Abstract
Understanding the contribution of macroinvertebrate diversity indices to community stability in urban rivers is critical for developing more effective strategies to manage and conserve the ecological health of urban rivers and to maintain sustainable regional economic and social development. However, knowledge regarding the relationship between environmental factors, multidimensional biodiversity, and community stability in urban rivers remains limited. In this study, we investigated the relationships among macroinvertebrate multidimensional diversity, secondary productivity-to-biomass ratio (SP/B), and average variation degree (AVD) in a typical urban river—the North Canal River basin in Beijing—to identify which biodiversity metric best indicates community stability. Macroinvertebrates were extensively sampled from September to October 2020 in the North Canal River basin (BYH), a typical urban river in Beijing. We comparatively analyzed the spatial variation in different types of diversity—species diversity (SD), functional diversity (FD), and phylogenetic diversity (PD)—as well as SP/B and AVD between the upstream and midstream–downstream reaches of the river under varying degrees of urbanization and human disturbance. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) was used to assess the relationships among multidimensional diversity, SP/B, and AVD. The results showed that upstream environmental factors and diversity indices together explained 52.9% and 52.0% of the variance in SP/B and AVD, respectively, while midstream–downstream factors explained 65.9% and 84.2%, respectively. These findings suggest that both SP/B and AVD are suitable indicators for examining the relationships between macroinvertebrate community stability, diversity indices, and environmental factors in the BYH. In the upstream region, total phosphorus (TP), FD, and PD were more indicative of SP/B in the central urban area, while SD and PD were more indicative of AVD. In contrast, in the midstream–downstream suburban areas, dissolved oxygen (DO), SD, and PD were more indicative of SP/B, while FD and PD were more indicative of AVD. These findings demonstrate that PD is a stronger indicator of both SP/B and AVD under varying anthropogenic disturbances and environmental conditions. The PLS-SEM results also indicated differences in the specific effects of FD and SD on community stability across the upstream and midstream–downstream sections, as well as differences in the direct effects of environmental factors such as TP and DO. These results suggest that PD is more sensitive than FD and SD in detecting the impacts of anthropogenic disturbances and environmental fluctuations on macroinvertebrate community stability in urban rivers. Our study provides evidence that PD outperforms FD and SD in predicting macroinvertebrate community stability in urban river ecosystems and that the combined use of SP/B and AVD better reveals the complex interactions between biodiversity and environmental factors influencing community stability. This combination can thus enhance our understanding of how biodiversity affects macroinvertebrate community stability in urban rivers.
1. Introduction
Urbanization, as an important indicator of a country’s development level, has intensified interactions between human society and the ecological environment [1], and its progression is closely linked to regional river systems [2]. Since the 1980s, China’s rapid socioeconomic development and the rapid expansion of urban areas [3] have exerted considerable pressure on the aquatic ecosystems of urban rivers [4]. In 2010, the global urbanization rate reached 50% [5], and it has now surpassed this figure. According to the published by the National Bureau of Statistics, China’s urbanization rate increased to 63.89% in 2020. In recent years, with societal and economic advancement and accelerated urban development, recurring global water ecological crises have significantly affected the water bodies and ecological environments of urban rivers. Problems such as water pollution and a drastic decline in biodiversity have increasingly emerged as key challenges to the healthy and sustainable development of urban river ecosystems [6,7,8].
Extensive urbanization has been shown to severely degrade water quality and habitat conditions and reduce biodiversity in river systems [9,10]. Intensive anthropogenic activities in urban areas can significantly alter aquatic environments and ecological processes through increased nutrient and pollutant inputs, thereby affecting community stability [11,12]. Compared with other freshwater organisms, river macroinvertebrates are particularly sensitive to anthropogenic disturbances [13,14]. Different macroinvertebrate taxa display varying degrees of sensitivity to changes in aquatic environments [6], and their community composition strongly reflects shifts in water quality and habitat conditions [15]. Macroinvertebrates also exhibit characteristics such as relatively fixed habitat use, long life cycles, and limited access to refugia [16,17,18,19], which make it feasible to collect high-quality large-scale datasets [20]. As a result, macroinvertebrates have become focal organisms in the study of urban river ecology [21].
As an important component in maintaining the structure and function of riverine aquatic ecosystems [22], macroinvertebrate community stability has become a prominent focus of current research. This is because long-term community stability is critical for sustaining the structure and function of riverine aquatic ecosystems [23]. Community stability primarily refers to the ability of a community to resist disturbances and to recover to its original equilibrium state after disturbance [24]. Biodiversity, as a key factor in characterizing the complexity of biological communities, plays a significant role in this context. Jiang et al. found that diversity indices based on taxonomic and functional trait characteristics were more sensitive to human disturbance, as they reflected distinct aspects of environmental variation and anthropogenic stress. Therefore, they concluded that using a combination of multidimensional biodiversity indicators could effectively capture the response of macroinvertebrate communities to urbanization, anthropogenic disturbance, and environmental change in relation to community stability [25]. However, the relationship between biodiversity and community stability remains under debate [26].
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) enables researchers to conduct sophisticated statistical analyses. SEM can not only address direct causal relationships between study variables but also simultaneously estimate measurement errors and model latent variables, thereby revealing complex relationships—both direct and indirect—among multiple variables. It has been widely applied in various disciplines, including biology and psychology, to examine interactions among multiple variables [27,28]. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is a type of SEM based on Partial Least Squares Path Modeling, in which causal relationships are expressed through linear conditional expectations to identify optimal predictive relationships. PLS-SEM also incorporates latent variables to estimate complex causal models. Unlike covariance-based structural equation modeling methods, PLS-SEM prioritizes the prediction of dependent variables and the alignment of the model with empirical data; thus, Goodness-of-Fit (GoF) is considered less critical. Instead, model loadings are generally considered acceptable when they exceed 0.7. Additionally, PLS-SEM is appropriate for exploratory research and is suitable for both small to medium sample sizes and large datasets. It is also robust to violations of multivariate normality assumptions [29]. Yang et al. demonstrated the applicability of PLS-SEM by using it to study the relationships among phytoplankton communities, diversity indices, environmental variables, and urbanization levels [30]. Chi Shiyun et al. applied PLS-SEM to examine the relationships among environmental factors, algal population dynamics, and macroinvertebrate diversity [31]. Beijing serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of China, and the North Canal River basin (BYH) is the only typical urban river originating within Beijing’s administrative boundaries [32,33]. Investigating the relationship between macroinvertebrate diversity indices and community stability in the BYH holds great significance for promoting the healthy and sustainable development of this urban river under intense anthropogenic pressures, as well as for informing biodiversity conservation in urban rivers globally.
In recent years, the relationship between community stability and biodiversity has attracted increasing attention from scholars. Liu Yang et al. found that phylogenetic diversity (PD) and functional diversity (FD) were better predictors of macroinvertebrate community stability [34]. It has also been suggested that the relationship between PD and community stability varies depending on the specific type of community and its ecological constraints [35]. Other studies have indicated that species diversity (SD) is the strongest predictor of macroinvertebrate community stability [26]. However, most of these studies have focused on macroinvertebrates in natural rivers or large priority lakes. Research on urban rivers—where high levels of urbanization and anthropogenic disturbance are prevalent—is limited, and understanding of the relationships among environmental factors, multidimensional biodiversity, and community stability in these ecosystems remains insufficient. Therefore, in the present study, we selected key environmental variables and representative biodiversity indices to construct PLS-SEM to analyze the effects of environmental factors and different dimensions of biodiversity on community stability. This approach aims to reveal the complex relationships among environmental variables, biodiversity, and community stability in urban rivers, while providing data-driven support for the ecological management of urban rivers and the sustainable development of both society and the economy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The BYH is the only river that originates within the administrative boundaries of Beijing, the capital and political and economic center of China. It also serves as the starting point of the historic Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal. The BYH originates from the southern foot of the Yanshan Mountains in Changping District, Beijing, and has a watershed area of 4293 km2 within the city’s jurisdiction [32,33]. From its source to Shahe Gate, The BYH is fed by the South Sha River, North Sha River, and Dongsha River. From Shahe Gate to Beiguan Gate, the upstream section flows eastward and southeastward, receiving tributaries such as the Lingou River, Qing River, Ba River, and Tonghui River, spanning a river length of 47.5 km. The midstream–downstream section begins at Beiguan Gate, flows through Yangwa Gate, and eventually leaves the administrative boundary of Beijing. Along this stretch, it receives additional tributaries, including the Liangshui River and Gangou River, with a total length of 40.0 km [19,36]. The BYH watershed accounts for approximately 26% of the total area of Beijing, supports 70% of the city’s population, and contributes over 80% of the city’s gross domestic product. As the main flood discharge channel in Beijing, the BYH receives approximately 90% of the city’s annual floodwater, making it the most densely populated, industrially developed, and urbanized river area in Beijing [6,33,37,38]. The region has a warm-temperate, semi-arid to semi-humid monsoon climate, with predominantly plain topography. The average annual temperature ranges from 11 °C to 12 °C, and the average annual precipitation is 581.7 mm, mostly concentrated between June and September [36,37,38]. To ensure that the sampling sites accurately reflected the status of the macroinvertebrate community in the BYH, site selection was primarily based on the intensity of anthropogenic disturbances in the region. Informed by a detailed river site survey, additional factors such as river morphology, population density, public accessibility, and the representativeness of each site, in terms of local watershed characteristics, were also considered [19,39]. Based on these criteria, a total of 35 sampling sites were surveyed and monitored between September and October 2020 (Figure 1). Among these, sites BY01–BY22 represent the upstream section of the BYH, primarily located in densely populated and commercially developed central urban areas. Sites BY23–BY35 represent the midstream–downstream sections, predominantly located in the suburban regions of Beijing.
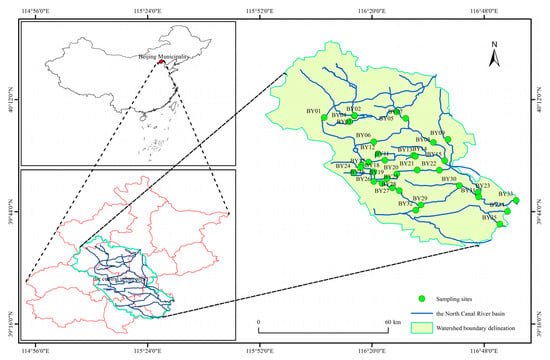
Figure 1.
