Abstract
Inland waters are warming at highly variable rates that often differ from regional air temperature trends. This variable warming is partially attributable to an individual lake’s geographical and morphological characteristics. In very large lakes, significant intralake variability in long-term warming trends has also been observed. In light of this intralake and interlake heterogeneity of lake surface water temperature (LSWT) and LSWT trends, we revisit the 1.1 km Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) record for the Laurentian Great Lakes. In this work, we have assembled a long-term (1986–2016) and high-spatial-resolution (0.018°) daily LSWT dataset using AVHRR record. Subtracting an empirically-determined mean diurnal cycle mitigates the effects of varying observation times. Adjustments in the georegistration of the images are made to reduce the impact of AVHRR navigational errors on the earlier platforms. Both the original daily composites, and a gap-filled product using locally weighted interpolation methods will be made available to support fine-scale physical and environmental research in the region.
1. Introduction
Globally, lake surface water temperatures (LSWTs) are warming at highly variable rates (global mean: 0.34 K decade−1; range: −0.7 to 1.3 K decade−1) [1], with high latitude lakes generally warming the fastest [2]. The warming water temperatures can have profound effects on freshwater ecosystems such as declining oxygen concentrations [3], increasing the basal metabolic rates of freshwater species [4,5], and facilitating the spread of invasive species [6,7]. The physical impacts experienced by inland waters as a result of lake warming include changes in wind speeds over lakes [8], decreases in ice cover [9,10], and changes in stratification of the water column [11,12]. Given these previously observed physical and ecological implications for inland waters, it is critical that a long-term monitoring system is able to diagnose the directionality and magnitude of long-term trends and the variability of LSWT. While long-term in situ records of water temperature are ideal for detecting such changes in many cases, these records are not available for most of the world’s lakes and are usually significantly lacking in spatial coverage of any one lake. Long-term satellite infrared observations have the ability to overcome this data limitation, as illustrated in several recent regional and global studies [1,2,13,14,15,16].
Trends in LSWT often exceed air temperature trends [1,10], with cold, deep lakes being particularly susceptible to interannual air temperature variability [17]. Others have noted significant spatial heterogeneity in summertime warming trends both within and between individual lakes in the Laurentian Great Lakes region [13] and other large lakes in the Northern Hemisphere [14]. It has been suggested that the variability in warming trends between lakes can be explained not only by climate drivers, but also a combination of other factors including wintertime ice-cover, latitude, and depth [1,10,17]. Similarly, intralake variability in summertime warming has also been associated with the variable bathymetry in large lakes with the deepest areas warming the fastest [14]. This motivates continued regional and global scale monitoring of inland water temperatures since few assumptions can be made about how surface water temperatures are changing with respect to air temperature trends, neighboring lakes, and other geomorphic factors individually.
One complicating factor in the measurement of sea surface temperature (SST) is the skin-effect and mean diurnal cycle of water temperature [18]. The depth at which the measurement is made is critical information due to the amount of variability that can occur in shallow temperature profiles [19]. Particularly, distinction is made between the skin temperature measured by infrared radiometers, and bulk temperatures often made by in situ measurements. The difference between these two sets of measurements is referred to as the skin-effect [20,21], and can have significant impact on interpretation of the measurement due to thermal stratification in the water column. Thus, it is a source of uncertainty in SST measurements [19]. These diurnal differences are largely a function of solar insolation and are lessened by mixing as wind speeds increase [21,22,23]. At low wind speeds, diurnal warming can elevate daytime surface temperature by 5 to 7 K above nighttime observations [24].
While most work on identifying diurnal variability in SSTs has been performed using satellite and in situ measurements over the ocean, much of what has been identified is also applicable to lakes. Cloud cover, high humidity, and wind speed can impact the magnitude of the lake skin-effect which is more variable in daytime observations [18]. While the oceanic skin-effect and the lake skin-effect are mechanistically similar, lakes undergo a wider range of atmospheric conditions that can drive skin-bulk differences [18]. There has also been an identified association between lake size and mean summer diurnal temperature range which could amount to 7 K for small lakes, and less than 2 K for very large lakes [25]. This can have an impact on the estimation of long-term trends, and day-to-day variability could be affected in cases where measurements from successive days reflect a significantly different portion of the mean diurnal cycle.
There are several satellite sensors capable of measuring LSWT accurately and at high resolution, but there are a select few with records long enough for climatological analysis. The longest of these for the Laurentian Great Lakes region begins with the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) data available continuously from NOAA-9 starting in 1986. The native spatial resolution of the sensor is 1.1 km at nadir, with a total swath width of 2900 km. All AVHRR-carrying satellites are in sun synchronous orbits providing at least twice-daily observations for nearly all locations on Earth. Altogether, the AVHRR record is the longest satellite record using a consistent set of imagers with similar channel selection and bandwidth.
There are well-documented errors in the navigation of the AVHRR sensors creating some uncertainty in the georegistration of the AVHRR images. These navigation errors are most problematic in regions with well-defined boundaries, like coastlines. AVHRR georegistration, in one particular case, has been documented to have a mean bias as large as three pixels in the cross-track direction [26]. Some proposed methods of correcting these errors involve using better defined orbital parameters or ground control points (GCPs) and have demonstrated improvement in the AVHRR navigation to within one-pixel accuracy [27,28].
The goal of this work is to leverage the length and fine spatial resolution of the 1.1 km AVHRR record to provide a refined long-term climatology of surface temperatures in the Laurentian Great Lakes. We have assembled a 31-year (1986–2016) daily LSWT dataset on a regular 0.018° grid from the observations made by NOAA-9, 11, 12, 14–19, MetOp-1, and MetOp-2. Despite increased uncertainty in daytime measurements, measurements from all hours of the day will be used to ensure adequate spatial and temporal coverage. We have attempted to mitigate error associated with diurnal variability by removing an empirically determined diurnal cycle from these data prior to creating daily composites. Navigation errors that are especially prevalent on earlier sensors will be corrected by linear adjustments to the regridded images. To facilitate the use of this record, gaps are filled by a combination of locally weighted interpolation methods and both the original and gap-filled datasets are made available. Other long-term records with a focus on LSWT have been assembled that include the Laurentian Great Lakes [29,30]. To our knowledge, the dataset produced here is currently the longest, and is of comparable or finer spatial resolution to others for the same region.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Datasets
The AVHRR observations used in this work are the 1.1 km High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) and the Full Resolution Area Coverage (FRAC). The HRPT data are available only for the locations around receiving stations. The HRPT record for the North American Great Lakes is available continuously after 1986 starting with NOAA-9 and sparsely on previous platforms for this region. On MetOp satellites, the FRAC data is available globally starting in late 2006 with the launch of MetOp-A. A continuous 1.1 km record of the Laurentian Great Lakes region was assembled by combining the regionally-available HRPT, with a regional cut-out of the globally available FRAC. These files are obtained from the NOAA CLASS archive.
