Abstract
Resource-based cities, characterized by a prolonged dependence on resource extraction and persistent urban expansion, frequently exhibit significant imbalances between the supply and demand of ecosystem services (ESs). Understanding how various types of resource-based cities respond to urbanization in terms of ESs supply–demand relationships is crucial for advancing sustainable urban development. This study examines three representative resource-based cities in Sichuan Province—Nanchong (growing), Luzhou (declining), and Panzhihua (mature)—to analyze changes in six key ESs from 2000 to 2020, including soil retention, carbon sequestration, water yield, habitat quality, food production, and recreational services. Ordinary least squares (OLS) regression and random forest (RF) models were employed to evaluate the effects of gross domestic product (GDP) density, construction land proportion (CLP), and population (POP) density on the ecosystem service supply–demand ratio (ESDR), and to explore variations in sensitivity among these cities. The results demonstrate that (1) ESs’ supply–demand patterns differ significantly among the three city types. Nanchong exhibited a declining supply and increasing demand for regulating services; Luzhou displayed improvements in its water yield and recreational services but persistent degradation of habitat quality; and Panzhihua achieved notable gains in carbon sequestration and habitat quality. (2) Urbanization generally reduced the ESDR across all three cities. However, the GDP density positively influenced the ESDR in Nanchong, while the CLP and the POP density exerted widespread negative effects. In Luzhou, the ESDR was primarily constrained by the CLP, whereas in Panzhihua, both the CLP and the POP density significantly reduced the ratio. (3) The sensitivity analysis revealed distinct response patterns: Nanchong was most sensitive to CLP, Luzhou responded most strongly to GDP density, and Panzhihua was highly sensitive to both GDP density and POP density. These findings underscore the necessity of formulating city-type-specific development strategies—such as land restoration, population control, and industrial upgrading—tailored to different types of resource-based cities, in order to reconcile urbanization with ecosystem service dynamics, promote green transformation, and contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
1. Introduction
Ecosystem services (ESs) comprise the diverse natural resources and ecological benefits generated—either directly or indirectly—by ecosystems through their intrinsic structures, functions, and processes, which underpin human survival and well-being [1,2,3]. The degree of matching between ESs’ supply capacity and human demand serves as a critical indicator of socio-ecological coordination [4,5]. However, rapid urbanization has significantly intensified anthropogenic pressures on ecosystems while concurrently amplifying societal demand for ESs, thereby exacerbating supply–demand mismatches [6]. According to the United Nations’ 2023 assessment of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), over 30% of the targets have stagnated or regressed [7], underscoring the degradation of ESs and escalating conflicts caused by overexploitation and environmental deterioration [8]. Therefore, elucidating the interplay between urbanization and ESs supply–demand dynamics is key to advancing sustainable development.
Resource-based cities, characterized by a fundamental dependence on resource extraction and processing for their establishment and evolution, have historically played a central role in national industrialization and economic growth [9]. However, under the dual pressures of intensive resource exploitation and rapid urbanization, these cities increasingly face pronounced spatial conflicts among production, living, and ecological (PLE) spaces [10]. Although short-term resource extraction can stimulate economic growth, it often results in long-term ES degradation and environmental decline [11], thereby jeopardizing the balance between urban development and ecosystem functionality [12]. China’s National Sustainable Development Plan for Resource-Based Cities (2013–2020) classifies 262 resource-based cities into four categories: growing (characterized by abundant resource potential and an early stage of development), mature (marked by stable exploitation), declining (with depleting reserves), and regenerative (undergoing post-resource transformation) [13]. Due to differences in resource endowments, industrial structures, and land use intensities, these city types exhibit distinct ES supply–demand challenges [14].
Previous studies on the relationship between urban development and ecosystem dynamics in resource-based cities have concentrated on several focal areas. First, ecological health assessments have often been conducted using frameworks, such as the Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response (DPSIR) model and the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), to evaluate ecological risks [15,16]. However, these studies frequently treat resource-based cities as homogeneous entities or focus solely on single cases, failing to systematically capture the differences in ecological vulnerability and risk intensity among city types. Second, research has quantified ecosystem service value (ESV) to analyze the spatiotemporal dynamics and drivers of change [17]; however, this has primarily focused on aggregate value fluctuations, overlooking the intertype heterogeneity in ESs’ supply–demand patterns. Third, urbanization–ecosystem interactions have been explored using coupling coordination models to assess overall development harmony [18], yet such studies remain largely descriptive and fail to elucidate how specific urbanization dimensions affect internal ES supply–demand matching. Additionally, studies investigating urban transformation, landscape evolution, and associated ecological effects often emphasize spatial morphology while neglecting the direct links to ESs’ supply–demand balance and human well-being [19]. Although ES supply–demand relationships have gained increasing attention [20], few studies integrate the developmental stages or city types of resource-based cities, limiting our insights into the manifestation of supply–demand conflicts and key urbanization drivers. Collectively, the existing research lacks a systematic investigation from the perspective of inherent city type differences into the heterogeneous characteristics of ES supply–demand patterns and the distinct mechanisms through which urbanization affects supply–demand matching. This study addresses this critical gap by focusing on the differences in ES supply–demand issues among resource-based city types and employing robust methods to analyze urbanization’s impact on underlying supply–demand relationships, offering significant theoretical and practical value for advancing sustainable transitions in these cities.
Sichuan Province, located in western China, is a core area of the Western Development Strategy and a key hub of both the Belt and Road Initiative and the Yangtze River Economic Belt [21]. Over the past decades, the province has experienced rapid and intensive urbanization. While its abundant natural and energy resources—significantly developed during the Third Front Construction period—established a strong industrial base, prolonged dependence on resource-intensive industries has led to overcapacity, environmental degradation, industrial monocultures, and growing regional disparities [6]. Existing studies on Sichuan’s resource-based cities, such as Panzhihua, predominantly focus on single cases [22], lacking systematic comparisons across city types or in-depth exploration of urbanization-driven ES supply–demand mechanisms.
