Abstract
The effects of climate change and of land use/cover change (LUCC) on streamflow as demonstrated by hydrological models are pressing issues on the frontiers of global environmental change research. The Nandu River Basin (NRB) as the largest of three river basins on the tropical Hainan Island, China, is subjected to an analysis of streamflow response to climate and to land-use change. It is based on the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) coupled with climate change signals extracted from the global climate model data in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) and with land-use change scenarios modeled by Cellular Automata (CA)—Markov. The results are summarized as follows: (1) Climate change contributed more to streamflow change than land-use change in the NRB, with contributions of 97.57% and 2.43%, respectively. Precipitation and temperature were the most important climate variables, contributing 92.66% and 4.91% to streamflow change. (2) In the tropical island basin from 1990 to 2015, LUCC regulated the hydrological processes in the NRB and affected hydrological processes by increasing evapotranspiration and decreasing surface runoff and subsurface flow, which resulted in decreasing streamflow. (3) Under the climate change and land-use change scenarios of the near-term period (2021–2040), the annual streamflow decreased as during the reference period (1995–2014); particularly, it decreased most (−6.16%) on the SSP126 path. These results present a case study for understanding the hydrological cycle of tropical island basins and to provide a theoretical basis for water resources management and regional sustainable development of tropical islands.
1. Introduction
The hydrological cycle of a basin is affected by both climate change and land use/cover change (LUCC), and streamflow is one of the important links in the hydrological cycle []. Thus, changes in streamflow can reflect the impact of climate change and LUCC. The range of streamflow change is most obvious under the influence of combined climate change and LUCC, as compared to climate change or LUCC scenarios individually []. Climate change affects and reshapes the spatial and temporal distribution of water resources by changing the patterns of rainfall and evapotranspiration []. LUCC is the main driving force of short-term hydrological changes, which can directly reflect the extent of human activities influencing the underlying surface, primarily through vegetation cover interception, surface water evaporation, and soil water infiltration, and how these factors are related to changes in runoff generation and the water cycle []. LUCC can alter the impact of rainfall on runoff or change the distribution of excessive rainfall. Therefore, the impact of both climate change and LUCC as the two main drivers affecting hydrological processes cannot be neglected when developing plans for continuing basin management [,].
Various methods are currently used to evaluate the effects of climate change and LUCC on streamflow, which is at the forefront of the research on global environmental change. This includes the elastic coefficient method [], the precipitation–runoff regression relationship method [], the method of reconstructing runoff by using or combining hydrological models [], etc. The SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool) model was developed for basin management by the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) and ARS (Agricultural Research Service) [] because it is relatively simple to operate and, due to its favorable performance in simulating hydrological and water-quality processes, it is widely used to capture the hydrological response to climate change and LUCC [,,]. SWAT presented a greater potential in the management of the risks of extreme hydrological events [,]. The SWAT model comprehensively considers the hydrological process differences of the underlying surface of the basin and found that climate change and LUCC have impacts on hydrological processes such as evapotranspiration (ET), runoff, infiltration, and hydrological response []. Hence, the comparison of hydrological processes changes under different climate changes and LUCC scenarios using SWAT models is important for understanding the response of hydrological processes to changing environments.
Numerous scholars have conducted studies on the impact of LUCC on streamflow and hydrological factors using the SWAT model. For example, studies showed that vegetation degradation such as agricultural land, grassland, and forest, as well as the increase of urban land, would all lead to a significant increase in streamflow or surface runoff [,,,]. The conversion of grassland to cultivated land resulted in an increase of flow, and the transformation from forest land to cultivated land, grassland to cultivated land, and grassland to forest land all weakened the regulation and storage capacity and easily changed the water yield of the sub-basin []. Afforestation (forest–evergreen) may reduce surface runoff and soil moisture and increase evapotranspiration []. The mutual transformation of cultivated land, forest land, and grassland caused significant changes in soil permeability, surface runoff, underground runoff, and water yield [,]. The study on the influence of LUCC on hydrological processes in tropical basins showed that the decrease of cultivated land and natural forest area, as well as the increase of rubber plantation and other economic forests, led to the decrease of runoff in Hainan and Southeast Asia [,,]. It indicated that LUCC mainly affected the hydrological processes of sub-basins by changing surface runoff, groundwater, and soil moisture. Generally, forest land and grassland had the functions of interception and storage, and cultivated land had a strong capacity for water yield, while the impervious surfaces of urban land contributed to an increase in streamflow.
Coupling the SWAT model and the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) is an important method for exploring streamflow changes in the future and assessing the impacts of climate change on the hydrology of river basins. At present, the SWAT model coupled with future climate scenarios in CMIP5 has been studied and found that changes in the water–thermal combination of precipitation and temperature have a profound impact on streamflow. Hydrological components were more sensitive to precipitation than to temperature changes, and blue water components were more sensitive than green water components [,]. As one of the important driving factors of hydrological model input, precipitation plays a crucial role in the performance of streamflow simulation []. Multiple climate products, such as gauge-based gridded data, ground-based weather radar, satellite precipitation, and climate reanalysis products, are being increasingly applied for hydrological modeling []. The study showed that annual streamflow had a consistent response to precipitation, but the response to temperature was more complex. For example, high temperatures in the warm season led to increased transpiration and decreased streamflow, but higher temperatures in the cold season led to more snowmelt and, thus, increasing streamflow in the Maumee Basin []. However, in the Mun River, annual streamflow was expected to increase under three future climate scenarios, while monthly streamflow changes correlated negatively with temperature []. In future climate scenarios, the peak discharge may likely shift from the summer to the spring months [], showing an upward trend in annual streamflow and increasing synchronously with the increase of radiative forcing of the path [,]. However, the impacts of climate change and LUCC on streamflow showed a nonlinear synergistic effect. Therefore, it is necessary to further explore the hydrological effects and comprehensive impacts of climate change and LUCC on streamflow [,]. A simulation of future climate and LUCC scenarios, as well as a study of streamflow change principles, is of great significance for guiding the water resources management of basins.
As unique natural ecosystems, islands are an indispensable and important part of coastal areas []. The Nandu River is the longest river on Hainan Island, China, characterized by a great disparity ranging from surface water abundance to drought and, in addition, to an inhomogeneous distribution of water resources within the basin (Nandu River Basin, NRB) []. Any change to its hydrological situation greatly affects the social and economic development of Hainan Province, China. Further, Hainan Island is characterized by the second-largest area coverage of rubber plantations in China. Since the 1990s, the area of rubber plantations has realized a trend from slow to rapid growth, and the land use of the island has also undergone drastic changes []. Hence, this study aimed at evaluating the responses of streamflow to climate and land-use change in the NRB based on the SWAT model coupled with CMIP6 and Cellular Automata (CA)—Markov model. Firstly, Section 2 describes the eco-hydrological setting, introducing the SWAT model localized in the NRB, revealing the climate change signals extracted from CMIP6 data being used to simulate streamflow changes under future climate scenario. The CA–Markov model is to be employed to simulate the future LUCC scenarios and explore the streamflow response under land-use change. Section 3 presents the results: different scenarios of land-use conditions and climate factors are set up and cross-combined to determine the sensitive factors of streamflow change to quantitatively analyze the contribution rate of climate change and LUCC on streamflow, as well as to analyze the streamflow response of the NRB under changes in different factors individually and their synergistic effect. Finally, the discussion and conclusion (Section 4 and Section 5) embed the results into a broader perspective; that is, as a case study relevant for the understanding the hydrological cycle of tropical basins and to provide a theoretical basis for water resources management and regional sustainable development of tropical islands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The main stream of the Nandu River originates in Baisha County, runs through the central and northern part of Hainan Island, and finally flows into the Qiongzhou Strait, passing a population of 2.256 million. Located at the northern edge of the tropical region, the NRB is exposed to dry and rainy seasons, a frequent occurrence of typhoons, and abundant rainfall, with streamflow concentrated in the flood season (from May to October), which accounts for more than 70% of the total annual streamflow [].
