Abstract
Since the 1960s, the countries of sub-Saharan Africa have been affected by an urban crisis due to the demographic explosion in cities and the resulting land pressure. These issues have resulted in the proliferation of spontaneous housing areas, which call the future of urban vegetation and its degree of inclusion in city planning into question. To analyze the current scientific knowledge on the development of urban landscapes, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, a literature review on urban forestry covering the period of 1998–2022 was carried out in order to better guide future research works towards a greater consideration of urban forestry and its contribution to combating the adverse effects of climate change. Out of the 110 scientific papers selected, 50 were considered relevant because of their direct link with urban forestry. Based on the analysis of these papers, a classification of the articles according to five themes was carried out. These themes are the management of green spaces in urban areas, the functions of trees in an urban environment, the development of urban forestry, the characterization of urban tree flora, and the financing of urban forestry. Thus, the “function of trees in an urban environment and the characterization of urban tree flora” are the most addressed issues, being raised in 42% and 28% of articles, respectively. “Financing urban forestry” is practically not addressed (2%). The analysis of the 50 selected articles reveals a significant geographic concentration of urban forestry research. Countries such as South Africa, Kenya, and Ghana are more represented in the literature, while vast regions in Central and Western Africa (e.g., the Democratic Republic of Congo, Chad, and Niger) are the object of minimal or no documented research with regard to urban forestry. Future research should address these underrepresented themes, as they are crucial for the long-term sustainability of urban forestry projects. Particularly, research on financing mechanisms is essential to unlocking sustainable funding sources for urban forestry, a critical barrier to its expansion.
1. Introduction
Urban settlements and landscapes have become increasingly vulnerable due to relentless urbanization, climate change, migration, and the transition to more globally competitive environments [1,2,3,4,5]. Thus, a steady erosion of the urban commons is taking place through privatization [6]. In sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), the settlements and landscapes that constitute the urban commons are held in high esteem by most traditional communities. Since their independence, the countries of SSA have been affected by a crisis in urban planning due to the demographic explosion of cities and the resulting pressure on land. These pressures are reflected in rapid urban sprawl, occurring via local horizontal planning approaches, and in the proliferation of informal settlements. These issues raise questions about the future of urban landscapes and the extent to which they are included in urban planning [7].
Urbanization is of even more recent vintage in Africa, especially in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). At the turn of the century, the proportion of Africans living in urban areas rose to 27 percent from 24 percent in the early 1990s [8]. By most estimates, the continent’s urban population is projected to double every 12 years [9], and some of the best-known projections hold that as much as 52 percent of the people in Africa will be living in towns and cities by 2025 [8]. Therefore, SSA is experiencing unprecedented rates of urbanization, with urban populations expected to double by 2050, rising a growing rate of 65 million urban dwellers annually [10]. The unprecedented pace of urban growth in SSA exerts significant pressure on ecosystems and green spaces, leading to biodiversity loss and intensifying climate challenges such as heat islands, air pollution, and flooding. Meanwhile, climate change is amplifying these risks, threatening urban sustainability and the livelihoods of millions.
Urban forestry, defined as the management and cultivation of tree populations within urban settings, presents a multifaceted solution to some of the most pressing environmental and social challenges faced by cities today. Unlike rural forests, urban forests serve a diverse array of functions, including climate regulation, air quality improvement, storm water management, and the provision of recreational spaces for urban populations. Many case studies show that the construction of road infrastructure in urban areas [11] sometimes requires the destruction of existing property and equipment and, above all, the cutting of trees. According to [12], large areas of urban forest or woodland are destroyed every year in Africa as a result of urbanization. For example, urban expansion in the city of Lubumbashi in the Democratic Republic of Congo has led to a decline in green space cover of around 3.6 km2 per year [13]. Also, in the city of Abomey-Calavi in Benin, road development and construction works have led to the felling of 620 trees [14].
This situation degrades the environment [15,16]. It is also partly responsible for the formation of urban heat islands (UHIs), which occur in cities, most often at night, and lead to the deaths of thousands of people worldwide [17]. However, urban forestry and the greening of degraded spaces offer a multitude of benefits to city dwellers [18].
In the context of developing countries, urban forestry debates appear to be poorly represented in the regional and international literature. A survey of peer-reviewed research confirms that nearly 80% of articles come from the context of the developed world, while publications on urban forestry and the environment from Africa are very poorly represented [18]. The few works carried out on the subject, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, relate to topics such as mature trees in cities [19]; floristic diversity [20]; managing green spaces [21]; characterizing the diversity of fruit trees in households [18]; the inventory and carbon sequestration of vegetation in the urban right-of-way [22]; the role of tree cover in mitigating heat islands in urban centres [23]; residents’ perceptions, attitudes, and expectations of urban green spaces [24]; municipal officials and decision-makers’ understanding of the distribution and abundance of trees along streets and in urban green spaces [25]; public policy for the management of green spaces [26]; people’s perceptions of urban forests [27]; the effect of population growth on the urban forest landscape; and the factors of urban forest degradation [28,29].
Despite the recognized benefits of urban forests, cities in SSA often lack comprehensive strategies for the integration and sustainable management of urban green spaces. Resource constraints, land-use conflicts, and insufficient public awareness further hinder the adoption of urban forestry initiatives across the region. Understanding the challenges, contributions, and future directions for urban forestry in this context is essential in order to combat climate change and restore urban ecosystems. In addition, the results of woodland management in the urban context are still very inconclusive, which does not facilitate a cross-reading of knowledge on urban forestry in SSA. The term “urban forestry” was first used in the late 1800s by municipalities referring to the silvicultural context, i.e., the care of individual trees in urban spaces [30]. According to [31], urban forestry combines arboriculture, ornamental horticulture, and forest management. It is closely linked to landscape architecture, urban agroforestry, and the development of parks and peripheral forests. In its broadest sense, urban forestry covers all urban green space developments such as woods, parks, gardens, squares, etc., and even row plantings and accompanying plantings, although the latter two expressions refer to landscaping and unavailable space, i.e., all peri-urban and rural green areas, in particular forest areas and green cuts [32]. The aim of this article is to analyze the state of our knowledge based on research that has already been carried out on the management of planted areas, particularly in SSA, in order to better guide future research work aimed at improving the well-being of urban populations and fighting against the harmful effects of climate change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location of the Study Area
This article only considers publications from the sub-Saharan African region, which covers an area of 24,328,299 km2 [33]. It is home to forty-eight states, whose borders are the result of decolonization (Figure 1). Its urban population increased more than threefold (3) between 1990 and 2020, rising from 136 million to 459 million, and more than 1.25 billion Africans will be living in cities by 2050 [34]. Cities in sub-Saharan Africa are expected to absorb almost 80% of the continent’s additional inhabitants between now and 2050.
