Biosorption and Isotherm Modeling of Heavy Metals Using Phragmites australis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Plant Biosorbents
2.2. Characterization of P. australis
2.3. Batch Biosorption Experiments
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm Models
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
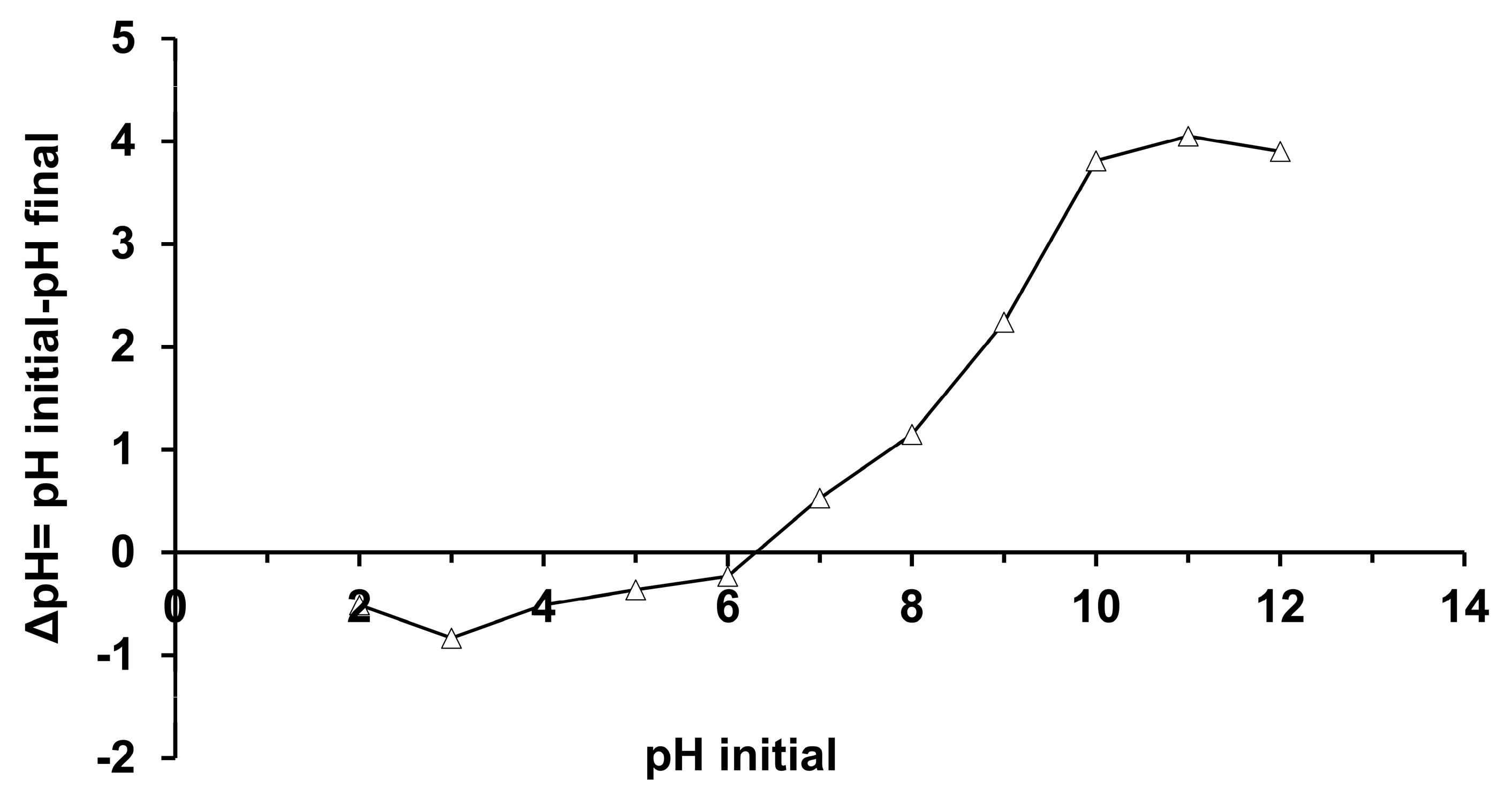
3.1. Determination of the Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
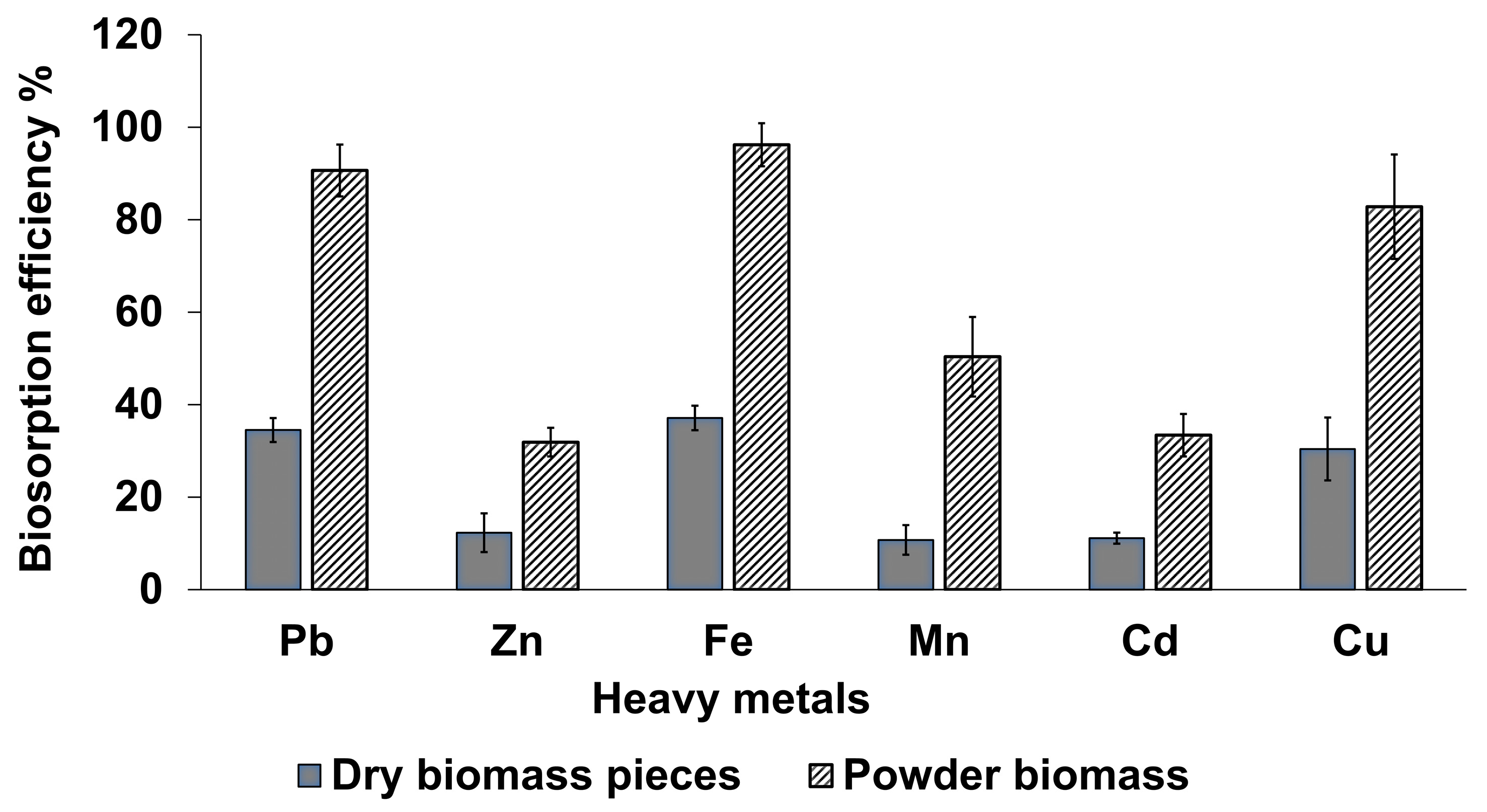
3.2. Effect of the Biomass’s Physical Form
3.3. Optimization of the Biosorption Parameters
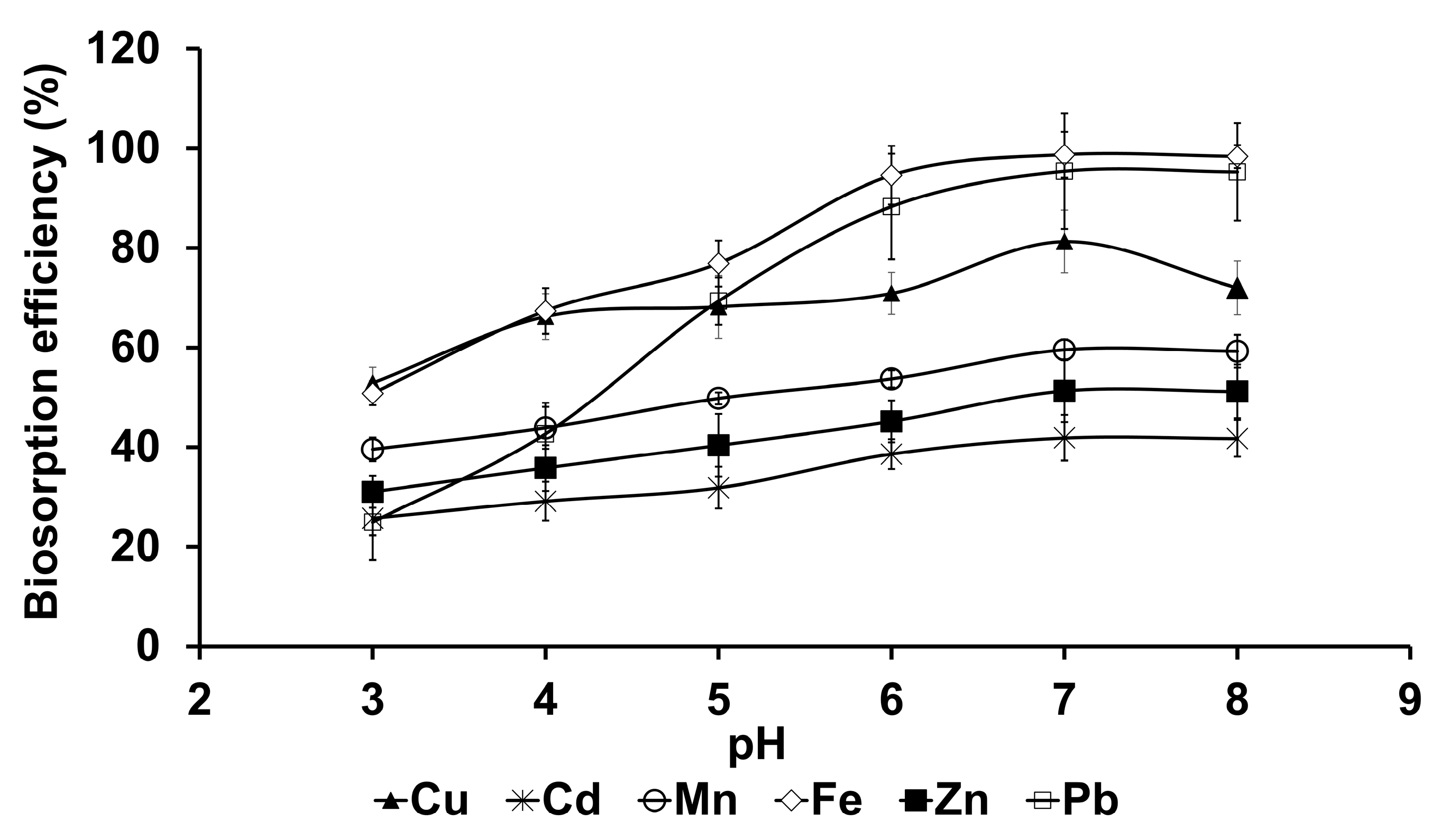
3.3.1. Effect of pH
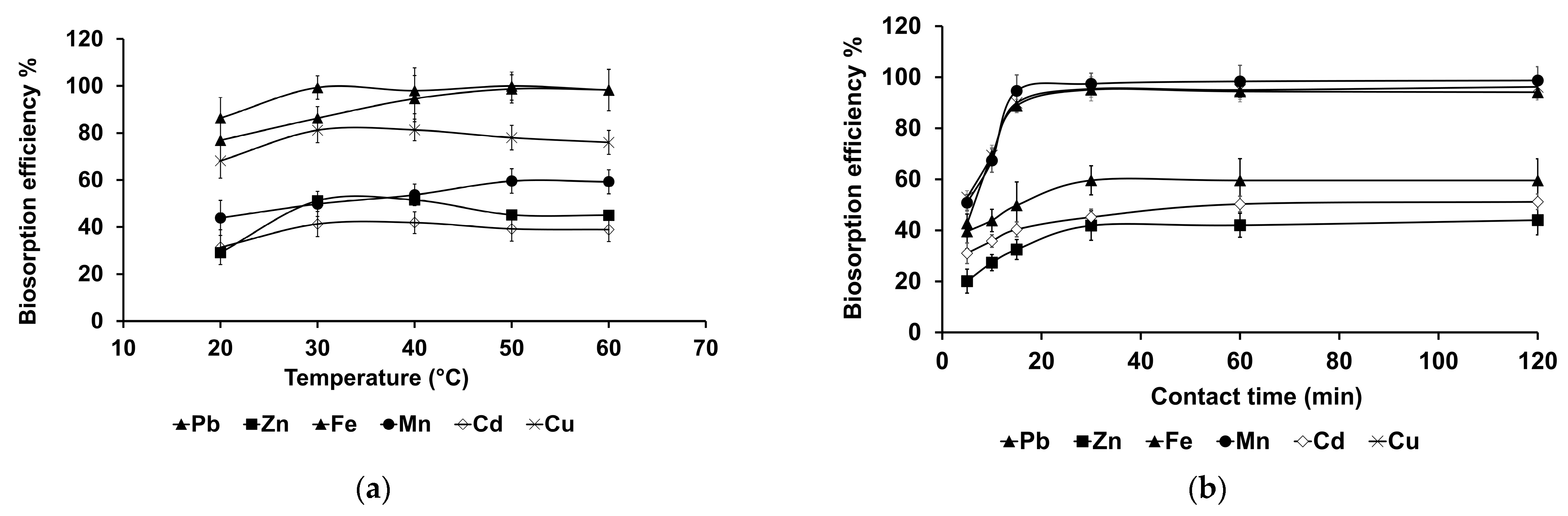
3.3.2. Effects of Temperature and Biosorption Time
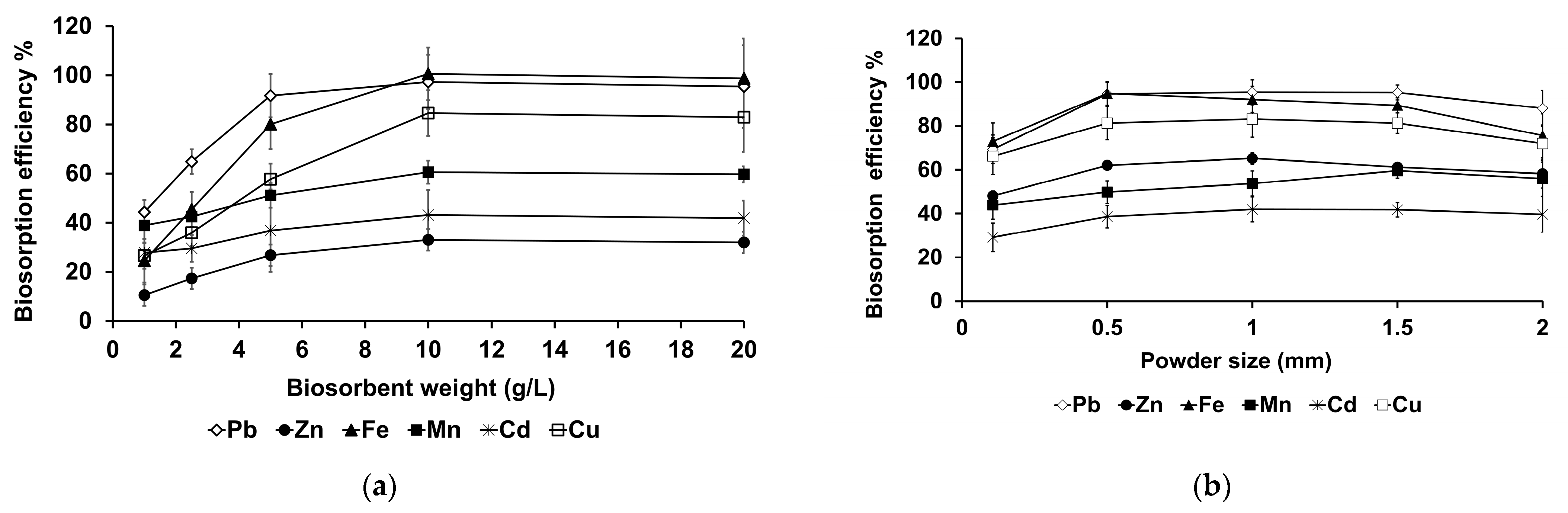
3.3.3. Effects of Powder Size and Weight Ratio on Biosorption
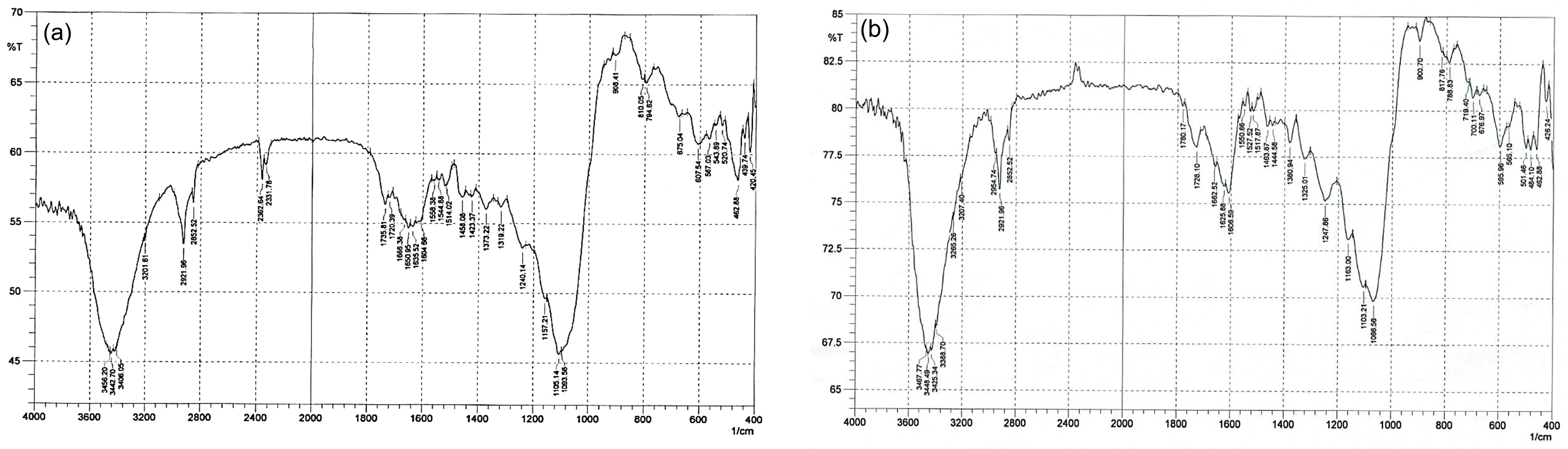
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
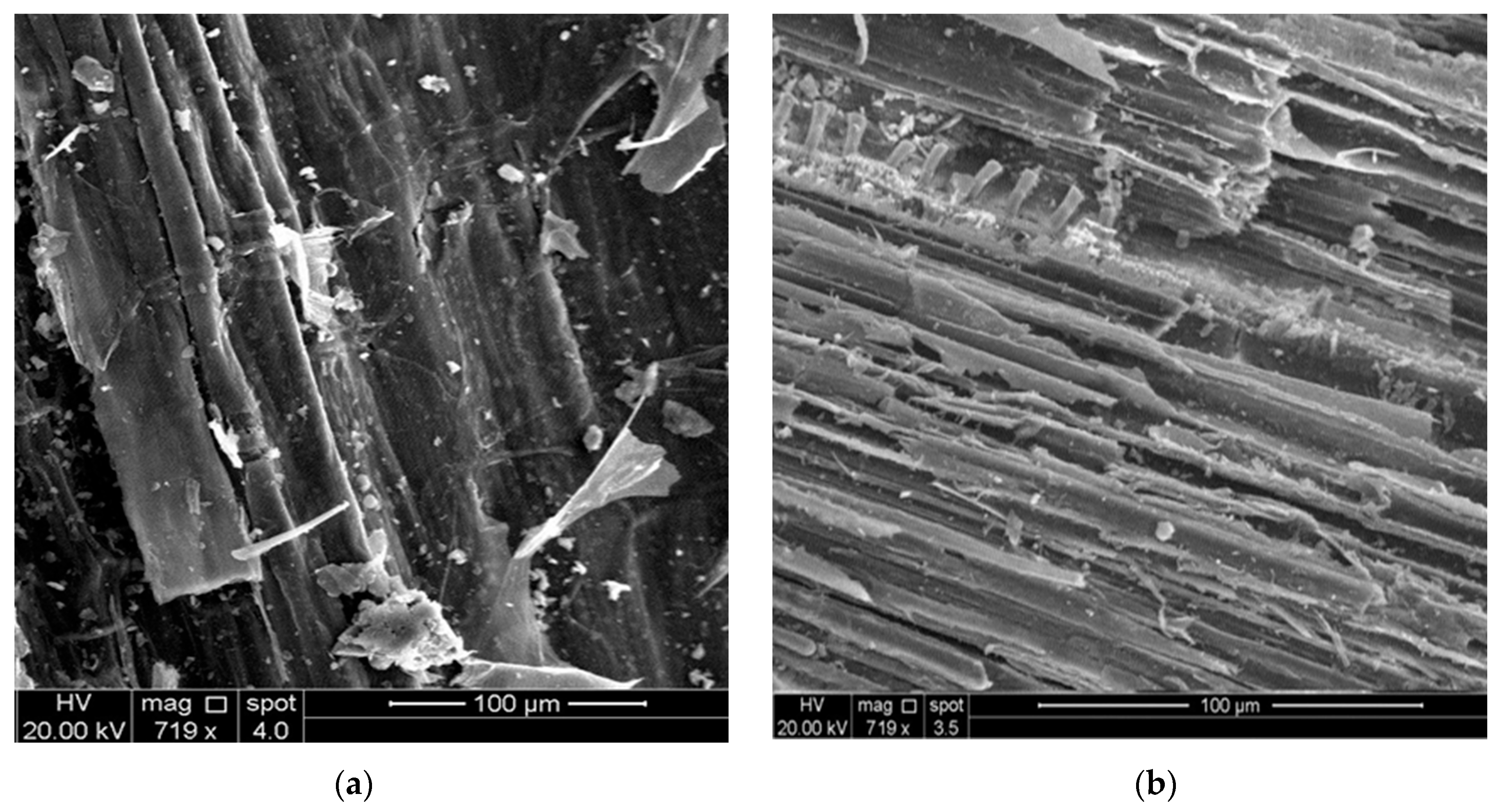
3.5. SEM Biomass Investigation
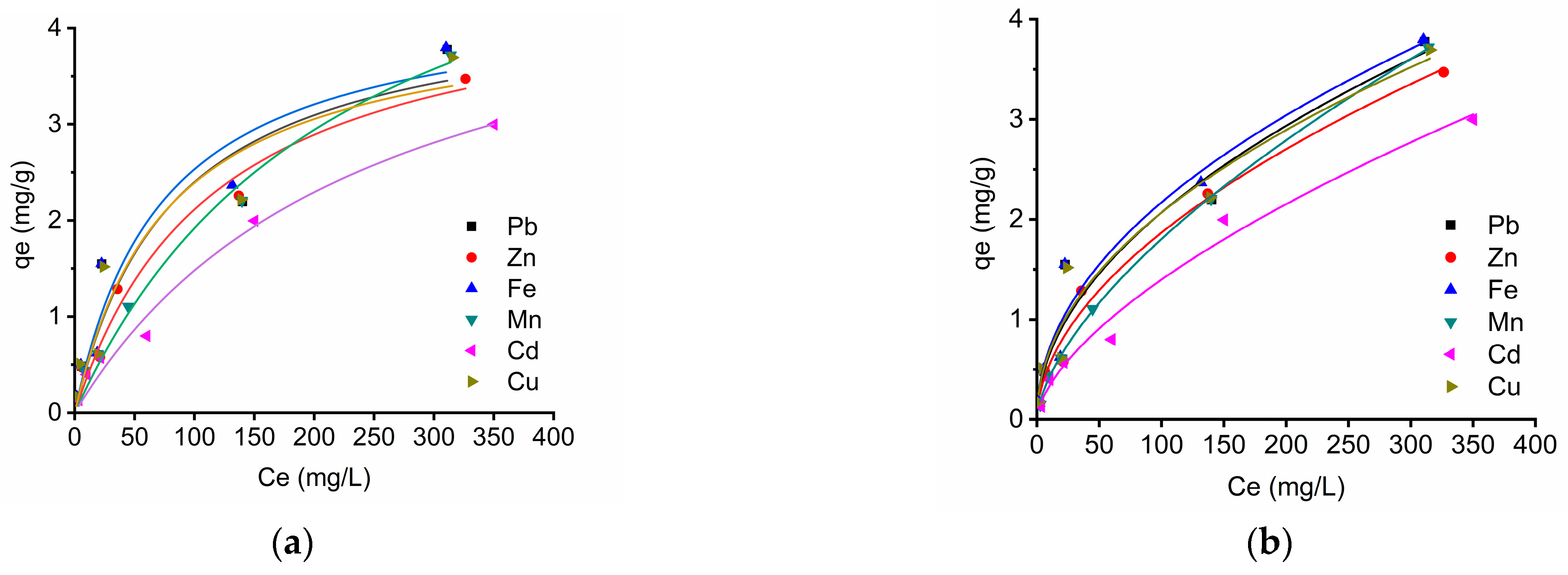
3.6. Isotherm Studies
3.6.1. Langmuir Isotherm
3.6.2. Freundlich Isotherm
3.7. Challenges and Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahamad, A.; Alshehrei, F.; Ali, S.A.; Khan, M.S. Impact of heavy metals on aquatic life: Recent scientific progress and future perspectives. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1374835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzaman, A.T.T.; Koohi, M.K.; Sadeghi, M.; Abedian, Z. Toxic mechanisms of cadmium and its possible risk of male infertility: A systematic review. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 09603271231210262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda [Internet]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.G.; da Silva, T.L.; de Souza, A.G. Environmental impacts related to drilling fluid waste disposal. Fuel 2022, 310, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.; Mandalia, H.C. Petroleum industries: Environmental pollution and its remediation. Int. J. Sep. Environ. Sci. 2012, 1, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Zaimee, A.A.; Jami, M.S.; Alam, L.; Bhawani, S.A. Heavy metals removal from water using natural adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beya, S.; Moulay, M.; Ramdhani, A.; Mehellou, M. Modern biotechnological methods for wastewater treatment. Chim. Technol. Acta 2022, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwikima, M.J.; Kayombo, S.; Mbuligwe, S.E. Potentials of agricultural wastes in removing heavy metals from contaminated water: A review. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertu, D.I.; Cheregi, M.-C.; Oancea, R.E. Modeling the biosorption process of heavy metals using different techniques. Processes 2022, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Naushad, M.; Alqadami, A.A.; ALOthman, Z.A. Orange peel as an effective adsorbent for the removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwiejuah, A.B.; Mutawakil, Z.; Oyelude, E.O. Eco-friendly banana peel biochar for adsorption of toxic metals from landfill treatment pond leachate. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2024, 27, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Rajendran, S.; Kumar, S. Pomegranate peel as a biosorbent for lead removal from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimus, A.D.; Pirvu, M.; Dragomir, R.E. Accumulation of heavy metals in Phragmites australis: A phytoremediation approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Coppi, A.; Nucci, S.; Antal, A.; Berardi, C.; Coppini, E.; Fibbi, D.; Del Bubba, M.; Gonnelli, C.; Colzi, I. Closing the loop in a constructed wetland for the improvement of metal removal: The use of Phragmites australis biomass harvested from the system as biosorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 11444–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Asgari, G. Potential of Phragmites australis to bioaccumulate heavy metals from landfill leachate. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertu, D.I.; Bulgariu, L.; Gavrilescu, M. Modeling and Optimization of Heavy Metals Biosorption by Low-Cost Sorbents Using Response Surface Methodology. Processes 2022, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Seshaiah, K.; Reddy, A.V.R.; Lee, S.M. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using Moringa oleifera bark: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I. Determination of sorbent point zero charge: Usefulness in sorption studies. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Park, J.; Rupani, P.F.; Darajeh, N.; Xu, X.; Shahrokhishahraki, R. Phytoremediation potential and control of Phragmites australis as a green phytomass: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7428–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Giudice, R.L. Heavy metal bioaccumulation by Phragmites australis (common reed) in a polluted Mediterranean river: Implications for phytoremediation. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E. Biosorption of heavy metals: Recent advances and future perspectives. Processes 2020, 8, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Li, K.; Sun, X. Removal of heavy metals by silica nanotubes functionalized with amine groups. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyairo, J.; Atieno, F.; Makhanu, S. Adsorption of heavy metals from water using modified food waste-derived adsorbents. Front. Environ. Chem. 2025, 6, 1526366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Devi, I. Biosorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous effluents utilising snail shell dust as a biomaterial. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 31879–31896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Trujillo, A.K.I.; Mussali-Galante, P.; de Hoces, M.C.; Blázquez-García, G.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A.; Rodríguez-Solís, A.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Ortiz-Hernández, L. Biosorption of heavy metals on Opuntia fuliginosa and Agave angustifolia fibers for their elimination from water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Ríos, P.C.; León-Romero, M.A.; Sukhbaatar, O.; Nishimura, O. Biosorption of Mercury by Reed (Phragmites australis) as a Potential Clean Water Technology. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y. Role of phosphorus-solubilizing organisms in biosorption of heavy metals. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akar, T.; Tosun, I.; Kiran, I.; Gedikbey, T. Biosorption of lead(II) ions onto waste biomass of Cucumis melo. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Islam, M.A.; Ahmed, M. Fibrous food waste-derived biosorbents for heavy metal removal. Molecules 2023, 28, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleem, M.; Rehman, R.; Khan, M.N. Cadmium and lead biosorption by Nostoc commune biomass. Molecules 2023, 28, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arief, V.O.; Trilestari, K.; Sunarso, J.; Indraswati, N. Biosorption of heavy metals using low-cost biosorbents: A review. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 937–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, H. Development of rice straw-based bioadsorbents for removal of heavy metals. BioResources 2023, 18, 3709–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, D.; Singh, N. Adsorption isotherm models and their comparison for heavy metal removal. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kamaraj, N.; Selvaraj, R.; Nanoth, R. Emerging trends and future outlook on chromium removal in the lab, pilot scale, and industrial wastewater system: An updated review exploring 10 years of research. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.K.; Mudhoo, A.; Lofrano, G.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Biomass-derived biosorbents for metal ions sequestration: Adsorbent modification and activation methods and adsorbent regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallhi, A.I.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Hussain, A.I.; Rizwan, M.; Bukhar, S.A.H.; Hussain, A.; Ahmad, P. Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of chromium through sunflower plants irrigated with tannery wastewater. Plants 2020, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayuo, J.; Rwiza, M.J.; Choi, J.W.; Mtei, K.M.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption and desorption processes of toxic heavy metals, regeneration and reusability of spent adsorbents: Economic and environmental sustainability approach. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 329, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, J. Environmental impacts and economic feasibility of biosorption for wastewater treatment: A case study with Phragmites australis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 12, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amro, A.N.; Abhary, M.K.; Shaikh, M.M.; Ali, S. Removal of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution by adsorption on a low-cost Phragmites Biomass. Processes 2019, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, E.L.; Mocanu, A.L.; Stroe, C.A.; Panciu, C.M.; Berca, L.; Sionel, R.M.; Mustatea, G. Agricultural Byproducts Used as Low-Cost Adsorbents for Removal of Potentially Toxic Elements from Wastewater: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.I.; Cortés, S.; Maluenda, P.; Soto, I. Biosorption of heavy metals with algae: Critical review of its application in real effluents. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Ion | qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | RL * | R2 | Kf (mg/g) | n | R2 | ||||
| Value | S.E. | Value | S.E. | Value | Value | Value | S.E. | Value | S.E. | Value | |
| Pb2+ | 4.363 | 0.965 | 0.0122 | 0.0070 | 0.450 | 0.904 | 0.202 | 0.093 | 1.981 | 0.347 | 0.944 |
| Zn2+ | 4.573 | 0.549 | 0.0086 | 0.0025 | 0.537 | 0.978 | 0.161 | 0.038 | 1.878 | 0.160 | 0.986 |