To address these gaps, this study selected three representative resource-based cities in Sichuan—Nanchong (growing), Panzhihua (mature), and Luzhou (declining)—to answer two core questions: (1) How do ES supply–demand patterns differ among the city types in terms of deficits and surpluses, and how have these patterns evolved spatiotemporally? (2) How does urbanization influence ESs’ supply–demand balance—does it alleviate or exacerbate mismatches? How does the sensitivity of different ESs to urbanization vary across city types? To answer these questions, we analyzed the dynamics of six ESs—soil retention (SR), carbon sequestration (CS), water yield (WY), habitat quality (HQ), food production (FP), and recreational services (RS)—from 2000 to 2020. Ordinary least squares (OLS) regression was employed to quantify the directional effects of urbanization on ES supply–demand matching, while random forest (RF) models were used to assess the heterogeneity in urbanization sensitivity across city types. This study provides a scientific basis for formulating differentiated policies, facilitating green transitions, and strengthening ecological governance in resource-based cities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
Sichuan Province (26°03′ N–34°19′ N, 97°21′ E–108°31′ E), located in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River in southwestern China, covers an area of approximately 486,000 km2 (Figure 1a) and is endowed with abundant and diverse natural resources. Under the National Sustainable Development Plan for Resource-Based Cities (2013–2020) issued by the State Council, Sichuan is identified as having 10 resource-based cities: Guangyuan, Nanchong, Dazhou, Guang’an, Zigong, Luzhou, Ya’an, Panzhihua, Aba Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, and Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture (Figure 1b). Due to data accessibility constraints, the analysis centers on prefecture-level cities in Sichuan, excluding Aba and Liangshan, due to their relatively low industrialization and marginal roles in the province’s broader resource-oriented development planning. Three representative cities—each exemplifying a distinct developmental typology—were selected from the northeastern, southeastern, and southwestern regions of the province (Figure 1c–e). Nanchong (30°10′ N–32°20′ N, 105°27′ E–107°28′ E), the only growing-type city in Sichuan, serves as the economic hub of northeastern Sichuan. It features a subtropical monsoon climate, with an economy that is historically centered on agriculture and is increasingly driven by the development of natural gas resources. Luzhou (27°39′ N–29°20′ N, 105°08′ E–106°28′ E), designated as a declining-type city, lies at the intersection of the Sichuan Basin and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. It experiences four distinct seasons. Once a national hub for natural gas-based chemical production, Luzhou was classified as resource-depleted in 2011 due to the exhaustion of its gas reserves. In response, the city has shifted the baijiu (liquor) industry, which now serves as its primary economic pillar. Panzhihua (26°05′ N–27°05′ N, 101°08′ E–102°15′ E), identified as a mature-type city, is situated at the confluence of the Hengduan Mountains, the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, and the Sichuan Basin. It is characterized by complex topography, dense river networks, and a distinct seasonal climate with an annual precipitation of approximately 850 mm. Panzhihua is globally recognized for its extensive reserves of vanadium–titanium magnetite (estimated at 6.64 billion tons), coal (approx. 3.45 million tons), and abundant solar and geothermal energy resources. It is the world’s largest producer of vanadium and the leading center of titanium production in China [23].
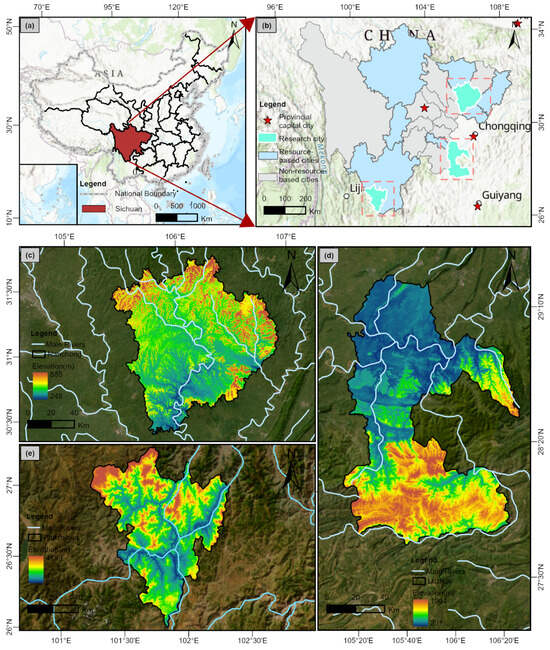
Figure 1.
Study area outline: (a) location of Sichuan Province; (b) distribution of resource cities in Sichuan Province; (c) Nanchong (growing); (d) Luzhou (declining); and (e) Panzhihua (mature).
2.2. Data Sources
The datasets utilized in this study, and their respective sources, are summarized in Table 1. Data corresponding to the years 2000, 2010, and 2020 were selected to capture the temporal dynamics. All datasets underwent preprocessing procedures to standardize the pixel resolution to 30 m and were reprojected to the WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_48N coordinate system to ensure spatial consistency.

Table 1.
Data requirements and sources.
2.3. Research Framework
The research framework of this study is illustrated in Figure 2. To explore the complex interrelationships between ESs’ supply–demand matching and urbanization processes across distinct types of resource-based cities, this research selected three representative resource-based cities in Sichuan Province: Nanchong (growing), Luzhou (declining), and Panzhihua (mature). Initially, multi-source datasets spanning 2000–2020 were collected and processed to derive and calculate the multi-dimensional urbanization indicators, including CLP, POP, and GDP. Subsequently, the spatiotemporal dynamics of six key ESs—SR, CS, WY, HQ, FP, and RS—were systematically evaluated. The balance state of these services was quantitatively represented using the Ecosystem Service Supply–Demand Ratio (ESDR) indicator. Finally, OLS regression and RF models were employed to examine the differential impacts of urbanization on ES supply–demand relationships and to identify the relative sensitivities of ESs to urbanization drivers across the selected city types.

Figure 2.
Research framework of the paper.
2.4. Urbanization Assessment
Urbanization processes in resource-based cities are inherently complex, involving interconnected dynamics of population migration, spatial land use transformation, and socioeconomic restructuring. This process primarily reflects the multi-dimensional coupling of demographic, land, and economic urbanization components [24]. Although urbanization is often viewed simply as population growth and spatial expansion, its essence lies in integrated metrics—such as the population concentration, land development intensity, and economic performance—that collectively capture the quality and sustainability of urban development [25]. Accordingly, this study employed three representative indicators: (1) population density (POP, persons/km2), which characterizes patterns of population agglomeration and migration, particularly toward resource extraction zones and urban centers (Figure 3a); (2) construction land proportion (CLP, %), which reflects the extent of urban land expansion, especially in mining areas, industrial parks, and newly developed districts (Figure 3b); and (3) GDP density per unit area (GDP, 104 CNY/km2), which measures the intensity of economic development and reveals the spatial imprint of resource-dependent industrial structures (Figure 3c). A variety of studies have employed these indicators to measure urbanization levels [26,27,28], providing an integrated view of demographic, spatial, and economic changes in resource-based urban areas.
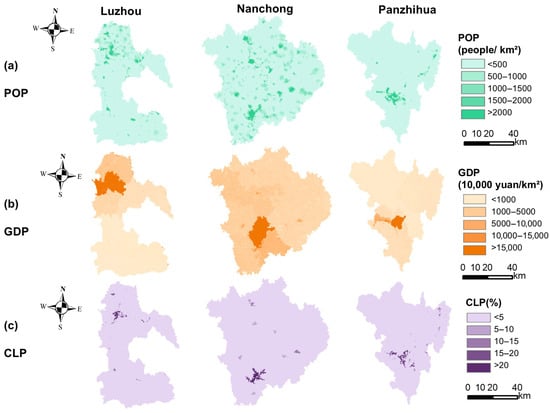
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of urbanization levels in Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growing), and Panzhihua (mature) in 2020: (a) Population density (POP, persons/km2), (b) GDP density (GDP, 104 CNY/km2), and (c) construction land proportion (CLP, %).
To further evaluate the potential multicollinearity among urbanization indicators, this study applied the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) as a diagnostic measure. Considering that GDP and POP have relatively large scales, both variables were subjected to natural logarithmic transformation prior to the analysis to reduce scale disparities and improve numerical stability. VIF values were computed for each indicator across different city types. The results revealed that the maximum VIF value was 1.28 for GDP in Luzhou, 1.07 for CLP in Nanchong, and 1.22 for GDP in Panzhihua. According to the empirical threshold proposed by O’Brien [29], a VIF value below 5 is typically indicative of minimal multicollinearity. Consequently, the urbanization indicators included in this study are unlikely to exert a significant influence on the interpretation of subsequent variable importance scores.
