Abstract
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology becomes increasingly prevalent in the tourism sector, an in-depth exploration of its opportunities and potential risks for the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is urgently needed. However, existing research falls short in constructing an integrated knowledge framework that systematically clarifies how AI can effectively advance sustainable tourism, leaving theoretical understanding and practical pathways relatively fragmented. To address this gap, this study employs a systematic literature review following the strict SPAR-4-SLR protocol and integrates a domain-based TCCM (i.e., theories, contexts, characteristics, and methods) analysis framework. A total of 177 core articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases were rigorously analyzed. This study first examines publication trends, key journals, and the citation impact of AI in tourism. It then systematically synthesizes the theoretical foundations, research contexts, characteristics, and methodologies. Most importantly, this review delves into the antecedents, decision-making processes (including mediating and moderating variables), and outcomes of AI applications in the tourism industry. This study not only delineates a clear direction and agenda for future academic inquiry but also provides theoretical support and practical guidance for policymakers and tourism managers to design and implement AI-driven sustainable tourism strategies.
1. Introduction
Information and communication technologies (ICTs) have long played a crucial role in the tourism sector, not only serving as a testing ground for new applications but also generating complex impacts across psychological, social, environmental, and economic dimensions within the framework of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [1]. With the continuous evolution of ICT and driven by the rapid iteration of technologies like human–computer interaction, machine learning, and pattern recognition, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as the most disruptive force today. AI is systematically reshaping the tourism industry’s ecosystem across multiple dimensions, from marketing and promotion and operational models to recommendation systems and service processes [2,3]. Concurrently, a deeper user or tourist awareness of sustainable practices and a growing demand for experiential travel are jointly driving a fundamental restructuring of modern tourism planning [4].
In the tourism industry, the advantages of AI-driven physical service robots in cost reduction and time efficiency enhancement serve as a crucial support for boosting the competitiveness of tourism enterprises [5]. It is predicted that the global robotics market will exceed USD 13 billion by 2030 [6]. Meanwhile, AI applications represented by conversational chatbots are widely deployed in scenarios such as hotel booking, itinerary customization, and user support, serving as core tools for improving service efficiency [7]. Data indicates that approximately 40% of global users utilize AI-enabled tools during travel planning [8]. While generative AI (GenAI) is a relatively new field, the tourism industry, as a core branch of the service sector, can use it for its potential for industrial transformation [9]. For example, the hotel industry can leverage GenAI to conduct market research, assist with marketing planning, and generate promotional content. This enables the achievement of multiple strategic goals, including improving employee productivity and creativity, optimizing operational efficiency, enhancing customer experience, and controlling costs [10].
From an academic perspective, the widespread penetration of AI in the tourism industry has prompted multifaceted scholarly exploration. On one hand, research confirms AI’s role as a core driver for enhancing operational efficiency within the sector [11]. Some scholars focus on specific application scenarios, such as tourism demand forecasting [12], the impact of AI on user decision-making behavior [13], and the technological implementation of service robots [14]. On the other hand, the potential risks and ethical trade-offs stemming from AI applications have also attracted academic attention and discussion [15]. Existing literature widely acknowledges the positive potential of AI in advancing the SDGs, particularly its contributions to optimizing tourist experiences and enhancing the well-being of local residents [16]. However, the depth and breadth of research on critical issues such as job displacement, data security and privacy risks, and the potential weakening of the tourism industry’s interpersonal nature still need to be expanded [17].
As the volume of AI research literature in the tourism sector continues to grow, there is an urgent need for a systematic review and in-depth analysis of existing research findings. Although there are already some review studies in the academic community, current research still has three significant limitations. First, there is a limited research scope. Existing reviews often focus on a specific branch of AI, failing to comprehensively reflect the current state of integrated technological applications (e.g., Li et al., 2025; Saleh, 2025, Prasanna et al., 2025, Chen et al., 2025) [18,19,20,21]. Given that the tourism industry now widely integrates GenAI, the information retrieval functions of conversational AI, and the applications of physical service robots for tasks like food delivery and destination guiding, a narrow focus fails to provide a comprehensive analysis of the integrated AI application landscape. Second, there is a lack of diverse literature sources. Due to limited data retrieval ranges (e.g., Fouad et al., 2024) [22], some studies include an insufficient number of representative articles. This undermines the universality and reliability of their conclusions. Third, there is insufficient analytical depth. Some reviews rely solely on bibliometric methods (e.g., Liao et al., 2025) [23], with their analysis often limited to descriptive statistics, lacking a deep exploration of core issues, theoretical frameworks, and practical implications. Crucially, given the rapid pace of literature updates in this domain, these reviews fail to connect the application logic of AI technology with the current path toward achieving the SDGs, thus making it difficult to provide substantial theoretical support for the sustainable development of the tourism industry.
In order to address this research gap and meet the pressing demand for aligning AI with the SDGs, this research proposes an integrative analytical framework for systematically scrutinizing AI’s deployment in tourism. The necessity of this goal is dual: On one hand, an integrative framework is required to structure the knowledge system currently characterized by fragmented studies on AI in tourism. On the other hand, the tourism industry, critical for achieving the SDGs, urgently needs a systematic review to identify AI’s supportive roles and potential risks against specific SDG targets, providing actionable guidance for industry and policy. Specifically, this research focuses on the following three core questions:
RQ1. What are the key antecedents, decision-making processes, and outcomes of AI application in the tourism domain?
RQ2. What is the current theoretical, contextual, and methodological landscape of research on AI in the tourism domain?
RQ3. How should the future research agenda be planned to guide the application of AI in the tourism domain toward a more sustainable, ethical, and inclusive direction?
The integrated analytical framework developed in this study differs fundamentally from existing reviews in two key dimensions. First, in terms of scope, this study is more inclusive, incorporating various forms of AI technology, including GenAI, conversational AI, and service robots, into a unified analysis. This provides comprehensive coverage of the entire spectrum of AI applications in tourism. Second, in terms of methodology, this study moves beyond the semi-structured analytical paradigm used in previous research (e.g., Tuo et al., 2025; Gössling & Mei, 2025) [2,24]. We introduce a framework-based systematic evaluation approach by adopting the TCCM (i.e., theories, contexts, characteristics, and methods) framework proposed by Paul and Rosado-Serrano (2019) [25]. This systematic deconstruction of the existing literature is designed to overcome the fragmentation of findings in prior studies and provide a structured foundation for the field’s knowledge system.
This study makes several key contributions. On a theoretical level, by integrating the theoretical foundations, research contexts, core characteristics, and methodological systems of the reviewed literature, we provide a clear synthesis of the antecedents, decision-making mechanisms, and outcome effects of AI applications in tourism. The resulting holistic insights will be instrumental in allowing researchers to accurately map the current state of knowledge and establish a theoretical foundation for subsequent research focused on sustainability. On a practical level, the findings will offer structured guidance to key tourism stakeholders (e.g., corporate executives, policymakers, and local communities). This will directly facilitate the refinement and realization of a sustainable development trajectory powered by AI, thereby contributing to the comprehensive implementation of the SDGs in the tourism domain.
2. Conceptual Background
AI in Tourism
The application of AI in various sectors is not a sudden transition but adheres to a distinct technical evolutionary pathway, a process inseparable from the exponential increase in computational capacity. Historically, AI’s function has evolved from being a statistical tool supporting data analysis to enabling big data analytics and web crawling for handling massive volumes of unstructured data. Currently, it manifests as advanced interactive capabilities through machine learning models and large language models [26]. A precise parallel of this evolution is observable in the tourism sector. The progression spans from using data models for forecasting demand and analyzing social media data to glean consumer emotion, to the ubiquitous deployment of intelligent customer service, robotic service agents, and personalized recommendation systems seen today.
The development of AI has progressed through distinct phases. Initially, AI systems were centered on rule-based approaches. This was followed by the advent of machine learning, which marked a significant technological shift. Subsequently, the integration of deep learning and neural networks led to the creation of more complex models. This technological evolution has been mirrored by an expansion in application scenarios, moving from physical service robots to conversational AI, and ultimately to GenAI, which is capable of creating diverse content.