Distribution of sampling sites in the North Canal River basin, Beijing.
2.2. Field Sampling
Macroinvertebrates were surveyed at 35 sampling sites along the BYH during the river water stabilization period from September to October 2020. Samples were primarily collected using hand nets and Peterson mud dredges. In wadeable sections of the river, a hand net, with a sampling area of 0.0625 m2 and a mesh size of 60 mesh (250 μm), was used. Macroinvertebrates within a 0.0625 m2 area in front of the net, in the direction of flow, were disturbed by kicking the substrate to dislodge organisms into the net. In non-wadeable sections, samples were collected using a Peterson dredge with a sampling area of 1/16 m2. Three replicate samples were collected at each site, combined into a single container, fixed and preserved in 95% ethanol, and transported to the laboratory for processing. In the lab, samples were sorted, identified, counted, and weighed. Macroinvertebrates were identified to the lowest possible taxonomic level (genus or species), following standard taxonomic literature [40,41,42,43].
Environmental factor data were collected simultaneously at each sampling site. Flow velocity (v) and water depth (D) were averaged from three replicate measurements at each site using a portable flow meter (LD-LS300A, Linede Intelligent Technology, Qingdao, China) and a high-precision telescopic water level ruler (GYP-TC005, TIQRI, Guangzhou, China), respectively. A portable multi-parameter water quality meter (YSI-Pro Plus, xylem, Washington, DC, USA) was used to measure water temperature (WT), electrical conductivity (Cond), total dissolved solids (TDS), salinity (Sal), and pH in situ. Habitat quality was assessed on-site using the Habitat Quality Assessment (HQA) scoring system developed by B.F. Cheng [44]. In accordance with the Methods of Analysis for Water and Wastewater Monitoring. Water samples were collected and transported to the laboratory within 48 h for the determination of various physicochemical parameters, including dissolved oxygen (DO), permanganate index (CODMn), chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand over five days (BOD5), ammonia nitrogen (NH4+-N), total phosphorus (TP), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), fluoride (F−), selenium (Se), arsenic (As), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), volatile phenols (VP), petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs), anionic surfactants (AS), sulfide (S2−), hexavalent chromium (Cr6+), and cyanide (CN−).
2.3. Dominance Index and Diversity Indices
The dominance index (Y) was used to identify dominant macroinvertebrate taxa, with taxa considered dominant when Y values exceeded 0.02. Diversity indices for macroinvertebrates [45,46] were calculated at each sampling site. SD was assessed using the Margalef richness index (d), Simpson diversity index (D), Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H′), and Pielou evenness index (J′), which are widely used to evaluate species diversity in ecological communities [46,47,48,49,50,51]. FD was assessed using the functional richness index (FRic), functional evenness index (FEve), functional divergence index (FDiv), and Rao’s quadratic entropy index (RaoQ) [52,53]. These indices were selected based on established methodologies [54,55,56,57]. Ten macroinvertebrates biological traits, which can be quantitatively categorized, were selected and classified into discrete trait categories. These traits have been shown to be key indicators of macroinvertebrate responses to various environmental gradients [56,58]. Functional traits were combined with species abundance data to calculate FD indices. FRic represents the range of functional traits present in the community; FEve quantifies the evenness of trait distribution within functional trait space; FDiv reflects the degree of divergence or variability in trait abundance [59]; and RaoQ incorporates both trait abundance and its variability in functional trait space [52]. PD was evaluated using the taxonomic diversity index (∆), taxonomic distinctness index (Δ*), average taxonomic distinctness index (∆+), and variation in taxonomic distinctness index (Λ+) [60]. PD was calculated based on six hierarchical taxonomic levels: phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species [55,61]. The index ∆ reflects the average taxonomic distance between any two randomly selected individuals. Δ* and ∆⁺ represent the average taxonomic distinctness between species, with Δ* accounting for species abundance and ∆⁺ representing unweighted distinctness. Λ⁺ captures the variation in taxonomic relatedness and reflects the unevenness of phylogenetic branching in the community [61].
2.4. Secondary Productivity-to-Biomass Ratio and Average Variation Degree
In this study, the secondary productivity-to-biomass ratio (SP/B) and average variation degree (AVD) were used to characterize macroinvertebrate community stability. SP/B serves as an indicator of the community’s maximum productivity. Higher SP/B values suggest that macroinvertebrates exhibit high turnover rates, rapid metabolic activity, greater adaptability to environmental change [62], and faster recovery following anthropogenic disturbances in urban rivers—all of which are indicated by higher community stability [26,63].
AVD is an index proposed and validated by Xun et al. [64] in 2021 to measure fluctuations in species abundance within microbial communities relative to the average degree of species divergence. This method enables researchers to assess how microbial communities respond to varying environmental conditions and to evaluate the role of biodiversity in community stability. AVD has the advantage of being independent of group sample size. Lower AVD values indicate greater stability within the community. Since its inception, AVD has been widely adopted in the study of microbial community stability [65]. In recent years, its application has expanded to encompass research on terrestrial plant [66] and aquatic biota such as phytoplankton communities [67,68], demonstrating its effectiveness in indicating the stability of these biological communities. However, AVD has yet to be applied in research related to macroinvertebrates. In the present study, we introduced AVD to evaluate macroinvertebrate community stability and compared its applicability to SP/B in assessing stability under urban river conditions.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Based on the collection of macroinvertebrate samples representing 74 taxa and a total of 2796 individuals (see Appendix A for details), differences in macroinvertebrate community structure between the upstream and midstream–downstream sections of the BYH were analyzed using Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) via the ‘vegan’ package in R. Analysis of Similarities (ANOSIM) was used to test the statistical significance of these structural differences. Representative environmental factors were screened in stages using discriminant power analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), and correlation analysis. Prior to further analysis, the selected environmental variables were standardized, and macroinvertebrate community data were transformed using the Hellinger method. Detrended Correspondence Analysis (DCA) was applied to the community data to determine gradient lengths. Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) was performed when the longest gradient exceeded 4.0, and Redundancy Analysis was used when the gradient was less than 3.0 [69]. Key environmental variables with significant influence on macroinvertebrate communities were identified using the Envfit function with Monte Carlo permutation tests (999 permutations) [46]. FD indices were calculated using the ‘dbFD’ function from the ‘FD’ package in R. PD indices were calculated using the ‘taxondive’ and ‘taxa2dist’ functions from the ‘vegan’ package. A t-test was used to determine the significance of differences in diversity indices, SP/B, and AVD between the upstream and midstream–downstream regions. To reduce the complexity of the structural equation model, representative diversity indices were selected using Spearman correlation analysis. Key environmental variables, representative diversity indices, SP/B, and AVD were used to construct PLS-SEM using the ‘plspm’ package in R to simulate and analyze the relationships among environmental variables, multidimensional biodiversity, and community stability. The path coefficient (Pc) was used to indicate the strength and direction of the relationships between variables [70]. All analyses and data visualizations were conducted using Origin 2022, Microsoft Excel 2016, and ArcGIS 10.2.
3. Results and Analyses
3.1. Macroinvertebrate Community Composition
A total of 74 macroinvertebrate taxa were identified in the BYH, belonging to 3 phyla, 6 classes, 14 orders, and 26 families. Among them, taxa in the class Insecta accounted for 67.57% of all recorded taxa, making it the overwhelmingly dominant taxon in the BYH. Taxa in the subclass Oligochaeta represented 12.16%, followed by Gastropoda (10.81%), Lamellibranchia (4.05%), and both Crustacea and Hirudinea, which each accounted for 2.70% of the total taxa. The spatial distribution of macroinvertebrate communities across sites is shown in Figure 2. Dominant taxa in the BYH, based on dominance index values (Y), included Bellamya purificata (Y = 0.075), Chironomus flaviplumosus (Y = 0.070), and Baetis sp. (Y = 0.026).
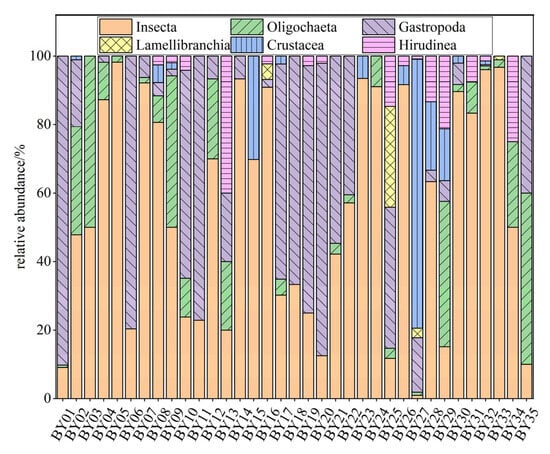
Figure 2.
Macroinvertebrate community composition of the North Canal River basin, Beijing.
The results of the NMDS analysis (Figure 3) revealed a clear spatial separation between the upstream and midstream–downstream sections in terms of macroinvertebrate community composition (Stress = 0.198). ANOSIM analysis further confirmed that the differences in community structure between upstream and midstream–downstream sections were statistically significant (p < 0.01). A total of 57 taxa, belonging to 3 phyla, 6 classes, 13 orders, and 21 families, were collected from the upstream section of the BYH. In comparison, 41 taxa belonging to 3 phyla, 6 classes, 12 orders, and 20 families were identified in the midstream–downstream sections. The overall macroinvertebrate community structure is presented in Figure 4. In terms of relative abundance, Diptera was the most dominant taxon in both the upstream and midstream–downstream regions, accounting for 50.88% and 46.34%, respectively. This was followed by Tubificida (14.04%, 9.76%) and Mesogastropoda (10.53%, 9.76%). The relative abundance of these dominant taxa declined in the midstream–downstream, while the relative abundance of Trichoptera and Odonata increased compared to the upstream section. Dominant taxa in the upstream included Bellamya purificata (Y = 0.148), Chironomus flaviplumosus (Y = 0.057), Baetis sp. (Y = 0.033), and Semisulcospira cancellata (Y = 0.032). In the midstream–downstream sections, dominant taxa included Chironomus flaviplumosus (Y = 0.075), Macrobrachium sp. (Y = 0.047), Polypedilum scalaenum (Y = 0.023), Cricotopus trifasciatus (Y = 0.022), and Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri (Y = 0.021).
