of peak flow, seasonal trend, and flood volume using newly calibrated and validated simulated and observed streamflow data. Time series plots of daily and monthly mean simulated vs. observed streamflow were generated after the calibration and validation processes, as shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9. The calibration process, which involved considering all the essential calibration parameters for a mountainous watershed, calibrating the models with 1000 simulation runs, and narrowing the range of fitted values of the calibrated parameters, led to a slight improvement in the model’s performance of all SPPs.
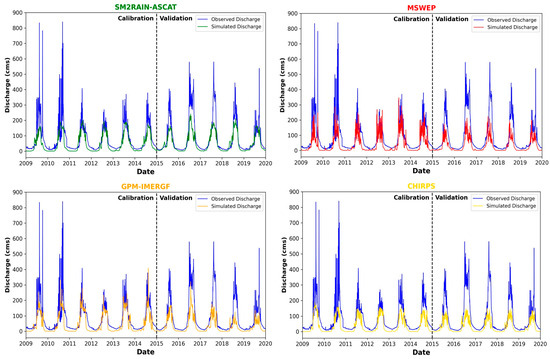
Figure 8.
The comparison of daily simulated versus observed streamflow for 4 SPPs after calibration and validation.
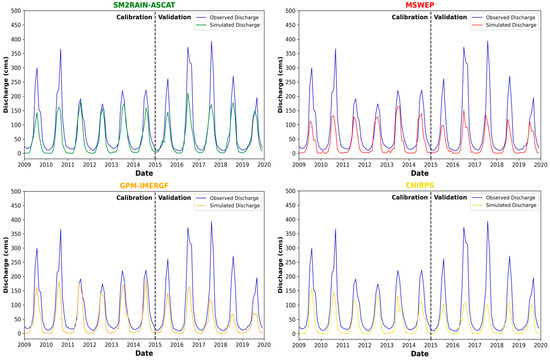
Figure 9.
The comparison of monthly simulated versus observed streamflow for 4 SPPs after calibration and validation.
While the peak simulated flows slightly increased, they underestimated the observed streamflow. However, the daily data showed less attenuation of peaks when compared with the plots before calibration, as observed in Figure 8. The SM2RAIN-ASCAT product exhibited improved performance in simulating peak flows and flood volume, while the GPM IMERGF product showed improvements in the calibration period but did not fare better in the validation period, as seen in Figure 9. The MSWEP and CHIRPS models also improved their performance but did not fare well compared with the SM2RAIN-ASCAT and GPM-IMERGF models.
Furthermore, the seasonal trend is closely related to the observed trend, as seen in Figure 9, which indicates that the hydrological dynamics are accurate but not precise enough for a mountainous watershed in Nepal. All models simulated the time to peak flow when compared against observed data, indicating that the streamflow seasonality was simulated accurately. Lastly, it can be deduced that the calibration process helped improve the model performance by improving the simulations to capture higher flood peaks and increase the flood volume of the watershed.
4.2. Quantitative Assessment
Table 4 and Table 5 present the model performance metrics in model evaluation (before calibration), calibration, and validation stages for evaluating simulated daily and monthly streamflow from four SPPs. The performance evaluation metrics, especially R2 and NSE, showed a significant increase after calibration, which adds confidence to the modeled data. GPM IMERGF performed better in the calibration process, whereas SM2RAIN-ASCAT performed better in the validation process, as indicated in the tables below. MSWEP and CHIRPS did not perform well in the calibration and validation periods.

Table 4.
Model performance metrics before and after calibration for evaluating simulated daily and monthly streamflow from 4 SPPs.

Table 5.
Model performance metrics after validation for evaluating simulated daily and monthly streamflow from 4 SPPs.
After calibration of daily data, GPM IMERGF and SM2RAIN-ASCAT were found to be the better-performing models, with higher NSE values (0.48 and 0.46, respectively) compared with CHIRPS and MSWEP (NSE values of 0.34 and 0.32, respectively). In addition, R2 values increased for all models after calibration, indicating improved performance with increased correlation between simulated and observed daily streamflow data.