Figure 1.
Map of Regions of Sub-Saharan Africa. Source: USDA, Economic Research Service.
According to the authors of [35], SSA is subdivided into five (5) regions. The first (i) is Sudano-Sahelian Africa (Burkina Faso, Chad, Gambia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Senegal, Somalia, and Sudan), a region whose vegetation mainly consists of savannahs dominated by grasses and trees, bordered to the south by open forests and to the north by grassy steppes and desert formations. The second (ii) is West Africa (Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Togo), which is humid and sub-humid.
The vegetation in the northern part of this region mainly consists of open forests, while dense evergreen and semi-deciduous forests predominate to the south and west. Lying between these two, there is a transitional zone comprising a mosaic of forest and savannah resulting from human intervention in the original dense forest. Extensive mangrove swamps can be found along the west coast of Africa. (iii) Central Africa (Cameroon, Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Central African Republic, and the Democratic Republic of Congo) is a humid region, whose central half is covered by the largest remaining tract of tropical rainforest in Africa (around 160 million hectares). The north and south are dominated by deciduous light forests, while the eastern part contains high-altitude forests and savannahs. (iv) East Africa (Burundi, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Rwanda, and Uganda) is sub-humid and mountainous. In the lowest and driest parts of this region, various types of open forest and savannah predominate. The remaining natural forests are mainly located on the slopes and are classified as state forests, and they are mainly used for the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of watersheds, or as national parks. (v) Southern Africa (Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe) is a sub-humid and semi-arid region. The main forest type in this region is open deciduous forest.
2.2. Methodological Approaches
This study was based on a review and analysis of the literature, providing an overview of the knowledge on urban forestry from 1998 to 2022. For this, we used the protocol, including identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion, to guide the selection of the articles (Figure 2). The choice of study period is related to the oldest article analyzed. The literature review covered scientific articles, dissertations, and theses dealing specifically with urban forestry issues.
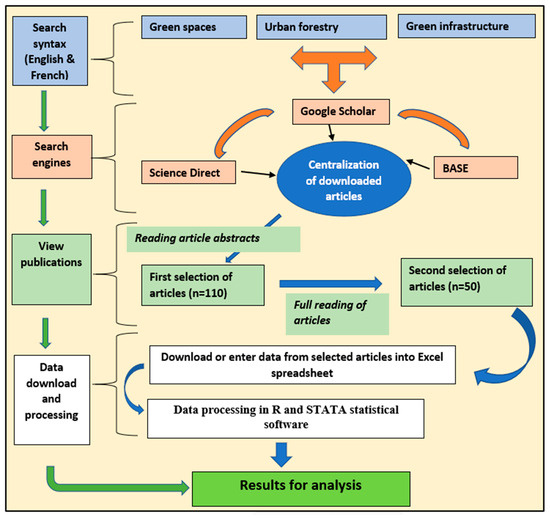
Figure 2.
The synthesis of selection processes used to select the articles included in the analysis.
The scientific articles were obtained via a bibliographic search using keywords relating to the theme of urban forestry in search engines such as Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com), Bielefeld Academic Search Engine (BASE, https://www.base-search.net), and Science Direct (www.sciencedirect.com). The approach used consisted of the following steps: (i) entering keywords relating to urban forestry in the search bar of the above-mentioned websites; (ii) selecting the search language and the documents to be searched; (iii) launching the search engine; and (iv) selecting and downloading the appropriate documents. Only articles published in “French” and “English” were analyzed. For the studies included in the review, we reported information on authors, publication year, countries involved, topics covered, geographic location of urban forestry research, etc.
Out of a total of one hundred and ten (110) articles selected, fifty (50) were deemed relevant because of their direct link with urban forestry (Appendix A). These documents were organized according to their research theme, year of publication, study area, and topics covered. The data were organized in an Excel spreadsheet and analyzed using STATA statistical software (STATA 18). By comparing the research topics in publications by country of origin, we were able to create a factorial map. Factorial correspondence analysis (FCA) was performed using R software (R-4.3.2) to establish relationships between research topics and the geographic origin of the associated publications (Figure 2).
3. Results
3.1. Research Focus and Thematic Gaps
The analysis of the 50 selected articles reveals a significant geographic concentration of urban forestry research. Countries such as South Africa, Kenya, and Ghana are more represented in the literature, while vast regions in Central and Western Africa (e.g., the Democratic Republic of Congo, Chad, and Niger) are the objects of little or no documented research on urban forestry.
A majority of the literature (over 60%) focuses on topics related to tree inventories, species diversity, and carbon sequestration. There are fewer studies on the socio-economic aspects of urban forestry, including community engagement, policy frameworks, and the integration of indigenous knowledge (Figure 3).
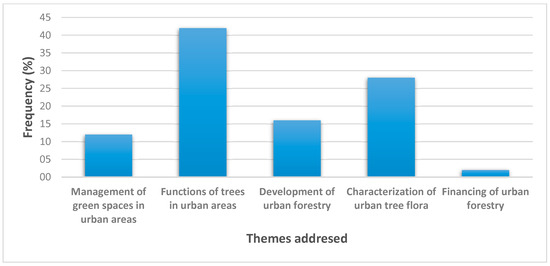
Figure 3.
Themes addressed in urban forestry research in sub-Saharan Africa.
