Abstract
This research delves into the effects of carbon dioxide emissions and energy consumption on economic growth in Korea from 1980 to 2022, employing a sophisticated nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model. The study unveils pivotal findings, most notably the positive association between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth, suggesting that periods of economic expansion in Korea have been accompanied by surges in emissions. Furthermore, the investigation highlights a significant, albeit asymmetrical, positive impact of primary energy consumption on economic growth, illuminating the critical role of energy in the nation’s economic trajectory. The analysis also identifies essential economic determinants—namely, the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net inflows of foreign direct investment—underscoring their pivotal contributions to economic proliferation. The reliability of these insights is corroborated through advanced econometric techniques, including fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares methods. A noteworthy discovery emerges from the Toda–Yamamoto causality test, revealing bidirectional Granger causality between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth, as well as between energy consumption and economic growth. Moreover, it uncovers a unidirectional causality flowing from labor, capital formation, and foreign direct investment towards economic growth. These findings elucidate the complex interplay between environmental and economic elements, highlighting the critical need for sustainable energy policies and proactive environmental stewardship in Korea. By advocating for a synthesis of economic advancement and environmental sustainability, this study presents indispensable insights for policymakers. It calls for a judicious approach to balancing Korea’s economic ambitions with its ecological responsibilities, thereby charting a sustainable path forward for the nation. Through its comprehensive analysis, this research contributes valuable perspectives to the discourse on economic development and environmental sustainability, offering guidance for Korea’s strategic planning and policy formulation.
1. Introduction
As an economically advanced nation, South Korea has witnessed rapid growth, paralleled by substantial increases in energy use and carbon dioxide emissions. While this economic model has been effective in terms of growth, it presents significant sustainability challenges, especially considering global environmental concerns and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Research by Saboori et al. [1] delves into the interplay between energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth in Korea, finding a strong link between these factors. Their work underscores the necessity for South Korea to transition towards sustainable energy sources as a strategic economic imperative. Further studies, such as those by Nam et al. [2], Jo and Jang [3], Ha and Byrne [4], Ifaei et al. [5], Hong et al. [6], Ghezelbash et al. [7], and Yeo and Oh [8], explore the role of renewable energy in enhancing Korea’s economic sustainability. These studies suggest that embracing renewable energy could mitigate the environmental downsides of traditional energy sources while supporting continued economic advancement. Moreover, analyses by Sonnenschein and Mundaca [9], Kim and Thurbon [10], and Bayarsaikhan et al. [11] examine Korea’s energy policies, highlighting the challenges and prospects of transitioning towards a low-carbon economy. Confronted with the dual imperative of maintaining economic growth and transitioning to environmental sustainability, South Korea’s heavy reliance on fossil fuels and its high per capita carbon dioxide emissions, particularly in comparison to other OECD countries, accentuate the urgency for change. Recent policy initiatives, including the Green New Deal and the 2050 Carbon Neutral Vision, demonstrate South Korea’s growing commitment to sustainable development. This paper offers an in-depth analysis of South Korea’s journey in aligning its economic progression with sustainable energy practices and reducing carbon emissions, consistent with global environmental norms. Achieving this equilibrium is not only vital for the country’s long-term economic health, but it is also imperative for its role in the global climate change mitigation effort. To deepen our understanding of the dynamics shaping Korea’s economic growth, we procured and analyzed raw GDP data from the World Bank. Figure 1 vividly demonstrates that Korea’s economy has consistently demonstrated robust growth momentum. This persistent trend is a testament to the sustainable nature of Korea’s economic expansion. Utilizing this foundational data allows us to construct a detailed narrative of Korea’s economic progression, showcasing a consistent upward trajectory in GDP throughout our study’s timeframe. Our analysis not only reaffirms the robustness of Korea’s economy but also lays the groundwork for evaluating its long-term growth prospects. A thorough exploration of annual changes and the determinants of economic equilibrium has enriched our insight into the fundamental drivers of Korea’s economic achievements, providing a valuable framework for understanding its enduring success.
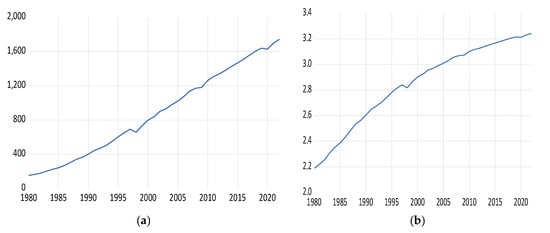
Figure 1.
The basic trend of Korean economic growth: (a) Billion USD constant 2015; (b) billion USD constant 2015 in log.
Based on this background above, this study investigates the interplay between carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth in South Korea from 1980 to 2022. By employing a nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model, it offers crucial insights into this complex relationship. The research identifies a clear correlation: economic growth periods in Korea have generally coincided with increased carbon dioxide emissions, suggesting that economic expansion has often been paralleled by environmental impacts. Furthermore, it brings to light the substantial positive influence of primary energy consumption on Korea’s economic growth, revealing a relationship that is both significant and asymmetrical. The study also examines how the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and the net flow of foreign direct investment contribute positively to economic growth. The robustness of these findings is further reinforced through econometric methods, including fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares analyses. Intriguingly, the application of the Toda–Yamamoto test uncovers complex causal patterns. It demonstrates a bidirectional Granger causality existing between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth and between energy consumption and economic growth. Additionally, the research points to a clear unidirectional causality from such factors as labor, capital formation, and foreign direct investment to economic growth. These findings emphasize the intricate connection between environmental and economic factors. The bidirectional causality observed underlines the urgent need for Korea to adopt sustainable energy policies and proactive environmental measures. It is crucial to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability, necessitating policies that merge economic advancement with ecological mindfulness. Therefore, this research is invaluable for policymakers, underscoring the need to develop strategies that dovetail economic development with environmental preservation, an essential aspect for guiding Korea’s future economic path.
This study makes four significant contributions to the field, each distinguished from existing research, thereby highlighting their importance. First, it establishes a positive correlation between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth in Korea, particularly during economic expansion periods. This nuanced understanding, offering a deeper dive than the broader correlations found in Jahanger et al. [12] and Adedoyin et al. [13], specifically addresses the environmental implications of Korea’s economic development. Second, the study reveals an asymmetric relationship between primary energy consumption and economic growth in Korea. This finding advances the dialogue beyond the direct correlations noted by Amin and Song [14] and Shahzad et al. [15], providing a more intricate view of how energy consumption impacts economic growth under varying circumstances in Korea. Third, the analysis of the roles of the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment as catalysts for economic growth in Korea contributes to the broader economic development literature. This specific focus contrasts with the more general perspectives offered by Ba and Winecoff [16] and Tsomb and Atangana [17], highlighting how these factors uniquely drive growth in the Korean context. Lastly, the study’s identification of bidirectional Granger causality between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth, as well as between energy consumption and economic growth, marks a notable advancement. This complex causality, differing from the unidirectional causality in Li et al.’s [18] and Bildirici et al.’s [19] research, underlines the complexity of environmental and economic interplay and underscores the need for sustainable policy approaches. Overall, this study enriches the understanding of the dynamic relationship between environmental and economic variables in Korea, offering valuable policy insights for achieving a harmonious balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability.
The organization of this paper is as follows. The second section conducts an in-depth review of the existing literature, scrutinizing relevant studies and integrating their insights with the aims of our study. The third section elaborates on our research methodology, detailing the specific variables and analytical models we have employed. Section four is dedicated to presenting the results of our research, followed by an exhaustive analysis of these findings. The paper culminates in the fifth section, where we consolidate the primary insights from our study, draw conclusions, and explore the wider implications of our findings within the scope of this research field.
2. Literature Review
The academic discourse on the effects of carbon dioxide emissions on economic growth is intricate and diverse. Some researchers, like Khan [20] and Adedoyin et al. [21], view increased carbon dioxide emissions as a natural consequence of economic growth, especially in developing, industrializing nations. They draw on the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) theory, which posits that economic development initially leads to environmental degradation, including heightened carbon dioxide emissions, until a certain income level is achieved. Ahmad et al. [22] and Magazzino et al. [23], who link different stages of economic development with environmental degradation, provide additional support for this idea. Contrastingly, other scholars argue that excessive carbon dioxide emissions could be detrimental to long-term economic growth. According to Rehman et al. [24], Omri and Belad [25], and Wen et al. [26], increased carbon dioxide emissions are a sign of environmental degradation, which may lower productivity and negatively affect economic growth. Fan et al. [27] and Hatipoglu et al. [28] extend this perspective, highlighting potential long-term economic risks associated with unchecked environmental impacts. The carbon dioxide emissions–economic growth relationship also varies across different global contexts. According to research by Adedoyin et al. [29], Dong et al. [30], and Ozcan et al. [31], the environmental policies and developmental stage of each country have an impact on this relationship. Similar findings are echoed in studies by Namahoro et al. [32], Rahman et al. [33], and Wang and Su [34], which examine this dynamic in various economic settings. Recent studies have shifted focus towards sustainable development, advocating for separating economic growth from carbon dioxide emissions. Alam and Murad [35] and Chien et al. [36] emphasize the potential for sustainable growth through technological advancements and renewable energy. Saidi and Omri [37] support this position by claiming that investments in efficient technologies and renewable energy can lessen the detrimental effects of carbon dioxide emissions on economic growth. Further supporting this are studies by Djellouli et al. [38], Khan et al. [39], and Habiba et al. [40], which highlight the role of renewable energy in this context. In summary, while there is evidence of a positive correlation between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth in the initial stages of a country’s development, the long-term effects of emissions pose substantial risks to sustained economic growth. Recent scholarship calling for a separation of economic advancement from environmental harm highlights how important this is in the global push for sustainable development. Based on the aforementioned analysis, we propose Hypothesis 1, as follows:
Hypothesis 1.
Carbon dioxide emissions contribute to economic growth.
The nexus between energy consumption and economic growth is a dynamic and widely debated subject within academic research, presenting a range of perspectives and evolving hypotheses. On one hand, a group of scholars, including Rahman et al. [41] and Topcu et al. [42], posit a direct, positive correlation between energy usage and economic output, a viewpoint further supported by Khan et al. [43] and Chen et al. [44]. These studies underscore energy’s integral role in driving industrial activities and, consequently, economic growth. In contrast, other academics urge a more nuanced interpretation. Xie et al. [45] and Usman et al. [46] contend that the energy–growth relationship is nonlinear, potentially diminishing over time due to advancements in energy efficiency and technology. This is echoed by Bithas et al. [47] and Wang and Jiang [48], who suggest that the returns from energy consumption might decrease as economies advance, pointing towards the possibility of decoupling energy consumption from economic growth in more developed stages. The complexity of this debate is further deepened by research indicating bidirectional causality. Nasreen et al. [49] and Baz et al. [50], for example, identify a reciprocal relationship between energy consumption and economic growth, suggesting a cyclical pattern where growth stimulates energy demand, which in turn contributes to further economic expansion. Recent scholarly focus has shifted towards sustainable development, emphasizing renewable energy as being crucial for maintaining economic growth while mitigating the environmental impact of traditional energy sources. This perspective is championed by Shahbaz et al. [51] and Destek and Sinha [52], and supported by Zafar et al. [53] and Zhao et al. [54], who highlight the long-term economic advantages of embracing cleaner energy alternatives. Furthermore, the impact of energy consumption on economic growth exhibits notable variations across different countries and regions, as evidenced by studies specific to the United States (Le et al. [55] and Chen et al. [56]) and other countries (Malik [57] and Dogan et al. [58]), indicating that local economic and energy conditions significantly influence this relationship. In summary, while there is substantial support for the positive impact of energy consumption on economic growth, particularly in developing economies, the relationship is multifaceted and complex. The academic discourse increasingly advocates for the adoption of sustainable and renewable energy sources, acknowledging the need for long-term economic growth that is environmentally sustainable and mindful of the diminishing returns associated with traditional energy sources. Drawing from the preceding discussion, we put forward Hypothesis 2, as follows:
Hypothesis 2.