The Pathfinder Atmospheres-Extended (PATMOS-x) dataset [31] is a global climate data record made up of the AVHRR Global Area Coverage. A high-resolution version of the PATMOS-x dataset was produced on a regular 0.018° latitude/longitude grid from the HRPT and FRAC. This dataset was produced for the Laurentian Great Lakes region bounded by the longitudes 95W to 73W, and the latitudes 40N to 50N. The PATMOS-x processing composites the ascending and descending nodes on a daily basis for each platform so the additional AVHRR coverage at high latitudes is not used. Since viewing angles larger than 45° are discarded, this has very minimal impact on the temporal resolution of this dataset. The satellite platforms used in this record all experience significant orbital drift over their lifetime with the exception of the MetOp platforms (Figure 1).
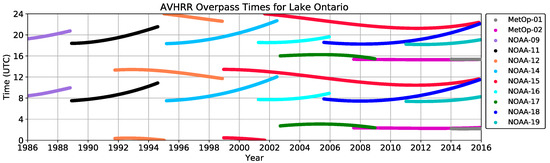
Figure 1.
Rolling mean observation times of each AVHRR sensor over Lake Ontario.
The Great Lakes Ice Cover Database documents ice concentration over the Laurentian Great Lakes since 1973. The data from 1973 to 2005 [32,33] are provided on an approximate 2.5 km grid. The data from 2006 onward are provided on a 1.275 km grid [34]. For this study, both of these datasets were nearest-neighbor interpolated in space and time to the 0.018° grid at a daily time step from 1986 to 2016. These data are used to remove surface temperatures that may be contaminated with significant ice cover where LSWT measurements may have low confidence.
Measurements of water temperature come from the in situ SST Quality Monitor (iQuam) [35]. iQuam implements additional quality control measures to ensure the accuracy of the in situ measurements from these platforms. In particular, we use hourly measurements at 60 cm or 100 cm depths from eight buoys in the Great Lakes that span the entire 31-year satellite record.
2.2. Georegistration Adjustments
As noted previously, some have demonstrated methods capable of achieving AVHRR image registration to within one-pixel accuracy. However, since the dataset assembled here involves subsampling the native resolution AVHRR to a relatively coarse grid and coastline-adjacent pixels are removed in proceeding steps, native resolution sub-pixel accuracy is not necessarily required. Therefore, a simple first-order correction involving zonal and meridional linear displacements is applied to the regridded time series. This computationally inexpensive method is similar to the one used in another surface temperature record for the Great Lakes [29] with a significantly relaxed requirement on maximum linear displacements.
This correction starts with calculating the sum of the squared forward differences in the zonal and meridional directions of the cloud-cleared channel 4 (10.3–11.3 µm) brightness temperatures for each grid cell. The resulting grid, hereafter the edge-enhanced image, reports high values along the coastlines. A similar calculation is performed for the land classification variable included in PATMOS-x (based on the MOD44W dataset; [36]) to create a reference image. Where changes in land classification occur, the pixel value is set to a value of 1, otherwise it is set to 0. A dot product is taken between the edge-enhanced image and the reference image at various linear displacements in the zonal and meridional directions. The combination of displacements that maximizes the dot product between the two images is recorded and used to offset the original brightness temperatures and cloud mask. This method of addressing the uncertainties in the AVHRR navigation performs best in clear-sky regions where coastlines are clearly visible. When either 95% of the land or water in a given image is cloudy, no adjustment is made.
2.3. Cloud, Ice, and Land Masking
Clouds negatively affect the derivation of the SST and LSWT coefficients and, thus, the accuracy of the resulting products. Clouds are removed using a naïve Bayesian cloud detection scheme [37] that is included in the PATMOS-x dataset. The algorithm produces a pixel-level naïve Bayesian probability of cloudiness. For our purposes, all pixels with >5% cloud probability were removed. Pixels that were not classified as water bodies were removed using the land classification variable. Lake ice coverage exceeding 20% is discarded and pixels that are immediately adjacent to those exceeding 20% and within one day of exceedance are also removed. This is done in an effort to mitigate issues introduced by interpolation to the grid used in this analysis and to give more conservative estimates of the ice-free lake surface.
2.4. Lake Surface Water Temperature Calculation
LSWT is calculated using a nonlinear split-window equation using channels 4 (10.3–11.3 µm) and 5 (11.5–12.5 µm) from the AVHRR sensor, the sensor viewing angle, and an initial guess. This is found by the Nonlinear Sea Surface Temperature (NLSST; Equation (1); [38,39]). The initial guess () in the NLSST equation is provided by the Multiple Channel Sea Surface Temperature (MCSST; Equation (2); [40]):
Coefficients are fit by a least-squares regression to moored buoy measurements in the North American Great Lakes. The AVHRR measurements are collocated in space (nearest pixel) and time (<15 min) to buoy measurements. A separate set of coefficients is fit for each year of the record for each AVHRR sensor. Others have found increased accuracy using smaller temporal windows for fitting coefficients [41]. We fit coefficients on a yearly basis because the in situ measurements, made in off-shore locations, do not experience the same range in temperatures as the in-shore locations in smaller temporal windows. Measurements made at a viewing angle greater than 45° are discarded.
2.5. Diurnal Correction
The mean diurnal variability is removed using a previously published method [42] with some modification in the selection of the data used to fit the diurnal cycle function. This method first involves fitting a two harmonic sine function:
where a, b, c, d, and e are the fitted coefficients, x is the time of day in hours, and F(x) is the LSWT. The daily maps are then composited by integrating over all satellite overpasses on a given day by:
where xobs and yobs represent the time of day that an observation was made, and the observed LSWT. The daily averaged LSWT is given by .
To fit the coefficients of Equation (3), the LSWTs are standardized by subtracting out the measurement made on the same day at some reference time. The reference was chosen to be the LSWT measured between 8 UTC and 11 UTC since there is an AVHRR overpass in this window each day for nearly the entire record and the variability in this window is also relatively small. The differences are then centered near zero and used to fit the coefficients of Equation (3). Days where there was not a measurement in the reference time window are not included. The observations are discarded if the surrounding 20 × 20 LSWT array is more than 15% cloudy or if the standard deviation of the 20 × 20 array differs from that of the reference by more than 1 K. This calculation is performed at all buoy locations for each month of the year. This is done to ensure that the measurements are not affected by near-shore variability, and appropriately capture the mean month-to-month variability of the mean diurnal cycle. 14-day time steps for fitting the coefficients of Equation (3) were considered, but this resulted in very minimal changes to the values of the daily composites, and the resulting fits were not consistent between successive periods. This is likely due the small amount of days where multiple AVHRR observations are made at all hours of the day during periods shorter than one month.
2.6. Gap-Filling
After the daily compositing, there still existed frequent gaps in the daily LSWT field. These gaps were typically over areas of the lakes that have experienced persistent cloudiness but sometimes occur because the data were not available for that day from the NOAA CLASS archive. Some previous studies have aimed to estimate LSWT under cloudy skies using purely time-series based interpolation techniques, like local regression [2,43] or harmonic analysis [15]. There are some cases where spatial information can improve the interpolated estimates from the time-series approaches. These cases involve situations where a time series at a pixel has a multi-day gap, but a neighboring or nearby pixel does not have an identical gap. Most frequently, this occurs along cloud or AVHRR swath edges.