In the realm of physical services, intelligent concierge and other service robots represent a significant advancement in optimizing service processes within the tourism industry [27]. Such applications are recognized for their potential to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs [28]. The subsequent phase saw the rise in conversational AI, primarily in the form of chatbots (e.g., Siri), which leverage real-time, human-like interaction to facilitate tasks such as hotel bookings and itinerary planning [7]. More recently, GenAI (e.g., ChatGPT-4, Grok 4, Sora 2, and DeepSeek-V3.2) has achieved breakthroughs in generating text, images, music, and video. In the tourism context, this technology can generate personalized travel itineraries and seamlessly integrate with online travel agency supply systems to create a unified service flow [18].
While the evolution of AI holds significant potential to advance the SDGs, it also introduces risks that could undermine these objectives [24]. These risks, which span environmental, economic, geopolitical, and technological domains, have been highlighted as a core issue in the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report [29]. The automation driven by AI may lead to job displacement and exacerbate economic inequality [30]. Furthermore, the explosive growth of content generated by GenAI has given rise to ethical dilemmas, including the spread of misinformation and data privacy breaches, which challenge existing regulatory frameworks [31]. In response to the calls from the literature (e.g., Li et al., 2025; Prasanna et al., 2025; Hall & Cooper, 2025) [18,20,32], this study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of AI’s multifaceted role in shaping the future of sustainable tourism. By doing so, it seeks to offer theoretical support for balancing the risks of AI with the realization of its positive value.
3. Methodology
3.1. Review Design
This study adopted a systematic literature review (SLR) method to collect research literature based on predefined screening criteria and specifically address the research questions [33]. As a core tool for integrating scientific knowledge in a specific field, the SLR enables a structured synthesis of core ideas and findings through a systematic process of literature screening and analysis [34]. SLR methodologies include domain-based, theoretical-based, methodological-based, meta-analytical, and meta-systematic review types. Paul and Barari (2022) [34] pointed out that a framework-based review model is more suitable for the integrated analysis of research findings in a specific domain. To effectively answer the core questions of this study, we introduced the TCCM framework proposed by Paul and Rosado-Serrano (2019) [25] to conduct an SLR of AI applications in tourism.
The TCCM framework comprises four core dimensions: theory (T), which refers to the theoretical perspective and analytical foundation of the study; context (C), which defines the specific setting and scope of the research; characteristics (C), which covers the core attributes of the research subjects and the key features of their environment; and method (M), which specifies the technical approach and analytical paradigm used to obtain empirical evidence. Previous research has confirmed that the TCCM framework can effectively integrate existing findings, provide structured support for building the domain’s knowledge base, and offer a methodological tool for scholars to replicate, verify, or innovate in future research [35]. By applying the TCCM framework, this study could systematically identify key issues in the field of AI applications in tourism that have not been fully explored, thereby laying a foundation for expanding future in-depth research.
3.2. Review Protocol
To ensure the systematicity, transparency, and reproducibility of the SLR, establishing a clear review protocol is a crucial prerequisite [36,37]. While the PRISMA framework is widely recognized for enhancing the transparency of systematic reviews, especially in the healthcare sector, it is less suited for the specific methodological rigor required for context-based arguments in business and management [20]. To address this limitation, we followed the scientific procedures and rationales for systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR) protocol [38] to ensure the rigor, transparency, and consistency of the review process [39]. The specific literature screening process is shown in Figure 1, with the detailed steps described below.
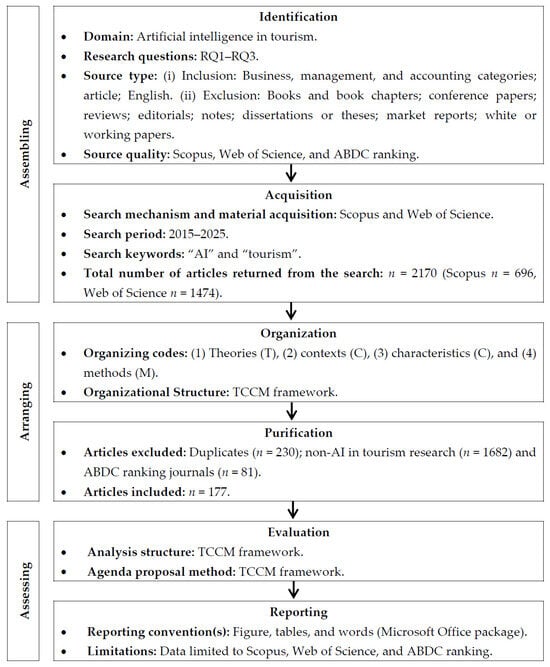
Figure 1.
The SPAR-4-SLR protocol for review research design adapted from Paul et al. (2021) [38].
3.2.1. Assembling
This study focused on the application of AI in tourism. Through a collective discussion within the research team and a preliminary literature review, we determined a search strategy that included terms related to both AI and tourism for use in the Scopus and Web of Science databases. These databases are highly regarded by the academic community for their stringent inclusion criteria (e.g., scientific merit and academic relevance) and comprehensive bibliometric information [38,40]. The search was limited to “article title, abstract, or keywords,” with the search string ((“artificial intelligence” OR “AI” OR “intelligent agent *” OR “AI system *” OR “intelligent system *” OR “robot *” OR “conversational artificial intelligence” OR “conversational AI” OR “generative artificial intelligence” OR “generative AI”) AND (“tourism” OR “sustainable tourism” OR “sustainability in tourism” OR “green tourism” OR “ecotourism” OR “eco-tourism *”)). Given that the large-scale application of AI technology in tourism began in the last decade, we set the publication date range from 2015 to June 2025 (the period immediately preceding the submission of this manuscript). The initial screening criteria included (1) subject area: business and management; (2) document type: journal article; (3) language: English. The initial search yielded 2170 documents.
3.2.2. Arranging
The 2170 documents were structured and coded, and we classified them according to the four dimensions of the TCCM framework, (1) theories (t), (2) contexts (c), (3) characteristics (c), and (4) methods (M), and then recorded the data in an Excel sheet. First, we removed 230 duplicate documents, and then we conducted a rigorous manual re-screening process. Initial filtering involved the exclusion of non-article literature (e.g., books and book chapters, conference papers, reviews, editorials, notes, dissertations or theses, market reports, and white or working papers), as well as articles published in fields outside of business and management—specifically computer science, engineering, and mathematics. We only included empirical studies that focused on the application of AI in tourism and related business contexts to ensure the literature provided data-driven evidence. Second, to ensure the quality and academic impact of the literature, we only included articles published in journals listed in the Australian Business Deans Council (ABDC) 2022 Journal Quality List. After this screening, a final set of 177 core articles were selected (see Supplementary Materials).
3.2.3. Assessing
Based on the four dimensions of the TCCM framework, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the 177 core articles. The results of this study are presented using a combination of figures, tables, and textual explanations to ensure clarity and comprehensive information delivery.
4. Research Findings (RQ1 and RQ2)
To address the three research questions posed in this study, we performed an analysis of the included literature based on the TCCM framework [25], as illustrated in Figure 2.
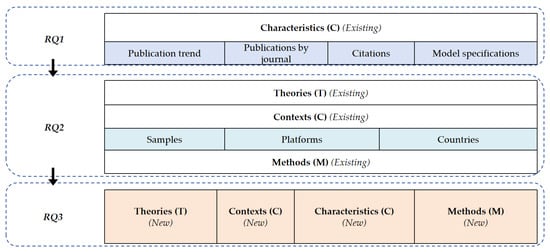
Figure 2.
The TCCM framework adapted from Paul and Rosado-Serrano (2019) [25].
4.1. Article and Yearly Publication Trends
Figure 3 illustrates the publication trends of AI research in the tourism sector. From 2015 to 2019, the number of articles focusing on the intersection of AI and tourism was relatively low. This likely reflects the early-stage exploration of technology during the Industry 4.0 era. At this time, the academic focus in tourism was only just beginning to shift toward digital technology applications and smart tourism, so relevant research had not yet gained scale. From 2020 to 2023, the annual number of publications in this field remained low, indicating limited overall attention and a slow development process. It was not until 2024 that the number of publications saw a rapid increase. This turning point may be closely related to the disruptive impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tourism industry. In the context of the pandemic, the tourism sector’s need to leverage AI technology for industrial transformation and sustainable development significantly increased, which, in turn, accelerated the pace of related research. The substantial surge in publications in 2025 shows that AI-empowered tourism has now attracted widespread academic attention and is generating significant scholarly impact. Based on the current research momentum, the intersection of AI and tourism is expected to continue as a core research area in the field of tourism management.
