Abstract
Manufacturing agglomeration (MA) is an important driving force for both sustained economic expansion and structural upgrading. Understanding whether and how MA contributes to energy conservation and pollutant mitigation is essential for promoting China’s green transition and offers valuable insight for emerging economies pursuing sustainable growth. The paper first theoretically examines the mechanisms linking MA, energy intensity (EI), and pollutant emission (PE). To overcome the regression bias caused by the heterogeneity of pollutant types among cities, the comprehensive index of PE is constructed. The empirical analysis yields two principal findings. First, MA significantly reduces PE, and this relationship remains robust after a series of tests. Second, EI plays a significant mediating role between MA and PE, that is, MA can achieve the reduction targets of PE by reducing EI. Therefore, in addition to its established role in fostering economic growth, MA should be utilized for its environmental advantages. Policymakers should give greater weight to the capacity of MA to enhance energy conservation and emission reduction, so as to stimulate the positive interaction among MA, EI, and PE, and thereby formulate more differentiated policies.
1. Introduction
China has experienced remarkable economic expansion since the late 1970s, creating the “China miracle” [1,2]. Yet the growth pattern built on intensive resource use and rising environmental pressure has raised increasing concerns since the 21st century. China became the world’s largest CO2 emitter in 2007 [3] and the largest energy consumer since 2011 [4]. However, China’s energy intensity (EI) remained significantly higher than that of advanced economies such as the United States and Japan [5]. Environmental deterioration is not only China’s problem but also represents a global challenge. Evidence shows that more than 95% of the world’s population breathes unsafe air [6], and pollution-related illnesses pose severe threats to public health, particularly for newborns [7]. In 2012 alone, air pollution contributed to 3.7 million deaths worldwide, 88% of which occurred in developing countries [8]. Addressing China’s environmental problems is therefore not only vital for the health and well-being of its own population, but also highly relevant for other developing countries. It carries broader implications for global energy conservation, emission reduction, and the transformation of manufacturing sectors around the world.
In real economic activities, industrial activity tends to concentrate rather than distribute evenly across space. Manufacturing firms often cluster geographically because of strong input–output linkages, substantial labor demand, and frequent knowledge spillovers [9,10,11]. This occurs not only in developed economies, such as the manufacturing belt in the United States [12,13], but also in developing regions, including eastern coastal China [14]. By 2020, China’s industrial added value reached CNY 31.3 trillion, contributing nearly 30% to the world’s manufacturing industry. However, rapid industrialization has also concentrated environmental pressures, with the industrial sector responsible for 67.9% of energy consumption and 83.1% of CO2 emissions [15]. Consequently, reducing EI and pollutant emission (PE) in the manufacturing sector has become central to addressing China’s environmental challenges.
To enhance the positive externalities generated by manufacturing agglomeration (MA) while curbing EI and PE, the Chinese government has introduced a series of policy initiatives. The Made in China 2025 strategy issued by the State Council emphasized that the manufacturing sector should pursue a sustainable path featuring lower EI and reduced PE, setting targets including cutting the sector’s carbon intensity by 40% from its 2015 level by 2025. The report of the 19th National Congress of China further stated the need to move China’s manufacturing sector up the global value chain and foster world-class advanced manufacturing clusters. Building on this direction, the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021–2025) called for deepening the integration of the Internet, big data, and artificial intelligence with manufacturing activities, and accelerating the development of advanced manufacturing clusters. On the one hand, these national strategies reflect China’s intention to achieve a dual gain of sustained economic growth alongside improvements in energy efficiency and emissions control. On the other hand, however, the reality presents a challenge: the three major urban clusters—the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region—where more than 70% of China’s manufacturing firms are concentrated, have also become the regions with the highest EI and the most severe PE. This contrast raises an important question: Can MA help reduce EI and PE? Accordingly, this paper seeks to examine the relationship between MA, EI, and PE through both theoretical analysis and empirical investigation.
This study contributes to the literature in three key ways. First, we develop a theoretical framework that systematically illustrates how MA affects EI and PE from the perspective of industrial agglomeration for the first time. This framework clarifies the mechanisms underlying the energy-saving and emission-reducing effects of MA and provides a conceptual foundation for subsequent empirical analysis. Second, China’s geographic digital elevation simulation data, combined with GIS technology, is adopted to construct the topographic relief level as the instrumental variable. This approach overcomes the estimation bias caused by ignoring the endogeneity of variables in previous studies. Third, rather than relying on a single pollution indicator as in many previous studies, we construct a comprehensive PE index using the entropy method. Drawing on original data on industrial SO2 emission, industrial wastewater discharge, and industrial soot emissions, this index captures China’s pollution structure more accurately and avoids measurement distortions associated with single-indicator metrics.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews the literature. On the basis of industrial agglomeration theory, Section 3 builds a theoretical framework to study the mechanisms of MA affecting EI and PE through externalities. Section 4 introduces the methodology, variables, and data. Section 5 displays the results to empirically analyze the hypotheses. Section 6 draws conclusions and discussions.
2. Literature Review
2.1. MA and EI
Since the late 19th century, MA has become a central topic in economic geography [16,17]. MA refers to the phenomenon in which firms engaged in manufacturing and related industries cluster within a spatial area [18]. Existing research has primarily examined how MA generates positive externalities that foster economic growth [19,20,21]. Studies exploring its effects on energy conservation and emission reduction, especially in developing countries, have grown only recently and represent an expanding frontier within the field.
Research examining the link between MA and energy efficiency has emerged only in recent years, so the research findings are quite divergent. Cerina and Mureddu [22] provided the earliest theoretical argument suggesting that MA exerts no significant influence on energy efficiency, a conclusion later supported by Han et al. [23]. In contrast, Otsuka et al. [24] empirically tested the effects of MA on energy efficiency using Japanese manufacturing data and found a significant positive relationship. Similar conclusions also appeared in studies of the agglomeration of Japan’s paper industry and China’s manufacturing industry [25,26]. Other research reveals a more complex relationship. Zhao and Lin [27] found that there is a nonlinear relationship between MA and energy efficiency based on the sample of Chinese textile industry. Wang et al. [28] also found similar evidence in China’s provincial samples.
2.2. MA and PE
Existing studies on the relationship between MA and PE remain inconclusive, and the findings can be broadly grouped into three perspectives.
The first perspective argues that MA aggravates PE. Using panel data for 28 Chinese provinces from 2007 to 2016, Lan et al. [29] showed that MA significantly increases regional carbon emissions. Similar results were reported by Sun and Yuan [30] in provincial-level analyses. After controlling variables endogeneity, time effect, and spatial effect, some other scholars also verified that the manufacturing industry can lead to environmental pollution [31,32].
The second perspective suggests that MA help reduce PE. Early theoretical work by Krugman [33] and Ehrenfeld [34] explained that MA can lower PE through scale effect, as well as knowledge and technology spillover effect. Building on this foundation, Zeng and Zhao [35] adopted a general equilibrium analysis to demonstrate the negative effect of MA on PE. Using panel data of 283 Chinese cities from 2003 to 2013, Fang et al. [36] found that MA is beneficial to suppress smog pollution. Similar findings were reported by Jiang and Zheng [37] based on data from 30 cities in the Yangtze River Delta in China.