The factorial correspondence analysis indicates a total inertia of 67.04% for both axes (Axis 1 and Axis 2). Axis 1 (40.02% inertia) reflects the geographical origin of the publications, while Axis 2 (27.02% inertia) presents a breakdown of the themes dealt with most. In terms of the topics covered by country, the management of green spaces in urban areas (GEVMU) was mostly addressed in relation South Africa and Niger. The functions of trees (FAMU) were addressed based on Togo, Ghana, Chad, Burundi, Cameroon, Kenya, and the Ivory Coast. The development of urban forestry (DFU) was mostly addressed based on Togo and Benin. The characterization of urban tree flora (CFAU) was mostly addressed based on the Democratic Republic of Congo. The topic of financing urban forestry was only addressed based on Nigeria (Figure 4).
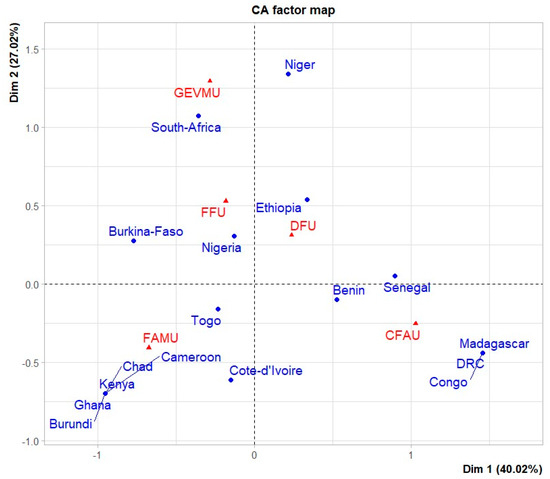
Figure 4.
Topics covered in the literature by country. Legend: Management of green spaces in urban areas (GEVMU), Functions of trees in urban areas (FAMU), Development of urban forestry (DFU), Characterization of urban tree flora (CFAU) et Financing urban forestry (FFU).
3.2. Impact of Urbanization on Urban Green Spaces and Role of Urban Forestry in Climate Change Mitigation
On average, cities in sub-Saharan Africa have lost 10–15% of their green space in the last two decades. For example, the case of Lubumbashi (DRC) shows a 3.6 km2 annual decline in green space. Urban forests contribute significantly to climate change mitigation by reducing urban heat islands (UHIs) and improving air quality. Studies, particularly those from South Africa, indicate that urban green spaces can reduce surface temperatures by 2–3 °C in densely populated areas.
Our review of published papers also revealed that urban forests in SSA have a substantial capacity for carbon sequestration, contributing to climate change mitigation. Studies indicate that mature urban trees can sequester between 22 and 45 kg of carbon per year. However, the main barriers identified for the development of urban forestry across the literature include the following:
- A lack of funding—cities often do not allocate a sufficient budget to urban forestry initiatives;
- Weak policy enforcement—although some cities have green space policies, the enforcement is often weak or non-existent;
- Limited public awareness—the benefits of urban forestry are not widely understood or prioritized by the general population and decision-makers.
3.3. Evolution over Time of Interest in Urban Forestry in Sub-Saharan Africa
According to the results of our analysis of the selected articles, Togo, Nigeria, Benin, Congo, and South Africa have carried out more work in the field of urban forestry. Togo accounts for 22% of publications, Benin and Nigeria account for 10%, and South Africa and Congo account for 8%. Burundi, Cameroon, Chad, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, and the DRC carried out little work in the field of urban forestry, with each country amounting to 2% of contributions (Figure 5).
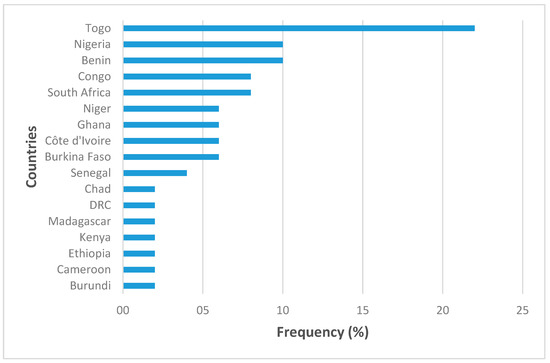
Figure 5.
Articles published on urban forestry by country.
In sub-Saharan Africa, an interest in urban forestry emerged just after 2011 and the share of work carried out rose from 2% to 12% by 2022 (Figure 6).
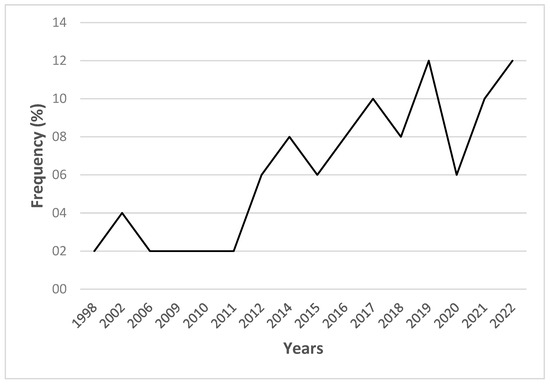
Figure 6.
Urban forestry articles by year.
3.4. Sources of Funding
An analysis of publications on urban forestry in sub-Saharan Africa shows that 34% of the scientific articles are published in English, compared with the 66% published in French. Of the forty-eight (48) countries in sub-Saharan Africa, 45.83% (https://www.axl.cefan.ulaval.ca/Langues/1div_cont_Afrique.htm, accessed on 14 September 2024) have French as their official language, while 39.58% speak English. The remaining 14.59% speak Portuguese, Arabic, Spanish, Amharic, and Somali. In the context of this review, the sources of funding include the following institutions: (i) UMR PALOC and Eco-anthropology; (ii) the International Foundation for Science (IFS), Stockholm, Sweden; (iii) the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); (iv) the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF); (v) the Sasagawa Scientific Research Fellowship of the Japan Society of Sciences; (vi) the A. P. Leventis Ornithological Research Institute (APLORI), University of Jos, Nigeria; (vii) the Development Cooperation Commission of the Academy of Research and Higher Education (ARES-CCD) in Belgium; (viii) GIZ, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit; (ix) TWAS (The World Academy of Sciences); (x) Matsumae international foundation (MIF); (xi) Afrox; (xii) Bradlows Foundation; and (xiii) the National Research Foundation of South Africa. Furthermore, funding from projects financed by internal resources (taxes, mining development funds, etc.) and by bilateral and multilateral technical and financial partners, such as citizens’ initiatives, private sector support, donations, and town twinning programmes, can also be used. The private sector should also participate in financing urban forestry to contribute to the global transition to a carbon-free economy. To achieve this, they should align their investment portfolio with the net zero emissions objective.
