Abstract
Traditional hard-grade asphalts for high-modulus asphalt concrete (HMAC) are produced by using natural hard-grade asphalt to modify matrix asphalts. However, natural hard-grade asphalts are scarce and expensive. To find a sustainable alternative, this study presented a method to synthesize hard-grade asphalts using phenol formaldehyde resin (PFR), hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) and matrix asphalts. Infrared radiation (IR) spectra analysis and fraction analysis for the modifiers and synthesize asphalts show that asphalt molecules can be cross-linked into larger polymeric groups by the thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin (TPFR) which is the reaction product of PFR and HMTA. This process increased the asphaltene and resin fraction in asphalt, thus transforming a matrix asphalt into hard grade. With the dosing combinations of 4% PFR/15~20% HMTA, 6% PFR/8~10% HMTA and 8% PFR/5~5.7% HMTA, dynamic modules of HMAC were 14,000~16,000 MPa, which satisfied the basic application requirements for HMAC. The rutting resistance of the new hard-grade asphalts with the above dosage combinations completely exceeds the traditional product using the Trinidad Lake asphalt as the raw material. Increasing the amount of PFR/HMTA can further improve the rutting resistance. However, to ensure the fatigue and cracking resistance of the HMAC can get a level like the traditional product, the dosages of HMTA should be controlled below 15%.
1. Introduction
High-modulus asphalt concrete (HMAC) originated in France in the 1980s and is now widely used around the world, which contributes to its excellent durability and low maintenance costs [1]. The original HMAC characteristic was that its dynamic modulus should exceed 11,000 MPa. This minimum was later increased to 14,000 MPa and was standardized in the first edition of the French standard for HMAC, NF P98-140, published in 1999 [2]. Meanwhile, this standard also specified that the fatigue parameter of the HMAC mixture should be above 130 to control the fatigue resistance of HMAC [3]. These two parameters have been introduced by most countries as the basic performance requirements for the development of HMAC in their countries [4].
To achieve the above two performance requirements of HMAC, using hard-grade asphalt as a binder is necessary. The hard-grade asphalt characterized by a low penetration, a high complex modulus and a high softening point compared with that common matrix asphalt. Early hard-grade asphalts used for HMAC were produced by using natural hard-grade asphalts modified the matrix asphalts [5]. These natural hard-grade asphalts include the lake asphalt produced in Trinidad Lake, the rock asphalt produced in Spain and Italy, and some produced by direct distillation from heavy crudes imported from Central America, etc. [6]. However, the small global reserves of natural hard-grade asphalt, combined with high mining and transportation costs, and the wide variation in product properties between different origins, make it difficult to support large-scale road construction projects [7]. In the 1970s, with the popularization of the vacuum distillation process, it has become possible to refine hard-grade asphalts with stable properties from common oil sources. Currently, France is the world’s largest producer of hard-grade asphalt, with an annual production of about 100,000 tons of the product of grades 10/20 and 15/25 in 2019 [1]. Currently, China shows great interest in high-modulus concrete and has paved several test roads using HMAC in various climatic zones across the country [8,9]. Due to the huge application demand, the market forecast for hard-grade asphalt as the binders for HMAC in China is well over 100,000 tons per year [10]. It is clear that the current capacity of hard-grade asphalt is difficult to meet the future expectations of the Chinese market. Natural hard-grade asphalt is a non-renewable resource like oil. However, the scale of natural hard-grade asphalt reserves in China is very small [7]. It is mostly rock asphalt stored in the southwest Sichuan basin, which is difficult to mine. In addition, Chinese natural hard asphalt has a higher wax content compared to Trinidad Lake asphalt, which severely impairs the low-temperature crack resistance of the asphalt. The cost of removing these waxes is extremely high. In addition, Shen reported that the wax content of natural hard asphalt in China is higher compared to that of Trinidad Lake asphalt, which severely impairs the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt [11,12]. The cost of wax removal is extremely high [13].
To find a sustainable supply of hard-grade asphalt, many Chinese research focused on alternatives to hard-grade asphalt in recent years [14,15,16,17]. Chen et al. summarized the characteristics of natural hard-grade asphalt from Buton Island, Indonesia, Albania, Lake Trinidad, Utah, USA and Sichuan, China, where the differences between them were significant and the latter two performed very poorly in terms of low-temperature crack resistance [4]. In order to cope with the variety of natural hard-grade asphalt properties from different origins, using polymer modifiers to prepare hard-grade modified asphalt is a common practice at present. Zhang et al. synthesized a novel high-modulus agent with natural rock asphalt, nanopolymer material and a stabilizer [18]. Zhu et al. prepared HMAC using reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) [9]. Wu et al. evaluated the long-term service performance of HMACs which used multiple types of hard-grade asphalts as binders based on the accelerated loading test [5]. Yan et al. characterized and compared the performance of seven types of hard-grade asphalt, including rubberized asphalt, SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) modified asphalt, SBS + Lake bitumen modified asphalt, SBS + rock bitumen modified asphalt, SBS + polyester fiber modified asphalt, SBS + PR.M.(a commercial HMAC additive from France) and common 50# hard-grade asphalts [8]. Al-Humeidawi et al. submitted using Novolac polymer (Phenol formaldehyde solid resin, cross-linking agent Hexamethylenetetramine and crumb rubber to prepare the hard-grade modified, and investigated its modification mechanism and rutting resistance [19]. In the study of Al-Humeidawi, the optimum ratios of three additives were determined by the penetration softening point, and ductility test for the modified asphalt, this work provides an important reference for this study. However, their studies only focused on the effects of these modifiers on the performance of asphalt layers and lacked investigations on the effects of these modifiers on asphalt mixtures. Actually, most of the similar studies about the modified or synthetic hard-graded asphalts only focused on whether the dynamic modulus and rutting resistance of HMAC can reach the desired threshold, but they ignored the possible adverse effects of these modification efforts on other properties (such as the low-temperature crack resistance and fatigue resistance) of the asphalt [20,21].
In this study, a hard-grade asphalt was prepared by phenol formaldehyde resin (PFR), hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) and matrix asphalts. Compared with previous studies, this study not only investigated the mechanism of modification and the dynamic modulus of the HMAC using this synthetic hard-grade asphalt as a binder, but also systematically analyzed the effect of PFR and HMTA dosing on the rutting resistance, fatigue resistance and low-temperature crack resistance of the HMAC. The results of this study may provide a sustainable solution to the shortage and inconsistent performance of hard-grade asphalt used in HMAC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modifiers of PFR and HMTA
The PFR and HMTA were used to be the modifier to produce hard-grade asphalt based on recycled asphalt in this study. The molecular formula of PFR is with CAS No: 9003-35-4, categorized as phenol and formaldehyde and the role of solid products. It is a thermoplastic phenolic solid resin and only melts when heated at about 145~155 and cannot be changed to an insoluble and infusible state [22]. HMTA is a curing agent for PFR and the molecular formula is with CAS No: 100-97-0. After the addition of HMTA, PFR can be converted into thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin (TPFR), in the amount of phenol (molar) more than the amount of aldehyde (molar) and acidic catalyst conditions. Reactions that take place in this process are shown in Figure 1.
