Evaluation of Deep Learning Segmentation Models for Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dataset
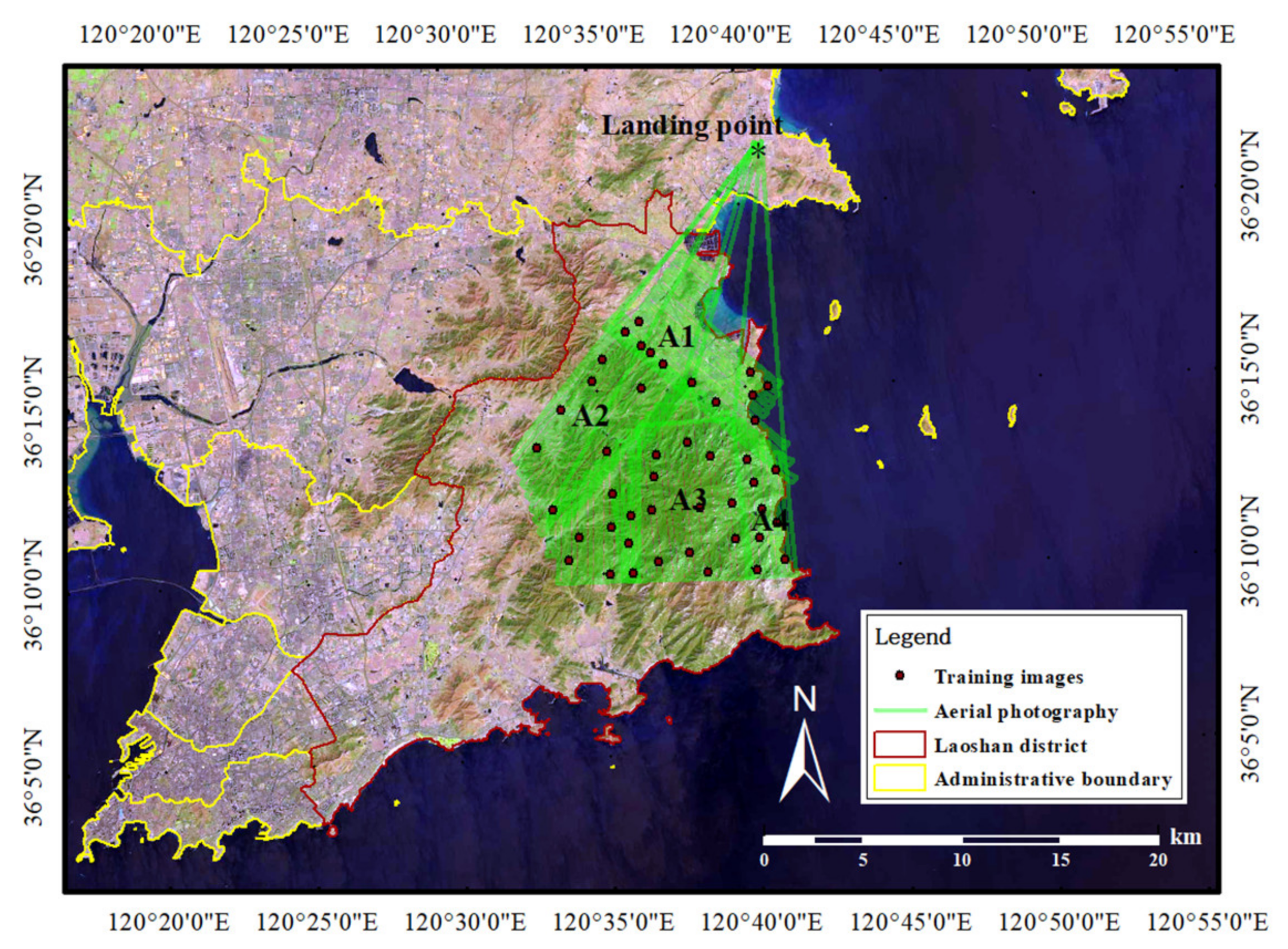
2.1. Study Area
2.2. UAV Image Collection
2.3. Field Survey
2.4. Data Annotation and Processing
3. Methods
3.1. Models
- Milestone segmentation fully convolutional networks (FCNs) for semantic segmentation [31].