The goal of this interpolation scheme is to give greater weight to values that, in a climatological context, have small differences compared to the location of the missing value. Taking advantage of both spatial and temporal information to make estimates of LSWTs in these gaps, a weighted average of surrounding neighbors in a local spatiotemporal neighborhood is used. First, the seasonality is removed from the time series using a smoothed average across all years for each day. When a missing value is encountered a search is made for values in a local spatiotemporal neighborhood. Here, only values within a radius of 13 grid cells, and five days are considered. The missing value is replaced by a weighted average of its neighbors. The average is weighted by the inverse of the climatological mean squared error at the corresponding spatial and temporal lag from the origin described in Equation (5):
In Equation (5), LSWTo is the surface temperature at the location of the missing value. LSWTx,y,t is the surface temperature at spatial lag of x grid cells in the zonal direction, y grid cells in the meridional direction and t days before or after LSWTo. n is the number of cases in the record where there are observations of both LSWTo and of LSWTx,y,t. wx,y,t is the computed weight at the corresponding spatiotemporal lags. The values of w are calculated separately for each month of the year. x and y range from −13 to 13 grid cells, and t ranges from −5 to 5 days. The weights are normalized and multiplied by the neighboring deseasonalized observations the result of which, if determined to be reliable by metrics described later, replaces the missing value.
This is attempted for each occurrence of a missing LSWT observation. In cases where there is not a sufficient amount of neighboring observations, or if the neighboring observations are determined to be poor estimators, the gap remained. The remaining gaps were filled using a locally weighted regression (LOESS) [44,45]. This local regression, along with other time series smoothing and interpolation methods has the significant disadvantage of dampening short-term variability. This dampening is somewhat reduced by performing this interpolation on a moving window of 20 days, and deseasonalizing the LSWT time series prior to interpolation.
In order to justify the computational expense of calculating the weights in Equation (5) explicitly for all locations and in all months, a simple cross-validation of these methods is performed. A one-year time series of surface temperature observations is taken from all locations on Lake Michigan. Ten observations from each time series are removed. The removed observations are interpolated using three methods: LOESS, a locally weighted average, or a combination of both where some select values are calculated using a locally weighted average prior to using LOESS. When the combination is used, the locally weighted average estimate is only inserted in the time series where there is a large number of observations in the local neighborhood and the standard deviation of the available neighbors is low. These two metrics are used to inform where we can have high confidence in the locally weighted average because they are computationally inexpensive and indicate homogeneity in the neighbors (i.e., where an average might be an appropriate estimate). Other studies have found success with more sophisticated interpolation schemes based on empirical orthogonal functions [30,46]. The method presented here is used due to its relative simplicity, reliance on nearby observations in a small local neighborhood, and the spatiotemporal uniformity in wintertime LSWT anomalies when interpolation is most needed.
3. Results
3.1. Georegistration Adjustments
An example of an adjustment made to a single image is shown in Figure 2a,b. These images illustrate how the largest gradients in clear-sky brightness temperature typically occur along land-water boundaries. In most cases adjustments were small, although 2.4% (3.6%) of images required a zonal (meridional) offset of the same magnitude or larger, as shown in Figure 2a,b. The largest adjustments appear to be in the meridional direction, however, the small zonal adjustments are more frequent. Given that the zonal distance of one grid cell (~1.5 km) is smaller than the meridional distance (~2.0 km) at this latitude, it is surprising that the meridional corrections are more often larger than the zonal ones when expressed as 0.018° grid cells. Table 1 shows the mean and standard deviation of the adjustments for each AVHRR platform. The largest adjustments are made to the earlier sensors (NOAA-9, NOAA-11, and NOAA-12). The largest mean bias also occurs in the earlier platforms, but no platforms launched after NOAA-14 show a bias greater than a single grid cell (0.018°).
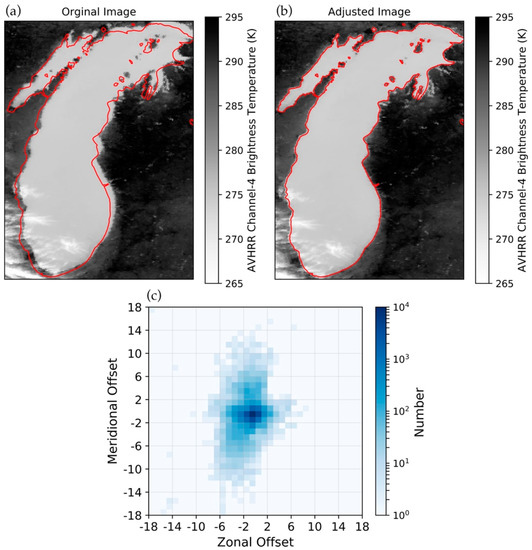
Figure 2.
Example of the (a) original and (b) adjusted georegistration of an HRPT image over Lake Michigan. The red outline indicates the actual coastline. A zonal offset of −4 grid cells and a meridional offset of −5 grid cells was applied between the original and the adjusted image; and (c) the frequency of georegistration corrections applied to each of the regridded HRPT and FRAC images in this record expressed in units of 0.018° grid cells.

Table 1.
Zonal and meridional georegistration adjustments for each AVHRR platform. The mean and standard deviations are expressed in units of 0.018° grid cells. Values for ascending and descending nodes are expressed separately with descending nodes in parentheses.
Mean adjustments less than a single grid cell could be attributable to the grid resampling by the PATMOS-x processing and not indicative of any navigational errors. However, in the earlier sensors, there are differences in sign of the mean zonal and meridional offsets between the ascending and descending nodes of each platform. This happens because AVHRR approaches the region from the opposite direction for each node. For platforms where the magnitude of the mean offsets of the ascending and descending nodes are similar, larger than a single grid cell, and the offsets have opposite signs, we attribute these adjustments to a mean bias in AVHRR navigation and not purely a factor of the grid resampling. This is particularly clear for the meridional offsets in NOAA-9, NOAA-11, and NOAA-12. Similarly, to some degree, the standard deviations of the adjustments can be attributed to uncertainties in our methods in cloudy scenes. However, comparison of the standard deviations between the early sensors and the more recent ones (such as NOAA-18, and NOAA-19) suggest larger variability in the georegistration of the early sensors.
3.2. Cloud and Ice Masking
There is strong seasonality to cloudiness in the North American Great Lakes region that has been recognized in the PATMOS-x AVHRR dataset [47]. This leads to a larger amount of clear-sky measurements during boreal summer and a relative scarcity of clear-sky measurements during boreal winter. As an example, Figure 3 shows the percentage of the lake surface obscured by clouds that are removed over the surface of Lake Ontario for each month averaged over all observations between 1986 and 2016. Together, the cloud and ice masking results in a much higher observation density of LSWT during the spring and summer compared to the winter.