Energy consumption has an asymmetric impact on economic growth.
The influence of the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment on economic growth presents a rich tapestry of academic inquiry and debate. Gao et al. [59] and Zhou et al. [60] have underscored the pivotal roles of labor and capital in fostering economic growth, a sentiment echoed in studies by Bustos et al. [61] and Yang et al. [62], which stress the key contributions of labor and capital accumulation in driving economic development. However, the discourse surrounding labor’s role in economic growth has evolved, with Ahmed et al. [63] and Zia et al. [64] introducing the critical concept of human capital. They argue that the quality of labor, enriched through education and training, is equally if not more important for economic growth. This perspective is further bolstered by Xu and Li [65], Goenka and Liu [66], and Gruzina et al. [67], who highlight human capital’s significance within endogenous growth models. The impact of gross fixed capital formation on economic growth, while widely recognized, is also a subject of discussion and analysis. Researchers, like Zhou et al. [68] and Das and Drine [69] propose that investments in physical capital and infrastructure are crucial for spurring technological progress and enhancing productivity. However, Zhang et al. [70] and Yasmeen et al. [71] urge caution, noting the importance of investment efficiency and the nature of capital formation in determining its true impact on growth. The role of net-flow foreign direct investment in economic growth is equally multifaceted and debated. Mohamed Sghaier [72], Henok and Kaulihowa [73], and Konstandina and Gachino [74] point to foreign direct investment as a catalyst for economic growth through technology transfer and human capital development. Contrarily, Han et al. [75] and Hanousek et al. [76] raise concerns about the potential adverse effects of foreign direct investment on domestic firms and markets. Contractor et al. [77] and Huang et al. [78] offer a more balanced view, suggesting that the impact of foreign direct investment on economic growth hinges on the specific economic conditions and regulatory environment of the host country. In conclusion, while the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment are acknowledged as essential elements of economic growth, their contributions are complex and diverse. The academic dialogue continues to emphasize a nuanced understanding of these dynamics, considering the quality of human capital, capital investment efficiency, and the contextual nuances influencing foreign direct investment’s impact. Following the analysis provided, we introduce Hypotheses 3, 4, and 5, as follows:
Hypothesis 3.
Labor force exerts a positive influence on economic growth.
Hypothesis 4.
Capital stock plays a pivotal role in fostering economic growth.
Hypothesis 5.
Foreign direct investment serves as a catalyst for economic growth.
3. Variable and Model
3.1. Variable
Dependent variable: This study explores the intricate dynamics between carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth in Korea from 1980 to 2022. It delves into the evolving interplay between environmental sustainability and economic progress over the last four decades. Employing annual data, this research scrutinizes the influence of Korea’s patterns of energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions on its economic trajectory. The focus is particularly on GDP, measured in billions of constant 2015 dollars, serving as the study’s dependent variable. This analysis aims to illuminate the complex relationships that underpin Korea’s journey towards sustainable economic development, offering valuable insights into the balancing act between environmental stewardship and economic sustainability.
Independent variable: At the heart of this investigation is the exploration of the pivotal environmental determinants—namely, carbon dioxide emissions, quantified in millions of metric tons, and primary energy consumption, denoted as equivalents of a million tons of oil. This study analyzes their symetric and asmetric impacts on the economic expansion of Korea. By employing both carbon dioxide emissions and primary energy consumption as independent variables, this research aims to unveil the intricate dynamics between Korea’s environmental footprint and its economic progression. Through this lens, we endeavor to provide a better understanding of the interdependencies shaping Korea’s journey towards sustainable economic development.
Control variable: In an effort to enrich the analytical depth of our investigation, this study thoughtfully integrates a suite of additional variables, thereby embracing the latest scholarly advancements in the realm of economic analysis. One of these is the labor force metric, which Azam et al. [79] explain as being important among these additions and which is expressed in millions to capture the crucial influence of human capital on economic growth. Moreover, we incorporate gross fixed capital formation, leveraging it as a critical indicator of capital stock. This metric, valued in billions of constant 2015 US dollars, adheres to the methodological frameworks established by Minh and Van [80] and Iqbal et al. [81], thus ensuring a robust appraisal of investment dynamics. Equally pivotal to our analysis is the inclusion of foreign direct investment, quantified in millions of constant 2015 US dollars. This decision, inspired by the empirical approaches of Appiah-Otoo et al. [82] and Tariq et al. [83], positions foreign direct investment as an essential control variable, recognizing its indispensable role in shaping economic landscapes. To tackle the nuanced challenge of heteroscedasticity and elevate the precision of our findings, we convert all variables into their logarithmic counterparts. This methodological refinement is not merely a statistical adjustment; it represents a strategic choice aimed at stabilizing variance across our dataset. More importantly, it facilitates a sophisticated examination of the elasticities and proportional interrelations among the variables under study. By adopting these methodological innovations, our study endeavors to illuminate the complex interplay between environmental and economic factors within Korea’s distinctive economic context. Our approach is designed not just to contribute to the academic discourse but to offer a nuanced, layered understanding of these interactions. Through this lens, we aim to provide insights that are both intellectually enriching and pragmatically valuable, reflecting the dynamism and complexity of Korea’s economic environment. Moreover, the dataset underpinning this study was sourced from the World Bank and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Data Center, ensuring a robust and comprehensive empirical foundation.
3.2. Theoretical Model
To achieve the objectives of our research, we have developed an enhanced Cobb–Douglas production function. This advanced formulation, inspired by the methodologies of recent studies by Wu et al. [84], and Fu et al. [85], is articulated in Equation (1). Our approach expands the traditional model by integrating additional, relevant variables, thereby enriching the analytical framework of our study. This extension is critical for a thorough examination of the complex interplay among key economic inputs—labor, capital, and technological advancement—and their collective impact on output. Equation (1) is shown as follows:
In Equation (1), integral to our augmented Cobb–Douglas production function, we assign specific symbols to represent key economic variables. signifies the year, injecting a chronological perspective into our analysis. , representing gross domestic product, serves as a crucial measure of economic output. , denoting the level of technology, encapsulates the advancements and efficiencies pivotal to productivity. The labor force, an essential engine of economic activity, is represented by , while corresponds to the capital stock, comprising the aggregate assets utilized in production. Additionally, stands for energy consumption, a variable of growing significance in modern economic studies due to its relevance to sustainability and operational efficiency. refers to foreign direct investment, highlighting the influence of international capital inflows on domestic production capacities. Furthermore, represents white noise, capturing stochastic elements and unaccounted variances within the model. The coefficients , , , and are assigned to the output elasticities of these variables: technology, labor force, capital stock, and energy consumption, respectively. These coefficients are pivotal as they quantify the sensitivity of the gross domestic product to variations in each of these inputs. This quantification provides critical insights into the relative significance of each factor and their respective roles in influencing the economy.
The Cobb–Douglas production function, as explicated by Wang and Henderson [86] and Smirnov et al. [87], stands out in the field of economics for its adept representation of the relationship between economic outputs and the inputs used in production. Its numerous advantages make it a model of choice for a range of applications. Primarily, it is renowned for its precision, which makes it equally applicable for broad macroeconomic overviews and detailed micro-level analyses, as noted by Ishikawa [88] and Zhou and Gao [89]. A hallmark of this model is the integration of a technology coefficient labeled ‘A’, emphasizing the role of technological advancement in production processes. This feature has been particularly highlighted by Ketokivi and Mahoney [90], Sass et al. [91], and Foss et al. [92]. Additionally, the Cobb–Douglas function excels at calculating the production elasticities of various inputs, including technology, which becomes particularly effective when the model is computed in logarithmic terms. This capability enhances the precision of economic modeling. The function’s coefficients are also notable for their alignment with advanced factor productivity metrics, a correlation supported by studies from Wang et al. [93], Zhang et al. [94], and Somjai et al. [95]. In our study, we adopted a two-pronged methodology leveraging the Cobb–Douglas production function to analyze the effects of carbon dioxide emissions on economic growth. This approach has been carefully crafted to accurately reflect the intricate ways in which carbon dioxide emissions interact with and influence economic productivity and expansion. This nuanced exploration is critical for understanding the broader economic implications of environmental factors in the modern world.
The first stage of our study concentrates on delineating the intricate relationship between technological progress and carbon dioxide emissions. This link is critical, as advancements in technology play a key role in driving both environmental and economic changes. Three primary aspects underscore this relationship: the capacity of technology to help economies conform to and manage emission reduction commitments, its role in promoting the shift towards eco-friendly energy alternatives, and its contribution to overall economic growth. The comprehensive influence of technological developments in these areas is thoroughly examined and supported by the research findings of Xie et al. [96], Cheng et al. [97], and Anser et al. [98]. To quantitatively represent this relationship, we introduce Equation (2) in our analysis. This equation is vital for a deeper understanding of how technological innovations interact with environmental factors, particularly carbon dioxide emissions, and their subsequent economic implications.
Within the framework of Equation (2), is established as a constant, unaffected by time. is designated to represent carbon dioxide emissions, a significant factor in environmental analysis. Additionally, is used to denote the technological elasticity of carbon dioxide emissions, a vital aspect of our study. Advancing to the subsequent phase, we amalgamate the insights gleaned from the initial stage into the classic Cobb–Douglas production framework. This process entails replacing the technology variable in the original equation with the relationships identified in Equation (2). Consequently, this leads to the development of Equation (3), effectively merging our initial findings with the broader economic model, thus providing a more comprehensive understanding of the interactions at play.
Applying a logarithmic transformation to both sides of Equation (3) allows us to reformulate it into Equation (4).
3.3. Econometric Model
The autoregressive distributed lag approach, as detailed by Pesaran and Pesaran [99], is proficient in handling variables that are stable at their initial levels, first differences, or even a mix of both. Nevertheless, as highlighted by Mohammed et al. [100] and Yeo et al. [101], the autoregressive distributed lag model faces challenges when dealing with variables that are stationary at the second difference due to its dependency on specific threshold values (lower for and upper for , or a combination thereof). This necessitates a preliminary check for the stationarity of variables before proceeding with deeper analysis. Despite the widespread use of the augmented Dicky–Fuller and Phillips–Perron tests in standard unit root analysis, their reliability dwindles in smaller sample sizes, as underscored by Ali et al. [102] and Khan et al. [103]. To address this, our research adopted the KPSS unit root test, as endorsed by Çağlayan Akay et al. [104] and Webb et al. [105], ensuring a more reliable assessment of the stationarity of the variables in question. In the process of selecting the most suitable lag length for our model, we explored various options. Ultimately, the Akaike information criterion was selected as the preferred method, particularly due to its effectiveness in small sample contexts. This choice, informed by the recommendations of Pretis [106], Grabowski and Welfe [107], and Yang and Lee [108], was made to enhance the precision and reliability of our analysis, especially considering the size constraints of our data set. This meticulous approach is in line with the analytical standards and preferences common among American scholars, ensuring a robust and credible methodological framework for our study.