In addition, surveys indicate that urban populations often undervalue the ecological services provided by trees, and green spaces are transformed into bars and football fields. However, those who are more aware of these benefits show strong support for urban greening projects, indicating that awareness campaigns could significantly enhance community engagement.
4. Discussion
Tree planting is an important tool for improving the attractiveness of cities, but it must be carried out properly. Many strategies exist that can be used to incorporate trees into cities. For example, the authors [12] identify five main types of urban and peri-urban forests: (i) peri-urban forests and wooded areas; (ii) city parks and urban forests (>0.5 hectares); (iii) mini-parks and gardens with trees (<0.5 hectares); (iv) trees in streets or public squares; and (v) other green spaces with trees. The urban forest model should respect the basic principles of landscape design in terms of unity and structure, scale, proportion and balance, the division and definition of space, light and shade, colour, texture, and form. Trees can be adapted to suit almost any situation, helping to address issues such as rainwater management and climate change, as well as meeting specific esthetic objectives.
The Santamour rule (sometimes called the “10 per cent rule”) proposes maximum percentages for tree species, types, and families in a plantation. This rule states that no more than 10 per cent of any one species, no more than 20 per cent of any one genus, and no more than 30 per cent of any one family should be planted in a plantation. The aim behind this rule is to maximize the protection against pest outbreaks. Urban forest models should also aim for an appropriate age distribution, i.e., trees in age brackets that allow for the planning of individual trees ageing, as well as the appropriate and sequential removal and replacement of dead or dying trees. Urban forestry can simultaneously produce multiple benefits such as improved rainwater management, the construction of islands of fresh air and habitats for species, the creation of jobs, the economic valorization of real estate, and even the emergence of new nature experiences that promote the well-being of all. It opens the door to the reinvention of the urban landscape and to the reconsideration of the intimate relationships that we have with the living environment. To implement it, real estate players can engage in the integration of these nature-based solutions into built space by bringing together trades (engineers, technicians, sociologists, architects, landscapers, economists, etc.) around the same subject and by building infrastructure adapted to their context. The Eikenøtt eco-district located in Gland in Switzerland and The Enabling Village in Singapore are just a few examples of this. These projects, which include green spaces, constitute an interesting opportunity to rethink “nature in the city” [36].
In order to address the impacts of rapid urbanization on urban forests, a radical revision of forestry policies is needed by African governments. Countries’ current forest management policies have been largely influenced by colonial forestry policies, without the participation of local people. This has led to local indifference towards developing urban forestry and the destruction of forests. For urban forests to be sustainable in Africa, a participatory management approach is needed that engages communities in the planning, design, creation, and maintenance of forests [36,37].
In [38], themes such as the value of trees and the inventory and composition of trees in urban landscapes were addressed more thoroughly than the theme of policy and legislation, while themes related to funding and human resources for urban forestry were neglected by research and even by municipalities. A survey of the peer-reviewed literature confirms that almost 80% of articles come from the developed world context, while publications from Africa are very poorly represented [39]. This reflects the greater availability of funding and research staff from developed countries to conduct research on a number of topics and, in particular, urban forestry [40]. This situation is also revealed by [41], whose authors indicate that publications on urban forestry from Africa in the world over the period from 1800 to 2015 represent only 1% of the literature on this topic. This rate is the highest in Central Europe (27%), followed by Asia (26%) and North America (17%). However, most regions have seen an increase in the number of publications since the 2010s, with an increase of more than 90% for publications in Africa.
In addition, the construction of urban infrastructures will also have to take urban forestry into account. In fact, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, with its 17 Sustainable Development Goals, has paved the way for environmental awareness in countries and cities around the world. Several of the Sustainable Development Goals are directly linked to, or indirectly refer to, the need to develop and/or invest in green infrastructure for the benefit of all. There are four (4) main categories of green infrastructure: the urban canopy, greened public spaces, green vertical structures, and green roofs [42]. The details of each of these infrastructures are as follows:
- The urban canopy refers to the extent of vegetation cover provided by trees in an area, including green alleys, street trees, and shrubs, as well as the urban forest.
- Vegetated public spaces include, among others, green belts, green corridors, green spaces, urban parks, and areas with vegetated ground cover.
- Green roofs are also known as eco-roofs, green roofs, rain roofs, and roof gardens. They have three main components: a vegetation layer, a light-growing medium layer, and a storage or drainage layer placed on top of an impermeable membrane [41]. There are two main types: extensive and intensive. The biggest difference between the two types is the thickness of the growing substrate [41]. Thus, the former has a substrate that is 15 cm thick or less, while the latter consists of a substrate that is more than 15 cm thick.
- The green vertical structure encompasses various phytotechnologies that can be installed on the exterior or interior walls of buildings on a permanent basis [42]. The terminology of green vertical structures includes biomurs, green facades, green walls, exterior or interior green walls, and vertical vegetation.
In the context of this analysis, no article has addressed green vertical structures and green roofs. Most of these infrastructures have been primarily installed to combat urban heat islands [39]. However, the four categories of green infrastructure offer numerous benefits and advantages for adapting to and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change, in particular for combating flooding and the effects of urban heat islands (Table 1).

Table 1.
Contribution of green infrastructure to the fight against climate change.