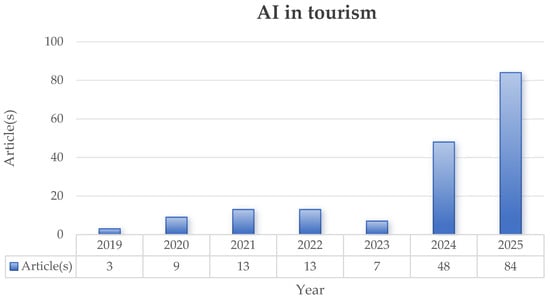
Figure 3.
Publication trend of AI in tourism research (2015–2025).
4.2. Journal Publication Trends
Table 1 shows the distribution of the top ten peer-reviewed journals by publication volume for AI research in the tourism sector. Current Issues in Tourism had the highest number of publications (n = 21), followed by the International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management (n = 19) and Tourism Management (n = 18). The table also indicates that Elsevier and Emerald are the core publishers for research in this field. Notably, 40% of the top ten journals are rated “A*” by the ABDC ranking, a finding that demonstrates the high level of recognition this interdisciplinary research has received from top academic journals. The exceptional academic quality and impact factors of these journals further validate the scholarly value and the robustness of the knowledge base for AI research in tourism.

Table 1.
List of journals with AI in tourism research.
4.3. Most Cited Publications
Table 2 presents the top ten most cited articles related to AI in tourism. The article with the highest citation frequency was the study by Pillai and Sivathanu (2020) [41] (TC: 662), which focused on the Indian hotel and tourism industry and analyzed users’ behavioral intentions and actual usage of chatbots. The second most cited article was by Li et al. (2019) [42] (TC: 544). Their research examined how companies can support the achievement of sustainable tourism goals through human resource stability strategies during their intelligent transformation. Ranking third was the study by de Kervenoael et al. (2020) [43] (TC: 443). This research assessed users’ willingness to use social robots and highlighted the crucial mediating role of human–robot interaction in harmonizing intelligent development with sustainable tourism objectives. An overview of the literature characteristics presented in Table 2 indicates that the early phase of this research domain centered on key topics related to user acceptance and behavioral intention toward AI technologies. With the progressive maturity of the field—further accelerated by external catalysts like the COVID-19 pandemic—the research trajectory has shifted toward more profound issues, such as organizational sustainability, staff management in tourism firms, and the broader macro-environmental consequences of AI adoption.

Table 2.
Most cited publications.
4.4. Model Specifications
Based on the TCCM framework, this study identified the core constructs in AI tourism research. From a variable relationship logic perspective, user decisions are both a response to antecedent variables and a critical link that drives subsequent outcomes, thereby forming the central path of the antecedent–decision–outcome model. To more precisely deconstruct the complex relationships between variables, we further systematically synthesized the potential influence mechanisms of mediating and moderating variables (see Figure 4). The following sections provide a detailed explanation of the key variable categories within the model.
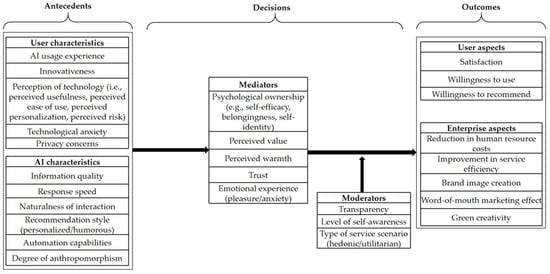
Figure 4.
Integrated conceptual framework.
4.4.1. Antecedent Variables
In the user characteristic dimension, both individual background and psychological attributes significantly influenced the interaction process with AI technology. Thirteen studies identified that prior experience is a key antecedent. For example, the research by Christensen, Hansen, and Wilson (2025) [51] emphasizes that AI usage experience is a critical antecedent variable, noting that previous interactions shape users’ perceived expectations and behavioral patterns regarding the use of AI. Furthermore, users’ innate innovativeness (n = 8) directly determined their tendency to adopt and explore new technologies [52,53]. Technology perception (n = 16) encompassed several sub-dimensions. Research by Sujood, Bano, and Siddiqui (2024) [54] indicates that perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use are fundamental factors influencing technology acceptance. This implied that users were more inclined to adopt AI services that enhanced their travel experience and had low operational costs. Perceived personalization [55] also grew in importance due to increasing user demand for customized services. Conversely, perceived risk [52] emerged as a key barrier to AI adoption. Additionally, technology anxiety (n = 5) and privacy concerns (n = 4) [56,57] were found to inhibit user AI usage.
On the AI technology characteristic dimension, the functional attributes and performance of the technology itself were the core determinants. The quality of information (n = 8) provided by the AI [58] was foundational to building user trust and satisfaction. Response efficiency (n = 9) and interaction naturalness (n = 8) were crucial for achieving a seamless, immersive experience, ideally requiring the ability to simulate human-like conversation [59,60]. The recommendation style (n = 11) [61] significantly affected user engagement and their cognitive evaluation of the service. Automation capability (n = 2) [62] was a key consideration, as users expected the technology to complete pre-set tasks stably and efficiently. Finally, the degree of anthropomorphism (n = 14), or the extent to which the AI exhibited human-like traits, could foster a sense of social presence and emotional connection, which in turn influenced user attitudes and behavioral decisions [63].
4.4.2. Mediating Variables
First, user psychological ownership (n = 7) comprised multiple dimensions, with self-efficacy [64] as a core component. This referred to users’ subjective confidence in their ability to successfully use the AI system to complete travel-related tasks. When the AI system featured operational convenience and clear feedback, users’ self-efficacy significantly increased, thereby enhancing their trust in and willingness to use the technology. Simultaneously, highly personalized recommendation mechanisms and customizable interaction interfaces strengthened users’ sense of belonging and self-identity, leading them to view the AI as a personal travel assistant rather than a mere technological tool.
Second, perceived value (n = 17) [63] was reflected in users’ subjective evaluation, which was formed after weighing the costs and benefits of using AI. AI technology with high information quality and quick response capabilities significantly elevated users’ perceived value. Perceived warmth (n = 6) [65] reflected users’ subjective judgment of the friendliness and empathy of the AI interaction process. Anthropomorphic design and a human-like linguistic style effectively enhanced users’ perceived warmth, laying the foundation for the establishment of an emotional connection.
Finally, trust (n = 26) [65] was the cornerstone of user adoption of AI travel services, and its formation depended on users’ beliefs in the AI technology’s reliability, information accuracy, and data security. Meanwhile, emotional experience (n = 11) referred to the immediate feelings users had during interactions with the AI. This included both positive emotions, such as pleasure, and negative emotions, such as anxiety stemming from technical failures or privacy concerns [66]. These emotional responses directly influenced the formation of users’ overall attitudes toward AI technology and further impacted their subsequent usage intentions.
4.4.3. Moderating Variables
First, transparency (n = 6) [67] was found to enhance users’ perceptions of AI information quality and reliability, making them more tolerant of recommendation biases and helping maintain high levels of trust. Conversely, a lack of transparency in AI decision-making amplified user uncertainty and risk perception, which weakened the positive influence of antecedent variables on user decisions.
Second, the level of individual self-awareness (n = 3) [68] moderated users’ responses to AI personalization. Highly self-aware users paid closer attention to the uniqueness and suitability of recommendations, whereas less self-aware users preferred more generalized recommendations. This difference in self-awareness caused the relationship between AI personalization and user decisions to diverge.
Third, the type of service scenario (n = 9) [52,69] had a significant moderating effect. In hedonic scenarios (e.g., exploring a novel destination), the emotional features of the AI had a more pronounced influence on decisions. In utilitarian scenarios (e.g., booking flights or hotels), the functional features of the AI were more critical. The variation in scenarios meant that the same AI characteristic had a different impact, thus moderating the strength of the relationship between antecedent variables and user decisions.
4.4.4. Outcome Variables
On the user level, satisfaction (n = 22) [69] was an emotional evaluation of the AI service’s overall performance, serving as the foundation for positive user behavior and a core indicator of AI acceptance. Intention to use (n = 24) measured users’ tendency for future continued use, which directly determined whether the AI would achieve sustained market adoption [51]. Intention to recommend (n = 15) [70] measured users’ subjective willingness to promote the AI service, representing both high recognition and a key outward expression of loyalty.