After calibration of monthly data, the model runs using GPM IMERGF and SM2RAIN-ASCAT were found to be the better-performing models, with higher NSE values (0.63 and 0.61, respectively) compared with CHIRPS and MSWEP (0.45 and 0.41, respectively). In addition, R2 values increased for all models except for MSWEP after calibration, indicating improved performance with increased correlation between simulated and observed monthly streamflow data.
SM2RAIN-ASCAT demonstrated the best performance in simulating daily and monthly streamflow in the validation period, with NSE values of 0.57 and 0.63, respectively, as indicated in Table 5. The GPM IMERGF model, on the other hand, displayed poor performance during the validation stage, in contrast to the calibration stage, with NSE values of only 0.29 and 0.33 for daily and monthly data, respectively. Notably, R2 values were higher for all models during validation, indicating an increased correlation between simulated and observed daily and monthly streamflow data.
Other performance metrics, such as RMSE and PBIAS, could not provide definitive evidence and support for model performance evaluations in any given scenario and period. Thus, the quantitative assessment for the model performance evaluation using RMSE and PBIAS values was inconclusive. However, NSE and R2 metrics proved adequate for evaluating model performance and drawing reasonable conclusions for this study.
5. Discussion
Nepal’s mountain hydrology is complex due to the heterogeneous topography. The various hydrological processes, such as precipitation, snow, and groundwater, are inextricably linked to the topography [69]. Nepal also experiences diverse climatic conditions owing to the heterogeneity in the country’s topography. The country’s diverse climatic conditions can be attributed to the heterogeneity in topography, with low-lying plains or areas having tropical and sub-tropical climates and high-elevation regions such as the Himalayas having tundra and polar frost climates [69,70]. Summer monsoons and westerlies are Nepal’s two dominant weather systems [70]. Most of the annual precipitation in Nepal falls during the monsoon period (June–September), and the rest falls during the pre-monsoon (March–May), post-monsoon (October–November), and winter (December–February) periods [14,70]. Due to the topographical differences, Nepal’s mountainous regions receive less rainfall than other regions. However, these areas possess ample snowpacks, glaciers, and ice that are crucial in driving and regulating the hydrological processes. To understand the hydrological patterns in Nepal’s mountainous terrain, it is essential to grasp the intricate interactions among different hydrological processes and the utilization of SPPs in hydrological modeling applications.
The variation in the SPPs themselves also presents limitations to the study. Each satellite product considered in this study varies in terms of its inherent characteristics for processing the estimates. The SPPs have different spatial and temporal resolutions. Differences in capturing the rainfall data in each product and how the estimates are calibrated and validated using ground observations also make a difference in simulating results and performing a model evaluation. Furthermore, due to complex topography, the high variability of precipitation patterns observed in both temporal and spatial scales within the watershed could affect the rainfall estimates from these products.
In this study, the SM2RAIN-ASCAT product performed better in predicting streamflow in the Myagdi Khola watershed. This can be attributed to the satellite’s rainfall retrieval algorithm incorporating a soil moisture dataset to detect rainfall events [55]. Since forests, snow, and glaciers largely cover the watershed, soil must be saturated to predict better surface runoff estimates. When the soil is saturated in the watershed, there is less infiltration, and most of the rainfall becomes surface runoff, ultimately reflecting on the river streamflow. The simulated streamflow obtained from the model utilizing the rainfall data from the SM2RAIN-ASCAT product closely aligns with the observed discharge, thereby supporting the above deductions.
It is worth noting that while the SM2RAIN-ASCAT product has been shown to perform well in the given watershed, several studies [8,49,55] have highlighted its limitations in providing accurate precipitation estimates in mountainous regions, particularly those covered by snow and glaciers. Thus, it is important to acknowledge that the SM2RAIN-ASCAT product may not be the optimal choice for every mountainous watershed, and alternative products should be considered based on the specific characteristics of the region under study.
The GPM IMERG product also uses an algorithm that attempts to intercalibrate, combine, and interpolate satellite microwave precipitation estimates, as well as microwave-calibrated infrared satellite estimates, rain gauge analyses, and other precipitation estimates at finer temporal and spatial scales [47]. This data product is further processed using monthly gauge data, providing precipitation estimates with more accuracy and reliability that ultimately reflects the model performance observed in this study. Because of the usage of microwave-calibrated estimates incorporated into the product’s algorithm, GPM IMERGF can easily detect light rainfall and snowfall, leading to better precipitation estimates. This is particularly useful for mountainous watersheds such as the Myagdi Khola watershed. Watersheds in mountainous regions typically receive light rainfall and snowfall. Therefore, advanced functionalities incorporated into the algorithm of the GPM-IMERG give more confidence to the model output and provide trust in accurately estimating river discharge in the complex mountainous Himalayan watersheds.