The Nandu River Basin (109°36′–110°34′ E, 19°9′–19°55′ N) uses Longtang Hydrographic Station as its outlet (Figure 1). The terrain is high in the southwest and low in the northeast, with an average altitude of 116 m and a total area of 5336 km2. The average annual precipitation in the basin was 1975 mm from 1990 to 2015. The precipitation in the rainy and dry seasons (the rainy season is from May to October and the dry season is from November to April) accounted for 81% and 19%, respectively, with greater rainfall in the south than in the north. In 2015 LUCC, other forest lands, that is tropical rain forests, secondary forests, and other tropical economic forests (except rubber plantations) were the main land-use type, accounting for 46.64% of the basin area, while rubber plantation and tillage land accounted for 21.38% and 26.13% of the basin area, respectively. Urban and unused land (unused land refers to the bare land with vegetation coverage below 5%) and water bodies comprised less area, accounting for 3.93% and 1.92% of the total basin area, respectively. There were 13 soil types in the NRB. Ephedra sand soil was the main soil, accounting for 51.96% of the basin area. Light hemp brick soil, meat mud field, and huguang rock pyroclastic soil accounted for 26.96%, 9.92%, and 4.37% of the basin area, respectively. The other nine soil types, including flat bone soil, chaozhou light sand soil, river sand mud field, red clay, ephedra brick soil, mud base soil, sand brick soil field, mixed sand yellow laterite, and purple brown soil, accounted for less than 2.04% of the basin area (Figure 1).
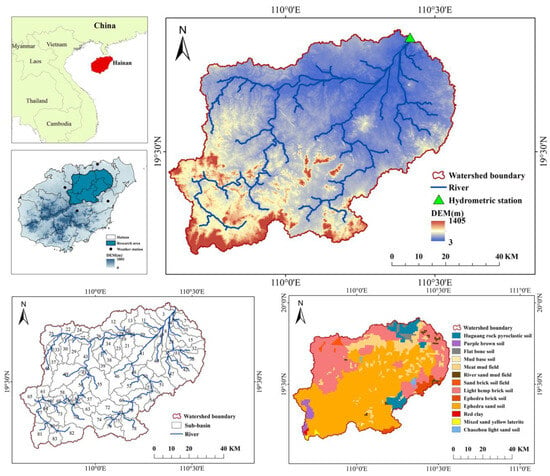
Figure 1.
Geographical location, river system distribution, sub-basin division, and soil types of the Nandu River Basin, Hainan Island, China.
2.2. SWAT Model
SWAT is a catchment-scale model originally used to determine the impact of land-management practices on surface water quality in large and complex catchments []. The version used in this study is SWAT 2012. The SWAT model had been successfully applied to streamflow simulation in the NRB []. This model is a component of soil- and water-assessment tools based on a constant time model, which can objectively predict the impact of land-management practices on water. It has high computational efficiency and can be used to evaluate the impact of various land-use and management practices on water quantity and water quality for a long period of time. The main components of the model include weather, hydrology, soil temperature and soil properties, plant growth, and land management, all of which can be simulated based on the water balance equation (Formula (1)) [].
where SWt (mm) is the final soil water content at time t (day); SWo (mm H2O) is the initial soil water content at day i; Rday (mm) is the precipitation at day i; Qsurf (mm) is the surface runoff at day i; ETa (mm) is evapotranspiration at day i; Wseep (mm) is the seepage water amount at the bottom of the soil at day i; and Qgw (mm) is the return flow at day i.
Streamflow or runoff (R) in the SWAT model consists of surface runoff, subsurface flow, and groundwater runoff. Underground runoff first becomes shallow percolation water, then part of it flows back into the river as the source of river flow in the form of base flow, with shallow water storage also being part of the process. In addition, the other part leaks into deep aquifer recharge. Since the subsurface flow can supplement the surface runoff, part of the groundwater runoff becomes the base flow, so the streamflow here can be simplified by the sum of the surface runoff and the base flow. Thus, the base flow index (BFI, calculated as base flow/streamflow) plus (surface runoff/streamflow) = 1 []. The water balance equation P = R + ET + ∆S [], where R is the streamflow, P is the precipitation, and ET is the evapotranspiration, treats deep recharge as water storage (∆S). This leads to runoff coefficient (R/P) plus drying index (ET/P) plus (deep recharge/P) = 1.
2.3. Data Source and Processing
Input data content and sources of the SWAT model are shown in Table 1. ArcSWAT, based on the ArcGIS platform, automatically extracts the river network according to the input Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and then sets the threshold of the catchment area to generate sub-basins. Then, the sub-basin is subdivided into Hydrological Response Units (HRUs) based on unique land use, soil classification, and slope. The spatial distribution data of soil types were generated based on the traditional Genetic Classification of Soil (GSCC) system in China and then classified into four classifications: soil, subclass, soil genus, and soil species, with the subclass as the basic mapping unit. After that, soil attribution data were obtained according to soil type codes corresponding to the book [], including major indices such as soil thickness, soil profile, soil mechanical composition, organic matter, and pH.

Table 1.
Basic data content and sources for the SWAT model.
In the process of constructing the SWAT model for the NRB employing the values of land use type, soil type, and slope (with the lowest proportion among the main proportion types), the thresholds are set as 20%, 20%, and 20%, respectively, and the study area was divided into 83 sub-basins and 242 HRUs (Figure 1). On this basis, meteorological input data provide a model database of precipitation, temperature, solar radiation, relative humidity, wind speed, and other measurements to calculate the runoff generation and confluence of each HRU.
2.4. Model Calibration and Validation
In this study, the SUFI-2 algorithm of SWAT–CUP (Calibration and Uncertainty Programs) was used to analyze, calibrate, and verify the sensitivity of SWAT models. SUFI-2 requires a relatively small number of runs, resulting in minimal uncertainty for most measurements []. The model fitting results were evaluated according to the determination coefficient (R2), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE), and the percentage bias (PBIAS) between the observed data and the simulated output []. The simulation accuracy of a model is considered satisfactory to be applied to other scenarios if the runoff calibration and validation meet |PBIAS| < 25%, R2 > 0.6, and NSE > 0.5 [].
2.5. Future Climate Scenarios
CMIP6 is the sixth Phase of CMIP. It has the largest number of experimental modes, the perfect experimental design, and the largest data simulation (in terms of the amount of data) ever since the implementation of CMIP []. SSP-RCP refers to the change scenario, combining different Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) and Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs). Therefore, this climate scenario is the most reasonable and reliable prediction available.
In this study, seven types of the latest climate change scenarios and data from five global climate models, including CanESM5, IPSL-CM6A-LR, MIROC6, MRI-ESM2-0, and CNRM-ESM2-1 in CMIP6, were selected []. SSP119, SSP126, SSP245, SSP370, SSP434, SSP460, and SSP585, respectively, represent the upgrade of RCP1.9 and RCP2.6 scenarios on sustainable development path SSP1; the upgrade of RCP4.5 scenarios on moderate development path SSP2; the upgrade to RCP7.0 scenario on partial development path SSP3; the upgrade to RCP3.4 and RCP6.0 scenario on unbalanced development path SSP4; and the upgrade to RCP8.5 scenario on conventional development path SSP5.
