Abstract
Although the e-commerce market is expanding rapidly, e-commerce platforms still capture only a small portion of the overall market, largely due to the limited habitual use of these platforms. This study examines the features that affect purchase intention when using an e-commerce channel. The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) serves as the theoretical aspect of the analysis. A survey was conducted, and the data were examined using structural equation modeling. The findings show that both performance expectancy and social influence have a strong positive impact on users’ purchase intention on new e-commerce platforms, whereas perceived risk negatively influences purchase intention. Perceived trust mediates the relationship between performance expectancy and purchase intention, social influence and purchase intention, and perceived risk and purchase intention. Furthermore, product quality perception moderates the connection between perceived trust and purchase intentions.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
E-commerce products represent an essential part of the retail market, making users’ lives easier. The development of digital media and online marketing has created a revolution in the communication dynamics between businesses and their customers. Social media channels constitute the latest area where individuals, companies, and governments can commercially, socially, diplomatically, and academically communicate with one another and share data, judgements, products, and facilities [1]. As reported in [2], more than fifty million small industries use Facebook business pages to communicate with customers [3], including two million who utilize it for direct marketing. Previous studies have also documented that ad relevance is an essential direct predictor of consumer attitudes [4] or indirectly through the consumer–brand bond [5]. Social media produce a huge amount of assessable useful information for analysts and vendors, whose main goal is to monitor and optimize interest targeting, promote branding loyalty, and further KPIs, interpreting this information effectively [6]. Prior scholars studied the motives of users accessing social media by viewing the uses and gratification theory (UGT), which can clarify the purpose of users who are active on digital platforms [7,8]. Gamification in e-commerce is a technique that allows consumers to receive extra incentives for their actions [9]. It incorporates gaming features and processes into e-commerce channels to enhance user interaction and foster ongoing engagement. Therefore, gamification significantly enhances consumer happiness and stickiness when using digital products [10]. This research’s main goal is to provide a better understanding and information concerning purchaser preference and user behavior in purchasing e-commerce products online. The theoretical model of UTAUT suggests that the actual use of technology is determined by behavioral intention. The perceived likelihood of adopting a technology is dependent on the direct effect of four key constructs, namely performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating conditions. The effect of predictors is moderated by age, gender, experience, and voluntariness of use [11].
1.2. Aim of the Study
The primary goal of this research is to deepen our understanding of purchaser preferences and user behavior in the context of online e-commerce. Additionally, the study explores how integrating information technology can expand the supply chain of unique products, particularly in markets where perishability is a critical concern. We also aim to increase further insights into how the supply chain of unique products would expand when merged with information technology.
1.3. Brief Statement of the Method
We approach the objective of our research using the method of the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), which is usually applied in researching individual behavior in several contexts, including teaching [12], E-learning [13], mobile payment [14], healthcare wearable devices [15], electronic health record [16], healthcare automaton assumption [17], website design quality and behavioral use [18], e-invoice service [19], online insurance [20], and online banking [21]. Although the UTAUT is used in multiple online backgrounds, limited knowledge regarding the online purchase of e-commerce products is accessible in a market where perishability is the most visible aspect. To achieve the research objectives, two statistical software programs, SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 23.0, were utilized. SPSS was used for descriptive and exploratory data analysis, while AMOS was employed for structural equation modeling (SEM) to validate the relationships among the constructs within the UTAUT framework. This dual-software approach ensures robust data analysis and comprehensive insights into the factors driving e-commerce user behavior.
2. Literature Review
The unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model is widely recognized in information systems research as a reliable framework for promoting IT adoption and utilization [22]. This is reinforced by previous studies providing evidence that performance expectancy, effort expectancy, facilitating conditions, and social influence, along with hedonic motivation (HM) and price value, determine the usage of digital platforms and social media [23,24]. In our study, the perception of “DP use” is related to both the usage rate and the diversity of use, referring to various behaviors of using technology (DPs) [25].
The traditional UTAUT model could not succeed in adding psychological elements, such as perceived risk [26], and demographic characteristics, such as gender and age [27]. Our study enhances the original conceptual framework of UTAUT within the framework of digital e-commerce channels. We define “perceived risk” as the independent variable, “perceived trust” to be a mediator, and “product quality perception” to be a moderator. The model identifies purchase intention as a dependent variable, while controlling for consumers’ demographic characteristics. The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) is a model that was developed by researchers [22] to explain how users intend to utilize an information system and apply it [11]. Since the introduction of UTAUT, it has been subjected to empirical testing and has been validated as an advanced theory that can describe the behavior of online shoppers [28]. The UTAUT model is particularly well-suited for this study because it provides a comprehensive model to understand and predict individual behavior in the adoption and use of technology.
2.1. Performance Expectancy at UTAUT
Performance expectancy is the degree to which e-commerce use will show profits to users in their business performance [22]. It is aligned with perceived usefulness in the TAM model, and it consistently develops as a potent predictor of the intent to utilize technology [11]. This indicates that customers are most expected to initiate and engage in using technologies they perceive as beneficial. Therefore, consumers’ anticipation of the digital e-commerce channel’s performance influences their buying propensity. Moreover, the more enhanced efficiency is provided by the digital e-commerce channel, the more consumers will use it. As mentioned by previous researchers [13], performance expectancy will affect behavioral intention. Hence, the following hypothesis is suggested:
H1.
Performance Expectancy has a positive and significant influence on purchase intention.
2.2. Effort Expectancy
Effort expectancy is the perceived level of effortlessness customers experience using technology (DPs), specifically in the framework of mobile e-commerce [22]. A previous research study confirmed perceived ease of use to be crucial for satisfaction with mobile shopping [29]. In addition, users’ expectations of the digital channel have a huge impact on purchase intention. When the process of the digital e-commerce channel is user-friendly and the procedure is straightforward, the consumer’s practicing cost diminishes, thus enhancing their intention to purchase through the platform. In the present context, effort expectancy refers to the ease and convenience that consumers feel while purchasing on the online e-commerce platform. Specifically, this construction includes the ease for consumers to find the products they need on the platform and the promptness that they have a solution when encountering specific issues [30]. Thus, the following hypothesis is suggested:
H2.