On the business level, in terms of operational efficiency, AI’s ability to automate repetitive tasks reduced reliance on human labor and lowered costs (n = 5) [71]. The capacity of AI to provide uninterrupted 24 h service and handle a massive volume of requests also shortened user waiting times [43]. From the perspective of SDG 8 (i.e., decent work and economic growth), these efficiency gains are foundational for tourism enterprises to maintain long-term economic vitality, achieve high productivity, and ensure sustainable economic growth. The enhanced efficiency (n = 4) also liberates employees from repetitive work, allowing them to focus their energy on high-value, creative, and decent work. For branding and marketing (n = 8), the successful application of AI conveyed a brand image of being innovative, efficient, and customer-oriented [49]. Positive user experiences also translated into favorable word-of-mouth, which had a marketing effect surpassing that of traditional advertising (n = 3). Regarding sustainable development, AI contributed to corporate green creativity by optimizing routes and managing energy consumption, which balanced innovation with environmental protection and enhanced the company’s social responsibility image (n = 1). This outcome directly corresponds to the objectives of SDG 12 (i.e., responsible consumption and production), specifically by realizing the efficient utilization of natural resources and promoting the adoption of environmentally friendly technologies.
4.5. Theories for AI in Tourism Research
The 177 core articles in this study utilized a variety of theories to analyze the mechanisms of AI in different tourism application scenarios. After a systematic review, we found that the technology acceptance model, theory of planned behavior, and the stimulus–organism–response model were the three most widely applied theories in this field. The following sub-sections provide a detailed explanation of each.
4.5.1. Technology Acceptance Model
The technology acceptance model (TAM), proposed by Davis (1989) [72], served as a core framework for explaining and predicting users’ willingness to accept new technologies and their actual usage behaviors. The key variables were perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use. The model was later expanded to include variables such as perceived risk and social influence to better suit complex scenarios [73].
In the context of AI research in the tourism industry, TAM was a primary framework for analyzing the adoption of AI tools by both users and industry practitioners. For users, the model explained their acceptance of AI tourism services, such as smart itinerary planning and voice guides. High perceived usefulness and high perceived ease of use increased the tendency for adoption. Conversely, services with impersonal recommendations or complex registration processes were likely to be rejected. For tourism practitioners, TAM helped analyze their acceptance of AI management tools. For example, hotel employees who believed that AI customer service could reduce repetitive work and that the system had low training costs were more willing to promote it, which helped improve operational efficiency [44]. More recently, research by Li et al. (2025) [74] further extended the applicability of the traditional TAM, providing a more comprehensive perspective for analyzing both the rational decision-making and emotional mechanisms driving users’ adoption of generative AI tools. This research offered important support for promoting the integration of AI with sustainable tourism services.
4.5.2. Theory of Planned Behavior
The theory of planned behavior (TPB), proposed by Ajzen (1991) [75], was designed to comprehensively explain individual behavioral intentions and actual decision-making processes. The core logic posited that behavioral intention was a central mediating variable for predicting actual behavior, and it was jointly influenced by three dimensions: attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control [75].
In the context of AI research in the tourism industry, TPB provided a solid foundation for analyzing the relationship between user behavioral intentions and their actual actions in complex decision environments [76]. For example, when users chose an AI-themed hotel, a positive attitude (believing that smart devices enhanced comfort), positive subjective norms (recommendations from social circles and positive social media reviews), and strong perceived behavioral control (easy booking and convenient transportation) all strengthened their intention to choose it. TPB has been widely used to explore users’ attitudes toward and adoption of new technologies in the tourism industry [77].
4.5.3. Stimulus–Organism–Response Model
The stimulus–organism–response (S-O-R) model, proposed by Mehrabian and Russell (1974) [78], originated in environmental psychology and has since been widely applied in fields like consumer behavior and digital marketing. The core constructs include stimulus (S), which refers to external environmental factors that elicit an individual’s response, such as technological features; organism (O), which represents the individual’s internal psychological processing, including emotions and cognition; and response (R), which is the behavioral outcome following the psychological processing, categorized as either approach or avoidance behavior [78].
More recently, Pham et al. (2024) [79] utilized the S-O-R model to investigate how AI anthropomorphic stimuli (e.g., perceived warmth, communication speed) influenced the user’s cognitive organism (e.g., trust in and attitude toward ChatGPT-4). The study also examined how the cognitive organism affected behavioral responses (e.g., satisfaction, continued usage intention) and analyzed the moderating role of technology anxiety on the relationship between satisfaction and continued usage intention. This research not only enriched the application of the S-O-R model in AI-related tourism studies but also provided a theoretical basis and practical guidance for the judicious use of ChatGPT-4 in the tourism industry.
4.6. Contexts for AI in Tourism Research
Based on the TCCM framework’s definition of context, this dimension focused on the specific characteristics of the research setting. A background analysis of 177 core articles centered on three dimensions: sample type, data collection platform, and country of study.
Table 3 shows that in terms of sample selection, users/tourists were the primary respondents in 154 studies, making them the most dominant sample type in AI research within the tourism industry. The second-largest sample group was business employees, which were involved in 15 studies. Additionally, eight studies used data from listed companies as a sample source. For data collection platforms, 125 studies used online platforms. Furthermore, 42 studies employed a hybrid online–offline data collection model to enhance sample representativeness and data reliability through multi-channel data complementarity. From the perspective of the country of study, China was the dominant location for AI research in tourism, with 70 studies conducted in this context. The United States was second, with 30 studies, and South Korea was third, with 10 studies. This distribution pattern partially reflected the varying levels of importance and development in AI technology application and academic research within the tourism industry across different countries.

Table 3.
Contextual coverage.
4.7. Methods for AI in Tourism Research
As shown in Table 4, the 177 core articles included in this study displayed clear differences in their choice of research methods. Quantitative research was the dominant methodology in the field of AI in tourism, with 134 studies employing this approach. Among these, regression analysis, structural equation modeling, and experimental methods were the three most widely used techniques. Qualitative research was relatively limited, used in only 16 studies. The core techniques included in-depth interviews, grounded theory, and content analysis. Furthermore, 27 studies used a mixed-methods approach, integrating the strengths of both quantitative and qualitative techniques to achieve a multi-dimensional analysis of the research questions and enhance the comprehensiveness and reliability of the conclusions.

Table 4.
Overview of the methods used in the articles.
4.8. Sustainability Impacts of AI in Tourism Research
This study additionally integrated findings from existing literature on the impact of AI on tourism sustainability from the three core dimensions of environmental, social, and economic, based on the United Nations SDGs and the core dimensions of sustainable development in tourism.
First, the core value of AI in the environmental sustainability of tourism was manifested in achieving efficient resource utilization through technological empowerment, directly addressing SDG 12 (i.e., responsible consumption and production). For instance, chatbots were used to promote pro-environmental behaviors [88]. It should be noted that AI’s own environmental footprint could pose a potential risk. The operation of data centers and algorithm training require substantial electricity, and if this power relies on fossil fuels, it could offset some of the carbon-reduction gains.
Second, the impact of AI on the social sustainability of tourism was bidirectional. It both advanced the implementation of goals such as SDG 3 (i.e., good health and well-being) and SDG 10 (i.e., reduced inequalities), while also raising ethical issues. In terms of enhancing well-being, AI benefited diverse groups through the optimization of services and experiences. For example, the research by Liu et al. (2024) [89] emphasized that AI-powered accessibility services (e.g., multi-language audio guides and intelligent assistance systems for the visually impaired) could lower travel barriers and improve travel convenience for special needs groups. On the ethical front, the central controversy focused on data privacy. For example, personal tourist data collected by AI, if lacking transparent governance, could lead to risks of privacy breaches [90].
Finally, AI’s empowerment of economic sustainability in tourism was primarily achieved by enhancing operational efficiency, directly supporting SDG 8 (i.e., decent work and economic growth). For instance, hotels and tourist attractions used AI to handle repetitive tasks (e.g., booking confirmations, ticket verification), which reduced labor costs and improved service response speeds (e.g., Park, 2020; Fang et al., 2024) [47,91]. However, the automation capabilities of AI also introduced potential negative economic impacts, particularly issues of structural unemployment and economic inequality that could arise from job displacement [92].