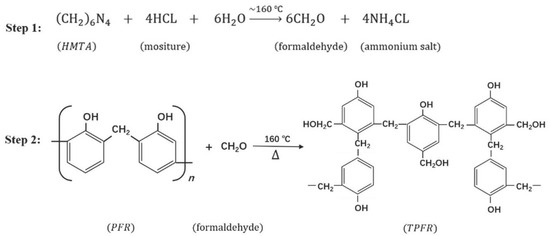
Figure 1.
Reactions in the process added HMTA into PFR at acidic catalyst conditions.
In the curing reaction for PFR (Step 2 in Figure 1), multiple PFR molecular fragments are cross-linked to become TRFP [23]. The TPFR changes to an insoluble and infusible state after being heated, and it is acid-resistant, alkali-resistant and heat-resistant. More importantly, TPFR has more reactivity to interact with polar components in asphalt and consequently increases the physical interaction between asphalt molecules. Acidic groups (-COOH) can be most likely functional groups that react with TPFR. Thus, while modifying asphalt with TPFR, Pyshyev et al. [22] assumed the reaction as shown in Figure 2.
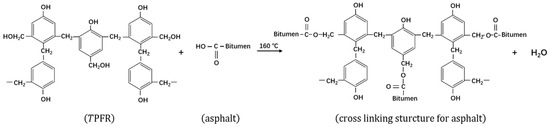
Figure 2.
Asphalt molecular cross-linked structure by reacting with TPFR according to the assumed of Pyshyev et al. [22].
Through the reaction in Figure 2, asphalt molecules are cross-linked into larger polymeric groups by TPFR. In this process, fraction ratios of asphaltenes and resins rise significantly in asphalt so that the asphalt is hardened. Some of the free PFR molecular fragments are added to the aged asphalt as aromatic fractions and act as regenerating agents. Theoretically, the molecular weight of the asphalt cross-linked structure increases with the amount of PFR and the ratio of HMTA to PFR, while the degree of hardening of the asphalt also increases [22,24].
2.2. Matrix Asphalt and the Control Hard-Grade Asphalt
The raw asphalt used to prepare the synthetic hard-grade asphalts is a PG 70-22 asphalt produced in Sichuan Zhonghai, an oil company in China. A widely used hard-grade asphalt was engaged in all the tests in this study as the control for the synthetic hard-grade asphalts, which were produced by using Trinidad Lake asphalt to modify the matrix asphalt. This control sample is labeled as TLA. TLA is recognized by many HMAC-pavement construction projects in China. The basic properties of the raw asphalt PG 70-22 and the control sample TLA are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic properties of the raw asphalt and the control sample of TLA.
2.3. Preparation Process of PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalt
The preparation process of PFR/HMTA-modified hard-grade asphalt includes five steps, as shown in Figure 3. First, heat the matrix asphalt to about 160 °C, which is slightly higher than the melting point of 150 °C for PFR. Second, transfer the hot matrix asphalt to the high-speed shear mixer and keep it heated. The shear speed is set as 2000 r/min. Third, gradually add the PFR into the matrix asphalt being sheared through the feed port of the high-speed shear to avoid agglomeration in the asphalt. Fourth, gradually add the HMTA and the hydrochloric acid to the matrix asphalt. Finally, continually mix PFR, HMTA and matrix asphalt in a high-speed shear mixer for 1 h to obtain PFR/HMTA synthetic hard asphalt.
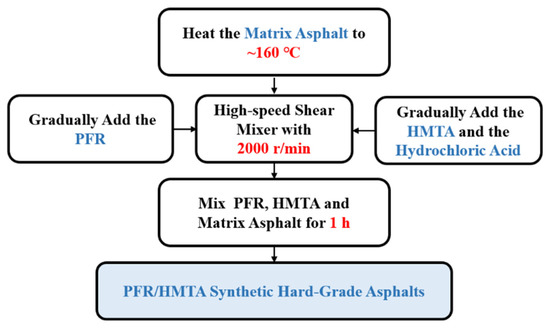
Figure 3.
Preparation Process of PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalt.
It is important to note that the intermediate product formaldehyde, which is classified as a human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), will be produced in the shear mixer during the preparation process. To ensure safety and health, operators should wear protective masks and clothing and pay attention to the ventilation of the test site, as well as to the treatment of exhaust gases.
2.4. Mineral Aggregate Gradation of HMAC
In this study, some experiments were designed for HMAC where the PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalt was used as the binder. The aggregate gradation used for the HMAC in this study was the French EME-14, which was introduced in the French LPC Bituminous Mixtures Design Guide [29]. The aggregates gradation is given in Table 2. The mineral type of the aggregate was basalt.

Table 2.
Aggregate gradation of French EME-14.
2.5. Experiment for Hard-Grade Asphalts
2.5.1. Spectral Measurement
To verify the synthetic process of hard-grade asphalts by PFR/HMTA, the spectral measurement was carried out on the modifier of PFR/HMTA, matrix asphalt and synthetic hard-grade asphalts. Infrared radiation (IR) spectroscopic studies were conducted using attenuated total reflectance (ATR) in Thermo Scientific™ NICOLET™ 6700 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The instrument’s resolution was 2 cm−1. The spectra were recorded in the range 4000–750 cm−1 and represent the averaging of 32 scans collected at intervals of 1 cm−1.
2.5.2. Fraction Analysis
The test of thin-layer chromatography with flame ionization detection (TLC-FID) was performed on hard-grade asphalt samples at various PFR/HMTA additions for evaluating the SARA (saturated, aromatic, resins and asphaltene) fraction changes in the asphalt before and after being modified. TLC-FID is recognized as an efficient, fast and cost-effective method to obtain quantitative information about crude oil composition [23]. In TLC-FID testing, a constructed chromatographic column that leverages the different diffusion heights of the four fractions of the asphalt in a toluene solution is scorched, during which the intensity of the electrons emitted by each fraction at the point of aggregation is recorded and converted into the amount of this fraction [30]. A detailed introduction of the composition of the SARA fraction of asphalt using TLC-FID quantitative analysis can be found in previous studies by our team [31,32].