Based on the combined changes of precipitation and temperature in 21 tropical regions under seven paths of the CMIP6 climate model [] (reference period 1995–2014), the future climate change signals were extracted for the near-term period (2021–2040), the mid-term period (2041–2060), and the long-term period (2081–2100) in the 21st century. This was used to simulate the streamflow response of the NRB under climate change scenarios in different periods in the future (Figure 2).
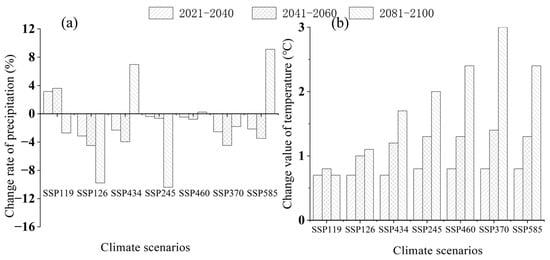
Figure 2.
Changes of (a) Precipitation and (b) Temperature in tropical regions under seven paths in the 21st century based on CMIP6, compared to the reference period of 1995–2014. (The climate scenarios for the seven paths are SSP119, SSP126, SSP434, SSP245, SSP460, SSP370, and SSP585.).
2.6. Land-Use Scenario Based on CA–Markov Model
IDRISI’s CA–Markov model, which combines the spatial dynamic simulation ability of the Celluar Automata (CA) model and the advantage of the Markov model in long-term predictions, has been widely discussed and applied by researchers at present []. In this paper, the following specific steps of the CA–Markov model application are employed:
(1) First, the actual land-use scenarios in the NRB from 1990 (LUCC 1990) to 2015 (LUCC 2015) were analyzed by superposition to obtain a transition probability matrix and transfer area matrix.
(2) Then, considering the actual terrain and geomorphic conditions of the basin and the development of the urban areas, the transformation of different LUCC types was constrained and restricted by adding data on elevation, slope, distance from cities, villages, and traffic lines. Thus, the suitability atlas of different LUCC types was obtained.
(3) Finally, based on the actual LUCC 2015, the transition probability and area matrix, the suitability map of each LUCC type transfer, and a 5 × 5 CA filter were adopted (the rectangular space within 5 km × 5 km around a cell has a significant impact on the state of the cell), with the cycle being repeated 25 times. The future land-use scenarios of the basin were simulated (LUCC 2040). The land-use change in the period from 2015–2040 was described by the CA–Markov model to maintain the change trend from 1990–2015. Thus, by comparing the simulation results the influence of climate or LUCC on streamflow could be quantitatively analyzed.
2.7. Calculation of Streamflow Contribution Rate
When one driver changes while the others remain constant, the simulation results isolate the influence of this single factor on hydrological components []. The contribution rates can be used to directly separate the effects of climate change and LUCC on streamflow []. We use climate conditions and land-use data for 1990 and 2015 as examples.
The difference between LUCC 1990’s streamflow under climate conditions in 2015 (Q2) and LUCC 1990’s streamflow under climate conditions in 1990 (reference period Q0) can be regarded as the impact of different climate conditions on streamflow changes in 1990 and 2015. Similarly, the change of streamflow between LUCC 2015 in the climate of 2015 (Q3) and LUCC 2015 in the climate of 1990 (Q1) can also be regarded as the influence of different climate conditions in 1990 and 2015 on the change of streamflow. Therefore, the influence of different climatic conditions in 1990 and 2015 (ΔQ9015C) on the streamflow should be expressed using the following formula:
In addition, the impact of land-use changes in 1990 and 2015 (ΔQ9015L) on streamflow can be determined by calculating the difference between Q1 and reference period Q0 or between Q3 and Q2:
The difference between Q3 and reference streamflow Q0 represents the combined impact of climate change and LUCC on streamflow change. We find that the combined effect (ΔQ9015C + ΔQ9015L) is equal to the sum of individual effects. Therefore, the percentage contribution of different climatic conditions (η9015C) and LUCC (η9015L) to streamflow change can be calculated using the following formula:
The contribution rate of precipitation and temperature to streamflow in the same LUCC scenario among climate factors can also be determined by the above principles [].
2.8. Research Framework
The research framework proposed in this study included four main components (Figure 3). Firstly, listing all data required for constructing the SWAT model and CA–Markov model. The second part involves the construction process of SWAT model, which, supported by the SWAT–CUP for calibration and validation, achieves the reconstruction of streamflow. Then, the third part selects the future climate scenario of CMIP6, using the CA–Markov model to generate potential land-use scenarios (LUCC 2040) as well as the methods to separate and quantify the streamflow contribution. The final part is about the input of the past and the future climate, as well as LUCC into the SWAT model to assess the responses of streamflow and other hydrological processes to climate change and LUCC under the different scenarios.
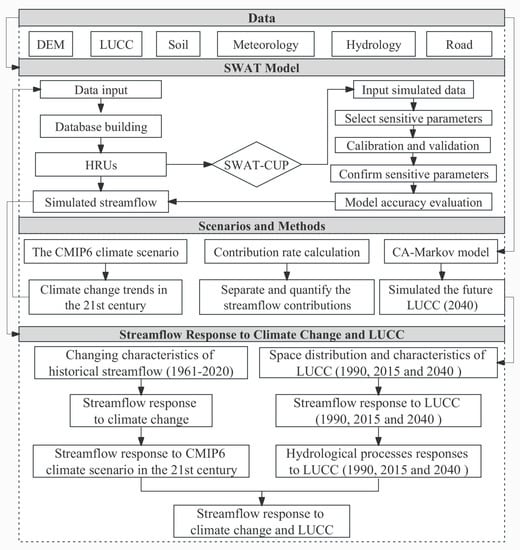
Figure 3.
Research framework.
3. Results
3.1. Streamflow Simulation Based on SWAT Model
3.1.1. SWAT Model Calibration and Validation
According to the streamflow observation data of Longtang Hydrological Station, the time interval from 1961–1976 was selected as the warm-up period of streamflow simulation; 1977–1987 and 2006–2013 were set as the calibration period and validation period, respectively (Figure 4). Calibration and validation of the SWAT model were based on LUCC 2015. Through sensitivity analysis of the ranking of parameters (Table S1), the fitted value of parameter calibration was substituted into the SWAT model to obtain optimal results of the runoff simulation. According to the parameter calibration results of the SWAT model, EPCO, SLSUBBSN, CH_K2, SOL_BD, and GW_DELAY occurred as the top five sensitive parameters among the 18 that are the most closely related to runoff generation in the NRB. The results indicated that streamflow in the NRB was sensitive to evapotranspiration, slope condition, soil condition, and groundwater processes.
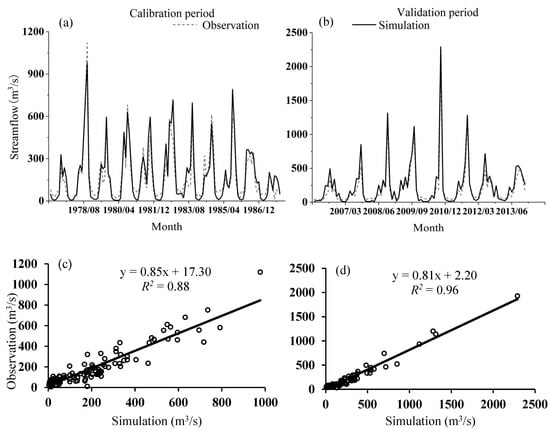
Figure 4.