5. Discussion
This study aimed to conduct an SLR and integration of the existing literature on the application of AI in the tourism sector. Covering a ten-year literature cycle from 2015 to 2025, the research identifies the highly productive core journals and high-impact cited works in the field. Simultaneously, it systematically deconstructs the theoretical foundations, research context characteristics, and methodological choices of relevant studies. Building upon this, this study further explores the antecedent variables, decision-making processes, and practical outcomes of AI application in tourism. Ultimately, this approach effectively addresses the first two core research questions posed in this study and leads to the following key findings.
The literature output trend indicates an exponential growth in cross-disciplinary research between AI and tourism. The volume of publications remained relatively limited prior to 2023, yet the number of articles rapidly surged to over 80 during the 2024–2025 period. This trend not only confirms the significant increase in academic attention toward AI in tourism but also reflects the widespread academic recognition of its core value in driving the digital transformation and supporting sustainable tourism development. Regarding journal distribution, research output is highly concentrated in top-tier journals for the field, including Current Issues in Tourism, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, and Tourism Management, suggesting high research quality and disciplinary recognition. In terms of citation impact, the study by Pillai and Sivathanu (2020) [41] stands as a foundational work with the highest citation frequency, followed closely by the research of Li, Bonn, and Ye (2019) [42] and de Kervenoael et al. (2020) [43], which provide crucial theoretical and empirical references for subsequent studies.
Based on the TCCM framework, this study deconstructs the application mechanism of AI in the tourism industry into three dimensions: antecedent variables, decision processes, and practical outcomes. This structured analytical perspective offers a clear framework for elucidating the dynamic action logic of AI in sustainable tourism. However, a noticeable limitation exists in the current theoretical foundations. While the TAM, TPB, and S-O-R models are the most widely applied theories, the majority of studies rely on a single theoretical framework. This reliance insufficiently explains the complex, multi-stakeholder, and multi-stage action mechanisms of AI technology in tourism contexts, resulting in a distinct lack of theoretical explanatory power.
Significant limitations are also evident at the research context and methodological levels. First, sample selection primarily concentrates on users/tourists. Second, data collection is heavily reliant on online platforms. Third, geographic coverage is imbalanced, with data mainly sourced from economically developed or tourism-mature countries/regions such as China, the United States, and South Korea. Regarding methodological choice, quantitative research holds absolute dominance, while the proportion of qualitative research and mixed-methods research is notably low.
Based on the aforementioned research conclusions and the limitations of the existing literature, the following section proposes targeted directions for future research to help the tourism industry achieve a balanced synergy of environmental, economic, and social equity, thereby progressing toward a sustainable and inclusive future.
6. Future Research Agenda (RQ3)
The accumulation of research on AI in tourism provides significant academic support for understanding its mechanisms and drivers. Although existing studies have attempted to integrate theoretical frameworks with empirical analysis, a systematic evaluation of the current state of research in this field remains limited. Building upon the analysis of core research questions RQ1 and RQ2 in the preceding sections, this section focuses on RQ3—future research directions for AI in tourism. It aims to construct a forward-looking research agenda that covers the four dimensions of the TCCM framework, offering guidance for the field’s future development.
6.1. New Theories
Section 4.5’s analysis of the theory dimension within the TCCM framework revealed a high concentration of current research on a few traditional models, such as TAM, TPB, and S-O-R. While these theories are helpful for understanding the initial stages of user adoption, they are insufficient for explaining the deeper issues associated with AI deployment, including complex organizational change, technical integration, and ethical or sustainability concerns. Consequently, future research must actively explore and incorporate new theoretical frameworks.
The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) [93] and its extended model, UTAUT2 [94], provide more comprehensive analytical frameworks [18]. Leveraging UTAUT’s social influence dimension, future research can explore how external factors like community advocacy and environmental awareness encourage users to adopt AI-powered low-carbon travel planning tools. The hedonic motivation dimension of UTAUT2 can reveal how the perceived enjoyment of green AI technologies motivates users to form sustainable behavioral habits. This framework can also be used to analyze the adoption mechanisms of AI applications—such as real-time carbon emission monitoring and intelligent green hotel recommendation systems—among different stakeholders, providing a theoretical basis for achieving SDGs like resource conservation and enhanced environmental awareness.
Furthermore, to more systematically understand the pathways through which AI enables sustainable tourism, future research could incorporate the technology–organization–environment (TOE) framework [95] and the service-dominant logic (SDL) [96]. From an organizational perspective, the TOE framework can be used to analyze AI’s potential: the technological dimension can assess its ability to reduce tourism enterprises’ carbon footprints and optimize resource allocation; the organizational dimension can analyze the supportive role of corporate green strategies and employee AI skills training; and the environmental dimension can explore the driving effects of industry competition and government environmental policies. The SDL, centered on value co-creation, can be applied to analyze how AI strengthens collaboration between tourism enterprises and local communities.
6.2. New Research Settings
Currently, AI research in tourism is concentrated in technologically advanced nations such as China, the United States, and South Korea. Future research needs to break through these geographical boundaries to broaden its scope and deepen the exploration of cross-cultural AI application mechanisms. From a regional perspective, AI-driven tourism demands vary significantly. In emerging markets like Southeast Asia and Latin America, AI primarily serves to compensate for hardware infrastructure shortcomings. By contrast, in developed regions such as Nordic countries, AI plays a pivotal role in high-end customized services and the synergy between smart cities and smart tourism. Cross-national comparative studies are crucial for uncovering the differentiated patterns of AI tourism applications across diverse economic and cultural contexts, providing a targeted basis for developing global AI tourism policies.
Furthermore, future research must move beyond traditional technical functionality assessments to focus on cross-cultural user behavior and preference differences [18]. For example, users from collectivist cultures may be more inclined to accept AI-generated group travel plans, while those from individualistic cultures may prefer highly personalized itineraries. It is also essential to evaluate AI’s performance in multilingual interaction and dialect recognition scenarios, as this is a critical standard for its adaptability to the global tourism market. It is particularly important to strengthen the discussion on AI’s cultural adaptability and ethical compliance [5,97]. AI should be positioned as a cross-cultural communication bridge, with local cultural knowledge modules—such as tips on customs and taboos, and explanations of cultural backgrounds—embedded within it. This helps users understand and respect destination cultures, avoid cultural conflicts, and, in doing so, both optimizes the travel experience and aligns with the ethical principles of responsible tourism.
6.3. New Constructs
This study centered on AI applications in the tourism industry, with a primary focus on user characteristics and AI technical attributes. First, at the user level, we examined the motivations and pathways for users’ adoption or rejection of AI-powered tourism services in specific contexts. Existing studies have provided initial empirical evidence on this topic [79,98]. However, future research needs to expand through comparative analysis and a cross-cultural perspective. For example, it could explore the differences in engagement with AI recommendation systems between introverted and extroverted users, or investigate how varying travel scenarios influence user–AI interactions. Such studies would provide insights into the contextualized design of AI services and the enhancement in user experiences. Second, at the AI technical level, future research can systematically explore how technical attributes like algorithmic explainability and interface usability, along with social factors such as social identity and group norms, collectively shape user behavior. For instance, do transparent algorithms strengthen user trust? Does public opinion moderate users’ attitudes toward AI? A deeper understanding of these micro- and macro-level factors can help define the drivers of AI adoption and the boundaries of its application.
The increasing penetration of AI in the tourism industry makes enterprise and destination adoption decisions a new focal point [99]. These decisions are influenced by technological feasibility, internal factors (e.g., organizational culture, willingness to innovate), and external factors (e.g., user behavior, market competition). Future research needs to investigate the role of these factors in adoption decisions to reveal the pathways of AI diffusion. Simultaneously, it is crucial to focus on the interactions between tourism practitioners and AI. This includes analyzing how AI can enhance employee efficiency and creativity, while also addressing concerns such as job replacement. There is an urgent need for research to establish a mechanism that balances AI application with employee well-being.
Despite the benefits AI brings to the tourism industry, its large-scale application raises ethical challenges, including algorithmic bias and data privacy [18]. It is important to note that while the transparency of AI systems does not directly improve ethical standards, it can provide decision-making guidance for stakeholders concerned with the long-term welfare of humanity and the planet, thereby promoting overall societal well-being [100]. Existing research on AI ethics in the tourism context is insufficient. Future work can address this in two ways: First, by developing a set of AI ethical assessment indicators (e.g., algorithmic transparency, bias correction) and exploring their integration with sustainable tourism frameworks. Second, by analyzing how tourism enterprises balance the benefits of AI with the risks to privacy and security, thus refining theoretical frameworks to address these new challenges.