2.5.3. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test
As the binder for HMAC, hard-grade asphalts should have high-complex modulus and low non-recoverable creep compliances at high temperatures [8]. The complex modulus is easily obtained in the test of high-temperature PG. In this study, the non-recoverable creep compliance of HMAC was measured by the MSCR test, which was conducted following Standard D7405-15 of ASTM. For each hard-grade asphalt sample, two stress levels of 0.1 kPa and 3.2 kPa were set. The parameter that results from the MSCR test is the non-recoverable creep compliance () and stress recovery ratio. The smaller and large stress recovery ratio represents a higher resistance to the permanent deformation of asphalt [33].
2.5.4. Thermal Stress and Critical Cracking Temperature Test
Poor deformability of hard-grade asphalts at low temperatures means that the cumulative rate of temperature stresses is extremely high when the temperature drops suddenly [34]. Although the HMAC was not commonly used in cold regions, it should exhibit a certain low-temperature strength and toughness to cope with possible low-temperature conditions. The effect of PFR/HMTA on the performance of the matrix asphalt is not clear. Therefore the low-temperature stress and critical cracking temperature for all hard-grade asphalt samples were measured by the notched specimen cracking test (NSCT) [35] as a supplementary index for low-temperature performance beyond PG classification. NSCT can simulate the actual thermal contraction state–strain level of asphalt pavement in the laboratory. In the NSCT, a continuous cooling temperature field was applied to a double-edged notched binder specimen in which contraction deformation was limited, and the thermal stress of the specimen can be calculated by measuring the force required to overcome its thermal contraction strain. In this test, the starting temperature of the cooling was set to 10 °C and the cooling rate to 2 °C/h.
2.6. Experiment for High-Modulus Asphalt Concrete
To investigate whether the asphalt concrete using PFR/HMTA hard-grade asphalt can replace the HMAC using traditional natural hard-grade asphalt, four experiments of Dynamic Modulus (DM) Test, Hamburg Rutting Wheel-Tracking Test (HWTT), Three-Point Bending (3 PB) Test and Four-Point Bending Fatigue Test (4 PB) were performed on the PFR/HMTA- HMAC. As the control, the HMAC using the TLA was also tested by these methods.
2.6.1. Dynamic Modulus (DM) Test
To verify whether the asphalt concrete using PFR/HMTA hard-grade asphalts can satisfy the modulus required for high-modulus asphalt concrete and to determine the optimal dosing range of PFR/HMTA modifier, the DM test was performed on the HMAC samples. In this study, the DM test was conducted following Standard T62-03 of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) [36]. The DM test is a stress-controlled test involving the application of a repetitive sinusoidal dynamic compressive-axial load (stress) to an unconfined specimen [37]. In this study, the dimensions of the cylinder HMAC specimen used in DM are 150 in diameter and 170 mm in height. For each sample, the DM test was performed with six replicates at the temperature of 25 °C and a loading frequency of 10 Hz. The parameter that results from the DM test is the dynamic complex modulus, E*, of the HMAC specimen and is expressed as Equation (1) [36].
where is the axial (compressive) stress (MPa), and is the axial (compressive) strain.
2.6.2. Hamburg Rutting Wheel-Tracking Test (HWTT)
Improving rutting resistance through the high-modulus is the main design aim of HMAC. Therefore, HWTT was performed to investigate the anti-rutting performance of HMAC using PFR/HMTA hard-grade asphalt at high temperatures. In this study, the HWTT was conducted following Standard T323 of AASHTO [38]. During the test, two cylindrical HMAC specimens were submerged in a water bath at a constant temperature of 60 ± 2 °C and subjected to a rubber wheel rolled back and forth by 42 cycles/min and at a contact pressure of 0.7 MPa. Dimensions of the cylinder HMAC specimen used in HWTT are 150 mm diameter and 63.5 mm in height. The HWTT pass–fail criteria are based on a maximum rutting depth of 10 mm and the number of loads passes of 20,000, whichever comes first.
2.6.3. Three-Point Bending (3 PB) Test at Low-Temperatures
To investigate the crack resistance at a low temperature of the HMAC using PFC/HMTA hard-grade asphalts, the 3 PB test was conducted for them. The 3 PB test was conducted following the Standard T0715-2011 of the Chinese Standard Test Method of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering (JTG E20-2011). For each sample, this test was performed on three replicates at −10 °C, using a Material Test System (MTS) closed-loop servohydraulic loading system. Dimensions of the prismatic HMAC beam used in a 3 PB test are 250 mm in length, 35 mm in height and 30 mm in width. During the test, the span length of the HMAC specimen is supported at 0.8 of the beam lengths (200 mm). The load transmission occurs with a displacement control system, where the top loading ring descends at a speed of 50 mm/min until the specimen fails. The maximum tensile strain at the bottom edge of the HMAC beam can be calculated using the tension bending beam equation as Equation (2) [39].
where is the height of the mixture beam, 35 mm; is the deflection of the mid-cross section; is the span of the testing fixture, 200 mm.
The schematic diagram of the 3 PB test for the asphalt mixture beam and the relevant parameters in Equation (2) are shown in Figure 4.
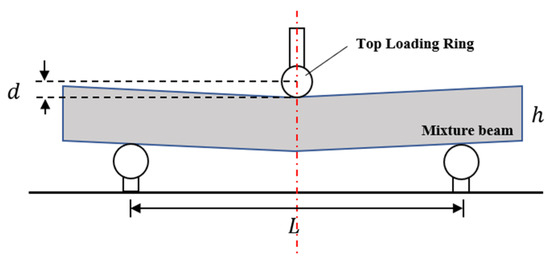
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the 3 PB test for asphalt mixture beam.
2.6.4. Four-Point Bending Fatigue (4 PB) Test
To investigate the fatigue resistance of the HMAC using PFC/HMTA hard-grade asphalts, the 4 PB test was conducted for them. The 4 PB test was conducted following the Standard T321-22 of AASHTO [40]. For each sample, this test was performed on four replicates at 10 °C, using the MTS closed-loop servohydraulic loading system. Dimensions of the prismatic HMAC beam used in a 4 PB test are 380 mm in length, 63.5 mm in height and 50 mm in width. During the test, the displacement at the top surface of the beam specimen is measured using a Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT). Based on the measured displacement, the maximum tensile strain and the stiffness modulus of the specimen are calculated [41]. The cyclic haversine loading waveform with a frequency of 10 Hz is applied during the test. The controlled strain mode is used. When the stiffness modulus of the specimen declines to 50% of the initial stiffness, the test is over and the number of load cycles is defined as fatigue life (). It should be noted that the only is the fatigue life of single mixtures beam. Analyzing the fatigue life for one type of mixture most often evaluates its parameter [42]. The first step for calculating the is regressing the curves using results from multiple replicate tests, as Equation (3) [41].
where is the fatigue life, is the strain during the fatigue test, , is the liner regression parameters and is the inclination of the fatigue line. After obtaining curves, the is the strain when input is 1 million loading cycles. A higher value of means potentially better fatigue properties.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determining Dosages of PFR/HMTA in Hard-Grade Asphalts by DM Tests
Considering the generalized application requirements of HMAC, the minimum value of its dynamic modulus should be greater than 14,000 MPa (at 15 °C and 10 Hz) according to the French standard NF P98-140 for high modulus concrete [43]. Besides, the statistical data of Wang et al. on the actual dynamic modulus of HMAC in existing highway pavements showed that the upper quartile value of this statistical interval was 16,000 MPa [44]. Therefore, dosages of PFR/HMTA are determined based on the following: the dynamic modulus of the HMAC which used PFR/HMTA modified asphalts as binder should be in the range of 14,000~16,000 MPa at 15 °C and 10 Hz.
