Abstract
Domestic and short-sea shipping play a crucial role in ensuring food and energy security, employment, and connectivity in Small Island Developing States (SIDSs) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs). Despite accounting for up to 26.2% of global maritime emissions by voyage activity, these sectors remain underrepresented in policy and academic discussions on greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction. This study presents a structured and transdisciplinary assessment of decarbonization pathways tailored to the unique operational characteristics of domestic fleets. It reviews key operational, technical, and port-based strategies, identifying both opportunities and challenges in the transition to zero-emission shipping. Highlighted measures include the adoption of carbon-neutral fuels, advanced energy-efficiency technologies, and optimized vessel design. The paper emphasizes the pivotal role of ports as clean energy hubs and advocates for integrating domestic shipping into National Action Plans and Nationally Determined Contributions. Coordinated stakeholder engagement, targeted public investment, and supportive regulatory frameworks are essential to unlock decarbonization potential—contributing not only to climate mitigation, but also to sustainable development and energy resilience in emerging maritime regions.
1. Introduction
Shipping, as the backbone of international trade, contributes 2.89% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions [1]. Building on these efforts, the IMO revised its GHG reduction strategy in 2023, setting ambitious targets for net-zero emissions by 2050. Interim goals include reducing total annual GHG emissions by 20–30% by 2030 and 70–80% by 2040, relative to 2008 levels. Furthermore, the IMO aims for at least 5%, ideally 10%, of the energy used by international shipping to come from zero- or near-zero-emission sources by 2030. Achieving these ambitious targets will require substantial investment across the maritime value chain, including technical innovations and operational improvements. To support this objective, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has adopted mid-term GHG reduction measures, including a goal-based marine fuel standard designed to progressively lower the carbon intensity of marine fuels [1]. Furthermore, the introduction of an economic mechanism represents a significant milestone in accelerating the transition towards zero-emission shipping.
Domestic shipping refers to trade or services conducted by vessels operating exclusively within a single country, while regional shipping refers to vessels trading across multiple countries within a specific region, such as intra-regional voyages. While international shipping has been the focus of significant decarbonization efforts, domestic shipping, which contributes approximately 26.2% of total shipping emissions on a voyage basis and 9.2% on a domestic shipping basis, has received comparatively less attention [1,2].
There are two models for calculating domestic sector emissions: (i) Vessel-based allocation: This model considers ships exclusively dedicated to domestic sectors, contributing 9.2% to global shipping emissions. (ii) Voyage-based allocation: This model, based on individual voyages, accounts for approximately 26.2% of emissions. It includes ships solely navigating between internal ports (9.2%), as well as international ships making occasional visits between two ports within the same country, treating the voyage and associated emissions as domestic. The contribution of international ships engaged in domestic voyages is calculated as (26.2% − 9.2% = 17%). Considering the trends in international shipping towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions through measures such as EEDI, EEXI, SEEMP, CII, GHG pricing mechanism, and GFS, it is expected that emissions from international ships (17%) within voyage-based scenarios will decrease, indirectly reducing domestic shipping emissions in this scenario (IMO, 2024) [2]. As international shipping progresses toward zero-emission targets, the relative contribution of domestic shipping to global GHG emissions is likely to increase unless governments adopt coordinated and proactive measures.
Addressing this gap, the present study highlights the critical importance of decarbonizing the domestic shipping sector. It identifies and evaluates optimal operational practices and green technologies currently applied in domestic shipping worldwide. Additionally, the study assesses the effectiveness of these solutions and explores their potential to drive the transition toward a more sustainable and decarbonized domestic shipping sector. The findings aim to provide actionable insights for ship owners, ports’ managers and operators, policymakers and decision-makers at both local and global levels. By outlining strategies to overcome existing barriers, this study aims to accelerate the transition toward zero-emission shipping in both international and domestic contexts, thereby promoting effective environmental management and enhancing environmental quality in port cities.
This study offers a novel, systematic, and transdisciplinary contribution to the literature by developing an integrated framework that addresses the decarbonization of domestic and short-sea shipping across technical, operational, policy, and port-based domains. Unlike prior studies that often examine these measures in isolation or focus primarily on international shipping routes, this paper adopts a holistic approach tailored to the specific characteristics of domestic maritime transport, including shorter voyage profiles, vessel scale constraints, infrastructural limitations, and region-specific socio-economic dependencies. The framework systematically assesses the deployment potential and trade-offs of a wide range of zero- and near-zero (ZnZ)-emission technologies, including alternative fuels (e.g., hydrogen, ammonia, methanol, biofuels), energy systems (e.g., electrification, hybrid propulsion, fuel cells), and efficiency technologies (e.g., hydrodynamic optimization, waste heat recovery, onboard carbon capture). Moreover, it incorporates enabling port-side measures such as shore power, renewable energy integration, smart grid systems, and port-as-energy-hub concepts.
The transdisciplinary dimension of this study lies in its integration of insights from engineering, environmental science, economics, maritime policy, and systems thinking—underpinned by empirical evidence from implementation projects carried out in collaboration with the IMO and national maritime administrations. Special attention is given to the needs and constraints of emerging maritime regions, particularly Small Island Developing States (SIDSs) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs), which are often marginalized in mainstream decarbonization discourse. Through this comprehensive lens, the paper not only advances the academic understanding of maritime energy transitions but also provides actionable guidance for policymakers, regulators, port authorities, vessel operators, and other stakeholders seeking to align domestic shipping with international climate goals and sustainable development objectives.
2. Methodology
This study employed a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) (The manuscript follows the full PRISMA checklist. Please refer to the Supplementary Section for further information) to identify, evaluate, and synthesize existing knowledge on decarbonization strategies applicable to domestic and short-sea shipping. The protocol was registered in PROSPERO on 28 April 2020 (registration No.: CRD42020159017) with the latest update on 23 February 2021.
The review was guided by four overarching research questions:
- What are the key decarbonization measures relevant to domestic and short-sea shipping operations?
- How do these measures compare in terms of implementation readiness, scalability, greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction potential, and applicability to domestic contexts?
- Which measures are most suitable for near-term deployment in small-scale and regional maritime operations, particularly in developing regions or infrastructure-limited settings?
- How can a systematic, multi-criteria framework support decision-making for selecting appropriate decarbonization strategies in the domestic maritime sector?
To address these questions, a structured research protocol was developed, consisting of clearly defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria encompassed peer-reviewed journal articles, high-quality conference proceedings, academic books, and reputable industrial and technical reports that directly addressed at least one of the research questions—particularly focusing on energy efficiency, alternative fuels, and decarbonization pathways within short-sea and domestic maritime contexts. The exclusion criteria removed duplicate records, non-peer-reviewed sources, low-quality industry documents, and materials not directly related to domestic shipping decarbonization.
A comprehensive literature search was conducted using academic databases including Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore, EBSCO, ProQuest, Google Scholar, and ResearchGate. Search terms were derived from the research questions and aligned with the inclusion criteria. This initial search yielded 1310 records.
The screening process involved a three-stage filtration:
- Stage 1: Title and abstract screening excluded 420 duplicated records.
- Stage 2: A more detailed abstract review removed an additional 481 irrelevant a record.
- Stage 3: Full-text reviews were performed on the remaining 409 documents, resulting in the exclusion of 226 studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria.
An additional 84 relevant publications were identified through forward and backward snowballing, yielding a final corpus of 272 sources, spanning the period 1990 to 2025.
Each selected study was appraised for methodological quality and thematic relevance. This process led to the final inclusion of 224 high-quality studies (See Figure 1). Data was then extracted from these sources and organized in relation to the four guiding research questions. The findings supported the development of a multi-criteria comparative framework, which was used to assess the 17 decarbonization measures in terms of implementation readiness, scalability, GHG reduction potential, and applicability to domestic and short-sea shipping contexts.
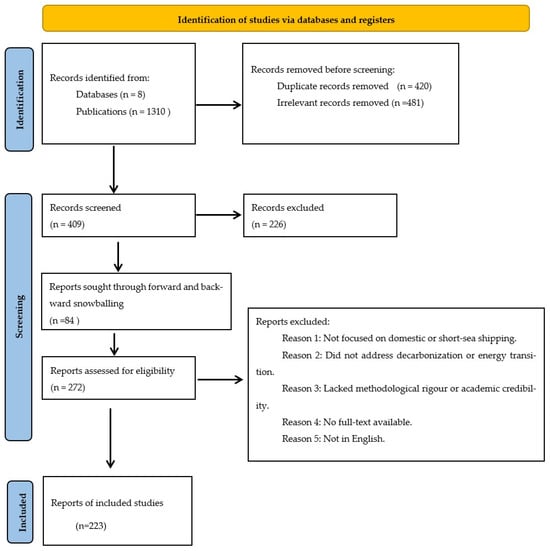
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram. The diagram illustrates the identification, screening, eligibility assessment, and inclusion of studies for the review. The process includes records identified from databases and publications, removal of duplicates and irrelevant records, screening, forward and backward snowballing, and the final selection of studies based on predefined eligibility criteria.
The structured synthesis enabled a robust, comparative evaluation of technological pathways, regional suitability, and strategic trade-offs. These insights underpin both the narrative analysis and the visual representation (radar chart) presented in Section 5.
3. Abatement Measures
While decarbonization efforts have largely focused on international shipping, increasing attention is now being directed toward addressing the unique challenges faced by Least Developed Countries LDCs (LDCs) and Small Island Developing States (SIDSs). However, research and literature on decarbonizing domestic shipping remain limited. In contrast, several European countries—such as Norway, the United Kingdom, and Sweden—have prioritized domestic shipping decarbonization [3]. To accelerate decarbonization within the short-sea shipping sector, it is critical to recognize the unique characteristics of domestic shipping, which typically involves shorter distances and fixed routes. As operational and technical solutions must be tailored to specific contexts, the decarbonization strategies for domestic shipping differ from those for deep-sea operations. Collaboration among shipping lines, ports, and terminals will be essential for data sharing and optimizing voyage planning, ensuring that decarbonization strategies are both feasible and effective.
3.1. Decarbonization Measures and Strategies in Domestic Shipping
The decarbonization of domestic shipping requires a comprehensive and multi-disciplinary approach, integrating operational, technical, and port-specific measures. Domestic shipping, with its unique operational characteristics—such as shorter routes, fixed schedules, and frequent port calls—offers distinct opportunities to implement green technologies and alternative fuels for reducing GHG emissions.
This subsection categorizes these measures and strategies into three main disciplines: operational measures, technical measures, and port initiatives. Each discipline encompasses specific actions aimed at optimizing energy efficiency, enhancing vessel performance, and incorporating alternative and renewable energy solutions.
- Operational measures focus on improving the efficiency of ship operations, such as passage planning, speed reduction, and maintenance practices, which can significantly minimize fuel consumption and emissions.
- Technical measures involve adopting advanced technologies and energy systems, including alternative fuels (e.g., hydrogen, methanol, LNG, ammonia), renewable energy sources (e.g., wind and solar), and energy-saving technologies like hydrodynamic optimization, waste heat recovery, and onboard carbon capture systems.
- Port initiatives play a vital supporting role in decarbonization, as ports serve as critical hubs for energy provision and operational improvements. Key measures include implementing shore power (cold ironing), renewable energy integration, and smart grid solutions to reduce emissions during vessel docking and cargo operations (See Figure 2).
Table 1 summarizes the key measures and strategies under each discipline that can be applied to achieve decarbonization in the domestic shipping sector.

Table 1.
Options to decarbonize shipping (the applicability of the proposed measures and technologies may vary significantly across different types of domestic and short-sea shipping. Factors such as vessel size, age, design, operational profile, and area of operation must be carefully considered. Therefore, these strategies should not be interpreted as universally applicable or one-size-fits-all solutions for the entire domestic fleet).
3.1.1. Operational Measures
Optimizing Passage Planning, Power Demand, and Weather Routing
Effective passage planning is a comprehensive process encompassing the appraisal, planning, execution, and monitoring of a vessel’s voyage [4]. This process not only enhances the safety of vessels, personnel, and cargo but also significantly improves energy efficiency in maritime operations [5]. By adhering to best practices, such as navigating familiar and safe routes, vessels can reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Key considerations during passage planning include weather conditions, monsoons, traffic density, and potential hazards at sea [6]. Skilled masters can further optimize energy use by leveraging local currents and tidal flows, reducing engine load, fuel consumption, and emissions. This is particularly relevant in domestic shipping, where fixed and regularly scheduled routes allow for meticulous planning to account for localized currents, tides, and eddies, especially in constrained or narrow passages. In addition, for short-sea vessels operating in shallow or constrained waters, optimizing vessel draft is critical to reducing hydrodynamic resistance and engine load [7]. This can be effectively supported by adopting multiple, incremental replenishment strategies for ship consumables—such as fuel, water, and provisions—to maintain a lower and more efficient operating draft throughout the voyage.
Weather routing, a technique that adjusts a vessel’s course based on prevailing weather conditions, has proven to be a powerful tool for enhancing energy efficiency, with potential improvements of up to 5% depending on the vessel’s type, size, and route characteristics. Wind propulsion systems and their usage on domestic vessels can benefit from weather routing, as it allows vessels to harness additional wind energy. Among these systems, rotor sails offer the greatest efficiency gains, followed by suction wings and, to a lesser extent, wing sails [8]. Optimizing routes based on weather conditions reduces resistance and engine load, leading to better fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced underwater noise pollution [9].
Speed Reduction and Just-in-Time (JIT) Operations
Speed reduction, a proven strategy in deep-sea shipping, offers varying levels of feasibility and effectiveness in short-sea and domestic shipping, requiring case-by-case assessment to address sector-specific challenges [2]. Since fuel costs account for approximately 60% of a vessel’s operational expenses [10], and speed directly influences fuel consumption and emissions, optimizing vessel speed can yield substantial economic and environmental benefits [11]. The power required for propulsion increases exponentially with speed, proportional to the cube of the vessel’s velocity [12]. For instance, a 10% reduction in speed can lower fuel consumption from 15% to 27% [13] and emissions by 10–15% [14]. Speed reduction is particularly impactful for high-speed vessels, such as container ships and vehicle carriers, compared to slower vessels [15,16].
While speed reduction provides an immediate solution, its implementation requires consideration of factors such as route characteristics, vessel type, weather conditions, cargo, market dynamics, and contractual obligations [17]. Complementary strategies, including JIT operations, improved port efficiency, and reduced waiting times, can enhance adoption [18,19]. Successful execution depends on flexible planning, stakeholder collaboration, and robust data exchange. Governments can support these efforts by enforcing the polluter-pays principle for non-compliance while providing incentives for adopting environmentally friendly practices.
A key challenge of speed reduction is its impact on vessel and fleet capacity. Slower speeds can reduce the operational efficiency of individual vessels, potentially requiring additional ships to maintain capacity [20]. While shipowners benefit from lower fuel costs, extended voyage durations may reduce revenues due to decreased cargo throughput. Cargo owners may face higher costs and opt for faster transportation modes, such as air or road, which could lead to higher emissions [15]. To address these issues, innovative solutions like JIT operations and benefit-sharing mechanisms are essential to promote fuel efficiency and sustainability [21].
In regions with elastic demand, such as SIDSs and LDCs, speed reduction introduces complexities, potentially impacting service frequency, reliability, and scheduling. This could lead to market losses and negatively affect food and energy security, safe navigation, and the economic and environmental development of the shipping sector [21]. Tailored policies, such as localized speed regulations within port jurisdictions or the introduction of fuel and emissions taxes, could mitigate these challenges.
The applicability of JIT practices in domestic shipping warrants careful consideration. JIT involves coordinating with destination ports to confirm berth availability, allowing optimized speeds en-route [22]. This approach reduces air emissions and underwater noise pollution while alleviating port congestion and streamlining logistics [23,24].
JIT strategies have demonstrated GHG emission reductions of 14–23% [25]. However, in domestic shipping, characterized by shorter distances, the impact may be less pronounced than on international routes. Nevertheless, JIT practice can enhance efficiency by minimizing port stays and streamlining logistics [26]. For domestic shipping types like scheduled ferry services, successful implementation relies on strong collaboration among shipping lines, ports, and terminals, as well as effective data exchange to optimize voyages.
Optimization of Ship Handling
Effective cargo handling is critical to enhancing energy efficiency and optimizing maritime operations in port environments. Vessels are typically designed with specific speed and draft configurations to maximize performance. By employing advanced cargo handling techniques alongside efficient fuel and ballast management, and maintaining optimal trim and draft within stability limits, hull resistance can be significantly reduced. This reduction in resistance directly translates into lower engine power requirements, estimated at approximately 5–10%—leading to decreased fuel consumption and reduced emissions [27,28].
Hull Coating and Cleaning Practices
The application of appropriate coatings, combined with regular hull and propeller cleaning, plays a key role in optimizing vessel performance. Research demonstrates that proper maintenance of the hull and propeller can improve energy efficiency by 7–10%, contributing to compliance with Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) requirements [29,30]. Hull and propeller fouling, often exacerbated by inadequate coatings or physical damage, increases hydrodynamic resistance, thereby raising fuel consumption and diminishing operational efficiency [11,31]. Biofouling accumulation is influenced by factors such as vessel speed, trading area, and operational activity levels.
Regular maintenance and cleaning schedules, supported by underwater inspections, are crucial for detecting mechanical damage and evaluating surface roughness [32]. Advanced anti-fouling systems, including specialized coatings and surface treatments, can further reduce biofouling, thereby minimize the spread of invasive species and improving vessel efficiency [33]. These measures not only lower fuel consumption but also contribute to reducing underwater radiated noise emissions [34,35].