6.4. New Methods
The analysis of research methods (Section 4.7) indicates a severe deficiency in qualitative research in this domain (with only 16 identified studies) and an over-reliance on traditional quantitative methods (such as regression analysis and structural equation modeling). Future AI research in the tourism industry should therefore promote the synergy between qualitative and quantitative approaches, the integration of multiple data sources, and the application of advanced AI-driven techniques to effectively address complex challenges.
First, qualitative research can be used to explore user experiences and perceptions of AI-powered green recommendation systems (e.g., for low-carbon transportation and eco-friendly accommodations) and AI’s role in enhancing community well-being. Second, quantitative research provides empirical data to validate qualitative hypotheses, analyzing how variables such as AI technology, user environmental awareness, and policy incentives jointly promote sustainable tourism practices. Fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) is particularly suitable for dissecting complex causal relationships. This mixed-methods approach can mitigate the biases of a single method and enhance the rigor and generalizability of research findings [101].
Furthermore, as AI technology evolves, advanced machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) offer new paradigms for sustainable tourism research. Causal inference methods, such as propensity score matching (PSM) and difference-in-differences (DID), can precisely evaluate the causal effect of AI recommendation systems on users’ low-carbon travel behaviors. DL techniques, such as natural language processing (NLP), can employ sentiment analysis to assess the mechanisms through which AI green services influence user satisfaction and pro-environmental behavior. Predictive modeling methods, including time-series analysis and random forest models, can forecast the impact of AI optimization solutions on the environmental carrying capacity of tourism destinations. Network analysis can be used to deconstruct the interaction networks among enterprises, users, and communities, evaluating AI’s role in resource optimization and value co-creation. These cutting-edge methods not only enhance the depth and precision of research but also provide data-driven support for policymakers, fostering the long-term development of sustainable tourism.
7. Implications of the Study
While previous review studies have explored AI applications in tourism from various dimensions (e.g., Li et al., 2025; Prasanna et al., 2025; Tuo et al., 2025; Liao et al., 2025) [2,18,20,23], a systematic integration of holistic insights into the field remains insufficient. Based on a systematic review of the existing literature, this study provides scholars and practitioners in the AI and tourism domain with a reference that is both innovative and practical. It does so by synthesizing the latest academic perspectives, analyzing research gaps, and proposing future research directions. The following sections elaborate on the theoretical and practical implications of this study.
7.1. Theoretical Implications
First, by analyzing the publication trends, core journal distribution, and characteristics of highly cited literature on AI in tourism, this study systematically delineates the field’s knowledge map and evolutionary trajectory. This systematic synthesis clarifies the academic influence and visibility of key topics, providing a clear knowledge base and directional guidance for scholars conducting future theoretical and empirical research.
Second, this study deepens the understanding of AI’s driving logic and operational pathways by systematically analyzing its application mechanisms in tourism from three core dimensions: antecedents, decision-making processes, and outcomes. By identifying the key factors influencing AI adoption, this study constructs a multi-dimensional integrated analytical framework that provides a standardized tool for future research. Furthermore, this study proposes the need to explore the dynamic relationship between data transparency and the AI interaction experience. For example, future research could focus on how algorithmic explainability and cultural background jointly influence user trust in AI recommendation systems, offering a new argumentative perspective for the theoretical optimization of AI services.
Third, the theoretical foundation of current AI in tourism research remains weak, with most studies relying on single theoretical frameworks, which limits their explanatory power for complex phenomena. This study systematically synthesizes the limitations of existing theories and proposes introducing multiple theoretical perspectives, such as UTAUT, UTAUT2, TOE, and SDL, to enrich the field’s theoretical toolbox. These theories provide differentiated perspectives for analyzing the adoption and implementation mechanisms of AI in the tourism industry.
Additionally, existing AI in tourism research is predominantly concentrated in technologically advanced economies like China, the United States, and South Korea, and this geographical limitation compromises the generalizability of research findings. This study emphasizes that research contexts in emerging economies hold significant theoretical value. The resource constraints (e.g., weak technological infrastructure), regulatory differences (e.g., varying data privacy policies), and cultural backgrounds (e.g., collectivist values) in these regions can significantly affect the implementation effectiveness of AI in tourism. Future cross-national comparative research can reveal the drivers and barriers of AI applications in different contexts, thereby improving the global adaptability of theoretical models.
Finally, current AI in tourism research heavily relies on traditional quantitative analytical methods, which are insufficient for fully uncovering the multiple concurrent causal relationships inherent in complex phenomena like AI adoption. This study recommends introducing innovative research methods such as fsQCA, ML, and DL. Combining innovative methods with appropriate theoretical frameworks can provide stronger empirical support for policymaking and industry practice. It is important to note that complex mixed methods are not necessarily superior to a single method, but if they can effectively answer core research questions and deepen the understanding of AI technology adoption in tourism, they should become an important direction for future research to pursue higher-level academic insights [5,18].
7.2. Practical Implications
Applying AI technology in tourism enterprises can not only enhance operational efficiency but also strengthen their social responsibility image and build stakeholder trust. Through AI-driven intelligent recommendation systems, businesses can accurately deliver personalized low-carbon travel plans to users. For example, algorithmic optimization of travel routes can reduce transportation carbon emissions, or eco-friendly accommodations and activities can be recommended based on user preferences. Such sustainable practices can both enhance a company’s brand reputation and contribute to the long-term realization of industry-wide SDGs. A case in point is Google Flights, which uses AI algorithms to integrate multi-dimensional data, such as aircraft model, flight distance, and seating configuration, to calculate and label the estimated carbon emissions of each flight. This embeds sustainable principles into the core of users’ travel decisions, guiding environmentally responsible consumption choices [102].
Second, the implementation of AI in tourism is a complex systemic project involving technological integration, organizational adaptation, and stakeholder coordination. This requires practitioners to possess systemic thinking and interdisciplinary collaboration skills. Sharing successful AI application cases and lessons learned through exchange platforms built by industry associations, cross-departmental collaboration mechanisms, or multi-stakeholder forums can help companies overcome common barriers (e.g., high technology implementation costs, low employee technology acceptance, insufficient user trust), thereby accelerating the industry-wide advancement of SDGs. For example, in 2024, the World Travel & Tourism Council collaborated with Microsoft to release a report on AI applications in tourism, and through global case-sharing sessions, it systematically showcased the practical pathways of AI in dynamic visitor management, providing an operational paradigm that can be emulated by tourism enterprises of different sizes and regions [103].
Finally, to ensure the sustainability and social responsibility of AI applications in tourism, practitioners must integrate principles of fairness, inclusivity, and accountability into the design, implementation, and regulation of AI systems. First, the development of AI systems should adhere to the international guidelines of the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC). When developing recommendation systems, algorithmic optimization should be used to avoid data bias and fully consider the needs of users from different cultural backgrounds, age groups, and economic levels to prevent discrimination. Second, to enhance public trust, transparent mechanisms must be established to clearly inform users about the logic and scope of personal information processing. Given that AI systems often handle a large amount of sensitive information, tourism enterprises must implement high-standard data security measures, including encryption protocols and transparent data governance policies, to strictly comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). They can also convey their commitment to data protection by regularly publishing data usage reports or providing user-friendly privacy settings interfaces. Finally, policymakers should build complementary regulatory frameworks to define the boundaries of AI applications in tourism, thereby preventing ethical risks such as algorithmic bias and data breaches. Corporate managers, in turn, need to clarify data protection processes and create a safe and trustworthy consumption environment through information transparency.
8. Conclusions
The past decade has witnessed a dramatic proliferation of research concerning AI within the tourism domain. This trend has been particularly pronounced in the last two years, with a surge in scholarly publications signifying the emergence of this interdisciplinary area as a focal point of academic inquiry. Notwithstanding this growing interest, the current research landscape remains fragmented. We identify a notable lacuna in the form of an integrated framework capable of consolidating and enriching the study of AI in tourism. Consequently, this SLR endeavors to elucidate the intellectual structure and inherent limitations of the extant literature. Furthermore, it proposes a forward-looking research agenda to broaden the comprehension of AI applications in tourism. Through the rigorous application of the SPAR-4-SLR protocol and the TCCM framework, this study conducts a robust review to construct an integrative framework, thereby providing both theoretical underpinnings and practical guidance for policy formulation.