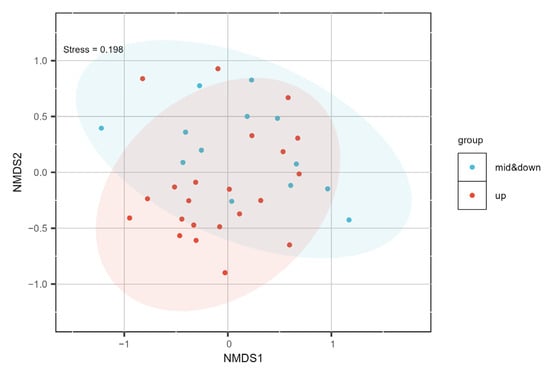
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution patterns of macroinvertebrate communities in the North Canal River basin, Beijing.
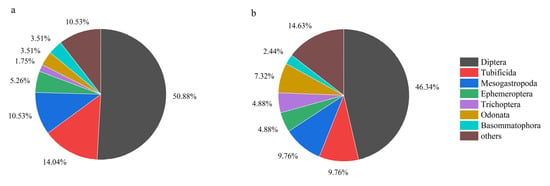
Figure 4.
Macroinvertebrate community composition in the upstream (a) and midstream–downstream (b) sections of the North Canal River basin, Beijing.
3.2. The Key Environmental Factors Affecting Macroinvertebrates Communities
Initially, environmental factors which exhibited low variability and weak discriminatory power (standard deviation, SD < 0.01) across the BYH, were excluded based on discriminant power analysis. Subsequently, the remaining environmental variables were standardized and subjected to PCA. Six principal components, with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 80%, were extracted using the maximum variance rotation method. Environmental variables with low eigenvalue contributions (rotated loadings below 0.6) were then excluded. Thereafter, further analysis of the remaining environmental variables were using Spearman’s correlation analysis. Among environmental variables exhibited redundancy and high pairwise correlations (|r| > 0.5), only one representative variable was retained. Ultimately, five representative environmental factors—DO, COD, Cu, pH, and TP—were retained based on the combined results of discriminant power analysis, PCA, and correlation analysis.
The results of DCA showed that the maximum length of the gradient for the macroinvertebrate community was greater than 4.0. Therefore, CCA was selected as the appropriate ordination method. The CCA results indicated that the first two axes—CCA1 (27.61%) and CCA2 (24.07%)—together explained 51.68% of the variation in macroinvertebrate community structure (Figure 5). Based on Monte Carlo permutation tests and Envfit fitting analysis, COD and TP were strongly positively correlated with Axis 1 (+1.000 and +0.861, respectively), while pH was strongly negatively correlated with Axis 1 (–0.732), suggesting that COD, TP, and pH were the primary environmental factors influencing community distribution along this axis. In contrast, DO and Cu were highly negatively correlated with Axis 2 (–0.906 and –0.900, respectively), while pH showed a strong positive correlation with Axis 2 (+0.682), indicating that DO, Cu, and pH were the main drivers of community variation along Axis 2. The explanatory power of each variable, as measured by adjusted R2 and tested via permutation, showed that TP (R2 = 0.595, p < 0.001) and Cu (R2 = 0.854, p < 0.001) had highly significant and strong explanatory power. COD (R2 = 0.276, p < 0.05) and DO (R2 = 0.285, p < 0.01) were also significant, though their explanatory power was lower. In contrast, pH (R2 = 0.023, p = 0.538) showed low and statistically non-significant explanatory power. When integrated with the findings in Table 1, it was evident that increasing COD and TP concentrations acted as negative drivers of macroinvertebrate community composition from the upstream to midstream–downstream sections of the BYH. Conversely, increasing DO and decreasing Cu concentrations were positive drivers of community change along the same gradient. However, these spatial differences in environmental influence were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Overall, the analysis identified DO, COD, TP, and Cu as the key environmental factors significantly shaping the spatial distribution of macroinvertebrate communities in the BYH (p < 0.05).
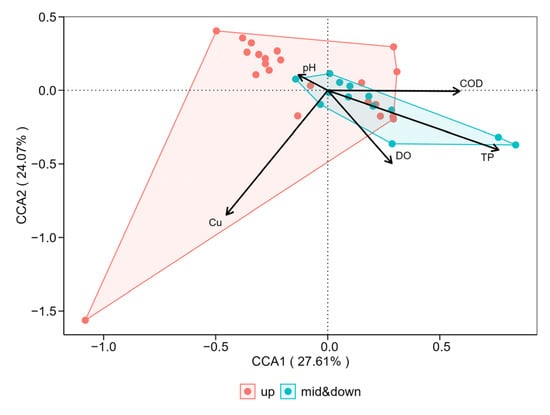
Figure 5.
Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) of environmental variables and macroinvertebrate community composition in the North Canal River basin, Beijing.

Table 1.
Summary of parametric statistics for key environmental variables in the North Canal River basin, Beijing.
3.3. Biodiversity and Representative Diversity Indices
Results of the t-test indicated no significant differences in SD and FD indices of macroinvertebrates between the upstream and midstream–downstream sections of the BYH (p > 0.05). However, the mean values of SD indices—including d, D, H′, and J′—were lower in the midstream–downstream (0.685, 0.62, 1.93, and 0.68, respectively) than in the upstream section (0.692, 0.67, 2.04, and 0.73, respectively). Conversely, the mean values of FD indices—including FRic, FEve, FDiv, and RaoQ—were higher in the midstream–downstream (11.80, 0.50, 0.83, and 7.33) compared to the upstream (8.27, 0.45, 0.75, and 5.99). As shown in the violin plots (Figure 6), the mean value ∆ for PD in the midstream–downstream section (43.69) was significantly lower than that in the upstream section (49.30) (p < 0.05). No significant differences were found for Δ*, ∆⁺, or Λ⁺ between the upstream and midstream–downstream sections (p > 0.05). However, the mean values of Δ* and Λ+ in the midstream–downstream section (69.20 and 493.83) were lower than those in the upstream (73.44 and 686.73), whereas the mean value of ∆⁺ was slightly higher in the midstream–downstream (78.10) compared to the upstream (77.49).
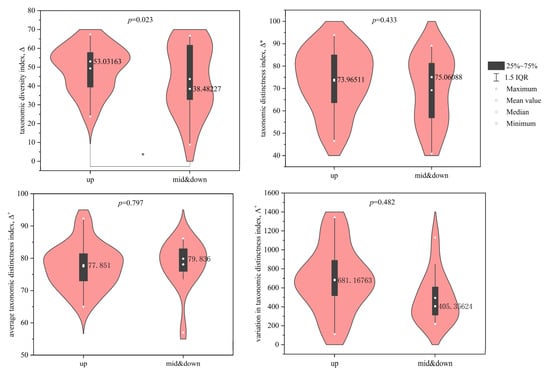
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic diversity indices of macroinvertebrates in the North Canal River basin, Beijing (* represents p < 0.05).
Spearman correlation analysis results are shown in Figure 7. A strong positive correlation (p < 0.01) was observed between H′ and d, D, and J′, with correlation coefficients of 0.65, 0.92, and 0.55, respectively. A high correlation coefficient (r = 0.78) was also found between D and J′, indicating overlapping information among these indices. Since H′ reflects broader ecological significance [71], it was selected to represent SD in this study. For FD, RaoQ exhibited a highly significant positive correlation with both FRic and FEve (p < 0.01). Notably, the correlation coefficient between RaoQ and FEve was 0.69, suggesting strong redundancy. In contrast, FDiv showed no significant correlation with the other FD indices, indicating that it captured unique aspects of functional structure not explained by FRic or RaoQ. Therefore, based on the principle of maximizing information retention while minimizing redundancy, FRic, FDiv, and RaoQ were selected as representative FD indices. For PD, strong positive correlations were observed among ∆, Δ*, and ∆⁺ (p < 0.01), with correlation coefficients of 0.67 (∆–Δ*), 0.54 (∆–∆⁺), and 0.61 (Δ*–∆⁺), respectively. In contrast, Λ⁺ showed significant negative correlations with all three indices (p < 0.05), suggesting it reflected different information. Considering these relationships and the significant upstream versus midstream–downstream differences in ∆, ∆ and Λ+ were selected as representative indices for PD.
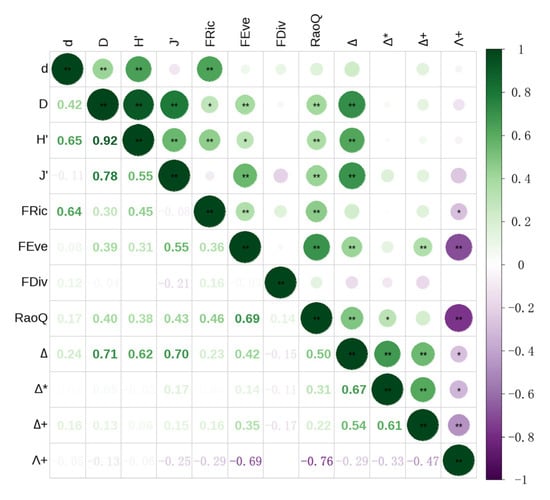
Figure 7.
Heatmap of Spearman correlation coefficients among macroinvertebrate biodiversity indices in the North Canal River basin, Beijing.
3.4. Spatial Variability of the Secondary Productivity-to-Biomass Ratio and Average Variation Degree
The results of the t-test, in combination with the violin plots (Figure 8), showed that there was no statistically significant difference in SP/B between the upstream and midstream–downstream macroinvertebrate communities in the Beiyunhe River (p > 0.05). However, the mean SP/B value in the midstream–downstream section (17.55) was higher than that in the upstream section (10.92). In contrast, the AVD of macroinvertebrates in the midstream–downstream section was significantly lower than that in the upstream (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that macroinvertebrate community stability was higher in the midstream–downstream section of the BYH compared to the upstream.
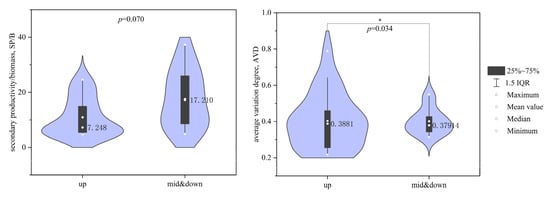
Figure 8.