| Fe2+ | 4.370 | 0.764 | 0.0137 | 0.0070 | 0.420 | 0.930 | 0.231 | 0.087 | 2.055 | 0.306 | 0.958 |
| Mn2+ | 6.285 | 0.94 | 0.0044 | 0.0012 | 0.694 | 0.987 | 0.099 | 0.007 | 1.588 | 0.035 | 0.999 |
| Cd2+ | 5.101 | 0.882 | 0.0040 | 0.0013 | 0.710 | 0.981 | 0.079 | 0.024 | 1.607 | 0.149 | 0.984 |
| Cu2+ | 4.228 | 0.832 | 0.0130 | 0.0074 | 0.434 | 0.916 | 0.222 | 0.088 | 2.064 | 0.323 | 0.955 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammed, A.H.; Shartooh, S.M.; Trigui, M. Biosorption and Isotherm Modeling of Heavy Metals Using Phragmites australis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5366. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125366
Mohammed AH, Shartooh SM, Trigui M. Biosorption and Isotherm Modeling of Heavy Metals Using Phragmites australis. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5366. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125366
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammed, Ali Hashim, Sufyan Mohammed Shartooh, and Mohamed Trigui. 2025. "Biosorption and Isotherm Modeling of Heavy Metals Using Phragmites australis" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5366. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125366
APA StyleMohammed, A. H., Shartooh, S. M., & Trigui, M. (2025). Biosorption and Isotherm Modeling of Heavy Metals Using Phragmites australis. Sustainability, 17(12), 5366. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125366