3.2. Loss Function and Model Training
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
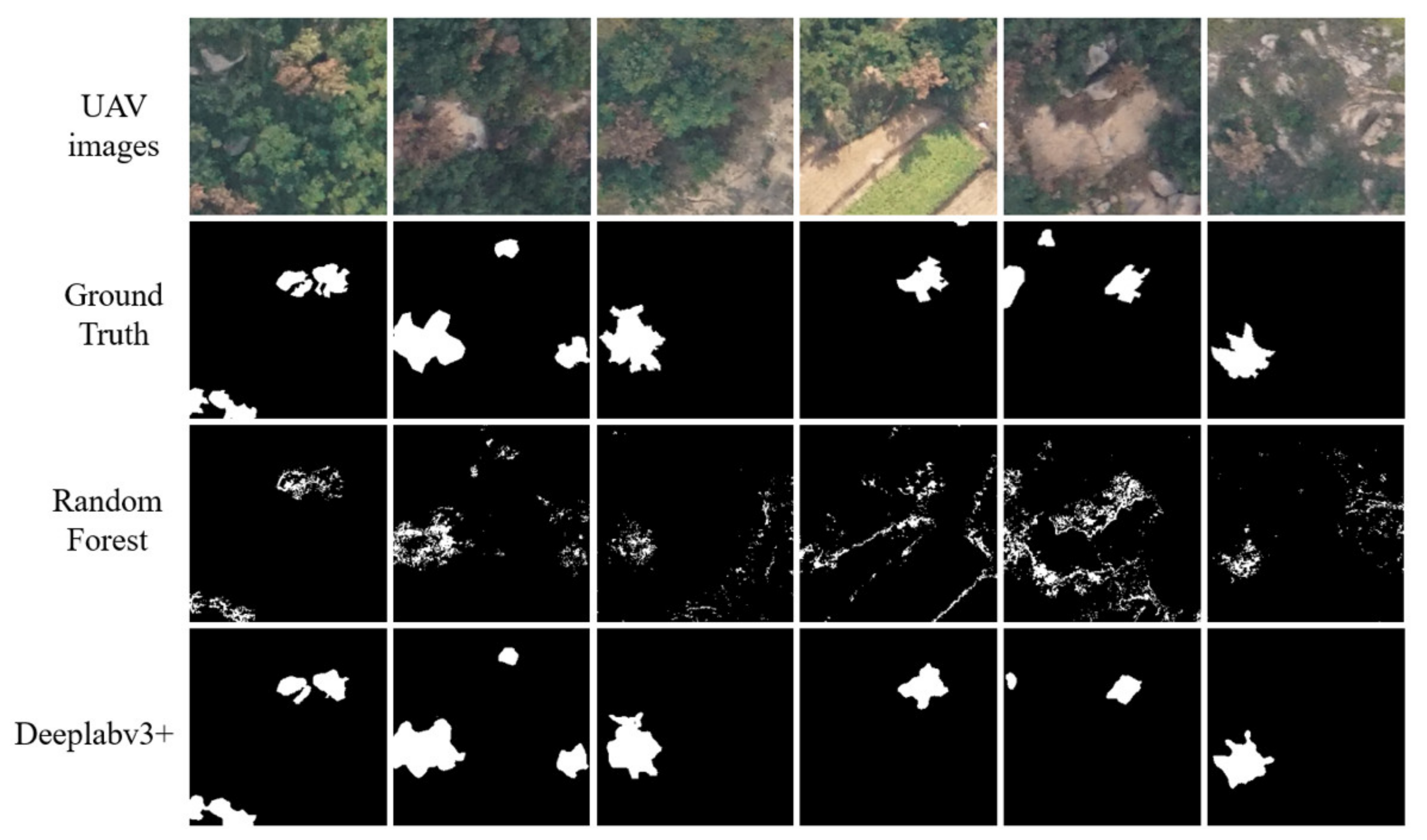
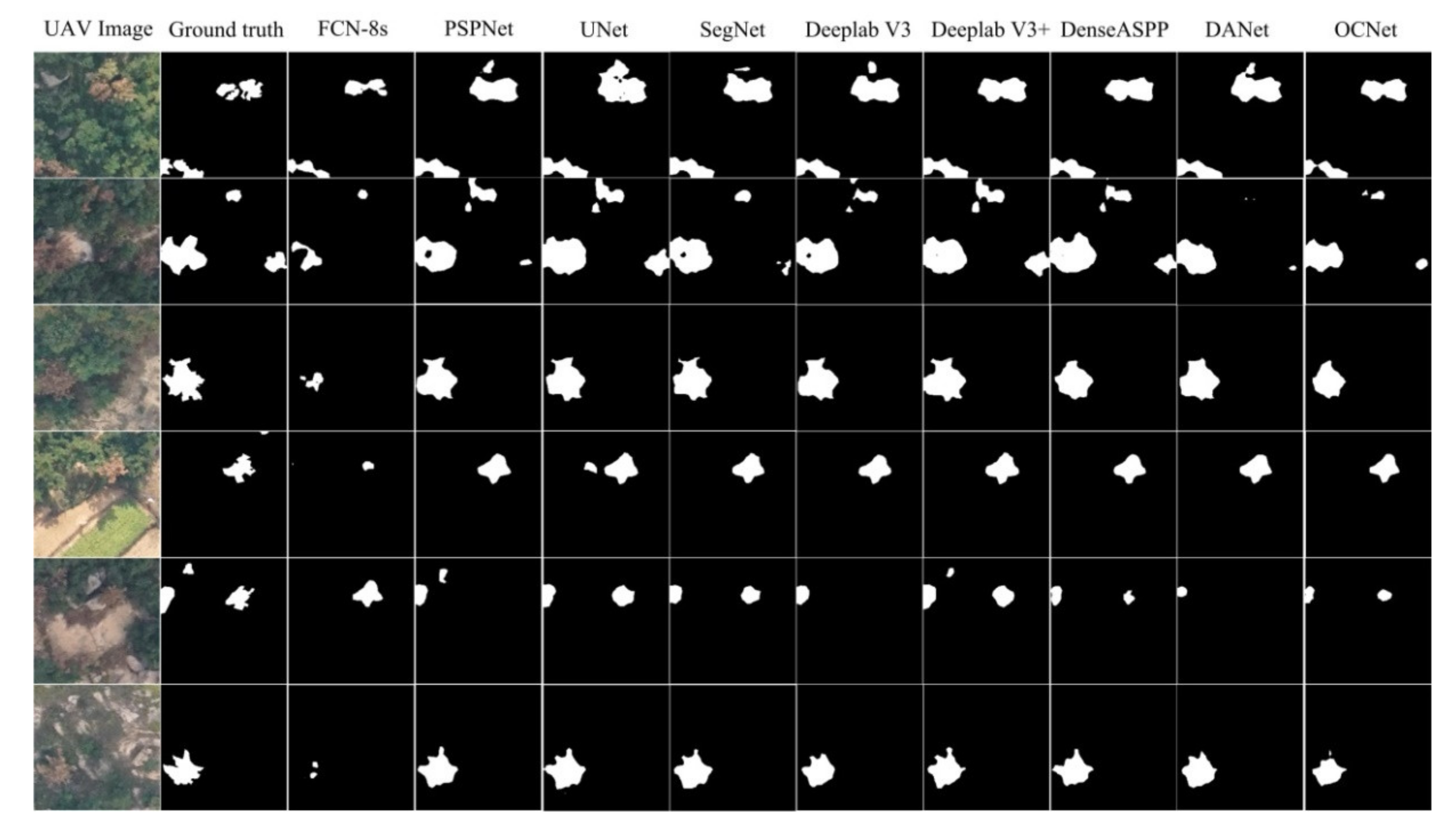