Our research employed the nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model, a concept formulated by Shin et al. [109], to analyze the asymmetric effects of energy consumption on Iran’s economic progression. This model is adept at capturing the dual impacts—both positive and negative—that an independent variable might exert on a dependent variable. This approach has been validated and utilized in various studies, including those by Cho et al. [110], Sam et al. [111], and Jordan and Philips [112]. The nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model stands apart from the linear autoregressive distributed lag model in several significant ways. Its first notable feature is the ability to dissect and examine the dual (positive and negative) influences of the independent variables on the dependent variable. Additionally, it excels at uncovering hidden cointegration among variables, ensuring a more thorough and intricate analysis. This aspect is particularly highlighted in the research by Jiang and Liu [113] and Long et al. [114]. In comparison to traditional analytical methods, both linear and nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag models offer substantial advantages. They are especially effective for analyses involving smaller datasets, as indicated by Merlin and Chen [115] and Barnett et al. [116]. They also adeptly handle potential endogeneity and autocorrelation concerns, as shown in studies by Kaur et al. [117], Ayad et al. [118], and Adebayo and Odugbesan [119]. Moreover, these models provide the flexibility to assign various lag lengths to different variables, a feature emphasized by Musa et al. [120], Aftab et al. [121], and Nur Mozahid et al. [122]. The simplicity of their single-equation framework also facilitates easier implementation and interpretation of results. To operationalize the nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model in our study, we began by estimating the long-term cointegration of variables using the unconditional linear correction model through the autoregressive distributed lag bounds testing approach. This methodology, as delineated by Pesaran et al. [123], is outlined in Equation (5) and forms the foundation for our subsequent, more detailed analysis.
In our analysis, Equation (5) employs as the symbol for the first differential operator, and denotes the drift components. The coefficients ranging from to provide insights into the long-term dynamics between the variables we are examining. To assess whether a cointegrating relationship exists among these variables, as proposed in Equation (6), we apply the Wald F-statistic. This involves testing the null hypothesis, , which suggests no cointegration, against an alternative hypothesis, . We then compare the calculated F-statistic against the critical bounds defined by Pesaran et al. [123], with the lower bound assuming that all variables are stationary at their initial levels and the upper bound assuming first difference stationarity. It is crucial to acknowledge that the critical values determined by Pesaran et al. [123] are more suited for larger samples (500 to 40,000 observations) and may yield biased results in smaller samples. Recognizing this, we have adopted alternative critical values for smaller samples (30 to 80 observations), as recommended by Kaur and Sarin [124], Ullah et al. [125], and Udemba et al. [126], in our study. Depending on the F-statistic relative to these critical bounds, we anticipate one of three possible outcomes. If the F-statistic surpasses the upper critical bound, it suggests rejecting the existence of a long-term relationship among the variables (supporting the null hypothesis). Conversely, an F-statistic below the lower bound would imply no long-term relationship, hence, not rejecting the null hypothesis. The F-statistic that lies between the two bounds would lead to inconclusive results, necessitating further analysis to determine the order of integration of the variables involved. In cases where the results are inconclusive, the presence of a negative and statistically significant error correction mechanism, as indicated by Smeekes and Wijler [127], Kraft et al. [128], and Atil et al. [129], can be interpreted as evidence of a long-term relationship among the variables. Utilizing the error correction mechanism enables us to estimate the short-term coefficients, which are detailed in Equation (6).
In Equation (6), the coefficients ranging from to are pivotal for delineating the dynamics of error correction. The coefficient ‘’ signifies the lagged error correction term within this model. For the model to effectively indicate a return to long-term equilibrium, it is essential that the coefficient be both negative and show statistical significance. In line with Shin et al.’s [109] approach, our study delves into the asymmetric impacts of energy consumption. To achieve this, we dissect the log-transformed energy consumption data into positive and negative segments. This division enables a more nuanced and accurate portrayal of energy consumption’s asymmetric effects, as detailed in Equation (7). This methodological choice is instrumental in enhancing the depth and precision of our analysis.
In Equation (7), . . Building upon the augmented Cobb–Douglas production function as depicted in Equation (4), our analysis extends to a thorough examination of energy consumption’s impact. This detailed assessment is conducted within the nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model framework, which is comprehensively represented in Equation (8).
In the context of the nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model, our analysis involves contrasting the Wald F-statistic’s null hypothesis () with the alternative hypothesis (). Subsequently, this leads us to establish the conditional error correction model, which is succinctly expressed in Equation (9).
In Equation (9), the coefficients ranging from to are crucial for outlining the short-term error correction dynamics. The coefficients and , specifically, are employed to describe the adjustments related to short-term symmetry in the model.
The Granger causality test, while widely used, has its limitations, notably its reliance on the integration order of variables, a concern raised by Contreras-Reyes and Hernández-Santoro [130] and Sun et al. [131]. To circumvent this issue, our study implements the T-Y test, renowned for its resilience to the integration order of variables. This approach, recommended by Zhu and Liu [132], Adolf et al. [133], and supported by Adeleye et al. [134] and Azam et al. [135], is particularly effective for assessing causal relationships between variables, regardless of their integration order. In cases where cointegration is detected between two or more time series, it usually suggests the existence of unidirectional or bidirectional Granger causality. However, this is not a hard-and-fast rule, as noted by Clarke and Mirz [136]. It is important to acknowledge that correlations might be influenced by external variables not accounted for in the model, as Shahzad et al. [137] have indicated. Therefore, verifying causality becomes a critical step after establishing cointegration. To thoroughly investigate this aspect, we employed the vector autoregressive model, detailed in Equations (10) and (11). This model is instrumental in examining the existence or absence of Granger causality, thereby providing a more comprehensive and reliable insight into the interactions among the variables in our research.
Equation (10) in our study is used to assess the null hypothesis, which claims that variable does not have a Granger causal effect on (), in comparison to an alternative hypothesis that suggests that does influence through Granger causality. In a similar vein, Equation (11) addresses the null hypothesis that does not Granger-cause () and contrasts it with an opposing hypothesis. When examining these equations, the existence of cointegration between the and series is inferred if either of the coefficients, or , are statistically significant and deviate from zero. This analysis yields four possible scenarios, determined by the specific values and statistical relevance of coefficients and . Scenario 1: , : causality is moving in a single direction from to . Scenario 2: , : causality that is solely directed from towards . Scenario 3: , : bidirectional causality between and . Scenario 4: , : absence of cointegration among the specified variables. Hence, for the purpose of determining Granger causality among the variables in question, we adopt the augmented vector autoregression model, originally conceptualized by Toda–Yamamato [138]. The determination of the most suitable lag length within this model is based on the Akaike Information Criterion. To further validate the model, a series of tests are conducted to verify that the residuals of the vector autoregression model do not exhibit serial correlation. In our study, to ascertain the accuracy of the long-term coefficients derived from the ARDL model, we employed two advanced econometric techniques: the fully modified ordinary least squares and the dynamic ordinary least squares. The application of fully modified ordinary least squares is supported by the findings of Gold et al. [139], Young [140], and Maydeu-Olivares et al. [141], while dynamic ordinary least squares is backed by the research of González Olivares and Guizar [142] and Neto [143]. These methods are sophisticated adaptations of the classic least squares technique, devised to effectively tackle the endogeneity that might arise in regressors from cointegration links and also to manage the impact of serial correlation. This approach is elaborated on in Equation (12).
This outcome is directly derived from the differential regression, as shown in Equation (13).
Let us consider and to represent the long-term covariance matrix calculated using the residuals denoted by . Under this assumption, we can express the adjusted data in the format presented in Equation (14). This formulation takes into account the intricate relationships captured in the covariance matrix, providing a foundation for further analysis and interpretation of the data within the specified model framework.
The bias correction term, as estimated in our analysis, is presented in Equation (15). This term plays a critical role in adjusting our model to ensure more accurate and reliable results by accounting for any potential biases in the estimation process.
Consequently, we express the fully modified ordinary least squares estimator through the formulation outlined in Equation (15). This estimator is crucial for our analysis as it enhances the accuracy of our estimations by correcting for any potential serial correlation and endogeneity in the regression models. The FMOLS approach, therefore, provides a more reliable and nuanced understanding of the underlying relationships within our dataset.
In Equation (16), . Formulating the long-term covariance matrix estimators, denoted as , is a crucial phase in the estimation of the fully modified ordinary least squares, as emphasized in the research conducted by Ozmec-Ban and Babić [144] and Balsalobre-Lorente et al. [145]. This step is fundamental to the accuracy and effectiveness of the FMOLS methodology. This approach involves enhancing the cointegrating regression by incorporating both lagged and leading elements, thereby ensuring that the error term of the cointegrating equation is uncorrelated with the complete historical sequence of stochastic regressor innovations. This technique is outlined in the works of Demetrescu et al. [146] and Kheifets and Phillips [147], and is succinctly encapsulated in Equation (17).
By incorporating lags and leads of the differenced regressors, the persistent correlation between variables and is effectively neutralized. This adjustment allows the estimation of through the least squares estimator to align with the asymptotic distribution achieved via the fully modified ordinary least squares method. Key strengths of these methodologies, as highlighted by Karimi et al. [148] and Maroufi and Hajilary [149], include their ability to circumvent such issues as endogeneity, serial correlation, and the biases often encountered in small sample sizes.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Fundamental Analyses
This section is dedicated to three fundamental analyses, including the Kwiatkowski–Phillips–Schmidt–Shin unit root test, the bounds test for determining cointegration, and six diagnostic evaluations to ascertain the robustness and accuracy of our model. The results from these extensive and detailed analyses are compiled and displayed in Table 1 for review. Together, these tests offer a comprehensive assessment of the characteristics of our data and the efficacy of the model we have employed.

Table 1.
Results of fundamental analyses.
Results from the Kwiatkowski–Phillips–Schmidt–Shin unit root test, presented in Table 2, Panel A, indicate that cointegration at the second order was not observed in any of the variables analyzed. Specifically, it was found that the dependent variable reached cointegration at the baseline level. On the other hand, the independent variables exhibited stationarity, either at their original levels or after implementing the first difference. Understanding the differences in stationarity between the dependent variable and the independent variables is essential for a comprehensive grasp of the dynamic interplay among them and the overall functioning of the model.

Table 2.
Results of long-run effects.
