Abstract
The availability of water resources is crucial to maintaining the sustainability of urbanization. Calculating the ecological footprint of water (EFW) is one of the ways to realize the protection of water resources in the process of urbanization. The minor settlements in border areas have been the focus of China’s urbanization development but have rarely received research attention. The objective of this study was to develop an improved model of the ecological footprint of water (EFW) to assess the water security status of urban areas in Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture (YKAP), and to demonstrate its authenticity compared with the traditional ecological footprint of water (EFW). The results showed that water pollution is the main reason for the increase in the EFW in each city, and the ecological water carrying capacity (ECW) showed strong fluctuations with the interannual variation in precipitation. Although the overall availability and quality of water resources are within safe limits, there are significant differences among cities, and water pollution poses a direct threat to the health and well-being of urban dwellers in some cities. Therefore, it is recommended that water resource management agencies adjust their water supply strategies based on the data from the EFW model, control wastewater discharge, improve their management systems and take urban economic development into account. This will significantly improve the sustainable management of water resources and ensure the health and well-being of urban residents.
1. Introduction
Water resources are key for human survival, social development and economic growth. Most of the world’s freshwater resources are found in glaciers or permanent snow and cannot be used by humans. Only 0.26% of freshwater resources are distributed in lakes and river systems [1,2]. The available freshwater resources are limited. The global population has grown to 7.5 billion people, and the continued growth of the population and urbanization will lead to long-term water-related problems [3]. China is currently the fastest country in terms of urbanization [4]. As of 2020, the urbanization rate has reached 63.89% [5]. Household water, production water and ecological water use a higher proportion of total water consumption, so direct water often becomes the focus of public attention because it directly affects the reserves of water resources [6]. The sustainability of urban water resources affects both urban residents and the wider community, which determines the water supply strategy of the regulatory agency and affects the environmental, social and economic development of the region. Therefore, the sustainability of water resources is critical in today’s world.
The Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture (YKAP) is located in the transnational urban agglomeration of the Tumen River in northeastern Asia [7]. It is adjacent to major port cities such as Vladivostok and Luojin. It is an important trade cooperation partner of Russia’s Far East and the Luoxian Economic Zone of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) [8]. YKAP represents an important part of the Chinese “Belt and Road” strategy, which has also been identified as a key component of the international China–Russia–DPRK–Mongolia channel [9,10]. Therefore, the development of YKAP’s cities based on the sustainability of water resources is of great importance to three countries.
The scale of urbanization will be further expanded in the future, and the security of water quantity and water quality will face unprecedented pressure [11]. However, the lack of interactions among basic users, individual water resource managers and policy-makers has led to a decrease in water volume and an increase in water pollution, which have increased the risks to all the developmental sectors that depend upon them. There are many methods of assessing water sustainability, but most of them are not sufficient to assess the differences in water sustainability among cities caused by different environmental conditions and production activities. One of the methods identified by the European Union for effectively assessing the sustainability of water resources is the assessment of the ecological footprint of water (EFW) [12]. The concept of the ecological footprint (EF) was proposed by William and introduced by Wackernagel in the field of assessing water resources [13,14]. The current research on EFW has concentrated on industrial production [15,16,17,18,19,20] and agricultural security [21,22,23,24], whereas quantitative assessments of urban water security are lacking [25]. However, the problem of water loss and polluted water have received increasing attention, which have made water companies, politicians, urban planners and other stakeholders use the concept of the ecological footprint of water to determine the direction of investment and policy implementation. For these reasons, examining the impact of adjusting the urban water supply and proposed solutions from quantitative perspectives is an important task for the application of EFW analysis in urban areas [26]. Water utilities can evaluate water consumption and the reserves of water resources as factors influencing the planning process of urban scale, land use and accommodating the population [27]. Water pollution damages aquatic ecosystems and poses a threat to residents’ health and well-being. It is necessary to adjust the water treatment technology to ensure the safety of residents’ water supply [28]. In the process of urban water management, the EFW model, which links the water supply, water use and the amount of polluted water, can serve as a cognitive tool for decision-making departments to improve water security and ultimately affect conservation activities [26,29].