The third perspective believes that the relationship between MA and PE is nonlinear. Using data from 28 manufacturing subsectors in China, Wang et al. [38] identified a significant inverted U-shaped relationship between MA and carbon emissions. Likewise, Liu and Zhang [39] documented a pronounced U-shaped association between MA and carbon productivity in provincial-level industry data.
Despite rich evidence on the pairwise relationships among MA, EI, and PE, several gaps remain in the existing literature. First, most studies do not examine MA, EI, and PE within a unified analytical framework, making it difficult to uncover the internal linkages and mechanisms connecting the three. Second, EI or PE may have a reverse causality relationship with MA, which is an endogenous process affecting each other. The failure to effectively solve this endogenous problem may be a crucial reason for the divergence in conclusions. Third, many studies rely on a single indicator to measure PE, which limits their ability to capture the overall pollution level in a comprehensive and accurate manner.
3. Theoretical Analysis and Hypothesis
3.1. Mechanisms Linking MA and PE
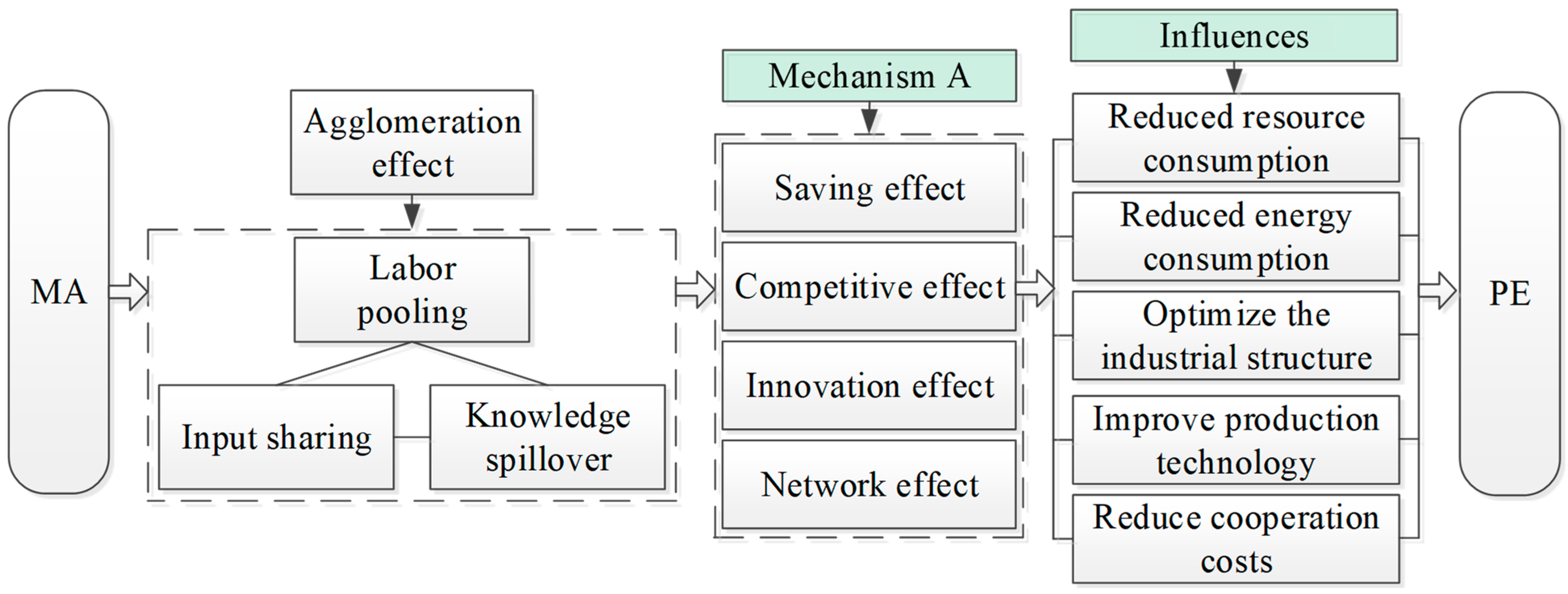
Agglomeration has long been a preferred organizational form in industrial development, particularly within the manufacturing sector [40]. This preference largely stems from the positive externalities generated when firms co-locate. Marshall [41] first described this externality as labor pooling, input sharing, and knowledge spillover, which Ellison et al. [16] later summarized as “labor,” “goods,” and “ideas.” Based on the classical agglomeration theory above, this paper examines the mechanisms of the effect of MA on PE from the aspects of the saving effect, the competitive effect, the innovation effect, and the network effect (Figure 1).
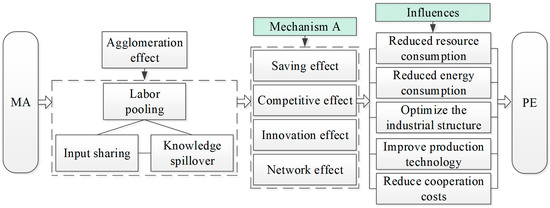
Figure 1.
Direct path of MA on PE.
The saving effect suggests that MA can lower PE by reducing the use of resources and energy. The spatial agglomeration of manufacturing industry can realize the sharing of infrastructure resources in the agglomeration area, as well as reducing the procurement and transportation costs, thus saving factor inputs and decreasing production costs. Meanwhile, MA can encourage firms to adopt more efficient production technologies and upgrade manufacturing processes, thereby decreasing overall energy consumption [42]. It can also achieve the goal of joint pollution control by giving play to economies of scale, thus improving the marginal benefit of emission reduction.
The competitive effect indicates that MA can promote industrial upgrading and structural optimization through the competition of the same or different industries, thereby reducing PE. When firms from the same industry cluster in the same location, competition in market share, product quality, and technological capability becomes more intense. Such competition exerts pressure on firms to innovate, upgrade production processes, and move toward higher segments of the value chain. In addition, the concentration of manufacturing and related industries in a single region intensifies competition [43], which is mainly manifested in public resources such as land use, resource distribution, and policy allocation. This resource pressure further motivates firms to expand and refine their value chains, which helps improve industrial structure and ultimately leads to lower energy consumption and reduced PE [44].
The innovation effect reflects that MA can reduce PE by encouraging technological innovation. Innovation within firms is often driven by interactions among employees, cooperation across firms, and linkages between industries. First, spatial proximity facilitates frequent face-to-face communication among employees from different firms, which helps generate new ideas. Second, firms located within the same cluster can collaborate more easily due to shorter distances, enabling the formation of shared standards, demonstration effects, and more favorable conditions for technology exchange. Third, the co-location of manufacturing and related industries promotes knowledge and technology spillovers through cross-industry linkages, while also reducing business risks and supporting stable regional development [45].
The network effect represents that MA can reduce PE by improving condition of cooperation. When enterprises, labor, capital, and information concentrate within the same region, their interactions give rise to a diverse and tightly connected collaboration network [46]. Such networks facilitate coordination between upstream and downstream industries, support the development of circular production systems, and enable seamless linkages along the supply chain. These improvements help firms lower production costs, enhance the reuse of intermediate products and by-products, and reduce resource waste, ultimately contributing to lower PE.