Combinations of the PFR with four dosages of 2%, 4%, 6% and 8% (by asphalt mass) and the HMTA with four dosages of 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% (by PFR mass) were selected to modify the matrix asphalt. Then, 16 obtained PFR/HMTA-modified asphalt samples were used to prepare the corresponding mixtures. The aggregate gradation used was the EME-14 as listed in Table 2. Then, the dynamic modulus of these PFR/HMTA mixtures was measured by the DM tests. Results of the dynamic modulus of HMAC at various dosage combinations of PFR and HMTA are shown in Figure 5.
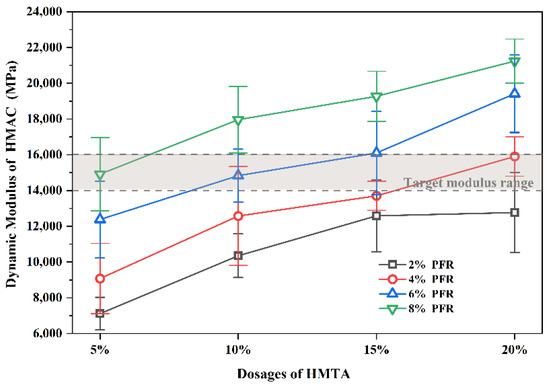
Figure 5.
Effects of dosage combinations of PFR and HMTA on dynamic modulus of HMAC.
Each hollow point in Figure 5 represents the mean of results of six replicate dynamic modulus tests at the same dose combination of PFR and HMTA. Clearly, the dynamic modulus increased with the dosage of PFR and HMTA. However, only mixtures at dosage combinations of 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 4% PFR/20% HMTA, 6% PFR/10% HMTA, 6% PFR/15% HMTA and 8% PFR/5% HMTA satisfied or close to the dynamic modulus requirement of 14,000~16,000 MPa for HMAC. In Al-Humeidawi’s study, the optimal value of additives was 4% PFR by mass of asphalt and 10 % of HMTA by mass of PFR. This dosage combination was determined according to the requirement of penetration, softening point and ductility for hard-grade bitumen in the EME2 design method. Clearly, the dosing range selected in this study deviates slightly from the optimal dosing given by Al-Humeidawi, which is due to the fact that the two were determined based on different benchmarks. The benchmark used in this study was the dynamic modulus of the asphalt mixture, while that used in the Al-Humeidawi’s study was the mandatory requirement for the performance of the asphalt in the current material standard. Of course, the dosing combinations given here are not the optimal combinations recommended in this study, and their effects on asphalt and asphalt mixes are discussed systematically in the subsequent sections.
3.2. FTIR for PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalts
The IR spectra for the modifier 4% PFR + 15% HMTA and asphalt samples of 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 6% PFR/15% HMTA and the matrix asphalt PG70-22 are shown in Figure 6.
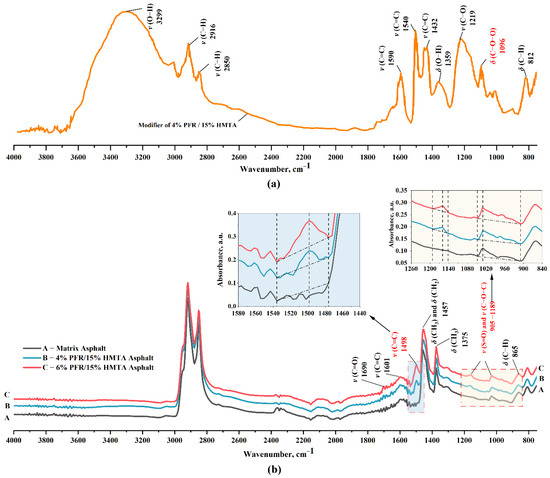
Figure 6.
FT- IR spectra for the modifier of 4%PFR/15%HMTA (a) and synthetic hard-grade asphalts (b).
Typical functional groups in the modifier of 4% PFR + 15% HMTA include phenolic hydroxyl group (), methylene (-CH2-), aroxyl (Ar-O-), methylidyne () and olefinic bond () in the benzene ring. The signal of the ether groups () at 1100 cm−1 indicates that some of the resins are “stitched up”, forming ethers, which verified the curing reaction for PFR in the Step 2 of Figure 1. After adding the modifier PFR/HMTA into the matrix asphalt, the absorption peaks increased at 905 and 1189 cm−1 [45], as shown in the right enlargement in Figure 6b. This is due to the increase in ether groups (). It should be noted here that the absorption peak of overlaps with that of sulfoxide (), so the increase in corresponding absorption peaks is not noticeable in the full-scale plot of the IR spectra for synthetic asphalts. The areas of the absorption peak of (within the signal bands of 1144~1192 cm−1 and 909~1047 cm−1) were calculated by the trapezoidal integration method in MATLAB, and the results are listed in Table 3. When the amount of PFR doping is increased from 4% to 6% (a 1.5-fold increase), the amount of this type of ether group () also increases by a factor of about 1.58. This indicates that the PFR in both samples reacted adequately with HMAT to produce TPFR (recall Figure 1).

Table 3.
Areas under absorption bands of IR spectra.