Effort expectation directly influences purchase intention positively and significantly.
2.3. Social Influence
Social influence stands as a major indicator in technology acceptance and usage research. In the e-commerce field, SI is preserved as the degree where users think that significant people around them, such as influencers and bloggers, recommend the usage of e-commerce [22]. Ref. [31] studied the factors influencing gratification and WOF in the field of mobile shopping and provided subjective norms as one of the best indicators of satisfaction. [32] mentioned that SI had a direct effect on customer gratification in mobile SM too. Accordingly, users are more attracted to buy on digital e-commerce platforms when effective marketing cultivates a favorable perception of the site. The influence of the society on customer satisfaction was also examined in several studies. Examined how social influence positively impacts an individual’s self-concept [33]. Hence, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H3.
There is a positive direct effect of social influence on purchase intention.
2.4. Preserved Risk
Perceived risk is described as the “potential of loss associated with seeking the expected outcome from using an e-service” [34]. In our research, the possibility that a customer would lose money on their transaction on the online e-commerce channel is known as the perceived risk. Since online products lack standardization, consumers’ perceptions and subjective experiences play a crucial role during the purchase procedure. With the emergence of online e-commerce channels as a novel method for distributing e-commerce products, consumers are increasingly concerned about uncertainties related to product value, delivery timeliness, transaction safety, and other factors. The perceived risk consequently influences its purchase intention. According to earlier research, consumers’ business intentions are significantly hampered by perceived risk [1]. Therefore, consumers’ purchase intention on digital e-commerce channels is affected by perceived risk. Therefore, we propose the following hypothesis:
H4.
Purchase intention has a strongly negative influence/impact on preserved risk.
2.5. Mediator: Preserved Trust
Mutual trust among the advertiser and its users is essential for establishing an effective relationship [35]. Perceived trust is a significant success factor that affects updated technology usage [1]. In our study, the degree to which digital e-commerce customers think that making purchases on the channel is dependable and secure is known as perceived trust. Customers’ performance expectations, effort expectancies, social influence, perceived risks, and, eventually, their intention to buy from digital e-commerce platforms are all influenced by their perception of trust. In this case, the four UTAUT core factors have a favorable impact on trust, which will raise purchase intention. Previous scholars have suggested that e-retailers initially exert effort to decrease the level of risk, which improves customer trust and ultimately increases purchase intention for buying online products/services. The privacy/security features of websites and shared values are also critical factors of trust in online shopping [36]. The following hypotheses are suggested:
H5a.
Preserved trust mediates the relationship between performance expectancy and purchase intention.
H5b.
Preserved trust mediates the relationship between effort expectation and purchase intention.
H5c.
Preserved trust mediates the relationship between social influence and purchase intention.
H5d.
Preserved trust mediates the relationship between preserved risk and purchase intention.
2.6. Moderator: Product Quantity Perception
Product consciousness reflects consumers’ level of concern about safety and quality matters [37]. Customers with varying degrees of consciousness may exhibit varying degrees of trust in the digital e-commerce channels, which in turn may manifest varying degrees of intention to buy. Customers’ intention to buy is directly impacted by their degree of trust in the platform. There are contradictory findings on the influence of perceived quality on online purchase intentions. In some studies, perceived quality has been found to have a positive direct effect on purchase intentions [38,39,40], whereas others report only an indirect effect through satisfaction [41,42]. Moreover, there is no agreement on whether there is an interaction effect between product quality and satisfaction on purchase intentions. Some researchers have suggested that there is no interaction effect [43], whereas some have reported an interaction effect between the two constructs on purchase intentions [44]. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is suggested:
H6.
Trust and purchase intention play a mediator role in product quantity perception.
2.7. Dependent Variable: Purchase Intention
E-commerce had remarkable success and provided significant economic and social benefits in developed countries; however, the picture is quite different in some developing countries. Many challenges in these economies have delayed the growth of e-commerce. In this regard, the authors of [45] indicate that consumers in developed countries have become accustomed to using the Internet and have benefited from e-commerce, changing their lifestyles. In contrast, consumers in developing countries are used to face-to-face transactions, do not trust electronic processes, and cannot afford the risk of loss. Purchase intentions can be used to test the implementation of new distribution platforms to help managers determine whether the concept deserves further development and decide which geographic markets and consumer segments to target through the platform [46]. Their importance lies in the fact that intentions are considered the key predictor of actual behavior [47]; therefore, their study is of the utmost importance for the success of any online retailer. This research proposes using purchase intentions as the key variable to be investigated. This situation demonstrates the need to study the crucial factors that could lead consumers in developing countries such as Lebanon to adopt e-commerce to enjoy the economic and social benefits of online advertising; the need to understand the intention by adopting online platforms; and, in this way, the need to determine the precursors of online purchase intention in an emerging economy. Based on a literature review, the variable online purchase intention has often been selected as the basis of purchasing-behavior studies. The literature shows that intention may be the main predictor of any behavior [48]; thus, this work uses purchase intention online as the main antecedent of purchase behavior from an online digital platform. The main theories that have impacted the prediction of human behavior to determine which factors influence online purchase intention (i.e., Theory of Planned Behavior, TPB; Technology Acceptance Model, TAM; and Diffusion of Innovation Theory, DIT) have strongly proved to be effective in predicting human behavior in many contexts. Figure 1 shows the research framework.
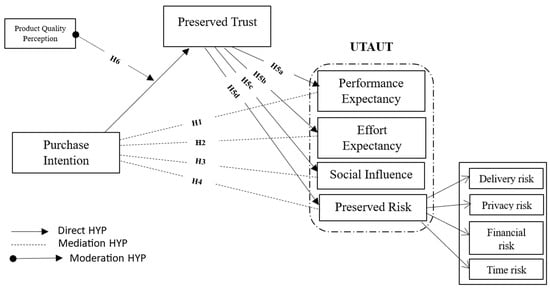
Figure 1.