Despite the calibration process, the model simulation runs failed to increase the baseflow and peak flow, and it is worth delving into why the models failed to simulate groundwater or snowmelt components in the Myagdi Khola watershed. The complex topography of this watershed, where most mountain areas are covered by glaciers and snow followed by forest cover, may be responsible for the failure to estimate or simulate groundwater and snowmelt flows. The land cover data used as a model input might not accurately represent the watershed, adding more uncertainties and limitations to the simulations. The precipitation product alone might not be sufficient to simulate the runoff in the watershed, and this might be why the model could not simulate enough flow even after calibrating the model with important groundwater and snow parameters. Further, SPPs that were considered might not have incorporated solid precipitation into their estimates, causing a big difference in the simulated and observed streamflow.
The results highlight that setting up a hydrological model for a mountainous Himalayan watershed is complex. There was an underperformance of modeled results with all four SPPs used in this study. There were some notable limitations when carrying out this study, which contributed to the underperformance of the models. Our study area has no observed rainfall data; thus, we rely only on precipitation from SPPs as model inputs. SPPs make many assumptions, and the data may not be accurate due to cloud cover or missing data from equipment malfunctions.
Additionally, the Myagdi Khola watershed is regarded as an ungauged watershed, with the only streamflow values available at the watershed’s outlet. The watershed was assessed using selected SPPs with limited observations. Utilizing observed climate data to calibrate and validate the satellite rainfall products before establishing a hydrological model to evaluate streamflow would likely have yielded more accurate results and definitive conclusions. Moreover, this study might have improved the simulation of streamflow results and higher accuracy in the model performance metrics if a larger watershed was considered for this kind of study, as carried out by [15,29].
The sensitivity analysis for the selected calibration parameters was not performed here as this study’s main objective was to evaluate different SPPs, keeping model parameters and model characteristics the same so that the results or output from the model show consistency and are capable of comparison across all SPPs that are under consideration. Different calibration parameters will be sensitive across four different SPPs under consideration, making it challenging to evaluate models fed by these SPPs’ precipitation estimates. The simulation, calibration, and validation period considered in this study was short to obtain accurate predictions on the river discharge; therefore, taking a more extended period would provide better prediction results.
6. Conclusions
This study aimed to evaluate the performance of SPPs in predicting the streamflow of a complex mountainous watershed in Nepal. The following are the main findings from this study:
- (1)
- The hydrological modeling approach using SPPs effectively predicts streamflow in mountainous watersheds with limited or no observed precipitation data. These products can be used to study hydrological processes in ungauged mountainous watersheds, albeit with some limitations.
- (2)
- Four finer-resolution SPPs were assessed, and SM2RAIN-ASCAT exhibited the best overall performance among other SPPs, followed closely by the GPM IMERGF in simulating streamflow more accurately when compared with observed streamflow at the outlet of the watershed.
- (3)
- Monthly streamflow simulations driven by SPPs outperformed daily streamflow simulations, and gauge-corrected satellite precipitation products fed into the model outperformed in simulating discharge estimates in the watershed. The study found that gauge-corrected SPPs can effectively simulate discharge in Himalayan watersheds, even with limited ground truth data.
- (4)
- Although the performance metrics did not show promising results as anticipated even after the extensive calibration process, they were within satisfactory to good performance levels.
Overall, this study highlights the capability of SPPs in predicting the streamflow of a mountainous watershed with minimal data available for validating estimates. The study’s findings suggest that SPPs can address hydrological complexities in mountainous watershed regions with some limitations. This study supports and highlights the use of SPPs for hydrological studies in mountainous watersheds.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs15194762/s1.