Accordingly, this paper proposes Hypothesis 1:
H1.
Under appropriate conditions, greater MA contributes to the reduction in PE.
3.2. Mechanisms Linking MA, EI and PE
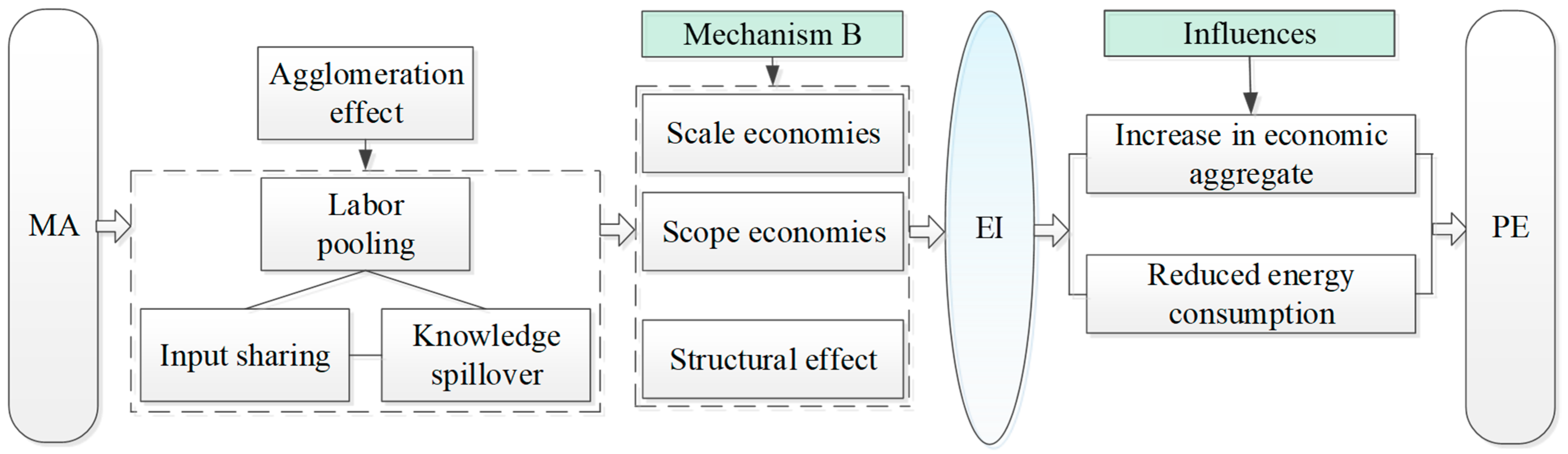
Economic development is often accompanied by rising energy use and PE. Nevertheless, the reduction in energy consumption per unit of output value can reduce PE and improve output efficiency. That is, energy saving necessarily means emission reduction, but emission reduction is not necessarily achieved by energy saving. From the perspective of mediating effects of EI, this paper further analyzes the emission reduction effects caused by scale economies, scope economies, and the structural effect of MA (Figure 2).
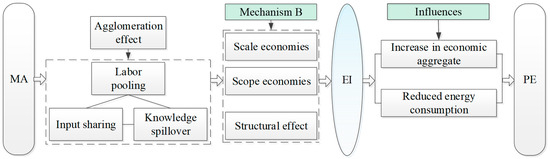
Figure 2.
Indirect path of MA on PE.
Scale economies imply that the expansion of MA can lower EI, thereby reducing PE. On the one hand, MA improves marginal revenue by reducing the production cost of enterprises (such as reducing the cost of raw material search and transaction) [47], thus cutting down the energy consumption per unit output. On the other hand, MA facilitates the formation of a circular economic circle through enhanced specialization and collaboration among firms, which contributes to lower overall energy consumption.
Scope economies means that MA can reduce PE by lowering EI through the extension and coordination of industrial chains. The strong input–output linkages among manufacturing sectors create ample room for cooperation across firms. On one hand, enterprises can reduce unit production costs by broadening their business scope and expanding product varieties. On the other hand, in order to reduce the production cost, manufacturing industry is likely to expand, extend, and refine the enterprise’s production chain through the upstream and downstream industries in the agglomeration area, and carry the business of suppliers and even distributors to realize closed-loop production [48].
The structural effect refers to that, by improving industrial structure, MA can reduce EI so as to achieve PE reduction. On the one hand, in a competitive market environment, firms must continuously adjust and optimize their industrial structure to remain competitive and avoid being displaced. On the other hand, through a self-reinforcing mechanism, MA tends to evolve from low-end to high-end industrial configurations. As the cluster matures, higher entry standards naturally emerge, pushing the industrial structure toward more advanced and efficient activities [49], resulting in the decrease in EI and PE.
Therefore, Hypothesis 2 is proposed:
H2.
In the Chinese context, MA reduces PE primarily through its ability to lower EI.
4. Research Design
4.1. Methodology
4.1.1. Model Specification
Considering the theoretical analysis above, we estimate the effect of MA on PE using the following econometric specification:
where i represents the city; t denotes the year; is the constant term. is the explained variable that means the level of PE; means the core explanatory variable that refers to the degree of MA; indicates a set of control variables. and are city and year fixed effects, respectively; is the error term. Measurement of variables are provided in the following section.
4.1.2. Mediating Effect Model
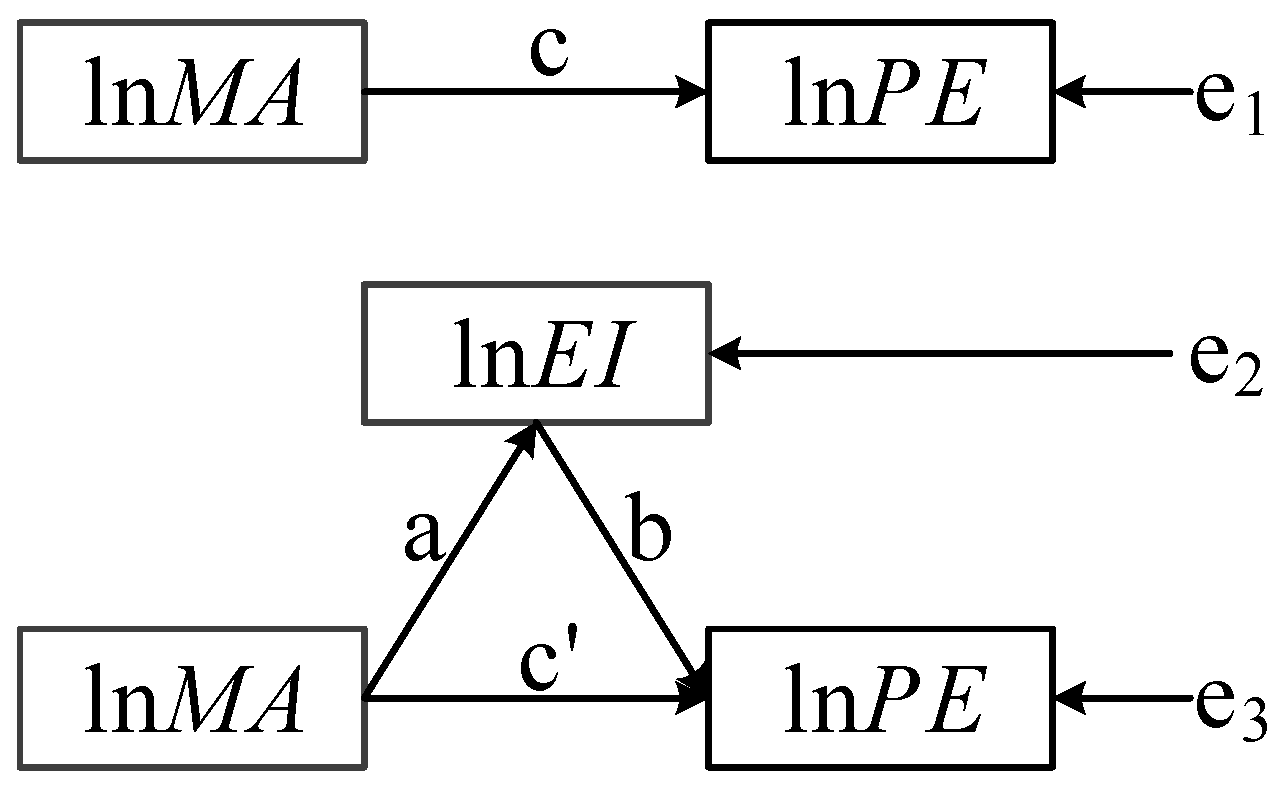
According to Hypothesis 2, MA has effects on PE through EI (Figure 3). Therefore, a mediating effect model is applied to empirically test whether EI acts as a mediating variable [50,51]. The specific steps refer to Han et al. [52].