This study offers several innovative contributions to the field of urban forestry, particularly in the context of sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike previous research that predominantly emphasizes the ecological and esthetic functions of urban trees [44], our analysis introduces a thematic classification framework that identifies five key research areas: the management of green spaces, urban tree functions, urban forestry development, tree flora characterization, and financing mechanisms. This framework not only highlights the diversity of urban forestry topics but also underscores critical gaps, such as the underexploration of sustainable funding strategies and policy integration, which have not been adequately addressed in prior studies. Additionally, this study expands the geographic focus of urban forestry research by incorporating data from underrepresented countries in SSA, providing a more comprehensive understanding of regional trends and challenges. Furthermore, the analysis bridges the gap between urban forestry and climate adaptation strategies, offering actionable recommendations for the integration of green spaces into urban planning and resilience frameworks. These innovations collectively enhance the relevance and applicability of urban forestry research to the pressing challenges of rapid urbanization and climate change in SSA.
5. Conclusions
This analysis of urban forestry in sub-Saharan Africa was carried out with regard to five (5) themes, namely, (1) the management of green spaces in urban areas; (2) the functions of trees in urban areas; (3) the development of urban forestry; (4) the characterization of urban tree flora; and (5) the financing of urban forestry. The findings from this review have several key implications. First, the geographic distribution of research is uneven, with countries such as Togo, Nigeria, Benin, Congo, and South Africa being the settings of the majority of studies, while other countries remain underrepresented. Second, there are research gaps that need to be addressed to develop a more comprehensive approach to urban forestry. For instance, while topics such as the functions of trees in urban environments and the characterization of urban tree flora dominate the literature, the development and funding of urban forestry are underexplored despite their importance in terms of the sustainability of urban forestry projects.
Furthermore, the decline of green spaces in urban environments highlights the urgent need for urban planning policies that prioritize the protection and expansion of urban forests. As cities in SSA grow, it becomes critical to incorporate urban forestry into broader urban planning frameworks to mitigate the negative impacts of urbanization, including a reduction in urban heat islands and the loss of biodiversity. Also, urban forestry plays a pivotal role in climate adaptation strategies, particularly in regions which are vulnerable to extreme heat stress. Finally, raising public awareness about the ecological, economic, and social benefits of urban forestry will foster broader support and engagement from both governments and local communities.
This study offers several innovative contributions to the field of urban forestry, particularly in the context of sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike previous research, which predominantly emphasizes the ecological and esthetic functions of urban trees, our analysis introduces a thematic classification framework that identifies five key research areas: the management of green spaces, urban tree functions, urban forestry development, tree flora characterization, and financing mechanisms. This framework not only highlights the diversity of urban forestry topics but also underscores critical gaps, such as the underexploration of sustainable funding strategies and policy integration, that have not been adequately addressed in prior studies.
Additionally, this study expands the geographic focus of urban forestry research by incorporating data from underrepresented countries in SSA, providing a more comprehensive understanding of regional trends and challenges. Furthermore, the analysis bridges the gap between urban forestry and climate adaptation strategies, offering actionable recommendations for integrating green spaces into urban planning and resilience frameworks. These innovations collectively enhance the relevance and applicability of urban forestry research to the pressing challenges of rapid urbanization and climate change in SSA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: K.A.; methodology: K.A., S.A. and K.K. (Kouami Kokou); validation: K.A., S.A., K.N.S., K.K. (Kossi Komi), J.-B.B.Z., C.A. and K.K. (Kouami Kokou); formal analysis: K.A., S.A., K.N.S. and K.K. (Kossi Komi); investigation: S.A., K.A., K.N.S. and K.K. (Kossi Komi); data curation: K.A., K.N.S., K.K. (Kossi Komi) and K.K. (Koumai Kokou); writing—original draft preparation: S.A. and K.A.; writing—review and editing: K.A., S.A., K.N.S., K.K. (Kossi Komi), J.-B.B.Z., C.A. and K.K. (Kouami Kokou); supervision: C.A. and K.K. (Kouami Kokou); project administration: K.A.; funding acquisition: K.A. and K.K. (Kouami Kokou). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received financial support from the African Centre of Excellence, Regional Centre of Excellence on Sustainable Cities in Africa (CERVIDA-DOUNEDON), through the grant awarded to the Forest Research Laboratory (LRF) of the University of Lomé for research and development work on “Opportunities for forest landscape restoration to combat urban heat islands (UHI) in the context of climate change in Greater Lomé, Maritime Region” (CONVENTION N° __/2022/CERViDA-DOUNEDON).