Comparison between simulated and observed monthly streamflow during calibration and validation periods in Nandu River Basin. Comparison of monthly observed and simulated streamflow during (a) Calibration period (1977–1987) and (b) Validation period (2006–2013); scatter diagrams of observed and simulated monthly streamflow during (c) Calibration period and (d) Validation period.
The R2, PBIAS, and NSE of streamflow simulation in the study area were obtained as 0.88, −5.81%, and 0.85 in the calibration period, and 0.96, −21.63%, and 0.89 in the verification period, indicating a good consistency between monthly streamflow simulation and observed values during both periods. That is, the SWAT model revealed a good adaptability in the NRB, indicating that it could be used to simulate streamflow and study its response to land-use change observed in the basin.
3.1.2. Streamflow Change from 1961 to 2020
Combining observed and simulated annual streamflow from 1961 to 2020 based on LUCC 2015, the variation trend of streamflow in the NRB from 1961 to 2020 was determined based on the LUCC 2015 (Figure 5). From 1961 to 2020, the annual streamflow in the NRB fluctuated greatly, about an average of 190 m3 s−1; it was accompanied with an overall slightly upward trend (Figure 5a). Furthermore, the annual streamflow in the NRB also revealed an overall slightly upward trend from 1990 to 2015, and according to the estimated results, the annual streamflows in 1990 and 2015 attained 180.71 m3 s−1 and 130.16 m3 s−1, respectively, both of which are years with low annual streamflow. The monthly mean streamflow of the basin was concentrated in the rainy season, especially from August to October, and a large variability is noted most obviously in September (Figure 5b). The average streamflows in the rainy and dry seasons of 301.48 m3 s−1 and 77.36 m3 s−1 account for 79.58% and 20.42% of the annual streamflow, respectively. The streamflow in the rainy season showed an insignificant rising trend over the years, while the streamflow in the dry season revealed a decreasing trend (Figure 5c). As the increase of streamflow during the rainy season was greater than the decrease of streamflow during the dry season, annual streamflow showed a slight increase. That is, the monthly streamflow was concentrated in the rainy season, and the rainy season streamflow provided the main contribution of annual streamflow.
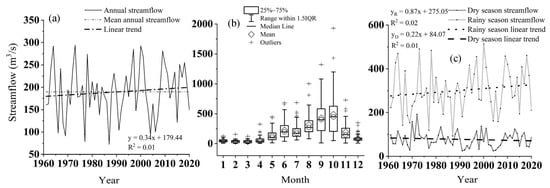
Figure 5.
(a) Annual, (b) Monthly, and (c) Seasonal streamflow and trends from 1961 to 2020 in Nandu River Basin.
3.2. Land-Use Change Analysis and Prediction
A comparison between land uses in 1990 (LUCC 1990) and land uses in 2015 (LUCC 2015) showed that the area of tillage land and other forest land decreased, accompanied by area increases of rubber plantation, water body, urban, and unused land. The potential land uses (LUCC 2020) in the NRB were predicted by the CA–Markov model based on the LUCC 1990 and LUCC 2005 data. Since the CA–Markov model can only simulate for equal annual intervals, the prediction accuracy of the model was determined by comparing the fitting degree between the simulated LUCC 2020 and the actual LUCC 2015 (used to replace actual LUCC 2020). The Kappa coefficient of 0.52 demonstrated the acceptable consistency between the predicted LUCC 2020 and the actual LUCC 2015.
As shown in Table 2 and Figure 6, the distribution of different land use types in 2040 was similar to the distribution in 2015, where other forest land dominated the largest part of the area, followed by tillage land and rubber plantation, while urban and unused land and water bodies were the least. Other forest land accounted for 43.39% of the basin area in LUCC 2040, followed by 27.59% of tillage land and 22.67% of rubber plantation. The urban and unused land and water bodies accounted for no more than 5% of the area. Other forest land decreased by a total of 6.96%, while the area coverage of the other four land-use types increased from 2015 to 2040 by varying magnitudes. Urban and unused land increased mainly near the river, the largest proportion (11.69%) of which was evident by comparing the LUCC images from the two periods (Figure 5). Then, in terms of area change, rubber plantation and tillage land increased by 6.06% and 5.56%, respectively, in the southeastern part of the basin at lower altitudes. The water body increased by the lowest proportion, 1.98%, mainly in the river buffer zone. It can be seen that the distribution of land use types in the NRB was dominated by other forest land, tillage land, and rubber plantation, and the sum of the three accounts for more than 90% of the basin, and the other forest land is most widely distributed.

Table 2.
Potential LUCC trend and area proportion in Nandu River Basin.
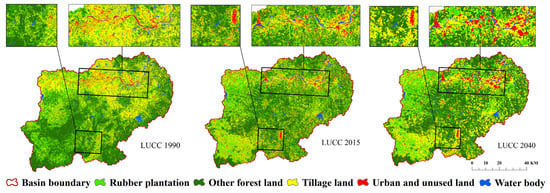
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of land use types in 1990, 2015, and 2040 in Nandu River Basin.
In summarizing, the results indicated that the NRB faces the situation of reduced other forest land in exchange for the development of other land-use types in the future. In other words, frequent future human activities in the study area will challenge the balance between ecological and environmental protection and economic and social development.
3.3. Impacts of Climate Change and LUCC on Streamflow from 1990 to 2015
3.3.1. Contributions of Climate Change and LUCC to Streamflow Change
To obtain the relative contributions of human activities and climate change to streamflow change in the NRB, Q0 was used as the reference period, and the dry and rainy season streamflow and annual streamflow change corresponding to Q1, Q2, and Q3 were calculated, respectively (Table 3).

Table 3.
Streamflow response to climate change and LUCC in Nandu River Basin in the years 1990 and 2015.
It can be concluded that the relative contributions of climate variables and LUCC to NRB streamflow change from 1990 to 2015 were 97.57% and 2.43%, respectively. This indicated that climate variables dictated most of the streamflow change with precipitation and temperature as the most important climate variables, which contribute 92.66% and 4.91%, respectively. Compared with Q0, streamflow in Q3 decreased by 26.54%, of which streamflow in the dry season decreased by 11.99%, and in the rainy season, it decreased by 30.27%. That is, the significant streamflow decrease in the rainy season was the main cause for the overall decreasing annual streamflow. Compared with Q0, Q1 induced an increase in annual streamflow by 0.17%, which shows that the impact of human activities on the underlying surface had a weak regulatory effect. Comparing several scenarios, climate change dominated streamflow change.
3.3.2. Impact of LUCC on Hydrological Processes
The changes in hydrological components caused by LUCC from 1990 to 2015 in the basin were as follows (Table S2): Potential evapotranspiration (PET) revealed the greatest increase from 1990 to 2015, followed by evapotranspiration (ET) and shallow percolation, while return flow, shallow water storage, and deep aquifer recharge increased only slightly. However, subsurface flow and surface runoff decreased (Table S2). That is, land-use change led to the intensification of evapotranspiration in the basin, with increases of ET and PET by 28.90 mm and 36.40 mm. At the same time, surface runoff and subsurface flow decreased, while shallow percolation water increased by enhanced return flow and deep aquifer recharge; shallow water storage also increased. Overall, LUCC in the NRB aggravated evapotranspiration, thus reducing surface runoff and subsurface flow, which led to a decrease in streamflow from 1990 to 2015.