where c represents the total effect of on , a is the effect of on mediating variable , and denotes the direct effect of on after controlling ; denote the means regression residual; the mediating effect is the product of the coefficients of a and b.
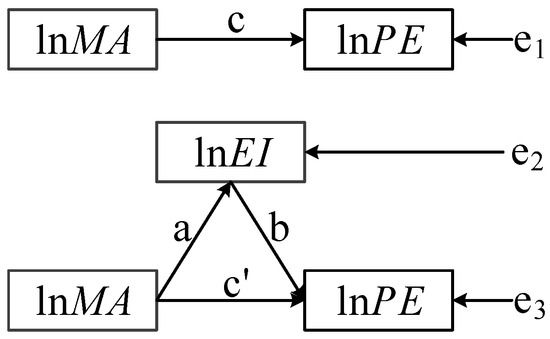
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of mediating effect.
4.2. Variables Selected
4.2.1. Explained Variable
Accurately capturing the level of PE across cities is essential for the empirical analysis. Existing studies generally use single indicators to measure regional PE level [53]. However, due to substantial differences in economic development, industrial composition, and natural conditions across Chinese cities, pollution patterns vary widely. The biggest defect of single pollutant index is that it cannot comprehensively reflect the pollution emission level of different regions. To address this limitation, we construct a composite PE index using the entropy method [54]. Specifically, we select three major types of industrial pollution in China, namely, industrial SO2 emissions, industrial waste water discharged, and industrial soot emissions.
4.2.2. Core Explanatory Variable
The measurement method of MA mainly includes concentration ratio (CR), the location quotient (LQ), locational Gini coefficient (LGC), HHI and Ellison–Glaeser index (EG). CR and LQ are suitable for measuring the degree of concentration of an industry in different regions, while LGC and EG are applicable to measure the agglomeration degree of different industries in the same region [36]. Based on data availability and existing research, this paper utilizes the LQ to calculate MA [39]. A key advantage of LQ is that it reflects the spatial distribution of regional factors more accurately by effectively eliminating the influence of regional size. The calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the MA level of city i in the t-th year; refers to the number of manufacturing employees of city i in the t-th year; indicates the total number of urban employees of city i at the end of the t-th year; means the number of manufacturing employees in China in the t-th year; means the number of total urban employees in China at the end of the t-th year.
4.2.3. Mediating Variable
EI is estimated by the ratio of total annual electricity consumption to GDP. As EI serves as the mediating variable, suitable measurement of EI is of vital importance to identify the mediating effect. EI is widely used to compare regional energy efficiency and environmental performance and reflects the degree to which economic activity depends on energy inputs [55]. Two authoritative approaches are commonly employed to quantify EI: energy consumed per unit of GDP and energy consumed per unit of output. The latter is sensitive to market price fluctuations, which compromises comparability across regions. Therefore, we adopt the former to capture EI at the city level. Because detailed energy consumption data for prefecture-level cities are not publicly available in China, this paper chooses the whole society’s electricity consumption to measure the energy consumption based on existing research [56].
4.2.4. Control Variables
Economic development level is calculated by the first and second terms of per capita GDP [57]. Referring to the environmental Kuznets hypothesis, with the improvement of economic level, PE will show a reversed “U-shape” trend [58]. This paper describes the effects of economic development level on PE with reference to the relevant theory.
Industrialization level is calculated by the logarithm of the added value of the secondary industry in GDP [10]. As the largest emitter of pollutants [59], rapid industrialization will strongly stimulate energy consumption, thus exacerbating PE [60]. Thus, its coefficient is expected to be positive.
Industrial structure is calculated by the logarithm of the output value of the tertiary industry to the secondary industry [61]. A more advanced industrial structure generally supports environmental governance and helps reduce regional PE [52]. Therefore, a negative coefficient is anticipated.
Environmental regulation is judged by the logarithm of the comprehensive index of industrial solid waste utilized rate, industrial dust removal rate, and industrial SO2 removal rate [62]. The specific measurement method is the same as the PE index. On the one hand, in order to relieve the pressure on environment, local governments tend to implement different types of environmental policies to control the emission of pollutants, hence improving the environmental quality [63,64]. On the other hand, “race-to-the-bottom” effect among regions may be triggered by the governments’ low standard of environmental regulation, since the governments may want to reduce the economic loss caused by the increase in production cost due to environmental regulation [65]. Thus, the expected sign of this coefficient is uncertain.
Population density is identified by the logarithm of the total population to the administrative area [66]. Population expansion increases demand for energy and resources, and in the absence of sustainable development practices, environmental pressure tends to intensify [61]. Accordingly, its coefficient is expected to be positive.
The definitions of variables are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Definitions of variables.
4.3. Data Source
This study uses panel data for 287 Chinese cities covering the period 2003–2016. The data comes from the China Urban Statistical Yearbook. To address missing observations and potential inconsistencies caused by statistical reporting issues, the interpolation method is utilized to supplement the missing data and outliers in the data set. To eliminate the influence of inflation, this paper adopts the GDP deflator method to adjust all price variables on the basis of 2003. Because the GDP index of prefecture-level cities is not fully published, the GDP index of the provinces in that year is adopted to supplement for the missing years. To reduce the influence of heteroscedasticity, continuous variables are transformed using natural logarithms.