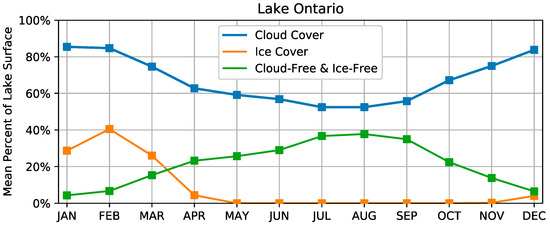
Figure 3.
Percent of the surface of Lake Ontario obscured by clouds (blue), covered by ice (orange), and free of both ice and clouds (green). The values indicated by the lines represent the average fraction of all overpasses in each month averaged for the whole record. Values do not necessarily sum to 100% due to viewing angles >45° being discarded for the mean cloud-free and ice-free amount, and since ice cover and cloud cover can be coincident.
3.3. LSWT Error
The root mean squared error (RMSE) between the AVHRR LSWT and the in situ measurements is determined to be 0.588 K across all sensors (Figure 4a). Fewer AVHRR to buoy matchups are made between 280 K and 285 K due to relatively rapid warming and cooling that typically occurs during the spring and autumn. The RMSE of the LSWT measurements changes slightly between each individual sensor (Figure 4b, Table A1). For example, earlier sensors like NOAA-12 have an RMSE as large as 0.706 K. More recently launched sensors like NOAA-19 and MetOp-1 have a lower RMSE of 0.514 K and 0.541 K respectively. Comparing the annual mean RMSE from 1986-2016 confirms the elevated RMSE during the period covered by the first three sensors (NOAA-9, NOAA-11, and NOAA-12; Figure 4b).
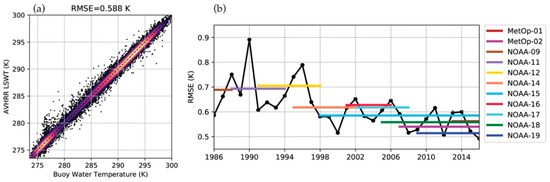
Figure 4.
(a) Comparison of the AVHRR LSWT measurements to their corresponding in situ buoy matchups for all platforms. Colored is the point density of observations with darker colors (black) indicating the lowest point density and brighter colors (yellow) indicating the highest point density. The dashed line indicates 1 to 1 correspondence. n = 18,680; (b) Yearly averaged RMSE are shown for all sensors (black), and the lifetime-averaged RMSE for each individual sensor (colored).
The time of day in which a measurement is made could also impact the calculated RMSE of each sensor. Based on our comparison, at low wind speeds, daytime measurements show a positive bias and nighttime measurements show a negative bias relative to the buoy water temperature (Figure 5). We have also identified low wind speeds to result in a larger variability in the daytime errors relative to the night. This is in agreement with previous measurements of the lake-skin effect [18]. These effects become smaller when wind speeds are larger 2 ms−1. 18.5% of all the AVHRR observations with buoys matchups in the region occur at wind speeds less than 2.5 ms−1.
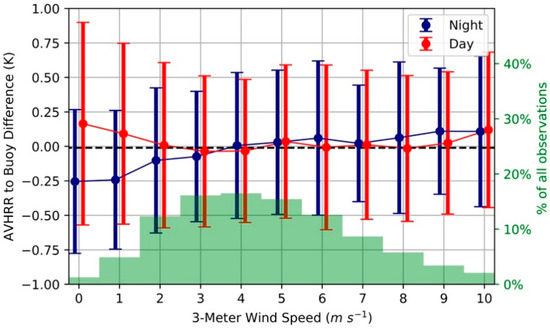
Figure 5.
Differences between the AVHRR LSWT and the buoy water temperature. Filled circles indicate the mean difference, the error bars indicate the standard deviation, and the overlaid histogram represents the percent of observations occurring at each wind speed in 1 m s−1 bins centered on each value.
The NLSST and MCSST equations yielded temperatures that were quite similar (Figure 6). The NLSST was developed to address the nonlinearity in water vapor absorption and at high temperatures. The summertime mean total precipitable water is 29.9 kg m−2 for the study region (data from North American Regional Reanalysis; [48]). It could be that typical atmospheric profiles in the study region are not moist enough nor temperatures warm enough for the nonlinearity to greatly affect LSWT calculations here. Of the 18,680 matchups, 92.75% of the differences were below 0.05 K, and the maximum NLSST to MCSST difference was 0.24 K. The largest positive differences between the MCSST occurred at very high (>295 K), and at very low (<275 K) water temperatures. More commonly, the NLSST showed only a very small negative difference (roughly −0.02 K) at more moderate water temperatures. The differences between the NLSST and MCSST were not found to vary greatly with year, viewing angle, or satellite platform.
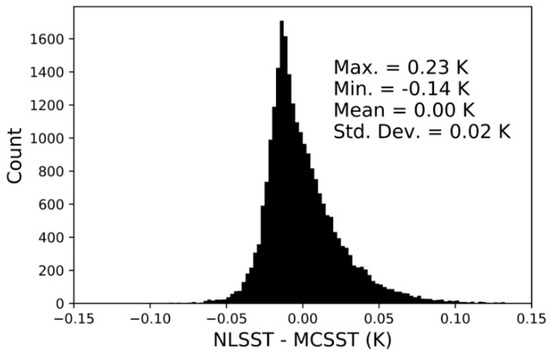
Figure 6.
Histogram of the difference between LWST estimates based on the NLSST and MCSST equations applied to AVHRR data from 1986 to 2016. Bin widths are 0.0025 K, n = 18,680, and other statistics are shown in the legend.
3.4. Diurnal Correction and Compositing
Altogether, the resulting independently calculated diurnal cycles from the buoy data and the AVHRR data show good agreement. The diurnal cycle amplitude in the buoys was expected to be dampened relative to that of skin temperatures observed by AVHRR because the surface is more sensitive to diurnal variability. However, the buoy measurements could perhaps still reproduce the shape of the average diurnal cycle and serve as a reference to ensure realistic results for the timing of the maximum and minimum of the fitted curve for the satellite observations.
We characterized the buoy diurnal cycle for each month by calculating the departure from the daily mean for all measurements made between 1986 and 2016. The amplitude of the diurnal cycle changes significantly between months, reaching its maximum amplitude in July (Figure 7). Since the buoys are removed from the lakes during the winter months, mean diurnal cycles are only shown when there were at least four years where the buoy was present for the entire month.
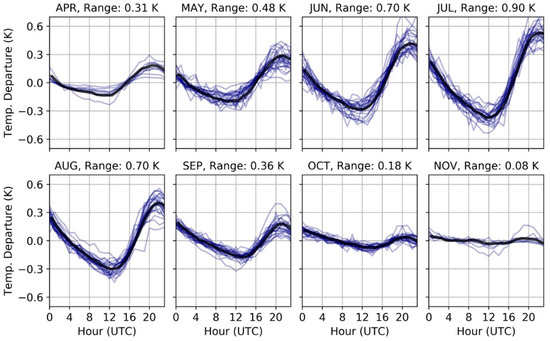
Figure 7.