Machinery Maintenance
Optimizing maintenance procedures can yield substantial improvements in energy efficiency and reduce emissions by 2–8% [36]. Well-maintained machinery ensures operational integrity, safeguarding both vessels and crew, while failure to follow proper maintenance protocols can compromise seaworthiness [37]. Implementing a Planned Maintenance Program ensures that regular inspections and maintenance are conducted in accordance with manufacturer and company standards, thereby improving vessel safety and performance [38].
The adoption of Industry 4.0 and artificial intelligence technologies is transforming the maritime sector, particularly through the use of real-time monitoring enabled by wireless sensors. These systems collect data on machinery performance, allowing for predictive maintenance and reducing the risk of major machinery failures [39]. Digital twinning, a technology that creates virtual replicas of physical assets like ship engines, allows for simulations and troubleshooting, further enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities [40]. By detecting potential issues early, these technologies reduce emergency repair costs and downtime, while also alleviating the workload on vessel personnel.
Economies of Scale
Deploying larger vessels and maximizing capacity utilization offers a promising opportunity to reduce the carbon footprint of maritime fleets. Through economies of scale, emissions reductions of up to 30% can be achieved [41,42]. However, realizing this potential requires significant financial investments and overcoming challenges related to economic constraints and port infrastructure limitations [43].
Ports play a crucial role in supporting economies of scale, particularly by ensuring adequate draft depths, berth lengths, and cargo handling infrastructure [44]. Ports that fail to upgrade their facilities risk losing market share to competitors [45]. To address operational inefficiencies and enhance service quality, government intervention may be necessary. This could involve the introduction of low-interest financial mechanisms, incentive schemes, and levies on fuel or carbon emissions, thereby supporting both shipowners and ports in decarbonization efforts [46].
Lifecycle Perspective on Ship Emissions
While the focus of emissions reduction efforts has traditionally been on a vessel’s operational lifespan, shipyards also play a critical role in mitigating air emissions during the construction phase of new vessels [3]. The integration of energy-efficient technologies and alternative fuels during shipbuilding is crucial. In this context, the role and potential of shipyards in supporting zero-emission shipping—by incorporating and providing such technologies—are essential. Despite its significance, the environmental impact of ship production has received relatively little attention. As the industry moves toward adopting cleaner technologies and renewable energy sources, the construction phase is expected to play an increasingly important role in the overall emissions reduction strategy [47]. To achieve meaningful decarbonization, a comprehensive lifecycle approach is needed, addressing air emissions across the entire ship lifecycle, including ship construction [48,49].
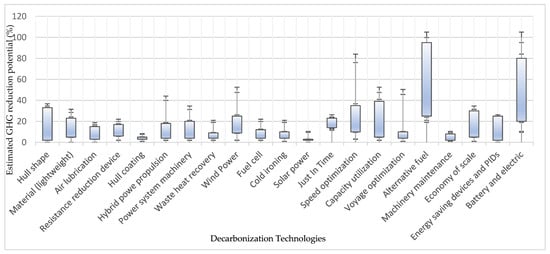
Figure 2.
Estimated GHG reduction potential of key decarbonization technologies and operational measures in shipping. The data reflects expected GHG reduction potential (in %) based on the literature and empirical evidence. Some measures—such as alternative fuels and voyage optimization—demonstrate high variability, indicating their sensitivity to vessel type, route, and implementation context. Source: [50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60].
3.1.2. Technical Measures
Alternative Fuels and Energy Sources
Aligned with the IMO’s revised strategy for reducing GHG emissions, the maritime industry is encouraged to transition toward zero to near-zero (ZnZ) fuels and renewable energy sources [61,62,63,64]. Achieving the IMO’s 2030 target will require approximately 17 million metric tons of carbon-neutral fuel, representing 30–40% of global production capacity, emphasizing the urgent need for robust technical and operational measures [55]. The financial challenges are equally significant, with an estimated USD 1.4 trillion investment needed to halve shipping emissions by 2050. Annual investments in new fuel and engine technologies are projected at USD 8–28 billion, while onshore fuel infrastructure will require USD 28–90 billion annually [54].
One critical challenge arises from the differing properties of alternative fuels compared to conventional marine fuels. As depicted in Figure 3, alternative fuels vary in volumetric and gravimetric energy densities, CO2 emissions, and overall emissions reduction potential. Figure 4 illustrates that the lower volumetric energy density of low- and zero-carbon fuels necessitates increased onboard storage to provide equivalent energy. This poses a significant operational challenge for smaller vessels in the domestic sector, where space limitations can restrict cargo capacity and impact economic viability [65].
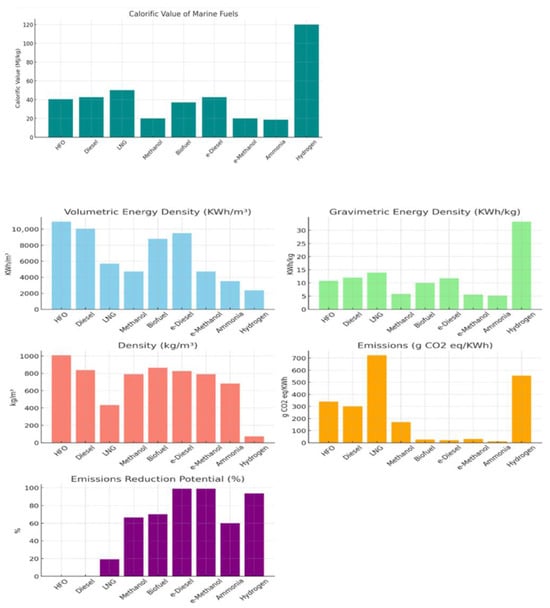
Figure 3.
Fuels’ characteristics. Source: [50,51,52,54,55,56,57,58,59,66].
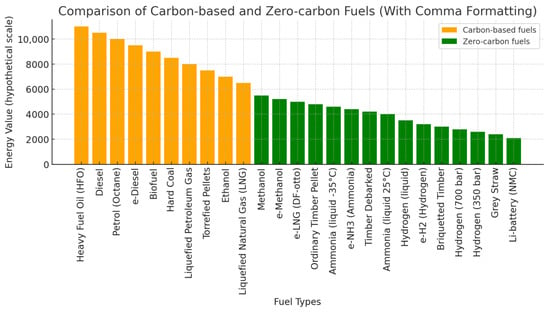
Figure 4.
Volumetric energy density of fuels. Source: [50,51,52,54,55,56,57,58,59,66].
The domestic shipping sector, characterized by shorter voyages and smaller vessels, faces unique challenges in adopting alternative fuels and renewable energy solutions. These include the need for tailored infrastructure, significant investments, and strategies adapted to the operational and economic realities of domestic fleets [2]. Despite these obstacles, integrating alternative fuels and innovative energy technologies is essential for reducing emissions and achieving long-term sustainability in line with the IMO’s decarbonization goals.
- Hydrogen
Table 2 presents the advantages and challenges of using hydrogen (H2) as a marine fuel. Hydrogen is emerging as a promising clean energy source with substantial potential to support the decarbonization of the domestic shipping sector. Hydrogen can be produced from various primary energy sources, including fossil fuels, biomass, and renewable electricity through methods such as steam reforming, gasification, partial oxidation, and electrolysis [67]. Among these, electrolysis powered by renewable energy—such as wind or solar—offers a zero-emission production pathway, positioning hydrogen as a key contributor to the IMO’s GHG Emissions Strategy [68].

Table 2.
Advantages and challenges of using hydrogen as a marine fuel. Source: [50,51,52,53,54,55,67,68,69].
Unlike conventional marine fuels, hydrogen combustion produces no CO2, particulate matter, or SOx emissions, though NOx emissions can occur at high combustion temperatures [69]. Hydrogen’s versatility allows it to be used in fuel cells, blended with conventional fuels, or employed as a direct substitute for marine fuels, making it well-suited for short-sea and domestic shipping applications [2,70].
Despite its potential, hydrogen faces critical challenges hindering widespread adoption in the maritime sector. These include:
- High production costs and the need for significant infrastructure investments for hydrogen storage and distribution.
- Low volumetric energy density, which complicates onboard storage, particularly for larger vessels [71].
However, in domestic shipping, innovative solutions such as deck-mounted hydrogen containers offer operational flexibility and efficiency, making hydrogen particularly suitable for smaller vessels operating on short routes with frequent refueling opportunities [72]. In addition, hydrogen fuel cells are already demonstrating feasibility in maritime operations. For instance, the MF Hydra, a 2700 GT RoPax ferry, operates with a 0.4 MW hydrogen fuel cell system, showcasing hydrogen’s potential as a clean maritime fuel [73]. Additionally, research into hybrid systems that combine hydrogen fuel cells with battery technologies highlights a scalable pathway for decarbonizing larger vessels.
- Methanol
Methanol is increasingly recognized as a promising alternative marine fuel, particularly for hydrogen transportation [74]. While most methanol production currently relies on natural gas, it can reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 25% compared to heavy fuel oil [75]. When combined with carbon capture technologies, methanol has the potential to become carbon-neutral—emitting no more CO2 than was absorbed during its production. However, this depends on the efficiency of the carbon capture process and the source of energy used to power it. Furthermore, methanol derived from renewable energy sources—referred to as e-methanol—can achieve near-100% reductions in GHG emissions [51].
Methanol’s growing suitability as a marine fuel is underpinned by the following characteristics:
- Availability and established infrastructure: Methanol benefits from a well-developed global supply chain and logistics network, streamlining its bunkering process [76].
- Compatibility: Methanol can be integrated into existing ship engine designs and maritime infrastructure at a relatively low cost [77].
- Environmental benefits: Methanol combustion significantly reduces SOx and NOx emissions compared to conventional marine fuels [78,79].
These attributes make methanol particularly attractive for domestic shipping, where capital and space constraints are more pronounced than in international operations [2].
Methanol’s feasibility as a marine fuel is already demonstrated in operational settings. For instance:
- The Stena Germanica passenger ferry operates on methanol-powered four-stroke engines.
- The Viking Line ferry MS Mariella has tested methanol storage and feed systems since 2017 [57].
Additionally, studies highlight methanol’s role in hybrid systems. The WAVEMASTER ZERO C project identified battery-methanol hybrid configuration as the most effective among alternative fuels (hydrogen, ammonia, electric, and biodiesel) for reducing emissions in vessels. The study emphasized methanol—particularly when produced using renewable electricity and carbon capture technologies—as a viable secondary option for achieving sustainability goals in the maritime sector [80]. Table 3 demonstrates the advantages and challenges in using methanol as a marine fuel.

Table 3.
Advantages and challenges of using methanol as a marine fuel. Source: [50,51,52,53,54,55,74,75,76,77,78,79].
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
LNG, primarily composed of liquefied methane stored at −162 °C, has been widely promoted as a transitional fuel for the maritime industry. While LNG can significantly reduce SOx and NOx emissions by over 90% and lower CO2 emissions by 20–30% compared to conventional marine fuels [81], its energy density is only 60% that of diesel, limiting its overall efficiency [82]. Despite its benefits, LNG cannot fully achieve zero-emission targets due to its carbon content. A major drawback is methane slip, which undermines LNG’s environmental advantages. When analyzed through a Well-to-Wake framework, LNG’s climate benefits diminish further, raising questions about its viability in meeting the IMO’s long-term decarbonization goals for 2050 [83,84,85].
Transitioning to LNG requires significant capital investment for retrofitting vessels, developing specialized engines, and building onboard and onshore storage infrastructure. LNG tanks occupy 2.5–3 times more space than Marine Gas Oil (MGO), resulting in cargo capacity losses of up to 4% and reduced operational efficiency [86,87]. These challenges are particularly pronounced for smaller vessels and domestic shipping, where space and budget constraints are significant concerns. Historically, LNG has been favored for domestic ferries [88,89], and its use has gradually expanded to larger vessels [90]. However, rising infrastructure costs and competition from alternative marine fuels, such as Very Low Sulfur Fuel Oil (VLSFO) and MDO, have reduced LNG’s appeal [2]. Many vessels equipped with dual-fuel engines are now opting for MDO due to its lower capital requirements and favorable cost structure. While LNG continues to play a transitional role in certain shipping segments, its limitations—particularly methane slip and high infrastructure costs—raise concerns about its long-term viability as a marine fuel. In the context of the IMO’s decarbonization goals, LNG’s role may decline as cleaner alternatives, such as hydrogen, ammonia, and e-fuels, become more competitive (See Table 4).

Table 4.
Advantages and challenges of using LNG as a marine fuel. Source: [50,51,52,53,54,55,81,82,83,84,85,87].
- Ammonia
Ammonia has emerged as a prominent alternative fuel in the maritime sector, recognized for its potential to significantly advance the decarbonization of shipping. As a zero-carbon tank-to-wake fuel, ammonia is positioned as a key enabler of the IMO 2050 decarbonization targets [91]. Technological advancements have prompted several shipping companies to invest in ammonia-powered vessels, often employing hybrid systems that combine ammonia with other fuels to optimize performance. However, the full life-cycle emissions of ammonia must be considered, as its production relies on hydrogen synthesis, which can result in substantial CO2 emissions depending on the hydrogen source [50].
The main advantage of ammonia lies in its ability to drastically reduce CO2 emissions while remaining economically viable. As a zero-carbon fuel from a tank-to-wake perspective, it aligns well with the maritime industry’s transition to cleaner energy [92]. Despite its benefits, ammonia faces challenges due to its low flame speed and high auto-ignition temperature, making it less suitable for high-speed engines. Instead, it is better suited for slow-speed engines commonly used in large vessels, where it can deliver greater operational efficiency [50].
Ammonia’s adoption is hindered by significant safety concerns, particularly its toxicity and associated risks to human health and the environment [93]. Exposure to ammonia poses serious dangers to seafarers, especially in the event of leaks or accidental releases, which are critical concerns in maritime operations. Furthermore, ammonia leaks can have severe environmental consequences, harming marine ecosystems and human populations, particularly in urban ports and densely populated coastal areas where domestic vessels frequently operate [94]. These safety risks and the potential for environmental damage make ammonia a less practical choice for domestic shipping.
Given these challenges, ammonia’s application in domestic fleets is limited, especially for smaller vessels operating near urban areas. Its toxicity and logistical issues in heavily populated ports render it unsuitable for domestic shipping. While ammonia holds promises for decarbonizing large international vessels, its role in the domestic sector is constrained by safety, operational, and environmental concerns (See Table 5).

Table 5.
Advantages and challenges of using ammonia as a marine fuel. Source: [50,51,52,53,54,55,91,92,93,94].
Renewable Energy
The integration of renewable energy technologies, such as wind-assisted propulsion and solar power, offers substantial potential to reduce fuel consumption, emissions, and operational costs in maritime operations. However, challenges such as the lack of financial incentives (e.g., subsidies or tax relief) and high upfront investment costs continue to hinder widespread adoption, particularly in comparison to fossil fuels [95,96].
- Wind-Assisted Propulsion Systems
Wind-assisted propulsion has emerged as a promising zero-emission solution, particularly for enhancing efficiency in short-sea and domestic shipping operations. These systems align with key IMO decarbonization indices, including the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI), Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI), and CII [97]. As a zero-emission energy source, wind power offers distinct advantages:
- No reliance on existing or future energy infrastructure.
- Elimination of pollution, emissions, or accidental discharges.
- Mitigation of fuel safety concerns (e.g., contamination, fire, or explosion).
- Resilience against regulatory changes, as wind power is classified as a zero-emission technology [98].
A variety of technologies—including soft sails, hard sails, Flettner rotors, suction wings, kites, turbines, and optimized hull designs—have demonstrated fuel cost reductions of 5–9% for specific ship types, with potential efficiency gains reaching 25% [99]. The extent of these improvements is influenced by factors such as vessel design, speed, machinery type, and weather conditions. Additionally, optimizing voyage planning and weather routing can further enhance performance.
While the IMO projects a modest 1.66% contribution of wind energy to maritime decarbonization by 2050, advancements in wind propulsion technologies and declining costs suggest a more optimistic outlook. Integrated strategies—combining wind propulsion, speed reduction, and carbon-neutral fuels—could achieve emission reductions of up to 47% by 2030, relative to 2008 levels [14].
Wind-assisted propulsion systems are increasingly applied across a broad range of vessels, including large tankers, bulk carriers, ferries, and fishing boats. For instance, retrofitting the Stena Jutlandica ferry with a turbine resulted in reduced energy consumption, while the M/S Viking Grace demonstrated the viability of rotor sails for passenger vessels [100,101]. In addition, smaller and domestic shipping sectors, particularly in SIDSs and LDCs, present significant opportunities for wind propulsion deployment. Early signs of adoption include traditional fishing vessels in African and Caribbean regions and innovative sail-assisted supply vessels operating in the Marshall Islands [102].
- Solar energy
In addition to wind energy, solar power presents significant potential for enhancing sustainability in domestic shipping, particularly for meeting onboard auxiliary power needs. While current solar technologies are not capable of fully powering large commercial vessels, they offer promising results when combined with other systems, such as wind-assisted propulsion and fuel cells, to reduce fuel consumption and advance decarbonization efforts [103,104].