2.5. ESs Supply and Demand Estimation
Drawing upon the classification frameworks of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) and the Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES), developed by the European Environment Agency, and in alignment with the SDGs, this study selected six key ESs: SR, CS, WY, HQ, FP, and RS. These services were chosen based on both the development needs and the specific challenges faced by resource-based cities, as well as data availability considerations. They directly address the common pressures and differentiated vulnerabilities encountered during urbanization in cities such as Nanchong, Luzhou, and Panzhihua, including farmland loss, soil erosion, water supply–demand imbalances, and elevated industrial carbon emissions. The overarching objective is to support three key sustainability goals: ecological restoration, low-carbon industrial transition, and enhanced urban livability. The InVEST model, integrated with ArcGIS, was utilized to quantitatively assess the spatiotemporal variations in ES supply–demand patterns in the three cities during 2000–2020.
2.5.1. Soil Retention (SR)
Soil retention was evaluated using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) by determining the gap between potential and actual soil erosion [30]. The equations are formulated as:
where denotes the soil retention supply (t·hm−2); represents the demand for this service, expressed as actual soil erosion (t·hm−2); refers to the rainfall erosivity coefficient; denotes soil erodibility, derived from the EPIC model; and and represent the slope length and steepness, respectively. accounts for vegetation cover, and indicates that support practices were implemented.
2.5.2. Carbon Sequestration (CS)
Carbon sequestration supply was quantified through the carbon storage module of the InVEST model, incorporating four carbon pools: aboveground and belowground biomass, soil carbon, and necromass. The total carbon sequestration was determined using the following expression [31]:
where the carbon sequestration supply is (t·hm−2); the aboveground biomass carbon storage is (t·hm−2); the belowground biomass carbon storage is (t·hm−2); the soil carbon storage is (t·hm−2); and the dead organic matter carbon storage is (t·hm−2).
The carbon sequestration demand was determined from the regional consumption of fossil fuels, including coal, coke, and crude oil, for the specified year. The end-use consumption of each energy type was converted into a standard coal equivalent using appropriate coal conversion factors. The total standard coal consumption was then multiplied by the carbon emission coefficients proposed by the IPCC to calculate the total carbon emissions. Finally, carbon emissions were combined with population density to calculate the carbon sequestration service demand [32].
where is the demand for carbon sequestration services (t·hm−2), is the per capita carbon emissions (t/people), and is the population density (people·km−2).
2.5.3. Water Yield (WY)
The InVEST Water Yield module, grounded in the Budyko water–energy balance framework, was applied to estimate the regional annual water yield [33]. The results were further validated using data from official water resources bulletins.
where is the water yield service supply (m3·hm−2), is the annual actual evapotranspiration of grid cell x (mm), and is the annual precipitation of grid cell x (mm).
The demand for water yield includes the total water consumption for agriculture, industry, domestic use, and ecological functions. In this study, it was estimated by multiplying the statistical data on water use by population density.
where is the water yield service demand (m3·hm−2), is the per capita water use (m3/people), and is the population density (people·km−2).
2.5.4. Habitat Quality (HQ)
The supply of habitat quality service was assessed using the Habitat Quality module of the InVEST model, which estimates habitat quality based on land use types, the distribution and intensity of threat factors, and other ecological parameters [34].
where is the supply of habitat quality services, denotes how well the land use type b supports suitable habitat conditions, indicates the habitat deterioration caused by external stressors, refers to the half-saturation threshold, while r serves as the scaling factor (with a value of 2.5).
Habitat quality demand was determined by calculating the gap between the average habitat quality standard within the administrative unit and the actual value of each grid cell [35].
where is the regional habitat quality demand standard (e.g., the mean value across the study area), and is the actual habitat quality of each grid cell, and is the resulting habitat quality demand (unitless or scaled index).
2.5.5. Food Production (FP)
The supply of food production service was derived from the significant linear relationship between the crop yield and NDVI, as demonstrated in previous studies [36]. In this study, food production supply was allocated to each grid cell according to the ratio of its NDVI value to the total NDVI of cultivated land in the region [37].
where is the food production supply (10,000 t·km−2), is the total food production in the region for the target year (10,000 t), represents the greenness index for cell x, and refers to the aggregated NDVI across all cultivated areas. Food demand was approximated as the product of individual food consumption rates and local population density:
where the food production demand (10,000 tons·km−2), and is the per capita food consumption (t/people).
2.5.6. Recreational Services (RS)
The supply of recreational services was estimated based on the total green space area within built-up regions and was further allocated to the grid cells using NDVI data as a proxy for vegetation coverage [38].
where is the supply of recreational services (hm2·km−2), is the total green space area within built-up areas (hm2), is the NDVI value of grid cell x, and is the total NDVI value of the entire study area.
The demand for recreational services was estimated by multiplying the population density by the per capita demand for urban green space:
where is the demand for recreational services (hm2·km−2), and is the per capita green space usage demand (hm2/people).
2.6. Quantifying Urbanization Impacts on Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Matching
Ecosystem service demand–supply matching was measured through the ecosystem service demand–supply ratio (ESDR) [39].
Where the represents the ecosystem service supply–demand ratio. When the ESDR is positive, supply surpasses demand; a negative value implies insufficient supply; and a value near zero indicates equilibrium. Here, and denote the supply and demand of ESs, respectively, while and represent their corresponding maximum values within the study area.
2.7. Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Linear Regression
To quantify the linear influence of urbanization metrics on the ESDR in resource-based cities, this study applied an ordinary least squares (OLS) regression approach, incorporating spatial heterogeneity into the model structure. Logarithmic transformations were applied to the GDP and population density (POP) metrics to standardize the scale disparities. The model characterized the urbanization effects based on both the direction (sign of β) and magnitude (|β|) of the estimated coefficients, with statistical significance assessed through hypothesis testing [38]. The regression specification was formulated as follows:
where denotes the ESDR, represents the urbanization metrics, and are the intercept and slope coefficients, respectively, while denotes the error term. The statistical significance of β was evaluated using the Wald test (t-statistic) with a significance threshold of p < 0.05. The coefficient of determination (R2) was used to assess model fitting and to indicate the explanatory power of the urbanization variables in capturing variations in the ESDR.
2.8. Random Forest (RF) Model
To assess the explanatory capacity of the urbanization indicators in influencing the ESDR variations and to examine the ESDR sensitivity to urbanization drivers across various resource-based city types, a random forest (RF) regression model was applied for sensitivity analysis. RF, an ensemble learning approach comprising multiple decision trees, is particularly effective in capturing complex nonlinear relationships [40]. RF is an ensemble learning algorithm that is composed of multiple decision trees. It exhibits strong nonlinear modeling capabilities, effectively addresses complex interactions among variables, and mitigates the impact of multicollinearity on result stability by assessing variable importance through feature selection during each tree’s training. This characteristic also helps prevent overfitting, ensuring robust generalization performance [41]. Three urbanization indicators—CLP, POP, and GDP—were included as independent variables, while the ESDRs of the six key ESs served as dependent variables to assess the relative importance of each predictor. The RF model was implemented in Python 3.10 using the scikit-learn library. Data were randomly divided into training (75%) and testing (25%) subsets for model development and validation, respectively. To optimize model performance, hyperparameter tuning was performed using RandomizedSearchCV and GridSearchCV, with the optimal parameter combination determined via cross-validation. Model performance was primarily evaluated based on the coefficient of determination (R2), with values approaching 1 indicating a high degree of model fitting and predictive reliability.