The findings presented in Panel B laid a robust foundation for investigating the nature of relationships—whether symmetric or asymmetric—among the studied variables, utilizing the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) and nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag (NARDL) frameworks. The selection of the most fitting models, ARDL (1, 1, 1, 1, 2) and NARDL (1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1), was guided by the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC). These models were characterized by an unrestricted constant while omitting any trend components. Within these models, the highest lag for the dependent variable (GDP) was established at 1, and the maximal lags for critical variables, such as carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and foreign direct investment were also precisely assigned. To further affirm the soundness and dependability of these models, a sequence of residual diagnostic tests was conducted, playing a vital role in confirming the models’ effectiveness and their aptitude for accurately reflecting the data’s intricate dynamics.
Panel C meticulously presents the results of our diagnostic tests. We utilized the Lagrange multiplier test and the autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity test to examine potential serial correlation and heteroscedasticity within our model. The outcomes from these tests indicated that our models did not suffer from either serial correlation or heteroscedasticity. Furthermore, the Ramsey regression equation specification error test was employed, confirming the appropriateness of the functional forms of our models. In addition, we verified the normality of all variables in our analysis using the Jarque–Bera test. To ascertain the robustness and enduring stability of our results, we employed both the cumulative sum and cumulative sum of squares tests. These tests are essential for evaluating the temporal consistency of the model parameters and detecting any potential structural breaks. The cumulative sum and cumulative sum of squares plots, depicted by a continuous line, consistently stayed within the critical bounds marked by a dashed line, signifying a 5% significance level. This compliance with the critical bounds underscores the enduring stability and parameter consistency of our model over the study period.
4.2. Long-Run Effects
The results in Table 1 clearly show that there is a significant long-term cointegration relationship between the two models that were looked at, which was confirmed at the 1% significance level. This is inferred from the F-statistic values, which notably exceed the upper critical bounds. Consequently, the results for both symmetric and asymmetric ARDL models, particularly concerning their long-term impacts, are comprehensively compiled in Table 2. This arrangement of data facilitates an enhanced understanding and facilitates a comparative analysis of how these models perform in terms of elucidating the long-term interconnections between the studied variables.
Table 2 shows a significant positive correlation between carbon dioxide emissions and long-term economic growth in Korea. A 1% increase in carbon dioxide emissions is associated with a 0.569% increase in Korea’s long-term economic growth. This finding can be contextualized within Korea’s unique economic and environmental backdrop, informed by various academic research. Firstly, Korea’s fast-paced industrialization, driven largely by energy-intensive sectors, has been a key contributor to its carbon dioxide emissions. Studies by Salman et al. [150], Koc and Bulus [151], and Fouquet [152] examine Korea’s economic ascent, which has been heavily reliant on heavy industries. While these sectors have fueled economic expansion, they have also escalated carbon emissions. Secondly, the focus of Korean energy policies on ensuring steady energy for industrial activities, primarily using fossil fuels, has paralleled the nation’s economic growth, contributing to increased carbon dioxide emissions. This aspect is detailed in research by Wang et al. [153], Rehman and Rehman [154], and Ali and Seraj [155], who discuss Korea’s dependency on imported fossil fuels and the corresponding impact on carbon emissions. Finally, Korea’s recent pivot towards technology and knowledge-driven sectors is discussed by Moon and Min [156], Nejat et al. [157], and Hille and Lambernd [158]. Although these sectors are more energy-efficient than traditional industries, they still contribute to overall carbon emissions, reflecting the complexities of Korea’s economic evolution and the environmental challenges it faces. In essence, the positive link between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth in Korea, particularly in the long term, as shown in Table 2, mirrors the country’s historical dependency on energy-demanding industries, its energy consumption patterns linked to economic activities, and its shift towards a more advanced, knowledge-based economy. These elements collectively shed light on the intricate interplay between Korea’s economic growth and its environmental footprint. Moreover, this evidence has further substantiated the veracity of Hypothesis 1.
The results also indicate an asymmetric influence of primary energy consumption on Korea’s long-term economic growth, where a 1% increase in the positive segment of energy consumption leads to 0.795% growth and a similar rise in the negative segment results in 0.772% growth. This nuanced effect of energy consumption can be interpreted from various theoretical perspectives and is supported by academic research. First, this theory suggests that changes in energy prices have varied effects on the economy. The positive correlation between energy consumption and economic growth could be linked to efficient energy use in key sectors. Research by Ozcan and Ozturk [159] and Bhat [160] reinforces this, indicating that in emerging economies, like Korea, where industrial and technological sectors rely heavily on energy, consumption plays a vital role in economic progress. Secondly, this hypothesis sees energy consumption as a fundamental driver of economic growth. The differing impacts of energy consumption on economic growth align with Korea’s reliance on energy for its industrial sector. Studies by Wei and Huang [161] demonstrate that fluctuations in energy availability and consumption significantly affect economies dependent on energy. Finally, this concept links economic growth with environmental impact, suggesting an initial increase in environmental degradation with economic growth, which diminishes at higher income levels. The positive impacts of both positive and negative changes in energy consumption on economic growth could be reflective of Korea’s position on the EKC, as discussed in research by Salman et al. [150] and Liu et al. [162]. Overall, the asymmetric impact of energy consumption on Korea’s economic growth is a complex interplay of factors. It emphasizes energy’s crucial role in Korea’s economic drive and elucidates the different ways energy consumption influences economic development. These insights are consistent with the theories of asymmetric energy price impacts, energy-driven growth, and EKC dynamics, highlighting the intricate relationship between energy consumption and economic growth. Furthermore, the gathered evidence has provided additional support for the authenticity of Hypothesis 2.
Additionally, the findings that the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment positively influence Korea’s long-term economic growth are noteworthy. A 1% increase in each of these factors leads to respective increases of 0.418%, 0.671%, and 0.141% in Korea’s economic growth over the long term. These dynamics can be interpreted through established theoretical perspectives, supported by recent academic research. Firstly, the beneficial impact of an expanding labor force on economic growth aligns with human capital theory, which asserts that a larger, more skilled workforce enhances productivity and, consequently, economic growth. Research by Prasetyo and Kistanti [163] and Jahanger et al. [164] underscores the importance of human capital in economic development. Korea’s experience, with its focus on building a skilled labor force in key sectors, like technology and manufacturing, exemplifies this relationship. Secondly, the link between gross fixed capital formation and economic growth finds support in the Solow growth model, emphasizing that investments in capital are vital for economic progress. The works of Sawng et al. [165] and Sarangi and Pradhan [166] illustrate how investments in infrastructure and technology are instrumental to economic growth, a pattern prominently observed in Korea’s industrial and technological evolution. Finally, the positive correlation between foreign direct investment and economic growth is consistent with the foreign direct investment-led growth hypothesis. This theory posits that foreign investments introduce not only capital but also technology and managerial know-how, spurring economic growth. Studies by Yu et al. [167] and Buckley et al. [168] highlight that foreign direct investment’s role extends beyond financial investment to include technology transfer and productivity enhancement. Foreign direct investment’s significance in Korea’s economic narrative is marked by its role in technology adoption and integrating the country into global markets. In sum, the observed positive impacts of the labor force, capital formation, and foreign direct investment on Korea’s economic growth are reflective of broader economic theories and empirical findings. These elements underscore the critical importance of human capital, capital investment, and international financial flows in driving the long-term economic trajectory of Korea. Additionally, this body of evidence has significantly reinforced the credibility of Hypotheses 3, 4, and 5. The corroboration of these hypotheses not only strengthens the foundation of our theoretical framework but also deepens the empirical integrity of our investigation.
4.3. Short-Run Effects
Drawing from the results outlined in Table 2, this subsection is dedicated to an in-depth analysis of the short-term impacts of the specified variables on Korea’s economic growth. Our objective is to closely examine how these variables influence the economy in a shorter timeframe, providing insights that complement our understanding of their long-term effects. The findings of this investigation, which focus on the immediate and more transient responses of Korea’s economy to changes in these variables, are systematically presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of short-run effects.
The findings in Table 3 shed light on the short-term influences of carbon dioxide emissions and primary energy consumption on the economic growth of South Korea. To fully grasp these results, it is imperative to consider them in the context of South Korea’s unique economic and environmental landscape, along with insights from pertinent scholarly research. Firstly, the correlation observed between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth in the short run, where a 1% increase in emissions results in a 0.219% increase in economic growth, can be contextualized against the backdrop of South Korea’s rapid industrial growth. The country’s economic expansion has historically been driven by energy-intensive heavy industries and manufacturing sectors, typically associated with high carbon emissions. This trend aligns with findings from such researchers as Adebayo et al. [169], Baek and Kim [170], and Kim [171], who highlight similar patterns in economies with robust industrial sectors.
Secondly, the asymmetric impact of primary energy consumption on economic growth reveals the intricate nature of South Korea’s energy sector. The observation that both increases and decreases in energy consumption positively affect economic growth (0.398% and 0.363% growth for a 1% increase in energy consumption, respectively) underscores a complex relationship between energy use, efficiency, and economic output. This relationship echoes the findings of Lee and Jung [172], Rong and Qamruzzaman [173], and Oryani et al. [174], who all underscore the significant short-term link between energy consumption and economic growth. Such dynamics in South Korea might be indicative of concerted efforts to enhance energy efficiency, diversify energy sources (including a shift towards renewables), and optimize energy use in both industrial and technological sectors. Moreover, the South Korean government’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and moving towards a more sustainable energy paradigm also plays a crucial role in this context. Policy measures aimed at improving energy efficiency, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and fostering renewable energy sources are poised to significantly reshape the interplay between energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth. In summary, the positive short-term relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth, along with the asymmetric effect of primary energy consumption observed in South Korea, reflect the current stage of the country’s economic development. These factors, along with its industrial and energy policies and ongoing efforts towards sustainability, are critical to understanding the economic trajectory of South Korea. As the nation continues to evolve economically, these dynamics are likely to undergo significant changes, especially as environmental and energy sustainability become increasingly prioritized.
The findings in Table 3 illuminate the short-term effects of various economic variables—namely, labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment—on South Korea’s economic growth. Firstly, the growth of the labor force demonstrates a notable positive impact on economic output in the short run. Specifically, a 1% increase in the labor force correlates with a 0.198% uptick in economic growth. This can be linked to South Korea’s strategic investment in human capital, characterized by a highly skilled workforce, a key aspect of its economic development approach. Studies by Dinh et al. [175], Tehseen Jawaid and Raza [176], and Kim et al. [177] reinforce this, underscoring the vital role of human capital quality in propelling short-term economic growth. Secondly, the significant role of gross fixed capital formation, which leads to a 0.386% increase in economic growth for every 1% increase in investment, emphasizes the critical importance of investments in physical assets, like infrastructure, machinery, and technology. This trend resonates with South Korea’s emphasis on technological progress and infrastructure development as primary drivers of economic expansion. Chen et al. [178] provide further insight into the short-run connection between capital formation and economic growth. Thirdly, the influence of net-flow foreign direct investment, manifesting in a 0.154% growth in the economy for each 1% increase in foreign direct investment, highlights South Korea’s successful integration into the global economy and its appeal as a destination for investment. Foreign direct investment not only brings capital but often includes technology transfer and management expertise, contributing to economic growth. The positive effects of foreign direct investment on economic expansion are elaborated upon in the research of Ghosh [179], who identifies foreign direct investment as a critical conduit for technology transfer and a stimulus for economic growth.