The main source of streamflow in the NRB was base flow, and the average runoff coefficient (the ratio of streamflow to precipitation) was 0.60 (Table S3). Compared with 1990, the base flow index was greater in 2015, but the runoff coefficient decreased, that is, the amount of precipitation converted into surface runoff has decreased significantly. Due to the increase of ET, the drying index also increased, but a change of the deep recharge was not obvious. In conclusion, the decreased surface runoff and subsurface flow caused by LUCC from 1990 to 2015 led to a decrease in streamflow, while the increase in ET was the main contributor to the decreasing surface runoff.
3.4. Streamflow Response to Future Climate Change and LUCC
3.4.1. Streamflow Response to Future Climate Change
(i) Monthly streamflow response
The average monthly streamflow in the reference period (1995–2014) of the NRB was 219 m3 s−1, so the variations of average monthly streamflow were −5.76–3.60%, −8.74–4.13%, and −18.30–9.84% in the near-term (2021–2040), mid-term (2041–2060), and long-term (2081–2100) period, respectively. According to the annual distribution of streamflow in the basin under future climate scenarios (Figure 7), the streamflow changes in the 21st century were mainly concentrated in the months from May to October, with the highest streamflow changes occurring from September to October. The streamflow changes in the long-term period (2081–2100) climate scenarios were greater than those in the near-term period (2021–2040) and the mid-term period (2041–2060). This indicates that the streamflow changes of Nandu River in the 21st century had typical characteristics of the dry and rainy seasons. With the intensification of precipitation under different climate paths, the variation range of monthly streamflow appeared to be significantly enhanced from May to October.
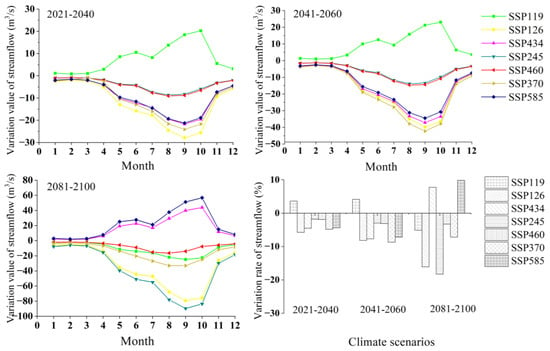
Figure 7.
Monthly streamflow changes in the 21st century under multiple paths of the coupled CMIP6 climate model in Nandu River Basin. The climate scenarios for the seven paths are SSP119, SSP126, SSP434, SSP245, SSP460, SSP370, and SSP585, respectively. The variation of streamflow indicates the rate of average monthly streamflow compared to the reference period (1995–2014).
(ii) Seasonal streamflow response
In different periods of the 21st century, the variation value of streamflow was much higher in the rainy season than in the dry season (Figure 8). The mean streamflows of dry and rainy seasons in the reference period were 76.32 m3 s−1 and 361.78 m3 s−1, respectively. Therefore, the variation range of dry and rainy seasons streamflow in the 21st century was −18.43–10.13%, while the variation of dry and rainy seasons under future climate scenarios was not much different. The increase in streamflow in dry and rainy seasons showed that within the same period and under the same path, the variation of streamflow was generally higher in the rainy season than in the dry season, and the decrease in streamflow was higher in the dry season than in the rainy season, which was basically consistent with the variation trend of precipitation in dry and rainy seasons.
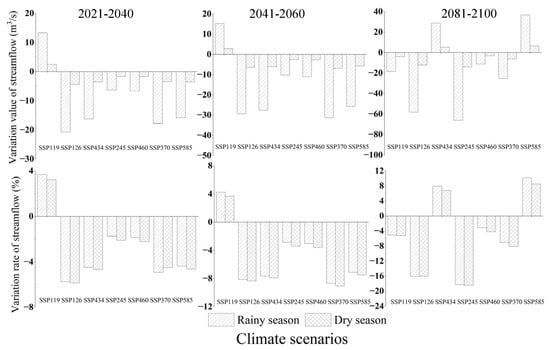
Figure 8.
Streamflow variation during the dry and rainy seasons in the 21st century under multiple paths of the coupled CMIP6 climate model in Nandu River Basin. The climate scenarios for the seven paths are SSP119, SSP126, SSP434, SSP245, SSP460, SSP370, and SSP585, respectively.
Under the SSP245 path from 2081–2100, the variation of streamflow was highest in the dry season, decreasing by 18.43% compared to the reference period and decreasing by 18.28% in the rainy season compared to the reference period. Under the SSP585 from 2081–2100, the increase rate of streamflow was highest in the rainy season (10.13%), followed by the dry season (8.5%). That is, the scenario with the highest variation of streamflow occurred in the late 21st century.
(iii) Annual streamflow response
Under the comprehensive influence of precipitation and temperature, the average annual streamflow variation ranged from −12.67 to 7.92 m3 s−1, −19.24 to 9.10 m3 s−1, and −40.28 to 21.66 m3 s−1 under the seven paths in the near-, mid- and long-term periods of the 21st century (Figure 9). The annual average streamflow in the reference period was 220.13 m3 s−1, so the variation of streamflow in the NRB in the near-term period (2021–2040) and the mid-term period (2041–2060) was −8.74–4.13%, and the range of streamflow change rate was increased to −16.09–9.84% in the long-term period (2081–2100) due to climate change. From 2081–2100, the annual streamflow of SSP245 decreased the most (18.30%), but from 2021–2040, the annual streamflow of SSP245 decreased the least (1.81%). From 2081–2100, SSP585 revealed the largest annual streamflow increase (9.84%), and from 2021–2040, SSP119 was the lowest (3.60%). In conclusion, the streamflow change in the NRB under future climate scenarios was relatively small in the near-term period (2021–2040) and relatively high in the long-term period (2081–2100).
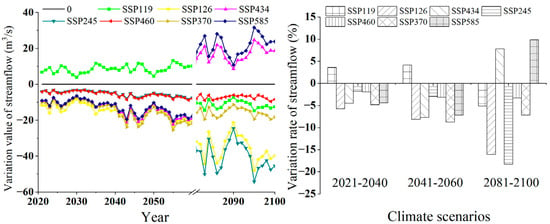
Figure 9.
Annual streamflow changes in the 21st century under multiple paths of the coupled CMIP6 climate model in Nandu River Basin. The climate scenarios for the seven paths are SSP119, SSP126, SSP434, SSP245, SSP460, SSP370, and SSP585, respectively.
3.4.2. Hydrological Processes Responding to Future LUCC
Compared with LUCC 2015, the hydrological components were, in the order of the greatest decrease in the LUCC 2040 scenario (Table S4), as follows: PET showed the largest decrease, followed by subsurface flow, then ET and shallow water storage. Components of greatest increase were shallow percolation water, followed by the return flow and surface runoff, as well as deep aquifer recharge, while the changes of shallow water storage and deep aquifer recharge were very small. This indicated that evapotranspiration and subsurface flow in the basin would be expected to be reduced in the future due to LUCC, while shallow percolation water and surface runoff could be expected to increase in relative terms. The decrease in ET slightly increased the surface runoff, but the decrease in subsurface flow was greater than the increase in surface runoff, leading to decreasing streamflow. The subsurface flow decreasing by 64.89% indicates that the reduction of subsurface flow caused by LUCC, especially the conversion of other forest land to other land-use types, could be expected as the main reason for decreasing streamflow in the future.
As shown in Table S5, the main source of future streamflow was base flow. Precipitation conditions remained unchanged; with reduced ET, the drying index decreased, and changes in deep recharge were not obvious. Thus, the runoff coefficient increased simultaneously, and the base flow index decreased from 2015 to 2040. That is, the amount of precipitation being converted into surface runoff increased. In conclusion, the decrease of subsurface flow caused by the degradation of potential LUCC, especially regarding other forest land, was identified as the main reason for the decreasing NRB streamflow from 2015 to 2040.