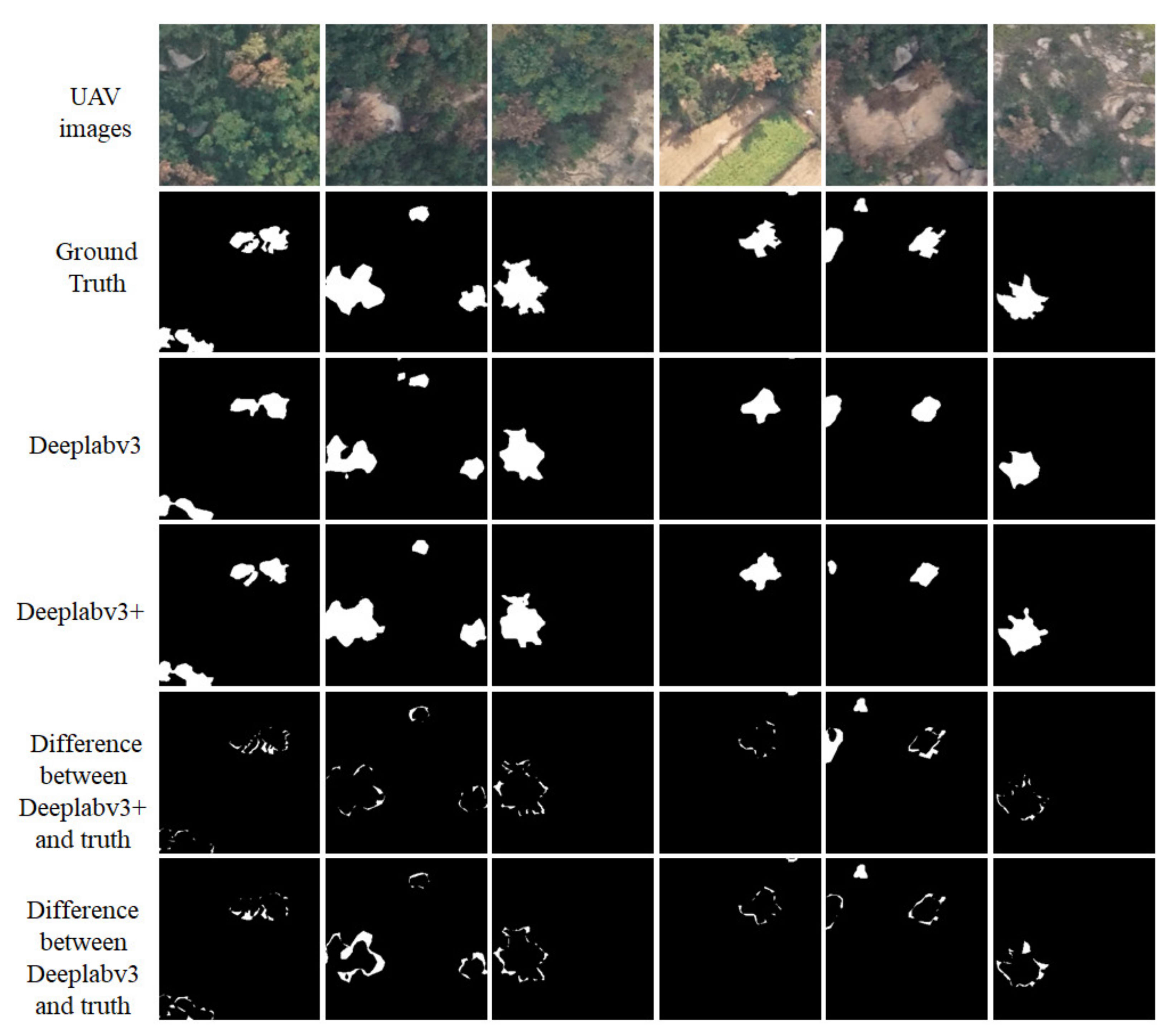
4. Results
- Milestone segmentation FCNs, with multiscale feature fusion using pyramid pooling or symmetric encoder–decoder.
- Multiscale feature fusion models using pyramid pooling or symmetric encoders–decoders.
- Models using dilated convolution to increase the receptive field and ASPP for multiscale feature fusion.