The current research on the sustainability of urban water resources has focused on calculating the water footprint in central cities, such as Beijing (China) [30], Berlin (Germany) [31], Seville (Spain) [32], Dalian (China) [33] and Tehran (Iran) [34], but few reports have considered border cities. Most of the studies on the ecological footprint of water in these cities have focused on the virtual water generated by food consumption [35,36]. However, government agencies and water management units have a limited impact on virtual water, and direct water use will have a greater impact on water management. At present, decision-making units support existing water resource management models by collecting large amounts of data on water supply and water use, and applying the data to traditional models of the ecological footprint of water. This may reduce the authenticity of assessments of the sustainability of water resources because of a failure to calculate the water pollution data. This limits the wide application of models of the ecological footprint of water in urban water resource management. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to propose an improved model to improve the calculation of the water footprint of urban water pollution by adjusting the method proposed by William et al. [13]. We quantitatively assessed the amount of water consumed by water pollution by incorporating the main pollutants into the model and calculating the amount of water required to degrade them, based on available data and overall water pollution indicators. The proposed model has been designed to objectively assess the sustainability of urban water resources, support the decision-making process of urban water management units and safeguard the health and well-being of residents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The YKAP is located in the eastern part of Jilin Province, China (41°59′–44°30′ N, 127°27′–131°18′ E). It has a total land surface of about 43,300 km2. The prefecture has eight cities under its jurisdiction: Yanji, Longjing, Helong, Tumen, Hunchun, Dunhua, Wangqing and Antu (Figure 1). The YKAP is situated in the moderate temperate zone and has a humid monsoon climate with an average annual amount of precipitation of about 274 × 108 m3. There are four main river systems present in the prefecture: the Tumen River, the Songhua River, the Suifen River and the Mudan River [37]. According to the “Outline of China’s Tumen River Regional Cooperation and Development Plan”, the YKAP will become an important gateway for China to provide access to the Sea of Japan [38]. Evaluating the water resources based on an improved model of the ecological footprint of water (EFW) is an important method for realizing the sustainable development of the cities of the YKAP and is an important way to ensure the implementation of the national strategy.
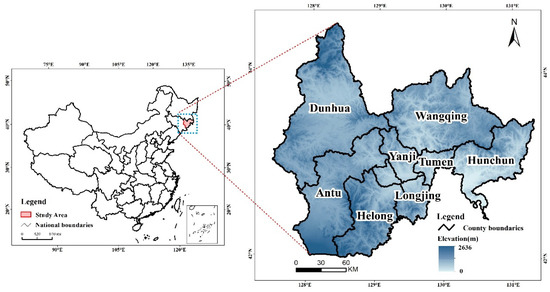
Figure 1.
Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture (YKAP).
2.2. Data
Demographic data as well as information about the GDP of the YKAP over the period 2005–2016 were acquired from Jilin Province’s statistical yearbook and Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture’s statistical yearbook [39,40]. Water resource data, including the amount of precipitation, total water consumption, per capita water consumption, total water resources, COD emissions, NH3-N emissions and the comprehensive water consumption rate, as well as additional regional data for the period 2005–2017, were derived from Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture Water Resources Bulletin [41]. However, due to the lack of data on COD emissions and NH3-N emissions for 2017–2019, the final ecological footprint of water resources and the ecological footprint of the aquatic environment were only calculated up to 2016.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Traditional Ecological Footprint Model of Water Resources
The traditional ecological footprint of water resources refers to the consumption level of water resources for production and domestic use, and can be described by the following equation [42,43]:
where EFW is the ecological footprint of water resources (Appendix A) (hm2), N is the total population, efw is the per capita ecological footprint of water resources (hm2/per person), WR is the per capita consumption of water resources (m3), Pw is the global average availability of water resources (m3·hm−2) and γ is the global equilibrium factor of water resources, which is the ratio of the average productivity of land with water resources to the average productivity of all different types of agricultural land in the world [44] (Table 1). According to previous research, the value of Pw is 3140 m3·hm−2.

Table 1.
Changes in the global equilibrium factor of water resources.
The ecological carrying capacity of water resources provides an estimate of the amount water resources available to sustain maximum socio-economic development [45,46,47] and is defined as
where ECW is the ecological carrying capacity of water resources (hm2), ecw is the per capita ecological carrying capacity of water resources (hm2/per person), W is the total volume of water resources (m3) and Φ is the factor of water resource outputs, which is the ratio of the production capacity of regional water resources to the production capacity of global water resources [48] (Table 2). If the utilization rate of water resources in a country or region exceeds 30–40%, deterioration in the environmental quality is likely to happen. Therefore, 60% of the total water resources were deducted from the calculation [49].

Table 2.
Water resource yield factors of counties in Yanbian prefecture.
The ecological surplus (EDW) and ecological deficit (ESW) of water resources refer to the quantitative relationship between utilization and the available reserves of water resources [50,51,52]. An EDW value greater than zero indicates that water resources in the region are not being depleted.
The ecological pressure index (EPIW) provides a measure of the ecological health and basically quantifies the ecological pressure on regional water resources [53,54]. Higher values of EPIW are indicative of an increasing chance of deterioration in the environmental quality and ecological health. Six categories of EPIW values can be discerned [55,56] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Division of water resources ecological pressure levels.
The utilization efficiency (EFI) is a measure of the relationship between the ecological footprint and the value of regional unit outputs expressed in GDP (G) [57]. High EFI values point towards a low utilization efficiency of the water resources.
The load index provides information about the development prospects of water resources in the study area [58] and is defined as
where C is the load index of water resources, S is the precipitation coefficient and R is the amount of precipitation [59]. The value of C can be categorized into several classes (Table 4).

Table 4.
Division of the ecological load levels of water resources.