Solar power is especially effective for auxiliary energy demands, contributing 1–3% reductions in auxiliary power usage under favorable weather conditions, compared to the 5–9% fuel savings achieved by wind-assisted propulsion systems [54]. Projections suggest that solar energy could account for up to 0.3% of shipping decarbonization by 2050 [105]. However, like wind and battery technologies, advancements in solar efficiency and cost reductions are expected to accelerate adoption, particularly in domestic shipping applications.
The unique operational profile of domestic shipping—comprising smaller vessels, shorter routes, extended port stays, and limited operational areas—creates a strategic opportunity for solar energy utilization as part of the pathway to net-zero emissions [2]. Integrating solar power, wind propulsion, and battery storage can significantly reduce reliance on conventional engines [106] and reduce emissions from the shipping industry.
Several implementations underscore the benefits of solar technologies. For instance, the installation of 134 kWp of solar panels on a 135 m inland vessel reduced annual fuel consumption by 12%, saving approximately 33,000 L of fuel and cutting CO2 emissions by 107 tonnes per annual [73]. Similarly, adopting solar systems on passenger ferries and small vessels, such as those operating on India’s National Waterway, has demonstrated measurable economic and environmental benefits [107].
- Biofuel
Biofuels, derived from plant-based or microbial sources, hold significant promise for decarbonizing the shipping industry by offering low sulfur emissions and potential CO2 reductions of 25–100%, depending on feedstock quality and production processes [108]. However, concerns about the sustainability of biofuel production, particularly related to land-use and socio-economic impacts, remain critical [109]. Addressing these challenges requires advanced production methods to mitigate issues like food insecurity and land-use conflicts associated with first-generation biofuels [110].
Biofuels are categorized into three generations based on their feedstock sources and environmental impact:
- First-Generation Biofuels: Produced from food crops (e.g., corn, sugarcane, and vegetable oils), including ethanol and biodiesel. These fuels face criticism for competing with food production and exacerbating land-use conflicts.
- Second-Generation Biofuels: Derived from non-food crops, agricultural residues, and waste biomass, these biofuels—such as cellulosic ethanol—have a lower environmental footprint and do not directly compete with food production.
- Third-Generation Biofuels: Produced from algae and microorganisms, these fuels offer advantages like high lipid yields and minimal impact on food resources, making them a promising long-term solution [111].
Biofuels are particularly well-suited for shipping due to their compatibility with existing marine engines and bunkering infrastructure, enabling a gradual transition to more advanced fuels like e-fuels [112,113]. This compatibility is especially significant for domestic shipping in LDCs and SIDS, where maintaining existing fleets remains a priority. Moreover, biofuels pose fewer environmental risks in the event of spills compared to fossil fuels and can be blended with conventional marine fuels or serve as direct replacements.
Key biofuels for maritime applications include:
- Biodiesel variants: Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO), Biomass-to-Liquids (BTL), and Fatty Acid Methyl Ester (FAME).
- Liquid Biogas (LBG): Primarily methane-based, LBG is an ideal alternative to Marine Diesel Oil (MDO) and Marine Gas Oil (MGO) and serves as a substitute for fossil LNG.
- Straight Vegetable Oil (SVO): A viable replacement for Heavy Fuel Oil [114].
Despite their potential, second- and third-generation biofuels face limitations, such as high production costs, limited availability, and scalability challenges. Policy interventions and increased investment are essential to expand production and accessibility, particularly in emerging economies (See Table 6).

Table 6.
Advantages and challenges of using biofuels as a marine fuel. Source: [50,51,52,53,54,55,109,110,111,112,113].
- Electric/propulsion system
Electric propulsion systems are increasingly being adopted across various vessel types, particularly in short-sea and domestic shipping, where they offer significant opportunities for reducing emissions [115]. The successful implementation of these systems relies on the development of sustainable port infrastructure, such as shore power systems, and advanced energy storage solutions, including batteries, flywheels, and supercapacitors [116]. Among these, supercapacitors stand out for their ability to rapidly store and discharge energy, outperforming traditional batteries in specific high-energy scenarios.
- Battery-powered/Hybrid vessels
Electric propulsion systems in the maritime sector are broadly classified into two main types: pure electric and hybrid systems. Both configurations depend on onshore power infrastructure for recharging and face common challenges, including battery size, weight, loss of cargo space, fire safety risks, and high costs [117,118]. Technological advancements, such as lightweight hull designs using carbon fiber composites, have been instrumental in mitigating weight-related issues, particularly in hybrid configurations [119,120]
Battery-powered and hybrid electric vessels are predominantly used in short-sea, domestic, offshore, and passenger transport sectors. Vessel applications span a range of types, including RoPax ferries (up to 11,000 gross tonnage), tugs (70 bollard pull), bunker ships, and 120 TEU container vessels [73]. Noteworthy examples include the following:
- The Zerocat 120, an electric ferry capable of transporting 120 cars and 360 passengers, with a rapid ten-minute recharge time [121].
- The Ellen ferry, which can travel 50 nautical miles on a single charge [101].
Pure electric systems rely entirely on batteries for propulsion and are best suited for short-sea routes due to current energy storage limitations. Prominent examples include the largest battery electric ship are a full battery ferry with capacity of 40 MWh energy storage system (ESS) [122], the Yara Birkeland, a 3000 GT autonomous container ship equipped with a 6.7 MWh of ESS, and a 10 MWh all-electric ferry under construction in Turkey that features high capacity recharging capabilities, enabling full recharge in just 12 min [73,123].
Hybrid systems, on the other hand, integrate fuel-driven engines with battery-based ESS to optimize fuel efficiency and vessel performance. These systems allow switching between electric, hybrid, or conventional modes, facilitating lower fuel consumption, reduced emissions, and decreased maintenance costs. Examples include the AIDAprima and AIDAperla cruise ships, each fitted with a 10 MWh ESS [124].
As of 2023, a total of 589 battery-powered vessels are in operation worldwide, with a further 171 vessels under construction [125]. This growth trend is driven by a significant decline in battery prices—from $273 per kWh in 2016 to a projected $73 per kWh by 2030 [79]—as well as by rising fuel costs and increasingly stringent environmental regulations [126]. However, the overall sustainability of battery-electric propulsion is closely linked to the carbon intensity of the energy mix used for recharging [116].
In addition to batteries, supercapacitors are gaining attention, particularly in short-sea applications. Their capacity to deliver rapid bursts of energy makes them ideal for operations requiring frequent power surges, such as berthing and unberthing [127]. A notable example is the AR Vegan Tredan, a passenger ferry that operates emission-free using supercapacitors to meet its short-duration energy demands [128].
- Fuel cell
Fuel cells, particularly Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) and Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs), offer a promising solution for reducing emissions in domestic and short-sea shipping. Their integration into hybrid systems, combined with advancements in fuel flexibility and energy efficiency, will play an important role in the maritime industry’s transition to zero-emission operations by 2050.
Fuel cells offer an efficient and clean method for generating electricity, providing higher electrical efficiency, as well as reduced noise and vibration compared to traditional internal combustion engines [129]. While their adoption in the maritime industry is limited due to high initial costs, commercialization barriers, and space requirements, fuel cells represent a compelling alternative for auxiliary, hybrid, and low-power propulsion systems, particularly in short-sea and domestic shipping.
Three main fuel cell technologies are emerging in the maritime sector:
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs):
- ⚬
- Low-Temperature PEMFCs (LT-PEMFCs): Offer fuel efficiency between 50 and 60% but are sensitive to hydrogen impurities, such as sulfur and carbon monoxide [130].
- ⚬
- High-Temperature PEMFCs (HT-PEMFCs): These are less sensitive to fuel impurities and can be combined with waste heat recovery systems to improve overall efficiency, making them suitable for larger vessels [79]. However, their application is currently restricted due to high costs and development constraints.
- 2.
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs):
SOFCs achieve an electrical efficiency of around 60%, which can increase to 85% when integrated with waste heat recovery systems [131,132]. Unlike PEMFCs, SOFCs are fuel-flexible, capable of utilizing ammonia, LNG, methanol, and hydrogen, providing higher energy efficiency and reduced fuel consumption—up to a 33% reduction for LNG-fueled very large crude carriers [55]. Additionally, hydrogen-powered fuel cells can achieve lifecycle emission reductions of up to 91.4% [133].
- 3.
- Alkaline and Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (AFC/MCFCs):
While AFC and MCFC technologies have been demonstrated in auxiliary systems, their adoption remains limited compared to PEMFCs and SOFCs due to technical and operational challenges [72].
Fuel cells are increasingly integrated into hybrid systems combining batteries, supercapacitors, and waste heat recovery technologies. These configurations enhance energy efficiency, stabilize power quality, and reduce underwater radiated noise, maintenance requirements, and air emissions [30,130]. Hybrid SOFC systems have shown particular promise in meeting peak energy demands for domestic and short-sea shipping, accelerating progress toward zero-emission targets by 2050.
Current deployments highlight the growing role of fuel cells in maritime applications, with Proton PEMFCs emerging as the most widely implemented technology, featured on 23 vessels with power capacities ranging from 5 to 3200 kW, and often integrated with battery storage systems to enhance dynamic performance [72]. In contrast, SOFCs, known for their high efficiency and suitability for combined heat and power generation, have been demonstrated on only two vessels with power capacities between 20 and 50 kW, a limitation attributed to their lower volumetric and gravimetric power densities [131]. Despite their potential, fuel cell adoption in shipping faces significant barriers, including high costs, durability concerns, and infrastructure limitations. Technological advancements, cost reductions, and supportive policy frameworks will be critical to overcoming these challenges and unlocking fuel cells’ full potential for maritime decarbonization.
Hydrodynamic Optimization in Shipping
Hydrodynamic optimization offers several avenues for enhancing energy efficiency in shipping, including the development of optimized hull designs, the use of lightweight construction materials, advancements in propeller and propulsion systems, reduction in frictional resistance, and improvements in wake flow dynamics. These measures contribute to lower fuel consumption and reduced GHG emissions, aligning with global decarbonization efforts in the maritime industry.
- Optimized Hull Designs
The design and shape of a ship’s hull are pivotal in determining its hydrodynamic performance. By employing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and model testing, hull designs can be optimized to minimize drag and resistance, thereby improving fuel efficiency [134]. Key features, such as smooth hull surfaces, streamlined shapes, and the inclusion of bulbous bows, have been shown to reduce resistance and enhance hydrodynamic efficacy. These designs contribute directly to improved operational efficiency, particularly in long-distance sea routes where small improvements in drag reduction can result in significant fuel savings [135].
- Propeller and Propulsion Design
Hydrodynamics also play a crucial role in the optimization of propulsion systems. The design of a ship’s propeller, including blade shape, pitch, and diameter, is critical for maximizing thrust efficiency while minimizing energy consumption [136]. Advanced methodologies such as CFD and model testing facilitate the refinement of propeller designs, leading to reduced hydrodynamic losses and enhanced energy efficiency. By optimizing these systems, shipping companies can achieve substantial reductions in fuel use and operating costs, particularly for vessels that operate at varying speeds and under different load conditions.
- Frictional Resistance Reduction
Frictional resistance is a major contributor to the overall resistance experienced by a vessel, especially at lower speeds [137]. This resistance directly impacts the power required to propel the ship, thus influencing both fuel consumption and energy efficiency. Hull design plays a key role in minimizing frictional resistance; smooth surfaces and streamlined shapes help to reduce drag [138]. Additionally, applying specialized hull coatings and adhering to regular cleaning protocols are essential strategies for maintaining low frictional resistance.
Emerging technologies, such as air bubble technology, also provide promising solutions for reducing frictional resistance [139]. By introducing air bubbles along the hull’s surface, these innovations reduce friction and improve the vessel’s overall hydrodynamic performance. This technology has been demonstrated to offer significant energy savings, particularly in commercial shipping operations.
- Air Lubrication Systems
Air lubrication systems are gaining recognition as a promising energy-efficient technology for reducing GHG emissions in the maritime sector. Currently, approximately 0.3% of the global fleet employs this technology, with growing adoption particularly on larger and faster vessels, such as passenger ships, cruise liners, and Ro/Ro vessels [52,55]. Its versatility enables application on both new builds and existing vessels as a retrofit solution. As of 2023, approximately 250 vessels have integrated air lubrication systems, reflecting increasing industry interest [55].
The system operates by injecting a layer of air bubbles beneath the ship’s hull, reducing hydrodynamic friction between the hull and seawater. This process minimizes resistance, decreases turbulence within the boundary layer, and enhances hydrodynamic performance [71,140,141].
There are three primary methods for generating the bubble layer, namely the air cavity method, air film method, and small bubble method. The small bubble method—which utilizes micro-bubbles and requires minimal hull modifications—has emerged as the most widely adopted due to its simplicity and effectiveness [142,143,144]. Scaled model tests demonstrate that air lubrication systems can deliver 4–15% energy efficiency improvements, depending on vessel type and operating conditions [145,146]. Additionally, the technology has been shown to reduce underwater radiated noise by more than 10 dB, offering environmental benefits beyond fuel savings (See Figure 5).
Figure 5.
The air lubrication system performance. Source: [140,147].
Wake Flow Enhancement in Shipping
Enhancing wake flow is essential for improving a ship’s hydrodynamic efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. Wake flow refers to the disturbed water patterns created by a moving vessel, particularly in the trailing region. By optimizing these flow patterns through advanced hydrodynamic principles and technologies, the maritime industry can significantly reduce fuel consumption, lower emissions and underwater noise, and promote sustainability in marine transportation [148].
- Energy-Saving Devices (ESDs) and Propulsion Improvement Devices (PIDs)
Energy-saving devices and propulsion improvement devices play an important role in boosting the energy efficiency of ship operations by addressing critical aspects such as hull shape, propulsion mechanisms, and vibration reduction [55]. These devices can be categorized into three groups: those positioned in front of the propeller to optimize inflow, devices that capitalize on the rotational flow of the propeller slipstream, and composite ESDs that combine features from both categories [149].
A significant milestone has been reached with the widespread adoption of ESDs and PIDs, with 6398 vessels—representing approximately 28.1% of total fleet tonnages successfully integrating these technologies [150]. Some of the most advanced innovations include propeller ducts, twisted rudders, gate rudders, bulbous bows, propeller cap turbines, pre-swirl stators, Mewis ducts, and propeller boss cap fins. These technologies have demonstrated considerable potential for enhancing energy efficiency, delivering energy savings ranging from 1.5% to 25%, and reducing URN from commercial vessels by up to 5 dB [9,151,152,153,154,155,156,157] (Figure 6).
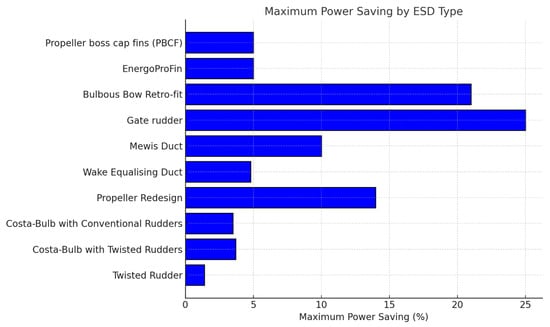
Figure 6.
Maximum energy savings from ESD for ships. Sources: [152,153,157].
When assessing the cost-effectiveness of these technologies, several key factors must be considered. These include the initial capital investment, the specific technology being implemented, the size of the vessel, the fuel savings achieved, and current fuel prices [2]. Crucially, many of these technologies offer a relatively short payback period, making them an economically viable option for ship operators seeking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce underwater radiated noise emissions.
Waste Heat Recovery (WHR)
Waste Heat Recovery is a technology employed across various industries to capture and repurpose heat that would otherwise be lost during industrial processes. In the maritime sector, WHR systems harness waste heat generated by ships’ internal combustion engines, significantly improving energy efficiency.
Prior to installing WHR systems, conducting an energy balance analysis is essential for optimizing performance [158]. This is particularly important because 48–51% of fuel energy is lost to the environment through exhaust gases and cooling water in marine engines [159,160]. WHR systems have been shown to reduce fuel consumption by up to 12%, depending on ship type [161]. The amount of energy recovered depends on engine size, operational conditions, and ambient temperature. Furthermore, when combined with strategies such as derating, slow steaming, and wind-assisted propulsion, WHR can yield an additional 1–3% fuel savings [162].
Among various WHR technologies, the Organic Rankine Cycle stands out for its ability to utilize low-temperature heat sources for power generation. Unlike the conventional Rankine Cycle, which requires high-temperature heat sources and uses water as the working fluid, the ORC operates efficiently with lower-temperature waste heat [163,164].
In domestic shipping, WHR systems can play a role in reducing emissions and enhancing energy efficiency depending on type and size of vessels. Studies highlight the substantial potential for recovering waste heat from exhaust gases and other sources in diesel engines used in passenger ferries [165,166]. Additionally, WHR systems can harness waste heat from fuel cells, further improving fuel conversion efficiency within fuel cell systems [167,168].
Onboard Carbon Capture (OCC)
Onboard Carbon capture (OCC) in shipping involves capturing and storing CO2 emissions produced by ships, a technology aimed at reducing the industry’s carbon footprint and advancing net-zero shipping goals [60]. OCC captures CO2 from exhaust gases post-fuel combustion. Several methods exist for this, including chemical absorption, membrane separation, pressure swing adsorption, and cryogenic capture. Among these, chemical absorption with amine solvents is the most mature and widely adopted method, especially in shore-based applications [55].