Average diurnal cycles found in the buoy observations for the Laurentian great lakes plotted as a function of departure from the daily average temperature. The thin blue lines indicate the mean for individual years for the specified month, while the thick black line indicates the mean across all years. The range indicates the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the mean across all years.
The AVHRR-derived diurnal cycles of LSWT are readily discernable after standardizing, and centering differences to the 8–11 UTC window (Figure 8). There is some agreement between the AVHRR derived cycles and the buoy derived cycles in the timing between the minima and maxima with a couple of exceptions. The differences between the maxima and minima are generally only slightly larger for the AVHRR diurnal cycles. Noteworthy exceptions occur for June and July which are 0.45 K and 0.38 K larger. There were not enough differences to fit diurnal cycles for the more cloudy months, so the observations for November and December were combined. The same was done for January and February. This could increase the error in our process, but the minimal diurnal variability in the colder months makes large errors unlikely.
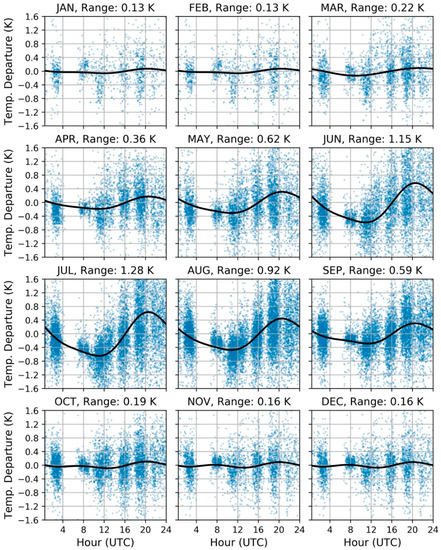
Figure 8.
Average diurnal cycles found in the AVHRR observations for each month. The blue points indicate the individual differences calculated between an observation at the specified time and the observation in the reference window (8–11 UTC) that are centered near zero. The black line indicates the diurnal cycle function fitted to the centered differences. The range indicates the difference between the maximum and minimum values of diurnal cycle function.
The fitted diurnal cycle functions in Figure 8 are used to create daily composites as noted previously. This reduces the total number of images in the time series from 63,470 ascending and descending node composites from all sensors to 11,323 daily images. Daily LSWT composites are only reported where there is at least one clear-sky and ice-free observation of the lake surface. The number of all-sky views and the number of days with at least one clear-sky and ice-free view of the lake increases throughout the record with the number of operational AVHRR sensors (Figure 9).
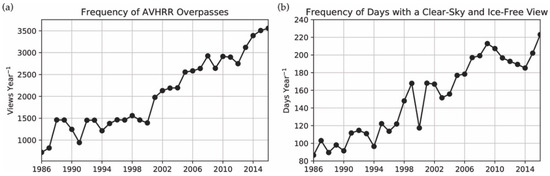
Figure 9.
(a) Number of all-sky views for a single location on Lake Ontario; and (b) the number of calculated daily composites.
3.5. Gap Filling and Cross-Validation
An example of the mean squared errors used to calculate the weights in Equation (5) are shown in Figure 10a for a location close to the western shoreline of Lake Michigan and in Figure 10b for a location in the middle of the lake for the month of July. As expected, differences typically increase as the spatial and temporal separation between two observations increases. However, there are many cases where distant observations have lower errors than nearby ones. This scenario commonly arises along shorelines, where points just offshore have much lower errors than those adjacent to the shoreline.
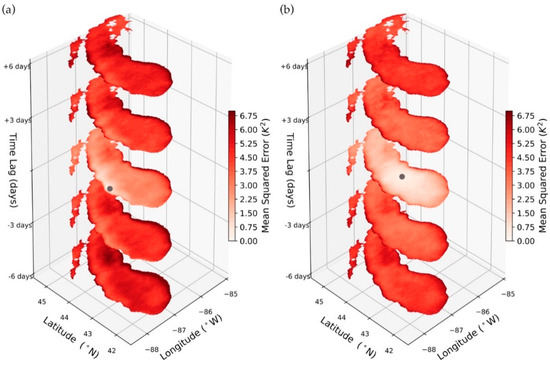
Figure 10.
The calculated mean squared errors between a location (a) near the western shoreline of Lake Michigan and (b) towards the middle of Lake Michigan plotted for time lags of −6, −3, 0, 3, and 6 days in July. The grey point indicates the location from which mean squared errors from all other locations are calculated to (where temporal, zonal, and meridional lags are zero).
During the month of February, deseasonalized LSWT is more homogenous than during the warmer months, resulting in spatiotemporal variation being relatively low. Despite there being a greater reliance on interpolation to fill missing values in the colder months (Figure 3), a given observation is likely to have only a small difference to its neighbors across space and time (Figure 11). This indicates that a given observation is, on average, more representative of its neighbors in the colder months, than in other times of the year.
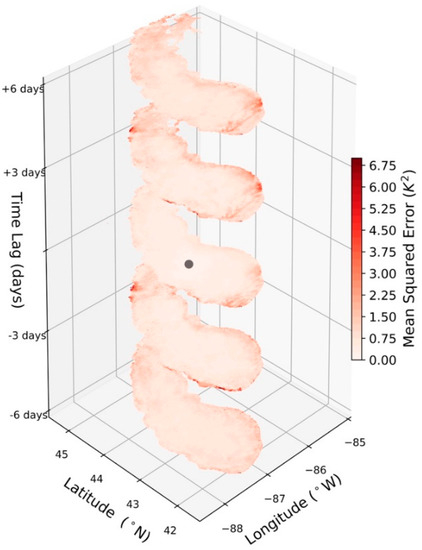
Figure 11.
Same as Figure 10, but for the month of February for a mid-lake point. For some locations, values are not computed due to an infrequency of clear-sky and ice-free observations of the lake during the winter.
Since clouds can often result in multi-day gaps spanning a large portion of the lake surface, a weighted average of local anomalies is not always optimal. We have performed a simple cross-validation to illustrate how a combination of local averaging and LOESS can give improved estimates of LSWT under cloudy conditions (Table 2).

Table 2.
Results from the cross-validation. Root mean squared error (RMSE), mean bias, and Pearson correlation coefficient (ρ) are calculated between the three different methods used: a locally weighted average (LWA), LOESS, and a combination of selective LWA and LOESS. n = 33,593.
The reported errors show that using LOESS alone (RMSE = 1.26 K) is suboptimal compared to selectively inserting locally weighted averages prior to using LOESS (RMSE = 1.10 K). All of these methods demonstrate low bias (0.1 K) and a moderate correlation between the estimated and observed residuals (ρ 0.67). The local averages perform relatively poorly where there are very few observations in a local neighborhood and where heterogeneity is large in the neighboring observations. No metric is used to assess the confidence of individual LSWT measurements, so the local averages can tend to propagate erroneous values when they are present. Thus, the aim is use local averages where there is small chance they will propagate erroneous values and improve the resulting LOESS fit by only inserting local averages into the time series where the local neighborhood is spatially and temporally homogenous.