4.4. Endogeneity and Instrumental Variables
The relationship between MA and PE may suffer from endogeneity for two main reasons. First, simultaneity may exist between MA and PE. As the high-emission areas are usually less developed cities, local officials seeking political promotion may relax environmental regulations to attract enterprises to settle down, thus promoting the regional MA [67]. Second, omitted variable bias may arise. Although this paper tries to comprehensively control the factors that may affect PE, unobserved determinants that jointly affect MA and PE may still remain. To solve the endogeneity caused by the above reasons, we adopt instrumental variables to alleviate the estimation errors and use the two-stage least square (2SLS) method for estimation.
According to the basic idea of constructing instrumental variables, the exclusivity principle should be satisfied, that is, instrumental variables should be exogenous variables that are only intrinsically related to MA but not directly related to disturbance terms. Looking for instrumental variables is usually performed from a geographic or historical perspective. Geographical indicators are naturally formed, and historical indicators are sufficiently distant in time. Therefore, it can be considered that neither of them directly affects the explained variables such as PE, thus satisfying the exogenous condition. At the same time, geographical or historical indicators may be correlated with some explanatory variables such as MA and meet the relevant condition. For example, from a geographical perspective, Barone and Narciso [68] took terrain slope as an instrumental variable of the activity degree of Italian Mafia and examined how organized crime shapes the allocation of commercial subsidies. From a historical perspective, Li and Lu [69] employed the size of the urban population in 1920 and the number of industrial firms in 1978 as the instrumental variables of manufacturing enterprise agglomeration to analyze the influence of geographic concentration on the vertical disintegration of labor in China’s manufacturing industry.
Reference to existing research [68], we adopt topographic relief degree as the instrumental variable of MA for two reasons. First, in terms of exogeneity, topographic relief is a natural geographic attribute and is therefore unlikely to exert a direct effect on PE. Second, in terms of relevance, variations in terrain shape the cost of infrastructure development, the concentration of population, the spatial layout of cities, and firms’ location choices. Because these elements are fundamental determinants of agglomeration, topographic relief is inherently linked to the degree of MA. Therefore, these features make topographic relief a theoretically sound and empirically plausible instrumental variable for MA. The specific measurement is as follows: GIS and 1:100,000 digital elevation model (DEM) is used, and raster data is extracted based on the specification of 1 km × 1 km. A 3 km × 3 km grid is selected as the measurement unit. Within each measurement unit (9 km2), the difference between the elevation of the highest point and the lowest point is calculated and defined as the topographic relief value of each city. DEM is derived from the Big Data Center of Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions (http://bdc.casnw.net/index.shtml (accessed on 18 January 2025)).
Since panel data is used in the paper, due to the fixed effect, only adopting urban topographic relief as the instrumental variable will make the model unable to measure. Therefore, it is necessary to construct an instrument that changes over time. Following Nunn and Qian [70], we create an interaction term between topographic relief (capturing cross-sectional variation) and the number of industrial enterprises in the following year (capturing time variation) to serve as a time-varying IV for the endogenous variable MA.
5. Empirical Results
5.1. Panel Stationarity Test
To avoid the pseudo-regression problem caused by the non-stationarity of data, we conduct stationarity tests for all key variables using both the Harris–Tzavalis test and the Im–Pesaran–Shin test. Results that include the intercept item and both the intercept item and the time trend item are reported in Table 2. All variables are stationary series, indicating that non-stationarity can be ignored in subsequent regression analysis.

Table 2.
Panel unit root test.
5.2. Regression Results of MA on PE
5.2.1. Baseline Model
Before testing Hypothesis 1, the instrumental variables are tested (Table 3). First, we apply the endogeneity test proposed by Davidson and MacKinnon [71]. Based on the first-stage estimation results, after controlling for individual fixed effects and time fixed effects, the Davidson–MacKinnon test rejects the hypothesis that there is no endogeneity at the 1% confidence level regardless of whether the control variables are added. Second, with or without control variables, the underidentification test significantly rejects the null hypothesis, indicating that the instrumental variables do not suffer from underidentification. Third, the F-statistic of the weak instrumental variable test is significantly greater than the critical value of 10 [72], implying that the instrumental variable does not have the problem of weak gentility, and the weak gentility robustness test also supports this conclusion. It shows that the instrumental variables satisfy the exogenous hypothesis. Fourth, instrumental variables and MA are positively correlated and pass the significance test of 1%. This means the correlation hypothesis of instrumental variable is satisfied. Accordingly, the instrumental variable selected in this paper is reasonable.

Table 3.
First stage results of 2SLS.
Table 4 reports the results of OLS and 2SLS in the second stage. It shows that whether control variables are included, the coefficient of MA estimated by OLS is consistently significantly negative and passes the 5% and 1% significance tests, respectively. This shows that MA can reduce PE and achieve emission reduction targets. Under the 2SLS estimation, the relationship between MA and PE also remains significantly negative regardless of the inclusion of control variables, and both results pass the 1% significance level. This is consistent with the results of OLS and confirms that MA reduces PE in China. This is consistent with the result of Fang et al. [36]. However, the coefficient of 2SLS is significantly larger than that of OLS, implying that failing to account for the endogeneity of MA leads to a downward-biased estimate. Consequently, the emission reduction effect of MA would be underestimated.

Table 4.
Estimated results of OLS and 2SLS.
5.2.2. Robustness Test
Using alternative proxy variables. To check whether the main findings depend on the choice of MA indicator, we replace the measure of MA with the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI). Having the advantages of both absolute concentration degree and relative concentration degree, it is independent of the number and size distribution of enterprises and can thereby better measure the change in MA. The calculation formula is [73] , where refers to the MA level of city i in the t-th year, and other variables are defined as above. The MA level is logarithmically processed to enhance the comparability of the results. According to column (1) of Table 5, MA significantly reduces PE, which denotes that the core conclusion does not depend on the specific measure of MA level.

Table 5.
Robustness test results.
Excluding extreme values. The maximum and minimum values of variables are quite different. Therefore, winsor is applied to indent all the original data by 1% to reduce the bias result from extreme values. As reported in column (2) of Table 5, the estimated effect of MA on PE remains negative after trimming extreme values. This suggests that the result is not driven by a few abnormal observations.
Using smoothed data. To reduce possible bias from strong year-to-year fluctuations, we smooth the series using a three-year moving average and then re-estimate the model with 2SLS approach. The results in column (3) of Table 5 show that the coefficient of MA is significantly negative and passes the significance test of 1%. This confirms that the main conclusion is robust.
Implementing the IV-GMM method. MA exhibits pronounced endogeneity in the process of urban economic development. On the one hand, MA may influence PE by affecting resource allocation efficiency, technological innovation, and the composition of factor use. On the other hand, pollution concentrations, regulatory intensity, and environmental carrying capacity may in turn shape the firms’ location choices and expansion decisions, thereby affecting the level of MA. This bidirectional causality implies that OLS estimates may be biased. To obtain consistent estimates and mitigate this endogeneity concern, we further employ an IV–GMM approach as a robustness test. As shown in column (4) of Table 5, MA significantly reduces PE under this approach. This again supports the main finding of the paper.