2.3.2. The Improved Ecological Footprint Model
The traditional ecological footprint model of water resources can be improved by incorporating information about water pollution. Chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are the general indicators of water pollution described in the “Water Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” of China’s 13th Five-Year Plan [60]. Based on the availability of water resource bulletins and water pollution data in Yanbian Prefecture, we selected chemical oxygen demand (COD) and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) as the main parameters to improve the traditional ecological footprint model. The maximum pollution footprint was chosen as the most suitable indicator, as both pollutants contribute to the overall environmental impact. The improved EF model can be described as
where EFw is the overall ecological footprint of water resources (hm2); EFWP is the ecological footprint of water pollution (hm2); EFN is the ecological footprint of ammonia nitrogen water pollution; EFCOD is the ecological footprint of organic matter water pollution; CN and CCOD are the amounts of ammonia nitrogen and organic matter discharged into the water in the study area, respectively; and PN and PCOD are the global average degradation capacities of ammonia nitrogen and chemical oxygen demand in water, respectively.
The global average degradation capacity of ammonia nitrogen and organic matter in the aquatic environment was calculated using the upper limit of ammonia nitrogen concentrations (NH3-N ≤ 1.0 mg/L) and chemical oxygen demand (COD ≤ 20 mg/L) for the Class III water standard of China’s Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard (GB3828-2002) and the global average production capacity of water resources. The values of PN and PCOD were 3.145 × 10−3 t/hm2 and 6.2893 × 10−2 t/hm2, respectively.
where ECW represents the ultimate ecological carrying capacity of water resources (hm2), ECWE represents the ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment (hm2), ECN and ECCOD are the environmental carrying capacity of water polluted by ammonia nitrogen and organic matter (hm2), UN and UCOD are the upper concentration limits of ammonia nitrogen and organic pollutants (t/m3) that are considered safe for the environment, Cw is the water consumption (m3) and K is the comprehensive water consumption rate. A factor of 0.88 is introduced as the bearing capacity coefficient to prevent the loss of biodiversity [46].
where EDW and ESW as well as EDWE and ESWE are in line with the ultimate ecological surplus or deficit of water resources and the aquatic environment.
where EPI·W represents the ultimate pressure index of the aquatic ecosystem, and EPIWE represents the ecological pressure index of the aquatic environment.
3. Results
3.1. The Ultimate Ecological Footprint of Water Resources
The ultimate per capita ecological footprint (efw) calculated using the improved EF model varied from 2.868 to 4.044 hm2. The values showed an increase at an average annual rate of 2.86% from 2005 to 2011, which was then followed by a decrease at an average annual rate of 6.63%. The calculated values of the ultimate per capita ecological carrying capacity (ec·w) fluctuated between 6.707 hm2 and 16.064 hm2 as a result of annual variations in the amount of precipitation (Appendix B). The trend of the values of ed·w was similar to that of ec·w. The values of epi·w and C were between 0.216 and 0.571, and between 1.143 and 4.278, respectively. In other words, it was in a safe condition, but there is much room for improvement in the future. Although the water use efficiency has increased over the years as a result of changes in industrial water use and the implementation of water-saving policies (Table 5), the current values indicate that further improvements are still needed.

Table 5.
Changes in the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources.
Considerable differences in the values of ef·w and ec·w were observed among cities in the YKAP. Some cities, such as Yanji, Tumen and Longjing, showed higher ef·w values, which were influenced by political functions and the industrial structure (Figure 2a). However, the values of ec·w were lower than those of other cities as a result of the regional water resource reserves (Figure 2b). Water resource deficits have been a major problem in these cities (Figure 2c). Compared with other cities, Yanji had the highest epi·w values, with a maximum of 13.082 in 2011 (Figure 2d).
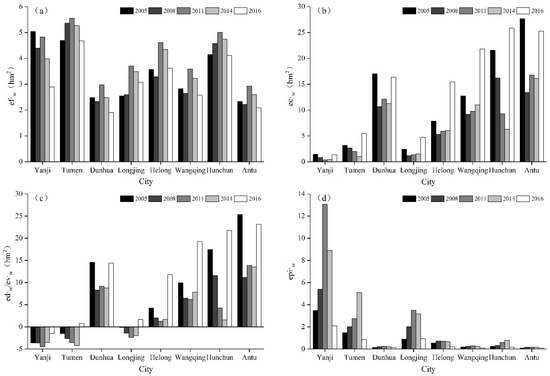
Figure 2.
The values of the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources: (a) the values of ef·w; (b) the values of ec·w; (c) the values of ed·w; (d) the values of epi·w.
3.2. The Traditional Ecological Footprint of Water Use
The values of efw in the YKAP varied between 0.475 and 0.800 hm2, and showed an average annual growth rate of 2.74%. The values of ecw ranged from 1.831 hm2 to 4.421 hm2, and the annual variation was similar to that of ec·w. The values of efw generally showed an upward trend but have been decreasing year by year since 2016 and are significantly different from the values of ecw. The trend of edw was in accordance with the ecological carrying capacity (1.085–3.650 hm2). The values of epiw varied between 0.152 and 0.422 with a fluctuating but upward trend (Table 6).

Table 6.
Changes in the traditional ecological footprint of water use.