Given the limitations of achieving carbon neutrality through alternative fuels alone, combining OCC technology with improved energy efficiency and alternative fuels can advance decarbonization efforts [56]. However, widespread adoption of CCS in shipping faces significant barriers, including high costs, substantial investments in the CCS value chain, the energy penalty for operating capture units, and the costs associated with CO2 transport and storage [60]. The feasibility of CCS largely depends on its cost-effectiveness, influenced by fuel penalties and the economic viability of CO2 storage solutions [58,61,169,170].
Despite these challenges, tangible progress is being made to demonstrate the feasibility of OCC in maritime applications—particularly within the deep-sea shipping sector. For instance, Wärtsilä’s pilot project aboard the Clipper Eos ethylene carrier targets a 70% reduction in CO2 emissions, representing a significant milestone in validating the technical viability of OCC systems [55]. Similarly, Stena Bulk conducted a real-world demonstration by retrofitting the Stena Impero with an onboard carbon capture prototype to assess operational performance. The trials successfully demonstrated the capability to capture CO2 directly from the ship’s exhaust stream, reinforcing the potential for scalable deployment of OCC in commercial fleets. Integration with shore-based CCS infrastructure is expected to further enhance operational logistics, crew training, and system optimization, paving the way for broader adoption across the sector.
However, OCC technology has yet to be implemented in domestic shipping due to smaller vessel sizes and shorter voyage distances, which limit the practicality of large-scale carbon capture systems. Additionally, the infrastructure required for CO2 storage and transportation, which is more developed for deep-sea shipping routes, remains underdeveloped in domestic and coastal regions [60].
3.1.3. Ports
Approximately 5% of total shipping CO2 emissions occur within ports [171]. Recognizing this, the IMO highlights the pivotal role of ports in achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. This goal involves implementing shore-based electricity supplies, ideally sourced from renewable energy to power vessels during port stays, developing efficient bunkering infrastructure for alternative fuels, promoting sustainability through incentive programs, and optimizing Just-In-Time (JIT) operations [1].
To effectively support maritime decarbonization goals, ports must evolve from traditional logistics hubs into energy hubs [65,172]. The growing importance of sustainable port infrastructure in facilitating this transition is widely acknowledged [173]. While ports’ role in decarbonization was first recognized through IMO resolution MEPC 323(74) [174] in 2019, their significance has been elevated under the updated IMO GHG emission strategy, which mandates the facilitation of alternative fuels for vessels.
The effective management of zero-emission initiatives can be divided into three areas: the port-ship interface, port operations, and the port-city interface [65]. Balancing these areas while addressing trade-offs among economic growth, social and environmental priorities, and regulatory compliance presents considerable challenges. Overcoming these requires systematic and transdisciplinary approaches [34]. By leveraging modern technologies and adopting innovative operational strategies, ports can enhance energy efficiency, accelerate the transition to zero emissions, and improve environmental performance [175,176,177,178].
The shift from a carbon-intensive port industry, traditionally reliant on fossil fuels, to a low-carbon model can be achieved through integrating renewable energy sources, electrifying equipment, adopting carbon-neutral fuels, and implementing advanced power distribution and energy management systems [2]. This transformation is primarily driven by technological innovation and the optimization of port operations.
The transition toward zero-emission ports can be further accelerated through automation, digitalization, and hybrid systems, alongside adopting cleaner fuels such as hydrogen and renewable energy sources [65,179,180]. Moreover, integrating operational and policy measures, aligned with incentive programs, circular economy principles, and international certifications such as ISO 50001 and ISO 14001, can expedite the shift toward sustainable port operations [181,182].
Shore Power
The implementation of shore power technology has the potential to cover up to 7% of the total energy consumption of ships while at ports [56]. This solution is particularly effective in mitigating air emissions in port areas, especially when the electricity supplied from the grid is sourced from cleaner, environmentally friendly alternatives compared to onboard generation [116]. In addition to reducing air pollution, shore power significantly decreases underwater noise pollution, enhancing the overall environmental performance of port operations [7,30,35]. The feasibility of adopting shore power depends on regional air quality regulations and the emissions intensity of the electricity supplied to ports [183].
Shore power technology has gained substantial traction in cruise ports and ferry terminals, where electricity demand is high due to hotel operations and the increasing adoption of hybrid and battery propulsion systems in ferry services [184]. Scandinavian ports have led the way in adopting shore power. The Port of Gothenburg has been a pioneer, followed by ports such as Ystad, Oslo (specifically for cruise terminals), and the Port of Rotterdam (for roll-on/roll-off vessels) [185]. Studies highlight the significant emissions reduction potential of shore power. For example, widespread adoption across European ports could cut approximately 800 kilotons of CO2 emissions annually [186]. A notable success is Stena Line, which implemented shore power systems for 13 ships at seven terminals, achieving savings of 3800 tons of oil, 12,340 tons of CO2, and 8 tons of SOx in 2018 [187].
Despite its significant potential to reduce emissions at the port-ship interface, as illustrated in Table 7, the implementation of shore power systems faces several challenges, which can be categorized as follows:

Table 7.
Challenges in using OPS at ports. Source: [65,188,189].
Equipment
Effective management of port operations is essential for maximizing productivity and optimizing the use of land, equipment, fuel, and human resources, thereby accelerating the decarbonization of the maritime industry [190]. Ports rely on a variety of equipment for efficient cargo handling, including Quay Cranes (QC) and Ship-to-Shore Cranes (STS) for loading and unloading, Rail-Mounted Gantry Cranes (RMG) and Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes (RTGC) for container stacking, Yard Trucks (YT) for horizontal container transfers, and Straddle Carriers (SC) for both stacking and transporting containers [191,192,193].
With advancements in automation and digitalization, many ports are integrating automated systems, such as QCs, STSs, RMGs, YTs, and SCs. This shift enhances operational efficiency and reduces reliance on manual labor [194,195]. Concurrently, ports are transitioning to cleaner and zero-emission fuels—including electricity, liquefied natural gas, and hydrogen—to align with sustainability goals [196]. This dual approach—combining automation with cleaner fuel adoption—not only improves efficiency but also drives significant progress toward sustainable port operations.
For instance, the Port of Felixstowe has invested in 48 battery-powered terminal tractors and 17 zero-emission Remote Controlled Electric Rubber-Tired Gantry (ReARTG) cranes. These innovations are projected to save 6662 tons of CO2 and 59.38 tons of NOx emissions annually. Since 2015, the port has achieved a 30% reduction in its carbon footprint and aims for an additional 20% reduction within the next five years [197].
Additionally, adopting electric, hybrid, and hydrogen-powered service vessels, such as pilot boats and tugs, can further reduce port-related emissions. For example, the Port of Antwerp–Bruges operates the Hydrotug, the world’s first hydrogen-powered tugboat. Equipped with two BeHydro V12 dual-fuel engines, it runs on hydrogen and conventional fuels. By storing 415 kg of hydrogen onboard, the Hydrotug offsets equivalent to 350 cars annually [198].
Lighting
Adequate and well-designed lighting is essential for ensuring safety and operational efficiency in port areas, particularly during nighttime operations. Effective lighting reduces the risk of accidents, enhances visibility for personnel, and strengthens overall port security. It also improves visibility in critical areas such as loading and unloading zones, container yards, and transportation routes, facilitating more efficient cargo handling and reducing vessel turnaround times [199].
The adoption of energy-efficient lighting technologies, particularly Light-Emitting Diode (LED) fixtures, offers significant advantages. LEDs are known for their long lifespan, reduced maintenance needs, and superior illumination quality, making them a sustainable alternative to traditional lighting systems such as incandescent and fluorescent lights. Additionally, smart lighting systems equipped with sensors and controls can optimize energy usage by dynamically adjusting lighting levels based on ambient light, occupancy, or operational demands. Such systems have demonstrated energy savings of 50–60% [200]. For example, the ECT Delta terminal in the Netherlands reported potential annual electricity savings of EUR 300,000 after implementing a lighting control system [201].
Furthermore, integrated lighting systems can synchronize with automated port operations, enabling programmed illumination during ship arrivals or cargo movements. This integration contributes to a streamlined workflow and enhances energy efficiency. Leveraging renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, combined with energy storage solutions like batteries, further reduces reliance on traditional energy grids, enhancing the overall sustainability of port operations [2]. The adoption of energy-efficient lighting aligns ports with global environmental objectives, supporting initiatives to reduce carbon emissions and minimizing the ecological footprint of maritime activities.
Micro and Smart Grid
Energy management—encompassing the control and optimization of energy demand, consumption, supply, and storage—is a critical component in enhancing the energy efficiency of ports. Energy demand in ports stems from various sources, including operational equipment, container refrigeration, shore power systems, and buildings, while energy supply may originate from the electrical grid or renewable energy systems integrated into port infrastructure [116,202].
The integration of smart grids and microgrids offers a comprehensive solution for optimizing energy use in ports. This strategy improves energy efficiency, facilitates the incorporation of renewable energy sources, and supports the transition toward zero-emission maritime operations [203].
Microgrids function as localized, decentralized energy generation systems within ports, offering greater efficiency, reduced transmission losses, and enhanced resilience compared to centralized grids [5]. When paired with energy storage solutions such as batteries, microgrids allow ports to store excess energy generated during periods of low demand or high renewable energy production. This stored energy can be utilized during peak demand, ensuring a stable and reliable supply [204]. In cases of grid disruptions or emergencies, microgrids can operate autonomously, providing uninterrupted power to critical port operations and ensuring resilience, functionality, and security [205,206].
Smart grids enable real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution within ports, facilitating dynamic energy management. This adaptability ensures efficient energy allocation, reduces waste, and optimizes energy use based on current demand and supply conditions. Smart grids also support demand response programs, allowing ports to adjust energy consumption in response to electricity price fluctuations or renewable energy availability. This flexibility not only lowers costs but also aligns operations with sustainable practices [207]. Additionally, smart grids seamlessly integrate renewable energy sources—such as solar and wind power—contributing to a cleaner energy mix and advancing the goal of zero-emission operations [116].
The incorporation of smart technologies in port facilities—such as energy-efficient lighting, intelligent cargo-handling equipment, and automated systems—further enhance energy conservation efforts. Leveraging data analytics and artificial intelligence allows ports to analyze consumption patterns, identify inefficiencies, and implement informed decisions to optimize energy use. Moreover, the electrification of port vehicles and equipment—supported by smart grids and microgrids—reduces reliance on fossil fuels and mitigates emissions. This transition extends to cargo-handling equipment, trucks, and other vehicles used in port operations, driving sustainable and low-carbon port activities.
Renewable Energy
Table 8 outlines the renewable energy options available for ports to reduce their carbon footprint. Integrating renewable energy is a critical step toward enhancing the sustainability of port operations, as evidenced by the growing adoption of renewable energy practices across various ports [208]. Transitioning from conventional to sustainable energy sources offers ports a significant opportunity to mitigate GHG emissions, improve energy resilience, reduce operational costs, and showcase environmental leadership within the maritime industry [65]. The strategic combination of multiple renewable energy sources serves as the cornerstone for decarbonization efforts and the establishment of sustainable port operations.

Table 8.
Renewable energy solutions for ports.
While the adoption of renewable energy in ports faces challenges such as high capital costs and technological complexities, several factors are accelerating this transition. These include heightened community awareness, stricter environmental regulations, and strong organizational commitments to environmental responsibility [209].
A 2019 report by the European Sea Port Organisation (ESPO) [210] highlighted these trends:
- 38% of member ports had invested in wind energy,
- 31% adopted solar energy solutions,
- 26% incorporated biomass into their energy mix, and
- Only 2% pursued wave energy, indicating limited adoption of this option.
This data underscores the increasing role of renewable energy in ports and the varied approaches being employed to support the broader goals of decarbonization and climate change mitigation.
In addition to harnessing renewable energy, the adoption of smart grid technologies enhances the efficient management and distribution of energy within ports. By integrating energy storage solutions, such as batteries, ports can store excess energy generated during periods of peak renewable energy production [211,212]. This stored energy can then be utilized during periods of low renewable energy availability, ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply. The strategic combination of renewable energy sources, smart grid technologies, and energy storage systems positions ports as leaders in sustainable practices within the maritime industry (See Figure 7).
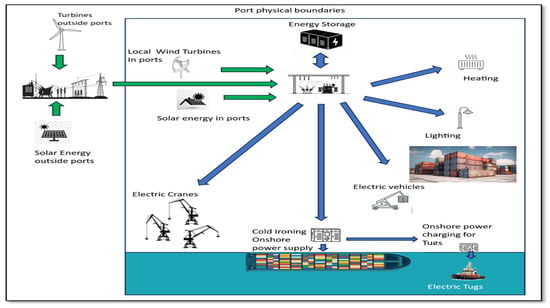
Figure 7.
Using renewable energy in ports.
Alternative Fuel
The adoption of clean fuels in ports is a crucial strategy for achieving zero emissions, significantly enhancing environmental sustainability while reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels. This approach involves the use of various alternative energy sources, underscoring commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable practices within the maritime industry. Clean fuels such as biofuels, LNG, renewable energy, and hydrogen play a key role in reducing carbon emissions from port operations and maritime shipping [213]. Table 9 illustrates the key aspects of using clean fuels in ports to achieve zero emissions.

Table 9.
The key aspects of using clean fuels in ports.
Port as Energy Hub
Ports are critical nodes in the maritime sector and play a central role in advancing the industry’s decarbonization efforts. As the focus shifts toward alternative fuels to achieve zero-emission shipping by 2050 and meet the IMO’s target of utilizing 5–10% of energy from carbon-neutral sources by 2030, ports must evolve from traditional cargo handling facilities into integral energy hubs within the maritime supply chain [65].
At the core of this transformation is the smart grid, which manages electricity flow between the national grid, microgrids, and renewable energy sources. In this integrated system, the information flows among the smart grid, the national grid, and microgrids that include power plants, renewable energy sources, and conventional generators. Simultaneously, the production and distribution of electricity from renewable sources, power plants, or conventional generators, which are delivered directly to end-users—such as vehicles, cranes, trucks, forklifts, and buildings—or stored in energy-saving systems. The smart grid ensures efficient coordination of this system, while Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) regulate electricity supply and enable autonomous operation of microgrids.
Conventional fuels or waste generated at ports can act as primary energy sources for power plants [178]. Ports can produce blue hydrogen through gasification processes and integrate Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) technologies to generate e-methanol [60]. Additionally, green hydrogen can be produced via electrolysis powered by renewable energy. By combining hydrogen with nitrogen, ports can synthesize ammonia [55]. This cycle continues with the production of hydrogen from liquid ammonia, which has a high hydrogen capacity, supporting various port operations and enabling intermodal transportation—including ships and trains—through clean fuels [155].
By distributing clean fuels across sectors, ports solidify their role as vital energy hubs, enhancing the maritime energy supply chain and supporting the transition to zero-emission shipping in alignment with the IMO’s revised GHG strategy [2,65].
4. Discussion and Road Map
4.1. Discussion
Although the operational and technological challenges differ from those in deep-sea shipping, shorter domestic routes offer an ideal platform for piloting and deploying innovative solutions. There is not a silver bullet, or a one size fit all solution for decarbonization of domestic and coastal shipping. Given the diversity of domestic shipping operations, a combination of tailored strategies, cross-sectoral collaboration among stakeholders, and deployment of holistic, systematic, and transdisciplinary approaches is vital to accelerate the adoption of zero-emission technologies [34].
- Technology
Evidence suggests that, similar to international shipping, the adoption of zero carbon-neutral fuels and energy sources is essential for the decarbonization of domestic shipping. The selection of alternative fuels for this sector must be informed by life-cycle assessments, particularly regarding their potential to reduce carbon emissions equivalent from well to tank wake [54]. Developing a strategic roadmap for future fuel adoption in the domestic sector also necessitates alignment with national energy policies. This highlights the need to situate the alternative fuel strategy within the broader energy transition framework, encompassing considerations related to energy production, storage, and supply chain factors that are critical for evaluating the feasibility and long-term viability of associated investments [2]. Such an approach enables a more regional assessment of fuel availability and economic viability. Nonetheless, the integration of alternative carbon-neutral fuels and energy systems faces several multidisciplinary barriers, including production uncertainties, inadequate infrastructure, financial limitations, and regulatory gaps. As a transitional measure, improving energy efficiency—through strategies such as speed optimization and the related technologies—remains vital [155]. In this situation deploying energy efficiency measures and ZnZ technology can play an important role to reduce emissions. However, deploying energy-efficient technologies also faces obstacles such as limited funding, technology immaturity, insufficient legislation, and a lack of trained personnel [2], but considering the low hanging fruit and cost-effective energy efficiency measures such as hull and propeller coatings and cleaning, and machinery maintenance remain practical options to enhance domestic fleet efficiency [116].
Advancements in hull design, propeller optimization, and propulsion systems can yield efficiency gains of up to 25% [119]. However, the high capital costs associated with these technologies, coupled with the prevalence of aging fleets, present considerable barriers—particularly in regions with constrained financial capacity. In such contexts, fleet renewal through the acquisition of second-hand but more energy-efficient vessels may serve as a pragmatic interim solution, especially if supported by targeted governmental financial mechanisms. Additionally, strategies that leverage economies of scale can improve overall fleet efficiency by up to 30% [41]. Nonetheless, realizing such gains is contingent upon adequate port infrastructure and sufficient cargo or passenger demand, which may be lacking in low-traffic or under-resourced regions [43].