5.3. Mediating Effect of EI
Theoretical analysis suggests that EI plays an intermediary role between MA and PE. To examine Hypothesis 2, the mediating effect model is applied, and 2SLS is used to address the endogeneity of MA.
Column (1) of Table 6 shows that the coefficient of MA is negative and significant at 1% confidence level, denoting that the total effect of MA on PE is significantly negative. The estimated coefficient of MA in column (2) is also significantly negative, implying that MA reduces EI and achieves the goal of energy saving. Liu et al. [74] found similar conclusions at the city level in China. In column (3), the coefficient of MA is still significantly negative and larger than the coefficient of total effect. In this case, the coefficient of EI is significantly negative, showing that a 1% rise in EI leads to a 0.006% reduction in PE. These findings imply that EI improves the emission reduction capacity of MA and plays an intermediary role between MA and pollution emission. In addition, the Sobel test is used to verify the significance of the mediating effect. The results show that the Z-value is 2.038 and has passed the significance test of 5%, manifesting that the mediating effect of EI is significant.

Table 6.
Results of mediation effect model.
This paper verifies the robustness of the mediating role of EI from three aspects.
First, an HHI is employed as an alternative indicator to re-measure the level of MA. Columns (1) to (3) of Table 7 indicate that the main conclusion remains unchanged when the explanatory variable is constructed using a different measurement. Second, to account for year-to-year variability in the data, the analysis applies a three-year moving-average procedure to smooth the series and reduce the influence of data volatility on the estimation outcomes. As shown in column (4) to (6) of Table 7, the main finding still holds under this procedure.

Table 7.
Robustness test for Hypothesis 2.
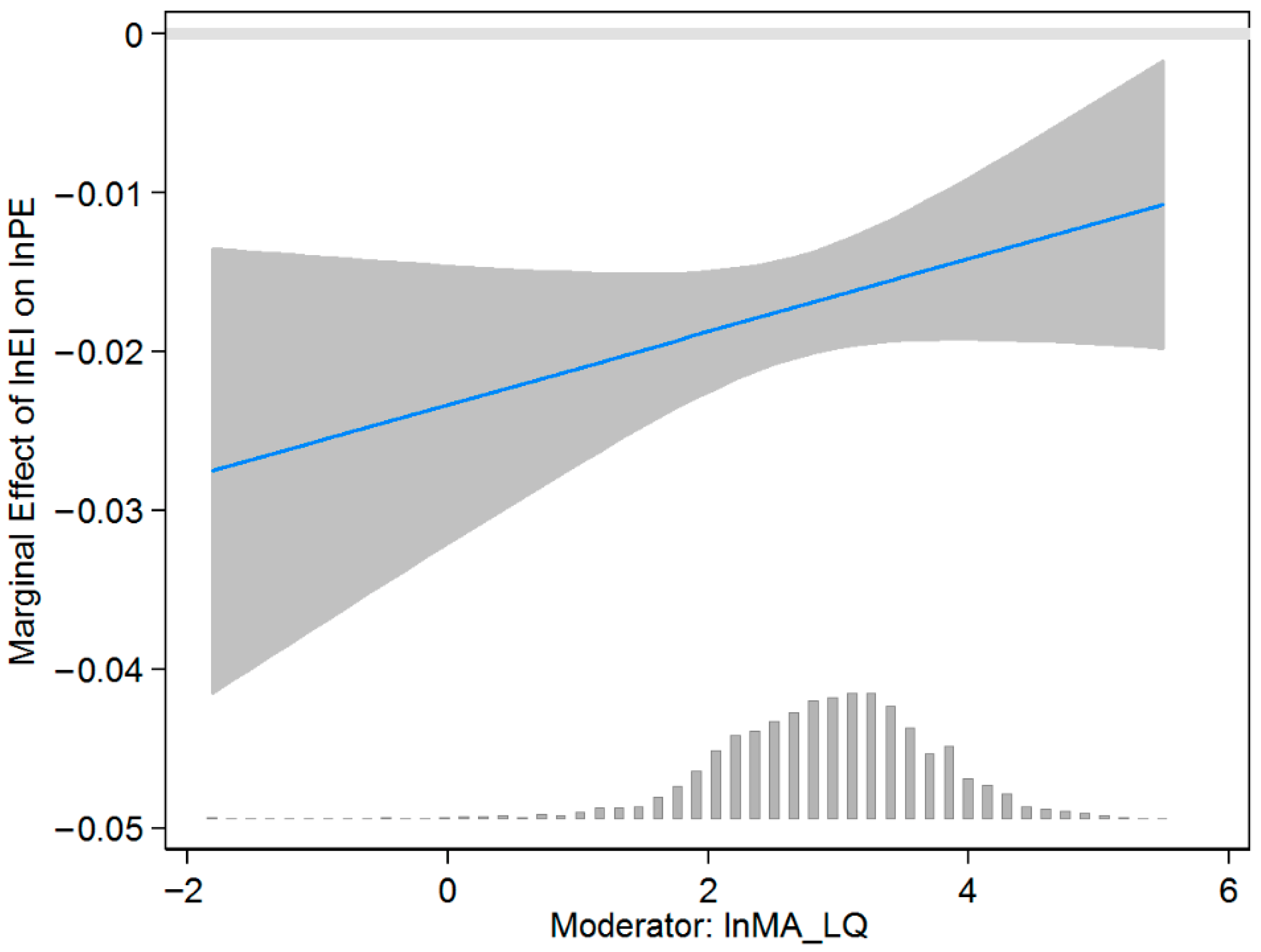
Third, considering the endogeneity caused by the artificial set of explained variables and explanatory variables in the mediating effect model, we investigate the mediating effect of EI by introducing an interaction term between MA and EI in the benchmark model and visualizing the interaction term coefficient. The above estimations are conducted using 2SLS. The results in Table 8 and Figure 4 prove that the conclusions of this paper are robust and support Hypothesis 2.

Table 8.
Interaction term model for Hypothesis 2.
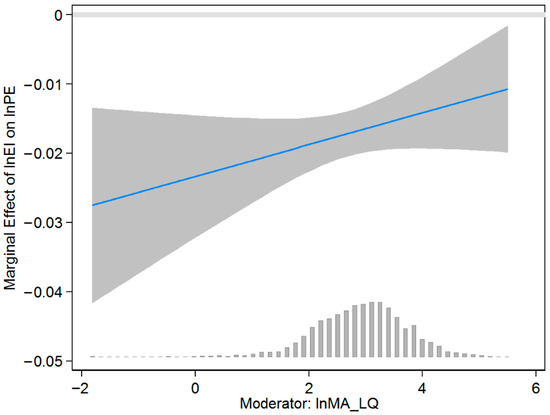
Figure 4.
Visualization of the interaction. Notes: The solid line depicts the estimated coefficient of the interaction term, with the shaded area representing the 95% confidence interval. The histogram shows the distribution of lnMA_LQ.
6. Conclusions and Discussion
This paper theoretically explains the mechanisms of MA, EI, and PE for the first time. Drawing on panel data for 287 Chinese cities, 2SLS and the mediation effect model are used to examine the energy-saving and emission-reduction effects of MA. The following conclusions can be drawn: (1) MA has the dual effects of energy saving and emission reduction. (2) MA has direct and indirect effects on PE, that is, MA can not only directly reduce PE but also promote PE reduction by inhibiting EI.