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of ESs’ Supply and Demand in Three Resource-Based Cities
3.1.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution of ESs’ Supply in Three Types of Resource-Based Cities
As illustrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5, the spatiotemporal evolution of ESs’ supply from 2000 to 2020 exhibited distinct variations among the three resource-based cities—Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growing), and Panzhihua (mature). In Luzhou, the southeastern hilly and mountainous zones were the primary areas of concentrated ES supply. CS remained stable at approximately 3.7 t·hm−2, while HQ was maintained around 0.51. Regulating services showed remarkable improvement: SR increased by over 34%, from 1123 to 1507 t·hm−2; WY, which was mainly distributed in the northern and southern regions, surged from 292 to 758 m3·hm−2, representing a 160% increase—the highest among the three cities—was likely driven by vegetation recovery and forest expansion in previously mined areas. FP increased by about 20%, from 292 to 353 t·km−2. RS also improved significantly, rising from 1.10 to 5.41 hm2·km−2, which was largely attributable to the transformation of abandoned mining sites into ecological parks, reflecting Luzhou’s proactive ecological restoration efforts. In Nanchong, the spatial distribution of ESs’ supply appeared fragmented, with a relatively low contrast between high- and low-value areas. HQ remained at around 0.35, and CS was the lowest among the three cities at approximately 1.99 t·hm−2, possibly due to the rapid expansion of built-up areas. WY consistently remained high, increasing slightly from 702 to 738 m3·hm−2. SR rose from 827 to 946 t·hm−2, a 14% increase. FP experienced minor growth, rising from 278 to 296 t·km−2. RS expanded significantly, from 1.54 to 4.91 hm2·km−2—more than tripling over the period—indicating an increasing demand for recreational space in the context of urban development. In Panzhihua, high ES supply zones are concentrated predominantly in the northern Jinsha River valley and the southern ecological buffer zones. CS remained above 5.50 t·hm−2, and HQ consistently exceeded 0.70, both representing the highest values among the three cities and reflecting the stability of the city’s ecological core. However, WY declined markedly, from 592 to 288 m3·hm−2—a reduction of 51.37%—likely due to ongoing mining activities and intensified agricultural water consumption. Despite its mountainous terrain, FP increased steadily from 1715 to 1946 t·km−2, supported by the development of high-efficiency agriculture. SR fluctuated slightly between 1140 and 1144 t·hm−2, showing no notable trend. Although RS grew from 2.51 to 4.27 hm2·km−2, its total value remained lower than that in Luzhou and Nanchong.
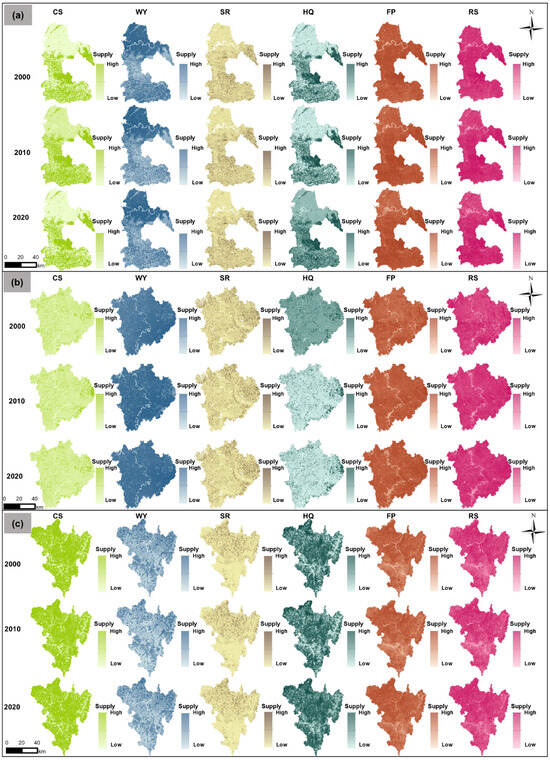
Figure 4.
ES supply distribution in (a) Luzhou (declining), (b) Nanchong (growing), and (c) Panzhihua (mature) (2000–2020).
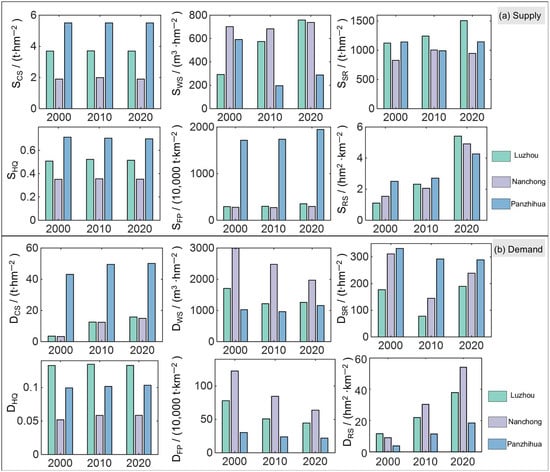
Figure 5.
Temporal changes (2000–2020) in (a) ES supply and (b) demand across city types: Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growing), and Panzhihua (mature).
3.1.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of ES Demands in Three Types of Resource-Based Cities
According to Figure 5 and Figure 6, in the declining city of Luzhou, the demand for CS increased markedly from 3.51 to 15.78 t·hm−2, reflecting a growth of over 350%, with high-value zones mainly located in the northern core urban region along the Yangtze River. Although the WY demand fluctuated over time, its spatial distribution remained relatively stable. The SR demand exhibited a northward shift, reflecting the spatial redistribution of ESs driven by land use change. The HQ demand was concentrated in northern industrial clusters. The FP and RS demands showed a core-periphery expansion pattern, with FP declining from 77.89 to 44.49 t·km−2 and RS rising from 11.54 to 37.82 hm2·km−2. In Nanchong, the growing city, the CS demand increased from 3.25 to 14.93 t·hm−2. Despite a decrease in WY from 2994.6 to 1971.7 m3·hm−2, it remained the highest among the three cities, with high-value regions concentrated in northern counties and the central urban area. The SR demand declined from 311.2 to 239.1 t·hm−2 and then rebounded to 289.2 t·hm−2, expanding spatially from the northeast to the whole region. The HQ and FP demands remained low, mainly distributed around urban-industrial fringes, with FP dropping from 122.3 to 63.8 t·km−2. The RS demand saw the most significant increase, from 9.12 to 54.12 hm2·km−2, with a growing number of high-value areas. In Panzhihua, the mature city, the CS demand rose from 43.15 to 50.17 t·hm−2, the highest among the three cities, with high-value zones widely distributed due to the high carbon regulation pressure from a heavy-industry-dominated structure. WY remained stable. The SR demand slightly declined from 331.6 to 289.2 t·hm−2 but stayed at a high level, with hotspots in the southern and northeastern mountainous regions. The HQ demand remained low but spatially concentrated. FP declined from 30.2 to 21.8 t·km−2, while RS rose from 3.87 to 18.38 hm2·km−2, although spatial changes were relatively limited.