- Alternative fuel and energy sources
Regions with abundant renewable energy resources could become key energy hubs for the maritime industry. Investigations into energy production, supply, storage, and use are essential for devising future energy strategies and evaluating the feasibility of pilot projects like green corridors [60]. As an example, Africa and the Caribbean regions are particularly well-positioned to benefit from solar technologies. The specific characteristics of domestic shipping—low power demands, short voyage distances, and extended port stays—make it an ideal candidate for solar energy adoption in these regions. In addition, given the rising costs of conventional fuels and the increasing emphasis on zero-emission strategies, wind-assisted propulsion systems represent a cost-effective and scalable solution for decarbonizing smaller and domestic shipping segments. Their role will be critical as the industry transitions toward achieving zero emissions by 2050 [2]. Wind-assisted propulsion has demonstrated fuel savings of up to 25% [219]. When combined with strategies such as speed reduction, hull optimization, and weather routing, savings can be even greater, depending on vessel characteristics and trade routes [21]. While the technology may have more benefits in larger vessels, it has the potential to be deployed in small vessels, especially fishing vessels [2].
Short-sea shipping offers a favorable environment for deployment of innovative ZnZ fuels and technologies compared to deep-sea shipping, thanks to shorter routes, fixed schedules, and localized ports. These characteristics facilitate the adoption of carbon-neutral fuels and energy solutions, such as hydrogen, methanol, LNG, fuel cells, and electrification [2,220]. In Europe, these alternative fuels have gained traction in the domestic sector. However, market uncertainties persist, particularly concerning the higher costs and price volatility of ZnZ fuels and technologies [57,221].
To reduce the carbon footprint of regional domestic ferry fleets in the short term, retaining the existing fleet and engine technologies while transitioning to sustainable biofuels, particularly biodiesel, is recommended. Biodiesel, already widely used in road transport, presents a feasible short-term solution for decarbonizing domestic shipping, offering advantages over alternatives such as e-fuels, LNG, and OCCS [99]. Biofuels require minimal retrofitting of ship engines and bunkering infrastructure, avoiding significant capital expenditure in the domestic sector [222]. Additionally, they provide a pathway to transition toward e-fuels in the future [113]. Promoting biofuel production and cultivation in regions with domestic ferry operations can reduce GHG emissions.
In addition, hydrogen plays a pivotal role in meeting the IMO’s ambitious decarbonization targets. Its flexibility, scalability, and capacity to enable zero-emission energy generation to position it as a viable long-term solution for domestic shipping, significantly contributing to the sector’s sustainability transition. Hydrogen-based fuel cell technologies, in particular, offer substantial potential for zero-emission propulsion in domestic fleets, underscoring their transformative capacity in short-sea and inland waterway operations [2]. However, high capital costs and the absence of supporting infrastructure remain major barriers to widespread adoption in the short-sea sector.
Meanwhile, green methanol—produced from renewable energy sources—also shows strong potential as an alternative marine fuel over the long term. Its compatibility with existing engines and relatively easier handling makes it a promising candidate for domestic vessels. Nevertheless, several challenges must be overcome, including the age and configuration of existing fleets, the costs associated with retrofitting, infrastructure development, and the scalability of sustainable methanol production [2].
In contrast, LNG and ammonia are less suitable for domestic shipping in the region. While LNG has been adopted as a transitional fuel in international shipping, its application in domestic fleets is constrained by smaller vessel sizes and high capital costs. Northern European shipping companies, supported by substantial resources, have invested in LNG-powered vessels and bunkering infrastructure, but similar conditions do not exist in other regions [223]. Ammonia, meanwhile, poses safety and environmental risks, including toxicity and potential leakage, making it impractical for domestic shipping, which frequently operates in densely populated areas [2].
- Electrification
The rapid advancements in battery and supercapacitor technologies, alongside declining costs, are accelerating the adoption of electric propulsion systems. However, achieving their full potential requires sustainable infrastructure, particularly onshore power supply at ports, and a comprehensive assessment of lifecycle emissions [65]. In the domestic shipping sectors, electric propulsion represents a pivotal solution for achieving zero-emission goals, aligning with the IMO 2050 decarbonization targets. Electric propulsion systems, powered by renewable energy, offer significant emission reduction potential, with projected reductions of 51.1% in the Caribbean and 62% in Africa domestic sector [2]. This approach not only minimizes emissions at sea but also reduces the environmental impact of port operations, which contribute to maritime emissions [65,171]. However, the deployment of electrification technologies necessitates significant capital investment, the establishment of sustainable port infrastructure—such as shore power systems—and the presence of a robust national electricity grid [116]. Moreover, it is essential that the electricity supplied by the national grid has a lower carbon intensity than the onboard energy sources it seeks to replace [65]. Furthermore, the integration of innovative design approaches—such as lightweight hull structures using carbon fiber or multihull configurations—can help mitigate challenges related to vessel weight and limited space [120].
- Ports
Ports are critical nodes connecting cities and facilitating international trade, yet they contribute approximately 5% of total shipping CO2 emissions [171]. Domestic vehicles, with their longer port stays, are responsible for a higher share of these emissions compared to international shipping. Ports also play a pivotal role in the transition to zero-emission shipping, as emphasized in IMO’s resolution. This highlights the need for sustainable infrastructure such as shore power systems, secure and efficient bunkering infrastructure for alternative fuels, incentive programs, and improved just-in-time policies to promote sustainable and carbon-free shipping practices [1].
Decarbonizing ports can be categorized into three key areas: the port–ship interface, port operations, and the port–city interface [116]. Achieving zero-emission operations in ports requires comprehensive databases and inventories to track air emissions and their sources. While some countries have initiated such measures, many states lack these initiatives for domestic shipping. The transition to zero-emission ports can be significantly advanced through automation, electrification, digitalization, and hybridization, combined with the adoption of cleaner and more sustainable alternative fuels [2].
At the port–ship interface, accelerating the adoption of alternative carbon-neutral fuels and energy infrastructure is crucial. Ports must shift from being seen solely as cargo hubs to functioning as energy hubs [65]. Battery-powered vessels hold great promise in regions with renewable energy sources, but the absence of sustainable infrastructure, such as shore power systems, remains a significant challenge. While a few ports have adopted these systems, their use primarily supports auxiliary engines of small vessels [2]. Barriers to widespread adoption include high costs, limited funding access, and inadequate national grid capacity [116]. A multi strategy combining automation, digitalization, and the adoption of alternative zero-emission fuels—such as electricity and hydrogen—can enhance efficiency and reduce air emissions from port activities. Using electric pilot boats and tugs, alongside renewable energy to power port buildings and lighting, can significantly improve sustainability. Leveraging the regions’ abundant renewable energy potential and integrating it with smart grid technologies can further overcome the limitations of national grid capacity and advance port decarbonization efforts [65,116].
- Policy
The divergence between international regulatory frameworks and domestic maritime governance reveals a critical gap that undermines the coherence and effectiveness of decarbonization efforts, particularly in aligning national policies with globally mandated climate objectives and enforcement mechanisms. Regulations must be tailored to each state’s unique circumstances and preceded by comprehensive impact assessments. These evaluations should consider the complexities of the maritime sector, including human factors, technological advancements, policy frameworks, operational measures, and economic conditions [3] (given the inherent complexities of the maritime sector, it is essential to identify and critically examine the principal barriers to achieving zero-emission targets. In this regard, Supplementary Document 2 in the study outlines the key challenges faced by SIDSs and LDCs across various thematic domains—including economic, technological, regulatory, and human capacity—and proposes actionable solutions to support the decarbonization of domestic and short-sea shipping). A state-specific, well-informed approach ensures the effective implementation of measures, ultimately expediting the transition to zero-emission domestic shipping.
Domestic and coastal shipping plays a critical role in ensuring food and energy security, creating jobs, and enhancing connectivity, particularly for SIDSs and LDCs. However, it contributes to 26.2% of shipping GHG emissions when considering domestic voyage-based calculations and 9.2% when assessed solely on ships exclusively engaged in domestic trade [1]. While decarbonization measures in international shipping—such as EEDI, EEXI, SEEMP, CII, the GHG pricing mechanism, and the forthcoming GFS—are expected to exert some indirect influence on domestic emissions, the residual 9.2% of emissions from purely domestic fleets remains outside the scope of the IMO’s regulatory framework [2] and demands tailored policy action. Without specific interventions, the relative share of domestic emissions in the overall maritime sector will continue to grow.
Achieving zero emissions in domestic shipping requires robust political commitment, strategic regulatory planning, and integrated financial mechanisms at the national level. Developing National Action Plans for domestic maritime decarbonization is a pivotal step—but their successful implementation hinges on access to sufficient financial and institutional resources [116]. In this context, aligning NAPs with Nationally Determined Contributions under the Paris Agreement can unlock additional international support and elevate domestic shipping within national climate agendas.
Given the estimated USD 1.4 trillion needed globally to halve shipping emissions by 2050, the mobilization of blended finance instruments is essential—particularly for emerging maritime nations. Public–private partnerships, climate finance (e.g., Green Climate Fund, World Bank maritime initiatives), and concessional lending schemes can de-risk investments and support infrastructure development. At the same time, private-sector incentives, such as tax relief, emissions-linked port fees, or performance-based subsidies, can catalyze innovation uptake among domestic operators. These mechanisms are especially critical for SIDSs and LDCs, where fragmented fleets, thin markets, and limited credit access hinder investment readiness.
The study also acknowledges the growing importance of carbon pricing, both as a regulatory tool and as a financing mechanism. However, its direct application in low-income and small maritime economies may be constrained by administrative capacity and market fragmentation. In such contexts, alternative approaches, including shadow pricing, emissions offset schemes, and differentiated levy structures—could offer more pragmatic, transitional solutions while reinforcing the polluter-pays principle.
Public funds and international climate finance—such as those administered through the IMO’s fund—should be strategically directed across the maritime value chain, including vessels, ports, bunker fuel producers, and distribution networks, to support the deployment of energy-efficient technologies and the adoption of ZnZ emission fuels and systems. To mitigate the risk of cost pass-through to consumers, governments must design well-calibrated incentive regimes that protect early adopters from competitive disadvantages. Such policy frameworks not only reflect strong governmental commitment but also provide regulatory certainty, thereby enabling long-term planning by shipowners and preserving competitiveness in a future low-carbon maritime economy.
Furthermore, regulatory adaptation must be synchronized with broader national development goals. Aligning domestic maritime policies with NDCs not only enhances international credibility but also fosters the diffusion of green technologies and supports a coherent, whole-of-economy approach to decarbonization. In doing so, domestic shipping can transition from being an overlooked emissions source to a strategic enabler of sustainable development and climate resilience.
- Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Decarbonization Measures
To enhance the clarity of the comparative analysis and support evidence-based decision-making, a radar chart (Figure 8) has been developed to visualize the prospects of 17 key decarbonization measures. The chart evaluates each measure across four dimensions: (i) implementation readiness, (ii) scalability, (iii) GHG reduction potential, and (iv) applicability to domestic and short-sea shipping. These criteria reflect a balance between technological maturity, deployment feasibility, and environmental impact. The comparative visualization reveals that operational and port-based measures such as speed reduction, shore power, and smart port infrastructure demonstrate high readiness and applicability, making them viable short-term interventions for domestic fleets.
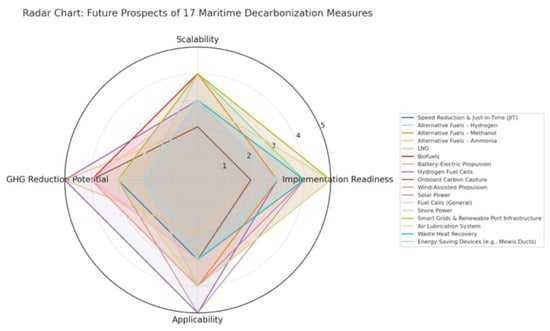
Figure 8.
Future prospects of maritime decarbonization measures.
Among alternative fuels, biofuels emerge as a strong candidate due to their high implementation readiness and compatibility with existing engines, especially for transitional use in domestic contexts. Methanol also shows promising scalability and moderate GHG reduction potential, with increasing commercial interest and ongoing pilot projects. In contrast, hydrogen and ammonia offer substantial long-term decarbonization potential but are currently constrained by low readiness, safety concerns, and a lack of bunkering and regulatory infrastructure. LNG, while mature and scalable, offers only marginal GHG benefits and may not align with long-term net-zero goals unless paired with carbon capture systems.
Battery-electric propulsion and fuel cells are particularly applicable to short-range vessels, especially in regions with clean electricity grids, though their scalability is influenced by energy density limitations and charging infrastructure. Finally, onboard carbon capture, though theoretically impactful for reducing CO2 emissions from fossil-fueled ships, remains at a low technology readiness level and is generally unsuitable for smaller domestic vessels due to space, energy, and cost constraints.
Overall, the chart illustrates that no single measure can achieve the sector’s decarbonization goals in isolation; rather, a portfolio approach, combining mature short-term solutions with scalable low- and zero-carbon technologies, is required to ensure a just and effective energy transition. The policymakers must consider the inherent trade-offs between technologies such as biofuels and electrification. For instance, biofuels may leverage existing fueling infrastructure and offer drop-in compatibility with current engines, yet face concerns over supply chain sustainability, land-use competition, and price volatility. In contrast, electrification (via batteries or hybrid systems) offers a cleaner long-term pathway, but often requires major capital investment, grid upgrades, and reliable renewable electricity generation, which may not yet be viable in remote island economies. These trade-offs must be carefully weighed through region-specific techno-economic feasibility assessments, accounting for vessel type, operational range, energy availability, and regulatory readiness.
- Stakeholder Roles and the Enabling Ecosystem
Decarbonizing domestic and short-sea shipping is a deeply transdisciplinary and multi-actor challenge that requires cohesive alignment across regulatory, technical, financial, and operational domains [2]. A systematic mapping of key stakeholders highlights their distinct but interdependent roles in enabling the transition to zero-emission maritime operations.
Governments and regulators serve as foundational enablers, setting climate policy, providing fiscal incentives (e.g., subsidies or tax relief), and integrating shipping into NDCs [65]. Their commitment to long-term regulatory clarity is essential for de-risking private investment.
Shipowners and operators are responsible for implementing technical and operational measures on vessels, such as retrofitting, fuel switching, and adopting digital voyage optimization tools. Their investment decisions are strongly influenced by the availability of supporting infrastructure, fuel costs, and access to green financing.
Financiers and insurers play a critical role in bridging the capital intensity of green transitions. Blended finance, public–private partnerships, and ESG-aligned funds can help unlock investment in low-carbon vessels, port retrofits, and alternative fuel supply chains [116]
Classification societies act as independent technical authorities that certify the safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance of new technologies and vessel configurations. Their involvement is crucial for scaling alternative fuels, fuel cells, battery-electric propulsion systems, and onboard carbon capture solutions. Moreover, they contribute to setting global and regional standards (e.g., notations for alternative fuel readiness), de-risking innovation through pilot approvals, and ensuring interoperability across regulatory jurisdictions.
The effectiveness of maritime decarbonization efforts ultimately hinges on the coordinated action of this broader ecosystem, underpinned by transparent governance, knowledge sharing, and capacity building—particularly in emerging maritime regions [2]. Strengthening institutional collaboration across these actors is a prerequisite for achieving net-zero emissions by around the mid-century.
4.2. Roadmap
This roadmap functions as a scenario-based pathway, structured into short-, medium-, and long-term timeframes aligned with policy and technology readiness levels. It provides a phased strategic vision to guide implementation under varying degrees of feasibility, infrastructure development, and stakeholder capacity—particularly in domestic and short-sea shipping contexts.
Reducing air emissions from domestic and short-sea shipping requires a holistic, systematic, and transdisciplinary approach that incorporates all relevant stakeholders across the maritime value chain. As illustrated in Figure 9, the proposed roadmap outlines a phased strategy that integrates policy, technological innovation, port and shipyard transformation, and stakeholder engagement to accelerate the transition toward zero-emission shipping.
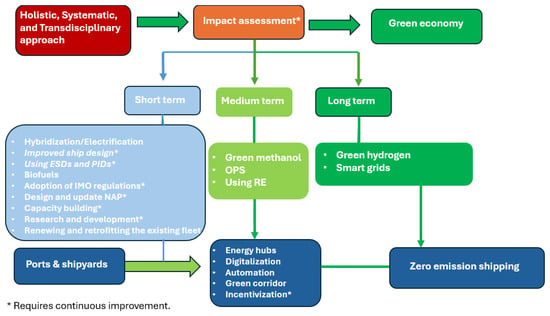
Figure 9.
A holistic roadmap for decarbonizing domestic and short-sea shipping.
The roadmap emphasizes the pivotal role of ports and shipyards as active players in driving decarbonization over the short, medium, and long term. It also situates the transition within the broader context of a green economy, underlining the significance of green supply chains, sustainable energy production, and integrated energy management systems. Prior to implementation, the roadmap stresses the necessity of conducting impact assessments to ensure the feasibility, effectiveness, and equity of proposed measures.
The timeframe and the associated costs for each phase vary across states and regions, depending on several factors such as the availability of sustainable infrastructure, the number, type, and size of vessels, as well as the prevailing economic conditions. In each phase—short-, medium-, and long-term—the implementation of technical and operational measures must be supported by the design and development of corresponding policy frameworks to ensure regulatory alignment, incentivize adoption, and facilitate effective enforcement.