Research framework.
3. Methodology
Our study used the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 (UTAUT2). This theory expands the previous model of UTAUT. It aims to explain the acceptance of users and utilization of numerous technologies, considering the influence of contextual, user, and social elements [49]. The UTAUT model has been implemented to study technology acceptance in a number of different areas, for example, the medical field [50], e-government [51,52], mobile internet [22], company system [53], and mobile banking and applications [54]. The claims of UTAUT established a solid dependence of purchase intention on the two perspective factors, perceived performance and perceived ease of use. In this study, UTAUT was tested in Lebanon to have a better understanding of the role of culture in technology adoption in the e-commerce sector. The UTAUT model aids in identifying the intention to utilize a specific technology. To establish an effective connection between the retailers and users, shared trust plays a critical role. Perceived trust as a mediator, being an effective success factor, affects the adoption of new technologies. In our research, perceived trust represents the level to which users of e-commerce reflect that online purchases are convenient, private, effective, and satisfying. Previous researchers have studied the positive effect of perceived trust on the incorporation of novel developments. The perceived trust of customers in e-commerce has a great effect on the potential and intention of users toward online buying. This trust is even improved with the improvement of product quality perception, which ultimately leads to high digital purchase behavior [55]. Lastly, the mediation effects in UTAUT allow practitioners to categorize which user segment requires more promotions to maintain loyalty and trust, deliver hedonic value, and determine better value for money [22]. This research used two statistical software programs, SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 23.0, for model assessment and hypothesis testing in two phases: reliability testing and discriminant validity testing. The structural equation model (SEM) was initiated, and confirmatory factor analysis, along with the proposed hypotheses and confirmation analysis, was implemented.
3.1. Sample and Data Collection Procedure
The data for this study were collected through an online questionnaire distributed to online shoppers in Lebanon. A total of 367 questionnaires were disseminated using various digital channels, including social media platforms, email invitations, and e-commerce forums. Out of the distributed questionnaires, 357 valid responses were received, resulting in an active response rate of 94%. The target respondents were individuals who have engaged in online shopping, ensuring a relevant and insightful dataset. The questionnaire was designed to capture a diverse demographic profile, including factors such as gender, age, online shopping experience, monthly available income, and education level [56,57].
As mentioned in Table 1, the majority of the valid responses in our research came from young-to-middle-aged women who have experienced sellers online through digital platforms, possess low-to-medium monthly available incomes, and hold higher education degrees. Regarding gender distribution, 111 respondents were male, representing 31% of the valid responses, while 246 respondents were female, comprising 69% of the total valid responses. The predominance of women in the effective sample can be attributed to two primary reasons. Firstly, women are more involved in buying on e-commerce platforms than men, making them more concerned about participating in related questionnaires. Secondly, women take the leading role in purchasing new products for their households. In addition, previous researchers used purposive sampling to examine the digital shopping experience of female online shoppers, as demonstrated in a study conducted in Lahore, Pakistan, which targeted women aged 20–50 who purchased products online rather than from traditional retail stores [58].

Table 1.
Segment size (Nb = 357).
Therefore, the gender statistics of the data align with real-world patterns. Regarding age distribution, the greater portion of participants below the age of 24, comprising 221 individuals or 61.9% of total surveys, and the individuals aged 24 to 35 were the 2nd, with 77 individuals, representing 21.5% of total surveys. Respondents under the age of 35 accounted for 83.4% of all samples, whereas younger and middle-aged groups were represented in smaller numbers. Given that digital buyers in Lebanon are from 20 to 35+ years old, the questionnaire of our research aligns with the facts. Concerning online shopping experience, 128 respondents, or 35.9% of the sample, five years or more of experience, while 120 respondents, or 33.6%, had three to four years of experience. In total, a minimum of 69.5% of respondents had 3 years of digital shopping experience, as summarized in Table 1. Our results confirm that buyers with online buying experience are expected to adopt the newest products in the Lebanese market. Additionally, after we compared the experience information with age composition, we concluded that younger buyers, including Generation Z, are more active in shopping digitally, which aligns with real-life patterns and examines the social media habits and preferences of female representatives of older Generation Z [59]. Previous researchers found that perceived risk, Internet-shopping anxiety, and gender had an empirical influence on trust and intention; however, perceived risk demonstrated an insignificant correlation with behavioral intention [60].
Regarding the monthly available income, the participants who made less than LBP 200 and those who made from LBP 201 to LBP 400 were 138 and 135, respectively, representing 38.5% and 38% (as mentioned in Table 1). Monthly available incomes of respondents are focused on the and low and middle level, showing the actual wage of the majority of digital buyers in Lebanon stated [61]. The number of participants holding a bachelor’s degree is 95, representing 26.4% of total valid samples, and the size holding a master’s degree or higher is 71, representing 20.1% of total valid samples. The percentage of individuals with an associate’s degree, bachelor’s degree, or lower is 53.5%, demonstrating a common fact that corresponds with the standard educational attainment of digital buyers in Lebanon [61]. The high proportion of participants in our study with higher education is impressive, signifying that individuals with advanced education are more inclined to embrace new innovations and possess a stronger capacity to manage risks. This study used a 5-point Likert scale to measure respondents’ attitudes and experiences related to online shopping (1 = strongly disagree; 5 = strongly agree). This scale was selected based on its effectiveness in capturing consumer perceptions and its widespread use in similar studies in the e-commerce field [56,57]. A detailed questionnaire sample is shown in Appendix A.