3.6. LSWT Spatial and Temporal Variation
After regions of persistent clouds have been filled, the result is a spatially and temporally continuous (excluding ice-cover) daily LSWT dataset. An example image from 14 June 1987 demonstrates a large range LSWT between and within each lake (Figure 12). It is typical for the shallower areas (Western Lake Erie, and Saginaw Bay) to reach higher temperatures earlier in the year compared the deepest areas of these lakes (Central Lake Superior). As expected, the southernmost regions typically reach higher temperatures more quickly than the northernmost regions as is evident in the 14 June 1987 image.
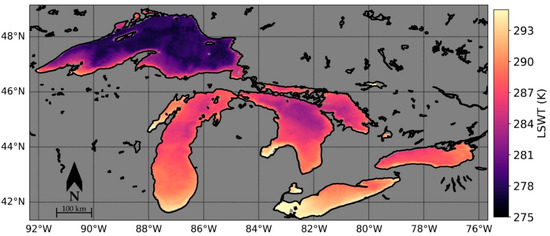
Figure 12.
Gap-filled LSWT for the Laurentian Great Lakes on 14 June 1987.
To examine the departures from climatology, the LSWT can be deseasonalized by subtracting out 1986–2016 means for each day of the year. For example, this is done on a monthly basis for Lake Michigan in 2012 (Figure 13). The late spring and early summer months for Lake Michigan in 2012 are anomalously warm. There is pronounced intra-lake variability in LSWT anomalies and variability between months. In June, the deepest areas of the Lake are more than 5 K warmer than average, while the shoreline remains very similar to the mean.
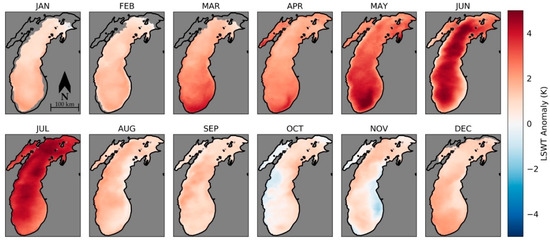
Figure 13.
The 2012 monthly averaged AVHRR LSWT anomalies for Lake Michigan. Anomalies are calculated with respect to the 1986–2016 mean for each month. LSWT anomalies are missing from months in areas where ice cover is flagged for more than five days.
This was repeated for 2015 (Figure 14). The year starts slightly colder compared to climatology and reaches its largest negative anomaly in June in the deepest areas of Lake Michigan. In September, October and November there are negative anomalies on the western or eastern coastlines while the rest of the lake surface is warmer than average. Given the location of these negative anomalies, they may be indicative of coastal upwelling that is frequent in this region [49].
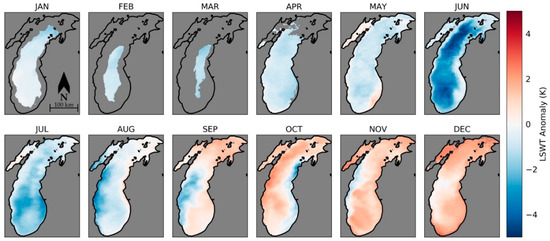
Figure 14.
The 2015 monthly averaged AVHRR LSWT anomalies for Lake Michigan. Anomalies are calculated with respect to the 1986–2016 mean for each month. LSWT anomalies are missing from months in areas where ice cover is flagged for more than five days.
Further demonstrating some aspects of the spatiotemporal variability in this dataset, we calculated an anomaly time series for the lake-wide mean surface temperature (Figure 15). There is a readily discernable coherence between lakes in their departures from climatology. This is most apparent in the relatively warm years of 1987, 1998, and 2012, and the relatively cold years of 1996 and 2014. All lakes demonstrate substantial intra-annual and interannual variation.
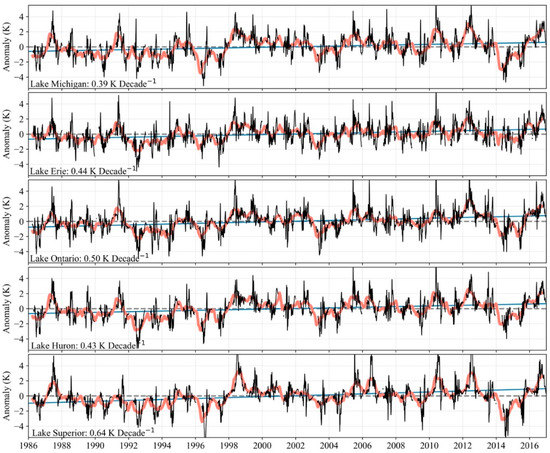
Figure 15.
Time series of lake-wide mean LSWT anomalies for the five largest lakes in the region Anomalies are calculated with respect to the 1986–2016 mean for each Julian day. Lake-wide mean anomalies are only plotted for days where less than 5% of the lake surface has been flagged for ice-cover. Black lines represent the lake-wide mean for a single day, blue lines represent the trend in July through September mean LSWT, and the salmon lines represent a 180-day moving average. The slope of the trend lines is shown in the bottom left of each panel.
4. Discussion
The are several potential explanations for differing LSWT RMSEs among the sensors. Some have noted a negative bias in SST associated with the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo in 1991 during the period covered by NOAA-11 and NOAA-12 [50]. While the largest impacts occurred in the tropics, there should be a change in LSWT accuracy in this region due to the global increases in aerosol optical depth after eruption [51]. These effects are largely mitigated by fitting coefficients on a yearly basis, but some residual error remains where large intra-annual changes in aerosol optical depth occur. Cloud detection plays a prominent role in assessing the accuracy of LSWT measurements. Clouds that are not screened out can contribute significantly to the calculated RMSE. The noise in channel-3 of AVHRR has been documented to be larger in earlier sensors [52,53] and could negatively impact cloud detection. The resulting higher frequency of missed clouds on the earlier sensors could increase the RMSE of their LSWT measurements. The relatively small differences between the NLSST and MCSST equations are in good agreement with others who found a similar result for the Great Lakes [54].
Overall, the largest impact of the georegistration adjustments occurs along coastlines where brightness temperature gradients are large. When these errors are left uncorrected, they can result in abrupt changes in LSWT for land-adjacent pixels. Since the largest errors occur in the earlier sensor records, the largest impact of these corrections occurs between 1986 and 1999. For images with extensive cloud cover where no adjustment is made, discarding values with extremely large and abrupt departures from the climatological mean for a given date can mitigate the impact of poorly georegistered brightness temperatures.