Short-Term Measures:
Short-term strategies include the hybridization and electrification of vessels, improved hull and ship design, and the implementation of economies of scale policies. For larger vessels, operational measures such as speed optimization, structured maintenance programs, and the use of ESDs and PIDs—including bulbous bows, ducts, and fins—are recommended (certain measures, such as ship design and the implementation of energy efficiency technologies, require continuous improvement and refinement over time).
In addition, the integration of wind-assisted propulsion and the adoption of advanced biofuels are proposed. A key advantage of biofuels is their compatibility with existing engine technologies, allowing for near-term fuel substitution without requiring major retrofitting. However, to ensure true sustainability, such biofuels must be derived from renewable feed stock and produced using low-emission energy sources. Considerations of availability, scalability, and sustainability are essential.
- Medium-Term Measures
During the medium term, the roadmap recommends a shift toward low-carbon alternative fuels, notably green methanol, and scaling up the development of OPS infrastructure powered by renewable energy. Ports and shipyards should be transformed into energy hubs capable of producing, storing, and distributing alternative fuels, thereby supporting national commitments under NDCs within the Paris Agreement framework.
Further, digitization, automation, and the deployment of energy-efficient port equipment are prioritized. Establishing energy management systems and green supply chain policies within maritime operations is encouraged to drive continuous energy optimization.
- Long-Term Measures
In the long term, the transition to zero-carbon fuels, such as green hydrogen, is envisioned. The implementation of smart grid systems in ports and shipyards will be necessary to facilitate flexible, intelligent energy use. Simultaneously, sustained training and capacity building for maritime personnel at all levels—vessel crews, port managers, and policymakers—must be institutionalized to support the evolving energy landscape.
Additionally, the roadmap recommends the creation of comprehensive data systems to track vessel activity, fuel consumption, emissions, and performance. These data would support the development of Key Performance Indicators to guide progress and align national targets with actual technical and economic capacity.
- Enabling Measures and Policy Instruments
The establishment of green corridors—dedicated routes between selected shipyards and ports where proposed measures can be piloted and monitored—is proposed to validate and refine the effectiveness of interventions. This is particularly relevant for the domestic ferry sector, where such corridors could facilitate early decarbonization and stimulate private and public investments.
In addition, the adoption of IMO regulations—such as EEDI, EEXI, SEEMP, CII, GHG pricing mechanisms, and GFS—can further accelerate the decarbonization of domestic shipping. Revenues generated from GHG pricing mechanisms can be used to support and incentivize the implementation of the roadmap, including the development of ZnZ emission technologies and the establishment of supporting infrastructure.
- Governance, Collaboration, and Market Conditions
Governmental support is identified as a cornerstone of successful implementation. National authorities must adopt and enforce green economy policies, internalize environmental externalities, and create favorable market conditions for low-emission technologies and services. In parallel, cross-sectoral collaboration among key actors, including power generation companies, land transport agencies, maritime authorities, port operators, shipyards, shipping companies, and coastguards—is essential.
Ultimately, achieving zero-emission domestic shipping will require long-term investment in sustainable infrastructure, coherent governance frameworks, multi-stakeholder cooperation, and robust impact assessments to ensure fair competition and equitable transitions across the maritime sector.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
The decarbonization of domestic and short-sea shipping is a critical enabler for achieving global climate neutrality, particularly as international regulatory mechanisms, including carbon pricing and fuel standard shift attention to emissions not covered by global measures. Without targeted action, domestic fleets, which already contribute approximately 9.2% of shipping GHG emissions when measured by fleet scope, risk becoming an emissions blind spot—especially in the maritime economies of SIDSs and LDCs.
This study presents a comprehensive, transdisciplinary framework for addressing this gap, combining technical, operational, and policy-level decarbonization pathways supported by multi-criteria assessment. Among the strategies evaluated, weather routing, speed optimization, and just-in-time arrival offer immediate implementation potential with up to 15–20% GHG savings at relatively low cost. Wind-assisted propulsion can contribute 5–25% fuel reduction depending on vessel type, the type of technology, and wind profile, while onshore power supply (OPS) eliminates up to 100% of emissions at berth, provided the local grid is decarbonized.
In the technical domain, ESDs—such as propeller ducts, rudder bulbs, and flow-improving fins—demonstrated up to 20% improvement in propulsion efficiency, representing a scalable retrofit option for aging domestic fleets with limited capital. In contrast, zero-emission fuels such as green hydrogen offers >90% lifecycle GHG reduction yet remain constrained by high fuel costs (2–4× fossil alternatives), limited bunkering infrastructure, and safety/regulatory uncertainty. Fuel-flexible engines and hybrid-electric systems present medium-term transition technologies, with emissions benefits in the range of 30–60%, depending on fuel blend and operational mode.
Ports are central actors in the decarbonization of domestic and short-sea shipping. Their role extends beyond infrastructure provision to include the aggregation of clean fuel demand, coordination with urban energy systems, and deployment of electrified or hydrogen-based refueling capabilities. However, port cities are not equally prioritized in national climate adaptation and mitigation strategies—particularly in SIDSs and LDCs, where institutional capacity and financial constraints limit the deployment of sustainable infrastructure. Targeted investments in OPS, microgrid integration, and digital energy management in these regions can yield disproportionately high returns in greenhouse gas reduction and air quality improvement. Ensuring equitable support for port development is therefore essential to achieving a just and inclusive global maritime transition.
However, technology deployment alone is insufficient. Regulatory coherence, financing mechanisms, and institutional capacity must evolve in parallel. Alignment with NDCs and dedicated maritime climate funds—including adaptation of carbon pricing schemes and subsidy frameworks—are crucial to derisk investments and enable early adopters to remain competitive. Blended finance and results-based funding models may be especially effective in addressing affordability and equity in developing maritime regions.
Ultimately, this study illustrates that while there is no universal solution, a combination of mature operational practices, cost-effective retrofits, and strategically deployed zero-emission technologies can deliver substantial emissions reductions in domestic shipping. Tailored roadmaps—rooted in local context, vessel profiles, and regulatory maturity—are essential for scaling impact. Without swift, inclusive, and well-financed action, domestic and short-sea fleets risk undermining broader maritime decarbonization ambitions. Conversely, unlocking their potential offers a strategic pathway to deliver resilient, low-carbon connectivity in some of the world’s most climate-vulnerable regions.
5.2. Recommendations
Considering the discussion in the study, the authors provide the following recommendations for decarbonization of domestic and short seas hipping. The following recommendations are derived from a comprehensive analysis of technological, operational, port-based, and regulatory measures discussed throughout the study. They align closely with the strategic objectives outlined in the IMO’s Revised GHG Strategy (2023), particularly in supporting member states—especially SIDSs and LDCs—to adopt zero- and near-zero-emission pathways. Priority should be given to actions with high mitigation potential and near-term feasibility, such as the inclusion of domestic shipping in NDCs, the adaptation of IMO frameworks for sub-5000 GT vessels, deployment of energy efficiency technologies, and the establishment of dedicated financing mechanisms and carbon pricing schemes. These recommendations aim to ensure domestic and short-sea shipping transitions are both equitable and impactful, accelerating progress toward IMO’s 2050 decarbonization targets.
- Considering the domestic shipping in National Determined Contribution of States: It is advisable that decarbonization of this sector be included in their NDCs under the Paris Agreement, accompanied by the submission of a related National Action Plan to the IMO.
- Enhancing energy efficiency: Improving energy efficiency is essential for achieving zero-emission domestic shipping. It not only delivers immediate reductions in GHG emissions but also establishes a critical foundation for the long-term sustainability and environmental performance of the maritime sector.
- Adopting IMO’s Energy Efficiency and Decarbonization Regulations for Domestic Shipping: The adoption and effective enforcement of IMO regulations on energy efficiency and GHG emissions are critical to advancing the decarbonization of domestic shipping. However, given that a large share of domestic vessels operates below the 5000 GT threshold, regulatory frameworks must be carefully adapted to ensure these vessels are not inadvertently excluded from compliance measures.
- Implementing Carbon Pricing and Establishing an Innovative Fund for Domestic Shipping: The implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms tailored to domestic shipping—similar to the EU ETS—can significantly accelerate decarbonization efforts. Revenues generated through such schemes could be strategically directed toward financing innovative ZnZ technologies and the development of sustainable infrastructure for alternative fuels and clean energy supply.
- Support to reduce the risk in investment of ZnZ technologies: To address prevailing uncertainties, national and local governments should foster the commercial feasibility of transitioning to low- and zero-emission energy sources within the domestic shipping sector. This may involve introducing carbon pricing mechanisms and developing fuel standards specifically designed for domestic operations. Additionally, governments can facilitate the transition by providing clear regulatory guidance and implementing targeted support schemes for innovative technologies and investments in essential sustainable infrastructure.
- Raising finance for decarbonization of domestic shipping: Accelerating the transition to zero-emission shipping will require fundamental changes to existing business models and GHG mitigation strategies. Revising these frameworks presents an opportunity to generate dedicated funding—potentially through carbon price mechanisms—which can support decarbonization initiatives. Prioritizing the allocation of such funds to Least Developed Countries and Small Island Developing States would enable targeted investments in port infrastructure, including facilities for alternative fuel production and shore power systems. Given the strategic role of ports in enabling low-emission maritime operations, these developments can significantly advance the decarbonization of domestic shipping.
- Capacity building and research and development (R&D): Capacity building and research and development are fundamental to enabling SIDSa and LDCs to effectively address the challenges of domestic shipping decarbonization. Capacity-building efforts should focus on enhancing technical expertise across key stakeholders, while R&D initiatives should support infrastructure development, data collection and analysis, and the transfer of clean technologies—thereby fostering sustainable growth and sectoral resilience.
- Ports as an energy hub: As with international shipping, ports are vital components of the maritime supply chain and play a central role in enabling the transition to zero-emission domestic shipping through the provision of sustainable infrastructure. Beyond their traditional function in cargo handling, ports are increasingly evolving into energy hubs—supplying clean fuels and renewable energy to support maritime decarbonization and strengthen national energy security.
- Establishment of Green Corridors: The development of green corridors is instrumental in accelerating decarbonization and advancing sustainable practices within domestic shipping networks. These initiatives involve connecting key domestic ports and deploying zero-emission vessels alongside emission reduction measures across the maritime value chain. While green corridors provide a valuable framework for piloting new technologies and operational strategies, their success depends on coordinated, innovative, and sustained collaboration among all relevant stakeholders.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17167294/s1, the paper includes two supplementary materials. The first presents the complete PRISMA checklist. The second outlines the key challenges faced by SIDSs and LDCs across economic, technological, regulatory, and human capacity domains, and proposes actionable solutions to support the decarbonization of domestic and short-sea shipping.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; methodology: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Validation: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Formal analysis: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Investigation: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Resources: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Data curation: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Writing—original draft preparation: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Writing—review and editing: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Visualization: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Supervision: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö.; Project administration: S.V., M.I., S.S. and A.Ö. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Some elements of this study form part of broader research initiatives supported by the International Maritime Organization. The authors gratefully acknowledge IMO for its support, which has been instrumental in enabling this research. We also extend our sincere thanks to all stakeholders and collaborators who provided valuable insights throughout the course of the study. In addition, the authors would like to sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers and the editorial board for their insightful comments, constructive feedback, and valuable suggestions, which have greatly improved the quality and clarity of this paper. Their time, expertise, and guidance have been instrumental in refining the manuscript and ensuring its contribution to advancing knowledge in the field of maritime decarbonization.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| AFC/MCFCs | Alkaline and Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells |
| APEC | Asia–Pacific Economic Cooperation |
| BASREC | Baltic Sea Region Energy Cooperation |
| BTL | Biomass-to-Liquids |
| CCUS | Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| CII | Carbon Intensity Indicator |
| P2P | Port to Pipeline |
| EEDI | Energy Efficiency Design Index |
| EEXI | Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index |
| ESDs | Energy-Saving Devices |
| ESPO | European Sea Port Organization |
| ESS | Energy Storage System |
| FAME | Fatty Acid Methyl Ester |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| HT-PEMFCs | High-Temperature PEMFCs |
| HVO | Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| ITF | International Transport Forum |
| JIT | Just-in-Time |
| LBG | Liquid Biogas |
| LDCs | Least Developed Countries |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| LNG | Liquefied Natural Gas |
| LT-PEMFCs | Low-Temperature PEMFCs |
| MBF | Marine Battery Forum |
| MDO | Marine Diesel Oil |
| MEPC | Marine Environment Protection Committee |
| MESD | Maritime Energy and Sustainable Development |
| MGO | Marine Gas Oil |
| NAPs | National Action Plans |
| OCC | Onboard Carbon Capture |
| OCCS | Onboard Carbon capture and storage |
| OGCI | Oil and Gas Climate Initiative |
| OPS | Onshore Power Systems |
| ORC | Organic Rankine Cycle |
| PEMFCs | Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells |
| PIDs | Propulsion Improvement Devices |
| QC | Quay Cranes |
| R&D | Research and Development |
| RINA | Royal Institution of Naval Architects |
| RMG | Rail-Mounted Gantry Cranes |
| ROBIO | Conf Robot Biomimetics |
| RTGC | Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes |
| ReARTG | Remote Controlled Electric Rubber-Tyred Gantry |
| SC | Straddle Carriers |
| SIDS | Small Island Developing States |
| SOFCs | Solid Oxide Fuel Cells |
| STS | Ship-to-Shore Cranes |
| SVO | Straight Vegetable Oil |
| VLSFO | Very Low Sulfur Fuel Oil |
| VPPs | Virtual Power Plants |
| WHR | Waste heat recovery |
| YT | Yard Trucks |
| ZnZ | Zero to near Zero |
References
- International Maritime Organisation (IMO). Initial IMO strategy on reduction of GHG emissions from ships. MEPC 2018, 72, 17. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organisation (IMO); Insel, M.; Vakili, S. IMO CARES Report on Decarbonisation of Domestic Shipping. 2024. Available online: https://www.porttechnology.org/news/imo-cares-report-stresses-decarbonisation-of-domestic-shipping-in-africa-caribbean/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Vakili, S.; Ölçer, A.I.; Schönborn, A.; Ballini, F.; Hoang, A.T. Energy-related clean and green framework for shipbuilding community towards zero-emissions: A strategic analysis from concept to case study. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 20624–20649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristić, M.; Žuškin, S.; Brčić, D.; Valčić, S. Zone of confidence impact on cross track limit determination in ECDIS passage planning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucma, M.; Deja, A.; Szymonowicz, J. Environmental solutions for maritime ships: Challenges and needs. Prod. Eng. Arch. 2023, 29, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brčić, D.; Kos, S.; Žuškin, S. Navigation with ECDIS: Choosing the proper secondary positioning source. TransNav Int. J. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2015, 9, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, S.; Lyridis, D.V.; Koliousis, I.G.; Tsioumas, V.; Sdoukopoulos, E.; Stavroulakis, P.J. The Dynamics of Short Sea Shipping: New Practices and Trends; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy, M.; Letournel, L.; Paakkari, V.; Rongère, F.; Sarsila, S.; Vuillermoz, L. Weather Routing Benefit for Different Wind Propulsion Systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovation in High-Performance Sailing Yachts and Wind-Assisted Ships, Lorient, France, 29–31 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Leaper, R.; Renilson, M.; Ryan, C. Reducing underwater noise from large commercial ships: Current status and future directions. J. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 9, 65–83. [Google Scholar]
- Golias, M.; Boile, M.; Theofanis, S.; Efstathiou, C. The berth-scheduling problem: Maximizing berth productivity and minimizing fuel consumption and emissions production. Transp. Res. Rec. 2010, 2166, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beşikçi, E.B.; Kececi, T.; Arslan, O.; Turan, O. An application of fuzzy-AHP to ship operational energy efficiency measures. Ocean Eng. 2016, 121, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, H.O.; Lützen, M. Prediction of resistance and propulsion power of ships. Clean Shipp Curr. 2012, 1, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Psaraftis, H.N.; Kontovas, C.A. Balancing the economic and environmental performance of maritime transportation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2010, 15, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.; van Seters, D.; Scholten, P. Shipping GHG Emissions 2030: Analysis of the Maximum Technical Abatement Potential; Report No.: 23.230208.097; CE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC). Analysis of the Impacts of Slow Steaming for Distant Economies; APEC Project: TPT 03 2018A; APEC Transportation Group: Singapore; Starcrest Consulting Group for APEC Secretariat: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen, E. Can slow steaming lower cost impacts of sulphur directive—Shippers’ perspective. World Rev. Intermodal Transp. Res. 2014, 5, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Z.; Woxenius, J.; Finnsgård, C. Slow steaming as part of SECA compliance strategies among RoRo and RoPax shipping companies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, B.; Tettenborn, A. Slow steaming clauses and international sales contracts: A successful marriage? In International Trade and Carriage of Goods; Informa Law from Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zis, T.; Psaraftis, H.N. The implications of the new sulphur limits on the European Ro-Ro sector. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, H.L.; Zhang, J. The impact of slow ocean steaming on delivery reliability and fuel consumption. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 76, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaraftis, H.N.; Zis, T. Impact assessment of a mandatory operational goal-based short-term measure to reduce GHG emissions from ships: The LDC/SIDS case study. Int. Environ. Agreem. Polit. Law Econ. 2021, 21, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perski, O.; Hébert, E.T.; Naughton, F.; Hekler, E.B.; Brown, J.; Businelle, M.S. Technology-mediated just-in-time adaptive interventions (JITAIs) to reduce harmful substance use: A systematic review. Addiction 2022, 117, 1220–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandri, T.; Diamant, R. Detection and characterization of ship underwater radiated narrowband noise. Comput. Netw. 2024, 248, 110480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, G.; Liu, M. Achieving a just–in–time supply chain: The role of supply chain intelligence. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca, J.; Giménez Maldonado, J.A.; Ferrús Clari, G.; Alonso i García, N.; Calabria, L.; Lara, J. Enabling a green just-in-time navigation through stakeholder collaboration. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2020, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.V.; Lützen, M.; Sørensen, J.C.; Rytter, N.G.M. Greening Smaller Ferries by Optimizing Operations. In Proceedings of the HullPic’21: 6th Hull Performance & Insight Conference, Pontignano, Italy, 30 August–1 September 2021; pp. 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hochkirch, K.; Bertram, V. Fluid Dynamic Options for Reducing CO2 Emissions. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual Green Ship Technology Conference, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 15–16 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mewis, F.; Hollenbach, U. Hydrodynamische Maßnahmen zur Verringerung des Energieverbrauches im Schiffsbetrieb. Hansa 2007, 144, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- MEPC 63/4/8; Transparent and Reliable Hull and Propeller Performance Standard. International Maritime Organisation (IMO): London, UK, 2011.