The values of efw in the different cities showed an overall upward trend (Figure 3a), while the values of ecw showed large internal variations as well as significant differences among cities as a result of varying amounts of precipitation (Figure 3b). An ecological water deficit is prevalent in Yanji, Tumen, Longjing and Helong (Figure 3c), and the ecological pressure on water resources in these cities was substantially higher than that of other cities in the YKAP (Figure 3d).
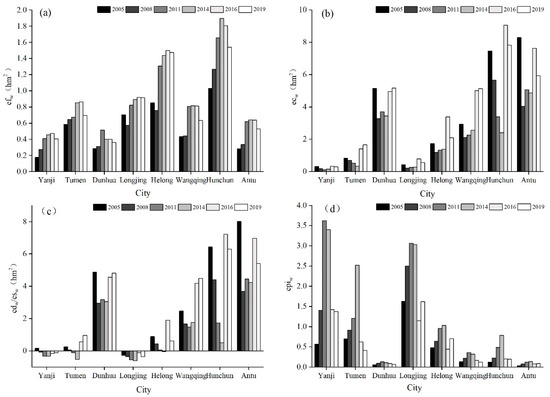
Figure 3.
The values of the traditional ecological footprint of water use: (a) the values of efw; (b) the values of ecw; (c) the values of edw; (d) the values of epiw.
3.3. The Ecological Footprint of the Aquatic Environment
The maximum ecological footprint and the minimum ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment in the YKAP over the years were mostly related to ammonia nitrogen emissions. These emissions have resulted in efwp values as high as 2.074–3.285 hm2 and ecwe values as high as 4.737–11.642 hm2. The environmental quality of water always showed a surplus (1.798–8.602 hm2). The values of epiwe ranged between 0.216 and 0.646, with an average annual decline of 4.4% (Table 7).

Table 7.
Changes in the ecological footprint of water pollution.
The values of efwp in the different cities showed an overall fluctuating but declining trend, with the per capita contribution to water pollution in Yanji and Tumen being the highest (Figure 4a). The values of ecwe in Yanji, Tumen and Longjing amounted to 0.714, 2.573 and 1.920 hm2, respectively (Figure 4b), thus demonstrating the large regional differences (Figure 4c). The ecological safety of water has been facing serious threats (Figure 4d).
Figure 4.
The values of the ecological footprint of water pollution: (a) the values of efwp; (b) the values of edwe; (c) the values of edwe and eswe; (d) the values of epiwe.
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the Improved EF Model
Compared with other indicators, the EPI·W is more suitable for evaluating the sustainable use of water resources [61]. Because traditional EF models only consider the impact of water consumption, earlier calculations have suggested that the water resources in the cities of the YKAP were within safe limits. Deterioration in the water quality caused by increased urbanization and economic activities was therefore underestimated. The improved EF model presented in this study accounted for the impact of water consumption as well as the negative effects of water pollution on the aquatic environment. The results showed that the EPIW of Yanji (Figure 5a), Tumen (Figure 5b), Dunhua (Figure 5c), Longjing (Figure 5d), Helong (Figure 5e), Hunchun (Figure 5g), Antu (Figure 5h) and Yanbian (Figure 5i) were higher than their EPIW. This was particularly evident in Yanji (Figure 5a) and Tumen (Figure 5b), where the ecological pressure status of water resources (Table 3) has escalated directly to very unsafe and extremely unsafe levels. The results are more in agreement with the actual state of water resource utilization, and can provide a reference for government departments to help them formulate policies (Figure 5).
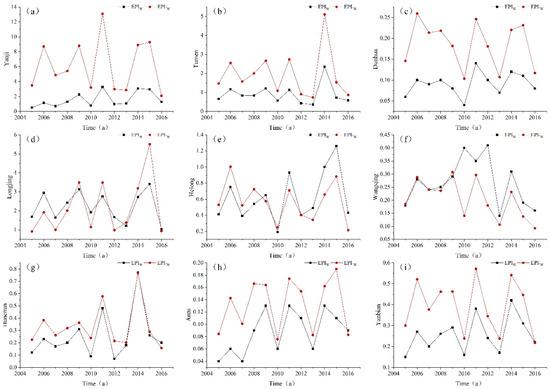
Figure 5.
Comparison of the improved model and the traditional model of ecological pressure: (a) Yanji City; (b) Tumen City; (c) Dunhua City; (d) Longjing City; (e) Helong City; (f) Wangqing City; (g) Hunchun City; (h) Antu City; (i) Yanbian Prefecture.
4.2. Contribution of the Ecological Footprint of the Aquatic Environment
Regarding changes in the values, the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources (EFW) consists of the traditional ecological footprint of water resources (EFW) and the ecological footprint of the water environment (EFWP). A comparison of the three graphs (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4) shows that the ecological footprint of the water environment had a greater impact, as can be clearly seen in the values of efw, ecw, ed∙w, es∙w and epiw. On the other hand, the magnitude of the change in the ecological footprint of the water environment can be easily seen as an important part of the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources (EFW).