SP/B and AVD of macroinvertebrate communities in the North Canal River basin, Beijing (* represents p < 0.05).
3.5. Relationships Between Environmental Factors, Biodiversity and Community Stability in Urban Rivers
To facilitate a clear presentation of the model results, paths with standardized coefficients less than 0.1 were excluded. The complex relationships between SP/B, AVD, representative diversity indices, and key environmental factors influencing the spatial distribution of macroinvertebrate communities were analyzed using PLS-SEM (Figure 9). The GoF for the upstream model and the midstream–downstream model are 0.4207 and 0.5234, respectively. Among the latent variables, only the FDiv within FD construct and the variation in Λ⁺ within PD construct had path loadings below 0.7 in the upstream model. In the midstream–downstream model, only FDiv exhibited a loading value below 0.7. All other observed variables had loadings above 0.7, indicating that the constructed PLS-SEM exhibited good reliability and model fit. In the upstream model (Figure 9a), environmental factors and diversity indices together explained 52.9% of the variation in SP/B and 52.0% of the variation in AVD. In the midstream–downstream model (Figure 9b), these variables explained 65.9% of the variance in SP/B and 84.2% of the variance in AVD.
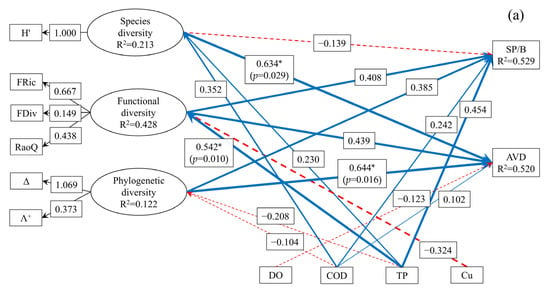
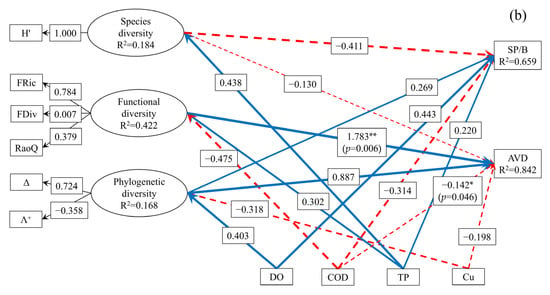
Figure 9.
Relationships among environmental factors, multidimensional biodiversity, SP/B, and AVD in the macroinvertebrate communities of the upstream (a) and midstream–downstream (b) sections of the North Canal River basin, Beijing (* represents p < 0.05, ** represents p < 0.01, numbers on each arrow indicate partial correlation coefficients associated with each causal relationship; solid lines indicate positive correlation, whereas dashed lines indicate negative correlation).
As shown in Figure 9, the effects of environmental factors and the spatial distribution of multidimensional biodiversity on the spatial distribution of macroinvertebrate SP/B in both the upstream and midstream–downstream sections of the BYH were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). However, in the upstream region, the positive path coefficients of COD, TP, FD, and PD on SP/B were 0.242, 0.454, 0.408, and 0.385, respectively. Among the environmental variables, elevated TP significantly promoted FD (Pc = 0.542, p < 0.05), while Cu suppressed FD (Pc = −0.324). Whereas TP suppressed PD (Pc = −0.208). These findings indicate that TP and Cu indirectly influenced SP/B in the upstream section through their effects on FD and PD. Compared to other environmental factors and SD, TP, FD, and PD had stronger indicative effects on SP/B in the upstream region. In the midstream–downstream section, the positive effects of DO, TP, and PD on SP/B were 0.443, 0.220, and 0.269, respectively, while the negative effects of COD and SD were –0.314 and –0.411, respectively. Elevated TP promoted SD (Pc = 0.438). Additionally, DO promoted PD (Pc = 0.403), whereas Cu suppressed PD (Pc = −0.318). These results suggest that DO, TP, and Cu indirectly influenced SP/B in the midstream–downstream region through their effects on SD and PD. Compared with the effects of other environmental variables and FD, DO, SD, and PD exhibited stronger indicative effects on SP/B in the midstream–downstream region. Overall, PD demonstrated the strongest indicative effect on macroinvertebrate SP/B across both upstream and midstream–downstream sections, suggesting its central role in reflecting community productivity and adaptability in urban rivers.
The spatial distributions of SD and PD significantly influenced the spatial distribution of macroinvertebrate AVD in the upstream section of the BYH (p < 0.05), with positive path coefficients of 0.643 and 0.644, respectively. Although the spatial distribution of FD did not show a statistically significant effect on AVD (p > 0.05), its positive path coefficient was 0.439, indicating a moderate contribution. In the upstream region, increases in COD and TP promoted SD (Pc = 0.352 and Pc = 0.230, respectively). Combined with the observed effects of TP and Cu on FD and PD, these results indicate that COD, TP, and Cu indirectly influenced upstream AVD through their effects on SD, FD, and PD. These analyses suggest that SD and PD had stronger indicative effects on macroinvertebrate AVD in the upstream region of the BYH. In the midstream–downstream section, the spatial distributions of COD and FD had significant effects on AVD (p < 0.05), with path coefficients of −0.142 (negative) and 1.783 (positive), respectively. Although PD did not significantly affect AVD in this region (p > 0.05), its path coefficient was 0.887, indicating a potentially important contribution. Elevated COD suppressed FD (Pc = −0.475, respectively). Considering the additional effects of DO and Cu on PD, these findings suggest that DO, COD, and Cu indirectly influenced AVD through FD and PD in the midstream–downstream section of the BYH. Overall, these results indicate that FD and PD were the primary contributors to variation in AVD in the midstream–downstream section, whereas SD and PD were more influential in the upstream section. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that PD is the most robust indicator of macroinvertebrate AVD in urban rivers such as the BYH. This conclusion aligns with earlier findings regarding SP/B, further validating AVD as an effective indicator of macroinvertebrate community stability in urban river ecosystems.
4. Discussion
4.1. Macroinvertebrates Community Structure and the Key Environmental Factors
Due to its primary functions in urban drainage and flood control, the BYH is highly channelized, with a large number of bridges, sluice gates, and other hydraulic and amenity facilities. Consequently, human activities exert substantial control and influence over the river system [71], leading to a simplified habitat structure. This, in turn, has contributed to the historically low species richness of macroinvertebrate communities in the BYH. In 2015, Gu Xiaoyun et al. reported a total of 23 macroinvertebrate taxa in the BYH [19,72], with dominant taxa including Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri, Limnodrilus claparedianus, Aulodrilus bretscheri, and Branchiura sowerbyi. With the introduction of China’s “Ecological Civilization” policy, Beijing launched the “Three-Year Action Plan for Sewage Treatment” in 2013, which has since been renewed every three years. As part of this plan, sewage outfalls along the BYH have been progressively intercepted and integrated into municipal pipelines to reduce pollutant discharge into the river. In 2017, China implemented the nationwide river chief system, and the BYH appointed 1560 river chiefs responsible for initiatives such as the “Clean River Action” and the “Four Disorder Rectification” campaign. In the same year, ecological greening of riparian zones was undertaken to enhance their capacity to intercept pollutants from urban runoff. As a result of these comprehensive ecological restoration efforts and improved management policies, the sewage treatment rate in the BYH rose from 67.2% in 2015 to over 90% in recent years. By 2020, a total of 74 macroinvertebrate taxa were recorded in the BYH—more than a twofold increase in species richness compared to 2015—indicating a substantially improved community structure. However, the community remained dominated by Bellamya purificata, Chironomus flaviplumosus, and Baetis sp., all of which are taxa with moderate to high tolerance to pollution. This finding is consistent with the conclusion by Xiong Chunhui et al. that macroinvertebrate communities in urban rivers are generally dominated by pollution-tolerant taxa [73,74].
The results of the NMDS, ANOSIM, and Y analyses indicated that the macroinvertebrate community structure in the BYH exhibited significant spatial variation. The relative abundances of dominant taxa—Diptera, Tubificida, and Mesogastropoda—declined from the upstream to the midstream–downstream sections. In particular, the species richness of Chironomidae within Diptera decreased markedly, a trend primarily associated with differences in urbanization intensity and anthropogenic activity across the river’s longitudinal gradient. The upstream section, located in the central urban area, is characterized by high urbanization, dense population, concentrated commercial activity, an advanced economy, and large volumes of domestic and industrial wastewater discharge. Additionally, this region exhibits a high degree of channelization, which negatively impacts macroinvertebrate community structure by facilitating pollutant runoff and sediment deposition during rainfall events [19]. In contrast, the midstream–downstream sections located in suburban areas are less channelized, feature more ecological berms, and have increased riparian vegetation. These riparian plants absorb N, P and other nutrients, enhancing DO levels in the water, thereby improving habitat conditions for macroinvertebrate communities [33]. However, suburban areas often lag behind in sewage pipeline infrastructure, and there is a greater risk of non-point source pollution from livestock, poultry, and untreated domestic wastewater. As a result, elevated COD and nutrient loads (e.g., N and P) continue to affect macroinvertebrate community structure in these regions [38,75,76]. This spatial variation is reflected in the shift in dominant taxa: from Bellamya purificata, Chironomus flaviplumosus, Baetis sp., and Semisulcospira cancellata in the upstream section, to Chironomus flaviplumosus, Macrobrachium sp., Polypedilum scalaenum, Cricotopus trifasciatus, and Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri in the midstream–downstream section.