Another major change in the IR spectra for the asphalt after adding the modifier PFR/HMTA is an absorption peak that occurred at 1498 cm−1, but it cannot be found in the IR spectra for the matrix asphalt. The area of this absorption peak increased with the dosage of PFR/HMTA, as shown in the left enlargement in Figure 6b. This is due to the shift in the absorption of bonds in various aromatic systems—benzene ring for the modifier PFR/HMTA and cross-linking structure for synthetic asphalts [22]. The corresponding absorption peak that occurred in 1478~1536 cm−1 represents the function groups of , the area of which should is related to the amount of aromatic systems (benzene ring) compounds that actually participate in the cross-linked structure of the asphalt. All the aromatic systems (benzene ring) were provided by the PFR, not the HMTA. Therefore, it is possible to verify whether all the PFR added is sufficiently involved in the construction of the cross-linked structure by calculating this peak area. In matrix asphalt, the peak area is 0 (Table 3). When the PFR doping was increased from 4% to 6% (a 1.5-fold increase), the area of this peak also increased by a factor of about 1.54. This indicates that the TPFR under both additive regimens fully participated in the creation of the asphalt cross-linked structure. One conclusion that can be obtained here is the dosages of modifier PFR/HMTA in asphalts can be verified by calculating the areas of ab-309 sorption peaks of the above two function groups (C-O-C and C=C). All of the above results from FTIR test indicate that the matrix asphalt and PFR/HMAT products undergo a condensation reaction, resulting in the formation of a larger molecular weight cross-linked structure. This is quite different from the conclusion given by Al-Humeidawi, who argued that there was only physical mixing occurred in the polymers and asphalt in presence of heat and mechanical mixing. This may be caused by the different positions of attention to the absorption bands of the asphalt functional groups in the two studies. Similar conclusions with this study can be found in the study of Pyshyev et al. [22] for Phenol-cresol-formaldehyde resins (PhCR-F).
3.3. Performance of PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalts
3.3.1. Basic Properties and SARA Fractions of PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalts
Basic properties, including penetration, softening point and PG of five PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalts at the initial state and corresponding short-aging state (after RTFOT) are shown in Table 4. The TLA is the control sample. At their original state, three synthetic asphalts of 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 4% PFR/20% HMTA and 6% PFR/15% HMTA possessed a relatively high softening point compared with not only the TLA but also the requirement of the General-Class grade hard-grade asphalt as specified in the British Standard EN 13924-1 [25]. Their penetration was also slightly smaller than TLA. After the RTFOT, their retained penetrations were smaller than that of the other two, and their increases in softening point were more significant. These three synthetic asphalts have an obvious commonality in that they had high HMTA dosages (HMTA 15%). Only the PG of asphalts with 4% PFR/15% HMTA and 4% PFR/20% HMTA changed before and after RTFOT, where the low-temperature PG of 4% PFR/15% HMTA reduced by one level and the high-temperature PG of 4% PFR/20% HMTA raised increased by one level. A preliminary conclusion that can be drawn is that the addition of more than 15% of HMTA may cause excessive hardening of the asphalt. However, whether this excessive hardening has negative effects on high-grade asphalts cannot be concluded from the parameters in Table 4. The results of Al-Humeidawi et al. [19] can provide some support for the conclusion of this study, where the asphalt hardness increased significantly with either PFR or HMTA admixture. However, the dosage combination determined in Al-Humeidawi‘s study to comply with the EME2 requirements (EN13924-1) was 4% PFR/10% HMAT, which is a slight deviation from the 6% PFR/10% HMAT and 8% PFR/5% HMAT given in Table 4. This may be due to differences in additive purity and deviations in the properties of the bitumen.

Table 4.
Basic properties of PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalts.
Results of SARA fraction analysis for five synthetic hard-grade asphalts and TLA (the control sample) are shown in Figure 7, which were obtained by the TLC-FID. Three synthetic asphalts with 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 4% PFR/20% HMTA and 6% PFR/15% HMTA processed larger asphaltene ratios and smaller resins ratios than TLA, which should be caused by the high additions of HMTA in them. Compared with them, SARA fraction compositions of synthetic asphalts with 6% PFR/10% HMTA, and 8% PFR/5% HMTA were closer to that of TLA. However, their asphaltene ratio was a little lower than that of TLA. Synthetic asphalts of 6% PFR/10% HMTA and 8% PFR/5% HMTA possessed higher saturated ratios than that of the other three and TLA. Previous studies indicated that a fraction saturated is the most unstable fraction in asphalts and it is highly susceptible to loss or conversion into other heavy fractions, such as asphaltene and resins during the aging process of asphalt [31]. This explains why the mass loss of these two samples after RTFOT was more than the other three and TLA.
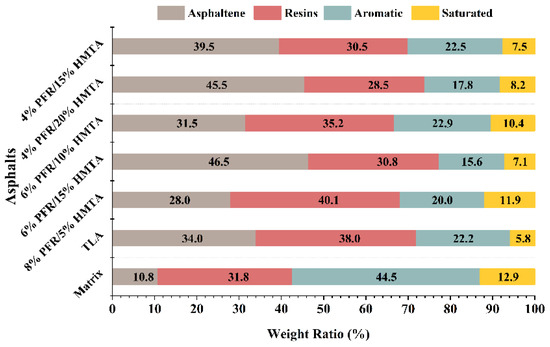
Figure 7.
SARA fractions of five synthetic hard-grade asphalts and the control.
3.3.2. Resistance to Permanent Deformation of PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalts
Figure 8a,b shows the results of the MSCR test for each sample at stress levels of 3.2 kPa and 0.1 kPa, respectively. The recovery rate represents the elastic response, and the indicates the permanent deformation sensitivity of asphalt binders. The higher recovery rate and lower value are desired to guarantee sufficient resistance to permanent deformation of hard-graded asphalt at high service temperatures, which is necessary for the rutting resistance of the corresponding asphalt mixtures. The descending order of resistance to permanent deformation for these PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalts based on the and recovery ratios are 4% PFR/20% HMTA, 6% PFR/15% HMTA, 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 6% PFR/10% HMTA, 8% PFR/5% HMTA and the control sample of TLA. As observed, all PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-graded asphalt samples performed considerably well than the control. This should be attributed to the cross-linking structure in the synthetic hard-grade asphalt strengthened by the modifier of PFR/HMTA. In asphalt samples with the same dosage of PFR, the resistance to permanent deformation increased with the dosage of HMTA. For example, the of 6% PFR/15% HMTA was 59% smaller than that of 6% PFR/10% HMTA. In asphalt samples with the same dosage of HMTA, the resistance to permanent deformation increased with the dosage of PFR as well. The of 4% PFR/15% HMTA was 48% smaller than that of 6%PFR/15%HMTA. However, HMTA seems to provide better enhancement of asphalt-rutting resistance than PFR. The sample with 4% PFR/20% HMTA (had the maximum dosage of HMTA among all samples) possessed the minimum , but the sample with 8% PFR/5% HMTA (had the maximum dosage of PFR among all samples) possessed the maximum . These indicate that increasing the amount of HMTA/PFR can enhance the resistance to permanent deformation of asphalt (reduce the and increase the elastic recovery rate), and this enhancement can be further improved by using a recipe with a higher-dosage ratio of HMTA and PFR.