3.4.3. Streamflow Response to Combined Future Climate Change and LUCC
The future streamflow was predicted under climate scenarios from 2021 to 2040 and LUCC 2040 scenarios in the NRB, with 1995–2014 as the reference period. Under the combined influence of future climate change and LUCC, the average annual streamflow variation ranged from −13.56 m3 s−1 to 7.06 m3 s−1 under the seven paths in the near-term period (2021–2040) (Figure 10). The average annual streamflow in the reference period was 220.13 m3 s−1, and the variation of streamflow in the NRB in the near-term period (2021–2040) was −6.16–3.21%. In the future scenario, the average annual streamflow in the study area was reduced in all seven paths, except for SSP119; SSP126 revealed the largest reduction of the average annual streamflow (−6.16%). Streamflow change in the basin was dominated by precipitation change, and when precipitation change was positive, streamflow increased, and vice versa; for precipitation change being negative, streamflow decreased. In conclusion, the average annual streamflow in the NRB would generally decrease under future LUCC and climate scenarios.
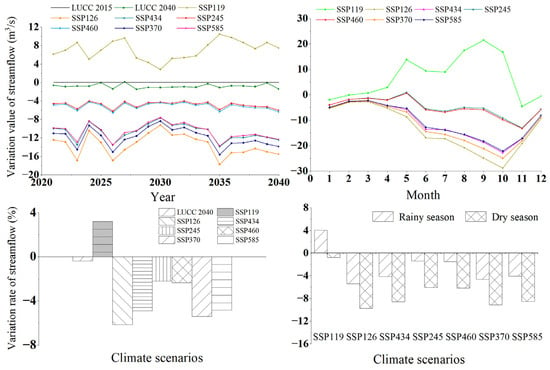
Figure 10.
Streamflow variation in the LUCC 2040 scenarios under multiple paths of the coupled CMIP6 climate model in Nandu River Basin. The climate scenarios for the seven paths are SSP119, SSP126, SSP434, SSP245, SSP460, SSP370, and SSP585. LUCC 2015 is the reference period, which represents the actual land-use scenario in 2015 in the NRB. LUCC 2040 represents the simulated land-use scenario in 2040 in the NRB.
The average streamflows of the dry and rainy seasons in the reference period were 76.32 m3 s−1 and 361.78 m3 s−1, respectively. The variation range of dry and rainy season streamflow in the NRB caused by climate change and LUCC in the near-term 21st century was −9.76–4.04%. In the near-term period (2021–2040), only the SSP119 path increased by 4.04% in the rainy season and decreased by 0.79% in the dry season. The other six paths decreased both in the dry and rainy seasons. The variation value of streamflow under the same path showed a significant decrease in the rainy season, but the variation of streamflow was higher in the dry season than in the rainy season. The results indicated that the streamflow in the NRB showed a decreasing trend in the dry and rainy seasons in the near-term period (2021–2040), which was consistent with the trend of precipitation in future climate scenarios. Therefore, no matter the annual scale or monthly scale, the water resources in the NRB are expected to be more scarce in the future. Therefore, timely measures are required to be available in order to guide the planning to ration and sustainably utilize the land resources, which actively respond to the challenges that climate change will bring to the regional water environment.
4. Discussion
Climate change and land-use cover change (LUCC) are the main driving factors of streamflow. Hydrological processes and their responses in a basin can be described realistically by coupling multiple models. Thus, hydrological responses to future climate change and potential land-use change in this study were predicted by combining the SWAT model with the global climate model data in the CMIP6 and with land-use change scenarios modeled by CA–Markov. There might be uncertainty in the simulation results of the SWAT model due to its complex structure and the large number of input parameters, which requires model uncertainty analysis to be the subject of future studies. Although the results differ from those of a similar Indian humid tropical basin, both studies found the effects of LUCC and climate change on hydrological elements, with climate change dominating the runoff change response [].
The LUCC 1990 and LUCC 2015 data were used to predict LUCC 2040, showing that the future land-use changes were relatively small. The potential land-use-type changes reflected by LUCC 2040 were consistent with the actual situation because the changes in land-use development were relatively stable for a long time, so the layout of the various types of land use did not change dramatically. Furthermore, the spatial scale was also relatively stable, as was the change in land-use type area, which is according to the development mode and the characteristics of each type. Overall, the change in land-use distribution during the time scale considered was reasonable. The inputs of DEM, slope, distance to railway, expressway, and highway measurements, which were used to restrict land-use development in the CA–Markov model, were based on actual landform conditions and human activity factors in the basin. However, these inputs were still uncertain, and they affected the resulting quantitative spatial distribution of future LUCC. Due to the background of ecological and environmental protection in Hainan Island, the actual land-use types in the basin, such as rubber plantation, exist in specific protected areas due to the influence of policy planning. How to restrict specific areas in the model to achieve a more accurate LUCC prediction is a problem that requires a solution. In recent years, LUCC prediction models have been newly developed, such as the coupled FLUS and the Markov–ANN models, which also support the potential LUCC data of the basin and also reduce the uncertainty of the input land-use data [,,].
The prediction of precipitation and temperature is necessary when evaluating the future impact of climate change on hydrology and water resources of a basin. Different climate scenarios will reveal obvious variability of the hydrological simulation results. The current climate scenarios selected in this study were the predicted future scenarios in tropical regions. For a specific watershed, the corresponding small-scale climate scenarios can reduce the input uncertainty of the model, which remains a challenge for subsequent work in future studies. It can depend on downscale climate scenario data or make future climate predictions combined with ground station assimilation data and compare the period of dry and rainy seasons to more accurately simulate the streamflow change characteristics of future climate scenarios at a watershed scale, in order to develop coping strategies for the NRB in Hainan Island. Although there are still uncertainties, specific scenarios can support decision-makers in identifying possible outcomes of climate change to runoff in the future, including their uncertainties. The HyCoX methodology uses the statistic as the objective function in the calibration process rather than the time series (i.e., flow statistics instead of time series), while the hydrological models are calibrated by maximizing the probability of the observed high-flow extremes []. Based on this target-oriented calibration, it can be applied to various hydrological scenarios and modeling methods in the future, which can achieve more accurate simulations of extreme runoff, and better consider the simulation of LUCC scenarios, such as to reduce the uncertainty of the simulation.
According to the response of streamflow to land-use changes in the NRB of Hainan Island, other forest land had a moderating effect on streamflow. Thus, a decrease of the other forest land area was not conducive to improve water and soil conservation in the study area, which is consistent with previous studies [,]. Under future LUCC scenarios in the NRB, conversion of the other forest land to rubber plantation also would have a certain interception effect, while conversion to cultivated land would have a streamflow increase effect. Although the change of the water yield caused by land-use change was relatively small, the results showed that the major trend where other forest land was exchanged for different land-use types, which would reduce the streamflow. With the current situation of rapid population growth, climate change and economic growth in the basin, as well as the water environment, will become more complex, and extreme events such as drought and flooding have become more frequent [,,]. Therefore, the proper management of other forest land and rubber plantation areas is an effective way to improve the ecosystem service function and provide a rational allocation of water resources in the NRB. Optimizing the structure of land and improving regional microclimate will help to reduce the negative effects of climate change on water resources by improving basin streamflow and the ecological environment, and also to ensure sustainable management of water resources and of the natural ecological system.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the SWAT model was used to evaluate the potential impact of both future climate change and land-use cover change (LUCC) on streamflow in the NRB of Hainan Island, China, and the following conclusions were drawn:
(1) The contribution of changing climate variables on streamflow change was much higher than that of LUCC, with contributions of 97.57% and 2.43%, respectively. Precipitation and temperature were the most important climate variables, contributing 92.66% and 4.91% to streamflow change.