Author Contributions
Concept: A.A.; research methodology: A.A. and T.-N.-D.T.; analysis: A.A.; writing—original draft: A.A.; writing-review and editing: A.A., T.-N.-D.T., B.K. and V.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Due to the confidentiality agreement between authors and providers, the data are not publicly accessible.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the developers of GPM IMERG, MSWEP, SM2RAIN-ASCAT, and CHIRPS in making these products publicly accessible. We extend our sincere gratitude to Kyung "Robin" Kim and Manh-Hung Le for helping us with data processing. We would also like to thank Sophia Bakar for helping with the editing process. Additionally, we would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments during this paper’s review period.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflict of interest in this study.
References
- Arshad, A.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Jehanzeb, M.; Cheema, M.; Jafari, M. Reconstructing high-resolution gridded precipitation data using an improved downscaling approach over the high altitude mountain regions of Upper Indus Basin (UIB). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Five Satellite-Based Precipitation Products in Two Gauge-Scarce Basins on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.Q.; Tran, T.N.D.; Grodzka-Łukaszewska, M.; Sinicyn, G.; Lakshmi, V. Assessment of Urbanization-Induced Land-Use Change and Its Impact on Temperature, Evaporation, and Humidity in Central Vietnam. Water 2022, 14, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharannya, T.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Barma, S.D.; Mahesha, A. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products in Simulating Streamflow in a Humid Tropical Catchment of India Using a Semi-Distributed Hydrological Model. Water 2020, 12, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Le, M.-H.; Zhang, R.; Nguyen, B.Q.; Bolten, J.D.; Lakshmi, V. Robustness of gridded precipitation products for Vietnam basins using the comprehensive assessment framework of rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2023, 293, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizi, H.; Sorman, A.A. Assessment of 13 Gridded Precipitation Datasets for Hydrological Modeling in a Mountainous Basin. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Zhang, R.; Aryal, A.; Łukaszewska, M.-G.; Sinicyn, G.; Lakshmi, V. Quantification of Gridded Precipitation Products for the Streamflow Simulation on the Mekong River Basin Using Rainfall Assessment Framework: A Case Study for the Srepok River Subbasin, Central Highland Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Tam, D.; Le, L.; Nguyen, T.D.; Vo, N.D.; Gourbesville, P. Evaluate the Influence of Groynes System on the Hydraulic Regime in the Ha Thanh Rive, Binh Dinh Province, Vietnam. In Advances in Hydroinformatics: Models for Complex and Global Water Issues—Practices and Expectations; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Lee, H.; Do, S.K.; Du, T.L.T.; Markert, K.; Hossain, F.; Khalique, S.; Piman, T.; Meechaiya, C.; Bui, D.D.; et al. Operational forecasting inundation extents using REOF analysis (FIER) over lower Mekong and its potential economic impact on agriculture. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 162, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.L.T.; Lee, H.; Bui, D.D.; Graham, L.P.; Darby, S.D.; Pechlivanidis, I.G.; Leyland, J.; Biswas, N.K.; Choi, G.; Batelaan, O.; et al. Streamflow Prediction in Highly Regulated, Transboundary Watersheds Using Multi-Basin Modeling and Remote Sensing Imagery. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gädeke, A.; Krysanova, V.; Aryal, A.; Chang, J.; Grillakis, M.; Hanasaki, N.; Koutroulis, A.; Pokhrel, Y.; Satoh, Y.; Schaphoff, S.; et al. Performance evaluation of global hydrological models in six large Pan-Arctic watersheds. Clim. Chang. 2020, 163, 1329–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall products through hydrologic simulation in a fully distributed hydrologic model. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.B.; Ali, M.; Aryal, D.; Paneru, L.; Shrestha, B. Spatial Pattern of Precipitation in GPM-Era Satellite Products against Rain Gauge Measurements over Nepal. Jalawaayu 2021, 1, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Lakshmi, V. Accessing the capability of TRMM 3B42 V7 to simulate streamflow during extreme rain events: Case study for a Himalayan River Basin. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 127, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.H.; Lakshmi, V.; Bolten, J.; Bui, D.D. Adequacy of Satellite-derived Precipitation Estimate for Hydrological Modeling in Vietnam Basins. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, R.; Silwal, P.; Duwal, S.; Shrestha, S.; Kafle, A.S.; Talchabhadel, R.; Kumar, S. Detectability of rainfall characteristics over a mountain river basin in the Himalayan region from 2000 to 2015 using ground- and satellite-based products. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 147, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, W.