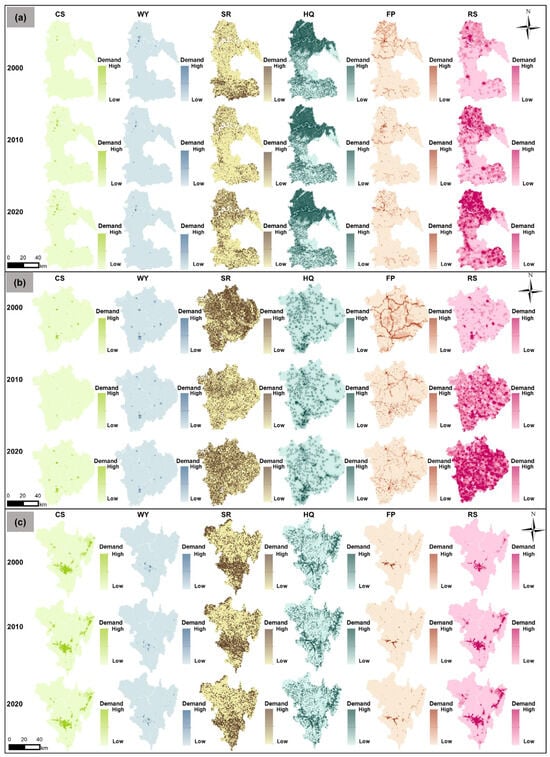

Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of the demand for ESs in (a) Luzhou (declining), (b) Nanchong (growing), and (c) Panzhihua (mature) from 2000 to 2020.
3.2. Comparison of ESs’ Supply–Demand Matching in Three Types of Resource-Based Cities
As shown in Figure 7, in the declining city of Luzhou, the CS, WY, and RS exhibited a surplus-dominant pattern, with surplus areas exceeding those that are in deficit. Deficit zones were mainly located in the central urban area, Xuyong County, and Gulin County, whereas high-value surplus regions were concentrated in forest park zones across the central and southeastern areas. In contrast, SR and HQ displayed broader deficit regions than the surplus ones, with severe deficits concentrated in the northern part of the city and limited surpluses confined to southeastern nature reserves. The FP deficit area gradually decreased over time, and by 2020, the surplus area had surpassed the deficit. In the growing city of Nanchong, CS, WY, FP, and RS all exhibited surplus-dominant distributions, with deficit regions mainly located in the central urban core and towns along the Jialing River, including Nanbu, Peng’an, and Yingshan. SR and HQ showed relatively limited surplus areas. Specifically, HQ surpluses were sparsely distributed in the low-mountain ecological buffer zone located in the central-eastern part of the city. In the mature city of Panzhihua, all five ESs, except SR, exhibited stable surplus patterns. SR, however, demonstrated a clear deficit-dominant trend, with deficit zones significantly exceeding surplus ones. Overall, deficit zones were largely concentrated in the northeastern Anning River Valley and the central Jinsha River Basin, with their spatial distribution remaining relatively unchanged.
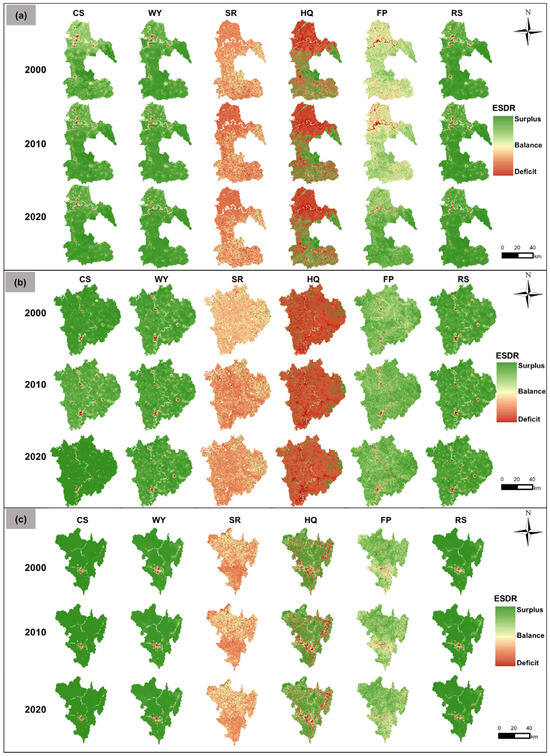
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of ESs’ supply–demand matching in (a) Luzhou (declining), (b) Nanchong (growing), and (c) Panzhihua (mature) from 2000 to 2020.
3.3. Impacts of Urbanization on ESs’ Supply–Demand Matching in the Three Resource-Based Cities
3.3.1. Effects of Urbanization on ESDR in Different Resource-Based City Types
The OLS regression outputs revealed that (Figure 8), the urbanization indicators—GDP, CLP, and POP—generally exhibited negative effects on the ESDR across Luzhou, Nanchong, and Panzhihua. However, substantial variations were observed among the cities and across different types of ESs. In Luzhou, a declining city, GDP exerted positive effects on WY and RS, with a statistically significant impact on WY (R2 = 0.42, p < 0.05). In contrast, GDP had significant negative effects on FP and SR. Although it was also negatively associated with HQ (R2 = 0.33, p > 0.05) and CS (R2 = 0.12, p > 0.05), neither of these associations reached statistical significance. CLP presented statistically significant negative effects on all ESs, with the strongest impacts observed on RS, WY, and HQ. POP had significant negative effects on all ESs except for CS, where the effect was weak and not significant. In Nanchong, a growing city, GDP had significant positive effects on FP, HQ, SR, and WY, although its explanatory power for WY was relatively low (R2 = 0.05, p < 0.05). However, GDP had negative associations with CS, HQ, and SR. CLP demonstrated significant negative correlations with all ESs except FP. POP exhibited significant negative effects on all ESs except on WY, with the most pronounced negative impact observed on RS (R2 = 0.53, p < 0.05). In Panzhihua, a mature city, GDP had positive effects on WY and RS but a significant negative effect on FP (R2 = 0.34, p < 0.05). Its impacts on SR, HQ, and CS were also negative, though not statistically significant. CLP showed significant negative correlations with all ESs, with the strongest influence observed on CS (R2 = 0.46, p < 0.05). POP exerted significant negative effects on most ESs, particularly on HQ (R2 = 0.52, p < 0.05) and FP (R2 = 0.38, p < 0.05).
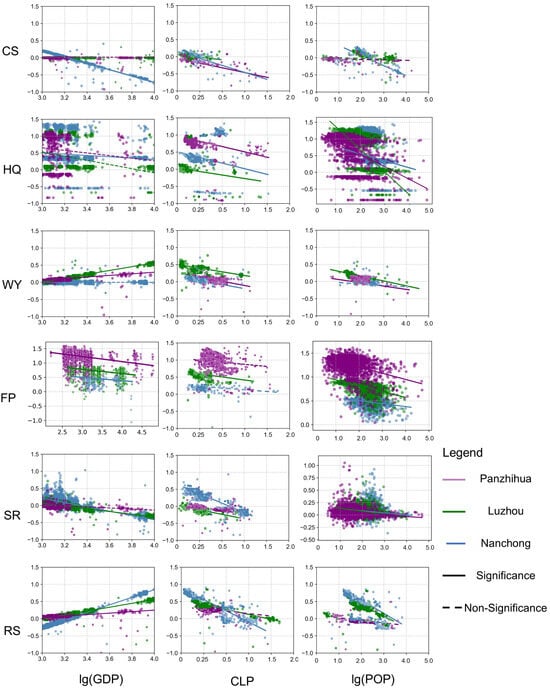
Figure 8.