(2) LUCC led to an increase of evapotranspiration and, subsequently, a decrease of surface runoff and subsurface flow in the basin. The decrease of surface runoff directly caused the reduction of streamflow, while the decrease of subsurface flow predominated the reduction of streamflow in future LUCC scenarios.
(3) Annual streamflow change under the climate scenarios was relatively small in the near-term period (2021–2040) and relatively high in the long-term period (2081–2100). The monthly streamflow showed obvious differences between dry and rainy seasons, and the streamflow was highest from September to October. The variation range of streamflow was obviously enhanced with the increasing precipitation intensity in rainy season.
(4) Under the combined influence of LUCC 2040 and climate change in the near-term period (2021–2040), the annual streamflow in the NRB showed a decreasing trend in all paths except for SSP119; it decreased most (−6.16%) in SSP126, and the streamflow increased in the SSP119 path only in the rainy season.
Therefore, whether at an annual or monthly scale, the streamflow of the NRB is expected to decrease in the near-term period (2021–2040) under the joint influence of both land use and climate change. Water resources in the basin are expected to become scarcer in the future, and the demand for water will become more severe. Therefore, measures should be developed leading to a plan of optimally utilizing the land resources on a suitable time scale in order to cope with the challenges lying ahead, which the regional water environment is confronted with, induced by climate change.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su151813941/s1, Table S1. Parameter information and fitted values. Table S2. Changes in hydrological components due to LUCC in the Nandu River Basin from 1990 to 2015. Table S3. Proportion of hydrological components in Nandu River Basin in the years 1990 and 2015. Table S4. Changes in hydrological components due to Future LUCC in Nandu River Basin. Table S5. Proportion of hydrological components in Nandu River Basin in the years 2015 and 2040.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S. and C.C.; methodology, C.C. and R.S.; software, C.C.; validation, C.C., R.S. and K.F.; formal analysis, Z.W. and Q.L.; investigation, C.C., R.S., B.C. and C.Y.; resources, B.C.; data curation, C.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C.; writing—review and editing, R.S. and K.F.; visualization, C.C.; supervision, R.S. and Q.L.; project administration, R.S.; funding acquisition, R.S. and Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences [1630022022003]; the High-level Talent Project of Hainan Basic and Applied Basic Research Program (Natural Science) [2019RC335], and the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System [CARS-33-ZP3].
Data Availability Statement
The DEM data were downloaded from the website of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (http://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/ (29 March 2023)). The land use/cover data were extracted based on Landsat images, and the detail was available in a previous study (Sun et al., 2020) [,]. The soil type data were derived from the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/ (19 June 2023)). The soil attribute data were searched from a book named “Soil Species of China: Volume Ⅲ” completed by the National Soil Survey Office of China (National Soil Survey Office, 1994) []. The meteorological data were obtained from the China Meteorological Data Service Centre (http://data.cma.cn/ (19 June 2023)). The hydrological data can be accessed in the Hainan Hydrologic Statistical Yearbook from the Hainan Provincial Water Department (http://swt.hainan.gov.cn/ (19 June 2023)). Due to confidentiality agreements, hydrological data can only be available to researchers. The future climate change datasets under seven paths of the CMIP6 were obtained from a re-analysis of existing data, and the details can be found in a previous study (Lü et al., 2021) [].
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (1630022022003), the High-level Talent Project of Hainan Basic and Applied Basic Research Program (Natural Science) (2019RC335), and the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-33-ZP3). We also want to express our gratitude to three anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ji, L.; Duan, K. What is the main driving force of hydrological cycle variations in the semiarid and semi-humid Weihe River Basin, China? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, I.; Mujumdar, P.P. Isolating the impacts of land use and climate change on streamflow. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 12, 2201–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Song, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Wei, B.; Zhao, S. Coupled effects of land use and climate change on water supply in SSP-RCP scenarios: A case study of the Ganjiang river Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Mo, C.; Yang, Q. Evaluation and hydrological impact of land-use changes in the Longtan basin. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyrani, F.; Morid, S.; Srinivasan, R. Assessing basin blue–green available water components under different management and climate scenarios using SWAT. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, P.A.; Lima, D.C.A.; Soares, P.M.M.; Cardoso, R.M.; Medas, D.; Dore, E.; Giudici, G.D. Future precipitation in a Mediterranean island and streamflow changes for a small basin using EURO-CORDEX regional climate simulations and the SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chang, J.; Yu, Y. Runoff response to changing environment in Loess Plateau, China: Implications of the influence of climate, land use/land cover, and water withdrawal changes. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Ding, A.; Wei, Y. Changes in the hydrological and sediment regimes of two neighboring catchments in the past sixty years. Catena 2023, 230, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, H. The runoff evolution and the differences analysis of the causes of runoff change in different regions: A case of the Weihe river basin, Northern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment; Part I, Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleguillos, M.; Gimeno, F.; Puelma, C.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Lara, A.; Rojas, M. Disentangling the effect of future land use strategies and climate change on streamflow in a Mediterranean catchment dominated by tree plantations. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.K.; Khare, D.; Kawasaki, A.; Meshesha, T.W. Integrated approach to simulate hydrological responses to land use dynamics and climate change scenarios employing scoring method in upper Narmada basin, India. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delia, K.A.; Haney, C.R.; Dyer, J.L.; Paul, V.G. Spatial analysis of a Chesapeake Bay sub-watershed: How land use and precipitation patterns impact water quality in the James River. Water 2021, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.G.; Dias, R.L.S.; Castro, J.D.S.; Santos, V.J.D.; Calijuri, M.L.; da Silva, D.D. Performance of hydrological models in fluvial flow simulation. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 66, 101453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busico, G.; Colombani, N.; Fronzi, D.; Pellegrini, M.; Tazioli, A.; Mastrocicco, M. Evaluating SWAT model performance, considering different soils data input, to quantify actual and future runoff susceptibility in a highly urbanized basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Meshesha, T.W.; Sen, I.S.; Bol, R.; Bogena, H.; Wang, J. Assessing Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Change on Stream Flow and Runoff in Rur Basin, Germany. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindy, B.M.; Ronal, S.P.; Dayam, C.R.; Angela, J.L.; Duvan, M.F. Spatio-temporal analysis of the hydrological response to land cover changes in the sub-basin of the Chicú river, Colombia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e7358. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Wang, C.; Eguchi, S.; Kuramochi, K.; Kohyama, K.; Yoshikawa, S.; Itahashi, S.; Igura, M.; Ohkoshi, S.; Hatano, R. Response of hydrological processes to climate and land use changes in Hiso River watershed, Fukushima, Japan. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2021, 123, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, O.; Maasikamäe, S.; Padari, A.; Tamm, T. Modelling the effects of land use and climate change on the water resources in the eastern Baltic Sea region using the SWAT model. Catena 2018, 167, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, C.R. Quantitative study on the impact of different land use patterns on ecohydrology in Aksu Region, Xinjiang. Ground Water 2020, 42, 123–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.P.; Zhang, F.E.; Geng, X.X.; Wang, W.; Ji, J.J. Hydrological response to land use changes in typical karst basin. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2021, 4, 45–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.L.; Zhang, M.; Leslie, L.M.; Yu, Q. Using an improved SWAT model to simulate hydrological responses to land use change: A case study of a catchment in tropical Australia. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, J.; Chen, X.; Li, L.J.; Wang, D.S. Effects of land use change on runoff in Yunlong Reservoir Basin. J. Guizhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2021, 38, 33–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, M.Z.; Li, H.W.