It is imperative to underscore that, in the context of the SDGs increasingly serving as a core directive for development across industries, integrating the study of AI in tourism with the SDGs has become a task of considerable urgency and necessity. As a pivotal industry that propels economic growth, fosters cultural exchange, and creates employment opportunities, the sustainable development of tourism aligns closely with SDG targets, including “decent work and economic growth,” “responsible consumption and production,” and “climate action.” The latent potential of AI technology to optimize the allocation of tourism resources, mitigate carbon emissions (e.g., through intelligent travel planning to reduce transport-related energy consumption), and preserve cultural heritage (e.g., through the digital reconstruction of cultural landscapes) provides critical leverage for the tourism sector to actualize the SDGs.
In summary, this research contributes not only a lucid intellectual roadmap and an integrative framework for the existing body of work on AI in tourism but also charts a future research trajectory guided by the SDGs. It is our aspiration that the insights and findings emanating from this study will serve as a valuable reference for researchers in cognate fields, empowering them to further their inquiry into the synergistic development of AI and tourism and to refine the theoretical architecture of the discipline. Simultaneously, this work aims to inspire tourism practitioners and policymakers to enact proactive strategies and industry norms for AI applications that are in harmony with the SDGs, ultimately enabling the sustainable, high-quality development of the tourism industry through the empowerment of AI technology.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17209080/s1, Table S1: List of articles included in the review.
Author Contributions
S.W.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Writing—Original Draft Preparation. Q.W.: Supervision, Validation, and Funding Acquisition. Q.C.: Formal Analysis and Data Curation. T.L.: Writing—Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Systematic Layout and Collaborative Mechanism Study of National Strategic Science and Technology Forces, grant number 23AGL001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gössling, S. Tourism, technology and ICT: A critical review of affordances and concessions. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Si, X. Artificial intelligence in tourism: Insights and future research agenda. Tour. Rev. 2025, 80, 793–812. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Luo, J.; Huang, S.S. Developing an artificial intelligence framework for online destination image photos identification. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2020, 18, 100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpi, D. Strangers or friends? Examining chatbot adoption in tourism through psychological ownership. Tour. Manag. 2024, 102, 104873. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Lim, W.M.; Cheah, J.H.; Lim, X.J. Working with robots: Trends and future directions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2025, 212, 123648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Size of the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Market Worldwide 2020–2030. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1259903/robotic-process-automation-market-size-worldwide/ (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Fatima, J.K.; Khan, M.I.; Bahmannia, S.; Chatrath, S.K.; Dale, N.F.; Johns, R. Rapport with a chatbot? The underlying role of anthropomorphism in socio-cognitive perceptions of rapport and e-word of mouth. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2024, 77, 103666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Use of AI for Travel Planning Worldwide 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1558304/ai-use-travel-planning-worldwide/ (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Gursoy, D.; Cai, R. Artificial intelligence: An overview of research trends and future directions. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dogru, T.; Line, N.; Mody, M.; Hanks, L.; Abbott, J.A.; Acikgoz, F.; Zhang, T. Generative artificial intelligence in the hospitality and tourism industry: Developing a framework for future research. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2025, 49, 235–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, S.; Duglio, S.; Beltramo, R. Robots in tourism and sustainable development goals: Tourism agenda 2030 perspective article. Tour. Rev. 2023, 78, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Bao, J.; Chen, K. Listen to the voices from home: An analysis of Chinese tourists’ sentiments regarding Australian destinations. Tour. Manag. 2019, 71, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Hailu, T.B. Effects of AI ChatGPT on travelers’ travel decision-making. Tour. Rev. 2024, 79, 1038–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, P.; Kaushik, N.; Sivathanu, B.; Pillai, R.; Vikas, J. Consumers’ adoption of artificial intelligence and robotics in hospitality and tourism sector: Literature review and future research agenda. Tour. Rev. 2022, 77, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samala, N.; Katkam, B.S.; Bellamkonda, R.S.; Rodriguez, R.V. Impact of AI and robotics in the tourism sector: A critical insight. J. Tour. Futures 2022, 8, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, G.M.; Tussyadiah, I.; Kim, Y.R.; Pal, A. Intelligent automation for sustainable tourism: A systematic review. J. Sustain. Tour. 2023, 31, 2421–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tussyadiah, I.P.; Zach, F.J.; Wang, J. Do travelers trust intelligent service robots? Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xi, J.; Hsu, C.H.; Yu, B.X.; Zheng, X.K. Generative artificial intelligence in tourism management: An integrative review and roadmap for future research. Tour. Manag. 2025, 110, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.I. Generative artificial intelligence in hospitality and tourism: Future capabilities, AI prompts and real-world applications. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2025, 34, 467–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, A.; Pushparaj, P.; Kushwaha, B.P. Conversational AI in Tourism: A systematic literature review using TCM and ADO framework. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2025, 64, 101310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, D.; Miao, M. Service robot acceptance: Agenda for tourism and hospitality research. Tour. Rev. 2025, 80, 871–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.M.; Salem, I.E.; Fathy, E.A. Generative AI insights in tourism and hospitality: A comprehensive review and strategic research roadmap. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2024, 24, 14673584241293125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Wu, M.; Du, P.; Filieri, R.; He, K. The past, present, and future of AI in hospitality and tourism: A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 37, 2287–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Mei, X.Y. AI and sustainable tourism: An assessment of risks and opportunities for the SDGs. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Rosado-Serrano, A. Gradual internationalization vs born-global/international new venture models: A review and research agenda. Int. Mark. Rev. 2019, 36, 830–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluka, O.; Harten, S.; Kocks, A.; Dvorak, J. Digitalization in evaluations and evaluations of digitalization: The changing landscape of evaluations. Evaluation 2025, 31, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Webster, C. Automated decision-making: Hoteliers’ perceptions. Technol. Soc. 2024, 76, 102430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, J.; Zeithaml, V. Cost-effective service excellence. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2018, 46, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WEF. World Economic Forum’s Global Risk Report. Available online: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_The_Global_Risks_Report_2024.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Seyitoğlu, F.; Costa, C.; Martins, M.; Malta, A.M. The future of tourism and hospitality labour: Challenges, requirements, trends, skills and the impact of technology. Curr. Issues Tour. 2023, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, B.; Citron, D. Deep fakes: A looming challenge for privacy, democracy, and national security. Calif. Law Rev. 2019, 107, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.M.; Cooper, C. Making tourism smart in the age of artificial intelligence. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Barari, M. Meta-analysis and traditional systematic literature reviews—What, why, when, where, and how? Psychol. Mark. 2022, 39, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Parthasarathy, S.; Gupta, P. Exporting challenges of SMEs: A review and future research agenda. J. World Bus. 2017, 52, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Breier, M.; Dasí-Rodríguez, S. The art of crafting a systematic literature review in entrepreneurship research. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2020, 16, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M.; Kumar, S.; Ali, F. Advancing knowledge through literature reviews: ‘What’, ‘why’, and ‘how to contribute’. Serv. Ind. J. 2022, 42, 481–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Lim, W.M.; O’Cass, A.; Hao, A.W.; Bresciani, S. Scientific procedures and rationales for systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR). Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, O1–O16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Karampela, M.; Tonner, A. Consumers’ brand personality perceptions in a digital world: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2022, 46, 1960–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Sivathanu, B. Adoption of AI-based chatbots for hospitality and tourism. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 3199–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Bonn, M.A.; Ye, B.H. Hotel employee’s artificial intelligence and robotics awareness and its impact on turnover intention: The moderating roles of perceived organizational support and competitive psychological climate. Tour. Manag. 2019, 73, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kervenoael, R.; Hasan, R.; Schwob, A.; Goh, E. Leveraging human-robot interaction in hospitality services: Incorporating the role of perceived value, empathy, and information sharing into visitors’ intentions to use social robots. Tour. Manag. 2020, 78, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.; Badu-Baiden, F.; Giroux, M.; Choi, Y. Preference for robot service or human service in hotels? Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 93, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, C. Discovering the tourists’ behaviors and perceptions in a tourism destination by analyzing photos’ visual content with a computer deep learning model: The case of Beijing. Tour. Manag. 2019, 75, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Does a cute artificial intelligence assistant soften the blow? The impact of cuteness on customer tolerance of assistant service failure. Ann. Tour. Res. 2021, 87, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Multifaceted trust in tourism service robots. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, O.H.; Gursoy, D.; Chi, C.G. Tourists’ attitudes toward the use of artificially intelligent (AI) devices in tourism service delivery: Moderating role of service value seeking. J. Travel Res. 2022, 61, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Chen, Q.; Huang, J.; Kong, S.; Li, Z. Customer-robot interactions: Understanding customer experience with service robots. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 99, 103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdim, K.; Belanche, D.; Flavián, M. Attitudes toward service robots: Analyses of explicit and implicit attitudes based on anthropomorphism and construal level theory. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 35, 2816–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Hansen, J.M.; Wilson, P. Understanding the role and impact of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) hallucination within consumers’ tourism decision-making processes. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 28, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, V.; Sepe, F.; Gursoy, D.; Prisco, A. Role of trust in customer attitude and behaviour formation towards social service robots. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 114, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Gupta, S.; Mahajan, R. The effect of motivated consumer innovativeness on the intention to use chatbots in the travel and tourism sector. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2023, 28, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujood Bano, N.; Siddiqui, S. Consumers’ intention towards the use of smart technologies in tourism and hospitality (T&H) industry: A deeper insight into the integration of TAM, TPB and trust. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2024, 7, 1412–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Z. Personalized tourism recommendations and the E-tourism user experience. J. Travel Res. 2024, 63, 1183–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. An eye for an eye: Exploring how human-robot service attributes affect customers’ negative electronic word-of-mouth. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 127, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfi, S.; Kim, M.J.; Nazifi, A.; Murdy, S.; Vo-Thanh, T. Understanding tourist barriers and personality influences in embracing generative AI for travel planning and decision-making. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 126, 104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batouei, A.; Nikbin, D.; Foroughi, B. Acceptance of ChatGPT as an auxiliary tool enhancing travel experience. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2025, 8, 1255319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, C.D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ngo, T.V.N.; Pham, T.T.P.; Vu, A.T.; Dang, N.S. Using generative artificial intelligence (ChatGPT) for travel purposes: Parasocial interaction and tourists’ continuance intention. Tour. Rev. 2025, 80, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Koo, C.; Chung, N. Is a shorter reaction time always better? Empirical investigation of the impact of response speed on ChatGPT recommendations. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 130, 104239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Baek, T.H.; Kim, C. ChatGPT personalized and humorous recommendations. Ann. Tour. Res. 2025, 110, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, B.A.; Cheng, M. Preferences and challenges towards the adoption of the fourth industrial revolution technologies by hotels: A multilevel concurrent mixed approach. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024, 27, 1912–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, R.A. Does consumers’ reveal engagement behaviours in artificial intelligence (AI)-based technologies? The dynamics of perceived value and self-congruence. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 126, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A. Artificial intelligence, self-efficacy and engagement in religious tourism: Evidence from Arbaeen pilgrimage. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2024, 7, 1660–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.A.; Liu, J. Artificial intelligence humor in service recovery. Ann. Tour. Res. 2022, 95, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y. Emotional expression by artificial intelligence chatbots to improve customer satisfaction: Underlying mechanism and boundary conditions. Tour. Manag. 2024, 100, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, H.; Xiong, M.; Wang, Y. Do word-of-mouth-based conversational AI recommendations enhance tourism consumers’ acceptance? The moderating role of transparency. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 28, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Shedding light on new technology: How ambient luminance influences acceptance of AI technologies. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 127, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.A.; Wen, N.; Liu, J. Empathic accuracy in artificial intelligence service recovery. Tour. Rev. 2024, 79, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, S.M.C.; Bilro, R.G. The role of commitment amongst tourists and intelligent virtual assistants. J. Promot. Manag. 2022, 28, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, F.; Al Zaidi, S.; Al Dhaheri, M.H. Automation and artificial intelligence in hospitality and tourism. Tour. Rev. 2022, 77, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Han, R.; Fu, T.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y. Tourists’ behavioural intentions to use ChatGPT for tour route planning: An extended TAM model including rational and emotional factors. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 28, 2119–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, I. Understanding the drivers of consumers’ acceptance and use of service robots in the hotel industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 37, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lee, M.; Girish, V.G.; Xiao, G.; Lee, C.K. Embracing the ChatGPT revolution: Unlocking new horizons for tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2024, 15, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology, 1st ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.C.; Duong, C.D.; Nguyen, G.K.H. What drives tourists’ continuance intention to use ChatGPT for travel services? A stimulus-organism-response perspective. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2024, 78, 103758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Qu, Z. An AI-driven approach to sustainability: The effect of AI accent on tourists’ pro-environmental behavioral intentions. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2025, 63, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, N.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Fan, Z.P. The Power of AI-Generated Content: Evidence From the Peer-to-Peer Accommodation Market. J. Travel Res. 2025, 64, 00472875251332951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, C.; Islam, H.; Ongan, S.; Şengöz, A.; Usanmaz, B. Artificial intelligence (AI) interacted ESG-based sustainable tourism: Economic insights. Tour. Econ. 2025, 31, 13548166251346306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-García, P.M.; Frías-Jamilena, D.M.; Polo-Peña, A.I. Virtual tours: The effect of artificial intelligence and intelligent virtual environments on behavioral intention toward the tour and the tourist destination. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, C.; Jhang, J.; King, B. When ChatGPT gives incorrect answers: The impact of inaccurate information by generative AI on tourism decision-making. J. Travel Res. 2025, 64, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kwon, W.; Back, K.J. Artificial intelligence for hospitality big data analytics: Developing a prediction model of restaurant review helpfulness for customer decision-making. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 33, 2117–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volchek, K.; Liu, A.; Song, H.; Buhalis, D. Forecasting tourist arrivals at attractions: Search engine empowered methodologies. Tour. Econ. 2019, 25, 425–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnain, M.; Zhang, Q.; Usman, M.; Hayat, K.; Shahzad, K.; Akhtar, M.W. How Chatbot negative experiences damage consumer-brand relationships in hospitality and tourism? A mixed-method examination. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2025, 126, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, G.M.; Tussyadiah, I.; Kim, Y.R.; Chen, J.L. Promoting pro-environmental behaviour spillover through chatbots. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Ma, E.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, S.; Grillo, T. AI and supportive technology experiences of customers with visual impairments in hotel, restaurant, and travel contexts. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 36, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Lei, S. The nonlinear effect of service robot anthropomorphism on customers’ usage intention: A privacy calculus perspective. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 107, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, T.M. Exploring the impact of AI-translated hotel reviews: The roles of reviewer nationality, cosmopolitanism, and review dispersion. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2024, 30, 1266–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Liu, M.T.; Ma, Y. How AI awareness can prompt service performance adaptivity and technologically-environmental mastery. Tour. Manag. 2024, 105, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.; Xu, X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornatzky, L.; Fleischer, M. The Process of Technology Innovation, 1st ed.; Lexington Books: Lexington, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Vargo, S.L.; Lusch, R.F. The four service marketing myths: Remnants of a goods-based, manufacturing model. J. Serv. Res. 2004, 6, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Wu, H.; Xiao, H.; Song, H.; Huang, S. Sustainable tourism paradigms across cultures: A continuum from Western to Eastern perspectives. J. Sustain. Tour. 2025, 33, 1235–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Yasar, B.; Ali, L.; Dogan, S. Antecedents and consequences of travelers’ trust towards personalized travel recommendations offered by ChatGPT. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 114, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbach, D.K.; Heiduk, L.; Blueher, G.; Schreiter, M.; Lahmann, A. The GenAI is out of the bottle: Generative artificial intelligence from a business model innovation perspective. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2024, 18, 1189–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, B.; Gold, A.; Gold, S. ESG disclosure and idiosyncratic risk in initial public offerings. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 179, 867–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheah, J.H.; Lim, X.J. Online shopping cart abandonment: A review and research agenda. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2023, 47, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt-Young, S. You Can Now Search for Flights on Google Based on Carbon Emissions. NPR. Available online: https://www.npr.org/2021/10/06/1043803529/google-flights-carbon-emissions-air-travel (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- WTTC. AI Set to Revolutionise Travel & Tourism, Says Latest WTTC Report. Available online: https://wttc.org/news/ai-set-to-revolutionise-travel-and-tourism-says-latest-wttc-report (accessed on 8 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).