Comparative analysis of OLS regression results for the effects of urbanization metrics (GDP, CLP, and POP) on supply–demand matching of six ESs in three resource-based cities: Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growing), and Panzhihua (mature).
3.3.2. Sensitivity of Different ESDRs to Urbanization Indicators
RF regression produced high R2 values, confirming that the ESDRs were highly responsive to urbanization indicators, with sensitivity patterns differing markedly among resource-based city types (Figure 9). However, the patterns of sensitivity varied significantly across city types. In Luzhou, the declining city, resource depletion has contributed to the weakening of traditional industries. To stimulate economic recovery, the city has undergone low-cost spatial expansion, particularly in ecological areas that provide CS (0.47) and FP (0.48), resulting in a high sensitivity of these services to changes in CLP. Meanwhile, previous unsustainable economic activities have led to habitat degradation, water pollution, and soil erosion, causing HQ, WY, and SR to be highly sensitive to GDP fluctuations (all above 0.40). In contrast, all ESs exhibited weak sensitivity to POP. In Nanchong, a growing city characterized by rapid CLP expansion, most ESs showed high sensitivity to CLP, except for RS (0.18). Rapid population growth placed increasing ecological pressures on CS, HQ, and WY, which demonstrated strong sensitivity to POP. In contrast, the overall sensitivity of ESs to GDP remained low, suggesting that economic growth has not yet emerged as a major driver of ES changes in this early urbanization stage. In the mature city of Panzhihua, where resource extraction has stabilized and population growth has slowed, CS, FP, and RS exhibited the highest sensitivity to GDP, reflecting the positive influence of economic transformation on ESs. HQ, WY, and FP were most sensitive to POP. Due to the slower urban expansion, the direct impact of CLP on ESs has diminished. Only SR showed high sensitivity to CLP (0.49), which is likely due to land development activities in ecologically vulnerable areas that have intensified soil erosion.
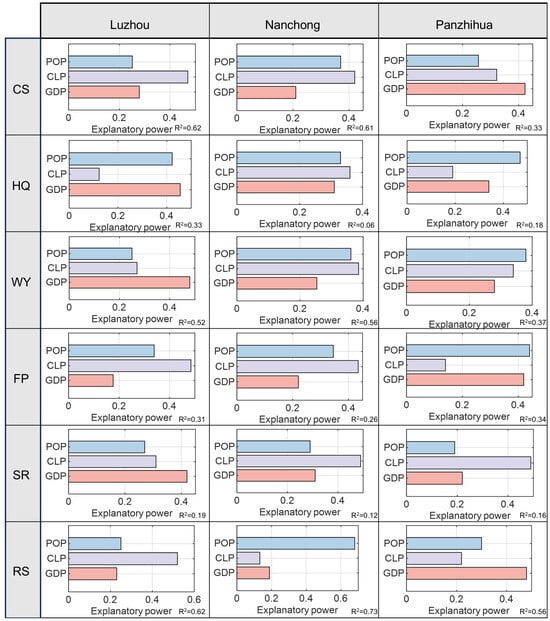
Figure 9.
Comparative sensitivity of supply–demand matching for six ESs to urbanization metrics (GDP, CLP, and POP) across three resource-based cities: Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growing), and Panzhihua (mature), based on random forest analysis.
3.3.3. Differences in ESDR Dynamics Under Urbanization from 2000 to 2020
As shown in Table 2 and Figure 10, the changes in the ESDR of the three types of resource-based cities over the past two decades under the influence of urbanization demonstrate distinct patterns. In the declining city of Luzhou, WY exhibited the greatest growth, increasing from 0.084 to 0.214, representing a rise of 0.13. FP and RS also increased by approximately 0.11 each. However, CS decreased slightly, while HQ exhibited the largest decline (−0.134). SR degraded most markedly (−0.07), decreasing from 0.017 to −0.053, shifting from surplus to deficit. These changes may be attributed to Luzhou’s prolonged pressure from resource extraction and the lack of effective economic transformation, which led to substantial degradation in regulating and supporting services. However, provisioning services, including WY, were partly sustained through mine reclamation and ecological restoration initiatives in the upper Yangtze River basin. In the growing city of Nanchong, FP demonstrated the largest improvement, increasing from 0.179 to 0.359 (+0.18). SR also recovered from −0.002 to 0.048, transitioning from a deficit to surplus, while WY showed a slight increase of 0.01. In contrast, CS, HQ, and RS all decreased to varying degrees. This reflects the impact of the expanding Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration on Nanchong, where rapid urban expansion has compressed ecological space, resulting in a decline in most ESDR values. In the mature city of Panzhihua, the overall improvement in ESs was the most significant. CS and HQ increased by 0.11 and 0.04, respectively. RS showed a notable enhancement (+0.13), while FP and WY increased by 0.17 and 0.08, respectively. SR rose from −0.006 to 0.018. These improvements benefited from Panzhihua’s industrial restructuring, development of clean energy and ecotourism, and implementation of ecological projects, such as the restoration of wetlands along the Jinsha River, resulting in an overall enhancement of ESs.

Table 2.
ESDR values in Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growing), and Panzhihua (mature) from 2000 to 2020.
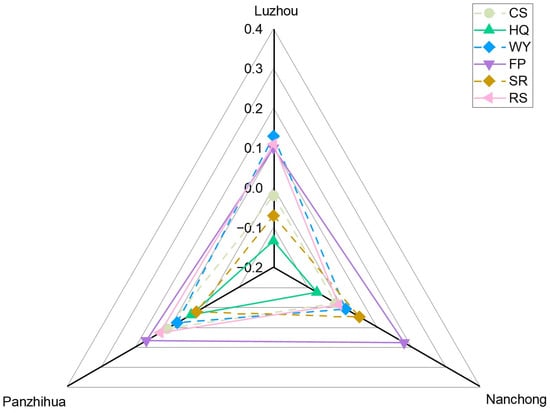
Figure 10.
Temporal evolution of supply–demand matching for Luzhou (declining), Nanchong (growth), and Panzhihua (mature) from 2000 to 2020.