This paper is closely related to the growing literature on the environmental effects of MA. These studies have examined the relationship between MA and PE from different perspectives, yet their conclusions remain highly divergent [25,32]. Some scholars find that MA improves environmental quality through technological innovation, industrial upgrading, and knowledge spillovers [75]. Others argue that MA may increase energy use and PE due to the negative externalities of innovation and the expansion of production scale [76]. This paper helps reconcile these differences by providing more comprehensive theoretical reasoning and empirical evidence. Compared with existing work, the novelty of this paper lies in three main areas. First, we are the first to reveal, from the perspective of EI, that MA can reduce EI through scale economies, scope economies, and structural effect, thereby lowering PE. Our results suggest that EI is a critical factor shaping the relationship between MA and PE, yet it has received limited attention in prior studies [77]. Second, we address the endogeneity of MA by using topographic relief as an instrumental variable, which is a geographic characteristic formed by natural conditions and therefore strictly exogenous. The use of this variable allows us to obtain more credible causal estimates. Although previous studies recognize that MA is endogenous to urban development and closely related to economic conditions and PE [21,78], few have used appropriate instrumental variables to address this issue, which may contribute to the inconsistencies in earlier findings. Third, we construct a more comprehensive and reliable index of PE to better capture the PE level of each city. Most studies rely on a single pollutant indicator, such as SO2, COD, or CO2, to approximate PE [79,80,81]. However, cities differ widely in development stage, industrial structure, and technological capability, leading to substantial variation in their major pollution sources [82]. A single indicator therefore cannot fully describe a city’s actual PE level.
According to the conclusions, several policy implications can be proposed.
First, since the manufacturing sector generates both energy-saving and emission-reducing effects, efforts should be made to build high-level MA parks to fully release these positive externalities. This requires moving away from a land-finance-driven development model and instead reducing land costs, improving infrastructure, and strengthening public service provision to create favorable conditions for MA. At the same time, a stricter entrance mechanism for firms entering the manufacturing cluster is needed. Screening out firms with high energy use, high emissions, and low productivity, and prioritizing high-end and intelligent manufacturing will help improve the overall efficiency of the manufacturing cluster.
Second, because MA reduces PE through both direct channels and the indirect channel of lowering EI, innovation should be viewed as a key lever to achieve combined benefits in energy saving and emission reduction. First, enhancing the degree of MA and leveraging agglomeration economies can promote technological progress, ease the pollution pressures associated with EI, and thereby improve the energy-saving outcomes generated by MA. Second, given that reductions in EI amplify the emission-reduction effect of MA, policymakers should explicitly incorporate the energy-saving benefits of MA into policy design, thus generating the maximum of the positive external benefits by realizing the benign interaction between policies.
We acknowledge that this study is subject to several limitations that suggest avenues for future research. First, because official statistics for key variables are not available beyond 2016, our sample period necessarily ends in that year, which may limit the contemporaneous relevance of the results. Future work could draw on big data techniques or alternative data sources to overcome this constraint and enhance the practical value of empirical findings. Second, MA is a dynamic and spatially interconnected process. Its environmental effects may involve nonlinearities and spatial spillovers that extend beyond the linear framework. Investigating these additional dimensions would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the environmental consequences of MA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.; Methodology, Y.F.; Software, H.Y.; Validation, Y.F.; Formal analysis, Y.F.; Investigation, Y.F.; Resources, H.Y.; Data curation, Y.F.; Writing—original draft, Y.F.; Writing—review & editing, H.Y.; Visualization, Y.F.; Supervision, H.Y.; Project administration, H.Y.; Funding acquisition, Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Education in China Project of Humanities and Social Sciences (24YJC790040); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (72403190); the Philosophy and Social Science Project of Education Department of Hubei Province (22Q063); the Scientific Research Fund of Wuhan Institute of Technology (K2023053).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Huang, Z.; Lv, L.; Yang, M. The effect of political influence on corporate social donations: Evidence from party-building reform in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 93, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Does the cultural consumption policy reduce carbon emission intensity in China? Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Industrial structure, technical progress and carbon intensity in China’s provinces. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xiao, B.; Song, L. What cause the decline of energy intensity in China’s cities? A comprehensive panel-data analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, M.; Li, S.; Jiang, L. Foreign direct investment and energy intensity in China: Firm-level evidence. Energy Econ. 2019, 80, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2018: Special Report on Global Exposure to Air Pollution and Its Disease Burden; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, L.; Du, M.; Kong, S. The effect of clean heating policy on individual health: Evidence from China. China Econ. Rev. 2024, 89, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Burden of Disease from Household Air Pollution for 2012; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, M.; Larsson, J.P.; Wernberg, J. The economic microgeography of diversity and specialization externalities: Firm-level evidence from Swedish cities. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Cen, Y. How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ. 2020, 92, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belderbos, R.; Fukao, K.; Ikeuchi, K.; Van Hove, J. Does industry agglomeration attract productive firms? The role of product markets in adverse selection. J. Reg. Sci. 2025, 65, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermeño, A.L. The driving forces of service localization during the twentieth century: Evidence from the United States. Eur. Rev. Econ. Hist. 2019, 23, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.Y.; Ma, Y.; Zimmermann, K. 100 years of rising corporate concentration. Am. Econ. Rev. 2024, 114, 2111–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wei, H.; Lu, S.; Su, H. Mismatch distribution of population and industry in China: Pattern, problems and driving factors. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 97, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Energy consumption, CO2 emission and sustainable development in Chinese industry. Econ. Res. J. 2009, 4, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, G.; Glaeser, E.L.; Kerr, W.R. What causes industry agglomeration? Evidence from coagglomeration patterns. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 1195–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.C. Dynamic agglomeration economies and learning by working in specialised regions. J. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Lin, B. Impact of industrial agglomeration on energy efficiency in China’s paper industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Williams, A.M.; Park, S.; Chen, J.L. Spatial spillovers of agglomeration economies and productivity in the tourism industry: The case of the UK. Tour. Manag. 2021, 82, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D. Cluster space among labor productivity, urbanization, and agglomeration of industries in Hungary. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 1008–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgüzel, C. Agglomeration effects in a developing economy: Evidence from Turkey. J. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 23, 823–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerina, F.; Mureddu, F. Is agglomeration really good for growth? Global efficiency, interregional equity and uneven growth. J. Urban Econ. 2014, 84, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Xie, R.; Lu, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, Y. The effects of urban agglomeration economies on carbon emissions: Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, A.; Goto, M.; Sueyoshi, T. Energy efficiency and agglomeration economies: The case of Japanese manufacturing industries. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2014, 6, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Managi, S. Industrial agglomeration effect for energy efficiency in Japanese production plants. Energy Policy 2021, 156, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, F.; Lv, K.; Li, W.; Luo, L. Industrial agglomeration and firm energy intensity: How important is spatial proximity? Energy Econ. 2022, 112, 106155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, B. Will agglomeration improve the energy efficiency in China’s textile industry: Evidence and policy implications. Appl. Energy 2019, 237, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, T. The impact of transportation infrastructure and industrial agglomeration on energy efficiency: Evidence from China’s industrial sectors. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Sun, L.; Pu, W. Research on the influence of manufacturing agglomeration modes on regional carbon emission and spatial effect in China. Econ. Model. 2021, 96, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Yuan, Y. Industrial Agglomeration and Environmental Degradation: Empirical Evidence in Chinese Cities. Pac. Econ. Rev. 2015, 20, 544–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Sun, C.; Chen, L. New evidence for the impact of financial agglomeration on urbanization from a spatial econometrics analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Heterogeneous industrial agglomeration, technological innovation and haze pollution. China Econ. Rev. 2022, 77, 101880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Space: The Final Frontier. J. Econ. Perspect. 1998, 12, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, J. Putting a Spotlight on Metaphors and Analogies in Industrial Ecology. J. Ind. Ecol. 2003, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.-Z.; Zhao, L. Pollution havens and industrial agglomeration. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2009, 58, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Tang, X.; Xie, R.; Han, F. The effect of manufacturing agglomerations on smog pollution. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2020, 54, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zheng, J. Economic Growth or Environmental Sustainability? Drivers of Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration in China. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2017, 53, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, W.; Ma, D.; Zhang, C. Carbon emissions and optimal scale of China’s manufacturing agglomeration under heterogeneous environmental regulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Industrial agglomeration, technological innovation and carbon productivity: Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 166, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. History and Industry Location: The Case of the Manufacturing Belt. Am. Econ. Rev. 1991, 81, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A. Principles of Economics, 8th ed.; Macmillan: London, UK, 1920. [Google Scholar]
- Head, K.; Ries, J.; Swenson, D. Agglomeration benefits and location choice: Evidence from Japanese manufacturing investments in the United States. J. Int. Econ. 1995, 38, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Clusters and the New Economics of Competition. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1998, 76, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Gong, J.; Zhao, X. FDI and environmental regulation: Pollution haven or a race to the top? J. Regul. Econ. 2012, 41, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malizia, E.E.; Ke, S. The influence of economic diversity on unemployment and stability. J. Reg. Sci. 1993, 33, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, A.; Su, H.; Su, S.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Weng, M. Does the establishment of development zones really improve industrial land use efficiency? Implications for China’s high-quality development policy. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Scott, A.J. Industrial Agglomeration and Development: A Survey of Spatial Economic Issues in East Asia and a Statistical Analysis of Chinese Regions. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 79, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.K.; Nelson, M.A. Do external quality certifications improve firms’ conduct? International evidence from manufacturing and service industries. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2020, 76, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, P.; Sheng, J.; He, K.; Wei, Y.-M.; Xie, R. Exploring the effect of industrial structure adjustment on interprovincial green development efficiency in China: A novel integrated approach. Energy Policy 2019, 134, 110946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Yu, N. Internet Use and Lower Life Satisfaction: The Mediating Effect of Environmental Quality Perception. Ecological Economics 2020, 176, 106725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, L.; Peng, K.; Wang, X. Does industrial upgrading promote eco-efficiency?—A panel space estimation based on Chinese evidence. Energy Policy 2021, 154, 112286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, F.L.V.; Halmenschlager, V.; Abdallah, P.R.; Teixeira, G.d.S.; Sumaila, U.R. The relation between fishing subsidies and CO2 emissions in the fisheries sector. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 185, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Huang, R. Whether foreign direct investment can promote high-quality economic development under environmental regulation: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21674–21683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Lin, B. What factors lead to the decline of energy intensity in China’s energy intensive industries? Energy Econ. 2018, 71, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, Y. Inconsistency of economic growth and electricity consumption in China: A panel VAR approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Does new-type urbanization policy promote green energy efficiency? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy Econ. 2023, 124, 106752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Lee, C.C. Convergence of the world’s energy use. Resour. Energy Econ. 2020, 62, 101199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Shao, S.; Fan, M.; Chen, S. Regional carbon imbalance within China: An application of the Kaya-Zenga index. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Nepal, R.; Alam, K. Impacts of human capital, exports, economic growth and energy consumption on CO2 emissions of a cross-sectionally dependent panel: Evidence from the newly industrialized countries (NICs). Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 121, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Shao, S.; Yang, L. High-speed rail and CO2 emissions in urban China: A spatial difference-in-differences approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liang, E.; Liu, C. “Size-dependent” environmental regulations and spatial labor allocation. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2025, 132, 103158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.S.; Walker, R. Why Is Pollution from US Manufacturing Declining? The Roles of Environmental Regulation, Productivity, and Trade. Am. Econ. Rev. 2018, 108, 3814–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, A.; Coggins, J.S.; Goodkind, A.L. Effectiveness of air pollution standards in reducing mortality in India. Resour. Energy Econ. 2020, 62, 101188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shao, S.; Fan, M.; Yang, L. Wage distortion and green technological progress: A directed technological progress perspective. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 181, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zou, L.; Feng, Y. How to achieve emission reduction without hindering economic growth? The role of judicial quality. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 209, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Baležentis, T.; Tian, Z.; Shao, S.; Geng, Y.; Wu, R. Environmental Performance and Regulation Effect of China’s Atmospheric Pollutant Emissions: Evidence from “Three Regions and Ten Urban Agglomerations”. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 74, 211–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.; Narciso, G. Organized crime and business subsidies: Where does the money go? J. Urban Econ. 2015, 86, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, Y. Geographic concentration and vertical disintegration: Evidence from China. J. Urban Econ. 2009, 65, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; Qian, N. US Food Aid and Civil Conflict. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 1630–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.; MacKinnon, J.G. Estimation and Inference in Econometrics, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Staiger, D.; Stock, J.H. Instrumental Variables Regression with Weak Instruments. Natl. Bur. Econ. Res. 1997, 65, 557–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S. London calling? Agglomeration economies in literature since 1700. J. Urban Econ. 2019, 112, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Does industrial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, X.; Dong, K. How does producer services’ agglomeration promote carbon reduction?: The case of China. Econ. Model. 2021, 104, 105624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Dong, K. How does ICT agglomeration affect carbon emissions? The case of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration in China. Energy Econ. 2022, 111, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Shao, J.; Shi, Z. Does financial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? Energy Policy 2020, 146, 111810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y. Military investment and the rise of industrial clusters: Evidence from China’s self-strengthening movement. J. Dev. Econ. 2023, 161, 103015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, J.; Voorheis, J.; Walker, R. What caused racial disparities in particulate exposure to fall? New evidence from the Clean Air Act and satellite-based measures of air quality. Am. Econ. Rev. 2023, 113, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Yu, M.; Chen, X. Pollution reduction effects of new transregional power transmission systems: Evidence from ultra-high-voltage projects of China. J. Dev. Econ. 2025, 179, 103641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Graff Zivin, J.; Kou, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Going green in China: Firms’ responses to stricter environmental regulations. Can. J. Econ. 2025, 58, 385–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Yao, X. Effects of industrial agglomeration on haze pollution: A Chinese city-level study. Energy Policy 2021, 148, 111928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).