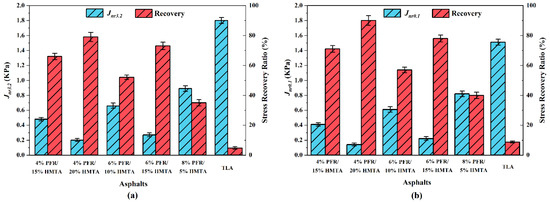
Figure 8.
The Jnr and elastic recovery ratios of five synthetic hard-grade asphalts and the control sample at stress levels of 3.2 kPa (a) and 0.1 kPa (b).
3.3.3. Critical Cracking Temperature of PFR/HMTA Synthetic Hard-Grade Asphalts
Figure 9a shows the development of the thermal stress during the cooling process of five synthetic hard-grade asphalts and the control sample, which was outputted by the NSCT. When the temperature reached critical cracking temperatures (), the accumulated thermal stress within the asphalt specimen was greater than its tensile strength. At this moment, cracking occurred rapidly in the asphalt specimen, while the thermal stress curve suddenly dropped to 0. Figure 9b shows the of all samples. The lower is desired to guarantee higher cracking resistance of hard-grade asphalt binders at low temperatures. The descending order of cracking resistance for these PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalts based on the are 8% PFR/5% HMTA, 6% PFR/10% HMTA, 4% PFR/15% HMTA, TLA, 6% PFR/15% HMTA and 4% PFR/20% HMTA. The gap between the highest of 4% PFR/20% HMTA and lowest of 4% PFR/20% HMTA reached 10 °C. As observed, the maximum stresses before cracking are at least 22% greater in all five types of synthetic hard-grade asphalts than in TLA, which indicates that the low-temperature strength (tensile) of synthetic asphalt has been improved. However, the growth rates of thermal stress with cooling were greater for the three samples with 15% and 20% HMTA addition than for TLA, which indicates that the deformability of these three synthetic asphalts at low temperatures is lower than that of TLA. Accordingly, although their low-temperature tensile strength performed well than TLA, their were higher than TLA due to the larger rate of thermal stress accumulation. Compared with these three, the two samples with 5% and 10% HMTA additions not only have greater low-temperature tensile strength, but also have a significantly lower rate of thermal stress accumulation with cooling than TLA. On the basis of these results, one can conclude that the modifiers of PFR and HMTA can improve the low-temperature tensile strength of asphalts, but the higher the addition of HMTA, the worse the deformation capacity of asphalts at low temperatures.
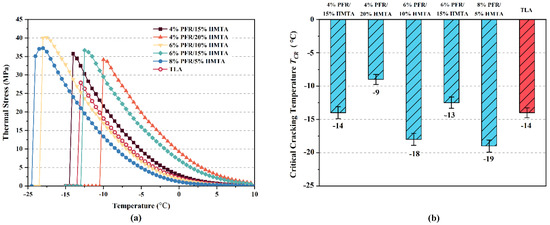
Figure 9.
Thermal stresses (a) and critical cracking temperatures (b) of five synthetic hard-grade asphalts and the control sample.
3.4. Performance of PFR/HMTA-HMAC
The rutting resistance, fatigue resistance and cracking resistance of the HMAC which used the PFR/HMAC synthetic hard-grade asphalts as binders were also investigated in this study. The used aggregate gradation for these PFR/HMTA-HMAC was the French EME-14 (Table 2). To ensure compaction quality, target air void ratios of this aggregate gradation should be controlled at 0~6% [2]. The actual air void rates for all HMAC specimens made were checked as shown in Table 5, all of which satisfied the requirement.

Table 5.
Air voids of PFR/HMTA-HMAC specimens.
3.4.1. Rutting Resistance
The results of HWTT for six HMACs which used the five PFR/HMTA modified asphalts and the control asphalt TLA as binders are shown in Figure 10. For each sample, three replicate tests were conducted. Figure 10a displays the rutting depth increased with the wheel loading cycles for these six HMAC samples in one set of tests. In five samples of PFR/HMTA-HMAC, rutting depths increased almost linearly with loading cycles. However, in the sample of TLA-HMAC, rutting depths increased rapidly in the first 5000 loading cycles, about 40% of total rutting depths occurred in this stage. In the following 15,000 loading cycles for TLA-HMAC, the growing rate of rutting depths declined slightly but it was also above that of the 8% PFR/5% HMTA which had the large growth rate among the PFR/HMTA-HMAC.
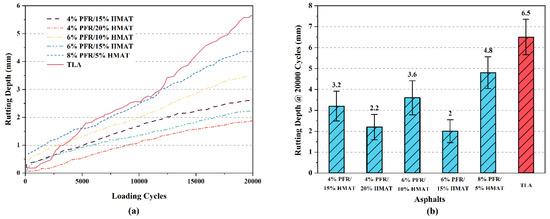
Figure 10.
Rutting depths versus loading cycles in HWTT (a) and final rutting depts (b) for five synthetic hard-grade asphalts and the control sample.
Figure 10b shows the averages of final rutting depths after 20,000 loading cycles for the six HMAC samples. No samples failed (rutting depths large than 10 mm) before the wheel loading cycles reached 20,000 cycles, and descending order of rutting resistance for these samples based on rutting depths are 6% PFR/15% HMTA, 4% PFR/20% HMTA, 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 6% PFR/10% HMTA, 8% PFR/5% HMTA and the control sample of TLA. This order of rutting resistance for asphalt mixtures given by HWTT is similar to the above results for asphalts given by MSCR. These also further verified the conclusion obtained above that PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalt exhibit a better rutting resistance than the TLA. In the same dosage of PFR, larger additions of HMTA can further improve the rutting resistance of HMAC. For example, in the two samples with 4% PFR, the rutting depths of 20% HMTA were 30% smaller than that of 15% HMTA. Similar results can be found in the two samples with 6% PFR. Similarly, using a large dosage of PFR in the sample with the same HMTA content can also improve the rutting resistance.
3.4.2. Fatigue Resistance
Poor resistance to fatigue cracking is a general shortcoming of high-modulus asphalt concrete, and many studies attempted to solve this problem. For HMAC using synthetic hard-grade asphalts as binders, their fatigue resistance should be at least better than that of those traditional hard-grade asphalts. Figure 11 shows the results of 4 PB fatigue tests for five PFR/HMTA-HMAC samples and the control of TLA-HMAC. The regressed curves (Wöhler fatigue curves) for all samples are also displayed in it and the parameters of corresponding curves are listed in Table 6.