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Q. Hydrological response simulation research of Dapoling Basin considering land use type. Water Resour. Power 2021, 39, 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chiarelli, D.D.; Passera, C.; Rulli, M.C.; Rosa, L.; Ciraolo, G.; D’Odorico, P. Hydrological consequences of natural rubber plantations in Southeast Asia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ye, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zou, Y. Impact from land use/land cover change on function of water yield service: A case study on National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2022, 53, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Xu, W.; Ye, C. Quantifying the impact of climate change and human activities on runoff at a tropical watershed in South China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githui, F.; Gitau, W.; Mutua, F.; Bauwens, W. Climate change impact on SWAT simulated streamflow in western Kenya. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, G.; Lienou, G.; Descroix, L.; Bamba, F.; Paturel, J.E.; Laraque, A.; Meddi, M.; Habaieb, H.; Adeaga, O.; Dieulin, C.; et al. The rivers of Africa: Witness of climate change and human impact on the environment. Hydrol. Process 2013, 27, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ndehedehe, C.E.; Farah, H.; Ahmad, B.; Wong, Y.; Adeyeri, O.E. Application of a conceptual Hydrological Model for Streamflow Prediction Using Multi-Source Precipitation Products in a Semi-Arid River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Gassman, P.W.; Liang, J.; Haywood, J.M. A review of alternative climate products for SWAT modelling: Sources, assessment and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Quiring, S.M.; Kalcic, M.M.; Apostel, A.M.; Evenson, G.R.; Kujawa, H.A. Optimizing climate model selection for hydrological modeling: A case study in the Maumee River basin using the SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fang, H. Assessment of climate change impacts on the streamflow for the Mun River in the Mekong Basin, Southeast Asia: Using SWAT model. Catena 2021, 201, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Sattar, H.; Khattak, M.S.; Wang, G.; Babur, M. Evaluation of adaptation options for reducing soil erosion due to climate change in the Swat River Basin of Pakistan. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, X.G.; Jin, J.L.; Bao, Z.X.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, G.X. Runoff simulation and prediction under climate change above Lazi Station in upstream of Yarlung Zangbo River. J. Chin. Hydrol. 2018, 38, 24–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.J.; Dong, X.H.; Zeng, Q.; Wei, C.; Yu, D.; Bo, H.J.; Guo, J. Long-term runoff change trend of Yalong River basin under future climate change scenarios. Clim. Chang. Res. 2019, 15, 596–606. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Fang, G.; Xu, Y.-P.; Tian, X.; Xie, J. Responses of hydropower generation and sustainability to changes in reservoir policy, climate and land use under uncertainty: A case study of Xinanjiang Reservoir in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 124609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Meng, J.L.; Guo, H.L.; Tian, Z.H. Effect of land use and climate change on runoff in Luohe River Basin. Water Resour. Power 2021, 39, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.R.; Chen, Z.Z.; Chen, X.H.; Li, Y.L.; Wu, T.T. Spatio-temporal changes of land use and ecosystem services value in Hainan Island from 1980 to 2018. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 4760–4773. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.B. Estimation of available quantity of water resources in Hainan Island. Water Resour. Informatiz. 2019, 6, 38–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.Y.; Kou, W.L.; Chen, B.Q.; Wu, Z.X.; Zhang, X.C.; Yung, T.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal changes of rubber plantations in Hainan Island over the past 30 years. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 47, 189–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.W.; Ji, Y.T.; Zhu, L.R.; Ye, C.Q. Analysis of water level—Discharge relationship variation of Longtang Station in Nandu River and its influential factors. Pearl River 2018, 39, 37–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Sun, R.; Wu, Z.X.; Li, Q. Responses of streamflow to climate change in upstream of Nandujiang River Basin based on SWAT model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 255–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Paul, M.; Negahban-Azar, M.; Shirmohammadi, A. Assessing crop water productivity under different irrigation scenarios in the Mid–Atlantic Region. Water 2021, 13, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Song, J.; Fu, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lyu, S.; Qi, S.; et al. Long-term baseflow responses to projected climate change in the Weihe River Basin, Loess Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Soil Survey Office. Soil Species of China: Volume III; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 122–159. (In Chinese)
- Sun, R.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, C.; Qi, D.; Lan, G.; Fraedrich, K. Effects of land-use change on eco-environmental quality in Hainan Island, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Chen, B.Q.; Wu, Z.X.; Lan, G.Y.; Qi, D.L.; Tao, Z.L.; Yang, C. Assessment of Eco-environmental Quality in Hainan Island Based on Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager Data. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2017, 38, 1587–1594. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Teshager, A.D.; Gassman, P.W.; Secchi, S.; Schoof, J.T.; Misgna, G. Modeling agricultural watersheds with the soil and water assessment tool (SWAT): Calibration and validation with a novel procedure for spatially explicit HRUs. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 894–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Deng, G.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, X.; Ma, J.; Cen, G.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of climate change and land-use changes on spatiotemporal distributions of blue water and green water in Ningxia, Northwest China. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhang, L.; Su, B.; Tao, H.; Jiang, T. Projections of precipitation over China based on CMIP6 models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 35, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Huang, J.; Tao, H. Simulation and projection of climate change using CMIP6 Muti-models in the Belt and Road Region. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2021, 12, 389–403. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Li, H.; Ai, N.; Huang, T.; Gu, J.S. Predicting spatiotemporal changes in land use and habitat quality based on CA-Markov: A case study in central Ningxia, China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 1969–1978. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; He, F.; Xiong, Y.J.; Qiu, G.Y. Effects of land use/land cover and climate changes on surface runoff in a semi-humid and semi-arid transition zone in northwest China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Chen, X. Evaluation of impacts of climate change and human activities on streamflow in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2562–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Jia, Y.W.; Wang, H. A new method to quantitatively separate the effects of multi-factors on the water cycle evolution. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 45, 658–665. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sadhwani, K.; Eldho, T.I.; Karmakar, S. Investigating the infuence of future landuse and climate change on hydrological regime of a humid tropical river basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.H.; Zhao, K. Advance in the impacts of watershed land use/cover change on hydrological processes. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 20, 301–308. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; He, P.; Yang, L.; He, X.; Lu, S.; Liu, D. Predicting future urban waterlogging-prone areas by coupling the maximum entropy and FLUS model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, C. Land use/land cover prediction and analysis of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under different scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majone, B.; Avesani, D.; Zulian, P.; Fiori, A.; Bellin, A. Analysis of high streamflow extremes in climate change studies: How do we calibrate hydrological models? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3863–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, M.; Dandpat, A.K.; Naik, B. Hydrological modeling with respect to impact of land-use and land-cover change on the runoff dynamics in Budhabalanga river basing using ArcGIS and SWAT model. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tola, S.Y.; Shetty, A. Land cover change and its implication to hydrological regimes and soil erosion in Awash River basin, Ethiopia: A systematic review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gan, R.; Feng, D.; Yang, F.; Zuo, Q. Quantifying the contribution of SWAT modeling and CMIP6 inputting to streamflow prediction uncertainty under climate change. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, M. Determining relative contributions of climate change and multiple human activities to runoff and sediment reduction in the eastern Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2023, 232, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Ni, F.; Deng, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhou, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, M.; Jiang, N.; Yue, Z. Spatiotemporal dynamics of blue and green water resources in a mountainous watershed: A case study of the Wujiang River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 48, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).