- Self-attention mechanism for multiscale feature fusion.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proença, D.; Grass, G.; Morais, P.V. Understanding pine wilt disease: Roles of the pine endophytic bacteria and of the bacteria carried by the disease-causing pinewood nematode. MicrobiologyOpen 2016, 6, e00415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Maximum Entropy Modeling to Predict the Impact of Climate Change on Pine Wilt Disease in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Zeng, Q.; Sun, F.; Li, D.-W.; Ye, J. Copy Number Variations of Glycoside Hydrolase 45 Genes in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Their Impact on the Pathogenesis of Pine Wilt Disease. Forests 2021, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Jeon, H.W.; Mannaa, M.; Jeong, S.I.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Park, A.R.; Kim, J.C.; Seo, Y.S. Induction of resistance against pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus using selected pine endophytic bacteria. Plant Pathol. 2019, 68, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.S.; Zhao, B.G.; Gao, R. Experiments on the relationship between the bacterium isolate B619 and the pine wilt disease by using Calli of Pinus thunbergii. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2001, 5, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, A.; Nakamura, K.; Nakao, K.; Kominami, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Ohashi, H.; Takano, K.; Takeuchi, W.; Matsui, T. Potential distribution of pine wilt disease under future climate change scenarios. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. Available online: http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/5462/20210521/114505021470794.html (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Firmino, P.N.; Calvão, T.; Ayres, M.P.; Pimentel, C. Monochamus galloprovincialis and Bursaphelenchus xylophilus life history in an area severely affected by pine wilt disease: Implications for forest management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 389, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Kawasaki, K.; Takasu, F.; Togashi, K.; Futai, K.; Shigesada, N. Modeling the spread of pine wilt disease caused by nematodes with pine sawyers as vector. Ecology 1999, 80, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liang, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, T.; Zou, Z.; Yang, D.; Tang, W.; Li, J.; Su, J. Application of conventional UAV-based high-throughput object detection to the early diagnosis of pine wilt disease by deep learning. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 486, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Hanan, J.; Qin, L. A hyperspectral GA-PLSR model for prediction of pine wilt disease. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 16645–16661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Research Progress on the Early Monitoring of Pine Wilt Disease Using Hyperspectral Techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liao, L.; Cheng, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q. Extraction of the Individual Tree Infected by Pine Wilt Disease Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Optical Imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 43, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ye, H.; Lu, W.; Huang, W.; Wu, B.; Hao, Z.; Sun, H. A Spatiotemporal Change Detection Method for Monitoring Pine Wilt Disease in a Complex Landscape Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xia, L.; Chen, L.; Xie, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, W. Recognition of wilt wood caused by pine wilt nematode based on U-Net network and unmanned aerial vehicle images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agricult. Eng. 2020, 36, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Brooks, D.; Reich, R.; Wheate, R.D. Detection of red attack stage mountain pine beetle infestation with high spatial resolution satellite imagery. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, J.A.; Logan, J. Mapping whitebark pine mortality caused by a mountain pine beetle outbreak with high spatial resolution satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2009, 30, 4427–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelcey, J.; Lucieer, A. Sensor Correction of a 6-Band Multispectral Imaging Sensor for UAV Remote Sensing. Remote. Sens. 2012, 4, 1462–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iordache, M.-D.; Mantas, V.; Baltazar, E.; Pauly, K.; Lewyckyj, N. A Machine Learning Approach to Detecting Pine Wilt Disease Using Airborne Spectral Imagery. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syifa, M.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, C.-W. Detection of the Pine Wilt Disease Tree Candidates for Drone Remote Sensing Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Engineering 2020, 6, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, M.; Bao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, D.; Yin, C. Detection of diseased pine trees in unmanned aerial vehicle images by using deep convolutional neural networks. Geocarto Int. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Tong, Z.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Z. Detection and Location of Dead Trees with Pine Wilt Disease Based on Deep Learning and UAV Remote Sensing. AgriEngineering 2020, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, D.; Deng, S.; Hu, H.; Xu, X.; Jing, W. Deep learning-based dead pine tree detection from unmanned aerial vehicle images. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2020, 41, 8238–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Ren, L. Early detection of pine wilt disease using deep learning algorithms and UAV-based multispectral imagery. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 497, 119493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, H. Identifying Pine Wood Nematode Disease Using UAV Images and Deep Learning Algorithms. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, S.; Trevor, D. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Philipp, F.; Thomas, B. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. Denseaspp for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3684–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene seg-mentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Ocnet: Object context network for scene parsing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00916. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, J.; Ding, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Robust liver vessel extraction using 3D U-Net with variant dice loss function. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 101, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]




| Model | Source | No. Parameters | Backbone | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | Long et al., 2015 | 15,305,667 | Xception | Milestone segmentation model |
| PSPNet | Zhao et al., 2017 | 48,755,113 | ResNet | Multiscale feature fusion using pyramid pooling or symmetric encoder–decoder |
| U-Net | Ronneberger et al., 2015 | 26,355,169 | ResNet | |
| SegNet | Badrinarayanan et al., 2015 | 16,310,273 | VGG16 | |
| DeepLabv3 | Chen et al., 2017 | 41,806,505 | ResNet | Dilated convolution |
| DenseASPP | Yang et al., 2018 | 27,161,537 | ResNet | |
| DeepLabv3+ | Chen et al., 2018 | 74,982,817 | ResNet | |
| DANet | Fu et al., 2019 | 49,607,725 | ResNet | Attention network |
| OCNet | Yuan et al., 2018 | 36,040,105 | ResNet |
| Model | IoU | F1 Score | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 0.672 | 0.798 | 0.805 | 0.791 |
| PSPNet | 0.649 | 0.781 | 0.753 | 0.811 |
| U-Net | 0.667 | 0.798 | 0.767 | 0.831 |
| SegNet | 0.652 | 0.778 | 0.764 | 0.793 |
| DeepLabv3 | 0.651 | 0.778 | 0.806 | 0.752 |
| DeepLabv3+ | 0.682 | 0.806 | 0.791 | 0.822 |
| DenseASPP | 0.676 | 0.798 | 0.806 | 0.790 |
| DANet | 0.634 | 0.771 | 0.769 | 0.773 |
| OCNet | 0.621 | 0.764 | 0.737 | 0.794 |
| Mean | 0.656 | 0.786 | 0.778 | 0.795 |
| Model | IoU | F1 Score | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 0.679 | 0.803 | 0.810 | 0.797 |
| PSPNet | 0.707 | 0.821 | 0.844 | 0.799 |
| U-Net | 0.708 | 0.819 | 0.824 | 0.815 |
| SegNet | 0.698 | 0.809 | 0.814 | 0.805 |
| DeepLabv3 | 0.699 | 0.819 | 0.863 | 0.780 |
| DeepLabv3+ | 0.720 | 0.832 | 0.838 | 0.826 |
| DenseASPP | 0.717 | 0.831 | 0.833 | 0.829 |
| DANet | 0.675 | 0.800 | 0.800 | 0.800 |
| OCNet | 0.708 | 0.825 | 0.838 | 0.813 |
| Mean | 0.701 | 0.818 | 0.829 | 0.807 |
| Improvement over models trained with Dice loss (%) | 6.86 | 4.08 | 6.56 | 1.51 |
| Model | Backbone | IoU | F1 | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSPNet | ResNet34 | 0.720 | 0.828 | 0.847 | 0.811 |
| ResNet50 | 0.707 | 0.821 | 0.844 | 0.799 | |
| ResNet101 | 0.706 | 0.821 | 0.856 | 0.789 | |
| ResNet152 | 0.710 | 0.823 | 0.820 | 0.825 | |
| DeepLabv3+ | ResNet34 | 0.720 | 0.832 | 0.831 | 0.832 |
| ResNet50 | 0.720 | 0.832 | 0.838 | 0.826 | |
| ResNet101 | 0.718 | 0.831 | 0.846 | 0.817 | |
| ResNet152 | 0.714 | 0.830 | 0.824 | 0.835 | |
| OCNet | ResNet34 | 0.718 | 0.832 | 0.841 | 0.823 |
| ResNet50 | 0.708 | 0.825 | 0.838 | 0.813 | |
| ResNet101 | 0.701 | 0.807 | 0.834 | 0.807 | |
| ResNet152 | 0.691 | 0.812 | 0.837 | 0.789 |
| Model | Backbone | IoU | F1 score | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3 | ResNet34 | 0.711 | 0.826 | 0.826 | 0.825 |
| ResNet50 | 0.699 | 0.819 | 0.863 | 0.780 | |
| ResNet101 | 0.701 | 0.819 | 0.844 | 0.795 | |
| ResNet152 | 0.706 | 0.819 | 0.820 | 0.819 | |
| DeepLabv3+ | ResNet34 | 0.720 | 0.832 | 0.831 | 0.832 |
| ResNet50 | 0.720 | 0.832 | 0.838 | 0.826 | |
| ResNet101 | 0.718 | 0.831 | 0.846 | 0.817 | |
| ResNet152 | 0.714 | 0.830 | 0.824 | 0.835 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Yi, T.; Wen, Y.; Ding, C.; Xie, C. Evaluation of Deep Learning Segmentation Models for Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183594
Xia L, Zhang R, Chen L, Li L, Yi T, Wen Y, Ding C, Xie C. Evaluation of Deep Learning Segmentation Models for Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(18):3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183594
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Lang, Ruirui Zhang, Liping Chen, Longlong Li, Tongchuan Yi, Yao Wen, Chenchen Ding, and Chunchun Xie. 2021. "Evaluation of Deep Learning Segmentation Models for Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images" Remote Sensing 13, no. 18: 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183594
APA StyleXia, L., Zhang, R., Chen, L., Li, L., Yi, T., Wen, Y., Ding, C., & Xie, C. (2021). Evaluation of Deep Learning Segmentation Models for Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Remote Sensing, 13(18), 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183594