Data Availability Statement
Data sources are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The study also benefited from support from the Forests4Future/GIZ Programme for field data collection. The authors of this publication would like to express their sincere thanks to this programme.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Summary of Papers Analyzed During the Review
| N° | Type of Document | Titles of the Publications | Authors | Year of Publication | Country | Thematics Developped | Search Motors |
| 1 | Article | Problem of managing green spaces in urban areas: conservation and development project for the green belt of Niamey in Niger | Banon, F., Danvidé, B., and Baye, A. Y. | 2021 | Niger | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 2 | Article | Public perceptions of Urban Forests in Okitipupa Nigéria: Implication for Environmental Conservation | Faleyimu, O. I. | 2014 | Nigeria | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 2 | Article | Public perceptions of Urban Forests in Okitipupa Nigéria: Implication for Environmental Conservation | Faleyimu, O. I. | 2014 | Nigeria | Financing urban forestry | Google Scholar |
| 3 | Article | City/nature connection in West Africa. Management systems and diversity of reports linked to plant biodiversity in the city of Bobo-Dioulasso (Burkina Faso) | Deronzier, M. | 2017 | Burkina Faso | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 4 | Article | Prayer and health-seeking beliefs in Ghana: understanding the ‘religious space’ of the urban forest | Okyerefo, M. P. K., and Fiaveh, D. Y. | 2016 | Ghana | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 5 | Article | Seeing the (urban) forest through the trees: governance and household trees in Niamey | Hungerford, H., and Moussa, Y. | 2016 | Niger | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 6 | Article | Urban forest development in West Africa: Benefits and challenges | Fuwape, J. A., and Onyekwelu, J. C. | 2010 | Nigeria | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar/Bielefeld Academic Search Engine |
| 7 | Article | Is there no urban forestry in the developing world | Shackleton, C. M. | 2012 | South Africa | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 8 | Master’s dissertation | Assessment and constraints of safeguarding mature street trees in the face of road developments in the city of Cotonou | Osseni, A. A. | 2022 | Benin | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar |
| 9 | Article | Diversité floristique des formations végétales urbaines au Sud du Bénin (Abomey-Calavi, Allada et Cotonou) | Sehoun, L. C., Osseni, A. A., Orounladji, M., Lougbegnon, T. O., and Codjia, J. C. T. | 2021 | Bénin | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 10 | PhD dissertation | Assessment of Urban Forest Tree Species Population and Diversity in Ibadan, Nigéria | Agbelade, A. D., Onyekwelu, J. C., and Apogbona, O | 2016 | Nigeria | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 11 | Article | Woody plant species used in urban forestry in West Africa: Case study in Lomé, capital town of Togo | Raoufou, R., Kouami, K., and Koffi, A. | 2011 | Togo | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar/Bielefeld Academic Search Engine |
| 12 | Article | Perceptions, trends and preferences in urban forestry: case of the city of Lomé | Polorigni, B., Radji, R., and Kokou, K. | 2014 | Togo | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 13 | Article | Inventory and carbon sequestration of vegetation in the urban area of the city of Dapaong | Folega F., Kombate B., Diwedjiga K., Wala K. W., and Akpagana K. | 2020 | Togo | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 14 | Article | Diversity and importance of the woody flora of the town of Sokode | Tourey, S., Boukpessi, T., Kpedenou, K. D., and Tchamie, T. K. T. | 2020 | Togo | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 15 | Article | Floristic composition and structure of urban forests in Sahelian cities: Case of Niamey and Maradi | Moussa, S. | 2019 | Niger | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar/Bielefeld Academic Search Engine |
| 16 | Article | The development visions and attitudes towards urban forestry of officials responsible for greening in South African towns | Gwedla, N., and Shackleton, C. M. | 2015 | South Africa | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 17 | Article | Multiple use patterns of medicinal trees in an urban forest in Nairobi | Furukawa, T., Kiboi, S. K., Mutiso, P. B. C., and Fujiwara, K. | 2016 | Kenya | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 18 | Article | Key drivers of avifauna in greenspace of institutional campuses in a state in Western Africa | Kumdet, P. S., Ivande, S. T., and Dami, F. D. | 2021 | Nigeria | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 19 | Article | Diversity, use and management of household-located fruit trees in two rapidly developing towns in Southeastern D. R. Congo | Useni, Y. S., Malaisse, F., Yona, J. M., Mwamba, T. M., and Bogaert, J. | 2021 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 20 | Article | Public policy for the management of green spaces in the city of Lomé in Togo | Polorigni, B., Radji, R. A., and Kokou, K. | 2015 | Togo | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar/Bielefeld Academic Search Engine |
| 21 | Article | Rehabilitation of urban forests in Addis Ababa | Horst A. | 2006 | Ethiopia | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar |
| 22 | Article | Flora of urban green spaces in the city of Atakpame in Togo | Fousséni, F., Wouyo, A., Madjouma, K., Djibril, K., Kissao, G., Kperkouma, W., and Koffi, A. | 2019 | Togo | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 23 | Article | Modelling dimensional growth of three street tree species in the urban forest of the city of Tshwane, South Africa | Stoffberg, G. H., Van Rooyen, M. W., Van der Linde, M. J., and Groeneveld, H. T. | 2009 | South Africa | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 24 | Article | Tree heritage on the Dakar campus: environmental issues of a changing socio-pedagogical space | Sy, T. B., Badiane, S. D., Dieng, S. D., Dème, M., and Guèye, M. | 2022 | Senegal | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar |
| 25 | PhD dissertation | Role of plant cover in mitigating heat islands in urban centres: case of the city of Lomé in Togo | Polorigni B. | 2019 | Togo | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 26 | Article | Management systems and diversity of reports linked to plant biodiversity in the city of Bobo-Dioulasso | Deronzier M. | 2017 | Burkina Faso | Management of green spaces in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 27 | Article | Trees and green spaces in Brazzaville | N’Zala, D., and Miankodila, P. | 2002 | Congo | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 28 | Article | Green spaces in urban and peri-urban areas in Kinshasa | Sambieni, K. R., Useni, S. Y., Cabala, K. S., Biloso, M. A., Munyemba Kankumbi, F., Lelo Nzuzi, F., and Bogaert, J | 2018 | Democratic Republic of Congo | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 29 | Article | Study on urban and peri-urban forestry in N’djamena | FAO | 2012 | Chad | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 30 | Article | Green spaces in Lome during the German period | Sebald, P. | 1998 | Togo | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 31 | Article | Multiple benefits and values of trees in urban landscapes in two towns in northern South Africa | Shackleton, S., Chinyimba, A., Hebinck, P., Shackleton, C., and Kaoma, H. | 2015 | South Africa | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar/Bielefeld Academic Search Engine |