- International Chamber of Shipping (ICS). The Impact of Shipping’s Energy Efficiency Measures on Reduction of Under-Water Radiated Noise, and Opportunities for Co-Benefit. 2023. Available online: https://www.ics-shipping.org/resource/the-impact-of-shippings-energy-efficiency-measures-on-reduction-of-underwater-radiated-noise-and-opportunities-for-co-benefit/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Speranza, N.; Kidd, B.; Schultz, M.P.; Viola, I.M. Modelling of hull roughness. Ocean Eng. 2019, 174, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Oliveira, D.R.; Yeginbayeva, I.; Leer-Andersen, M.; Bensow, R.E. Review and comparison of methods to model ship hull roughness. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 99, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC). 2023 Guidelines for the Control and Management of Ships’ Biofouling to Minimize the Transfer of Invasive Aquatic Species (Resolution MEPC.378(80), MEPC/17/Add.1), adopted 7 July 2023. 2023. Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.378(80).pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Vakili, S.; White, P.; Turnock, S. Advancing a sustainable maritime future: Integrating energy efficiency and underwater radiated noise reduction strategies in commercial shipping. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 215, 117835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipton, M.; Obradović, J.; Ferreira, F.; Mišković, N.; Bulat, T.; Cukrov, N.; Diamant, R. A database of underwater radiated noise from small vessels in the coastal area. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, P.; Newell, A.; Rojon, I.; Milligan, B.; Irvin, A. Pacific Island domestic shipping emissions abatement measures and technology transition pathways for selected ship types. Mar. Policy 2021, 132, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, C.; Celik, M. A human reliability assessment of marine auxiliary machinery maintenance operations under ship PMS and maintenance 4.0 concepts. Cogn. Technol. Work. 2020, 22, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanivuk, T.; Stazić, L.; Vidović, F.; Čobanov, A. Ship Planned Maintenance System Data Analysis. Int. J. Traffic. Transp. Eng. 2020, 10, 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- Raptodimos, Y.; Lazakis, I.; Theotokatos, G.; Varelas, T.; Drikos, L. Ship sensors data collection and analysis for condition monitoring of ship structures and machinery systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Ship Technology, London, UK, 26–27 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Fuenmayor, E.; Hinchy, E.P.; Qiao, Y.; Murray, N.; Devine, D. Digital twin: Origin to future. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstad, H.; Asbjørnslett, B.E.; Strømman, A.H. The importance of economies of scale for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions from shipping. Energy Policy 2012, 46, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, K.P.B.; Khanna, M. Economies of scale in large container ships. J. Transp. Econ. Policy 1999, 33, 185–208. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D. Environmentally sustainable cruise tourism: A reality check. Mar. Policy 2022, 26, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros Chaos, S.; Pallis, A.A.; Saurí Marchán, S.; Pino Roca, D.; Sánchez-Arcilla Conejo, A. Economies of scale in cruise shipping. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2021, 23, 674–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PIANC. Guidelines for Cruise Terminals; Report of PIANC InCom WG 152; PIANC: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vakili, S.; Schönborn, A.; Ölçer, A.I. Techno-economic feasibility of photovoltaic, wind and hybrid electrification systems for stand-alone and grid-connected shipyard electrification in Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Mi, S.; Tong, T.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Intelligent initial model and case design analysis of smart factory for shipyard in China. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijwaard, G.E.; Knapp, S. Analysis of ship life cycles—The impact of economic cycles and ship inspections. Mar. Policy 2009, 33, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Roh, G.; Lee, S.; Choung, C.; Kang, H. Comparative life cycle assessments and economic analyses of alternative marine fuels: Insights for practical strategies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABS. Ammonia as Marine Fuel. Sustainability Whitepaper. 2020. Available online: https://absinfo.eagle.org/acton/media/16130/sustainability-whitepaper-ammonia-as-marine-fuel (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- ABS. American Bureau of Shipping (ABS). Methanol as a Marine Fuel: Sustainability Whitepaper; ABS: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; Available online: https://safety4sea.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Sustainability-Methanol-as-Marine-Fuel.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- ABS. Beyond the Horizon: Carbon Neutral Pathway and Transformational Technologies. 2024. Available online: https://ww2.eagle.org/en/interactive/interactive-publications/current/outlook-2024.html (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Bouman, E.A.; Lindstad, E.; Rialland, A.I.; Strømman, A.H. State-of-the-art technologies, measures, and potential for reducing GHG emissions from shipping—A review. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNV. Energy Transition Outlook: Maritime Forecast to 2050. 2022. Available online: https://www.dnv.com/maritime/maritime-forecast/#:~:text=An%20unprecedented%20era%20of%20technological%20exploration%20underway%20and,to%20meeting%20the%20IMO%E2%80%99s%20GHG%20emission%20reductions%20targets (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- DNV. Energy Transition Outlook: Maritime Forecast to 2050. 2023. Available online: https://www.dnv.com/maritime/maritime-forecast/?utm (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- DNV. Energy Transition Outlook: Maritime Forecast to 2050. 2024. Available online: https://www.isesassociation.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/DNV_Maritime_Forecast_2050_2024-final-3.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- DNV GL. Assessment of Selected Alternative Fuels and Technologies. 2019. Available online: https://www.dnv.com/publications/assessment-of-selected-alternative-fuels-and-technologies-rev-june-2019--116334/#:~:text=This%20paper%20provides%20an%20overview%20of%20selected%20alternative,selected%20alternative%20fuels%20and%20technologies (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Dos Santos, V.A.; da Silva, P.P.; Serrano, L.M.V. The maritime sector and its problematic decarbonisation: A systematic review of the contribution of alternative fuels. Energies 2022, 15, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstad, E.; Lagemann, B.; Rialland, A.; Gamlem, G.M.; Valland, A. Reduction of maritime GHG emissions and the potential role of E-fuels. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2022, 101, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, S.; Manias, P.; Armstrong, L.M.; Turnock, S.; Teagle, D.A. Technical, economic, and environmental assessment of CO2 ship transport in carbon capture and storage. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Enazi, A.; Okonkwo, E.C.; Bicer, Y.; Al-Ansari, T. A review of cleaner alternative fuels for maritime transportation. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1962–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilhan, S.; Park, S.; El-Halwagi, M.M.; Atilhan, M.; Moore, M.; Nielsen, R.B. Green hydrogen as an alternative fuel for the shipping industry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2021, 31, 100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, D.; Losos, A.; Raucci, C.; Smith, T. The Potential of Zero-Carbon Bunker Fuels in Developing Countries; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/35435 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Joung, T.H.; Kang, S.G.; Lee, J.K.; Ahn, J. The IMO initial strategy for reducing Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, and its follow-up actions towards 2050. J. Int. Marit. Saf. Environ. Aff. Shipp. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, S.; Ölçer, A.I. Techno-economic-environmental feasibility of photovoltaic, wind and hybrid electrification systems for stand-alone and grid-connected port electrification in the Philippines. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd’s Register (LR). The Future of Maritime Fuels: What You Need to Know. 2023. Available online: https://maritime.lr.org (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Thepsithar, P. Alternative Fuels for International Shipping; Maritime Energy & Sustainable Development (MESD) Centre of Excellence: Singapore, 2020; Available online: https://www.ntu.edu.sg/mesd-coe/publications (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Bicer, Y.; Dincer, I. Clean fuel options with hydrogen for sea transportation: A life cycle approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallouppas, G.; Yfantis, E.A. Decarbonisation in shipping industry: A review of research, technology development, and innovation proposals. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.; Shabani, B. Where does hydrogen fit in a sustainable energy economy? Procedia Eng. 2012, 49, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd’s Register; UMAS. Techno-Economic Assessment of Zero-Carbon Fuels; Lloyd’s Register: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Stuart, C.; Spence, S.; Chen, H. Alternative fuel options for low carbon maritime transportation: Pathways to 2050. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Maritime Organisation (IMO). ISWG-GHG 15/INF.2. Further consideration and finalization of the development of the draft revised strategy on reduction of GHG emissions from ships. In Commercial Readiness of Absolute Zero GHG Technologies; International Maritime Organisation (IMO): London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Pei, Y.; An, Y. Methanol as a fuel for internal combustion engines. In Engines and Fuels for Future Transport; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 281–324. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, P.; Athanassiadis, D.; Yacout, D.M.; Tysklind, M.; Upadhyayula, V.K. Environmental impact and environmental cost assessment of methanol production from wood biomass. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, M.; Ellis, J.; Lundgren, J.; Landälv, I. Renewable methanol as a fuel for the shipping industry. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fournas, N.; Wei, M. Techno-economic assessment of renewable methanol from biomass gasification and PEM electrolysis for decarbonisation of the maritime sector in California. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 257, 115440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Márquez Salazar, C.M. Methanol as a Marine Fuel Report. London: FCBI Energy (FC Business Intelligence Ltd), Prepared for the Methanol Institute; October 2015. Report Length 46 Pages. Available online: https://www.methanol.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/FCBI-Methanol-Marine-Fuel-Report-Final-English.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- International Transport Forum (ITF). Decarbonising Maritime Transport: Pathways to Zero-Carbon Shipping by 2035; ITF/OECD: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- BIBBY Marine. An Introduction to the WaveMaster Zero C Project. 2023. Available online: https://www.bibbymarine.com (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Sharples, J. LNG Supply Chains and the Development of LNG as a Shipping Fuel in Northern Europe; The Oxford Institute for Energy Studies: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.W.C.; Felby, C. Biofuels for the Marine Shipping Sector. IEA Bioenergy 2017, 39, 9–83. [Google Scholar]
- Le Fevre, C.N. A Review of Demand Prospects for LNG as a Marine Fuel; The Oxford Institute for Energy Studies: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dotto, A.; Campora, U.; Satta, F. Feasibility study of an integrated COGES-DF engine power plant in LNG propulsion for a cruise-ferry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 245, 114602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey & Company. The Shipping Industry’s Fuel Choices on the Path to Net Zero. 2023. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/travel-logistics-and-infrastructure/our-insights/charting-fuel-choices-as-the-shipping-industry-sails-toward-net-zero (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Hua, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H. Alternative fuel for sustainable shipping across the Taiwan Strait. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 254–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakov, S.; Halvorsen, N.G.; Valland, H.; Williksen, D.H.; Æsøy, V. Emission characteristics of GTL fuel as an alternative to conventional marine gas oil. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2013, 18, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.G. LNG Emerging as Fuel of Choice for Vessels and Ferries. 2013. Available online: https://www.aogr.com/web-exclusives/exclusive-story/lng-emerging-as-fuel-of-choice-for-vessels-ferries (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Goodstein, J. First Danish Ferry Powered by LNG. 2015. Available online: https://www.oskdesign.com/news/princess-isabella-awarded-danish-ship-of-the-year-2015-by-maritime-danmark (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- McKinlay, C.J.; Turnock, S.; Hudson, D. A comparison of hydrogen and ammonia for future long distance shipping fuels. In Proceedings of the LNG/LPG and Alternative Fuel Ships, London, UK, 29–30 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organisation (IMO). MEPC 80/WP.12. Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships. Revised GHG Reduction Strategy for Global Shipping Adopted. 2023. Available online: http://www.imo.org/en/About/Pages/Default.aspx (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Balci, G.; Phan, T.T.N.; Surucu-Balci, E.; Iris, Ç. A roadmap to alternative fuels for decarbonising shipping: The case of green ammonia. Res. Transp. Bus Manag. 2024, 53, 101100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cames, M.; Wissner, N.; Sutter, J. Ammonia as a Marine Fuel: Risks and Perspectives; Öko-Institut e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- International Transport Forum (ITF). Decarbonisation, Coastal Shipping and Multimodal Transport: Summary and Conclusions; ITF Roundtable Reports, No. 192; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lagouvardou, S.; Lagemann, B.; Psaraftis, H.N.; Lindstad, E.; Erikstad, S.O. Marginal abatement cost of alternative marine fuels and the role of market-based measures. Nature Energy 2023, 8, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, S.; Kanda, W.; Anderberg, S. Drivers for and barriers to biogas use in manufacturing, road transport and shipping: A demand-side perspective. Biofuels 2022, 13, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Wei, J. An improved ship weather routing framework for CII reduction accounting for wind-assisted rotors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC). Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships: White Paper on Wind Propulsion; MEPC 81/INF.39. Submitted by Comoros, France, Solomon Islands and IWSA; Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC): London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- DNV. Study on the Readiness and Availability of Low- and Zero-Carbon Ship Technology and Marine Fuels; IMO Future Fuel and Technology Project (FFT Project). MEPC 80/INF.8; DNV: Oslo, Norway, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Greenabode. World’s First Ferry with Onboard Wind Power. 2022. Available online: https://www.greenabode.co.uk/ferry-wind-power/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Offshore Energy. All-Electric Ferry Sails 90 km on a Single Battery Charge, Setting World Record. 2022. Available online: https://www.offshore-energy.biz/all-electric-ferry-sails-90-km-on-single-battery-charge-setting-world-record/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- TradeWinds. Marshall Islands to Get Wind-Powered Solution to Help Decouple from International Bunker Prices. 2023. Available online: https://www.tradewindsnews.com (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Huang, M.; He, W.; Incecik, A.; Cichon, A.; Królczyk, G.; Li, Z. Renewable energy storage and sustainable design of hybrid energy powered ships: A case study. J. Energy Storage. 2021, 43, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Z.Y.; Konovessis, D. Sustainable energy propulsion system for sea transport to achieve United Nations sustainable development goals: A review. Discov. Sustain. 2023, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Maritime Organisation (IMO). Fourth IMO GHG Study 2020—Final Report. MEPC 75/7/15. 2020. Available online: http://www.imo.org/en/about/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Elsisi, M.; Amer, M.; Su, C.L.; Aljohani, T.; Ali, M.N.; Sharawy, M. A comprehensive review of machine learning and Internet of Things integrations for emission monitoring and resilient sustainable energy management of ships in port areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 218, 115843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Kothari, D.P. Solar PV potential for passenger ferry boats in India’s National Waterways. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 January 2018; pp. 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nallusamy, S.; Sendilvelan, S.; Bhaskar, K.; Prabu, N.M. Analysis of performance, combustion and emission characteristics on biofuel of novel pine oil. Rasayan J. Chem. 2017, 10, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, D.F.; Beyer, H.L.; Fargione, J.E.; Hill, J.D.; Possingham, H.P.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Schenk, P.M. Towards the implementation of sustainable biofuel production systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moirangthem, K.; Baxter, D. Alternative Fuels for Marine and Inland Waterways; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova, M.V.; Poudyal, R.S.; Tiwari, I.; Voloshin, R.A.; Zharmukhamedov, S.K.; Nam, H.G.; Zayadan, B.; Bruce, B.; Hou, H.; Allakhverdiev, S. Biofuel production: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 8450–8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNV. Ship Energy Efficiency: Measures for Ship Design and Operation to Save Costs and Meet Decarbonisation Requirements. 2023. Available online: https://www.dnv.com (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Oil and Gas Climate Initiative (OGCI). Economically Viable and Sustainable Biomass for Marine Fuel Use. 2023. Available online: https://3971732.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/3971732/OGCI_Biomass_White_Paper_COVERS.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- DNV GL. Comparison of Alternative Marine Fuels; DNV: Oslo, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Antariksa, A.; Semedi, B.; Wahyudi, S. Implementation of fully electric propulsion and variable speed drive to reduce ships emissions for sustainable maritime technology. Edelweiss Appl. Sci. Technol. 2025, 9, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, S.; Ölçer, A.I. Are battery-powered vessels the best solution for the domestic ferry segment? Case study for the domestic ferry segment in the Philippines. Energy 2023, 282, 128323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantatos, K. Feasibility study on retrofitting a conventional ferry operating on the Argostoli–Lixouri route into a battery-powered vessel [diploma thesis]. Athens (Greece): National Technical University of Athens, School of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering. 2022. Available online: https://dspace.lib.ntua.gr/xmlui/handle/123456789/54514 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Wu, P.; Bucknall, R. Hybrid fuel cell and battery propulsion system modelling and multi-objective optimisation for a coastal ferry. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3193–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelakowski, A.S.; Herdzik, J.; Skiba, S. Maritime shipping decarbonisation: Roadmap to meet zero-emission target in shipping as a link in the global supply chains. Energies 2022, 15, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, C.; Qian, H. Design and implementation of a novel adaptive multihull sailboat with liftable side hulls. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Int Conf Robot Biomimetics (ROBIO), Koh Samui, Thailand, 4–9 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Marine Insight. ZeroCat 120—World’s First Electric Ferry Receives Ship of the Year 2014 Award; Marine Insight: Bengaluru, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- INCAT. History Made on the River Derwent: Incat Launches the World’s Largest Battery-Electric Ship. 2025. Available online: https://www.incat.com.au (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Scandlines. Zero Direct Emission-Freight Ferry. 2024. Available online: https://www.scandlines.com/about-us/our-green-agenda/zero-direct-emission-freight-ferrys/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Kunze, H. AIDAperla Will Receive the Largest Battery Storage System in Passenger Shipping in 2020; Carnival Corporation & Plc: Miami, FL, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.csrwire.com/press_releases/42526-aidaperla-will-receive-the-largest-battery-storage-system-in-passenger-shipping-in-2020 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Marine Battery Forum (MBF). Ship Register. 2023. Available online: https://www.maritimebatteryforum.com/ship-register (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Kortsari, A.; Mitropoulos, L.; Heinemann, T.; Mikkelsen, H.; Aifadopoulou, G. Evaluating the economic performance of a pure electric and diesel vessel: The case of E-ferry in Denmark. Trans. Marit. Sci. 2022, 11, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, L.; Dong, Z. Modeling, simulation and assessment of a hybrid electric ferry: Case study for mid-size ferry. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 18–21 August 2019; Volume 59292, p. V009T12A028. [Google Scholar]