Xu Saisai et al. reported that the distribution of macroinvertebrate communities was primarily influenced by DO, followed by nutrients such as P and other chemical constituents in the water body [77]. King et al. investigated urban rivers and found that organic pollution resulting from urban wastewater discharges was a key driver of community degradation and biodiversity loss in urban rivers [78]. Similarly, Qu et al. (2017), in their study of the Longgang River in Shenzhen [79], identified TP and NH₄⁺-N as the main factors contributing to macroinvertebrate community degradation. In the BYH, Hu Xiaohong et al. identified TP, BOD5, NH4+-N, F−, and DO as major environmental drivers of macroinvertebrate communities in 2015 [6]. Du Fang et al., through a study of urban river water quality in the BYH from 2018 to 2020 [38], identified COD, TP, and TN as the key factors affecting the river’s ecological carrying capacity. These two studies analyzed the BYH environmental drivers from different perspectives—ecological sensitivity (Hu Xiaohong) and pollutant loading impacts (Du Fang). In the present study, CCA and Envfit analysis identified DO, COD, TP, and Cu as the key environmental drivers of spatial variation in macroinvertebrate community structure in the upstream and midstream–downstream sections of the BYH in 2020. Furthermore, the directional effects—both positive and negative—of DO, Cu, COD, and TP on macroinvertebrate spatial distribution were examined in conjunction with Table 1 and the corresponding spatial community structure. These findings closely align with those reported by Hu Xiaohong et al. and Du Fang et al., reinforcing the critical roles of DO, nutrients, and specific pollutants (e.g., Cu) in shaping macroinvertebrate communities in urban rivers such as the BYH [6,38]. Compared with natural river systems, several studies have demonstrated that environmental factors such as DO, COD, and nutrients play significant roles in shaping macroinvertebrate community structure. Chen Xiaohua et al. found a strong spatial response of macroinvertebrate distribution to variations in DO levels in natural rivers [80]. Similarly, reported that COD had a substantial negative impact on macroinvertebrate community composition [81]. Chen Li and Yan Yunjun et al. also observed that nutrient concentrations, particularly N and P, influenced the spatial distribution patterns of macroinvertebrates in river ecosystems [82,83]. These findings collectively support the conclusion that DO, COD, and TP serve as reliable indicators of macroinvertebrate community dynamics. In contrast, due to intense anthropogenic activity and high urbanization in urban rivers such as the BYH, this study identified Cu, a heavy metal pollutant, as a significant environmental factor influencing macroinvertebrate community structure. This result is consistent with the findings of Zhang Qi et al., who reported that Cu was a key factor affecting macroinvertebrate communities in the Xiangjiang River Basin [84]. However, Cu is less frequently reported as a major influencing factor in studies of natural rivers, suggesting that its ecological impact is more pronounced in urbanized settings.
4.2. Community Stability and Diversity Indices for Macroinvertebrates
The results of the t-test, combined with the violin plot analysis, showed no statistically significant differences in SD, FD, and SP/B between the upstream and midstream–downstream sections of the BYH. This outcome is likely related to the relatively homogeneous habitats characteristic of urban rivers and the elevated concentrations of pollution from anthropogenic activities. These findings are consistent with those of Latinopoulos et al. [85], who reported that nutrient and organic pollution loads in peri-urban Mediterranean rivers reduced macroinvertebrate abundance and biodiversity, resulting in the loss of seasonal and temporal variation in community structure and leading to homogenization of biological functions and taxonomic composition. SD is a fundamental metric that quantifies the number of species and their relative abundances, yet it fails to account for the functional or phylogenetic distinctiveness of species. In urban rivers, SD may be constrained by anthropogenic disturbances, thereby failing to accurately reflect community stability [86]. FD focuses on the range of functional traits within a community, which is crucial for understanding how communities respond to environmental changes. However, urban rivers typically lead to the simplification of ecological functions, as the loss of specialized species and the dominance of generalized species result in the homogenization of functional traits, rendering FD less informative and limiting its predictive capacity in highly urbanized areas [87]. Despite the increased presence of ecological berms in the midstream–downstream region of the BYH, the construction of sewage infrastructure in suburban areas remains insufficient, and livestock farming continues to expand. Although these berms support the survival and reproduction of a few non-pollution-tolerant taxa, the species richness of highly pollution-tolerant taxa has declined markedly. This decline is the primary reason that species diversity in the midstream–downstream section was slightly lower than in the upstream section. Moreover, the increased habitat complexity in the midstream–downstream region likely contributed to a reduction in the dominance of single pollution-tolerant taxa such as Chironomidae, while allowing a broader range of macroinvertebrate populations to establish. This shift in community composition led to greater differentiation in functional traits, which likely explains the slightly higher functional diversity observed in the midstream–downstream section compared to the upstream. In contrast, the upstream region of the BYH, particularly in the central urban area, is dominated by single, highly channelized habitats with fine sediment substrates. Under conditions of high urbanization, intense anthropogenic disturbance, and serious water pollution, pollution-tolerant macroinvertebrates such as snails—characterized by large body size and high tolerance—emerged as dominant taxa. In the midstream–downstream suburban areas, dominant macroinvertebrate taxa were primarily characterized by small body size and short life-history cycles, which are associated with higher turnover rates and thus greater ecological resilience [26,62]. Additionally, the elevated FD observed in these regions contributes to both higher resistance and resilience to environmental disturbances [88], which is the primary reason why SP/B was higher in the midstream–downstream section than in the upstream. The ∆ of PD and the AVD of macroinvertebrate communities in the midstream–downstream section were significantly lower than those in the upstream section. The reduction in PD was associated with decreased species richness, reflecting shifts in survival strategies in response to varying disturbance intensities across the upstream and midstream–downstream regions. These species-level shifts resulted in closer phylogenetic relationships among co-occurring taxa, which, in turn, contributed to lower AVD values—indicating stronger interspecific cohesion and greater community stability under environmental stress. This aligns with the conclusions drawn by Davies et al. in their study of macroinvertebrate communities in urbanizing rivers of southeastern Australia, where a gradient of urban development was observed to be positively correlated with the severity of community impairment [89].
From an ecological perspective, H′ integrates both species abundance and evenness, making it a widely used metric for evaluating SD and biological integrity in macroinvertebrates communities [79,90,91]. As such, H′ is considered highly representative of SD. Among FD indices, FRic quantifies the volume of ecological niche space occupied by species within a community, effectively capturing ecological niche breadth. FDiv reflects the degree of niche differentiation and potential resource competition among species by measuring the variability of their biological traits [52]. RaoQ evaluates niche complementarity and functional redundancy by incorporating both trait dissimilarity and species abundance [52]. Therefore, the selected FD indices—FRic, FDiv, and RaoQ—comprehensively reflect the functional trait diversity of macroinvertebrate communities. For PD, Δ captures the average taxonomic distance between any two species in a community and can be used to assess phylogenetic relatedness [92]. In contrast, Λ⁺ is independent of sample size and sampling method, and provides an integrated assessment of both phylogenetic variability and the homogeneity of evolutionary relationships among taxa [93]. Thus, the combined use of Δ and Λ⁺ effectively captures multiple dimensions of PD. Taken together, the selected indices—H′ for SD; FRic, FDiv, and RaoQ for FD; and Δ and Λ⁺ for PD—are ecologically meaningful and representative of macroinvertebrate diversity patterns in the BYH.
4.3. Relationship Between Macroinvertebrate Diversity Indices and Community Stability
The results of the PLS-SEM analysis demonstrated that environmental factors and biodiversity jointly regulate macroinvertebrate community stability. This finding is consistent with the conclusions of Liu Yang et al., who reported that environmental factors can indirectly influence SP/B by modulating biodiversity [34]. In this study, AVD, which was incorporated as an additional indicator of community stability, followed a similar pattern. In the upstream (central urban) region of the BYH, which is subject to stronger anthropogenic disturbance, environmental and diversity variables jointly accounted for moderate variation in both SP/B and AVD. In contrast, in the midstream–downstream (suburban) region, where anthropogenic disturbance is lighter, the explanatory power of the model—particularly for AVD—was higher, suggesting increased sensitivity of community stability indicators in less-disturbed environments. Both SP/B and AVD showed that PD had the strongest indicative effect. Thereby validating the utility of AVD in characterizing macroinvertebrate community stability in urban river ecosystems. PD captures the evolutionary relationships among species, reflecting the historical accumulation of traits in both closely and distantly related species. Because closely related species may share similar niches and thus be more susceptible to similar threats, while distantly related species may occupy different niches, thereby enhancing the resilience of the entire community. Ecological niche complementarity refers to the differences in resource utilization among species within a community, which reduces interspecies competition and promotes coexistence. Consequently, PD offers a better predictive capacity for community stability in urban rivers, which are typically characterized by high levels of anthropogenic disturbance and low habitat heterogeneity [94]. However, the effects of specific diversity indices on SP/B and AVD varied across different river sections. In the upstream central urban area, in addition to PD, FD had a strong effect on SP/B, while SD contributed more significantly to AVD. This divergence may be attributed to the different conceptual and computational foundations of the two indices. SP/B quantifies community stability by evaluating the turnover rate, specifically the ratio of secondary productivity to biomass, thereby reflecting the community’s recovery capacity following disturbances [26]. FD emphasizes variation in species’ functional traits [95], and such variation enables macroinvertebrate communities to withstand and recover from environmental disturbances more effectively by adapting to varying habitat conditions and environmental stressors [96,97,98]. AVD, by contrast, characterizes community stability through fluctuations in species abundance and the average degree of species divergence within a community. It focuses on the extent of discrete community variability following environmental disturbance [64]. SD, on the other hand, emphasizes species richness and relative abundance, and is sensitive to changes in species number and distribution [99,100]. Therefore, the distinct response dynamics of resilience—reflected in functional diversity trait FD—and SD—representing richness and evenness—are key factors underlying the differential effects observed between the two characterizations of community stability (SP/B and AVD). In the midstream–downstream suburban sections of the BYH, in addition to PD, SD also exhibited a strong indicative relationship with SP/B. Conversely, FD was more strongly associated with AVD in these sections. This pattern may be attributed to the higher habitat complexity, urbanization gradients, and varying intensities of human disturbance in these regions. Due to the reproductive strategies of macroinvertebrates, fluctuations in habitat conditions can readily influence their abundance, thereby altering SD [101,102,103]. Functional redundancy refers to the phenomenon where multiple species within a community possess similar functional traits, conferring resilience to the community against external disturbances. In contrast, in ecosystems with high functional redundancy, the loss of certain species may not compromise overall community function, as remaining species with similar functional traits can compensate and help maintain community stability [104,105,106].