Regarding the impact on ranking, the ecological footprint of the aquatic environment (EFWP) had a greater impact on the ranking among cities than the traditional ecological footprint of water resources (EFW). This was especially reflected in the value of efw, as the ranking in terms of the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources for Yanji and Tumen changed directly from seventh and fourth (Figure 3a) to third and first (Figure 2a), respectively. The rankings of other the cities also changed.
The contribution of the ecological footprint of the aquatic environment to the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources was clearly demonstrated by the changes in the values and rankings.
4.3. Relationships with Influencing Factors
The relationships between the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources and the influencing factors (Appendix B) were explored. The ultimate ecological footprint of water resources (EF·W) was positively correlated to EFWP (r > 0; p < 0.001) and Cn (r > 0; p < 0.001); the traditional ecological footprint (EFW) was positively correlated to Wr (r > 0; p < 0.001) and negatively related to EFI (r < 0; p < 0.001) and N (r < 0; p < 0.05); the ecological footprint of the aquatic environment (EFWP) was positively correlated to Cn (r > 0; p < 0.001) and N (r > 0; p < 0.05). This shows that pollutants had a significant impact on the ultimate ecological footprint of water resources, that water consumption has a strong impact on the traditional ecological footprint of water resources and that the ecological footprint of the aquatic environment is closely correlated to pollutants. The relationships between the ultimate ecological carrying capacity of water resources and the influencing factors were also examined. The ultimate ecological carrying capacity of water resources (EC·W) was positively correlated with ECW (r > 0; p < 0.001), ECWE (r > 0; p < 0.001), W (r > 0; p < 0.001), pre (r > 0; p < 0.001), sur (r > 0; p < 0.001) and gro (r > 0; p < 0.01); the carrying capacity of water resources (ECW) was positively correlated with ECWE (r > 0; p < 0.001), W (r > 0; p < 0.001), pre (r > 0; p < 0.001), sur (r > 0; p < 0.001) and gro (r > 0; p < 0.01); the ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment (ECWE) was positively correlated with W (r > 0; p < 0.001), pre (r > 0; p < 0.001), sur (r > 0; p < 0.001) and gro (r > 0; p < 0.01). All of these findings indicate that the total amount of water resources made a significant contribution to the ultimate ecological carrying capacity of water resources, the ecological carrying capacity of water resources and the ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment.
4.4. Recommendations for Improving the Health and Well-Being of Local Residents
Shortages of water resources and increasing water pollution are posing serious threats to the health and well-being of urban residents. According to a study published by the World Meteorological Organization in 2021, 5 billion people worldwide are expected to face water scarcity by 2050 [62], and about 1.4 million people die of preventable diseases every year because of lack of access to safe drinking water. Without the implementation of effective measures against drug resistance, this will become an important cause of death from infectious diseases worldwide by 2050 [63].
The Chinese government has formulated a number of policies and regulations at all levels to ensure the supply and quality of water in the YKAP through the implementation of the “Water Pollution Prevention and Control Law of the People’s Republic of China” in 2008, the revision of the “Water Law of the People’s Republic of China” in 2016, the review of the “Work Program for Fully Implementing the River Length System in Jilin Province” in 2017, the implementation of the “Regulations on Environmental Protection of Drinking Water Sources in YKAP” in 2017 and the adoption of the “Collaborative Mechanism on the Establishment of River and Lake Chiefs plus River and Lake Sheriffs plus Procurators plus Court Presidents: Guiding Opinions” in 2021.
Increasing urbanization and expansion of the tourism industry have, however, led to increased pressure on the water resources in the area. The increase in both industrial as well as urban sewage discharge has resulted in further pollution of the surface water as well as groundwater. In addition, inefficient urban and agricultural use has caused large-scale water losses. It is suggested that the government should use data based on the EF·W models, refine the relevant laws and regulations, and adjust the water supply strategies and increase the sewage treatment methods, considering social and economic development and the protection of water resources to realize the sustainability of water resources.
4.5. Limitations and Future Outlook
The improved EF model described in this study still has various limitations. It only describes the consumption and pollution of water resources on a macroscopic level by selecting two main parameters, but did not give specific details of the specific water consumption sources such as production, life, ecology, etc. In addition, other major pollution parameters were not added because of a lack of data, and the model could provide more information on the ecological pressure of the aquatic environment over a longer period of time. Nevertheless, the results showed that the ecological footprint of human water consumption in the YKAP increased from 2006 to 2019, in line with earlier findings by Zhao [64].
To better understand the factors influencing the overall ecological footprint of water resources in the YKAP, we will provide a more detailed account of the various sources in future research [65]. In addition, we will try to collect basic data on water resources at the township level, and carry out assessments of the water resources and the ecological environment.