| 32 | Article | Perception of green spaces and their ecosystem services by local stakeholders in the city of Bujumbura | Kabanyegeye, H., Masharabu, T., Yannick, U. S., and Bogaert, J | 2020 | Burundi | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 33 | Memoire | State of the plant cover of greater Lome in the maritime region | Sawaba, A. | 2022 | Togo | Development of urban forestry | - |
| 34 | Article | Urban plant diversity and estimation of carbon stock: case of the commune of Plateau Abidjan | Vroh, B. T. A., Tiebre, M. S., and N’Guessan, K. E. | 2014 | Ivory Coast | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 35 | Article | Urban forestry and its contribution to carbon sequestration: Case of the city of Lome | Simza, D. | 2012 | Togo | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 36 | Article | Assessment of carbon stock in woody vegetation for the mitigation of atmospheric CO2 émissions at Natitingou city in North Benin | Wari, B. O., Zakari, S., Djaouga, M., Chouti, W. K., Baloubi, D., Yabi, I., and Imorou, I. T. | 2022 | Benin | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 37 | Article | Assessment of floristic diversity and estimation of the carbon sequestration rate of trees along road lines in the municipality of Daloa | Kouassi, J. K., Kouassi, H. K., and Kouassi, H. R. | 2018 | Ivory Coast | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 38 | Article | Perception, Attitude and Expectations of Residents towards Urban Green Spaces in Yamoussoukro | Hervé, K. R., Richard, N. G. J., Jean-Clovis, K. Y., and Augustin, A. A. S. | 2019 | Ivory Coast | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 39 | Article | Urban forestry and atmospheric carbon sequestration potential in the urban and peri-urban area of Kpalime | Folega, F., Kanda, M., Konate, D., Pereki, H., Wala, K., Atakpama, W., and Akpagana, K. | 2017 | Togo | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar/Bielefeld Academic Search Engine |
| 40 | Article | Tree in the city, urban forestry study in Brazzaville, | N’zala, D. | 2002 | Congo | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 41 | Article | Study of allochthonous arborescent flora and urban forestry in Brazzaville | Kimpouni, V., Mbouba, S. D., and Motom, M. | 2017 | Congo | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 42 | Article | Intercultural urban forestry, a challenge for decentralized local authorities | Andréa, P., and Blaise, C. | 2022 | Cameroon | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 43 | Article | Urban forestry: Structural study of trees and wooded areas with a view to landscape silviculture | University of Antananarivo | 2022 | Madagascar | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 44 | Article | Analysis of the viability constraints of urban vegetation: case of street trees in the city of Porto-Novo | Aziz, O. A., Brice, S., and Ismaïla, T. I. | 2014 | Benin | Development of urban forestry | Google Scholar |
| 45 | Article | Structure, diversity, and carbon stocks of the tree, community of Kumasi | Nero, B. F., Callo-Concha, D., and Denich, M. | 2018 | Ghana | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 46 | Article | Diversity and structure of woody vegetation in the town of Malanville | Wari, B. O., Zakari, S., Djaouga, M., Imorou, I. T., Yabi, I., Tente, B. A., and Djego, J. G. | 2021 | Benin | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar |
| 47 | Article | Potential for carbon sequestration by developed green spaces in the city of Bobo-Dioulasso | Gomgnimbou A. P., Ouedraogo W. O., Ssnon, A., Kone, M., ILBoudo, D., and Nacro H. B. | 2019 | Burkina Faso | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 48 | Article | Quantifying the aboveground biomass and carbon storage of urban tree species in Sokoto Metropolis | Murtala, D., Abd Manaf, L., Ramli, M. F., Yacob, M. R., and Makmom, A. A. | 2019 | Nigeria | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
| 49 | Article | Diversity and structure of urban green spaces in the city of Ziguinchor | Charahabil, M. M., Cesar, B., Hamadou, B., Ndiaye, S., and Diatta, M. | 2018 | Senegal | Characterization of urban tree flora | Google Scholar/Science Direct |
| 50 | Article | Urban green spaces enhance carbon sequestration and sonserve biodiversity in cities of the Global South: Case of Kumasi | Nero, B. F., Borgemeister, P. D. C., and Schmitt, P. D. D. C. B. | 2017 | Ghana | Functions of trees in urban areas | Google Scholar |
References
- Abubakari, M.; Ibrahim, A.-S.; Dosu, B.; Mahama, M. Sustaining the urban commons in Ghana through decentralized planning. Helyion 2023, 9, e15895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, S.R.; Iaione, C. Design principles and practices for the urban commons. In Routledge Handbook of the Study of the Sommons; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 235–255. [Google Scholar]
- Roggero, M.; Bisaro, A.; Villamayor-Tomas, S. Institutions in the climate adaptation literature: A systematic literature review through the lens of the Institutional Analysis and Development framework. J. Inst. Econ. 2018, 14, 423–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, R.R.; Kotani, K.; Kamijo, Y. Sustainability of common pool resources. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, H.; Manjunatha, B.; Nagendra, H. Contested urban commons: Mapping the transition of a lake to a sports stadium in Bangalore. Int. J. Commons 2016, 10, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, D. Reconstituting the urban commons: Public space, social capital and the project of urbanism. Urban Plann. 2019, 4, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvergne, S. Les Espaces Urbains et Péri-Urbains à Usage Agricole dans les Villes D’afrique Sub-Saharienne (Yaoundé et Accra): Une Approche de l’intermédiarité en Géographie. Ph.D. Thesis, ENS LYON, Lyon, France, 2011; 385p. NNT: 2011ENSL0679. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-00682525 (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Korah, A.; Koch, J.A.M.; Wimberly, M.C. Understanding urban growth modeling in Africa: Dynamics, drivers, and challenges. Cities 2024, 146, 104734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoh, A.J. Urbanization and development in sub-Saharan Africa. Cities 2023, 20, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, J.; Santoro, J. Urbanization in Sub-Saharan Africa. Meeting Challenges by Bridging Stakeholders. In Report; Center for Strategic & International Studies (CSIS): Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. Available online: https://www.csis.org/ (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Alvey, A.A. Promoting and preserving biodiversity in the urban forest. Urban For. Urban Green 2006, 5, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borelli, S.; Conigliaro, M.; Chen, Y. Directives sur la Foresterie Urbaine et Périurbaine; Étude FAO: Forêts (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2017; 178p. [Google Scholar]