3.2. Reliability Analysis (RA)
Reliability analysis determines the level to which a measurement is trustworthy or consistent. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient, a mature reliability statistic for Likert-type scales, compares the outcomes of each item nominated in the measuring survey to the outcomes of each variable [62]. Generally, a larger Cronbach’s alpha coefficient leads to greater reliability on the scale. There were 7 measured variables tested in our research, focusing on performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, perceived risk, perceived trust, product quality perception, and online purchase intention. In addition, perceived risk was assessed through 4 scopes: time risk (Pr1), financial risk (Pr2), product delivery risk (Pr3), and privacy risk (Pr4). The measured findings after completing the reliability analysis for each measurement item are mentioned in Table 2.

Table 2.
Reliability analysis (Nb = 357).
Table 2 indicates the Cronbach’s alpha of each element, and the total element of the scale is more than 0.7, showing the positive reliability of the variables. The Corrected Item-Total Correlation (CITC) of the revised element is higher than 0.5, proving that the studied element satisfies the conditions.
3.3. Common Method Bias Analysis
The primary issue with the data was that they were reported individually, and there was common method bias, influenced by reliability motifs and social desirability [63,64]. Therefore, we investigated an arithmetical to evaluate the common method bias. Via SPSS25, the Harman single-factor examination [65] was created for the core variables stated in the theoretical framework, which are effort expectancy (Ee); preserved risk (Pr); product quantity perception (PQp); and purchase intention (Pi), including performance expectancy (Pe), social influence (Si), and preserved trust (Pt). The total variance per factor was 33.333%, and the suggested threshold was 40%, confirming that common method bias would not affect the results.
3.4. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
KMO test and Bartlett spherical test: Confirmatory factor analysis was used on our study’s validity test, showing that the KMO test (Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin) index value of more than 0.6 and the Bartlett spherical outcomes are positive. The KMO was measured by principal component analysis, and the Bartlett spheroid results were later conducted. Refer to Table 3 for each variable’s KMO values and the Bartlett spheroid test results. Clearly, KMO values per variable exceed 0.7, and Bartlett’s test yielded an outcome of 0.000, signifying that scale data in our test are suitable for factor analysis (refer to Table 3).

Table 3.
KMO value and Bartlett spherical outcome (Nb = 357).
Convergence and validity analysis were used to evaluate variables that assess the factor structure via experimental procedures and can be categorized at the same factor level. Three components were employed to test the confirmatory factor analysis model’s convergence efficiency. Firstly, the factor load > 0.5. The average variance extracted is the second > 0.5. The last aspect is composite reliability (CR), with an appropriate 0.7.
In our study, ten dimensions were used, performance expectancy (Pe), effort expectancy (Ee), social influence (Si), perceived trust (Pt), product quality perception (PQp), purchase intention (Pi), perceived risk (Pr), time risk (Tr), financial risk (Fr), and preserved risk (Pr). A total of 30 measurement themes were assessed. As mentioned in Figure 2, a CFA model is completed through AMOS 23.0. For fitting confirmation, we loaded data into SPSS25.0 and positioned variables consistently in the AMOS 23.0 measurement model. Table 4 displays the outcomes of the model fitting. The CMIN/DF was 2.078 < 3. The adjusted goodness-of-fit index, non-normative fit index, comparison fit index, and normative fit index all reached or exceeded 0.9. The root mean square of the difference was 0.029 < 0.08. The estimated error was 0.016 < 0.08 of the root mean square. Overall, each model fit index aligns with the requirements. Table 5 shows the summary of the results of AMOS 23 and the output of average variance extracted and composite reliability.
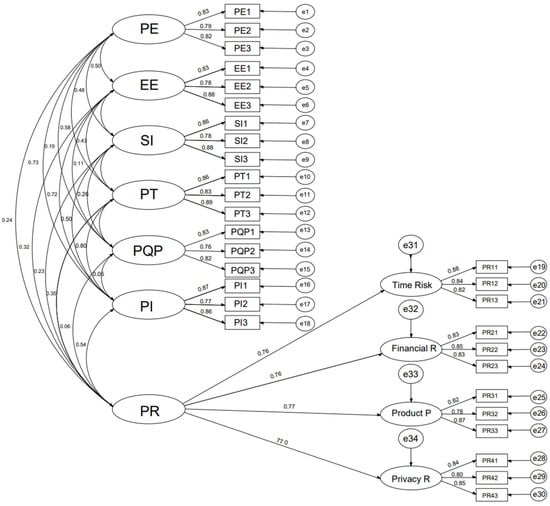
Figure 2.
Confirmatory factor analysis.

Table 4.
CFA modeling fit.

Table 5.
Factor load, CR, and AVE value.
As referred to in Table 5, the factor loadings in this test exceed 0.6, meeting the 1st condition. The composite reliability (CR) is more than 0.7, fulfilling the 2nd condition. Additionally, the typical variance extracted (AVE) surpasses 0.5, satisfying the third condition. In summary, all variables demonstrate strong convergent validity, and the study’s overall convergence efficiency aligns with the desired standard.
Discriminant validity analysis: This method determines whether the validity coefficients in groups of samples differ significantly from one another [66]. In our case, each factor’s typical variance extracted (AVE) is linked to the squared correlation coefficient among constructs (R2). Discriminant validity is considered suitable when the AVE surpasses R2. Table 6 provides facts of the differential validity method, with ** indicating the significance of p < 0.01.

Table 6.
Discriminant validity (Nb = 357).
Table 6 confirms that each factor’s square root of the AVE value is higher than that for the crucial threshold of 0.7. Further evidence that the factors have distinct validity comes from the fact that the discriminant root of every variable’s typical variance extracted value is higher than the correlation coefficient per any factor.
4. Testing Hypothesis and Bootstrapping Results
Before conducting the empirical study, we developed a model including the structural equation and measurement model. First, it is crucial to define the role of each variable and its interrelationships with the others. Our research identifies six main variables: PE, EE, SI, PR, PT, and PI. Figure 2 shows the theoretical framework.
Model analysis: Data from the valid questionnaire were imported to AMOS 23.0, and SEM was performed in alignment with the theoretical framework in Figure 3.