Lastly, the resilience of South Korea’s economy is evident in its capacity to revert to a steady state following a shock, adjusting at a rate of 0.026% in the subsequent period. This resilience can be attributed to the robustness of the country’s economic policies and institutions, designed to effectively absorb and adapt to economic fluctuations. In summary, the short-term positive impacts of labor force growth, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment on South Korea’s economic growth, coupled with the economy’s resilience to external shocks, can be interpreted through South Korea’s strategic investments in human capital, infrastructure, technology, and its integration into the global economy. These elements, supported by strong economic policies and institutions, collectively contribute to the dynamism and resilience of the South Korean economy. As the nation continues to face global economic challenges, these characteristics are expected to play a crucial role in its ongoing economic development.
4.4. Causality Test
In this study, the scope of analysis extended beyond simply determining the long-term cointegration of key variables, such as economic growth, energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment. To gain a deeper understanding of how these factors interact, the research focused on identifying and analyzing the causal relationships among them. Employing the Toda–Yamamoto procedure within an enhanced vector autoregression framework proved instrumental in this endeavor. This methodological choice facilitated a nuanced examination of the causal links, discerning whether they were unidirectional—indicating a one-way influence from one variable to another—or bidirectional, suggesting a reciprocal influence among the variables. The use of an augmented vector autoregression model, aligned with the Toda–Yamamoto procedure, was crucial in decoding the intricate web of interactions and dependencies among these vital economic and environmental factors. This approach sheds light on their dynamic interplay over time, offering valuable insights into the complexities of these relationships. The findings of this comprehensive analysis are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Results of causality test.
Table 4’s findings offer insightful revelations into the causal dynamics among key economic indicators within South Korea’s economic landscape. Notably, the result indicates a bidirectional Granger causality between both carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth and energy consumption and economic growth. Additionally, there’s a clear unidirectional Granger causality from the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment towards economic growth. To begin with, the mutual causality between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth reflects the intricacies of South Korea’s rapid industrial growth. This two-way relationship suggests a cyclical pattern: economic growth spurs increased carbon dioxide emissions due to industrial activity, which in turn feeds back into the economic growth trajectory. This interaction is consistent with studies by Kim et al. [180] and Kang et al. [181], which concentrate on the environmental effects of economic expansion. The bidirectional causality between energy consumption and economic growth speaks volumes about the energy dependence of South Korea’s economy. In this scenario, economic growth fuels the demand for energy, while the availability and consumption of energy reciprocally propel economic development. Studies by Shahbaz et al. [182] and Balcilar et al. [183] effectively underscore the pivotal role of energy in bolstering economic growth.
Conversely, the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment exhibit a one-way causal relationship with economic growth. According to Yang and Greaney [184] and Zang and Baimbridge [185], the expansion of the labor force, particularly skilled labor, is a crucial driver of economic growth. The significant role of gross fixed capital formation in economic advancement, via investments in infrastructure and technology, is emphasized in the studies by Lee et al. [186]. Finally, the positive impact of net-flow foreign direct investment on economic growth, through capital inflow and technology transfer, is highlighted in the research by Akkermans [187]. In conclusion, these findings within the South Korean context reveal the complex and multifaceted nature of economic growth. They underscore the critical interplay between environmental, energy, and economic policies, emphasizing the necessity of integrating these considerations in the development of future strategies aimed at sustainable economic growth.
4.5. Robustness Test
This research took rigorous steps to ensure the accuracy and dependability of its findings, particularly regarding the outcomes derived from the autoregressive distributed lag model. To achieve this, a thorough robustness check of the autoregressive distributed lag model’s results was undertaken, employing two well-regarded econometric techniques: fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares. The utilization of fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares was pivotal in reinforcing the validity of the autoregressive distributed lag model’s conclusions. By applying these methods, the study not only enhances the robustness of its results but also aligns with high standards of empirical rigor. This comprehensive approach to verification ensures that the findings are both credible and reliable. The details of these results are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Results of robustness Test.
Table 5 evaluates the estimated parameters, emphasizing both their size and statistical significance. Notably, the results from using fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares are very similar to the results from the first autoregressive distributed lag model. This consistency across fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares, in relation to the autoregressive distributed lag model, robustly affirms the initial model’s precision. The harmonious findings across these diverse econometric methodologies not only bolster the credibility of the autoregressive distributed lag model but also validate the dependability of the study’s outcomes. The similarity seen suggests that the initial autoregressive distributed lag model was well written and correctly captured the main dynamics of the variables being studied. Employing this thorough method of cross-validation, which integrates various analytical approaches, solidifies the strength and trustworthiness of the research’s conclusions.
5. Conclusions
This study examines the dynamics between carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth in Korea, spanning from 1980 to 2022. Employing a nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model, the research uncovers several pivotal insights. It establishes a positive link between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth, indicating that periods of economic expansion in Korea have historically coincided with increased emissions. Furthermore, the study identifies a pronounced and positive effect of primary energy consumption on economic growth, revealing an asymmetric relationship in this regard. The research also sheds light on the beneficial impacts of the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and net-flow foreign direct investment as key drivers of economic growth. The robustness of these findings is reinforced through validations via fully modified ordinary least squares and dynamic ordinary least squares methods. In terms of causality, the Toda–Yamamoto test outcomes present a complex picture. There is a bidirectional Granger causality between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth and a similar bidirectional relationship between energy consumption and economic growth. Additionally, there is a clear unidirectional Granger causality leading from the labor force, gross fixed capital formation, and foreign direct investment to economic growth. These insights highlight the intertwined nature of environmental and economic factors. The bidirectional causality observed suggests that sustainable energy policies and proactive environmental management are crucial for Korea. Ensuring that economic growth proceeds without jeopardizing environmental sustainability is imperative. Therefore, this study offers essential guidance for policymakers, emphasizing the need to develop strategies that harmonize economic growth with environmental stewardship, a crucial balance for Korea’s future development trajectory.
In light of this study’s findings, four key policy recommendations emerge for Korea. Firstly, to sever the link between economic growth and rising carbon dioxide emissions, a strategic shift towards green technologies and industries is imperative. Korea should champion the adoption of renewable energy sources, like solar and wind power, and foster low-carbon technologies in sectors, such as manufacturing and transportation. Accelerating this transition can be achieved through incentivizing research and development in the green technology sphere. Secondly, a national emphasis on enhancing energy efficiency across all economic sectors is crucial. This strategy aims to curb overall energy consumption while maintaining economic growth. Diversifying the energy portfolio to include a greater proportion of renewable energy sources will also help diminish the dependency on traditional, non-renewable energies. Implementing rigorous energy efficiency standards, coupled with subsidies or tax benefits for renewable energy initiatives, could prove to be effective measures. Thirdly, the focus should be on nurturing a labor force that is aligned with the demands of an environmentally conscious economy. This can be achieved through targeted education and training programs. Additionally, promoting investments in sustainable infrastructure and technology is vital. Crafting policies to attract and direct sustainable foreign direct investment into eco-friendly projects is also recommended. Lastly, the formulation of an integrated policy framework is necessary. This framework should harmonize economic growth ambitions with environmental sustainability objectives. This could entail setting definitive targets for reducing emissions, incorporating sustainability criteria into economic planning and investment processes, and establishing a comprehensive legal and regulatory framework that advocates for sustainable economic activities. To effectively implement these recommendations, a collaborative effort encompassing government, industry, academia, and civil society is essential. Such a multidimensional approach will ensure that Korea’s path towards economic growth is not only vigorous but also environmentally responsible.
In light of the findings of this study, several areas for future research emerge, addressing the identified limitations. First, the study’s timeframe, spanning from 1980 to 2022, offers a substantial historical perspective but also leaves room for extension. Future research could broaden this temporal range, either by delving into data predating 1980 or by including more recent information post-2022. Such an expansion would provide a deeper understanding of the evolving dynamics over an extended period, particularly relevant in the context of the rapidly changing global economic and environmental landscape. Second, the focus of this study on Korea, while providing in-depth insights, also presents a limitation in terms of geographic scope. Future studies could adopt a more comparative approach, examining these dynamics across different countries or regions. This broader scope would offer valuable perspectives on how varying economic policies and environmental conditions across the globe affect the interplay between carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth. Third, our investigation reveals certain constraints in how technology is conceptualized, particularly noted in Equation (2), where its influence is attributed exclusively to carbon dioxide emissions. This observation underscores the imperative for a broader interpretation of technology, extending beyond its traditional confines to encompass a wider spectrum of production technologies, inclusive of, but not limited to, ‘green technology’. It is essential for forthcoming research to adopt refined methodologies for evaluating technology’s contribution to economic growth. This could be effectively achieved through the innovative lens of ‘green GDP’, a concept that integrates environmental considerations into economic assessments. Future inquiries should delve into the diverse impacts of technology on economic progress, taking into account an expanded array of determinants that influence both GDP and environmental sustainability. Such an approach promises to enrich our comprehension of the intricate dynamics interlinking economic expansion, technological evolution, and environmental stewardship. Lastly, the study’s concentration on specific economic indicators, namely carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, labor force, capital formation, and foreign direct investment, suggests an opportunity for future research to integrate additional variables. Including such factors as technological innovation, sectoral changes within economies, and environmental policy measures would provide a richer, more intricate picture of the interactions between economic activities and environmental outcomes. By addressing these limitations, future research endeavors can further illuminate the complex relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability. Such comprehensive investigations would be invaluable for policymakers and academics, offering enhanced insights for informed decision making in an increasingly interconnected world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H.; methodology, Y.H.; software, Y.L.; validation, Y.L.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, Y.L.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.H.; visualization, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Soft Science Project of the Henan Science and Technology Development Plan “Research on the Mechanism and Realization Path of Green Innovation in Manufacturing Industry of Henan Province under the goal of ‘Double Carbon’ by Digitization” (Project No.: 232400411186), the Universities’ Humanities and Social Science General Research project of Henan Province (2023-ZZJH-018), and the Research Start-up Foundation of Henan Finance University (2021BS009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Saboori, B.; Rasoulinezhad, E.; Sung, J. The Nexus of Oil Consumption, CO2 Emissions and Economic Growth in China, Japan and South Korea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7436–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Hwangbo, S.; Yoo, C. A Deep Learning-Based Forecasting Model for Renewable Energy Scenarios to Guide Sustainable Energy Policy: A Case Study of Korea. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 122, 109725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-K.; Jang, G. An Evaluation of the Effect on the Expansion of Photovoltaic Power Generation According to Renewable Energy Certificates on Energy Storage Systems: A Case Study of the Korean Renewable Energy Market. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Byrne, J. The Rise and Fall of Green Growth: Korea’s Energy Sector Experiment and Its Lessons for Sustainable Energy Policy. WIREs Energy Environ. 2019, 8, e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifaei, P.; Charmchi, A.S.T.; Loy-Benitez, J.; Yang, R.J.; Yoo, C. A Data-Driven Analytical Roadmap to a Sustainable 2030 in South Korea Based on Optimal Renewable Microgrids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.; Son, W.; Shin, H.; Kim, N.; Lee, W.K.; Kim, J. Long-Term Energy Strategy Scenarios for South Korea: Transition to a Sustainable Energy System. Energy Policy 2019, 127, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezelbash, A.; Seyedzadeh, M.; Khaligh, V.; Liu, J. Impacts of Green Energy Expansion and Gas Import Reduction on South Korea’s Economic Growth: A System Dynamics Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Oh, I. Evaluating the Impacts of Renewable Energy Promotion Policies on Sustainable Development: A Computable General Equilibrium Model Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, J.; Mundaca, L. Decarbonization under Green Growth Strategies? The Case of South Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 123, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Thurbon, E. Developmental Environmentalism: Explaining South Korea’s Ambitious Pursuit of Green Growth. Politics Soc. 2015, 43, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarsaikhan, T.; Kim, M.-H.; Oh, H.J.; Gim, T.-H.T. Toward Sustainable Development? Trend Analysis of Environmental Policy in Korea from 1987 to 2040. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 66, 1640–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanger, A.; Usman, M.; Murshed, M.; Mahmood, H.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. The Linkages between Natural Resources, Human Capital, Globalization, Economic Growth, Financial Development, and Ecological Footprint: The Moderating Role of Technological Innovations. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, F.F.; Gumede, M.I.; Bekun, F.V.; Etokakpan, M.U.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Modelling Coal Rent, Economic Growth and CO2 Emissions: Does Regulatory Quality Matter in BRICS Economies? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, N.; Song, H. The Role of Renewable, Non-Renewable Energy Consumption, Trade, Economic Growth, and Urbanization in Achieving Carbon Neutrality: A Comparative Study for South and East Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 12798–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, U.; Elheddad, M.; Swart, J.; Ghosh, S.; Dogan, B. The Role of Biomass Energy Consumption and Economic Complexity on Environmental Sustainability in G7 Economies. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2023, 32, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Winecoff, W.K. American Financial Hegemony, Global Capital Cycles, and the Macroeconomic Growth Environment. Econ. Politics 2023, 36, 334–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsomb, E.I.B.T.; Atangana, H.O. Multilateral Environmental Agreements and the Growth of Total Factor Productivity in Developing Countries: Evidence from the Foreign Direct Investment Channel. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 12965–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Irfan, M.; Samad, S.; Ali, B.; Zhang, Y.; Badulescu, D.; Badulescu, A. The Relationship between Energy Consumption, CO2 Emissions, Economic Growth, and Health Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.; Genç, S.Y.; Ersin, Ö.Ö. Effects of Fiscal and Monetary Policies, Energy Consumption and Economic Growth on CO2 Emissions in the Turkish Economy: Nonlinear Bootstrapping NARDL and Nonlinear Causality Methods. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. CO2 Emissions and Sustainable Economic Development: New Evidence on the Role of Human Capital. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, F.F.; Nwulu, N.; Bekun, F.V. Environmental Degradation, Energy Consumption and Sustainable Development: Accounting for the Role of Economic Complexities with Evidence from World Bank Income Clusters. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2021, 30, 2727–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Muslija, A.; Satrovic, E. Does Economic Prosperity Lead to Environmental Sustainability in Developing Economies? Environmental Kuznets Curve Theory. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22588–22601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzino, C.; Toma, P.; Fusco, G.; Valente, D.; Petrosillo, I. Renewable Energy Consumption, Environmental Degradation and Economic Growth: The Greener the Richer? Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Ma, H.; Ozturk, I.; Ulucak, R. Sustainable Development and Pollution: The Effects of CO2 Emission on Population Growth, Food Production, Economic Development, and Energy Consumption in Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 17319–17330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omri, A.; Belaïd, F. Does Renewable Energy Modulate the Negative Effect of Environmental Issues on the Socio-Economic Welfare? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Mughal, N.; Zhao, J.; Shabbir, M.S.; Niedba\la, G.; Jain, V.; Anwar, A. Does Globalization Matter for Environmental Degradation? Nexus among Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, and Carbon Dioxide Emission. Energy Policy 2021, 153, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zheng, M.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, F. Nexus between Economic Recovery, Energy Consumption, CO2 Emission, and Total Natural Resources Rent. Resour. Policy 2023, 87, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatipoglu, E.; Soytas, M.A.; Belaïd, F. Environmental Consequences of Geopolitical Crises: The Case of Economic Sanctions and Emissions. Resour. Policy 2023, 85, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, F.; Abubakar, I.; Bekun, F.V.; Sarkodie, S.A. Generation of Energy and Environmental-Economic Growth Consequences: Is There Any Difference across Transition Economies? Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Hochman, G.; Timilsina, G.R. Do Drivers of CO2 Emission Growth Alter Overtime and by the Stage of Economic Development? Energy Policy 2020, 140, 111420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Tzeremes, P.G.; Tzeremes, N.G. Energy Consumption, Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation in OECD Countries. Econ. Model. 2020, 84, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namahoro, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Xue, S. Impact of Energy Intensity, Renewable Energy, and Economic Growth on CO2 Emissions: Evidence from Africa across Regions and Income Levels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 147, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Nepal, R.; Alam, K. Impacts of Human Capital, Exports, Economic Growth and Energy Consumption on CO2 Emissions of a Cross-Sectionally Dependent Panel: Evidence from the Newly Industrialized Countries (NICs). Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 121, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, M. Drivers of Decoupling Economic Growth from Carbon Emission–an Empirical Analysis of 192 Countries Using Decoupling Model and Decomposition Method. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 81, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Murad, M.W. The Impacts of Economic Growth, Trade Openness and Technological Progress on Renewable Energy Use in Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development Countries. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.; Ajaz, T.; Andlib, Z.; Chau, K.Y.; Ahmad, P.; Sharif, A. The Role of Technology Innovation, Renewable Energy and Globalization in Reducing Environmental Degradation in Pakistan: A Step towards Sustainable Environment. Renew. Energy 2021, 177, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, K.; Omri, A. The Impact of Renewable Energy on Carbon Emissions and Economic Growth in 15 Major Renewable Energy-Consuming Countries. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djellouli, N.; Abdelli, L.; Elheddad, M.; Ahmed, R.; Mahmood, H. The Effects of Non-Renewable Energy, Renewable Energy, Economic Growth, and Foreign Direct Investment on the Sustainability of African Countries. Renew. Energy 2022, 183, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Hou, F.; Zakari, A.; Tawiah, V.K. The Dynamic Links among Energy Transitions, Energy Consumption, and Sustainable Economic Growth: A Novel Framework for IEA Countries. Energy 2021, 222, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Xinbang, C.; Anwar, A. Do Green Technology Innovations, Financial Development, and Renewable Energy Use Help to Curb Carbon Emissions? Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.U.; Khattak, S.I.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, A. A Disaggregated-Level Analysis of the Relationship among Energy Production, Energy Consumption and Economic Growth: Evidence from China. Energy 2020, 194, 116836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, E.; Altinoz, B.; Aslan, A. Global Evidence from the Link between Economic Growth, Natural Resources, Energy Consumption, and Gross Capital Formation. Resour. Policy 2020, 66, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Hou, F.; Irfan, M.; Zakari, A.; Le, H.P. Does Energy Trilemma a Driver of Economic Growth? The Roles of Energy Use, Population Growth, and Financial Development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Trade Openness, Economic Growth, and Energy Intensity in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 179, 121608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Liu, Y.; Guan, F.; Wang, N. How to Coordinate the Relationship between Renewable Energy Consumption and Green Economic Development: From the Perspective of Technological Advancement. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Ozturk, I.; Hassan, A.; Zafar, S.M.; Ullah, S. The Effect of ICT on Energy Consumption and Economic Growth in South Asian Economies: An Empirical Analysis. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 58, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bithas, K.; Kalimeris, P.; Koilakou, E. Re-estimating the Energy Intensity of Growth with Implications for Sustainable Development. The Myth of the Decoupling Effect. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, R. Is Carbon Emission Growth Decoupled from Economic Growth in Emerging Countries? New Insights from Labor and Investment Effects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, S.; Mbarek, M.B.; Atiq-ur-Rehman, M. Long-Run Causal Relationship between Economic Growth, Transport Energy Consumption and Environmental Quality in Asian Countries: Evidence from Heterogeneous Panel Methods. Energy 2020, 192, 116628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, K.; Cheng, J.; Xu, D.; Abbas, K.; Ali, I.; Ali, H.; Fang, C. Asymmetric Impact of Fossil Fuel and Renewable Energy Consumption on Economic Growth: A Nonlinear Technique. Energy 2021, 226, 120357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Raghutla, C.; Chittedi, K.R.; Jiao, Z.; Vo, X.V. The Effect of Renewable Energy Consumption on Economic Growth: Evidence from the Renewable Energy Country Attractive Index. Energy 2020, 207, 118162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Sinha, A. Renewable, Non-Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Trade Openness and Ecological Footprint: Evidence from Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.W.; Shahbaz, M.; Sinha, A.; Sengupta, T.; Qin, Q. How Renewable Energy Consumption Contribute to Environmental Quality? The Role of Education in OECD Countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Patwary, A.K.; Qayyum, A.; Alharthi, M.; Bashir, F.; Mohsin, M.; Hanif, I.; Abbas, Q. The Determinants of Renewable Energy Sources for the Fueling of Green and Sustainable Economy. Energy 2022, 238, 122029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-H.; Chang, Y.; Park, D. Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, and Emissions: International Evidence. Energy J. 2020, 41, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pinar, M.; Stengos, T. Renewable Energy Consumption and Economic Growth Nexus: Evidence from a Threshold Model. Energy Policy 2020, 139, 111295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A. Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, and Environmental Quality Nexus in Turkey: Evidence from Simultaneous Equation Models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 41988–41999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, E.; Altinoz, B.; Madaleno, M.; Taskin, D. The Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption to Economic Growth: A Replication and Extension of Inglesi-Lotz (2016). Energy Econ. 2020, 90, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ge, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Decoupling of Provincial Energy-Related CO2 Emissions from Economic Growth in China and Its Convergence from 1995 to 2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Song, M.; Cui, L. Driving Force for China’s Economic Development under Industry 4.0 and Circular Economy: Technological Innovation or Structural Change? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, P.; Garber, G.; Ponticelli, J. Capital Accumulation and Structural Transformation. Q. J. Econ. 2020, 135, 1037–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Abbas, Q.; Hanif, I.; Alharthi, M.