- Useni, Y.S.; Malaisse, F.; Yona, J.M.; Mwamba, T.M.; Bogaert, J. Diversity, use and management of household-located fruit trees in two rapidly developing towns in Southeastern DR Congo. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amontcha, A.A.M.; Lougbegnon, T.; Tente, B.; Djego, J.; Sinsin, B.A. Aménagements urbains et dégradation de la phytodiversité dans la Commune d’Abomey-Calavi (Sud-Bénin). J. Appl. Biosci. 2015, 91, 8519–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.; Mattes, A.; Meier, M.; Kurths, A. Reorienting urban green infrastructure planning towards biodiversity–Perspectives and ongoing debates from Germany. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 90, 128155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, B.; Buchholz, S.; Kowarik, I.; Herrmann, J.; Neuerburg, L.; Wendler, J.; Winker, L.; Egerer, M. Land sharing between cultivated and wild plants: Urban gardens as hotspots for plant diversity in cities. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Myint, S.W. Exploring the effect of neighboring land cover pattern on land surface temperature of central building objects. Build. Environ. 2016, 95, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, S.; Chinyimba, A.; Hebinck, P.; Shackleton, C.; Kaoma, H. Multiple benefits and values of trees in urban landscapes in two towns in northern South Africa. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 136, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osseni, A.A. Bilan et contraintes de la sauvegarde des arbres matures d’alignement face aux aménagements routiers dans la ville de Cotonou. Afr. Sci. 2022, 20, 112–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sehoun, L.C.; Osseni, A.A.; Orounladji, M.; Lougbegnon, T.O.; Codjia, J.C.T. Diversité floristique des formations végétales urbaines au Sud du Bénin (Afrique de l’Ouest). Rev. Marocaine Sci. Agron. Vétérinaires 2021, 9, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Banon, F.; Danvidé, B.; Baye, A.Y. Problématique de la gestion des espaces verts en milieu urbain: Projet de conservation et de valorisation de la ceinture verte de Niamey au Niger. Managing green spaces in urban areas: Conservation and valorization of the Niamey green belt in Niger. Rev. Écosystèmes Paysages 2021, 1, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folega, F.; Bimare, K.; Konate, D.; Wala, K.; Kanda, M.; Akpagana, K. Inventaire et séquestration de carbone de la végétation de l’emprise urbaine de la ville de Dapaong, Togo. Espace Géographique Société Marocaine 2020, 41/42, 273–289. [Google Scholar]
- Polorigni, B. Rôle du Couvert Végétal Dans L’atténuation des Îlots de Chaleur dans les Centres Urbains: Cas de la Ville de Lomé au Togo. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lomé, Lomé, Togo, 2019; 168p. [Google Scholar]
- Hervé, K.R.; Richard, N.G.J.; Jean-Clovis, K.Y.; Augustin, A.A.S. Perception, attitude et attentes des résidents à l’égard des espaces verts urbains de Yamoussoukro (Côte d’Ivoire). Eur. Sci. J. 2019, 15, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwedla, N.; Shackleton, C.M. The development visions and attitudes towards urban forestry of officials responsible for greening in South African towns. Land Use Policy 2015, 42, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polorigni, B.; Radji, R.A.; Kokou, K. Politique publique de gestion des espaces verts de la ville de Lomé au Togo. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 9, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleyimu, O.I. Public perceptions of urban forests in Okitipupa Nigeria: Implication for environmental conservation. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2014, 18, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Vilanova, C.; Ferran, J.S.; Concepción, E.D. Integrating landscape ecology in urban green infrastructure planning: A multi-scale approach for sustainable development. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 94, 128248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; MacKenzie, A. Trade-offs and synergies in urban green infrastructure: A systematic review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 94, 128262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konijnendijk, C.C.; Ricard, R.M.; Kenney, A.; Randrup, T.B. Defining urban forestry—A comparative perspective of North America and Europe. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Étude sur la foresterie urbaine et périurbaine de N’djaména, Tchad rôle et place de l’arbre en milieu urbain et périurbain. In Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; 95p. [Google Scholar]
- Choumert, J. Analyse Économique d’un Bien Public Local: Les Espaces Verts. Ph.D. Thesis, Université d’Angers, Angers, France, 2009; 426p. NNT; HAL Id: Tel-00477749. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-00477749v1 (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Word Bank. World Development Indicators. 2020. Available online: http://data.worldbank.org/data-catalog/world-development-indicators (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Wheldon, M.C.; Kantorová, V.; Ueffing, P.; Dasgupta, A.N.Z. Methods for Estimating and Projecting Key Family Planning Indicators Among All Women of Reproductive Age; Population Division, Technical; Paper No. 2; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; World Bank. Farming systems and poverty: Improving farmers’ livelihoods in a changing world. In Summary; FAO: Rome, Italy; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Arnould, P.; Le Lay, Y.-F.; Dodane, C.; Méliani, I. La nature en ville: L’improbable biodiversité. Géographie Econ. Société 2011, 13, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampelmann, S. Knock on wood: Business models for urban wood could overcome financing and governance challenges faced by nature-based solutions. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 62, 127108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen, P.C.; Crawford, B.R.; Corro, L.M.; Bagstad, K.J.; McNellis, B.E.; Jenerette, G.D.; Diffendorfer, J.E. Urban tree cover provides consistent mitigation of extreme heat in arid but not humid cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, E.; Pellerin, S. Portrait des infrastructures vertes and des ouvrages phyto technologiques dans l’agglomération de Montréal. In Rapport Final; Fondation Espace pour la vie: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2018; 44p. [Google Scholar]
- Bartesaghi Koc, C.; Osmond, P.; Peters, A. Towards a comprehensive green infrastructure typology: A systematic review of approaches, methods and typologies. Urban Ecosys. 2017, 20, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, J.; Long, H. Dynamic analysis of international green behavior from the perspective of the mapping knowledge domain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6087–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, S.; Perisamy, E.; Hussein, H.; Myeda, N.E.; Zainon, N. Vertical Greenery System in urban tropical climate and its carbon sequestration potential: A review. Ecol. Indicat. 2018, 91, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatriz, O.R. les infrastructures vertes et les synergies possibles pour favoriser l’atténuation et l’adaptation aux changements climatiques. In Maitrise En Environment; Université de Sherbrooke: Sherbrooke, QC, Canada, 2020; 81p. [Google Scholar]
- Tyrväinen, L.; Silvennoinen, H.; Kolehmainen, O. Ecological and aesthetic values in urban forest management. Urban For. Urban Green. 2003, 1, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).