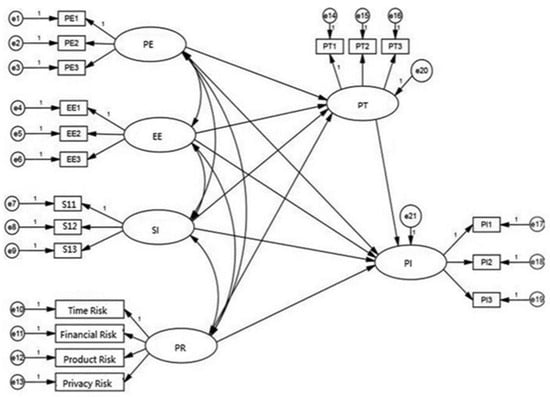
Figure 3.
SEM.framework.
Table 7 shows the experimental outcomes for the model fit test. The CMIN/DF was 2.138 < 3, and the other model-fitting indexes all reached or exceeded 0.9. The residual root mean square is 0.022 < 0.08. The root mean square of the estimation error is 0.04 < 0.08. As a result, each model fit index fulfills the conditions, and therefore our model meets the criteria.

Table 7.
Model-fitting test results.
Direct-effect test: As illustrated through Table 8, EE had a non-notable influence on PT (β = 0.039, p > 0.05), whereas PE significantly increases PI (β = 0.380, p < 0.05). SI has a considerable positive outcome on PT (β = 0.230, p < 0.05), whereas PR has a significant negative outcome on PT (β = −0.190, p < 0.05). PE also positively influences PI (β = 0.250, p < 0.05), and EE strongly affects PI (β = 0.330, p < 0.05). But SI does not significantly affect PI (β = 0.049, p > 0.05). PR significantly reduces PI (β = −0.219, p < 0.05), whereas PI is favorably influenced by PT (β = 0.410, p < 0.05).

Table 8.
Path coefficient.
Mediating-effect test: We chose the Bootstrapping method from no parametric statistics to approve the mediation result. If the Bootstrap confidence interval does not include zero, the direct, indirect, and total effects are considered to be significant and are combined. The bootstrap method was run five thousand times using AMOS 23. Table 9 shows level values that were bias-corrected within a confidence of ninety-five percent.

Table 9.
Total effect, indirect effect, and direct effect.
As Table 9 shows, perceived risk has a total effect value of −0.297 for purchase intention, social influence has a total effect value of 0.169, effort expectancy has a total effect value of 0.344, and performance expectancy has a total effect value of 0.403. Clearly, the Bootstrap confidence interval excludes zero for the four outcomes listed overhead, indicating that the total effect is present.
Regarding indirect impacts, perceived risk had a −0.074 indirect effect on purchase intention. Perceived trust has an indirect effect of 0.119 on purchase intention due to social influence. Purchase intention was indirectly impacted by effort expectancy by 0.018. Performance expectancy had an indirect effect of 0.155 for purchase intention. Significantly, the Bootstrap confidence interval for the four outcomes does not include 0, suggesting that the indirect effect is present for all variables except effort expectancy.
Perceived risk has a −0.222 direct effect on buying intention. Social influence had a 0.052 direct effect on purchase intention, and 0.329 is the direct relationship between effort expectancy and purchase intention. Performance expectancy had a 0.248 direct effect on purchase intention. For the four outcomes listed above, the Bootstrap confidence interval specifically excludes 0, suggesting that the indirect impact is present for all variables except social influence.
Moderate effect test: Table 10 shows the moderate results of product quality perception.

Table 10.
Moderate effect results.
Table 10 shows the outcomes of the moderating effect test.
Product quality perception has a significant positive effect on the connection among perceived trust and purchase intention (β = 0.180, p < 0.05). This indicates that when consumers have higher perceptions of product quality, they are expected to make purchases on the online channel once they trust the platform, compared to consumers with low perceptions of product quality. Figure 4 illustrates the relationship between perceived trust and purchase intention in the context of product quality perception.
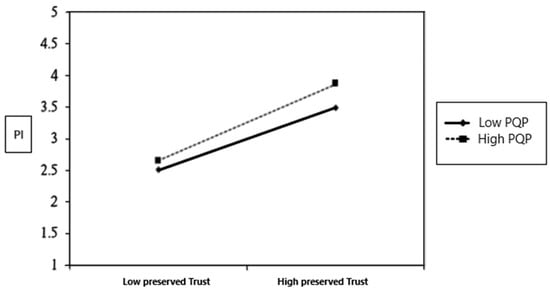
Figure 4.
The moderate effect of product quality perception.
5. Discussion and Finding
Our study explores the reasons impacting purchase intention in the field of digital channels. Table 11 summarizes the nine hypotheses suggested.

Table 11.
Empirical results of hypotheses.
Hypothesis 2 tested as being insignificant, signifying that the positive effect of effort expectancy on purchase intention is not statistically effective (refer to Table 8). Similarly, Hypothesis 5b was considered insignificant, since the indirect effect of effort expectancy on purchase intention was insignificant (as indicated in Table 9). Particularly, the impact on effort expectancy contrasts with findings related to previous research [54,67]. The prior literature examined different markets and varied products. The non-significant outcome of effort expectancy suggests that consumers, who have become more careful when buying online in the field of e-commerce recently, exhibit diminished sensitivity to marginal technological updates of online platforms.
This research’s findings present a contrasting perspective to Abu Afifa’s [68] study. While Abu Afifa’s [68] research suggested that effort expectancy positively influenced the intention to use online business performance, with social influence playing a comparatively smaller role, this study reveals different results. Specifically, authors find that effort expectancy (EE) does not exert a direct impact on online business performance [69].