5. Conclusions
This study has presented an improved water ecological footprint model, providing a reference for the formulation of urban water management strategies and various solutions through quantitative evaluations of water consumption and water pollution. Although pollution data for 2017–2019 were lacking, it is not difficult to conclude that the ecological footprint of water resources in the YKAP increased between 2005 and 2019, mainly through increased water pollution. Because of annual fluctuations in the amount of precipitation, the values of EC·W showed strong fluctuations. Although the overall availability and quality of water resources was within safe limits, there were large differences among cities, and in some cities, water pollution could pose a direct threat to the health and well-being of local residents. It is recommended that water resource management agencies adjust their water supply strategies based on data from the EFW model, control wastewater discharge, improve their management systems and take urban economic development into account. The findings will significantly improve the sustainable management of water resources and ensure the health and well-being of urban residents.
Author Contributions
Methodology, T.G. and M.Z.; Formal analysis, C.Z.; Investigation, T.G. and M.Z.; Resources, M.Z.; Data curation, T.G. and M.Z.; Writing – original draft, M.Z.; Writing – review & editing, C.Z.; Project administration, C.Z.; Funding acquisition, C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41830643), the Jilin Provincial Fundamental Research Fund for Central Guidance of Local Science and Technology Development (202002024JC) and the Applied Basic Project of Yanbian University (Yanda Kehezi No. 18 in 2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors thank the Statistical Bureau of Jilin Province, Statistical Bureau of Yanbian State and Water Conservancy Burea of Yanbian State for providing the data freely.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Weihong Zhu from Yanbian University for her helpful suggestions and inspiration, which greatly improved the manuscript. We also want to express our respect and gratitude to the anonymous reviewers and editors for their professional comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Nomenclature.
Table A1.
Nomenclature.
| Acronyms | |
|---|---|
| EFW | The ecological footprint of water resources |
| EF·W | The ultimate ecological footprint of water resources |
| EFWP | The ecological footprint of water pollution |
| EFN | The ecological footprint of water pollution by ammonia nitrogen |
| ED·W (ES·W) | The ultimate ecological deficit of water resources |
| EDW (ESW) | The ecological surplus of water resources |
| EDWP (ESWP) | The ecological surplus of the aquatic environment |
| EPIW | The ecological pressure index |
| EPI·W | The ultimate pressure index of the aquatic environment |
| EPIWE | The ecological pressure index of the aquatic environment |
| EFI | The utilization efficiency of water |
| EC·W | The ultimate ecological carrying capacity of water resources |
| ECW | The ecological carrying capacity of water resources |
| ECWE | The ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment |
| C | The load index |
| ECN | The environmental carrying capacity of water polluted by ammonia nitrogen |
| efw | The per capita ecological footprint of water resources |
| ef·w | The ultimate per capita ecological footprint of water resources |
| efwp | The per capita ecological footprint of water pollution |
| EFCOD | The ecological footprint of water pollution by organic matter |
| ed·w (es·w) | The ultimate per capita ecological deficit of water resources |
| edw (esw) | The per capita ecological surplus of water resources |
| edwp (eswp) | The per capita ecological surplus of the aquatic environment |
| epiw | The per capita ecological pressure index |
| epi·w | The ultimate per capita pressure index of water ecology |
| epiwe | The per capita ecological pressure index of the aquatic environment |
| efi | The per capita utilization efficiency of water |
| ec·w | The ultimate per capita ecological carrying capacity of water resources |
| ecw | The per capita ecological carrying capacity of water resources |
| ecwe | The per capita ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment |
| ECCOD | The environmental carrying capacity of water polluted by organic matter |
Appendix B
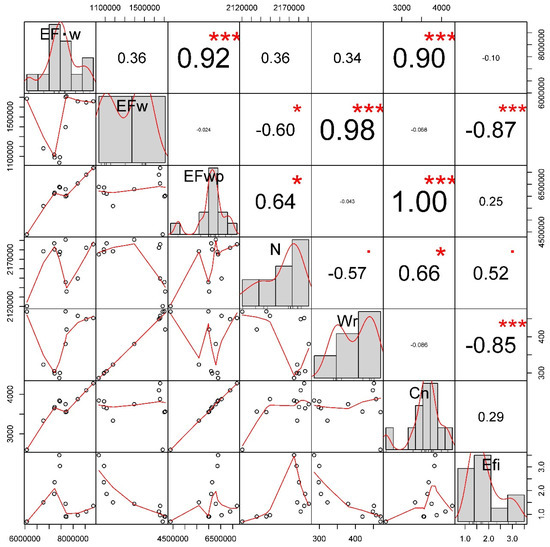
Figure A1.
The relationships between EF·W and the influencing factors. Note: *** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05.
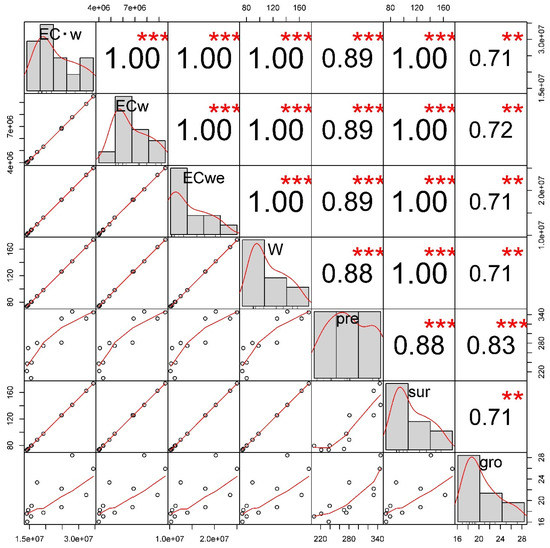
Figure A2.