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Aziz, B.; Mohsin, M. Short-and Long-Run Influence of Energy Utilization and Economic Growth on Carbon Discharge in Emerging SREB Economies. Renew. Energy 2021, 165, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Asghar, M.M.; Malik, M.N.; Nawaz, K. Moving towards a Sustainable Environment: The Dynamic Linkage between Natural Resources, Human Capital, Urbanization, Economic Growth, and Ecological Footprint in China. Resour. Policy 2020, 67, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, S.; Rahman, M.U.; Noor, M.H.; Khan, M.K.; Bibi, M.; Godil, D.I.; Quddoos, M.U.; Anser, M.K. Striving towards Environmental Sustainability: How Natural Resources, Human Capital, Financial Development, and Economic Growth Interact with Ecological Footprint in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52499–52513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, A. The Relationship between Innovative Human Capital and Interprovincial Economic Growth Based on Panel Data Model and Spatial Econometrics. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 365, 112381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, A.; Liu, L. Infectious Diseases, Human Capital and Economic Growth. Econ. Theory 2020, 70, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzina, Y.; Firsova, I.; Strielkowski, W. Dynamics of Human Capital Development in Economic Development Cycles. Economies 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Raza, A.; Sui, H. Infrastructure Investment and Economic Growth Quality: Empirical Analysis of China’s Regional Development. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 2615–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.G.; Drine, I. Distance from the Technology Frontier: How Could Africa Catch-up via Socio-Institutional Factors and Human Capital? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 150, 119755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, D.-H. Contribution of Factor Structure Change to China’s Economic Growth: Evidence from the Time-Varying Elastic Production Function Model. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2020, 33, 2919–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, H.; Tan, Q.; Zameer, H.; Vo, X.V.; Shahbaz, M. Discovering the Relationship between Natural Resources, Energy Consumption, Gross Capital Formation with Economic Growth: Can Lower Financial Openness Change the Curse into Blessing. Resour. Policy 2021, 71, 102013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Sghaier, I. Foreign Capital Inflows and Economic Growth in North African Countries: The Role of Human Capital. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 2804–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henok, W.; Kaulihowa, T. The Impact of FDI on Human Capital Development in SACU Countries. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 2022, 49, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstandina, M.S.; Gachino, G.G. International Technology Transfer: Evidence on Foreign Direct Investment in Albania. J. Econ. Stud. 2020, 47, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. FDI and Firm Productivity in Host Countries: The Role of Financial Constraints. J. Int. Money Financ. 2022, 124, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanousek, J.; Shamshur, A.; Svejnar, J.; Tresl, J. Corruption Level and Uncertainty, FDI and Domestic Investment. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2021, 52, 1750–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, F.J.; Dangol, R.; Nuruzzaman, N.; Raghunath, S. How Do Country Regulations and Business Environment Impact Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Inflows? Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wei, H.; Xiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Akram, R. The Impacts of FDI Inflows on Carbon Emissions: Economic Development and Regulatory Quality as Moderators. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 820596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ateeq, M.; Shafique, M.; Rafiq, M.; Yuan, J. Primary Energy Consumption-Growth Nexus: The Role of Natural Resources, Quality of Government, and Fixed Capital Formation. Energy 2023, 263, 125570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.B.; Van, H.B. Evaluating the Relationship between Renewable Energy Consumption and Economic Growth in Vietnam, 1995–2019. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Tang, X.; Rasool, S.F. Investigating the Nexus between CO2 Emissions, Renewable Energy Consumption, FDI, Exports and Economic Growth: Evidence from BRICS Countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 2234–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Otoo, I.; Chen, X.; Ampah, J.D. Exploring the Moderating Role of Foreign Direct Investment in the Renewable Energy and Economic Growth Nexus: Evidence from West Africa. Energy 2023, 281, 128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, G.; Sun, H.; Fernandez-Gamiz, U.; Mansoor, S.; Pasha, A.A.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.S. Effects of Globalization, Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth on Renewable Electricity Consumption. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Geng, Y.; Pan, H. Whether Natural Gas Consumption Bring Double Dividends of Economic Growth and Carbon Dioxide Emissions Reduction in China? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Álvarez-Otero, S.; Sial, M.S.; Comite, U.; Zheng, P.; Samad, S.; Oláh, J. Impact of Renewable Energy on Economic Growth and CO2 Emissions—Evidence from BRICS Countries. Processes 2021, 9, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Henderson, D.J. Estimation of a Varying Coefficient, Fixed-Effects Cobb–Douglas Production Function in Levels. Econ. Lett. 2022, 213, 110354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, R.G.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z. The Cobb-Douglas Production Function for an Exponential Model. In Advances in Econometrics, Operational Research, Data Science and Actuarial Studies; Terzioğlu, M.K., Ed.; Contributions to Economics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–12. ISBN 978-3-030-85253-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, A. Why Does Production Function Take the Cobb–Douglas Form? In Statistical Properties in Firms’ Large-Scale Data; Evolutionary Economics and Social Complexity Science; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 26, pp. 113–135. ISBN 9789811622960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Gao, X. Production Function with Single Factor for Intelligent Manufacturing by Workshop Agent. J. Knowl. Econ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketokivi, M.; Mahoney, J.T. Transaction Cost Economics As a Theory of Supply Chain Efficiency. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 1011–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, W.; Boeve-de Pauw, J.; Olsson, D.; Gericke, N.; De Maeyer, S.; Van Petegem, P. Redefining Action Competence: The Case of Sustainable Development. J. Environ. Educ. 2020, 51, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, N.J.; Klein, P.G.; Lien, L.B.; Zellweger, T.; Zenger, T. Ownership Competence. Strateg. Manag. J. 2021, 42, 302–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, H.; Tian, Z.; Bei, J.; Zhang, H.; Ye, B.; Ni, J. A Method for Estimating Output Elasticity of Input Factors in Cobb-Douglas Production Function and Measuring Agricultural Technological Progress. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26234–26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, T. The Impact of Green Supplier Integration on Firm Performance: The Mediating Role of Social Capital Accumulation. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2020, 26, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjai, S.; Chankoson, T.; Jermsittiparsert, K. An Economic Analysis of Agricultural Production Function on the Paddy Fields of Thailand. Entrep. Sustain. Issues 2020, 7, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, S. How Technological Progress Affects the Carbon Emission Efficiency? Evidence from National Panel Quantile Regression. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, X.; Dong, K.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z. How Does Technological Innovation Mitigate CO2 Emissions in OECD Countries? Heterogeneous Analysis Using Panel Quantile Regression. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anser, M.K.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.A.; Zaman, K.; Nassani, A.A.; Askar, S.E.; Abro, M.M.Q.; Kabbani, A. The Role of Information and Communication Technologies in Mitigating Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Panel Quantile Regression. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21065–21084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Pesaran, B. Working with Microfit 4.0; Camfit Data Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, B.U.; Wiysahnyuy, Y.S.; Ashraf, N.; Mempouo, B.; Mengata, G.M. Pathways for Efficient Transition into Net Zero Energy Buildings (nZEB) in Sub-Sahara Africa. Case Study: Cameroon, Senegal, and Côte d’Ivoire. Energy Build. 2023, 296, 113422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.; Dongo, K.; Mertenat, A.; Lüssenhop, P.; Körner, I.; Zurbrügg, C. Material Flows and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction Potential of Decentralized Composting in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Case Study in Tiassalé, Côte D’Ivoire. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Radulescu, M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. A Dynamic Relationship between Renewable Energy Consumption, Nonrenewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, and Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Asian Emerging Economies. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 3529–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Chenggang, Y.; Hussain, J.; Kui, Z. Impact of Technological Innovation, Financial Development and Foreign Direct Investment on Renewable Energy, Non-Renewable Energy and the Environment in Belt & Road Initiative Countries. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Çağlayan Akay, E.; Oskonbaeva, Z.; Bülbül, H. What Do Unit Root Tests Tell Us about Unemployment Hysteresis in Transition Economies? Appl. Econ. Anal. 2020, 28, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.; Linn, S.; Lebo, M.J. Beyond the Unit Root Question: Uncertainty and Inference. Am. J. Political Sci. 2020, 64, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretis, F. Econometric Modelling of Climate Systems: The Equivalence of Energy Balance Models and Cointegrated Vector Autoregressions. J. Econom. 2020, 214, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, W.; Welfe, A. The Tobit Cointegrated Vector Autoregressive Model: An Application to the Currency Market. Econ. Model. 2020, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lee, L. Estimation of Dynamic Panel Spatial Vector Autoregression: Stability and Spatial Multivariate Cointegration. J. Econom. 2021, 221, 337–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Yu, B.; Greenwood-Nimmo, M. Modelling Asymmetric Cointegration and Dynamic Multipliers in a Nonlinear ARDL Framework. In Festschrift in Honor of Peter Schmidt; Sickles, R.C., Horrace, W.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 281–314. ISBN 978-1-4899-8007-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.S.; Greenwood-Nimmo, M.; Shin, Y. Recent Developments of the Autoregressive Distributed Lag Modelling Framework. J. Econ. Surv. 2023, 37, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, C.Y.; McNown, R.; Goh, S.K. An Augmented Autoregressive Distributed Lag Bounds Test for Cointegration. Econ. Model. 2019, 80, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.; Philips, A.Q. Cointegration Testing and Dynamic Simulations of Autoregressive Distributed Lag Models. Stata J. 2018, 18, 902–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, Y. The Asymmetric Effect of Crude Oil Prices on Stock Prices in Major International Financial Markets. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2021, 56, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, K.; Wu, S. Do the RMB Exchange Rate and Global Commodity Prices Have Asymmetric or Symmetric Effects on China’s Stock Prices? Financ. Innov. 2021, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, M.L.; Chen, Y. Analysis of the Factors Affecting Electricity Consumption in DR Congo Using Fully Modified Ordinary Least Square (FMOLS), Dynamic Ordinary Least Square (DOLS) and Canonical Cointegrating Regression (CCR) Estimation Approach. Energy 2021, 232, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, W.A.; Ghosh, T.; Adil, M.H. Is Money Demand Really Unstable? Evidence from Divisia Monetary Aggregates. Econ. Anal. Policy 2022, 74, 606–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Singh, K.; Chaudhary, R.; Vashishtha, S. How Economic Growth, Sustainable Energy and Carbon Emission Impact Each Other? New Insights from India Using ARDL Approach. OPEC Energy Rev. 2023, 47, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, H.; Mishra, P.; Kumari, B.; Ray, S.; Nuţă, F.M.; Gautam, R.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Nuţă, A.C.; Zamfir, C.G. The Spillover Effects of Uncertainty and Globalization on Environmental Quality in India: Evidence from Combined Cointegration Test and Augmented ARDL Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1144201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Odugbesan, J.A. Modeling CO2 Emissions in South Africa: Empirical Evidence from ARDL Based Bounds and Wavelet Coherence Techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9377–9389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, M.; Gao, Y.; Rahman, P.; Albattat, A.; Ali, M.A.S.; Saha, S.K. Sustainable Development Challenges in Bangladesh: An Empirical Study of Economic Growth, Industrialization, Energy Consumption, Foreign Investment, and Carbon Emissions—Using Dynamic ARDL Model and Frequency Domain Causality Approach. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.; Ahmed, A.; Chandio, A.A.; Korankye, B.A.; Ali, A.; Fang, W. Modeling the Nexus between Carbon Emissions, Energy Consumption, and Economic Progress in Pakistan: Evidence from Cointegration and Causality Analysis. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4642–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Mozahid, M.; Akter, S.; Hafiz Iqbal, M. Causality Analysis of CO2 Emissions, Foreign Direct Investment, Gross Domestic Product, and Energy Consumption: Empirical Evidence from South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65684–65698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds Testing Approaches to the Analysis of Level Relationships. J. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Sarin, V. The Saving–Investment Cointegration Across East Asian Countries: Evidence from the ARDL Bound Approach. Glob. Bus. Rev. 2021, 22, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Hussain, S.; Rustandi Kartawinata, B.; Muhammad, Z.; Fitriana, R. Empirical Nexus between Chinese Investment under China–Pakistan Economic Corridor and Economic Growth: An ARDL Approach. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2022, 9, 2032911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udemba, E.N.; Magazzino, C.; Bekun, F.V. Modeling the Nexus between Pollutant Emission, Energy Consumption, Foreign Direct Investment, and Economic Growth: New Insights from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17831–17842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeekes, S.; Wijler, E. An Automated Approach towards Sparse Single-Equation Cointegration Modelling. J. Econom. 2021, 221, 247–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, P.W.; Key, E.M.; Lebo, M.J. Hypothesis Testing with Error Correction Models. Political Sci. Res. Methods 2022, 10, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atil, L.; Fellag, H.; Sipols, A.E.; Santos-Martín, M.T.; De Blas, C.S. Non-Linear Cointegration Test, Based on Record Counting Statistic. Comput. Econ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Reyes, J.E.; Hernández-Santoro, C. Assessing Granger-Causality in the Southern Humboldt Current Ecosystem Using Cross-Spectral Methods. Entropy 2020, 22, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Fang, W.; Gao, X.; An, S.; Liu, S.; Wu, T. Time-Varying Causality Inference of Different Nickel Markets Based on the Convergent Cross Mapping Method. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Liu, H. Confidence Intervals for Parameters in High-Dimensional Sparse Vector Autoregression. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2022, 168, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, J.K.; Loossens, T.; Tuerlinckx, F.; Ceulemans, E. Optimal Sampling Rates for Reliable Continuous-Time First-Order Autoregressive and Vector Autoregressive Modeling. Psychol. Methods 2021, 26, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, B.N.; Akam, D.; Inuwa, N.; James, H.T.; Basila, D. Does Globalization and Energy Usage Influence Carbon Emissions in South Asia? An Empirical Revisit of the Debate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 36190–36207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Uddin, I.; Khan, S.; Tariq, M. Are Globalization, Urbanization, and Energy Consumption Cause Carbon Emissions in SAARC Region? New Evidence from CS-ARDL Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 87746–87763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.A.; Mirza, S. A Comparison of Some Common Methods for Detecting Granger Noncausality. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2006, 76, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, U.; Asl, M.G.; Khalfaoui, R.; Tedeschi, M. Extreme Contributions of Conventional Investments Vis-à-Vis Islamic Ones to Renewables. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.Y.; Yamamoto, T. Statistical Inference in Vector Autoregressions with Possibly Integrated Processes. J. Econom. 1995, 66, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, D.; Lederer, J.; Tao, J. Inference for High-Dimensional Instrumental Variables Regression. J. Econom. 2020, 217, 79–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A. Consistency without Inference: Instrumental Variables in Practical Application. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2022, 147, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydeu-Olivares, A.; Shi, D.; Fairchild, A.J. Estimating Causal Effects in Linear Regression Models with Observational Data: The Instrumental Variables Regression Model. Psychol. Methods 2020, 25, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Olivares, D.; Guizar, I. Estimation of Continuous and Discrete Time Co-Integrated Systems with Stock and Flow Variables. J. Time Ser. Econom. 2021, 13, 145–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, D. Adaptive LASSO for Selecting Fourier Coefficients in a Functional Smooth Time-Varying Cointegrating Regression: An Application to the Feldstein–Horioka Puzzle. Math. Comput. Simul. 2021, 179, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmec-Ban, M.; Babić, R.Š. A Literature Review of Recent Causality Analyses between Air Transport Demand and Socio-Economic Factors. Transp. Res. Procedia 2023, 73, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Driha, O.M.; Bekun, F.V.; Adedoyin, F.F. The Asymmetric Impact of Air Transport on Economic Growth in Spain: Fresh Evidence from the Tourism-Led Growth Hypothesis. Curr. Issues Tour. 2021, 24, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetrescu, M.; Kusin, V.; Salish, N. Testing for No Cointegration in Vector Autoregressions with Estimated Degree of Fractional Integration. Econ. Model. 2022, 108, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheifets, I.L.; Phillips, P.C. Fully Modified Least Squares Cointegrating Parameter Estimation in Multicointegrated Systems. J. Econom. 2023, 232, 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Karamelikli, H.; Dinç, D.T.; Khan, Y.A.; Sabzehei, M.T.; Abbas, S.Z. Dynamic Linkages between Renewable Energy, Carbon Emissions and Economic Growth through Nonlinear ARDL Approach: Evidence from Iran. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufi, N.; Hajilary, N. The Impacts of Economic Growth, Foreign Direct Investments, and Gas Consumption on the Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis CO2 Emission in Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 85350–85363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Long, X.; Dauda, L.; Mensah, C.N. The Impact of Institutional Quality on Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Indonesia, South Korea and Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, S.; Bulus, G.C. Testing Validity of the EKC Hypothesis in South Korea: Role of Renewable Energy and Trade Openness. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29043–29054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouquet, R. Path Dependence in Energy Systems and Economic Development. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ali, A.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X. An Empirical Analysis of the Impact of Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Consumption on Economic Growth and Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Seven Northeast Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 75041–75057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, E.; Rehman, S. Modeling the Nexus between Carbon Emissions, Urbanization, Population Growth, Energy Consumption, and Economic Development in Asia: Evidence from Grey Relational Analysis. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 5430–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Seraj, M. Nexus between Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Emission: Evidence from 10 Highest Fossil Fuel and 10 Highest Renewable Energy-Using Economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 87901–87922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Min, D. Assessing Energy Efficiency and the Related Policy Implications for Energy-Intensive Firms in Korea: DEA Approach. Energy 2017, 133, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, P.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Taheri, M.M.; Gohari, M.; Majid, M.Z.A. A Global Review of Energy Consumption, CO2 Emissions and Policy in the Residential Sector (with an Overview of the Top Ten CO2 Emitting Countries). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, E.; Lambernd, B. The Role of Innovation in Reducing South Korea’s Energy Intensity: Regional-Data Evidence on Various Energy Carriers. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Ozturk, I. Renewable Energy Consumption-Economic Growth Nexus in Emerging Countries: A Bootstrap Panel Causality Test. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 104, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, J.A. Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Consumption—Impact on Economic Growth and CO2 Emissions in Five Emerging Market Economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35515–35530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, L. Does Renewable Energy Matter to Achieve Sustainable Development? Fresh Evidence from Ten Asian Economies. Renew. Energy 2022, 199, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kim, H.; Liang, S.; Kwon, O.-S. Export Diversification and Ecological Footprint: A Comparative Study on EKC Theory among Korea, Japan, and China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, P.E.; Kistanti, N.R. Human Capital, Institutional Economics and Entrepreneurship as a Driver for Quality & Sustainable Economic Growth. Entrep. Sustain. Issues 2020, 7, 2575. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanger, A.; Yang, B.; Huang, W.-C.; Murshed, M.; Usman, M.; Radulescu, M. Dynamic Linkages between Globalization, Human Capital, and Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Empirical Evidence from Developing Economies. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 9307–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawng, Y.; Kim, P.; Park, J. ICT Investment and GDP Growth: Causality Analysis for the Case of Korea. Telecommun. Policy 2021, 45, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, A.K.; Pradhan, R.P. ICT Infrastructure and Economic Growth: A Critical Assessment and Some Policy Implications. Decision 2020, 47, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Fan, F. Cross-National Knowledge Transfer, Absorptive Capacity, and Total Factor Productivity: The Intermediary Effect Test of International Technology Spillover. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 34, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, P.J.; Driffield, N.; Kim, J.-Y. The Role of Outward FDI in Creating Korean Global Factories. Manag. Int. Rev. 2022, 62, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Awosusi, A.A.; Kirikkaleli, D.; Akinsola, G.D.; Mwamba, M.N. Can CO2 Emissions and Energy Consumption Determine the Economic Performance of South Korea? A Time Series Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38969–38984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Kim, H.S. Is Economic Growth Good or Bad for the Environment? Empirical Evidence from Korea. Energy Econ. 2013, 36, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. The Effects of Foreign Direct Investment, Economic Growth, Industrial Structure, Renewable and Nuclear Energy, and Urbanization on Korean Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Jung, Y. Causal Dynamics between Renewable Energy Consumption and Economic Growth in South Korea: Empirical Analysis and Policy Implications. Energy Environ. 2018, 29, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Qamruzzaman, M. Symmetric and Asymmetric Nexus between Economic Policy Uncertainty, Oil Price, and Renewable Energy Consumption in the United States, China, India, Japan, and South Korea: Does Technological Innovation Influence? Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 973557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryani, B.; Moridian, A.; Rezania, S.; Vasseghian, Y.; Bagheri, M.; Shahzad, K. Asymmetric Impacts of Economic Uncertainties and Energy Consumption on the Ecological Footprint: Implications apropos Structural Transformation in South Korea. Fuel 2022, 322, 124180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.T.-H.; Vo, D.H.; The Vo, A.; Nguyen, T.C. Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in the Short Run and Long Run: Empirical Evidence from Developing Countries. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2019, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehseen Jawaid, S.; Raza, S.A. Workers’ Remittances and Economic Growth in China and Korea: An Empirical Analysis. J. Chin. Econ. Foreign Trade Stud. 2012, 5, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lim, H.; Park, D. Does Productivity Growth Lower Inflation in Korea? Appl. Econ. 2013, 45, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, T. Examining the Resource Curse Phenomenon, Digital Finance Integration, and Their Impacts on Economic Growth: Empirical Insights from South Korea. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Foreign Direct Investment, Female Education, Capital Formation, and Economic Growth in Japan and South Korea. Int. Econ. J. 2019, 33, 509–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Nam, K. The Relationship between CO2 Emissions and Economic Growth: The Case of Korea with Nonlinear Evidence. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 5938–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Li, Z.; Jeong, D. An Effect of Carbon Dioxide and Energy Reduction on Production Efficiency and Economic Growth: Application of Carbon Neutrality in Korea. Sustainability 2022, 14, 17054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Zakaria, M.; Shahzad, S.J.H.; Mahalik, M.K. The Energy Consumption and Economic Growth Nexus in Top Ten Energy-Consuming Countries: Fresh Evidence from Using the Quantile-on-Quantile Approach. Energy Econ. 2018, 71, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcilar, M.; Ozdemir, Z.A.; Arslanturk, Y. Economic Growth and Energy Consumption Causal Nexus Viewed through a Bootstrap Rolling Window. Energy Econ. 2010, 32, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Greaney, T.M. Economic Growth and Income Inequality in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Comparative Study of China, Japan, South Korea, and the United States. J. Asian Econ. 2017, 48, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Baimbridge, M. Exports, Imports and Economic Growth in South Korea and Japan: A Tale of Two Economies. Appl. Econ. 2012, 44, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Won, Y.J.; Jei, S.Y. Study of the Relationship between Government Expenditures and Economic Growth for China and Korea. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkermans, D.H. Net Profit Flow per Country from 1980 to 2009: The Long-Term Effects of Foreign Direct Investment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, V.; He, S.; Zhang, B. State and Parameter Joint Estimation of Linear Stochastic Systems in Presence of Faults and non-Gaussian Noises. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 30, 6683–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.M.; Ridgway, G.R.; Webster, M.A.; Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Permutation Inference for the General Linear Model. Neuroimage 2014, 92, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-H.; Zhang, S.S. Confidence Intervals for Low Dimensional Parameters in High Dimensional Linear Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2014, 76, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).