Empirical research built on the UTAUT method presents the following findings: First, performance expectancy has a positive influence on consumers’ purchase intentions when employing online e-commerce platforms, aligning with the common previous studies [27,70,71]. It highlights the effectiveness and cost benefits that digital platforms provide in comparison to traditional retailers as key factors in attracting qualified users. Second, social influence positively impacts the purchase intention of buyers on digital channels, similar to previous research [27,67,72,73]. This shows the importance of peer effects in adopting new technology. Strategies such as advertising and promotions that make the platform appear trendy and widely accepted are critical for attracting and retaining users. Third, perceived risk negatively affects consumers’ purchase intentions, in line with earlier findings [1,27]. Thus, for digital marketers specializing in advertising e-commerce items, the online e-commerce channel is anticipated to mitigate perceived risk over product quality assurance, optimized delivery and return processes, and enhanced payment security. Fourth, perceived trust mediates the relationship between Pi and Pe and between Si and Pr. This highlights the need for e-commerce channels to improve not only their services but also communicate these improvements effectively to users. Fifth, product quality perception is moderating between perceived trust and purchase intention. Therefore, platforms should provide evidence of product quality to strengthen consumer trust and drive purchase intentions.
6. Conclusions
Due to the new AI technologies, the e-commerce platform demonstrates significant potential for online retailing. Abiding by the UTAUT method, this study offers insights into customer preferences and behavioral intentions with shopping on social media. The empirical analysis for our research indicates that performance expectancy and social influence have a considerably beneficial impact on users’ propensity to buy from a digital e-commerce channel; however, perceived risk has a negative influence. Additionally, the perceived trust acts as the mediator, whereas the product quality perception is the moderator. Furthermore, it is recommended that the online e-commerce channel advances its efficacy, decreases its cost, targets more potential users, and promotes its initiatives and enhancements. Moreover, the digital channels are suggested to choose the right audience, aligning with the objective for each platform, when promoting their initiatives in product quality. Our study enhances understanding among consumers in Lebanon regarding the use of digital media platforms for purchasing products digitally. So, this research will be beneficial for e-commerce inventors, marketers, and online e-commerce developers in guiding them to have better strategies to advertise on online platforms.
Author Contributions
Conception, Q.Y.; methodology, R.F.; data collection, M.A.O.A.; interpretation or analysis of data, M.A.O.A. and G.H.; preparation of the manuscript, M.A.O.A. and R.F.; revision for important intellectual content, Q.Y.; supervision: Q.Y.; funding acquisition: Q.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72271022 and No. W2441021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Higher Institute of Electronic Commerce Systems in Sohag.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request.
Acknowledgments
This study acknowledges financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72271022 and No. W2441021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Questionnaire for Online Shopping Behavior
The researcher aims to conduct the current study—“E-commerce for a Sustainable Future: Integrating Trust, Product Quality Perception, and Online Shopping Satisfaction”.
Because of your experience and expertise in your field of work, the researchers ask you to kindly fill in the attached questionnaire and indicate your good opinion and views regarding the following statements of this questionnaire. It is hoped that an appropriate indication will be made in front of each statement to the extent to which you are aware of its content in terms of what it is intended to measure.
Appendix A.1. Demographic Information
| 1- Gender | |
| A. Male | B. Female |
| 2- Age | |
| A. Below 24 | B. 24 to 35 |
| C. 36 to 45 | D. 46 and 55 |
| E. 56 and above | |
| 3- Online Shopping | |
| A. Never shop online | B. 1 year or Less |
| C. 1–2 Years | D. 3–4 Years |
| E. 5 years and above | |
| 4- Monthly available wage | |
| A. 200$ and below | B. 201$ to 400$ |
| C. 401$ to 700$ | D. 701$ to 1000$ |
| E. 1001$ to 1500$ | F. 1501$ and above |
| 5- level of Education | |
| A. Middle school or less | B. Middle school |
| C. Associate Bachelor | D. Bachelor’s degree |
| E. Master’s degree & above |
Appendix A.2. Questions of the Questionnaire
Technology acceptance factors (5-point Likert scale) (1 = strongly disagree; 5 = strongly agree).
| Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Perceived risk (PR) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 1 | I am concerned about the security of online payments. | |||||
| 2 | I worry about product delivery issues when shopping online. | |||||
| 3 | I am concerned about privacy risks when shopping online. | |||||
| 4 | I worry about the quality of products purchased online. | |||||
| Performance expectancy (PE) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 5 | I find online shopping useful in my daily life. | |||||
| 6 | Online shopping increases my productivity. | |||||
| 7 | Online shopping enhances my shopping efficiency. | |||||
| Effort expectancy (EE) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 8 | Online shopping platforms are easy to use. | |||||
| 9 | Learning to use online shopping platforms is easy for me. | |||||
| 10 | I find it easy to navigate and search for products online. | |||||
| Social influence (SI) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 11 | People important to me think I should use online shopping. | |||||
| 12 | Friends and family encourage me to shop online. | |||||
| 13 | Social media influences my online shopping behavior. | |||||
| perceived trust (PT) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 14 | I trust online shopping platforms to keep my information secure. | |||||
| 15 | I feel confident in the privacy of my online transactions. | |||||
| 16 | Online stores provide reliable information about their products. | |||||
| Product quality perception (PQP) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 17 | Online products meet my quality expectations. | |||||
| 18 | The product descriptions online are accurate and reliable. | |||||
| 19 | I am satisfied with the quality of products I purchase online. | |||||
| Purchase intention (PI) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| To what extent | ||||||
| 20 | I intend to continue shopping online in the future. | |||||
| 21 | I am likely to recommend online shopping to others. | |||||
| 22 | I plan to frequently use online shopping platforms. | |||||
Thank you for your cooperation in filling this questionnaire.