The relationships between EC·W and the influencing factors. Note: *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01. pre: precipitation; sur: surface water resources amount; gro: ground water resources amount.
References
- Lee, J.M.; Kwon, E.H.; Woo, N.C. Natural and Human-Induced Drivers of Groundwater Sustainability: A Case Study of the Mangyeong River Basin in Korea. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiklomanov, I.A. Appraisal and Assessment of World Water Resources. Water Int. 2000, 25, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global Water Resources: Vulnerability from Climate Change and Population Growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.J. China’s Rapid Urbanization. Science 2013, 342, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.Y.; Liu, Q.; Cao, S.X. Real estate supports rapid development of China’s urbanization. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Zhao, Y. Indirect effects of carbon taxes on water conservation: A water footprint analysis for China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 279, 111747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Sun, P.; Zhu, W.H.; Xu, Z.; Fu, J.; Man, W.D.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, J.; Qin, L. Landscape dynamics and driving forces of wetlands in the Tumen River Basin of China over the past 50 years. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 13, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, R.V.; Russian Mission in Asia. “Berdyaev Readings” in Vladivostok. Polis. Political Stud. 2015, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-W.; Suthiwartnarueput, K.; Abareshi, A.; Lee, P.T.-W.; Duval, Y. Key factors in developing transit trade corridors in Northeast Asia. J. Korea Trade 2017, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.J. Northeast Asian Economic Cooperation and the Korean Peninsula Economy: The Impact of the Changjitu Development Plan. Korea J. 2011, 51, 130–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Evaluating the dynamic sustainability and resilience of a hybrid urban system: Case of Chengdu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 291, 125719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A Blueprint to Safeguard Europe’s Water Resources; COM(2012) 673 Final; European Centre for River Restoration: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, W.E. Ecological footprints and appropriated carrying capacity: What urban economics leaves out. Int. Inst. Environ. Dev. 1992, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M. Ecological Footprint and Appropriated Carrying Capacity: A Tool for Planning toward Sustainability. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Nezamoleslami, R.; Hosseinian, S.M. An improved water footprint model of steel production concerning virtual water of personnel: The case of Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasooriya, R.; Liyanage, L.; Rathnappriya, R.; Bandara, W.; Perera, T.; Gunarathna, M.; Jayasinghe, G. Industrial water conservation by water footprint and sustainable development goals: A review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 12661–12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, P.; Arena, A.P.; Civit, B.; Curadelli, S.; Feldman, S.; Jozami, E.; Mele, F.; Piastrellini, R.; Silva, J. The Water Footprint in Bionergy-A Comparison of Four Biomass Sources to Produce Biofuels in Argentina. In Environmental Water Footprints; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 52, pp. 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, C.H. New insights from grey water footprint assessment: An industrial park level. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batuecas, E.; Ramón-Álvarez, I.; Sánchez-Delgado, S.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Carbon footprint and water use of alkali-activated and hybrid cement mortars. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Han, R.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Li, N. China’s industrial gray water footprint assessment and implications for investment in industrial wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7188–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wu, N.; Engel, B.A.; Hua, E.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Multi-dimensional evaluation of water footprint and implication for crop production: A case study in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoam, E.J.; Angnes, G.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Romanelli, T.L. Energy, carbon and water footprints on agricultural machinery. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 198, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovella, T.; Paiano, A.; Lagioia, G. A meso-level water use assessment in the Mediterranean agriculture. Multiple applications of water footprint for some traditional crops. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, X.W.; Han, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.K.; Men, X.L. Study on the Matching Method of Agricultural Water and Land Resources from the Perspective of Total Water Footprint. Water 2022, 14, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Oliveira, S.; Braga, C.C.; Brito, J.I.; Sousa, F.; Holanda, R.; Campos, J.; Souza, E.P.; Braga, A.C.; Almeida, R.; et al. Virtual water and water self-sufficiency in agricultural and livestock products in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, W.; Rushforth, R.; Ruddell, B.L.; Konar, M.; Ahams, I.C.; Gironás, J.; Mijic, A.; Mejia, A. Water Footprint of Cities: A Review and Suggestions for Future Research. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8461–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzardo, A.; Mazzi, A.; Loss, A.; Butler, M.; Williamson, A.; Scipioni, A. Lessons learned from the application of different water footprint approaches to compare different food packaging alternatives. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4657–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.A.; Hulland, K.R.S.; Robert, D.; Farhana, S. Sustained adoption of water, sanitation, and hygiene interventions: Systematic review. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2018, 23, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzardo, A.; Loss, A.; Fialkiewicz, W.; Rauch, W.; Scipioni, A. Methodological proposal to assess the water footprint accounting of direct water use at an urban level: A case study of the Municipality of Vicenza. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Ding, T. Assessment on the flow and vulnerability of water footprint network of Beijing city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finogenova, N.; Dolganova, I.; Berger, M.; Núñez, M.; Blizniukova, D.; Müller-Frank, A.; Finkbeiner, M. Water footprint of German agricultural imports: Local impacts due to global trade flows in a fifteen-year perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pérez, M.R.; Alba-Rodríguez, M.D.; Marrero, M. Evaluation of Water Footprint of Urban Renewal Projects. Case Study in Seville, Andalusia. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Yue, W. Optimal water utilization and allocation in industrial sectors based on water footprint accounting in Dalian City, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Tabesh, M. Effects of inflow, infiltration, and exfiltration on water footprint increase of a sewer system: A case study of Tehran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrien, M.M.; Aldaya, M.M.; Rodriguez, C.I. Water Footprint and Virtual Water Trade of Maize in the Province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Water 2021, 13, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhuo, L.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Jin, J.; Wu, P. Non-negligible regional differences in the driving forces of crop-related water footprint and virtual water flows: A case study for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture Government Official Website. Available online: http://www.yanbian.gov.cn/ (accessed on 26 March 2019). (In Chinese)
- Jilin Provincial Government Official Website. Available online: http://www.chinajilin.com.cn/2013zhuanti/node_31159.htm (accessed on 26 March 2019). (In Chinese).