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Supply–Demand Matching Across Resource-Based Cities
Previous studies on ESs in resource-based cities have frequently assumed functional homogeneity among these cities, resulting in uniform assessments of supply–demand relationships [42]. However, this approach often overlooks significant differences in resource types, environmental carrying capacities, development intensities, and urbanization trajectories, which can lead to misinterpretations of actual supply–demand patterns. For instance, Zhu et al. [43] found that intensive coal resource extraction in semi-arid regions did not substantially reduce ES levels, whereas Deng et al. [42] identified coal mining as a major driver of ES degradation in Tangshan. These contrasting findings suggest that even cities with similar resource types may exhibit markedly different ES supply–demand dynamics. More importantly, ES supply–demand represents a dynamic process of matching natural resource endowments with evolving human needs within specific spatiotemporal contexts [14]. Therefore, assessing the ESDR in resource-based cities requires a differentiated approach that accounts for the city type, developmental stage, and resource characteristics. This comparative analysis of Nanchong (growing), Luzhou (declining), and Panzhihua (mature) further reinforces this perspective. Between 2000 and 2020, Panzhihua demonstrated consistent improvements in the ESDR, particularly in CS, HQ, and RS, aligning with the ecological assessment results reported by Liu et al. [44]. Although Nanchong experienced gains in WY and FP, its overall ecological functionality declined. Luzhou showed only minor improvements in WY and SR, while widespread deterioration was observed in other ESs. These supply–demand dynamics are primarily driven by urbanization processes, but they are also influenced by the inherent environmental carrying capacities of each city. Fan et al. [23] suggested that mature resource-based cities like Panzhihua benefit from relatively stable carrying capacities, which, when combined with innovative planning and effective ecological management, can lead to an improved ESDR. In contrast, declining cities, such as Luzhou, may initially possess high and stable carrying capacities, but these often deteriorate due to insufficient economic support and weak governance during urbanization. Growing cities like Nanchong typically exhibit more favorable but less stable capacities, making them particularly vulnerable to external pressures such as rapid urban expansion.
4.2. Insights into the Impact of Urbanization on ESDR
This study distinguishes itself from previous work that relied solely on a single land use metric to assess urbanization and its impacts on ES supply [45]. Instead, it decomposes urbanization into three dimensions—land, population, and economy—thereby capturing the multifaceted mechanisms linking urbanization with ESs’ supply–demand. CLP quantifies built-up land expansion and ecological space encroachment, exerting direct pressure on supply. POP represents a demand for food and water, while GDP reflects the combined impacts of energy use and emissions on ESs. This study also addresses the methodological limitations of previous correlation or single-regression analyses (e.g., geographically weighted regression) [46], which are prone to multicollinearity and lack sensitivity assessment diagnostics. By applying OLS and RF models to three resource-based cities, we shift from linear explanation to nonlinear sensitivity analysis, offering a more nuanced understanding of ES responses during urbanization.
The results showed that WY in Luzhou and Panzhihua was highly sensitive to GDP and CLP. Accordingly, declining and mature cities should prioritize land restoration, strengthen wetland and watershed protection, and regulate economic investments in water resources to mitigate further stress. For CS, POP was the main influencing factor in Nanchong and Panzhihua, suggesting the need to control emissions that are associated with population growth while expanding green coverage and forest-based carbon sinks. FP was negatively affected by CLP in all cities, highlighting the importance of strict farmland protection and optimized land use planning to secure food supplies. HQ and SR were largely influenced by POP, underscoring the need for robust ecological redline enforcement and the establishment of ecological corridors to buffer high-density urban areas. GDP showed a dual role, promoting RS and WY while constraining CS and SR.
These findings align with prior studies, which have noted that the coupling between urbanization and ESs has shifted from an “urbanization lag” to an “ecosystem lag” phase in most regions, with growing tensions between the two systems over time [6]. This underscores the necessity of systematically assessing how urbanization affects ES supply–demand during the sustainable transformation of resource-based cities. Balancing the ES supply–demand is critical to urban sustainability [47], as ESs underpin core SDG targets, including water security (SDG 6), food security (SDG 2), and climate adaptation (SDG 13) [48]. Therefore, sustainable development frameworks for resource-based cities should integrate urbanization processes with ESs’ supply–demand responses. Declining cities should focus on restoring developed land, improving water and soil conservation, and boosting carbon sequestration; for example, Luzhou could leverage its liquor industry to promote waste recycling and ecotourism, thereby supporting WY while limiting new land expansion. Growing cities should prioritize managing POP and farmland protection by fostering low land-consumption industries, encouraging intensive land use, and maintaining contiguous farmland to stabilize FP. Mature cities must align industrial restructuring with ecological restoration by advancing decarbonization, developing healthcare and green tourism, and alleviating ecological pressure through population redistribution and ecological space rehabilitation. By adopting such strategies, resource-based cities can better harmonize urbanization with ESs’ supply–demand and advance SDG attainment. Other resource-dependent cities can adapt this framework to their urbanization stage and industrial structure and employ ES sensitivity analyses to guide sustainable regional development.
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
This study has several limitations that warrant further research. First, although the use of CLP, POP, and GDP effectively captures the broad pressures of land expansion, population growth, and economic development on ESs, it overlooks features unique to resource-based cities, such as the spatial extent of mining zones, changes in population structure, and the masking of economic quality, environmental costs, and industrial transformation by aggregate GDP. Future studies could incorporate indicators, such as mining landscape indices, the proportion of green GDP, and resource extraction intensity, to establish a more comprehensive urbanization assessment framework. Second, the exclusive focus on resource-based cities in Sichuan limits the generalizability of the findings across cities with different economic development levels. Developing a multi-dimensional classification system based on dominant industries or transformation would enable cross-regional comparisons and reveal how geographic, economic, and policy variations influence ESs’ supply–demand responses. Third, the current assessment of ESs is restricted to the municipal scale and does not account for spatial heterogeneity. Future research should adopt multi-scale analytical approaches that are based on resource distribution to approaches based on resource distribution patterns to better capture the spatial complexity of urbanization–ES interactions. Finally, this study examines only the timeframe of 2000–2020. Scenario-based simulations could be employed to quantify the long-term impacts of urbanization on ESs under different development pathways, offering forward-looking insights for sustainable urban and ecological planning.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the dynamics of ES supply–demand matching in types of resource-based cities—declining (Luzhou), growing (Nanchong), and mature (Panzhihua)—throughout the urbanization process, and explored how different urbanization indicators influence this matching across city types. The key findings are as follows: (1) ES supply–demand patterns vary significantly across the three city types. Declining cities exhibit surpluses in CS, WY, and RS, but experience persistent deficits in SR and HQ, with deficit zones concentrated in the northern regions and urban cores. Growing cities show limited overall improvement in supply–demand matching. Although most ESs are in surplus, SR and HQ remain largely in deficit with uneven spatial distribution. Mature cities demonstrate the most favorable supply–demand balance, with all ESs except SR maintaining stable surpluses. (2) The OLS regression results indicate that GDP, CLP, and POP generally exert negative effects on the ESDR across all three cities, though the direction and magnitude of influence vary significantly by city and ES type. Notably, GDP consistently enhances WY and RS in all three cities, whereas CLP emerges as the most widespread and strongly negative driver of the ESDR. (3) Sensitivity to urbanization indicators differs among city types. The RF results reveal that in declining cities, CS and FP are most sensitive to CLP; in growing cities, most ESs respond strongly to both CLP and POP; in mature cities, CS, FP, and RS are mainly driven by GDP, whereas WY and HQ are more sensitive to POP. (4) These findings underscore the need for differentiated strategies to harmonize urbanization and ES supply–demand, offering practical pathways toward SDG realization. Declining cities should focus on land restoration and strengthening SR and CS; growing cities should emphasize farmland protection, population control, and low land-consumption industries; and mature cities should integrate ecological restoration with service provision during industrial transformation and advance green, low-carbon development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.W., M.L. and L.B.; Data curation, T.W.; Methodology, T.W. and M.L.; Software, T.W.; Visualization, T.W. and L.B.; Writing—original draft, T.W.; Writing—review and editing, M.L., L.B. and W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41871324), the Doctoral Startup Project of China West Normal University (Grant No. 22kE001), and the Innovative Exploration Project in Natural Sciences of China West Normal University (Grant No. 23kc002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request. Data required for scientific research in accordance with the laws of the People′s Republic of China can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author. Data will be provided upon approval.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ESs | Ecosystem Services |