We have attempted to remove the effects of diurnal variability on our dataset by empirically determining and subtracting the mean diurnal cycle. The differences between the maxima and minima are generally only slightly larger in the AVHRR measurements compared to the buoys. The differences between diurnal cycle amplitudes from the two platforms could be exaggerated because the AVHRR LSWT diurnal cycles are biased towards clear-sky observations, whereas the buoy diurnal cycles represent a wider range of conditions and are more representative of the bulk temperature. Furthermore, the diurnal correction we have applied ignores possible variation across space. Lake surface area and light attenuation (albeit much less so than surface area) have influence over the diurnal temperature range of many lakes [25]. It seems plausible that smaller bay areas of these lakes (i.e., Green Bay, Travers Bay, and Saginaw Bay) could have mean diurnal cycles larger than those calculated using offshore time series due to spatial variation of mean mixed layer depth. This method relies on the assumption that the mean diurnal cycle of LSWT for each month is similar between years. Figure 7 implies small variation of the mean diurnal cycle between years, but could be a factor of the small sample size for each year. Changes in over-lake wind speed [8], and cloud cover [47] in the region could impact the shape and amplitude of the diurnal cycle. Additionally the spatial variation and long-term changes in water clarity experienced in these lakes [55] could perhaps alter the vertical heating profile resulting in changes in mean diurnal variability at the surface.
Gaps due to cloud cover were filled using a combination of locally weighted methods. The calculated weights for one inshore location and one offshore location demonstrate that there are distinct differences in the relationship between a given location on the lake surface and its neighboring observations. These relationships vary with the reference location, and the zonal, meridional, and temporal separation. Therefore, weighted averages using these empirically-determined weights should produce a better result than an unweighted average that ignores these subtleties. It should be noted that the RMSEs reported here may not necessarily be indicative of the errors when interpolating missing values. In practice, interpolation is needed more often in data-sparse regions and times that may not be well represented in our cross-validation. The cross-validation employed here neglects the fact that interpolation is most needed during the winter months where the lake is more homogenous. When the lake is more homogenous, errors from all methods will be lower. Thus, the RMSE values in Table 2 should only be interpreted in a relative sense, to indicate that LOESS supplemented by select locally weighted averages typically results in smaller errors than using LOESS, or locally weighted averages alone. Due to the low frequency of observations (particularly in the early portion of the record), care should be taken when using the gap-filled product in the winter months where cloud-cover is frequent. When possible, wintertime LSWT features observed in the gap-filled product should be verified in the original daily composites.
5. Conclusions
A long-term (31 years), fine-resolution (0.018°) dataset of daily lake surface water temperature (LSWT) was developed from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) record for the Laurentian Great Lakes region. In this work, we have made three significant adjustments to the AVHRR LSWT record. Errors in the AVHRR navigation have been identified to be particularly large in the earliest sensors, amounting to a mean bias of over two 0.018° grid cells in the meridional direction in some cases. The removal of these navigation errors results in more accurate LSWT measurements near shorelines. A mean diurnal cycle was found and subtracted from the LSWT time series to mitigate bias associated with including measurements made at different times of day. The amplitude of the diurnal cycles ranged from 1.28 K in the summer to 0.13 K in the winter. Missing LSWT values were filled using a combination of locally weighted interpolation schemes. We have additionally characterized the LSWT observations to have a root mean squared error of 0.588 K compared to buoy measurements. Both the original daily LSWT composites and the gap-filled product will be made available to support fine-scale physical and environmental research in this region. These data can be found through the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Space Science and Engineering Center at ftp://ftp.ssec.wisc.edu/pub/cwhite/.
Author Contributions
A.K.H. and C.H.W. prepared the data; C.H.W. performed the analysis and wrote the paper; A.K.H., P.B.M., S.A.A. supervised the work and contributed to the review and editing of the paper.
Funding
This research was funded by NOAA grant NA15NES4320001.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Michael J. Foster (CIMSS) for aiding in the implementation of the diurnal correction, and Simon J. Hook (NASA JPL) for discussion of this work in its early stages. AVHRR data were provided by the NOAA CLASS archive. Ice data were provided by Great Lakes Environmental Research Lab. Buoy measurements are from the NOAA in situ Quality Monitor. The views, opinions, and findings contained in this report are those of the author(s) and should not be construed as an official National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or U.S. Government position, policy, or decision.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Root mean squared error and number of matchups between the AVHRR LSWT and the in situ water temperature reported for the entire lifetime of the sensor.
Table A1.
Root mean squared error and number of matchups between the AVHRR LSWT and the in situ water temperature reported for the entire lifetime of the sensor.
| Platform | LSWT RMSE | Matchups |
|---|---|---|
| NOAA-9 | 0.690 K | 583 |
| NOAA-11 | 0.694 K | 1327 |
| NOAA-12 | 0.706 K | 1387 |
| NOAA-14 | 0.619 K | 2017 |
| NOAA-15 | 0.586 K | 6685 |
| NOAA-16 | 0.628 K | 1881 |
| NOAA-17 | 0.618 K | 1523 |
| NOAA-18 | 0.559 K | 3083 |
| NOAA-19 | 0.514 K | 3397 |
| MetOp-A | 0.541 K | 1227 |
| MetOp-B | 0.563 K | 4547 |
References
- O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Gray, D.K.; Hampton, S.E.; Read, J.S.; Rowley, R.J.; Schneider, P.; Lenters, J.D.; McIntyre, P.B.; Kraemer, B.M.; et al. Rapid and highly variable warming of lake surface waters around the globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10773–10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Hook, S.J. Space observations of inland water bodies show rapid surface warming since 1985. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Di Toro, D.M. Effects of Climate Warming on Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations in Lake Erie. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1990, 119, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillooly, J.F. Effects of Size and Temperature on Metabolic Rate. Science 2001, 293, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, B.M.; Chandra, S.; Dell, A.I.; Dix, M.; Kuusisto, E.; Livingstone, D.M.; Schladow, S.G.; Silow, E.; Sitoki, L.M.; Tamatamah, R.; et al. Global patterns in lake ecosystem responses to warming based on the temperature dependence of metabolism. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahel, F.J.; Olden, J.D. Assessing the Effects of Climate Change on Aquatic Invasive Species. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.L.; Hewitt, N.; Klenk, N.; Bazely, D.R.; Yan, N.; Wood, S.; Henriques, I.; MacLellan, J.I.; Lipsig-Mummé, C. Effects of climate change on the distribution of invasive alien species in Canada: A knowledge synthesis of range change projections in a warming world. Environ. Rev. 2012, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.R.; Austin, J.A.; Bennington, V.; McKinley, G.A. Stronger winds over a large lake in response to weakening air-to-lake temperature gradient. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.J. Historical Trends in Lake and River Ice Cover in the Northern Hemisphere. Science 2000, 289, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, J.A.; Colman, S.M. Lake Superior summer water temperatures are increasing more rapidly than regional air temperatures: A positive ice-albedo feedback. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, B.M.; Anneville, O.; Chandra, S.; Dix, M.; Kuusisto, E.; Livingstone, D.M.; Rimmer, A.; Schladow, S.G.; Silow, E.; Sitoki, L.M.; et al. Morphometry and average temperature affect lake stratification responses to climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4981–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, L.A.; Read, J.S.; Hansen, G.J.A.; Rose, K.C.; Robertson, D.M. Seasonality of change: Summer warming rates do not fully represent effects of climate change on lake temperatures: Seasonal heterogeneity in lake warming. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 2168–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, L.A.; Riseng, C.M.; Gronewold, A.D.; Rutherford, E.S.; Wang, J.; Clites, A.; Smith, S.D.P.; McIntyre, P.B. Fine-scale spatial variation in ice cover and surface temperature trends across the surface of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Clim. Chang. 2016, 138, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Merchant, C.J. Intralake Heterogeneity of Thermal Responses to Climate Change: A Study of Large Northern Hemisphere Lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3087–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareeth, S.; Salmaso, N.; Adrian, R.; Neteler, M. Homogenised daily lake surface water temperature data generated from multiple satellite sensors: A long-term case study of a large sub-Alpine lake. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Li, H.; Xie, H.; Hong, Y.; Long, D.; Zhao, L.; Han, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; et al. A comprehensive data set of lake surface water temperature over the Tibetan Plateau derived from MODIS LST products 2001–2015. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.I.; Merchant, C.J. Amplified surface temperature response of cold, deep lakes to inter-annual air temperature variability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.C.; Hook, S.J.; Schneider, P.; Schladow, S.G. Skin and bulk temperature difference at Lake Tahoe: A case study on lake skin effect. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10332–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlon, C.J.; Minnett, P.J.; Gentemann, C.; Nightingale, T.J.; Barton, I.J.; Ward, B.; Murray, M.J. Toward Improved Validation of Satellite Sea Surface Skin Temperature Measurements for Climate Research. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluessel, P.; Emery, W.J.; Grassl, H.; Mammen, T. On the bulk-skin temperature difference and its impact on satellite remote sensing of sea surface temperature. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnett, P.J.; Smith, M.; Ward, B. Measurements of the oceanic thermal skin effect. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2011, 58, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Clayson, C.A.; Curry, J.A. Clouds, Radiation, and the Diurnal Cycle of Sea Surface Temperature in the Tropical Western Pacific. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 1712–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentemann, C.L. Diurnal signals in satellite sea surface temperature measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentemann, C.L.; Minnett, P.J.; Le Borgne, P.; Merchant, C.J. Multi-satellite measurements of large diurnal warming events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Jones, I.D.; Maberly, S.C.; French, J.R.; Livingstone, D.M.; Monteith, D.T.; Simpson, G.L.; Thackeray, S.J.; Andersen, M.R.; Battarbee, R.W.; et al. Diel surface temperature range scales with lake size. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordes, P.; Brunel, P.; Marsouin, A. Automatic Adjustment of AVHRR Navigation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.F.; Melia, J. A method for accurate geometric correction of NOAA AVHRR HRPT data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.G.; Emery, W.J. A systematized approach to AVHRR image navigation. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 17, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, D.J.; Leshkevich, G.A.; Muhr, G.C. Automated Mapping of Surface Water Temperature in the Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 1999, 25, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, S.N.; Merchant, C.J. Surface water temperature observations of large lakes by optimal estimation. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Foster, M.J.; Walther, A.; Zhao, X. The Pathfinder Atmospheres–Extended AVHRR Climate Dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assel, R.A.; Norton, D.C.; Cronk, K.C. Great Lakes Ice Cover, First Ice, Last Ice, and Ice Duration: Winters 1973–2002; NOAA Technical Memorandum GLERL-121; NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2002.
- Assel, R.A. Great Lakes Ice Cover Climatology Update: Winters 2003, 2004, and 2005; NOAA Technical Memorandum GLERL-135; NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2005.
- Wang, J.; Assel, R.A.; Walterscheid, S.; Clites, A.H.; Bai, X. Great Lakes Ice Climatology Update, Winters 2006–2011, Description of the Digital Ice Cover Dataset; NOAA Technical Memorandum GLERL-155; NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2012.
- Xu, F.; Ignatov, A. In situ SST Quality Monitor (iQuam). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.L.; DiMiceli, C.M.; Wooten, M.R.; Hubbard, A.B.; Sohlberg, R.A.; Townshend, J.R.G. MOD44W MODIS/Terra Land Water Mask Derived from MODIS and SRTM L3 Global 250m SIN Grid V006; NASA EOSDIS Land Process DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Evan, A.T.; Foster, M.J.; Walther, A. A naive Bayesian cloud-detection scheme derived from Calipso and applied within PATMOS-x. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, C.C. Nonlinear Multichannel Algorithms for Estimating Sea Surface Temperature with AVHRR Satellite Data. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1988, 27, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, C.C.; Pichel, W.G.; Sapper, J.F.; May, D.A. The development and operational application of nonlinear algorithms for the measurement of sea surface temperatures with the NOAA polar-orbiting environmental satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 27999–28012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillin, L.M.; Crosby, D.S. Theory and validation of the multiple window sea surface temperature technique. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, K.A.; Podestá, G.P.; Evans, R. Overview of the NOAA/NASA advanced very high resolution radiometer Pathfinder algorithm for sea surface temperature and associated matchup database. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 9179–9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.J.; Heidinger, A. PATMOS-x: Results from a Diurnally Corrected 30-yr Satellite Cloud Climatology. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffler, M.; Lieberherr, G.; Wunderle, S. Lake surface water temperatures of European Alpine lakes (1989–2013) based on the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) 1 km data set. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2015, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Devlin, S.J.; Grosse, E. Regression by local fitting: Methods, properties, and computational algorithms. J. Econ. 1988, 37, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvera-Azcárate, A.; Barth, A.; Rixen, M.; Beckers, J.M. Reconstruction of incomplete oceanographic data sets using empirical orthogonal functions: Application to the Adriatic Sea surface temperature. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A.; Heidinger, A.; Foster, M.J.; Maddux, B. Satellite Regional Cloud Climatology over the Great Lakes. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6223–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesinger, F.; DiMego, G.; Kalnay, E.; Mitchell, K.; Shafran, P.C.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Jović, D.; Woollen, J.; Rogers, E.; Berbery, E.H.; et al. North American Regional Reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattner, S.; Mason, D.M.; Leshkevich, G.A.; Schwab, D.J.; Rutherford, E.S. Classifying and Forecasting Coastal Upwellings in Lake Michigan Using Satellite Derived Temperature Images and Buoy Data. J. Great Lakes Res. 2006, 32, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W. Impact of Mount Pinatubo Aerosols on Satellite-derived Sea Surface Temperatures. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.P.; Thomason, L.W.; Trepte, C.R. Atmospheric effects of the Mt Pinatubo eruption. Nature 1995, 373, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, A. Noise characteristics of the AVHRR infrared channels. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D. AVHRR channel-3 noise and methods for its removal. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pichel, W.; Clemente-Colón, P.; Krasnopolsky, V.; Sapper, J. Validation of coastal sea and lake surface temperature measurements derived from NOAA/AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Greenberg, T.A.; Watson, S.B.; Rastin, S.; Gould, J. Long term water clarity changes in North America’s Great Lakes from multi-sensor satellite observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1976–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).