The results of Figure 7, based on Spearman correlation analysis, show that Δ, a component of PD, was highly positively correlated with D, H′, J′, and FRic, a component of FD, was highly positively correlated with d, with correlation coefficients of 0.71, 0.62, 0.70, and 0.64, respectively (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that both PD and FD are, to some extent, correlated with SD. PD quantifies the extent to which closely related species share more similar trait values than distantly related ones [107,108,109]. Srivastava proposed that PD may capture latent interactions among ecological communities that are not detectable through species abundance or functional traits alone [108]. The FD indices were calculated based on species’ functional traits that reflect both redundancy and complementarity of ecological roles [110,111]. Higher FD values indicate greater ecological niche complementarity among species, providing functional information beyond species abundance and enabling access to diverse resources, which enhances community stability [96]. Prior studies have demonstrated that both PD and FD are correlated with SD and may outperform SD in predicting macroinvertebrate community stability [34]. In addition, there was a significant negative correlation between Λ+ and both FEve and RaoQ, with correlation coefficients of −0.69 and −0.76, respectively (p < 0.05). This further supports the presence of links between PD and specific FD components. Thompson et al. [112] found that evolutionary processes influence the development of biological traits, which may subsequently enhance ecological niche complementarity—suggesting that functional trait differences are at least partially phylogenetically structured. However, Fritz et al. showed that phylogenetic relatedness only partially accounts for variation in functional traits, a conclusion consistent with this study’s observation that PD is only partially associated with FD [113]. Cadotte et al. also emphasized that PD captures aspects of functional trait diversity that are otherwise unmeasurable or difficult to quantify [112,114]. When communities exhibit complex sets of biological traits, PD has been found to be a better predictor of community stability than FD [96,108,114,115]. Collectively, the above findings on the interrelationships among diversity indices indicate that PD was the most effective predictor of macroinvertebrate community stability in the North Canal River basin, outperforming SD and FD—consistent with previous research [116].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we examined the relationship between multidimensional biodiversity and community stability of macroinvertebrates in the BYH in Beijing, China, with the aim of identifying which dimensions of diversity best indicate community stability under varying phenological and anthropogenic conditions. In the upstream region of the BYH, environmental factors and diversity indices jointly explained 52.9% of the variance in SP/B and 52.0% in AVD, while midstream–downstream factors explained 65.9% and 84.2%, respectively. In the upstream central urban area, TP, FD, and PD were more indicative of SP/B, while SD and PD were more indicative of AVD. These findings suggest that PD had the strongest overall predictive capacity for both community resilience (as indicated by SP/B) and community variability (as indicated by AVD). FD exhibited a stronger influence on community resilience than SD, whereas SD was more strongly associated with community variability than FD. Additionally, TP exerted a stronger direct effect on SP/B in the upstream urban region. In the midstream–downstream suburban regions, DO, SD, and PD were more indicative of SP/B, while FD and PD were more indicative of AVD. These results reinforce the importance of considering multiple biodiversity dimensions—particularly PD—in understanding and predicting macroinvertebrate community stability across gradients of environmental disturbance and urbanization. These findings indicate that PD is a stronger predictor of both community resilience and community variability under varying environmental conditions. In the midstream–downstream sections of the BYH, where habitat complexity increases due to urbanization, intensified human disturbance, and environmental fluctuations, FD exhibited a declining influence on community resilience but an increasing influence on community variability. Conversely, SD showed a decreasing influence on community variability and an increasing influence on community resilience. In this region, DO exerted a stronger direct effect on community resilience, as measured by SP/B. Collectively, these results suggest that PD is more sensitive than FD and SD in detecting the effects of anthropogenic disturbances and environmental changes on macroinvertebrate community stability in urban river systems. Therefore, PD was found to be superior to FD and SD in predicting macroinvertebrate community stability in the urban river ecosystem of the BYH. The PLS-SEM results further revealed that the specific pathways through which FD and SD influenced the two stability metrics—SP/B and AVD—varied between the upstream and the midstream–downstream sections. Additionally, the effects of environmental variables such as TP and DO differed by location and stability metric. These variations highlight the complex interplay between environmental factors, biodiversity dimensions, and macroinvertebrate community stability. Therefore, we recommend using both SP/B and AVD in combination to better capture the multifaceted effects of biodiversity on macroinvertebrate community stability in urban river ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.P. and Q.C.; Data curation, L.D., M.Z., Y.Z., J.G., H.Z. and Y.X.; Formal analysis, L.D. and M.Z.; Investigation, L.D., Y.Z., Y.Y. and X.Q.; Methodology, L.D., M.Z., J.G. and C.Z., Project administration, M.Z. and X.Q.; Writing—original draft, L.D. and M.Z.; Writing—review and editing, L.D., M.Z. and X.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2024YFC3212600), Project of State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin, China (SKL2024YJTS04), and National Water Pollution Control and Control Scientific and Technological Special Project, China (2018ZX.7101005).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Taxa of macroinvertebrates collected and identified from the North Canal River basin, Beijing (+ indicates the presence of this taxon within the river section).
Table A1.
Taxa of macroinvertebrates collected and identified from the North Canal River basin, Beijing (+ indicates the presence of this taxon within the river section).
| Macroinvertebrate Taxa | Upstream | Midstream–Downstream | Macroinvertebrate Taxa | Upstream | Midstream–Downstream |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arthropoda | Odonata | ||||
| Insecta | Lestidae | ||||
| Diptera | Lestes sp. | + | + | ||
| Chironomidae | Corduliidae | ||||
| Chironomus anthracinus | + | + | Cordulia sp. | + | |
| Chironomus flaviplumosus | + | + | Gomphidae | ||
| Chironomus sp. | + | Orientogomphus sp. | + | + | |
| Cladotanytarsus mancus | + | Crustacea | |||
| Cryptochironomus rostratus | + | Decapoda | |||
| Cryptotendipes sp.A | + | Palaemonidae | |||
| Dicrotendipes lobifer | + | + | Macrobrachium sp. | + | + |
| Dicrotendipes nervosus | + | + | Amphipoda | ||
| Dicrotendipes tritomus | + | Gammaridae | |||
| Glyptotendipes cauliginellus | + | Gammarus sp. | + | ||
| Glyptotendipes salinus | + | Annelida | |||
| Glyptotendipes sp.A | + | Hirudinea | |||
| Glyptotendipes sp.B | + | Ganthobdellida | |||
| Glyptotendipes tokunagai | + | Hirudinidae | |||
| Harnischia fuscimana | + | Hirudo sp. | + | + | |
| Kiefferulus sp. | + | Rhynchobdellida | |||
| Micropsectra atrofasciata | + | Glossiphoniidae | |||
| Parachironomus arcuatus | + | Glossiphonia complanata | + | + | |
| Polypedilum nubeculosum | + | Oligochaeta | |||
| Polypedilum paraviceps | + | Tubificida | |||
| Polypedilum scalaenum | + | + | Fridericia | ||
| Chironominae sp.A | + | Fridericia sp. | + | + | |
| Tanytarsus tamaoctavus | + | Tubificidae | |||
| Tanytarsus formosanus | + | Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri | + | + | |
| Cricotopus albiforceps | + | Aulodrilus pluriseta | + | ||
| Cricotopus trifasciatus | + | + | Aulodrilus pigueti | + | |
| Cricotopus vierriensis | + | Ilyodrilus templetoni | + | ||
| Nanocaldius dichromus | + | Branchiura sowerbyi | + | + | |
| Nanocaldius distinctus | + | Naididae | |||
| Orthocaldius dubitatus | + | Nais communis | + | ||
| Orthocaldius kanii | + | Dero digitata | + | ||
| Orthocaldius vaillanti | + | Branchiodrilus hortensis | + | ||
| Orthocaldius yagashimaensis | + | Mollusca | |||
| Propsilocerus akamusi | + | Gastropoda | |||
| Thienemanniella majuscula | + | Mesogastropoda | |||
| Ablabesmyia sp. | + | Viviparidae | |||
| Procaldius sp.A | + | Bellamya purificata | + | + | |
| Rheopelopia joganflava | + | Hydrobiidae | |||
| Rheopelopia sp. | + | Alocinma longicornis | + | + | |
| Tanypus punctipennis | + | + | Parafossarulus striatulus | + | |
| Tipulidae | Stenothyra glabra | + | + | ||
| Tipulia sp. | + | Bithynia fuchsiana | + | + | |
| Ephemeroptera | Melaniidae | ||||
| Baetidae | Semisulcospira cancellata | + | |||
| Baetis sp. | + | + | Basommatophora | ||
| Caenidae | Lymnaeidae | ||||
| Caenis sp. | + | + | Radix swinhoei | + | + |
| Leptophlebiidae | Planorbidae | ||||
| Leptophlebiidae spp. | + | Hippeutis cantori | + | ||
| Trichoptera | Lamellibranchia | ||||
| Hydroptilidae | Eulamellibranchia | ||||
| Orthotrichia sp. | + | Corbiculidae | |||
| Ecnornidae | Corbicula fluminea | + | |||
| Ecnomus sp. | + | + | Unionidae | ||
| Hemiptera | Schistodesmus lampreyanus | + | |||
| Micronectidae | Anisomyaria | ||||
| Micronecta sp. | + | + | Mytilidae | ||
| Limnoperna lacustris | + |

Table A2.
Brief Introduction to Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM).
Table A2.