- Statistical Bureau of Jilin Province. Statistical Yearbook of Jilin (2001–2019); Chinese Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2001–2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Statistical Bureau of Yanbian State. Statistical Yearbook of Yanbian (2001–2019); Chinese Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2001–2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Water Conservancy Burea of Yanbian. Water Resources Bulletin of Yanbian State (2001–2019); Chinese Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2001–2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, M.S.; Galli, A.; Niccolucci, V.; Lin, D.; Hanscom, L.; Wackernagel, M.; Bastianoni, S.; Marchettini, N. Stocks and flows of natural capital: Implications for Ecological Footprint. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasslabend, W. The Silk Road: A Political Marketing Concept for World Dominance. Eur. View 2015, 14, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Wide Fund for Nature or World Wildlife Fund. Available online: http://wwf.panda.org/knowledge_hub/all_publications/living_planet_report_timeline/lpr_2002/ (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- Ress, W.E.; Wackernagel, M. Ecological Footprints and Appropriated Carrying Capacity: Measuring the Natural Capital Requirements of the Human Economy. Focus 1994, 6, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wackernagel, M.; Rees, W.E. Perceptual and structural barriers to investing in natural capital: Economics from an ecological footprint perspective. Ecol. Econ. 1997, 20, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M.; Kitzes, J.; Moran, D.; Goldfinger, S.; Thomas, M. The Ecological Footprint of cities and regions: Comparing resource availability with resource demand. Environ. Urban. 2006, 18, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, R.; Zeng, X. Water resources utilization efficiency and influence factors under environmental restrictions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Aoudia, M.N.; Berezowska-Azzag, E. Water resources carrying capacity assessment: The case of Algeria’s capital city. Habitat Int. 2016, 58, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubacek, K.; Guan, D.; Barrett, J.; Wiedmann, T. Environmental implications of urbanization and lifestyle change in China: Ecological and Water Footprints. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, X. Evaluation of ecological instream flow using multiple ecological indicators with consideration of hydrological alterations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Heijungs, R.; de Snoo, G.R. Theoretical exploration for the combination of the ecological, energy, carbon, and water footprints: Overview of a footprint family. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ture, C. A methodology to analyse the relations of ecological footprint corresponding with human development index: Eco-sustainable human development index. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2013, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, S. Assessment of Eco-Environmental Stress in the Western Taiwan Straits Economic Zone. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2716–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.S.; Galli, A.; Coscieme, L.; Niccolucci, V.; Lin, D.; Pulselli, F.M.; Bastianoni, S.; Marchettini, N. Exploring ecosystem services assessment through Ecological Footprint accounting. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Deng, X.; Jin, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. Ecological security assessment based on ecological footprint approach in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 101, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachidananda, M.; Webb, D.P.; Rahimifard, S. A Concept of Water Usage Efficiency to Support Water Reduction in Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemmali, H. Mapping water poverty in Africa using the improved multidimensional index of water poverty. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H.; Gou, S. Water shortages raised a legitimate concern over the sustainable development of the drylands of northern China: Evidence from the water stress index. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 590, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology, People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/zcwj/gwywj/201811/t20181129_676575.shtml (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- GB 3828-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environmental Sciences Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- World Meteorological Organization. Wake Up to the Looming Water Crisis, Report Warns. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/media/press-release/wake-looming-water-crisis-report-warns (accessed on 11 June 2022).
- United Nations Environment Programme. Global environment outlook. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 36, 337–338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.Z.; Jin, M.J. Dynamic research on the ecological footprint and load-carrying capacity of water resources in Yanbian area. J. China Agric. Univ. 2017, 22, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, A. On the rationale and policy usefulness of Ecological Footprint Accounting: The case of Morocco. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).