References
- Alalwan, A.A.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P. Factors Influencing Adoption of Mobile Banking by Jordanian Bank Customers: Extending UTAUT2 with Trust. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2017, 37, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, M. 40 Essential Social Media Marketing Statistics for 2018. Available online: https://www.wordstream.com/blog/ws/2017/01/05/social-media-marketing-statistics (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Galov, N. Social Media Marketing Statistics and Trends to Know in 2023. 2023. Available online: https://Review42.Com/Resources/Social-Media-Marketing-Statistics/ (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- Zhang, G. The Influence of Social Media Marketing on Consumers’ Behavior. Adv. Econ. Manag. Political Sci. 2023, 20, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzeta, C.; De Keyzer, F.; Dens, N.; De Pelsmacker, P. Branded Content and Motivations for Social Media Use as Drivers of Brand Outcomes on Social Media: A Cross-Cultural Study. Int. J. Advert. 2024, 43, 637–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misirlis, N.; Vlachopoulou, M. Social Media Metrics and Analytics in Marketing—S3M: A Mapping Literature Review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 38, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, L.; Ruiz, C.; Curras, R.; Hernandez, B. The Role of Travel Motivations and Social Media Use in Consumer Interactive Behaviour: A Uses and Gratifications Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.J.; Krallman, A.; Adams, F.G.; Hancock, T. One Size Doesn’t Fit All: A Uses and Gratifications Analysis of Social Media Platforms. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2020, 14, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, C.; Behl, A. The Dark Side of Gamification in Interactive Marketing. In The Palgrave Handbook of Interactive Marketing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 939–962. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.E.; Yu, C. Exploring Gamification for Live-Streaming Shopping—Influence of Reward, Competition, Presence and Immersion on Purchase Intention. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 57503–57513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.L.S.; Abdullah, M.S. A Review of UTAUT and Extended Model as a Conceptual Framework in Education Research. J. Pendidik. Sains Dan Matemaitk Malays. 2021, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbad, M.M.M. Using the UTAUT Model to Understand Students’ Usage of e-Learning Systems in Developing Countries. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 7205–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalilzadeh, J.; Ozturk, A.B.; Bilgihan, A. Security-Related Factors in Extended UTAUT Model for NFC Based Mobile Payment in the Restaurant Industry. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 70, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H. RESEARCH ON ELDERLY USERS’ INTENTIONS TO ACCEPT WEARABLE DEVICES BASED ON THE IMPROVED UTAUT MODEL. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1035398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, P.; Jinka, S.; Aswini Priya, S. User Acceptance of Electronic Health Records: Cross Validation of Utaut Model. Sona Global Manag. Rev. 2016, 10, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Alaiad, A.; Alsharo, M.; Alnsour, Y. The Determinants of M-Health Adoption in Developing Countries: An Empirical Investigation. Appl. Clin. Inf. 2019, 10, 820–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qeisi, K.; Dennis, C.; Alamanos, E.; Jayawardhena, C. Website Design Quality and Usage Behavior: Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 67, 2282–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.W. Critical Factors for Cloud Based E-Invoice Service Adoption in Taiwan: An Empirical Study. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2015, 35, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Aparicio, M.D.; Izquierdo-Yusta, A.; Jiménez-Zarco, A.I. Consumer Expectations of Online Services in the Insurance Industry: An Exploratory Study of Drivers and Outcomes. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatiasevi, V. An Extended UTAUT Model to Explain the Adoption of Mobile Banking. Inf. Dev. 2016, 32, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Consumer Acceptance and Use of Information Technology: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Kumar Kar, A. Why Do Small and Medium Enterprises Use Social Media Marketing and What Is the Impact: Empirical Insights from India. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, A.S.T.; Hossain, M.A.; Whiteside, N.; Mercieca, P. Social Media and Entrepreneurship Research: A Literature Review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, E.; Venkatesh, A.; Chen, S.; Kruse, E. Dynamic Use Diffusion Model in a Cross-National Context: A Comparative Study of the United States, Sweden, and India. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2013, 30, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.W.-H.; Lee, V.H.; Lin, B.; Ooi, K.-B. Mobile Applications in Tourism: The Future of the Tourism Industry? Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2017, 117, 560–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.W.-H.; Ooi, K.-B. Gender and Age: Do They Really Moderate Mobile Tourism Shopping Behavior? Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 1617–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. Examining location-based services usage from the perspectives of unified theory of acceptance and use of technology and privacy risk. J. Electron. Commer. Res. 2012, 13, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Agrebi, S.; Jallais, J. Explain the Intention to Use Smartphones for Mobile Shopping. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2015, 22, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnoush, S.M.M.; Khalifa, G.S.A. The effect of users’ effort expectancy on users’ behavioral intention to use m-commerce applications: Case study in libya. Int. J. Recent. Trends Bus. Tour. 2021, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martín, S.; Prodanova, J.; López Catalán, B. What Makes Services Customers Say “Buy It with a Mobile Phone”? J. Serv. Mark. 2016, 30, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.H.; Chang, J.J.; Tang, K.Y. Exploring the Influential Factors in Continuance Usage of Mobile Social Apps: Satisfaction, Habit, and Customer Value Perspectives. Telemat. Inform. 2016, 33, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, K. Exploring the Impact of Self-Concept and IT Identity on Social Media Influencers’ Behavior: A Focus on Young Adult Technology Features Utilization. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2023, 40, 6941–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, P.A. Consumer Acceptance of Electronic Commerce: Integrating Trust and Risk with the Technology Acceptance Model. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2003, 7, 101–134. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saedi, K.; Al-Emran, M.; Ramayah, T.; Abusham, E. Developing a General Extended UTAUT Model for M-Payment Adoption. Technol. Soc. 2020, 62, 101293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, R.M.R.; Patro, C.S. Influence of Web Attributes on Consumer Purchase Intentions. In Research Anthology on Strategies for Using Social Media as a Service and Tool in Business; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 337–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Conklin, M.; Cranage, D.A.; Lee, S. The Role of Perceived Corporate Social Responsibility on Providing Healthful Foods and Nutrition Information with Health-Consciousness as a Moderator. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, J.M. Consumer perceptions of service quality: An assessment of the SERVQUAL dimensions. J. Retail. 1990, 66, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Boulding, W.; Kalra, A.; Staelin, R.; Zeithaml, V.A. A DYNAMIC PROCESS MODEL OF SERVICE QUALITY: FROM EXPECTATIONS TO BEHAVIORAL INTENTIONS. J. Mark. Res. 1993, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L.; Parasuraman, A. The Behavioral Consequences of Service Quality. J. Mark. 1996, 60, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.J.; Taylor, S.A. Measuring Service Quality: A Reexamination and Extension. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.C.; Soutar, G.N.; Johnson, L.W. The Role of Perceived Risk in the Quality-Value Relationship: A Study in a Retail Environment. J. Retail. 1999, 75, 77–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou-Llusar, J.C.; Camisón-Zornoza, C.; Escrig-Tena, A.B. Measuring the Relationship between Firm Perceived Quality and Customer Satisfaction and Its Influence on Purchase Intentions. Total Qual. Manag. 2001, 12, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.A.; Baker, T.L. Assessment of the Relationship between Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in the Formation of Consumers’ Purchase Intentions. J. Retailing 1994, 70, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.U.; Uwemi, S. What Are E-Commerce Possible Challenges in Developing Countries: A Case Study of Nigeria. Int. J. Bus. Syst. Res. 2018, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morwitz, V.G.; Steckel, J.H.; Gupta, A. When Do Purchase Intentions Predict Sales? Int. J. Forecast. 2007, 23, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, D.; Kasprzyk, D.; TAPLIN, S.H. The theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behavior. Health Behav. Health Educ. Theory Res. Pract. 2002, 3, 67–98. [Google Scholar]
- ajzen, I.; Fishbein, M. Attitude-behavior relations: A theoretical analysis and review of empirical research. Psychol Bull 1977, 84, 888–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumbuko, C.; Phiri, J. Technology Adoption as a Factor for Financial Performance in the Banking Sector Using UTAUT Model. Afr. J. Commer. Stud. 2024, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.-C.; Hwang, H.-G.; Hung, W.-F.; Li, Y.-C. Physicians’ Acceptance of Pharmacokinetics-Based Clinical Decision Support Systems. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2007, 33, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.W.; Yim, C.K.; Lam, S.S.K. Is Customer Participation in Value Creation a Double-Edged Sword? Evidence from Professional Financial Services across Cultures. J. Mark. 2010, 74, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Dasgupta, S.; Gupta, A. Adoption of ICT in a Government Organization in a Developing Country: An Empirical Study. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2008, 17, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Jaiswal, M. Determinants of Acceptance of ERP Software Training in Business Schools: Empirical Investigation Using UTAUT Model. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2016, 14, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Hui, M.K. Non-Local or Local Brands? A Multi-Level Investigation into Confidence in Brand Origin Identification and Its Strategic Implications. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2010, 38, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JinKyo Professor, S.; Saithibvongsa, P.; Jae Hyeok, C. Country Image, Perceived Product Quality and Purchase Intention: The Moderating Roles of Quality Warranty Certificate and Country-Image Transferred Strategies. Int. J. Econ. Manag. 2019, 1, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, H. Evaluation of Tourism E-Commerce User Satisfaction. J. Organ. End. User Comput. 2021, 33, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewska, T.; Zimon, D. Study of the Logistics Factors That Influence the Development of E-Commerce Services in the Customer’s Opinion. Arch. Transp. 2018, 45, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Batool, S.H.; Rafiq, M.; Safdar, M. Examining Digital Information Literacy as a Determinant of Women’s Online Shopping Behavior. Inf. Technol. People 2022, 35, 2098–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, A. Social Media and Generation Z: A Qualitative Inquiry into Usage Patterns and Motivations of Women of Older Gen Z. 2024. Available online: https://mau.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1866883&dswid=2594 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Faqih, K.M.S. Internet Shopping in the Covid-19 Era: Investigating the Role of Perceived Risk, Anxiety, Gender, Culture, and Trust in the Consumers’ Purchasing Behavior from a Developing Country Context. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouad, L. Rethinking the Lebanese Economic Miracle: The Extreme Concentration of Income and Wealth in Lebanon, 2005–2014. J. Dev. Econ. 2023, 161, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L.J. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951, 16, 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Saraf, N.; Hu, Q.; Xue, Y. Assimilation of Enterprise Systems: The Effect of Institutional Pressures and the Mediating Role of Top Management. MIS Q. 2007, 31, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Organ, D.W. Self-Reports in Organizational Research: Problems and Prospects. J. Manag. 1986, 12, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.W. Differential Validity, Differential Prediction, and College Admission Testing: A Comprehensive Review and Analysis; College Board Research Report No. 2001-6; College Entrance Examination Board: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P.; Jeyaraj, A.; Clement, M.; Williams, M.D. Re-Examining the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT): Towards a Revised Theoretical Model. Inf. Syst. Front. 2019, 21, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Afifa, M.M.; Vo Van, H.; Le Hoang Van, T. Blockchain Adoption in Accounting by an Extended UTAUT Model: Empirical Evidence from an Emerging Economy. J. Financ. Report. Account. 2023, 21, 5–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluarachchi, S.; Nagalingam, N. Triangulating the Moderate Impact of Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, and Social Influence in Social Media Marketing: A Study of Business Performance in Sri Lanka’s Cashew Industry. Qual. Quant. 2024, 58, 4407–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Ismagilova, E.; Hughes, D.L.; Carlson, J.; Filieri, R.; Jacobson, J.; Jain, V.; Karjaluoto, H.; Kefi, H.; Krishen, A.S.; et al. Setting the Future of Digital and Social Media Marketing Research: Perspectives and Research Propositions. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 59, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimperman, M.; Makovec Brenčič, M.; Trkman, P. Analyzing Older Users’ Home Telehealth Services Acceptance Behavior—Applying an Extended UTAUT Model. Int. J. Med. Inf. 2016, 90, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, D.J.F.; Tzeng, G.H. Social Influence on the Use of Clinical Decision Support Systems: Revisiting the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology by the Fuzzy DEMATEL Technique. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunney, A.; Cunningham, N.R.; Eastin, M.S. Wearable Fitness Technology: A Structural Investigation into Acceptance and Perceived Fitness Outcomes. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).