Brief Introduction to Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM).
| Table of Contents | Brief Introduction |
|---|---|
| Overview | Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is a statistical modeling approach that integrates Partial Least Squares (PLS) with Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). This method is particularly well-suited for analyzing small sample sizes, non-normal data distributions, and complex relationships among multiple variables. PLS-SEM optimizes model parameters iteratively, offering both explanatory and predictive capabilities, and finds widespread application in various fields such as biology, psychology, social sciences, and management. |
| Definition and Basic Concepts | PLS-SEM is a prediction-oriented statistical method that utilizes PLS to process data while incorporating the causal modeling principles of SEM to elucidate relationships between latent variables. Its core lies in the combination of principal component analysis and multiple regression, employing an iterative estimation approach to optimize model parameters. |
| Model Structure | The PLS-SEM model comprises two components: 1. Measurement Model: This component describes the relationships between latent variables and their observed indicators (Observed Variables). It ensures the reliability and validity of the construct measurements. 2. Structural Model: This component depicts the causal relationships between the latent variables themselves, specifying the paths and directions of influence. |
| Key Features | 1. Iterative Algorithm: PLS-SEM employs an iterative algorithm to estimate model parameters, making it computationally efficient, especially for complex models. 2. Predictive Orientation: PLS-SEM emphasizes predictive power, whereas CB-SEM (Covariance-Based SEM) places greater emphasis on theoretical model verification. 3. Handling of Complex Models: PLS-SEM is well-equipped to handle complex models and can quickly estimate parameters. 4. Path Modeling: PLS-SEM is often referred to as variance-based SEM, which is a special case of path analysis. It is also known as soft modeling in contrast to CB-SEM’s hard modeling. 5. Data Requirements: PLS-SEM is more flexible in terms of data requirements, making it suitable for small sample sizes and non-normal data. |
| Application Domains | PLS-SEM is widely used in biology, psychology, marketing, management, and other disciplines, particularly excelling in the analysis of multivariate relationships and causal inference. |
References
- Zhang, J.Y.; Song, X.M.; Wang, G.Q.; He, R.M.; Wang, X.J. Development and challenges of urban hydrology in a changing environment: I: Hydrological response to urbanization. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, M.Y.; Zhao, L.F. Assessment of urban river habitats: Application and methodology. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2007, 27, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Fan, J.T.; Zhang, Y. Freshwater Ecosystem Health and Ecological Civilization Construction at the Watershed Scale. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, L.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.T.; Wang, Z.B.; Sun, D.Z. Solutions and roadmap for comprehensive remediation of water ecological environment in urban areas of the middle and lower reaches of the yangtze river. Environ. Eng. 2023, 41, 1–11+41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Hong, S. Global Urbanization Research from 1991 to 2009: A Systematic Research Review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 104, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.H.; Zuo, D.P.; Liu, B.; Huang, Z.F.; Xu, Z.X. Quantitative Analysis of the Correlation Between Macrobenthos Community and Water Environmental Factors and Aquatic Ecosystem Health Assessment in the North Canal River Basin of Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, H.; Chen, D.L. Research on the Evaluation of Water Ecological Health of Urban River Based on Improved Random Forest. Haihe Water Resour. 2019, 6, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Gu, X.Y.; Zuo, D.P. Studies on the health assessments: From aquatic ecosystems to Rivers/Lakes. China Flood Drought Manag. 2018, 28, 17–24+29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Rosemond, A.; Paul, M.; Leigh, D.; Wallace, J. Stream macroinvertebrate response to catchment urbanisation (Georgia, USA). Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.; McIntyre, P.; Gessner, M.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.; Sullivan, C.; Reidy Liermann, C.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Beermann, A.J.; Goessler, G.; Neumann, J.; Tollrian, R.; Wagner, R.; Wlecklik, A.; Piggott, J.J.; Matthaei, C.D.; Leese, F. Multiple-stressor effects on stream invertebrates: A mesocosm experiment manipulating nutrients, fine sediment and flow velocity. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Kainz, M.J.; Sheldon, F.; Bunn, S.E. Effects of light and nutrients on periphyton and the fatty acid composition and somatic growth of invertebrate grazers in subtropical streams. Oecologia 2016, 181, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohet, A.; Hlúbiková, D.; Wetzel, C.E.; L’Hoste, L.; Iffly, J.F.; Hoffmann, L.; Ector, L. Influence of Thermal Regime and Land Use on Benthic Invertebrate Communities Inhabiting Headwater Streams Exposed to Contrasted Shading. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. Predicting the Effect of Land Use and Climate Change on Stream Macroinvertebrates Based on the Linkage between Structural Equation Modeling and Bayesian Network. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J. Biological indicators of stream health using macroinvertebrate assemblage composition: A comparison of sensitivity to an urban gradient. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.C.; Ni, J.R. Roles of benthos in the aquatic ecosystem health assessment. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 17, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.X.; Yang, L.F. Bioassessment of Qinhuai River using a river biological index. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.W.; Wang, J.C.; Ding, Z.J.; Jiang, Y.W. Large Benthonic Invertebrates’ Tolerance Values and Water Quality Evaluation in Liaoning Province. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2013, 39, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; Xu, Z.X.; Wang, M.; Yin, X.W.; Liu, L.F.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, D.P. Macroinvertebrates community structure and water quality assessment in the North Canal River Basin, Beijing, China. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, A.H.; Bressler, D.W.; Paul, M.J.; Barbour, M.T.; Rankin, E.T.; Carter, J.L.; Resh, V.H. Assessment tools for urban catchments: Developing biological indicators based on benthic macroinvertebrates. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P. The urban stream syndrome: Current knowledge and the search for a cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Wu, W.; Yin, X.W. Community structure characteristics and health assessment of aquatic ecosystem in Weihe Basin, China. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2016, 1, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Simons, N.K.; Jung, K.; Prati, D.; Renner, S.C.; Boch, S.; Fischer, M.; Hölzel, N.; Klaus, V.H.; Kleinebecker, T.; et al. Land use imperils plant and animal community stability through changes in asynchrony rather than diversity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, A.R.; Klug, J.L.; Gross, K. Stability and species richness in complex communities. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Pan, B.; Jiang, X.; Shi, P.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, N. A Comparative Study on the Indicative Function of Species and Traits Structure of Stream Macroinvertebrates to Human Disturbances. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, W.J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.D.; You, Q.H. Effects of macroinvertebrate diversity on community secondary productivity and stability in the Poyang Lake wetland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 3337–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaeb, Z.A.; Summers, J.K.; Pugesek, B.H. Using structural equation modeling to investigate relationships among ecological variables. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2000, 7, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B.; Schoolmaster, D.R.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Little, A.M.; Mitchell, B.R.; Miller, K.M.; Schweiger, E.W. Guidelines for a graph-theoretic implementation of structural equation modeling. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulland, J. Use of Partial Least Squares (PLS) in Strategic Management Research: A Review of Four Recent Studies. Strateg. Manag. J. 1999, 20, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Al, M.A.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Yang, J.R.; Isabwe, A.; Luo, A.; Yang, J. Urbanization Reduces Resource Use Efficiency of Phytoplankton Community by Altering the Environment and Decreasing Biodiversity. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.Y.; Deng, Y.Q.; Hu, J.X.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, S.Z.; Min, X.; Hu, Y.X.; Chen, J.L. Macroinvertebrate diversity related to environmental factors in lakes of Jiangxi Province. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Gong, Z.N.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.F. Change of vegetation coverage and assessment of ecological environment quality in BeiyunRiver Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2022, 42, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.C.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.Y.; Wu, D.L. Analysis of the Seasonal Changes in Planktonic Microbial Diversity in Urban River Supplied with Reclaimed Water: A Case Study of the North Canal River. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4097–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Peng, W.Q.; Qu, X.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Du, L.F.; Wu, N.C. Phylogenetic and Functional Diversity Could Be Better Indicators of Macroinvertebrate Community Stability. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Graham, C.H.; Lavergne, S.; Pellissier, L.; Münkemüller, T.; Thuiller, W. The productivity-biodiversity relationship varies across diversity dimensions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qin, J.L.; Yu, S. Application of improved comprehensive water quality identification index method in water quality evaluation of the main channel of the North Canal in Beijing. Beijing Water 2023, S2, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.M.; Huang, B.B.; Ye, Z.H.; Chang, G.L. Study on the rapid evaluation of ecological health in the North Canal. Beijing Water 2020, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Peng, J.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, W. Water Ecological Carrying Capacity and Identification of Key Control Factors: A Case Study of Beijing Section of North Canal. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Qu, X.D.; Peng, W.Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.P.; Du, L.F.; Zhang, S.C. Health Assessment of the Stream Ecosystem in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 5478–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental. Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Aquatic Monitoring Manual; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kathman, R.D.; Brinkhurst, R.O. Guide to the Freshwater Oligochaetes of North America; Aquatic Resources Center: Owensboro, KY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T. Fauna Sinica: Annelida Hirudinea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.C.; Wang, X.H. Tendipes in the North of China; China Yan Shi Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.B. Study of indicators and methods for river habitat assessment of Liao River Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2007, 27, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.M.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Song, D.; Zhao, C.; Huang, X.L.; Wang, H.B.; Huo, T.B. Effects of land use and aquatic environmental factors on secondary productivity of macroinvertebrates: A case of Lake Lianhuan Group, northeast China. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, L.F.; Chen, W.; Shao, K.; Wu, W.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, H.; Ma, P.M. Macroinvertebrates community structure in relation to environmental variables in the lower reaches of the Yalong River. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.O. Diversity and evenness: A unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology 1973, 54, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Wilson, J.B. A Consumer’s Guide to Evenness Indices. Oikos 1996, 76, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.M.; Chen, P.M.; Li, X.G.; Qin, C.X.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Yuan, H.R. Macrobenthic species diversity in the waters surrounding Zhelin Bay. J. Fish. Sci. China 2015, 22, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouriani, H.; Ezzati, R. Application of Simpson Quadrature Rule and Iterative Method for Solving Nonlinear Fuzzy Delay Integral Equations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2020, 400, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, F.; Han, D.H.; Zhao, W.B.; Zhou, D.K.; Wang, G.; Zhao, R.; Liang, R.C. Macroinvertebrate community characteristics and driving factors in the Chishui River (Renhuai section). Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, M.A.; Villéger, S.; Mason, N.W.H.; Mouillot, D. Functional diversity measures: An overview of their redundancy and their ability to discriminate community assembly rules. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Zhang, G.J.; Li, L.; Mu, R.L.; Xu, L.; Yu, R.X. Relationship between functional diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality of alpine meadow along an altitude gradient in Gannan, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 5, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, L.; Olden, J.D.; Vieira, N.K.M.; Finn, D.S.; Simmons, M.P.; Mackay, R.J.; Mackay, R.J.; Poff, N.L.; Kondratieff, B.C. Functional Trait Niches of North American Lotic Insects: Traits-Based Ecological Applications in Light of Phylogenetic Relationships. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 25, 730–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Heino, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, T.; Xie, Z. Discriminating the Effects of Local Stressors from Climatic Factors and Dispersal Processes on Multiple Biodiversity Dimensions of Macroinvertebrate Communities across Subtropical Drainage Basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.M.; He, S.S.; Zhuo, L.L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H.K.; Cai, Q.H. Study of macroinvertebrate functional traits and diversity among typical habitats in the New Xue River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; Qu, X.D.; Wu, N.C.; Jia, X.H.; Cai, Q.H. Study on Species Diversity and Functional Diversity of Aquatic Insects in the Xiangxi River Basin, Shennongjia Region. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; He, F.Z.; Cai, Q.H. Spatial distribution patterns of trait composition and functional diversity of aquatic insects in the Xiangxi River system. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mason, N.W.H.; Mouillot, D.; Lee, W.G.; Wilson, J.B. Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: The primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 2010, 111, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhang, Q. Seasonal Variations in Macrobenthic Taxonomic Diversity and the Application of Taxonomic Distinctness Indices in Bohai Bay, Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsen, K.E.; Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Taxonomic Distinctness as a Measure of Diversity Applied over a Large Scale: The Benthos of the Norwegian Continental Shelf. J. Anim. Ecol. 2005, 74, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, B.L. The secondary production of macrobenthos in Jiaozhou bay, Shandong. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2005, 36, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumbiolo, M.L.; Downing, J.A. An Empirical Model for the Prediction of Secondary Production in Marine Benthic Invertebrate Populations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 114, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Specialized metabolic functions of keystone taxa sustain soil microbiome stability. Microbiome 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, S.; Zhang, C.; Du, P. Pollutant Removal Capacity Influence Soil Bacterial Community Stability: Insights from Two Agricultural Soils. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wu, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Plant Community Stability, Indicator Species and Their Driving Factors at a Gradient of Grazing Intensity in an Alpine Meadow. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, Q. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in Baihua Reservoir: Implications for Ecosystem Management. Biology 2025, 14, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Huang, M.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Tang, J.; Jiang, G.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Dong, K.; et al. Ecological Stoichiometry Influences Phytoplankton Alpha and Beta Diversity Rather than the Community Stability in Subtropical Bay. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.F.; Xu, Z.X.; Yin, X.W.; Li, F.L.; Wang, M. Response of aquatic organism richness to physiochemical factors at different regions in Jinan City. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, B. Cause and Correlation in Biology: A User’s Guide to Path Analysis, Structural Equations, and Causal Inference; Cambridge University Press: New York, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.F.; Zhang, J.; Qu, X.D.; Zhang, M.; Ge, J.J.; Zhang, H.P.; Chen, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.H. Research on Comprehensive Assessment Methods of the Evaluation of Urban River Water Eco-Environment Quality in Fengtai District, Beijing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2025, 38, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, B.H.; Meng, Y.F.; Ma, S.Q.; Yang, L.; Yin, X.W.; Xu, Z.X.; Hao, C.Q. Studies on Diversity and Temporal-spatial Dynamics of Macrobenthos Functional Feeding Groups in the Rivers of North Canal in Beijing. J. Guandong Ocean Univ. 2018, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.H.; Zhang, R.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Zhang, W.; Chen, P.P.; Wang, L.Q. Health assessment on rivers in Shanghai City using benthic index of biotic integrity. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. Effect of Urban River Morphology on the Structure of Macroinvertebrate Communities in a Subtropical Urban River. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.W.; Zhang, Z.G.; Guo, J. Water pollution characteristics and pollution sources of Bei Canal river system in Beijing. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.L.; Liu, Z.J.; Du, J. Environmental quality condition and water quality analysis of the North Canal River Main stream. Beijing Water 2023, S01, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.S.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J. Correlation analysis of maerobenthos community structure with plankton and environmental factors in theChaiqu Zangbo Basin in Tibet. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.S.; Baker, M.E.; Kazyak, P.F.; Weller, D.E. How novel is too novel? Stream community thresholds at exceptionally low levels of catchment urbanization. Ecol. Appl. A Publ. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2011, 21, 1659–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.D.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, M.; Peng, W.Q.; Zhu, L.; Lei, X. Application of Rapid Bioassessment Indices of Macroinvertebrates in Ecological Evaluation of Urban Streams. J. Hydroecol. 2021, 42, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Kang, L.J.; Sun, C.J.; Yang, Q. Development of multi-metric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates to assess river ecosystem of a typical plain river network IN China. ACTA Hydrobiol. Sin. 2013, 37, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, K.; Chen, Q.W.; Wang, M.; Wang, L. The community structure of macroinvertebrate and its relationship to the environmental factors in summer and autumn within typical reaches of Huai River Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, D.B.; Jun, S. Macroinvertebrate community structure and relationships with environmental factors in the Lhasa River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Li, X.Y.; Liang, Y.L. A Comparative Study on Community Structure of Macrozoobenthos Between Macrophtic and Algal Lakes. J. Lake Sci. 2005, 17, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.M.; Luo, Y.P.; Huang, Z.T.; Huang, H.X.; Hu, S.L.; Chen, B.B.; Liu, Y.D. Macroinvertebrate Community Structure and Relationship with the Xiangjiang River Environment. J. Hydroecol. 2018, 39, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latinopoulos, D.; Ntislidou, C.; Lazarina, M.; Papaevangelou, V.; Akratos, C.; Kagalou, I. Macroinvertebrate Community Responses to Multiple Pressures in a Peri-Urban Mediterranean River. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Y. Constructing sustainable landscape patterns for enhancing urban biodiversity. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 5905–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Lu, Q.; Xia, S.; Li, J.S. An overview of advances in soil microbial diversity of urban environment. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 22186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakschewski, B.; Bloh, W.; Boit, A.; Poorter, L.; Peña-Claros, M.; Heinke, J.; Joshi, J.; Thonicke, K. Resilience of Amazon forests emerges from plant trait diversity. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.J.; Wright, I.A.; Findlay, S.J.; Jonasson, O.J.; Burgin, S. Impact of urban development on aquatic macroinvertebrates in south eastern Australia: Degradation of in-stream habitats and comparison with non-urban streams. Aquat. Ecol. 2010, 44, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Qu, X.D.; Wang, S.M.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhang, M.; Sun, S.j. River Health Assessment of Hun River Basin Based on Benthic Index of Biological Integrity. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.D.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Duan, L.F.; Peng, W.Q. Relationship Between Macrophyte Communities and Macroinvertebrate Communities in an Urban Stream. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.F.; Chen, B.; Yu, W.W.; Lin, J.H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Liao, J.J. Discussion on taxonomic diversity indices and taxonomic sufficiency for macrobenthos in Xiamen Bay. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5554–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzen, V.; Anderson, M.J.; Roberts, C.D.; Diebel, C.E. Increasing variation in taxonomic distinctness reveals clusters of specialists in the deep sea. Ecography 2011, 34, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yibo, H.; Huizhong, F.; Youhua, C.; Jiang, C.; Xiangjiang, Z.; Hua, W.; Baowei, Z.; Meng, W.; Wenyan, Z.; Lin, Y.; et al. Spatial patterns and conservation of genetic and phylogenetic diversity of wildlife in China. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 2375–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J. Patterns of functional biodiversity and function-environmentrelationships in lake littoral macroinvertebrates. Limnol Ocean. 2008, 53, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, M.W.; Carscadden, K.; Mirotchnick, N. Beyond species: Functionalddiversity and the maintenance of ecological processes and services. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmera, D.; Heino, J.; Podani, J.; Erős, T.; Dolédec, S. Functional diversity: A review of methodology and current knowledge in freshwater macroinvertebrate research. Hydrobiologia 2017, 787, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.C.B.; Ray, C.A. Unifying functional trait approaches to understand the assemblage of ecological communities: Synthesizing taxonomic divides. Ecography 2019, 42, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Mykra, H.; Hamalainen, H.; Aroviita, J.; Muotka, T. Responses of taxonomic distinctness and species diversity indices to anthropogenic impacts and natural environmental gradients in stream macroinvertebrates. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1846–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, B.J.; Dornelas, M.; Gotelli, N.J.; Magurran, A.E. Fifteen Forms of Biodiversity Trend in the Anthropocene. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, A.; Schmid, B. Diversity-dependent production can decrease the stability of ecosystem functioning. Nature 2002, 416, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.D.; Peng, W.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Z.; Wu, N.C.; Liu, X.B. Networks and Ordination Analyses Reveal the Stream Community Structures of Fish, Macroinvertebrate and Benthic Algae, and Their Responses to Nutrient Enrichment. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Muñoz-Mas, R.; Martínez-Capel, F.; Qu, X.D.; Zhang, H.P.; Peng, W.Q.; Liu, X.B. Determining the Macroinvertebrate Community Indicators and Relevant Environmental Predictors of the Hun-Tai River Basin (Northeast China): A Study Based on Community Patterning. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Cabido, M. Vive La Différence: Plant Functional Diversity Matters to Ecosystem Processes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; Inchausti, P.; Bengtsson, J.; Grime, J.P.; Hector, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Huston, M.A.; Raffaelli, D.; Schmid, B.; et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science 2001, 294, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, P.D.; Patrício, J.; Marchini, A.; Cid, N.; Neto, J.M.; Marques, J.C. A Biological Trait Approach to Assess the Functional Composition of Subtidal Benthic Communities in an Estuarine Ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 20, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, D.R.P.; Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. The Application of an Indicator Based on Taxonomic Distinctness for UK Marine Biodiversity Assessments. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 78, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, D.S.; Cadotte, M.W.; MacDonald, A.A.; Marushia, R.G.; Mirotchnick, N. Phylogenetic diversity and the functioning of ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weglarz, K.M.; Saunders, W.C.; Wagenen, A.V.; Pearse, W.D. Phylogenetic Diversity Efficiently and Accurately Prioritizes Conservation of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Communities. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, B.; Gascón, S.; Quintana, X.; Comín, F.A. How to Choose a Biodiversity Indicator–Redundancy and Complementarity of Biodiversity Metrics in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Meng, X.; Heino, J.; Jiang, X.; Xiong, X.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z. Different Responses of Taxonomic and Functional Structures of Stream Macroinvertebrate Communities to Local Stressors and Regional Factors in a Subtropical Biodiversity Hotspot. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.L.; Davies, T.J.; Gonzalez, A. Ecosystem functions across trophic levels are linked to functional and phylogenetic diversity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.A.; Purvis, A. Phylogenetic diversity does not capture body size variation at risk in the world’s mammals. Proceedings. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, M.W.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Tilman, D.; Oakley, T.H. Using phylogenetic, functional and trait diversity to understand patterns of plant community productivity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, D.F.B.; Microtchnick, N.; Jain, M.; Palmer, M.I.; Naeem, S. Functional andphylogenetic diversity as predictors of biodiversity-ecosystem-functionrelationships. Ecology 2011, 92, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, D.; Eisenhauer, N.; Pearse, W.D.; Hautier, Y.; Isbell, F.; Roscher, C.; Bahn, M.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Bönisch, G.; Buchmann, N.; et al. Multiple facets of biodiversity drive the diversity-stability relationship. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).