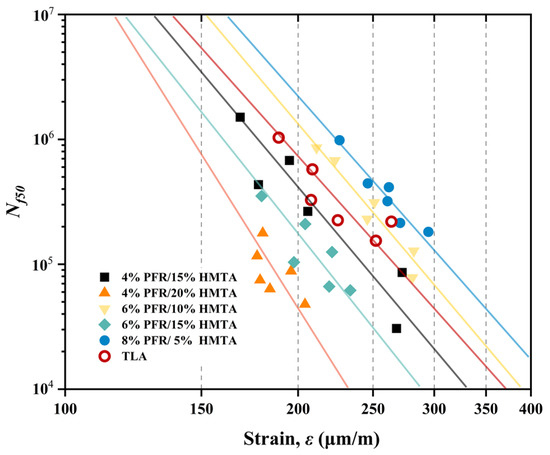
Figure 11.
Results of 4 PB fatigue tests and the regressed curves for five PFR/HMTA-HMAC and the control sample.

Table 6.
Parameters of curves for all HMAC samples.
The descending order of fatigue resistance for these HMAC based on are 8% PFR/5% HMTA, 6% PFR/10% HMTA, TLA, 4% PFR/15% HMTA, 6% PFR/15% HMTA and 4% PFR/20% HMTA. In some European countries, the parameter of high-modulus asphalt concrete must be greater than 130 [42]. Obviously, the HMAC samples of 4% PFR/20% HMTA cannot satisfy it, and the 6% PFR/15% HMTA just crossed this threshold. Compared with them, the of two samples with 5% and 10% HMTA were about 69.2% and 61.5% above this threshold, and they were also about 23.1% and 17.9% above the sample of TLA. Slopes of curves for 6% PFR/15% HMTA, and 4% PFR/20% HMTA are large than other curves, which means a strong sensitivity for the fatigue life to strain in these two samples. This slight increase in the strain (corresponding to heaver vehicle load cycles or thermal cycles with large temperature gaps) may lead a significant decrease in the fatigue life of pavements [24]. All of these indicate that the dosage of HMTA in the asphalt should avoid exceeding 15% to ensure enough fatigue resistance of the HMAC.
3.4.3. Cracking Resistance
The results of a 3 PB beam test for six HMAC samples are shown in Figure 12. The descending order of cracking resistance for these mixture samples based on the is identical to the order for PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalt samples obtained by NSCT. This is due to the fact that the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures at a low temperature is highly dependent on the crack resistance of the asphalt binders. The of samples with HMTA doping of more than 10% of samples did not reach the level of the control group of TLA. None of the samples doped with more than 10% HMTA reached the same level of as the TLA control. However, of samples of 8% PFR/5% HMTA and 6% PFR/10% HMTA were 48.8% and 36.0% higher than the control group, respectively. In general, the cracking resistance of modified asphalt synthesized by adding modifier PFR/HMTA at low temperatures can completely reach a level similar to that of traditional hard-grade asphalt, but the dosage of HMTA should not exceed 10%.
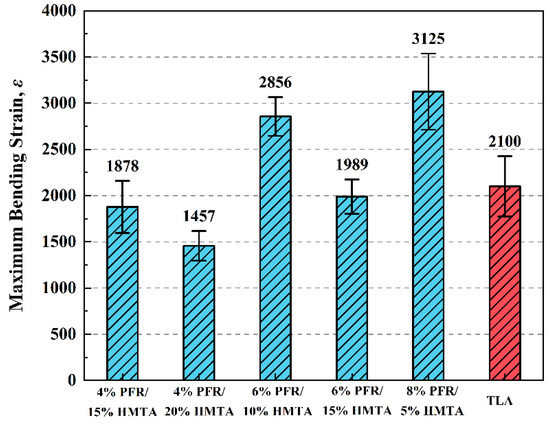
Figure 12.
Results of 3 PB beam tests for five PFR/HMTA-HMAC and the control sample.
4. Conclusions
This study introduced a method to synthesize hard-grade asphalts using phenol formaldehyde resin (PFR), hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) and matrix asphalt, and investigated the effects of multiple dosing combinations of PFR and HMTA on the performance of hard-grade asphalts and the corresponding HMAC. Major conclusions can be summarized as follows
(1) To satisfy the basic application requirements of HMAC, i.e., the dynamic modules of HMAC should be in the range of 14,000~16,000 MPa, the dosing combinations of PFR and HMTA were determined as 4% PFR/15~20% HMTA, 6% PFR/8~10% and 8% PFR/5~5.7%.
(2) IR spectra and SARA fraction analysis for the PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalts verified the assumed reaction that asphalt molecules can be cross-linked into larger polymeric groups by the TPFP which is the reaction product of PFR and HMTA. This process increased the asphaltene and resin fraction in the asphalt, thus transforming the matrix asphalt into hard grade. The higher dosage of PFR/HMTA the harder asphalt can be obtained.
(3) The rutting resistance of PFR/HMTA synthetic hard-grade asphalts under the above dosage combinations completely exceeded that of a widely used hard-grade asphalt which was produced by using Trinidad lake asphalt to modifier the matrix asphalt. Increasing the amount of PFR/HMTA can enhance the rutting resistance of asphalt (reduce the and increase the elastic recovery rate), and further enhancement can be obtained by using a recipe with a higher dosage ratio of HMTA to PFR.
(4) The fatigue resistance of PFR/HMTA-asphalt mixtures can reach and even exceed that of TLA just in case of the HMTA dosage was lower than 15%. If the dosage of HMTA is over 15%, the sensitivity of the fatigue life to strain increases. Furthermore, the fatigue parameter of the asphalt mixture with 20% HMTA content cannot meet the application requirements.
(5) Similarly with their fatigue resistance, the cracking resistance of PFR/HMTA-asphalt mixtures at a low temperature reached and even exceeded TLA only on the condition that the HMTA was lower than 15%. Although the PFR/HMTA enhanced the tensile strength of asphalts at low temperatures, the inner accumulation rate of thermal stress was also increased due to the increase in the hardness and the decline in the deformability of the asphalt.
In general, PFR/HMAC synthetic hard-grade asphalts can be considered as an alternative to traditional hard-grade asphalt as binders for high-modulus asphalt concrete. The aging resistance of it and the effect of the performance of matrix asphalt on it will be considered in subsequent studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.X. and H.X. (Haining Xu); methodology, Y.L.; software, Y.Z.; validation, R.Z. and H.X. (Haichuan Xu); formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, R.Z. and H.X. (Haichuan Xu); resources, H.L.; data curation, Q.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.X.; writing—review and editing, Q.X.; visualization, Y.L.; supervision, H.L.; project administration, H.L.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by NATIONAL NATURAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION OF CHINA, grant number 52278444 and POSTGRADUATE RESEARCH & PRACTICE INNOVATION OF JIANGSU, CHINA, GRANT NUMBER grant number KYCX21_0139.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jinhui Huang of Kunming University of Medical Sciences.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Corté, J.-F. Review of the development and uses of hard grade asphalts in France. J. Road Eng. 2021, 1, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF P98-140; AFNOR Editions Asphalt Concrete-Base Layers: High Modulus Asphalt Concrete (EME). Association Francaise de Normalisation: Paris, France, 1999.