- Passenger Ship Technology. Commuter Craft Prototype Creates No Emissions. 2012. Available online: https://www.stirlingdesign.fr/presses/articles/stirling_design_lorient_passenger-ship-technology_10_2012.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Olabi, A.G.; Wilberforce, T.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Fuel cell application in the automotive industry and future perspective. Energy 2021, 214, 118955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Biert, L.; Godjevac, M.; Visser, K.; Aravind, P.V. A review of fuel cell systems for maritime applications. J. Power Sources 2016, 327, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkafas, A.G.; Rivarolo, M.; Gadducci, E.; Magistri, L.; Massardo, A.F. Fuel cell systems for maritime: A review of research development, commercial products, applications, and perspectives. Processes 2022, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Yao, J.; Qian, C.; Yang, F.; Porpatham, E.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z. High-efficiency conversion of natural gas fuel to power by an integrated system of SOFC, HCCI engine, and waste heat recovery: Thermodynamic and thermo-economic analyses. Fuel 2020, 275, 117883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, R.T.; Klebanoff, L.E.; Caughlan, S.A.M.; Pratt, J.W.; Leach, T.S.; Appelgate, T.B., Jr.; Kelety, S.Z.; Wintervoll, H.-C.; Haugom, G.P.; Teo, A.T.Y.; et al. Feasibility of the Zero-V: A zero-emissions hydrogen fuel-cell coastal research vessel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 25328–25343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njaka, T.; Brizzolara, S.; Stilwell, D. CFD investigation of hull-rudder interaction for improved maneuvering models. In Proceedings of the SNAME Maritime Convention, Tacoma, DC, USA, 30 October–1 November 2019; p. D033S004R003. [Google Scholar]
- Molland, A.F.; Turnock, S.R. Marine Rudders, Hydrofoils and Control Surfaces: Principles, Data, Design and Applications; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, A.B.; Turnock, S.R.; Furlong, M. The use of computational fluid dynamics to aid cost-effective hydrodynamic design of autonomous underwater vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2010, 224, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.L.; Suastika, I.K.; Utama, I.K.A.P. A practical empirical formula for the calculation of ship added friction-resistance due to (bio) fouling. Ocean Eng. 2023, 271, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y. A new method for parametric design of hull surface based on energy optimization. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2019, 24, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, G. Drag reduction by gas lubrication with bubbles. Ocean Eng. 2022, 258, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Murai, Y. Power-saving device for air bubble generation using a hydrofoil to reduce ship drag: Theory, experiments, and application to ships. Ocean Eng. 2015, 95, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, J. Numerical investigation of a novel device for bubble generation to reduce ship drag. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2018, 10, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccio, S.L. Friction drag reduction of external flows with bubble and gas injection. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkiharju, S.A.; Perlin, M.; Ceccio, S.L. On the energy economics of air lubrication drag reduction. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 4, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, Y.; Sakamaki, H.; Kumagai, I.; Park, H.J.; Tasaka, Y. Mechanism and performance of a hydrofoil bubble generator utilized for bubbly drag reduction ships. Ocean Eng. 2020, 216, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillemi, M.; Raffaele, M.; Sfravara, F. A Review of Advanced Air Lubrication Strategies for Resistance Reduction in the Naval Sector. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Institution of Naval Architects (RINA). Damen to Supply Air Cavity System to Amisco for Reduced Emissions. 2023. Available online: https://www.rina.org (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Silverstream Technologies. What Is Air Lubrication? 2023. Available online: https://www.silverstream-tech.com (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Molland, A.F.; Turnock, S.R.; Hudson, D.A. Ship Resistance and Propulsion; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.E.; Choi, B.J.; Chung, S.H.; Seo, H.W. Development of energy-saving devices for a full slow-speed ship through improving propulsion performance. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2015, 7, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson. Green Technology Tracker: July 2023; Clarkson: Oxfordshire, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Sun, S.; Zhi, Y.; Yuan, Y. Investigation of the effects of a fan-shaped Mewis duct before a propeller on propulsion performance. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2019, 24, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinke, H.J.; Hellwig-Rieck, K. Investigation of scale effects on ships with a wake equalizing duct or with vortex generator fins. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Marine Propulsors (smp’11), Hamburg, Germany, 15–17 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Heinke, H.J.; Lübke, L.O. Maßnahmen zur Energieeinsparung. Schiff & Hafen 2014, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mizzi, K.; Demirel, Y.K.; Banks, C.; Turan, O.; Kaklis, P.; Atlar, M. Design optimisation of Propeller Boss Cap Fins for enhanced propeller performance. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 62, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelić, V.; Bukovac, O.; Radonja, R.; Degiuli, N. The impact of slow steaming on fuel consumption and CO2 emissions of a container ship. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, F.; Mendes, S.; Bertucci, F.; Breitzke, M.; Ciappi, E.; Cresci, A.; Debusschere, E.; Ducatel, C.; Folegot, T.; Juretzek, C.; et al. Addressing Underwater Noise in Europe: Current State of Knowledge and Future Priorities; European Marine Board: Ostend, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wärtsilä. Power-Saving Devices. 2022. Available online: https://www.wartsila.com/encyclopedia/term/power-saving-devices (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Scappin, F.; Stefansson, S.H.; Haglind, F.; Andreasen, A.; Larsen, U. Validation of a zero-dimensional model for prediction of NOx and engine performance for electronically controlled marine two-stroke diesel engines. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 37, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzida, M.; Girtler, J.; Dzida, S. On the possible increasing of efficiency of ship power plant with the system combined of marine Diesel engine, gas turbine and steam turbine in case of main engine cooperation with the gas turbine fed in series and the steam turbine. Pol. Marit. Res. 2009, 16, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Liang, Y.; Wei, H.; Tian, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L. A review of waste heat recovery on two-stroke IC engine aboard ships. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillig, F.; Mao, W.; Ringsberg, J.W. Systems Modelling for Energy-Efficient Shipping [Technical Report No. 15:153]; Chalmers University of Technology, Department of Shipping and Marine Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2015; Available online: http://www.transportportal.se/Energieffektivitet/Systems%20modelling%20for%20energy-efficient%20shipping.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Faber, J.; Nelissen, D.; Hon, G.; Wang, H.; Tsimplis, M. Regulated Slow Steaming in Maritime Transport: An Assessment of Options, Costs and Benefits; International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Gu, C.W. Parametric analysis of a dual loop Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) system for engine waste heat recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loni, R.; Najafi, G.; Bellos, E.; Rajaee, F.; Said, Z.; Mazlan, M. A review of industrial waste heat recovery system for power generation with Organic Rankine Cycle: Recent challenges and future outlook. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lümmen, N.; Nygård, E.; Koch, P.E.; Nerheim, L.M. Comparison of organic Rankine cycle concepts for recovering waste heat in a hybrid powertrain on a fast passenger ferry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 163, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürgen, S.; Altin, İ. Novel decision-making strategy for working fluid selection in Organic Rankine Cycle: A case study for waste heat recovery of a marine diesel engine. Energy 2022, 252, 124023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wang, X.; Rezazadeh, A. Electrical energy storage from a combined energy process based on solid oxide fuel cell and use of waste heat. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 48, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Fooladi, H. Performance evaluation of a polygeneration system based on fuel cell technology and solar photovoltaic and use of waste heat. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zincir, B.A.; Zincir, B.; Deniz, C.; Usluer, H.B.; Arslanoglu, Y. Environmental impact investigation of combined CCS and SCR on a ship by a case study. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobetti, F.; Pio, G.; Bucelli, M.; Miani, L.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Cozzani, V. Onboard carbon capture and storage (OCCS) for fossil fuel-based shipping: A sustainability assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 470, 143343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, O. Shipping Emissions in Ports. International Transport Forum Discussion Paper No 2014/20; OECD/International Transport Forum: Paris, France; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/content/dam/oecd/en/publications/reports/2014/12/shipping-emissions-in-ports_g17a26d0/5jrw1ktc83r1-en.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Nosar, N.S. Unraveling interactions: Mechanisms shaping the transition of small and medium-sized ports to energy hubs. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2025, 31, 101417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Aziz, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Yap, P.S. Digitalization and innovation in green ports: A review of current issues, contributions and the way forward in promoting sustainable ports and maritime logistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC). Invitation to Member States to Encourage Voluntary Cooperation Between the Port and Shipping Sectors to Contribute to Reducing GHG Emissions from Ships; Resolution MEPC.323(74); Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC): London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shahidehpour, M.; Alabdulwahab, A.; Abusorrah, A. Optimal expansion planning of energy hub with multiple energy infrastructures. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2302–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadiga, A.; Ferreira, L.M.D.; Bigotte, J.F. Decarbonising maritime ports: A systematic review of the literature and insights for new research opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine-Wright, P. Decarbonisation of industrial clusters: A place-based research agenda. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2022, 91, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, Ç.; Lam, J.S.L. A review of energy efficiency in ports: Operational strategies, technologies and energy management systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Assessing energy efficiency of port operations in China—A case study on sustainable development of green ports. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2015, 3, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Varriale, L.; Alvino, F. Key performance indicators for developing environmentally sustainable and energy efficient ports: Evidence from Italy. Energy Policy 2018, 122, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, F.; Ölçer, A.I. Energy manager role in ports. In Trends and Challenges in Maritime Energy Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- de Langen, P.; Sornn-Friese, H. Ports and the circular economy. In Green Ports; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- Innes, A.; Monios, J. Identifying the unique challenges of installing cold ironing at small and medium ports–The case of Aberdeen. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifakis, N.; Vichos, E.; Smaragdakis, A.; Zoulias, E.; Tsoutsos, T. Introducing the cold-ironing technique and a hydrogen-based hybrid renewable energy system into ports. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 20303–20323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippinen, I.; Federley, J. Fact-Finding Study on Opportunities to Enhance the Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impacts of Ports in the Baltic Sea Region; Baltic Sea Region Energy Cooperation (BASREC): Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Winkel, R.; Weddige, U.; Johnsen, D.; Hoen, V.; Papaefthimiou, S. Shore side electricity in Europe: Potential and environmental benefits. Energy Policy 2016, 88, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, A.; Cullinane, K. Potential for, and drivers of, private voluntary initiatives for the decarbonisation of short sea shipping: Evidence from a Swedish ferry line. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2021, 23, 632–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, N.N.A.; Bazmohammadi, N.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. Electrification of onshore power systems in maritime transportation towards decarbonization of ports: A review of the cold ironing technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 178, 113243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, C.L.; Borges, F.A.; Marinho, L.; Hernández, J.C.; Batista, T. Onshore Power Supply in Multi-Terminal Maritime Ports. Energies 2025, 18, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomano, A.; Del Papa, G.; Giuzio, G.F.; Palombo, A.; Russo, G. Future pathways for decarbonization and energy efficiency of ports: Modelling and optimization as sustainable energy hubs. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerlings, H.; van Duin, J.H.R.; van Rossum, T.R.; Heij, R. A Top-Down Methodology to Calculate the CO2-Footprint for Terminal Operations; the 6-Step Approach; Erasmus University Rotterdam: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kusakana, K. Optimal energy management of a retrofitted Rubber Tyred Gantry Crane with energy recovery capabilities. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Jin, Q.; Huang, H.; Tandon, P.; Zhu, Y. Life cycle assessment of Quayside Crane: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarero Orive, A.; Santiago, J.I.P.; Corral, M.M.E.I.; González-Cancelas, N. Strategic analysis of the automation of container port terminals through BOT (business observation tool). Logistics 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z. Scheduling quay cranes and yard trucks for unloading operations in container ports. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 273, 455–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Huang, P.C.; Tu, J.S. Life cycle assessment of yard tractors using hydrogen fuel at the Port of Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Energy 2019, 189, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port of Felixstowe. Port of Felixstowe: Home. 2023. Available online: https://www.portoffelixstowe.co.uk (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- CMB.TECH. CMB.TECH & Port of Antwerp-Bruges welcome Hydrotug to Belgium. 2023. Available online: https://www.cmb.tech (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Yau, K.L.A.; Peng, S.; Qadir, J.; Low, Y.C.; Ling, M.H. Towards smart port infrastructures: Enhancing port activities using information and communications technology. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83387–83404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdoukopoulos, E.; Boile, M.; Tromaras, A.; Anastasiadis, N. Energy efficiency in European ports: State-of-practice and insights on the way forward. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, J.H.R.; Geerlings, H.; Froese, J.; Negenborn, R.R. Towards a method for benchmarking energy consumption at terminals: In search of performance improvement in yard lighting. Int. J. Transp. Dev. Integr. 2017, 1, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asmus, P.; Wheelock, C. Microgrids: Distributed Energy Systems for Campus, Military, Remote, Community, and Commercial & Industrial Power Applications. Pike Res. Q. 2012, 1, 2012. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Yoldaş, Y.; Önen, A.; Muyeen, S.M.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Alan, I. Enhancing smart grid with microgrids: Challenges and opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, G.; Parise, L.; Martirano, L.; Chavdarian, P.B.; Su, C.L.; Ferrante, A. Wise port and business energy management: Port facilities, electrical power distribution. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 52, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Advances and trends of energy storage technology in microgrid. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 44, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jin, C.; Zhu, D.; Tang, Y.; Loh, P.C.; Choo, F.H. Distributed control for autonomous operation of a three-port AC/DC/DS hybrid microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, R.; Mahmood, A.; Razzaq, S.; Ali, W.; Naeem, U.; Shehzad, K. Prosumer based energy management and sharing in smart grid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M.; Ghiara, H.; Cusano, M.I. Energy management in sea ports: A new role for port authorities. Energy Policy 2014, 71, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, M.; Ketter, W.; Collins, J. Renewable energy cooperatives: Facilitating the energy transition at the Port of Rotterdam. Energy Policy 2018, 121, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESPO. Environmental Report: EcoPortsinSights 2019; European Sea Ports Organisation: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Marei, M.I.; Alajmi, B.N.; Abdelsalam, I.; Ahmed, N.A. An integrated topology of three-port dc-dc converter for PV-battery power systems. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2022, 3, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo-López, A.B.; Carrillo, C.; Díaz-Dorado, E. Contribution of Onshore Power Supply (OPS) and Batteries in Reducing Emissions from Ro-Ro Ships in Ports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Ports Organization. 2024: A Turning Point for the Maritime Industry’s Clean Energy Transition. 2023. Available online: https://www.worldports.org (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Port of Valencia. H2 Ports/Fuel Cells and Hydrogen in Ports. 2019. Available online: https://sustainableworldports.org/project/Port-of-Valencia-h2ports (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Misra, A.; Venkataramani, G.; Gowrishankar, S.; Ayyasam, E.; Ramalingam, V. Renewable energy based smart microgrids—A pathway to green port development. Strateg. Plan. Energy Environ. 2017, 37, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PortSEurope. The New Tugboat, Powered by LNG, Is Officially Part of Fleet in Bilbao. 2022. Available online: https://www.portseurope.com (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- PORTTECHNOLOGY. Antwerp Launches the World’s First Hydrogen-Powered Tug. 2022. Available online: https://www.porttechnology.org (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Song, D.P. A literature review of seaport decarbonisation: Solution measures and roadmap to net zero. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Kosmas, V.; Acciaro, M.; Renken, K. A comeback of wind power in shipping: An economic and operational review on the wind-assisted ship propulsion technology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagatsi, E.; Estrup, T.; Halatsis, A. Exploring the potentials of electrical waterborne transport in Europe: The E-ferry concept. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNV GL. Alternative Fuel for Shipping; Strategic Research & Innovation Position Paper; DNV: Oslo, Norway, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- EMSA. Update on Potential of Biofuels in Shipping; European Maritime Safety Agency: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou Raftis, C.; Vanelslander, T.; van Hassel, E. A global analysis of emissions, decarbonization, and alternative fuels in inland navigation—A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).