| SR | Soil Retention |
| CS | Carbon Sequestration |
| WY | Water Yield |
| HQ | Habitat Quality |
| FP | Food Production |
| RS | Recreation Service |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares |
| RF | Random Forest |
| CLP | Construction Land Proportion |
| POP | Population Density |
| GDP | GDP Density |
| ESDR | Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Ratio |
| DPSIR | Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response |
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| ESV | Ecosystem Service Values |
| VIF | Variance Inflation Factor |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World′s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.; Banzhaf, S. What Are Ecosystem Services? The Need for Standardized Environmental Accounting Units. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; DeFries, R.S.; Díaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Oteng-Yeboah, A.; Pereira, H.M.; et al. Science for Managing Ecosystem Services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, M.O.; Eppinga, M.B.; de Boer, H.J.; Damm, A.; Petchey, O.L.; Santos, M.J. The Relationship between Ecosystem Services and Human Modification Displays Decoupling across Global Delta Systems. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Duan, C.; Chen, B. The Shift in the Spatiotemporal Relationship between Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services and Its Drivers in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. Conflict or Coordination? Assessment of Coordinated Development between Socioeconomic and Ecological Environment in Resource-Based Cities: Evidence from Sichuan Province of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 66327–66339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, J. Recognizing Ecosystem Service’s Contribution to SDGs: Ecological Foundation of Sustainable Development. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Qi, W. Construction of Cultivated Land Ecological Network Based on Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services and MCR Model: A Case Study of Shandong Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xie, D. Transformation and Development of Resource-Based Cities in China: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 975669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C. Increasing urban ecological resilience based on ecological security pattern: A case study in a resource-based city. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Ye, X.; Lee, J.; Lu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, K. Effects of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in a Mineral Resource-Based City. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, B.; Ao, Y.; Bahmani, H.; Chai, B. The Coupling and Coordination Degree of Urban Resilience System: A Case Study of the Chengdu–Chongqing Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Identification and Classification of Resource-Based Cities in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, C.; Gao, M. Investigation of the Relationship between Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services and the Influencing Factors in Resource-Based Cities in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Risk from the Perspective of Service Flow to Support Regional Ecosystem Management: A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Tian, S.; Yuan, X.; Ma, Q.; Hao, H. Evaluation and Improvement Path of Ecosystem Health for Resource-Based City: A Case Study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, H. Evolution of Land Use Functions and Their Trade-Offs/Synergies Relationship in Resource-Based Cities. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zeng, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, W. The Nexus between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services Balance in China: A Coupling Perspective. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B. Has the Sustainable Development Planning Policy Promoted the Green Transformation in China’s Resource-Based Cities? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xia, P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Lan, T.; Yu, S. Ecosystem Services Research: From Golden Era to next Crossing. Trans. Earth Environ. Sustain. 2023, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, Y.D.; Ning, Y. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Urban Systems in China during Rapid Urbanization. Sustainability 2016, 8, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, Y. Using Net Primary Productivity to Characterize the Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Ecological Footprint for a Resource-Based City, Panzhihua in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, K.; Feng, T.; Zhou, Z. Research on the Spatiotemporal Characteristics of RECC in Resource-Based Cities Based on the EWM-CPM: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Research on Coupling Coordination and Key Factors of Urbanization and Ecological Resilience in Resource-Based Cities. Master’s Thesis, Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, Dalian, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P. China’s Urbanization at a Turning Point—Challenges and Opportunities. Science 2025, 388, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Meersmans, J. Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand Response to Urbanization: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X. Interactive Relationship and Zoning Management between County Urbanization and Ecosystem Services in the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W. Different Impacts of Urbanization on Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand across Old, New and Non-Urban Areas in the ChangZhuTan Urban Agglomeration, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, R.M. A Caution Regarding Rules of Thumb for Variance Inflation Factors. Qual. Quant. 2007, 41, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, D.; Liao, Q.; Xiao, M. Linking Landscape Dynamics to the Relationship between Water Purification and Soil Retention. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023, 59, 101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z. Balancing Future Urban Development and Carbon Sequestration: A Multi-Scenario InVEST Model Analysis of China’s Urban Clusters. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Hu, T.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, S.; Deng, S. Matching Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand in China’s Urban Agglomerations for Multiple-Scale Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, H.; Shan, R. Comparison of the SWAT and InVEST Models to Determine Hydrological Ecosystem Service Spatial Patterns, Priorities and Trade-Offs in a Complex Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Yang, F. Advancing Sustainable Development in Large Lake Basins: A Static–Dynamic Integrated Management Framework for Ecosystem Service Supply–Demand Matching. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Miao, C. Spatial Pattern Evolution and Prediction Scenario of Habitat Quality in Typical Fragile Ecological Region, China: A Case Study of the Yellow River Floodplain Area. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, W.; He, J. Spatial Pattern and Driving Factors of Cropland Ecosystem Services in a Major Grain-Producing Region: A Production-Living-Ecology Perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Understanding the Spatial Relationships and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Mismatches towards Spatially-Targeted Management of Social-Ecological System. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; He, S.; Gan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, K. Impacts of Urbanization and Landscape Pattern on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, F. Matching between supply and demand of ecosystem services based on the “water-energy-food” nexus: A case of the urban agglomeration on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains. Arid Land Geogr. 2025, 48, 571–585. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/65.1103.X.20250217.1544.006 (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Pei, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yun, C.; Ma, D.; et al. Research on the influencing factors of urban atmospheric dust reduction based on geographic detector and random forest model: A case study of “2+26” city. Environ. Chem. 2025. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1844.X.20250321.1044.004 (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Zhao, W.; Xiong, L.; Ding, H.; Tang, G. Automatic Recognition of Loess Landforms Using Random Forest Method. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zhu, S.; Guo, J.; Sun, X. Exploring the Quality of Ecosystem Services and the Segmental Impact of Influencing Factors in Resource-Based Cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, S. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Ecosystem Services in Resource-Based Cities in Semiarid Regions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Fan, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, T. Research on the Coordinated Development of Resource-Based Cities in Sichuan Province: From the Perspective of Industrial Structure and Ecological Environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1194584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Qiao, D.; Liu, Q. Impact of Land Use Intensity Changes on Ecosystem Services in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 1003–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, T.; Das, A. Urbanization Induced Changes in Land Use Dynamics and Its Nexus to Ecosystem Service Values: A Spatiotemporal Investigation to Promote Sustainable Urban Growth. Land Use Policy 2024, 144, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. Responses of Spatial Relationships between Ecosystem Services and the Sustainable Development Goals to Urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Cherubini, F.; Fu, B.; Pereira, P. Prioritizing Sustainable Development Goals and Linking Them to Ecosystem Services: A Global Expert’s Knowledge Evaluation. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).