- EN 12697-24; CEN Bituminous Mixtures-Test Methods-Part 24: Resistance to Fatigue. European Committee for Standardizaiton: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; You, Z. High modulus asphalt concrete: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Shan, L. Long-Term Service Performance of Hard-Grade Asphalt Concrete Base Pavement Based on Accelerated Loading Test of Full-Scale Structure. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, J.W. Perpetual Bituminous Pavements; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Fishwick, R.; Wood, J.; Leeke, G.; Rigby, S.; Greaves, M. A review of novel techniques for heavy oil and bitumen extraction and upgrading. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Leng, Z.; Ling, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, L. Characterization and comparison of high-modulus asphalt mixtures produced with different methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, T.; Fan, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhou, Y. Experimental study of high modulus asphalt mixture containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Jiangping, G.; Hao-yuan, L.; Qigong, Z.; Hijie, L.; Fei, Y. Low-temperature performance of composite modified hard asphalt used in high modulus asphalt concrete. J. Jilin Univ. Technol. Ed. 2022, 52, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J. Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures Road Performance; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J. Climate zoning and key technical indexes of road asphalt and asphalt mixture. China J. Highw. Transp. 1997, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Hesp, S.A.M. Quantification of crystalline wax in asphalt binders using variable-temperature Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Fuel 2020, 277, 118220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Shen, B.; Liu, J.; Yao, Z.; Fang, W. Preparation and evaluation of 30# hard grade asphalt. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, F.; Ghasemirad, A.; Moghaddam, T.B.; Bayat, A.; Hashemian, L. Performance Evaluation of High Modulus Asphalt Concrete (HMAC) Prepared Using Asphaltenes-Modified Binders. J. Test. Eval. 2022, 50, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y. Recycling aged asphalt using hard asphalt binder for hot-mixing recycled asphalt mixture. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yu, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, J. Rheological behaviors and microstructure of SBS/CR composite modified hard asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Rui, H. Laboratory Evaluation of Dynamic Characteristics of a New High-Modulus Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Humeidawi, B.H.; Kadhim Medhlom, M.; Kadhim Hameed, K.; Kadhim, H.A. Production of Hard Grade Bitumen for Using in High Modulus Asphalt Concrete. J. Univ. Babylon Eng. Sci. 2018, 26, 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y. High-Temperature Rheology Characteristics of Hard Petroleum Asphalt Used in China. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4901879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Han, Y.; Wei, J. Comparative Study on Road Performance of Low-Grade Hard Asphalt and Mixture in China and France. Coatings 2022, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyshyev, S.; Demchuk, Y.; Poliuzhyn, I.; Kochubei, V. Obtaining and use adhesive promoters to bitumen from the phenolic fraction of coal tar. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2022, 118, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nciri, N.; Song, S.; Kim, N.; Cho, N. Chemical Characterization of Gilsonite Bitumen. J. Pet. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, M.; Bańkowski, W.; Pronk, A.C. Evaluation of fatigue life of high modulus asphalt concrete with use of three different definitions. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN13924-1:2015; British Standard Bitumen and Bituminous Binders—Specification Framework for Special Paving Grade Bitumen Part 1: Hard Paving Grade Bitumens. European Committee for Standardizaiton: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- ASTM D6373-21a; American Society for Testing and Material (ASTM) Standard Specification for Performance-Graded Asphalt Binder. American society for Testing and Material: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM D5/D5M-20; American Society for Testing and Material(ASTM) Standard Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials. American society for Testing and Material: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- ASTM D36/D36M-14; American Society for Testing and Material(ASTM) Standard Test Method for Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus). American Society for Testing and Material: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Laboratoire Central des Ponts et Chaussées. LPC Bituminous Mixtures Design Guide; Laboratoire Central des Ponts et Chaussées: Lyon, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Huang, X. Research on the Change of Performance and Component of Recycled Oil Regenerated Asphalt during Secondary Aging. China J. Highw. Transp. 2021, 34, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Huang, X.; Tian, R.; Huang, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, D.; Liu, B. Analysis of relationship between component changes and performance degradation of Waste-Oil-Rejuvenated asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Luo, H.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, L. Correlation Analysis between Mechanical Properties and Fractions Composition of Oil-Rejuvenated Asphalt. Materials 2022, 15, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Ding, H.; Rahman, A.; Wang, W. Damage characteristics of waste engine oil bottom rejuvenated asphalt binder in the non-linear range and its microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Leng, H.; Ding, H.; Xu, J.; Lin, H.; Ai, C.; Qiu, Y. Low-temperature cracking resistance, fatigue performance and emission reduction of a novel silica gel warm mix asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Tian, R.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Huang, X. Notched specimen cracking test: A novel method to directly measure low-temperature thermal stress of asphalt binder. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO TP62-03; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) Standard Method of Test for Determining Dynamic Modulus of Hot-Mix Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. American society for Testing and Material: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- Walubita, L.; Zhang, J.; Das, G.; Hu, X.; Mushota, C.; Alvarez, A.; Scullion, T. Hot-mix asphalt permanent deformation evaluated by Hamburg wheel tracking, dynamic modulus, and repeated load tests. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2296, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO-T324-22; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) Standard Method of Test for Hamburg Wheel-Track Testing of Compacted Asphalt Mixtures. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- JTG E20-2011; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- AASHTO-D321-22; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) Standard Method of Test for Determining the Fatigue Life of Compacted Asphalt Mixtures Subjected to Repeated Flexural Bending. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Fatigue behaviours of asphalt mixture at different temperatures in four-point bending and indirect tensile fatigue tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowski, W. Evaluation of fatigue life of asphalt concrete mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF P98-140; Association Francaise de Normalisation Enrobés Hydrocarbonés-Couches d’assises: Enrobés à module élevé (EME)-Définition-Classification-Caractéristiques-Fabrication-Mise en oeuvre. Association Francaise de Normalisation: Paris, France, 1999.
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Fu, Y. Preparation and performance of UHMWP modified asphalt and its high modulus mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Qiu, Y.; Su, T. Evaluation of the Performance of SMC Modified Asphalt Mixtures and Its Environmental Benefits Analysis. Adv. Transp. Geotech. IV 2022, 164, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).