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Ji, X. Hydrological Simulation Using TRMM and CHIRPS Precipitation Estimates in the Lower Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunilkumar, K.; Yatagai, A.; Masuda, M. Preliminary Evaluation of GPM-IMERG Rainfall Estimates Over Three Distinct Climate Zones with APHRODITE. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Arakawa, O.; Kamiguchi, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Nodzu, M.I.; Hamada, A. A 44-Year Daily Gridded Precipitation Dataset for Asia Based on a Dense Network of Rain Gauges. SOLA 2009, 5, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, D.M.; Kansakar, S.R.; Gerrard, A.J.; Rees, G. Flow regimes of Himalayan rivers of Nepal: Nature and spatial patterns. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Lutz, A.F.; Andrade, M.; Bahl, A.; Biemans, H.; Bolch, T.; Hyde, S.; Brumby, S.; Davies, B.J.; Elmore, A.C.; et al. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 2019, 577, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamal, K.; Khadka, N.; Rai, S.; Joshi, B.B.; Dotel, J.; Khadka, L.; Bag, N.; Ghimire, S.K.; Shrestha, D. Evaluation of the TRMM Product for Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Precipitation over Nepal (1998–2018). J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Lakhankar, T.; Jha, A.K. Evaluating Satellite Products for Precipitation Estimation in Mountain Regions: A Case Study for Nepal. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4107–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Tartari, G.; Bellocchi, G. Geospatial Rainfall Modelling at Eastern Nepalese Highland from Ground Environmental Data. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2703–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam Md, N.; Das, S.; Uyeda, H. Calibration of TRMM derived rainfall over Nepal during 1998–2007. Open Atmos. Sci. J. 2010, 4, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Yu, B.; Cartwright, N. Assessment and comparison of five satellite precipitation products in Australia. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; He, D.; Guo, R.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Yue, C.; Liu, C. Evaluation of bias correction methods for APHRODITE data to improve hydrologic simulation in a large Himalayan basin. Atmos. Res. 2020, 242, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Amarnath, G.; Ghosh, S.; Park, E.; Baghel, T.; Wang, J.; Pramanik, M.; Belbase, D. Assessing the Performance of the Satellite-Based Precipitation Products (SPP) in the Data-Sparse Himalayan Terrain. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Li, J.; Feng, P.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Q. Evaluation of Multiple Satellite Precipitation Products and Their Use in Hydrological Modelling over the Luanhe River Basin, China. Water 2018, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviroli, D.; Dürr, H.H.; Messerli, B.; Meybeck, M.; Weingartner, R. Mountains of the world, water towers for humanity: Typology, mapping, and global significance. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.K.; Ueno, K.; Nakamura, K. Comparison of Satellite Precipitation Products with Rain Gauge Data for the Khumb Region, Nepal Himalayas. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 89, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, R.; Arshad, A.; Shafeeque, M.; Liu, J.; Baig, A. Combining APHRODITE Rain Gauges-Based Precipitation with Downscaled-TRMM Data to Translate High-Resolution Precipitation Estimates in the Indus Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, P.; Sood, A. Estimation of sediment load for Himalayan Rivers: Case study of Kaligandaki in Nepal. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N.; Najeebullah, K. Evaluation of gridded precipitation datasets over arid regions of Pakistan. Water 2019, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Tran, T.N.D.; Nguyen, Q.B. Applying semi distribution hydrological model SWAT to assess hydrological regime in Lai Giang catchment, Binh Dinh Province, Vietnam. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Sustainability in Civil Engineering (CSCE’20), Capital University of Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 12 August 2020; Available online: https://csce.cust.edu.pk/archive/20-404.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, P.K.; Talchabhadel, R. Evaluation and application of a SWAT model to assess the climate change impact on the hydrology of the Himalayan River Basin. Catena 2019, 181, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, P.K.; Talchabhadel, R. Modelling the impact of past and future climate scenarios on streamflow in a highly mountainous watershed: A case study in the West Seti River Basin, Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Pradhanang, S.M. Estimation of flow regime for a spatially varied Himalayan watershed using improved multi-site calibration of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Asce, M.; Patra, K.C. Evaluating the Uncertainties in the SWAT Model Outputs due to DEM Grid Size and Resampling Techniques in a Large Himalayan River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22, 04017039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.D.; Nguyen, B.Q.; Le, M.-H.; Lakshmi, V.V.; Bolten, J.D.; Aryal, A. Robustness of Gridded Precipitation Products in Hydrological Assessment for Vietnam River Basins. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 December 2022; p. H22M-07. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.N.D.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Vo, N.D.; Marshall, R.; Gourbesville, P. Assessment of Terrain Scenario Impacts on Hydrological Simulation with SWAT Model. Application to Lai Giang Catchment, Vietnam. In Advances in Hydroinformatics: Models for Complex and Global Water Issues—Practices and Expectations; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA JPL. NASADEM Merged DEM Global 1 Arc Second V001; Distributed by OpenTopography; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FRTC/ICIMOD. Land cover of Nepal [Data Set]; ICIMOD: Lalitpur, Nepal, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Harmonized World Soil Database—19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World. Available online: http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/harmonized-world-soil-database-v12/en/%0Ahttp://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soil-survey/soil-maps-and-databases/harmonized-world-soil-database-v12/en/ (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Wood, E.F.; Pan, M.; Fisher, C.K.; Miralles, D.G.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; McVicar, T.R.; Adler, R.F. MSWep v2 Global 3-hourly 0.1° precipitation: Methodology and quantitative assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Filippucci, P.; Hahn, S.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Schüller, L.; Bojkov, B.; Wagner, W. SM2RAIN-ASCAT (2007–2018): Global daily satellite rainfall data from ASCAT soil moisture observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1583–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, B.; Shi, C.; Cui, W.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. Evaluation of hydrological utility of IMERG Final run V05 and TMPA 3B42V7 satellite precipitation products in the Yellow River source region, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; De Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25° global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5128–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaravalloti, F.; Brocca, L.; Procopio, A.; Massari, C.; Gabriele, S. Assessment of GPM and SM2RAIN-ASCAT rainfall products over complex terrain in southern Italy. Atmos. Res. 2018, 206, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Hahn, S.; Kidd, R.; Melzer, T.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S.; Figa-Saldaña, J.; De Rosnay, P.; Jann, A.; Schneider, S.; et al. The ASCAT soil moisture product: A review of its specifications, validation results, and emerging applications. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part I: Model Development. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. SWAT Input Data. 2012. Chapter 29. pp. 393–406. Available online: https://swat.tamu.edu/docs/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil & Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 1–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapas, M.; Etheridge, J.R.; Howard, G.; Lakshmi, V.V.; Tran, T.N.D. Development of a Socio-Hydrological Model for a Coastal Watershed: Using Stakeholders’ Perceptions. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 December 2022; p. H22O-0996. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, A.; Mirchi, A.; Samimi, M.; Ahmad, B. Combining downscaled-GRACE data with SWAT to improve the estimation of groundwater storage and depletion variations in the Irrigated Indus Basin (IIB). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, A.; Tran, T.N.D.; Kim, K.Y.; Rajaram, H.; Lakshmi, V.V. Climate and Land Use/Land Cover Change Impacts on Hydrological Processes in the Mountain Watershed of Gandaki River Basin, Nepal. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Chicago, IL, USA, 14 December 2022; p. H52L-0615. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, A.; Le, M.H.; Lakshmi, V. Land use, climate, and water change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta (VMD) using earth observation and hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.D.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Vo, N.D.; Le, M.H.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Lakshmi, V.; Bolten, J. Quantification of Global Digital Elevation Model (DEM)—A Case Study of the Newly Released NASADEM for a River Basin in Central Vietnam. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 45, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Rouholahnejad, E.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H.; Kløve, B. A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: Calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J.; Maximov, I.; Siber, R.; Bogner, K.; Mieleitner, J.; Zobrist, J.; Srinivasan, R. Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D.; Sharma, S.; Hamal, K.; Khan Jadoon, U.; Dawadi, B. Spatial Distribution of Extreme Precipitation Events and Its Trend in Nepal. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 9, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, B.; Shrestha, D.; Sharma, S.; Shrestha, M.S.; Aryal, D.; Shrestha, N. Assessment of GPM-Era Satellite Products’ (IMERG and GSMaP) Ability to Detect Precipitation Extremes over Mountainous Country Nepal. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).